Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
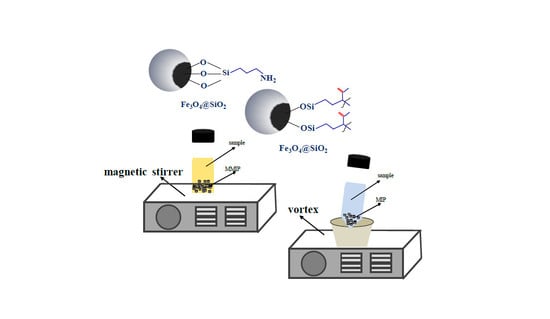
2. Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction with MIPs
2.1. Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction with Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MMIPs)
2.1.1. Classification of MMIPs
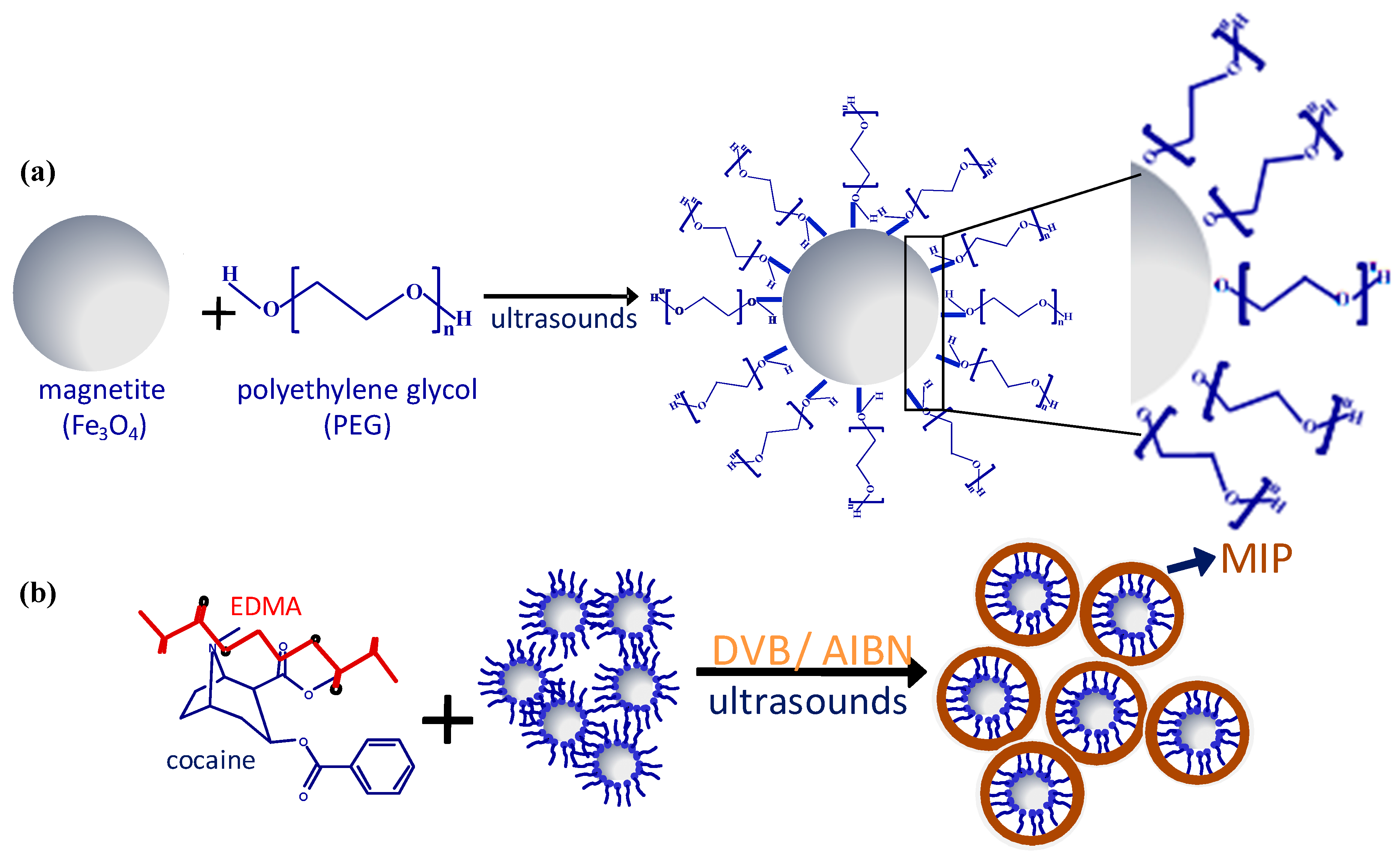
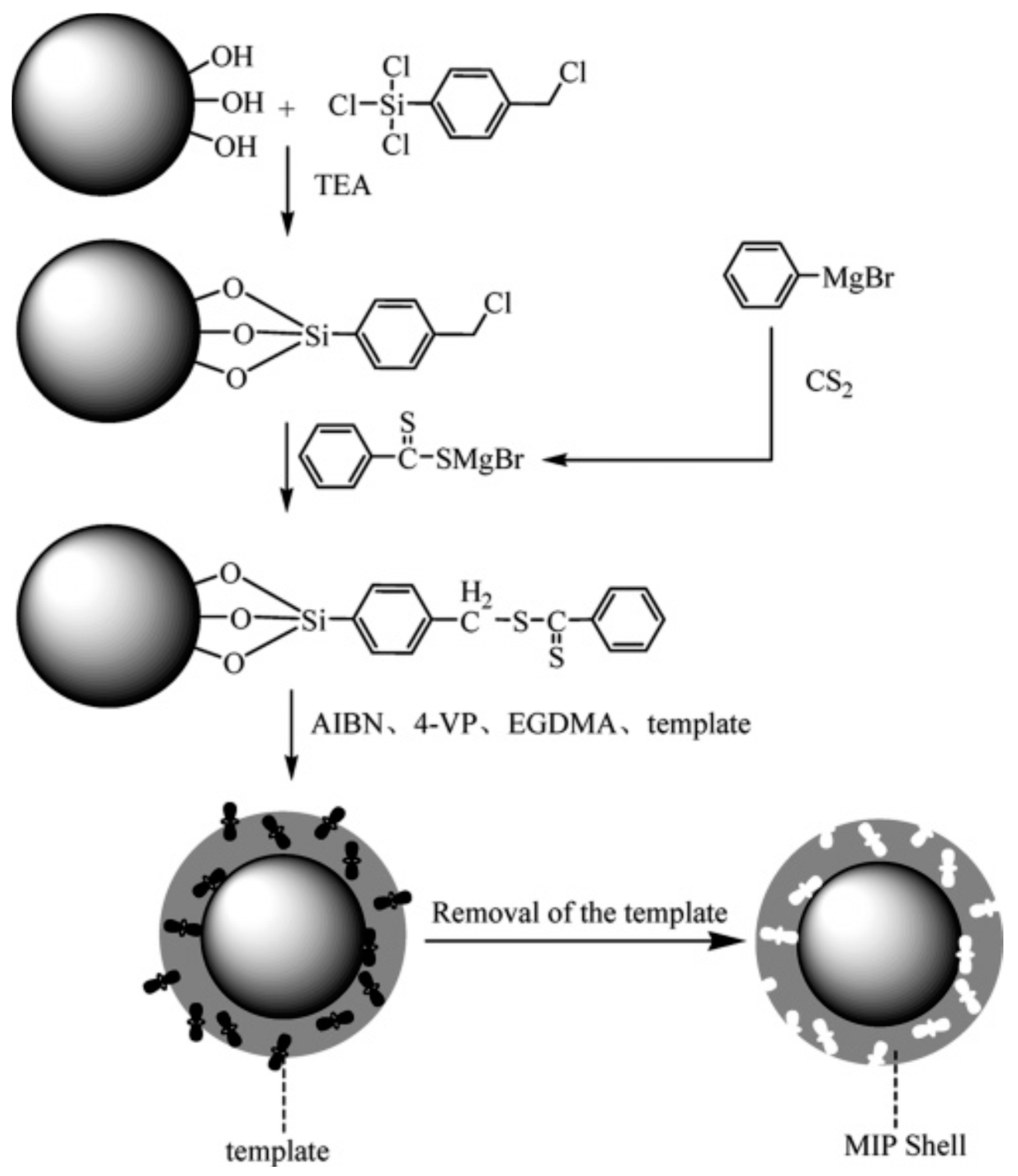
2.1.2. Magnetite Surface Functionalization for Core–Shell MMIPs
Surface Functionalization with Hydroxyl (Diol) and Vinyl-Based Reagents
Surface Functionalization with Silica-Based Reagents
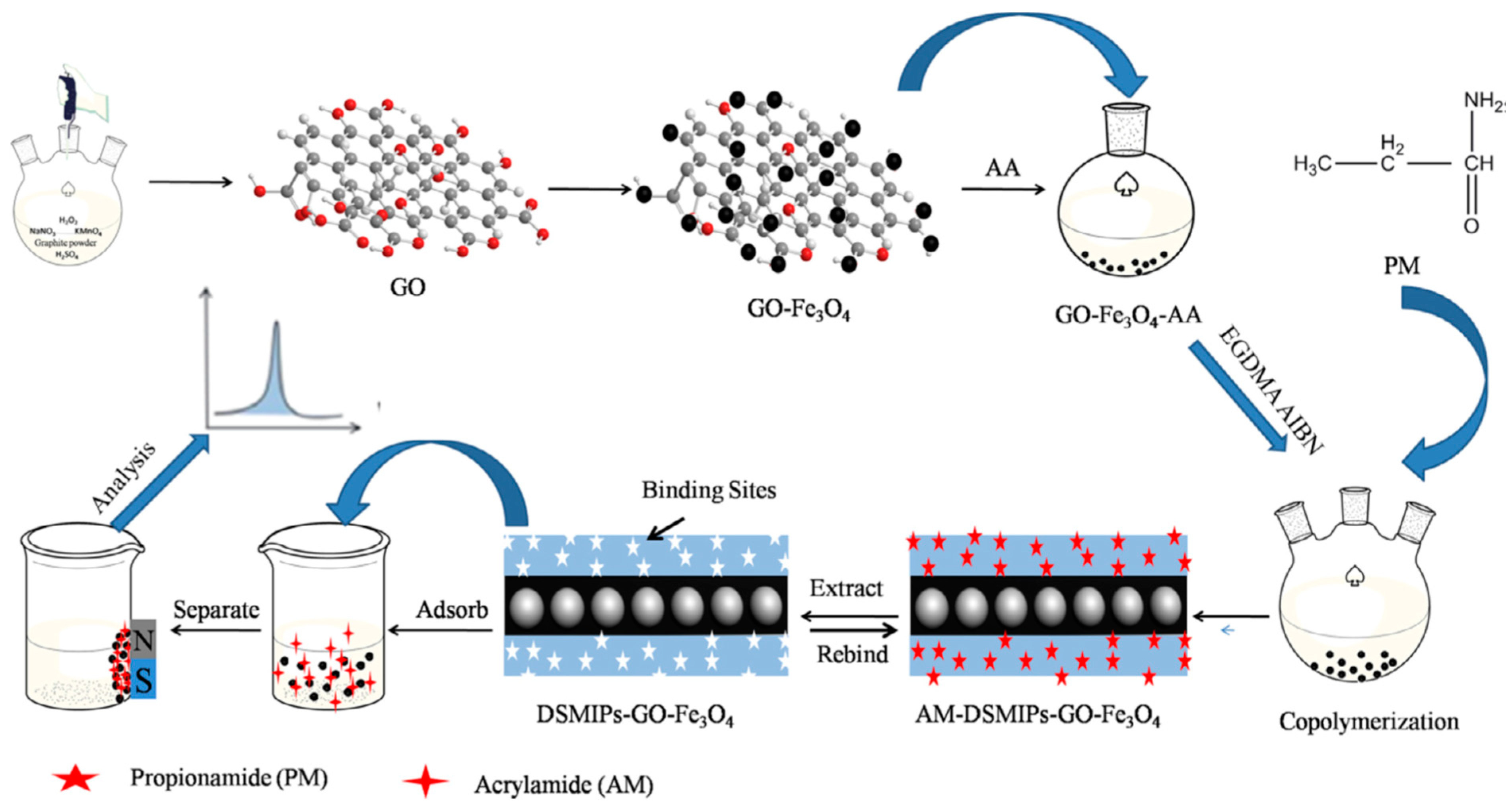
2.1.3. Magnetite Surface Functionalization for Magnetic Nanotube-Supported and Magnetic Nanosheet-Supported MIPs
2.1.4. Magnetite Functionalization for Magnetic Porous MIPs
2.1.5. Other Mixed Composites for MMIPs
2.2. Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction and Microsolid Phase Extraction with Non-Magnetic MIPs
3. Drawbacks and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pawliszyn, J. New directions in sample preparation for analysis of organic compounds. Trends Anal. Chem. 1995, 14, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based microextraction techniques. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Sole, R.D.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pichon, V.; Delaunay, N.; Combès, A. Sample Preparation Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; LA Barbera, G.; Montone, C.M.; Piovesana, S.; Laganà, A. Recent Applications of Magnetic Solid-phase Extraction for Sample Preparation. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1251–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Recent configurations and progressive uses of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for drug analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Scalabrini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Profumo, A. Newest applications of molecularly imprinted polymers for extraction of contaminants from environmental and food matrices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Bottaro, C.S. A critical review of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of organic pollutants in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Aghamohammadhassan, M.; Chamsaz, M.; Akhlaghi, H.; Pedramrad, T. Dispersive solid phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Aghamohammadhassan, M.; Ghorbani, H.; Zabihi, A. Trends in sorbent development for dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, C.B.; Rojas, F.S. Vortex-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Microextraction (VALLME): The Latest Applications. Chromatographia 2017, 81, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Combined assisted extraction techniques as green sample pre-treatments in food analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, Y.G. Sonochemistry: Environmental Science and Engineering Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 4681–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Cano, F.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction with ionic liquid-modified silica for the determination of organophosphate pesticides in water by ultra performance liquid chromatography. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P.; Lun, X.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Hou, X. A joint experimental-computational investigation: Metal organic framework as a vortex assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction sorbent coupled with UPLC-MS/MS for the simultaneous determination of amphenicols and their metabolite in aquaculture water. Microchem. J. 2017, 130, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaie, A.B.; Hadjmohammadi, M.R. Fe3O4@p-Naphtholbenzein as a novel nano-sorbent for highly effective removal and recovery of Berberine: Response surface methodology for optimization of ultrasound assisted dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction. Talanta 2016, 156, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dil, E.A.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Mehrabi, F.; Bazrafshan, A.A.; Ghaedi, A.M. Trace determination of safranin O dye using ultrasound assisted dispersive solid-phase micro extraction: Artificial neural network-genetic algorithm and response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, M.; Stanisz, E. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction with nano-TiO2 as adsorbent for the determination of mercury species. Talanta 2016, 161, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansell, R.J.; Mosbach, K. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for drug radioligand binding assay. Analyst 1998, 123, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y. Molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for determination of the herbicide chlorotoluron by gate-controlled electro-catalytic oxidation of hydrazine. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly-imprinted polymers as a versatile, highly selective tool in sample preparation. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 45, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Yang, X.; Fan, Z.; Yang, L.; Dong, X. Preparation of a bifunctional pyrazosulfuron-ethyl imprinted polymer with hydrophilic external layers by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization and its application in the sulfonylurea residue analysis. Talanta 2013, 114, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Zhou, W.-H.; Han, B.; Yang, H.-H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.-R. Surface-Imprinted Core−Shell Nanoparticles for Sorbent Assays. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5457–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Li, Y.; Chu, J.; Qi, J.; Li, X. Preparation of core-shell molecularly imprinted polymer via the combination of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization and click reaction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 680, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Controlled/“living” radical precipitation polymerization: A versatile polymerization technique for advanced functional polymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, E.; Abdouss, M.; Salami-Kalajahi, M.; Mohammadi, A. Molecular Recognition Ability of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nano- and Micro-Particles by Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Polymerization. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 557–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Shahhoseini, F.; Bottaro, C.S. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization for dispersive solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, F.; Xie, L.; Ouyang, G. Synthesis and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in sample preparation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3991–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Barrado, E. Magnetic solids in analytical chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, G. Application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in sample preparation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chen, L. Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon nanotubes—Application for trace analysis of pyrethroids in fruit matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Masoum, S. A multi-walled carbon nanotube-based magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as a highly selective sorbent for ultrasonic-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction of sotalol in biological fluids. Analyst 2018, 143, 2862–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; Qiu, T.; Wang, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Xiong, H. Dummy-surface molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and selective quantification of acrylamide in heat-processed (including fried) foods. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ma, X.; Guo, L.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Novel magnetic multi-templates molecularly imprinted polymer for selective and rapid removal and detection of alkylphenols in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Li, B. Magnetic molecular imprinting polymers based on three-dimensional (3D) graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid composites for analysis of melamine in milk powder. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-B.; Li, J.; You, B.; Yong, G.-P.; Tong, H.-W.; Liu, S.-M. Hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer nanosphere for fast and efficient recognition of bisphenol A. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9778–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. High-capacity magnetic hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymers for specific extraction of protocatechuic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1404, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostovan, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Arabi, M.; Asfaram, A. Hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymer for highly selective clean-up followed by influential pre-concentration of ultra-trace glibenclamide from bio-fluid. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1520, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, K.; Tian, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, G.; Li, L. Rapid extraction of trace bisphenol A in real water samples using hollow mesoporous silica surface dummy molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3926–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Zhao, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, C. Fabrication and evaluation of hollow surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid and selective adsorption of dibenzothiophene. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-H.; Shu, H.; Xu, X.-Y.; Guo, P.-Q.; Liu, R.-L.; Luo, Z.-M.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Combined magnetic porous molecularly imprinted polymers and deep eutectic solvents for efficient and selective extraction of aristolochic acid I and II from rat urine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Purkait, M.K. Novel strategy for synthesis of magnetic dummy molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based on functionalized silica as an efficient sorbent for the determination of acrylamide in potato chips: Optimization by experimental design methodology. Talanta 2016, 154, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostovan, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Arabi, M. Fabrication of water-compatible superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted biopolymer for clean separation of baclofen from bio-fluid samples: A mild and green approach. Talanta 2018, 179, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Long, R.; Tong, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Shi, S. Shell thickness controlled hydrophilic magnetic molecularly imprinted resins for high-efficient extraction of benzoic acids in aqueous samples. Talanta 2019, 194, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q. Surface molecularly imprinted thermo-sensitive polymers based on light-weight hollow magnetic microspheres for specific recognition of BSA. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of highly monodisperse water-dispersible hollow magnetic microspheres and construction of photonic crystals. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Chen, X.-H.; Pan, S.-D.; Zhu, H.; Shen, H.-Y.; Jin, M.-C. Self-assembly of a surface bisphenol A-imprinted core–shell nanoring amino-functionalized superparamagnetic polymer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11648–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-G.; Zhou, L.-X.; Pan, S.-D.; Zhan, P.-P.; Chen, X.-H.; Jin, M.-C. Fast determination of 22 sulfonamides from chicken breast muscle using core–shell nanoring amino-functionalized superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted polymer followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1345, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhou, T.; Luo, D.; Feng, J.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mei, S. Bioaccumulation of tetrabromobisphenol A in a laboratory-based fish–water system based on selective magnetic molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabzadeh, N.; Akbarzadeh, R.; Mohammadi, A.; Darwish, M. Green synthesis and application of nanomagnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for fast solid-phase extraction of brilliant blue FCF from real samples. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Rostamkhani, S.; Hamidi, M. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for dispersive micro solid-phase extraction and determination of buprenorphine in human urine samples by HPLC-FL. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Pham-Huy, C.; He, H. Core-shell nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2677–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Tan, W.; Li, G. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads prepared by microwave heating for selective enrichment of β-agonists in pork and pig liver samples. Talanta 2011, 84, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mao, H.; Huang, W.; Guan, W.; Zou, X.; Pan, J.; Yan, Y. Preparation of magnetic imprinted polymer particles via microwave heating initiated polymerization for selective enrichment of 2-amino-4-nitrophenol from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-González, J.; Tabernero, M.J.; Bermejo, A.M.; Bermejo–Barrera, P.; Moreda–Piñeiro, A. Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for solid phase extraction of cocaine and metabolites in urine before high performance liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 147, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-González, J.; Barreiro-Grille, T.; Cabarcos, P.; Tabernero-Duque, M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer based—Micro-solid phase extraction of cocaine and metabolites in plasma followed by high performance liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2016, 127, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on a green synthesis strategy for magnetic solid-phase extraction of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 2019, 195, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; You, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Water-compatible temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and extraction of bisphenol A. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1435, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Li, G. Microwave Heating in Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Beads for Trace Triazines Analysis in Complicated Samples. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, H.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Isolation of transferrin by imprinted nanoparticles with magnetic deep eutectic solvents as monomer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6237–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdarian, M.; Ramezani, Z. Rapid microwave-assisted distillation–precipitation polymerization for the synthesis of magnetic molecular imprinted polymers coupled to HPTLC determination of perphenazine in human urine. New J. Chem. 2018, 43, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, S.; Tu, T. Efficient vitamin B12-imprinted boronate affinity magnetic nanoparticles for the specific capture of vitamin B12. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 561, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, Z.; Xing, R.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Precision Imprinting of Glycopeptides for Facile Preparation of Glycan-Specific Artificial Antibodies. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9845–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, S.-E.; Liu, R.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.-E.; Liu, H. Multiplexed derivatization strategy-based dummy molecularly imprinted polymers as sorbents for magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction of globotriaosylsphingosine prior to UHPLC-MS/MS quantitation. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-Y.; Ma, R.-T.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-P. Boronate-affinity based magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the efficient extraction of the model glycoprotein horseradish peroxidase. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3729–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-Y.; Ma, R.-T.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-P. Magnetic boronate modified molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetite microspheres modified with porous TiO2 (Fe3O4@pTiO2@MIP) with enhanced adsorption capacity for glycoproteins and with wide operational pH range. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hou, X.; Tong, Y.; Tian, M. Determination of sialic acid in serum samples by dispersive solid-phase extraction based on boronate-affinity magnetic hollow molecularly imprinted polymer sorbent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5394–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, T.; Du, H.; Dai, Q.; Xia, H.; Niu, J.; Hao, Q.; Mei, S.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for recognition of lysozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, L.; Cai, R.; Chen, H. A sensitive and selective molecularly imprinted sensor combined with magnetic molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction for determination of dibutyl phthalate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, C.; Chu, J.; Qi, J.; Li, X. Surface molecular imprinting onto fluorescein-coated magnetic nanoparticles via reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization: A facile three-in-one system for recognition and separation of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azodi-Deilami, S.; Abdouss, M.; Asadi, E.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Sadeghi, S.; Farzaneh, S.; Asadi, S. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for solid-phase extraction of carvedilol in serum samples. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azodi-Deilami, S.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Asadi, E.; Abdouss, M.; Kordestani, D. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the solid-phase extraction of paracetamol from plasma samples, followed its determination by HPLC. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-P.; Xu, X.-K.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zhu, J.-H. Preparation and characterization of molecular imprinted polymer functionalized with core/shell magnetic particles (Fe3O4@SiO2@MIP) for the simultaneous recognition and enrichment of four taxoids in Taxus × media. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Wang, S. Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer strategy and its application in the Sudan dyes residue analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1405, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.S.; Wu, M.S.; Zuo, H.G.; Jiang, C.; Jin, S.F.; Lu, Y.C.; Yang, H. Core–Shell Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Sorbent for Sulfonylurea Herbicide Residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3634–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuriaga-Sánchez, R.J.; Khan, S.; Wong, A.; Picasso, G.; Pividori, M.I.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Magnetically separable polymer (Mag-MIP) for selective analysis of biotin in food samples. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Teng, W.; Tan, J.; Liang, Y.; Tang, Y. Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer with binary monomer for the fast and selective extraction of bisphenol A from milk. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1462, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcudia-León, M.D.C.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.; Aranzana, M.S.C. Selective extraction of Bactrocera oleae sexual pheromone from olive oil by dispersive magnetic microsolid phase extraction using a molecularly imprinted nanocomposite. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1455, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.A.; Ranjbar, M.; Akbarpoor, M. Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Selective Adsorption and Separation of β-Estradiol. J. Clust. Sci. 2016, 27, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, S.A.; Abbasi, S. Biocoacervation extraction combined with dispersive solid phase extraction using a reversed-phase core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted sorbent for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid prior to its determination by HPLC. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; He, R.; Chen, K.; Peng, R.; Huang, C.; Yang, R.; Tang, Y. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry for determination of aflatoxins using dummy molecularly imprinted polymers deposited on silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Saeidi, M.; Moghadam, M.R. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Diazinon after Its Magnetic Dispersive Solid-Phase Microextraction Using Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, A.; Herrera-Chacon, A.; Pupin, R.; Sotomayor, M.; Pividori, M. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation and detection of biotin and biotinylated biomolecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; He, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for dispersive solid-phase extraction and determination of bisphenol A in water samples and orange juice. Talanta 2017, 162, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.-F.; Liu, H.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, Y.-Y.; Li, L. Synthesis, properties and application research of atrazine Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tang, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, C. Computer-aided design of magnetic dummy molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of ten phthalates from food prior to their determination by GC-MS/MS. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, F.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Shu, H.; Tu, X. A magnetic copper(II)-imprinted polymer for the selective enrichment of trace copper(II) ions in environmental water. Microchim. Acta 2012, 179, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Tan, L.; Xia, Z.; Wang, C.-Z.; Zhou, L.-D.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, C.-S. Preparation and evaluation of temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers for the specific enrichment of formononetin. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dil, E.A.; Doustimotlagh, A.H.; Javadian, H.; Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M. Nano-sized Fe3O4@SiO2-molecular imprinted polymer as a sorbent for dispersive solid-phase microextraction of melatonin in the methanolic extract of Portulaca oleracea, biological, and water samples. Talanta 2021, 221, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Ayoub, A.T.; Nebsen, M. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for simultaneous extraction and determination of 6-mercaptopurine and its active metabolite thioguanine in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Castillo, A.L.; Mistlberger, G.; Fernandez-Sanchez, J.F.; Carretero, A.S.; Klimant, I.; Gutierrez, A.F. Novel Strategy To Design Magnetic, Molecular Imprinted Polymers with Well-Controlled Structure for the Application in Optical Sensors. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Du, X.; Sun, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental water samples based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer extraction followed by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, N.; Ding, L. Determination of β-lactam antibiotics in milk based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer extraction coupled with liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 3421–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.-H.; Xu, R.; Yuan, G.-L.; Lu, H.; Gu, B.-R.; Xie, H.-P. Preparation of chlorogenic acid surface-imprinted magnetic nanoparticles and their usage in separation of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 675, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xu, L.; Dai, J.; Li, X.; Hang, H.; Huo, P.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on attapulgite/Fe3O4 particles for the selective recognition of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Xie, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y. A novel polychloromethylstyrene coated superparamagnetic surface molecularly imprinted core–shell nanoparticle for bisphenol A. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 9232–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, N.; Qiao, X. Vortex-assisted magnetic dispersive solid-phase microextraction for rapid screening and recognition of dicofol residues in tea products. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Baleg, A.A.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E.; Amine, A. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of nanostructured magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for 17-β-Estradiol determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Thomas, J.L.; Ho, M.-H.; Yuan, C.; Lin, H.-Y. Synthesis of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) Nanoparticles and Their Uses in the Extraction and Sensing of Target Molecules in Urine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzuriaga-Sánchez, R.J.; Wong, A.; Khan, S.; Pividori, M.I.; Picasso, G.; Sotomayor, M.D. Synthesis of a new magnetic-MIP for the selective detection of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, a highly allergenic compound. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyrovi, M.; Hadjmohammadi, M.; Saeidi, I. Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticle-based molecularly imprinted polymer as a selective sorbent for efficient extraction of ezetimibe from biological samples. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilktaç, R.; Gumus, Z.P.; Aksuner, N.; Coskunol, H. Highly sensitive and selective method for the rapid determination and preconcentration of haloperidol by using a magnetite-molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Deng, F.; Luo, S.; Tu, X.; Yang, L. Grafting of molecularly imprinted polymers from the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles containing double bond via suspension polymerization in aqueous environment: A selective sorbent for theophylline. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.; Lv, Y.; Qin, P.; Li, H.; Li, J.-P.; Tan, T. Selective binding of heparin oligosaccharides in a magnetic thermoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 2019, 201, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, C.; Abd EI-Aty, A.M.; Baranenko, D.A.; Hacimüftüoğlu, A.; She, Y. Assessment of magnetic core-shell mesoporous molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition of triazoles residual levels in cucumber. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1132, 121811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Carreiro, E.P.; Ramalho, J.P.P.; Mirao, J.; Burke, A.; da Silva, M.D.R.G.; Freitas, A.M.C.; Cabrita, M.J. A magnetic controllable tool for the selective enrichment of dimethoate from olive oil samples: A responsive molecular imprinting-based approach. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.-Y.; Zhao, H.-T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, A.-J.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Selective recognition and fast enrichment of anthocyanins by dummy molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1572, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lei, C.; Wang, N.; Jiang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zou, L.; He, L.; Liu, S.; Ao, X.; et al. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers with double functional monomers for the extraction and detection of chloramphenicol in food. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1100, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, H.; Jin, R.; Xing, J. Comparative study of capsaicin molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by different polymerization methods. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, L.; Long, R.-Q.; Chen, C.-L. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for enrichment of sanguinarine from the extraction wastewater of M. cordata. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 66, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Muhammad, T.; Yigaimu, A.; Muhammad, K.; Chen, L. Preparation of stoichiometric molecularly imprinted polymer coatings on magnetic particles for the selective extraction of auramine O from water. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Hu, Q.; Ke, R.; Zhen, X.; Bu, Y.; Wang, S. Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine haemoglobin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Guo, M.H.; Mao, J.H.; Xiong, X.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, Y. Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticle for the rapid and selective enrichment of trace diuron from complicated matrices. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 177, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Wang, J.; Ge, C.; Lian, Z. Fast extraction of chloramphenicol from marine sediments by using magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y. Fabrication of magnetic polymers based on deep eutectic solvent for separation of bovine hemoglobin via molecular imprinting technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1048, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Diao, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for separating aromatic amines from azo dyes—Synthesis, characterization and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landarani, M.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. A magnetic ion-imprinted polymer composed of silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles and polymerized 4-vinyl pyridine and 2,6-diaminopyridine for selective extraction and determination of lead ions. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 7561–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Moghadam, M.R.; Saeidi, M. MultiSimplex optimization of the dispersive solid-phase microextraction and determination of fenitrothion by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2018, 15, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, Z.; Yan, F.; Sun, B. Extraction of the toluene exposure biomarkers hippuric acid and methylhippuric acid using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer, and their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzajani, R.; Keshavarz, A. The core–shell nanosized magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective preconcentration and determination of ciprofloxacin in human fluid samples using a vortex-assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 2291–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Lia, M.; Li, L. Fabrication and evaluation of molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for selective recognition and magnetic separation of lysozyme in human urine. Analyst 2018, 143, 5849–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Sadeghi, H.; Ghaedi, M. Simple and selective detection of quercetin in extracts of plants and food samples by dispersive-micro-solid phase extraction based on core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16144–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Tan, S.; Abd EI-Aty, A.M.; Hacımüftüoğlud, A.; She, Y. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of aminopyralid in milk using dispersive solid-phase extraction. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Lu, R.; Chen, H.; Xie, X. Fast and high-efficiency magnetic surface imprinting based on microwave-accelerated reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization for the selective extraction of estrogen residues in milk. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1562, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Nie, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yan, Z.; Kuang, L. Synthesis and characterization of core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective recognition and determination of quercetin in apple samples. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Dong, C.; Qi, J.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer by the surface RAFT polymerization for the fast and selective removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Xiong, H.; Xu, S.; Shen, D.; Song, X.; Chen, L. One-pot synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted microspheres by RAFT precipitation polymerization for the fast and selective removal of 17b-estradiol. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Kong, J. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers synthesized by surface-initiated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization for the enrichment and determination of synthetic estrogens in aqueous solution. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Surface-imprinted magnetic particles for highly selective sulfonamides recognition prepared by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 408, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Zhang, B.; Guo, P.; Chen, G.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Facile preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective extraction and determination of dexamethasone in skincare cosmetics using HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Guo, L.; Mao, X.; Tan, T.; Wan, H.; Wan, Y. A magnetic hydrophilic molecularly imprinted material with multiple stimuli-response properties for efficient recognition of bisphenol A in beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, E.; Şahin, F. Molecularly imprinted biocompatible magnetic nanoparticles for specific recognition of Ochratoxin A. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016, 227, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, L.; Chen, J.; Yao, S. Preparation of core–shell magnetic ion-imprinted polymer for selective extraction of Pb(II) from environmental samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 178, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, D.; He, H. Computational-aided design of magnetic ultra-thin dummy molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction and determination of morphine from urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1473, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urraca, J.L.; Huertas-Pérez, J.F.; Cazorla, G.A.; Gracia-Mora, J.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction: Determination of citrinin in rice samples by liquid chromatography with UV diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3033–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the fluorescent detection of trace 17β-estradiol in environmental water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y. Preparation and Application of Novel Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Composites for Recognition of Sulfadimethoxine in Feed Samples. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Liang, R.-P.; Wang, X.-N.; Qiu, J.-D. A norepinephrine coated magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for simultaneous multiple chiral recognition. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1409, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, D.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.-J. Preparation and Recognition Properties of Bovine Hemoglobin Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Jia, L. Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer modified magnetic particles for chiral separation of tryptophan enantiomers in aqueous medium. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid determination of bisphenol A in environmental water and milk samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.Y.; Da Chen, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, D. Determination of Tributyltin in Seafood Based on Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. J. Food Qual. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Cai, R.; Yin, Y.; Long, F.; Zhang, Z. Magnetic dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for rapid selective solid-phase extraction of 4-nonylphenol in aqueous samples. Talanta 2014, 128, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrani, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Mansoorkhani, M.J.K.; Ostovan, A. A highly selective nanocomposite based on MIP for curcumin trace levels quantification in food samples and human plasma following optimization by central composite design. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1040, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaei, M.; Dashtian, K.; Rafiee, Z.; Ghaedi, M. Ultrasonic-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction of morphine in urine samples by new imprinted polymer-supported on MWCNT-Fe3O4-NPs: Central composite design optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, C.; Dai, H.; Peng, J.; He, J.; Zhang, K.; Kong, S.; Qiu, P.; He, H. Applications of magnetic surface imprinted materials for solid phase extraction of levofloxacin in serum samples. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Dramou, P.; Xiong, N.; He, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, D.; Dai, H. Development of novel molecularly imprinted magnetic solid-phase extraction materials based on magnetic carbon nanotubes and their application for the determination of gatifloxacin in serum samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1274, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, R.; Heidari, B.; Kazemi, S. Novel magnetic ion-imprinted polymer: An efficient polymeric nanocomposite for selective separation and determination of Pb ions in aqueous media. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26297–26306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Taher, M.A.; Afzali, D.; Mostafavi, A. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer coated magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective removal of dibenzothiophene. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 40, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.-P.; Wang, H.-Y.; He, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-K. Metal chelation dual-template epitope imprinting polymer via distillation-precipitation polymerization for recognition of porcine serum albumin. Talanta 2018, 185, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-P.; Liao, D.-D.; Xie, Y.-L.; Zheng, B.; Yu, J.-X.; Cao, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-H.; Peng, H.-L. A molecular imprinted polymer on the surface of superparamagnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide (MIP@Fe3O4@GO) for simultaneous recognition and enrichment of evodiamine and rutaecarpine inEvodiae fructus. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, A.; Kazemi, E.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H. Synthesis/characterization of molecular imprinted polymer based on magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide for selective separation/preconcentration of fluoxetine from environmental and biological samples. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 46, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ma, X.; Xie, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zeng, G.; Fan, Y. Preparation of dual-dummy-template molecularly imprinted polymers coated magnetic graphene oxide for separation and enrichment of phthalate esters in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lin, H.; He, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, M.; El-Aty, A.A.; Afifi, N.A.; Han, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers doped with graphene oxide for the selective recognition and extraction of four flavonoids from Rhododendron species. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gao, Y.; Tan, K.; Wei, W.; Liu, X. Preparation of a Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Graphene Composite Highly Adsorbent for 4-Nitrophenol in Aqueous Medium. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3316–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; She, C.; Qi, Z.; Xu, X. Magnetic-graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction of microsystin-LR prior to the determination by HPLC. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K. Rapid ultrasound-assisted magnetic microextraction of gallic acid from urine, plasma and water samples by HKUST-1-MOF-Fe3O4-GA-MIP-NPs: UV–vis detection and optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Gan, N.; Pan, D.; Hu, F.; Li, T.; Long, N.; Shen, H.; Feng, Y. Development of a novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer coating using porous zeolite imidazolate framework-8 coated magnetic iron oxide as carrier for automated solid phase microextraction of estrogens in fish and pork samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1365, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, N.; Huang, Z.; You, L.; He, L.; Zhang, S. Solid-phase extraction of aflatoxins using a nanosorbent consisting of a magnetized nanoporous carbon core coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvinizadeh, F.; Daneshfar, A. Fabrication of a magnetic metal–organic framework molecularly imprinted polymer for extraction of anti-malaria agent hydroxychloroquine. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8508–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Synergetic dual recognition and separation of the fungicide carbendazim by using magnetic nanoparticles carrying a molecularly imprinted polymer and immobilized β-cyclodextrin. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-L.; Liu, W.-T.; Huang, X.-C.; Ma, J.-K. Preparation and application of a magnetic plasticizer as a molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbing material for the determination of phthalic acid esters in aqueous samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3806–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Cui, Y.; Hu, F.; Liu, W.; Du, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, J.; Huang, T.; Fizir, M.; He, H. Selective extraction and determination of carbamazepine in biological samples by magnetic imprinted polymer coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1591, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, R.; Shahmari, M.; Taheri, A.; Gholami, K. Ultrasonic-assisted micro solid phase extraction of arsenic on a new ion-imprinted polymer synthesized from chitosan-stabilized pickering emulsion in water, rice and vegetable samples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 61, 104802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffete, N.; Li, H.; Lamouri, A.; Redeuilh, C.; Chen, K.; Dong, C.-Z.; Nowak, S.; Ammar, S.; Mangeney, C. Magnetic nanocrystals coated by molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of bisphenol A. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 22, 1807–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Long, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase microextraction for determination of sulfamethazine by capillary electrophoresis. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Xie, J.; He, L. Determination of macrolide antibiotics residues in pork using molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with LC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Li, R. Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography for determination of azoxystrobin residues in cucumber. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Luo, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, K.; Xia, Z. Selective separation and purification of polydatin by molecularly imprinted polymers from the extract of Polygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma et Radix, rats’ plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1156, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Ming, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction of phenolic compounds in aqueous samples coupled with capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Domínguez-González, R.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Miniaturized vortex assisted-dispersive molecularly imprinted polymer micro-solid phase extraction and HPLC-MS/MS for assessing trace aflatoxins in cultured fish. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, M.; Cui, R.; Chen, L. Dual-template molecularly imprinted polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in water samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 2019, 144, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinadasa, K.K.; Peña-Vázquez, E.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Ionic imprinted polymer—Vortex-assisted dispersive micro-solid phase extraction for inorganic arsenic speciation in rice by HPLC-ICP-MS. Talanta 2020, 220, 121418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.-X.; Li, D.-M.; Li, S.-X. Molecularly imprinted dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of pyraclostrobin in ginseng. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadali, A.; Es’Haghi, Z.; Khatibi, A. Selective extraction of progesterone hormones from environmental and biological samples using a polypyrrole molecularly imprinted polymer and determination by gas chromatography. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, P.; Monasterio, R.P.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A.; Sesay, A.M.; Fernandez-Sanchez, J.F. Development of a folic acid molecularly imprinted polymer and its evaluation as a sorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-R.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.-R.; Jiao, H.-F.; Zhao, J.; Sun, A.-L.; Shi, X.-Z.; Chen, J. Development and Application of the dispersive solid-phase extraction method based on molecular imprinted polymers for removal of matrix components of bivalve shellfish extracts in the GC–MS/MS analysis of amide/dinitroaniline/substituted urea herbicides. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 961–970. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Feng, C.; Qu, P.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, J.P. Determination of Tetracyclines in Chicken by Dispersive Solid Phase Microextraction Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks/Molecularly Imprinted Nano-polymer and Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K. Ultrasound assisted combined molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of nicotinamide in human urine and milk samples: Spectrophotometric determination and optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xue, M.; Xue, F.; Mu, X.; Xu, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhu, G.; Shea, K.J. Molecularly imprinted hollow spheres for the solid phase extraction of estrogens. Talanta 2015, 140, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Arabi, M.; Bagheri, A.R. Preparation of hollow porous molecularly imprinted and aluminum(III) doped silica nanospheres for extraction of the drugs valsartan and losartan prior to their quantitation by HPLC. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Gao, R.; Mu, H. A Novel Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Carbon Nanotubes for Selective Determination of Dioctyl Phthalate from Beverage Samples Coupled with GC/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Pan, S.; Ding, C.; He, J.; Wang, C. Dispersive solid-phase microextraction with graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymers for determining bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in environmental water. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1511, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Jia, L. Molecularly imprinted polymer functionalized silica nanoparticles for enantioseparation of racemic tryptophan in aqueous solution. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fe3O4@OH Functionalization | |
|---|---|
| Diol-based reagents | Ref. |
| Polyethylene glycol (PEG) | [53,54,55,56,57,58] |
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) | [59] |
| Acrylic acid | [60] |
| Methacrylic acid (MAA) | [61] |
| Boronic acids: | |
| 2,4-Difluoro-3-formyl-phenylboronic acid (DFFPBA) a,b | [62,63] |
| 4-Formylphenylboronic acid (FPBA) plus sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) | [64,65] |
| 4-Vinylphenboronic acid (VPBA) c | [66] |
| 3-Aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) d | [67] |
| Silica-based reagents | |
| Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) | [52,58,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90] |
| Fe3O4@CH=C2H4 functionalization | |
| Oleic acid (OA) | [91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] |
| Silica-based reagents: | |
| 3-(Trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate (TMSMA) | [103] |
| 3-Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPS or KH-570) | [27,71,72,75,76,77,80,81,82,83,84,90,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114] |
| Vinyl trimethoxy silane (VTMOS) | [72] |
| Vinyl triethoxy silane (VTEO or VTES) | [115,116,117,118] |
| Fe3O4@NH2 functionalization | |
| Silica-based reagents: | |
| (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) | [78,105,119,120,121,122,123,124] |
| Methacryloyl chloride | [125] |
| Fe3O4@COOH functionalization | |
| Silica-based reagents | |
| Poly(ethylene glycol)bis(carboxymethyl) ether e | [123] |
| Fe3O4@X, X= Cl or Br functionalization | |
| Silica-based reagents | |
| 4-Chloromethyl phenyl trichlorosilane (4-CPS) f | [74,77,126,127,128,129,130,131] |
| 3-Bromopropyl trimethoxy silane (BPTS) | [132] |
| Sample | Target | Composite | Functionalization Reagent/Monomer | Detection Technique | Sample Pre-Treatment: | Performance: LOD and Analytical Recovery | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Pyrethroids | Fe3O4-CNT | TEOS and KH570/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIP particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (3 mL ACN extract) Rebinding media: Water/ACN Extraction time: 15 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 97:3 ACN/acetic acid (2 × 1.0 mL), 30 s (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.0035–0.0072 mg kg−1 Recovery: 82.4–101.7% | [31] |
| Human urine and plasma | Sotalol | Fe3O4-MWCNT | --*/AM | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIP particles (15 mg) Sample volume: 5.0 mL for plasma (30 mL after pH adjustment at 7.0 with phosphate buffer solution) Rebinding media: Water/Methanol Extraction time: 15 min (mechanical shaking) plus 2.0 min (vortex shaking) plus 5 min (ultrasound water-bath) Desorption solvent: 90:10 methanol/acetic acid (10 mL), 5 min (ultrasound water-bath) | LOD: 0.31µg L−1 Recovery: 94.6–102.5% | [32] |
| Heat processed foods | Acrylamide | GO-Fe3O4 | AA (grafting)/AA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL water/methanol extract from 2.0 g of sample Rebinding media: Water/Methanol Extraction time: 60 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (2.0 mL), 120 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 15µg kg−1 Recovery: 86.7–94.3% | [33] |
| Water | BPA, 4-tert-OP, 4-NP | GO-Fe3O4@mSiO2 | CTAB, TEOS/VTTS | HPLC-PDA | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 50 mL (pH adjustment at 6.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 8.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: acetone (1.0 mL), 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.013, 0.010 and 0.010 μg L−1 Recovery: 81.5–104.1% | [34] |
| Milk powder | Melamine | GO-Fe3O4@mSiO2 | CTAB, TEOS/VTTS | UPLC-MS/MS | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 50 mL (pH adjustment at 6.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 8.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: acetone (1.0 mL), 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.00045 mg kg−1 Recovery: 90.3–95.7% | [35] |
| Water | 4-nonylphenol | Fe3O4-MWCNT | PEG/4-VP | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 20 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 20 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 90:10 methanol/acetic acid (2.0 mL), 40 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.15 µg L−1 Recovery: 88.6–98.1% | [143] |
| Food / human plasma | Curcumin | Fe3O4-MWCNT | PEG/AM | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (31 mg) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 20 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 4:1 methanol/DMSO (0.25 mL), 40 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.028 µg L−1 Recovery: >98% | [144] |
| Urine | Morphine | Fe3O4-MWCNT | VTMOS/MAA | UV-Visible spectrophotometry | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (50 mg) Sample volume: pH adjusted at 4.0 Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 20 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: methanol (1.0 mL), 3.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.18 mg L−1 Recovery: 96.4–105.6% | [145] |
| Urine | Levofloxacin | Fe3O4-CNT | --/MAA | HPLC-PDA | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 2.5 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 60 min (incubation) Desorption solvent: 6:4 methanol/acetic acid (5.0 mL) | LOD: 0.01 mg L−1 Recovery: 78.7–83.4% | [146] |
| Serum | Gatifloxacin | Fe3O4-CNT | --*/MAA | HPLC-PDA | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 2.5 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 60 min (incubation) Desorption solvent: 6:4 methanol/acetic acid (5.0 mL) | LOD: 6.0 µg L−1 Recovery: 79.1–85.3% | [147] |
| Water | Pb(II) | Fe3O4-MWCNT | MAPTMS, DTZ/AM | FAAS | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (15 mg) Sample volume: pH adjusted at 6.0 Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 0.5 M thiourea in 0.5 M HCl (5.0 mL), 15 min | LOD: 11 µg kg−1 Recovery: >98.4% | [148] |
| --- | Dibenzothiophene | Fe3O4-MWCNT | KH570/MAA | UV-Visible spectrophotometry | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (10 mg) Rebinding media: Hexane Extraction time: 120 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (mechanical shaking) | LOD: -- Recovery: -- | [149] |
| Porcine serum | Porcine serum albumin | Fe3O4-CNT | TEOS, MPS/zinc acrylate | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (40 mg) Sample volume: 4.0 mL (diluted in PBS, pH 7.0) Rebinding media: Water Desorption solvent: 10% (m/v) SDS and 10% (v/v) acetic acid | LOD: -- Recovery: -- | [150] |
| Extracts from of Evodiae fructus | Evodiamine and rutaecarpine | GO-Fe3O4 | --*/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 20 mL (methanolic extract from 1.0 g of sample) Rebinding media: Methanol Extraction time: mechanical shaking Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid | LOD: -- Recovery: -- | [151] |
| Water, urine drug capsules | Fluoxetine | GO-Fe3O4-Chm | AA/MAA | UV-Visible spectrophotometry | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: pH adjusted at 4.5 Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 10 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (0.1 mL), 5.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.03 µg L−1 Recovery: 95.7–104.0% | [152] |
| Water | PAEs | GO-Fe3O4- mSiO2 | CTAB, TEOS/PTMOS, APTES | GC-MS | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 100 mL (pH adjusted at 7.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 30 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: ethanol (3.0 mL), 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.01–0.05 µg L−1 Recovery: >92.9% | [153] |
| Rhododendrons species | Flavonoids | Fe3O4@SiO2-GO | APTES, THPMP/4-VP | HPLC-MS | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Rebinding media: ACN Desorption solvent: 6:4 methanol/acetic acid, 11 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.06–0.08 µg L−1 Recovery: >64.0% | [154] |
| Water | 4-Nitrophenol | GO-Fe3O4 | --*/PTEOS, TMOS | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 100 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 5.0 min (incubation) Desorption solvent: 4:1 methanol/acetic acid (5.0 mL) | LOD: --- Recovery: 94.7–101.2% | [155] |
| Water | Microcystin-LR | GO-Fe3O4 | --*/Dopamine | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIPs particles (10 mg) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 25 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 8:2 methanol/acetic acid (0.1 mL) | LOD: 0.08 µg L−1 Recovery: 86–113% | [156] |
| Sample | Target | Composite | Reagents/Monomer | Detection Technique | Sample Pre-Treatment: | Performance: LOD and Analytical Recovery | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
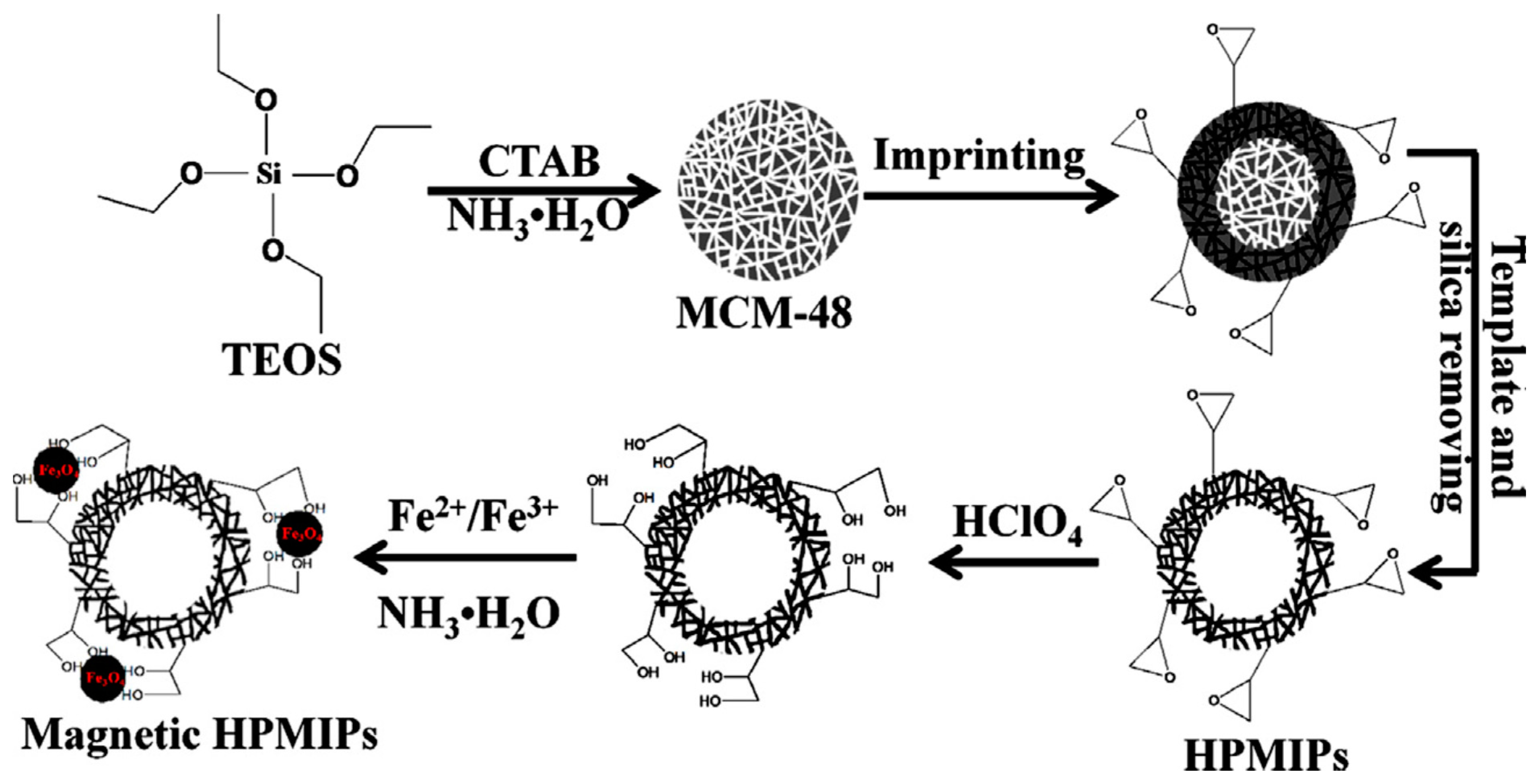
| Spices | Protocatechuic acid | Fe3O4-HPMIP | TEOS, CTAB/4-VP, GMA | HPLC-PDA | Sorbent: MHPMIP particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 3.0 mL Rebinding media: ACN Extraction time: 25 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (0.8 mL) | LOD: 0.4 mg L−1 Recovery: 94.2–101.1% | [37] |
| Rat urines | Aristolochic acid I and II | MMC@MIP | APTES/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMC@MIP particles (80 mg) Sample volume: 3.0 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 30 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 3:1 methanol/DES-1 (3.0 mL) | LOD: 0.03 and 0.17 mg L−1 Recovery: 86.7–94.3% | [41] |
| Potato chips | Acrylamide | Fe3O4@ DMIP | TEOS/APTMS | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: Fe3O4@ DMIP particles (30 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (aqueous extract, pH 4.0, from 1.0 g of sample) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 35 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 45:45:10 ACN/methanol/acetic acid (2.0 mL) (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.35 µg kg−1 Recovery: 94–98% | [42] |
| Urine | Baclofen | SMIBP | TEOS, Chm/--* | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: SMIBP particles (35 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted at 11) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 24 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 45:45:10 methanol/deionized water/ammonium hydroxide (2.0 mL) (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.26 µg L−1 Recovery: 94–98% | [43] |
| Water, fruit juices, human serum | Benzoic acids | MMIR | Melamine, formaldehyde | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MMIR particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 3.0 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: mechanical shaking Desorption solvent: 3:3:1 methanol-water-acetic acid (3.0 mL) | LOD: 0.02–1.0 mg L−1 Recovery: 81.8–108.7% | [44] |
| Chicken meat | Sulfonamides | CS-NR-Mag-MIP | TEPA/GMA | HPLC-MS/MS | Sorbent: CS-NR-Mag-MIP particles (15 mg) Sample volume: 3.0 mL (aqueous extract, pH adjusted at 5.0 from 1.0 g of sample) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 10 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 2.0% ammonia solution in methanol. (3 × 0.5 mL) | LOD: 0.013–0.099 µg kg−1 Recovery: 81.8–108.7% | [48] |
| Water, urine, plasma | Gallic acid | HKUST-1-MOF-Fe3O4-MIP | HKUST-1 MOF, VTMOS/-- | UV-Visible spectrophotometry | Sorbent: CS-NR-Mag-MIP particles (1.6 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted at 3.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 2.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: ethanol (0.18 mL), 2.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 1.377 µg L−1 Recovery: 92.3–100.6% | [157] |
| Pork meat, fish | Estrogens | Fe3O4@ZIF-8-MIP | Fe3O4@ZIF-8/APBA | HPLC-PDA | Sorbent: coated-SPME fiber Rebinding media: n-hexane Desorption solvent: 99:1 methanol/acetic acid | LOD: 0.4–1.7 µg kg−1 Recovery: 92.3–100.6% | [158] |
| Corn | Aflatoxins | ZIF-L-based Co-MNPC@MIP | Co-MNPC/MAA | HPLC-MS/MS | Sorbent: ZIF-L-based Co-MNPC@MIP particles (80 mg) Sample: methanol/water extract Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 10 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 6:4 ACN/water (1.2 mL), 5.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.05–0.07 µg L−1 Recovery: 75.1–99.4% | [159] |
| Corn | Hydroxychloroquine | Ni@MIL-100(Fe)@MIP | Ni@MIL-100(Fe)/APTES | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: Ni@MIL-100(Fe)@MIP particles (23 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted at 9.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 1.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: methanol (50 µL), 3.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.2 µg L−1 Recovery: 96–103% | [160] |
| Vegetables | Carbendazim | Fe3O4-β-CD@MIP | β-CD, Au NPs/MAA | UHPLC-MS | Sorbent: Fe3O4-β-CD@MIP particles (packaged SPE column) Sample volume: (ACN extract from 25 g of sample), flow rate 1.0 mL min−1 Rebinding media: ACN Desorption solvent: methanol/acetic acid (flow rate 1.0 mL min−1) | LOD: 3.0 ng L−1 Recovery: 90.5–109% | [161] |
| Water | PAEs | MIP@mSiO2-β-CD@Fe3O4 | β-CD, APTES/MAA | GC-MS | Sorbent: MIP@mSiO2-β-CD@Fe3O4 particles (30 mg) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 10 min Desorption solvent: 8:2 methanol/acetic acid (6.0 mL), 10 min | LOD: 1.0–5.0 µg L−1 Recovery: 80.2–103% | [162] |
| Urine, serum | Carbamazepine | Fe3O4@CS@MIP | CS DCMA, DCC/4-VP | HPLC-DAD | Sorbent: Fe3O4@CS@MIP (4.0 mg) Sample volume: 4.0 mL serum, 20 mL urine (pH adjusted at 9.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 30 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 8:2 ethanol/acetic acid (3 × 4.3 mL for serum; 2 × 4.6 mL for urine), 28.7 min (serum), 25.3 min (urine), mechanical shaking | LOD: 1.0 µg L−1 (urine), 9.6 µg L−1 (serum) Recovery: 88.2–101.2% | [163] |
| Water, rice, vegetables | As | Fe3O4@OA-IIP | 2-ABT/4-VP | HG-AAS | Sorbent: Fe3O4@OA-IIP (88.18 mg) Sample volume: 4.0 mL serum, 20 mL urine (water and acid digests adjusted at pH 7.25) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 47.63 min, 30 °C (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 0.75 M nitric acid (0.50 mL) | LOD: 0.003 µg L−1 Recovery: 88.2–101.2% | [164] |
| Sample | Target | Composite | Reagents/Monomer | Detection Technique | Sample Pre-Treatment: | Performance: LOD and Analytical Recovery | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | Glibenclamide | HPMIP | TEOS, CTAB/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MHPMIP particles (30 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted at 4.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 15 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 5:5:1 DMSO/ethanol/acetic acid (3.0 mL), resuspension | LOD: 3.5 µg L−1 Recovery: 87.7–104.3% | [38] |
| Water | Bisphenol A | HM-DMIP | TEOS/ICPTES | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: HM-DMIP particles (30 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 30 min (static absorption conditions) Desorption solvent: 90:10 methanol/acetic acid (3.0 mL), static absorption conditions | LOQ: 0.2 mg L−1 Recovery: 98.7–101.7% | [39] |
| Milk | Sulfamethazine | MIP | --*/MAA | CE-UV | Sorbent: MIP particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted with 20 mM phosphate buffer) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (0.30 mL), 10 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 1.1 µg L−1 Recovery: 89–110% | [166] |
| Pork meat | MALs | MIP | --*/MAA | HPLC-MS/MS | Sorbent: MIP particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 5.0 mL (1% (v/v) acetic acid in ACN extract from 1.0 g of sample) Rebinding media: ACN Extraction time: 30 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 10% (v/v) acetic acid in methanol (5.0 mL), 10 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.2–0.5 µg kg−1 Recovery: 68.6–95.5% | [167] |
| Cucumber | Azoxystrobin | HMIM | --*/HPMA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: HMIM particles (100 mg) Sample volume: 5.0 mL (methanol extract from 25 g of sample) Rebinding media: Methanol Extraction time: 30 min (water-bath oscillation plus 30 min without oscillation) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (8.0 mL), water-bath oscillation | LOD: 0.324 µg kg−1 Recovery: 85.9–88.9% | [168] |
| PCRR, and plasma and urine from rat | Polydatin | MIP | --*/4-VP | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MIP particles (10 mg for PCRR, 5.0 mg for plasma and urine) Sample volume: 1.5 mL (extracts from PCRR), 0.20 mL (plasma), 0.050 mL (urine) Rebinding media: 8:2 water/methanol (extracts from PCRR), water (plasma and urine) Extraction time: 3.0 h, mechanical shaking Desorption solvent: 1.5 mL of 8:2 water/methanol and 3.0 h (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.125 mg L−1 Recovery: 89.2–91.6% | [169] |
| Water | Phenolic compounds | MIP | --*/MAA | CE-DAD | Sorbent: MIP particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 1.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 9:1 ACN/acetic acid (30 µL), 4.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.18–0.44 µg L−1 Recovery: 70.7–106.7% | [170] |
| Fish | Aflatoxins | MIP | --*/MAA | HPLC-MS/MS | Sorbent: MIP particles (40 mg) Sample volume: 1.5 mL (60:40 ACN/phosphate buffer extract from 1.g of sample) Rebinding media: 60:40 ACN/phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 Extraction time: 3.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 97.5:2.5 ACN/formic acid (0.50 mL), 4.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.29–0.61 µg kg−1 Recovery: 83–98% | [171] |
| Water | FQs | dt-MIP | --*/MAA | HPLC-DAD | Sorbent: dt-MIP particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 3.0 h (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 90:10 methanol/acetic acid (0.15 mL), 5.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.2 (NOR) and 0.67 (ENR) µg L−1 Recovery: 80.9–101.0% | [172] |
| Rice | Inorganic As | IIP | 1-vinylimidazole-/MAA | HPLC-ICP-MS | Sorbent: IIP particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 1.5 mL (1:1 methanol/water extract from 1.g of sample) Rebinding media: 1:1 methanol/water (pH 8.0) Extraction time: 1.0 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: water (0.15 mL), 1.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.20 (As(III)) and 0.41 (As(V)) µg kg−1 Recovery: 95–103% | [173] |
| Ginseng | Pyraclostrobin | MIP | --*/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MIP particles (100 mg) Sample volume: 2.0 mL (ACN extract from 25 g of sample) Rebinding media: ACN Extraction time: 50 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid (8.0 mL), 50 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.01 mg kg−1 Recovery: 95–103% | [174] |
| Water, urine, serum | Progesterone | MIP | --*/pyrrole | GC-FID | Sorbent: MIP particles (100 mg) Sample volume: 20 mL (pH adjusted at 6.5) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 35 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: methanol (0.5 mL), 40 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.625 µg L−1 Recovery: 88–101% | [175] |
| Food | Folic acid | MIP | --*/VBTMAC | HPLC-MS | Sorbent: MIP particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (aqueous extract) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 20 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: 1:1 methanol/hydrochloric acid (10 mL), 30 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.003 mg L−1 Recovery: 79–83% | [176] |
| Seafood | Herbicides | MIP | --*/MAA | GC-MS/MS | Sorbent: MIP particles (50 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (ACN/acetic acid aqueous extract from 2.0g of sample) Rebinding media: ACN/water Extraction time: 15 min (mechanical shaking) DSPE for clean-up | LOQ: 0.03–8.88 µg kg−1 Recovery: 81–109% | [177] |
| Chicken meat | TCs | MIP-MOF | UiO-66 MOF/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MIP-MOF particles (5 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (aqueous extract, pH adjusted at 4.0, from 1.0 g of sample) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 15 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: methanol (1.0 mL), 5.0 min (mechanical shaking) | LOD: 0.2–5.0 µg L−1 Recovery: 69.6–94.7% | [178] |
| Urine, milk | Nicotinamide | MIP-MOF | HKUST-1 MOF/MAA | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | Sorbent: MIP-MOF particles (2 mg) Sample volume: 10 mL (pH adjusted at 5.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 5.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: ACN (0.20 mL) | LOD: 1.96 µg L−1 Recovery: 95.8–101.3% | [179] |
| Water | Estrogens | MIHS | Colloidal silica, KH570/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: MIHS particles (10 mg) Sample volume: 1.0 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 15 min (dispersion) Desorption solvent: 8:2 methanol/acetic acid (1.0 mL) | LOD: 0.1–0.26 µM L−1 Recovery: 69.6–94.7% | [180] |
| Urine | Valsartan and losartan | HP-MIN | CNPs/TEOS | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: HP-MIN particles (40 mg) Sample volume: 15 mL (pH adjusted at 6.0) Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 27 min (ultrasound dispersion) Desorption solvent: 90:10 methanol/acetic acid (2.0 mL), ultrasound dispersion | LOD: 1.5 (VAL) and 1.4 (LOS) µg L−1 Recovery: 93–99% | [181] |
| Beverages | DOP | MWCNT-MIP | MWCNTs/MAA | GC-MS | Sorbent: MWCNT-MIP particles (60 mg) Sample volume: 20 mL (ACN extract) Rebinding media: ACN Extraction time: 30 min (oscillation) Desorption solvent: 9:1 methanol/acetic acid | LOD: 2.3 ng L−1 Recovery: 88.6–93.0% | [182] |
| Water | DEHP | GO-MIP | GO/MAA | HPLC-UV | Sorbent: GO-MIP particles (20 mg) Sample volume: 600 mL Rebinding media: Water Extraction time: 30 min (mechanical shaking) Desorption solvent: acetone (6.0 mL), 5.0 min (ultrasound dispersion) | LOD: 0.92 µg L−1 Recovery: 82–92% | [183] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review. Separations 2021, 8, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070099
Jayasinghe GDTM, Moreda-Piñeiro A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review. Separations. 2021; 8(7):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070099
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayasinghe, G. D. Thilini Madurangika, and Antonio Moreda-Piñeiro. 2021. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review" Separations 8, no. 7: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070099
APA StyleJayasinghe, G. D. T. M., & Moreda-Piñeiro, A. (2021). Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review. Separations, 8(7), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070099