Abstract
The dissociation constant is an important physicochemical property of drug molecules that affects the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of drugs. In this study, the distribution coefficients of 16 active ingredients extracted from herbal materials were determined at different pH values in liquid–liquid equilibrium systems; the active ingredients were sinomenine, aescin A, aescin B, aescin C, aescin D, chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid A, isochlorogenic acid B, isochlorogenic acid C, baicalin, wogonoside, calycosin-7-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside. The dissociation constants of these active ingredients were calibrated and compared with reported values. The dissociation constants obtained were close to those reported in other studies, which means that the results of this work are reliable.
1. Introduction
The dissociation constant (pKa) of a drug molecule affects its adsorption, distribution, and metabolism. Therefore, pKa data are important data for drug molecules. The liquid–liquid extraction [1], precipitation [2], adsorption [3], or percolation of drug compounds [4] are methods where the dissociation constants can be used in the process design and optimization. Accordingly, pKa data are useful for the pharmaceutical industry. The determination of pKa values is of great significance for the research and development of new drugs, production processes, and clinical pharmaceuticals.
Commonly used methods for determining pKa values include potentiometric titration [5], ultraviolet spectrophotometry [6], capillary electrophoresis [7], liquid chromatography [8], and conductivity methods [9]. The liquid–liquid equilibrium method can simultaneously determine the pKa and distribution coefficient (Dapp) values of multiple active ingredients in a complex mixture [10], such as an herbal extract. The Dapp data are useful for the selection of an extractant [11]. When 1-octanol is used as the extractant to reach the liquid–liquid equilibrium, the logP data of the active ingredients can also be calibrated.
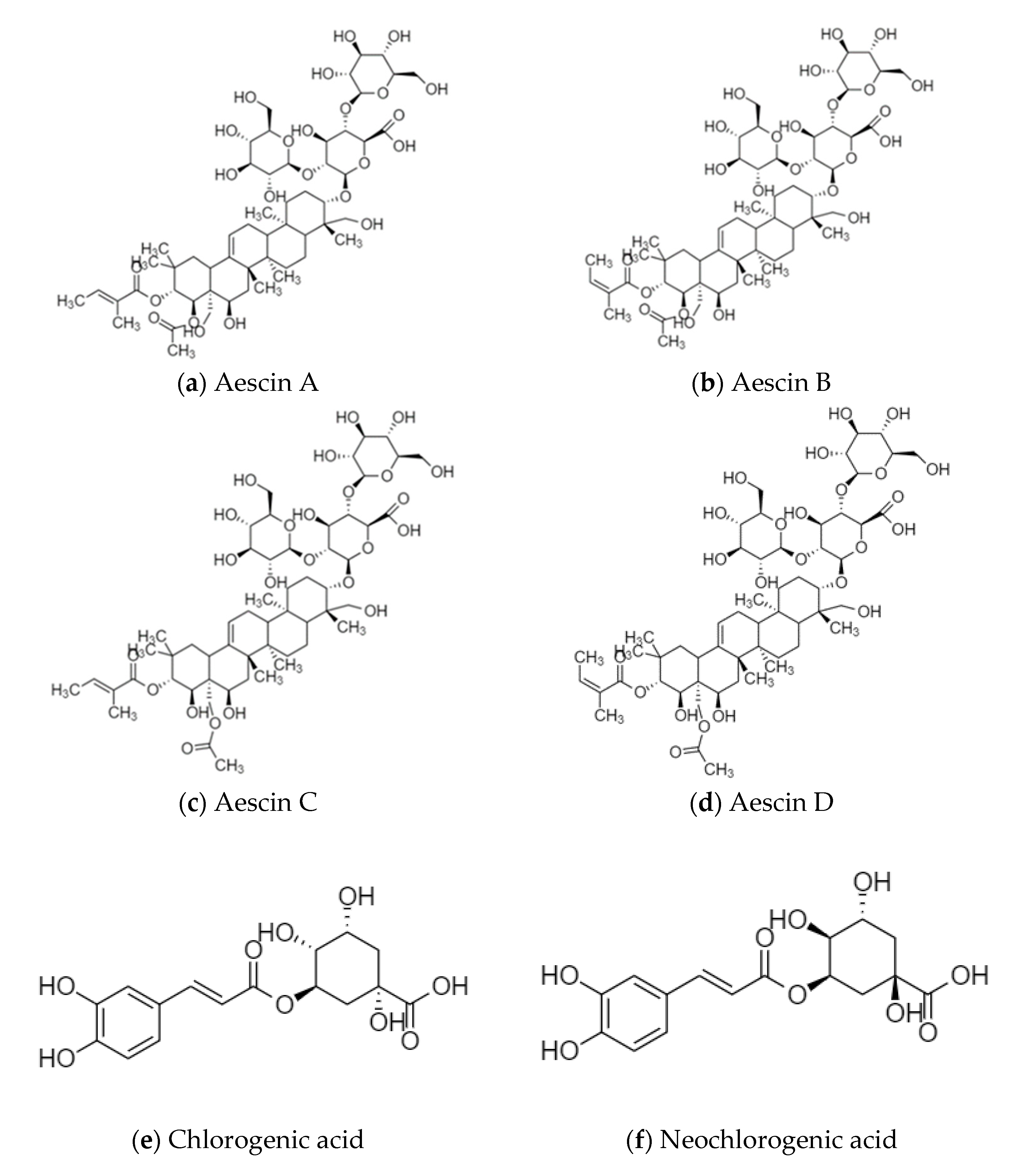
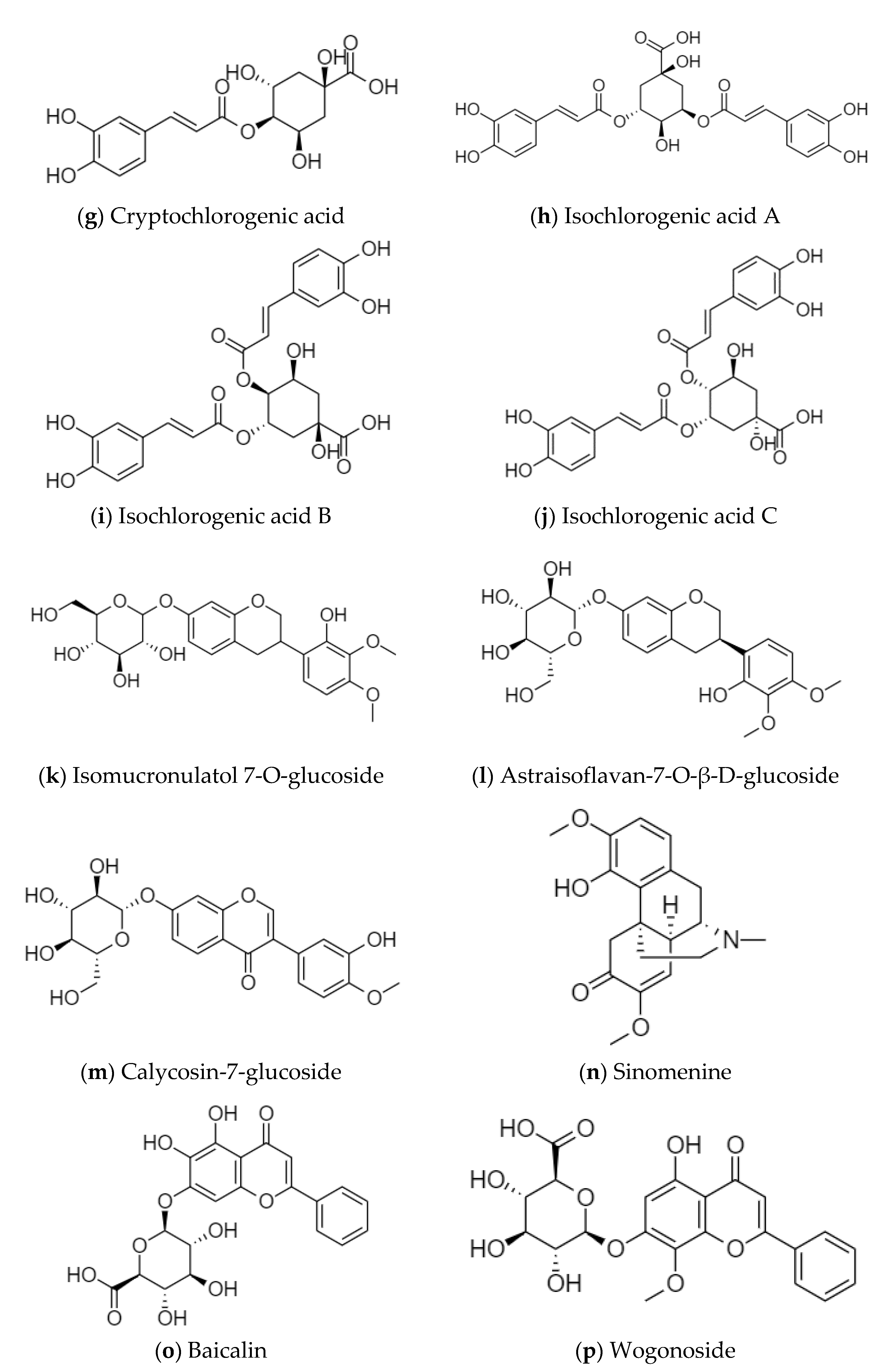
Sinomenine is the main active ingredient of Caulis Sinomenii, which has anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive, analgesic and sedative, anti-arrhythmic, and antitumor activities [12]. Aescins are the main active ingredients of Semen Aesculi, which have various activities, such as anti-inflammatory, anti-swelling, anti-exudation, improving microcirculation, antioxidation, and antitumor activities [13]. Organic acids, such as chlorogenic acid and isochlorogenic acid, are the main active ingredients of Flos Lonicerae, which have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, hemostatic, and immune regulation activities [14]. Flavonoids, such as baicalin and wogonoside, are the main active ingredients of Radix Scutellariae. Baicalin has the effect of scavenging superoxide free radicals, and wogonoside plays a role in protecting the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems [15]. Calycosin-7-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside are the main active ingredients of Radix Astragali. They have the functions of strengthening the exterior, an antiperspirant, promoting diuresis and detumescence, improving body fluid and blood circulation, clearing stagnation and unblocking arthralgia, preventing soreness, and promoting muscle regeneration [16]. The structural formulas of the active ingredients in the above-mentioned medicinal herbs are shown in Figure 1.
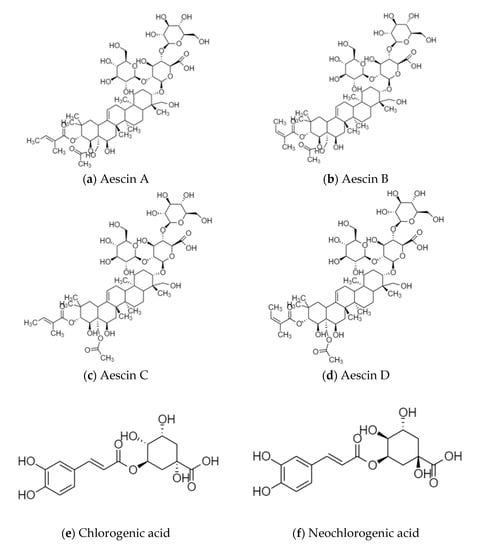
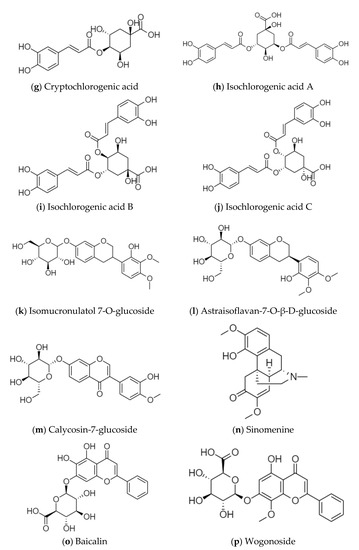
Figure 1.
Structural formulas of the active ingredients in various medicinal herbs, (a) Aescin A; (b) Aescin B; (c) Aescin C; (d) Aescin D; (e) Chlorogenic acid; (f) Neochlorogenic acid; (g) Cryptochlorogenic acid; (h) Isochlorogenic acid A; (i) Isochlorogenic acid B; (j) Isochlorogenic acid C; (k) Isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside; (l) Astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside; (m) Calycosin-7-glucoside; (n) Sinomenine; (o) Baicalin; (p) Wogonoside.
However, there are few reports on the pKa value and Dapp of these active ingredients. In this work, the liquid–liquid equilibrium method was used to determine their pKa and Dapp data, which can be used to optimize the conditions for the extraction or analysis of these active ingredients.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
Semen Aesculi was provided by the Harbin Sanctity Biological Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Harbin, China). Flos Lonicerae was provided by Shanghai Kaibao Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Caulis Sinomenii was purchased from Bozhou Yonggang Decoction Pieces Co., Ltd. (Bozhou, China). Radix Astragali was provided by Limin Pharmaceutical Factory of Livzon Group (Zhuhai, China). Radix Scutellariae was purchased from Gudun Chinese Medicine Clinic of Baozhentang (Hangzhou, China).
Methanol (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytically pure), ethanol (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytically pure), 1-butanol (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytically pure), ethyl acetate (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytically pure), and trichloromethane (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytical purity) were purchased from the Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Methyl isobutyl ketone (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytical purity) and ethylenediamine (purity ≥ 99%, chromatographic purity) were purchased from the Aladdin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Methanol (purity ≥ 99.9%, chromatographic purity) was purchased from Merck Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Darmstadt, Germany). 1-Octanol (purity ≥ 99.5%, analytical purity) was purchased from Shanghai Rhawn Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Sodium aescinate (33.5% aescin A, 31.4% aescin B, 17.8% aescin C, 14.2% aescin D) was purchased from the China Institute for Food and Drug Control. Sinomenine (≥98%), neochlorogenic acid (>99%), chlorogenic acid (>99%), cryptochlorogenic acid (>99%), isochlorogenic acid B (>99%), isochlorogenic acid A (>99%), isochlorogenic acid C (>99%), isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside (>99%), astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside (>99%), calycosin-7-glucoside (>99%), baicalin (>99%), and wogonoside (>99%) were purchased from the Shanghai Winherb Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Preparation of Medicinal Material Extract
2.2.1. Preparation of Caulis Sinomenii Extract
A total of 100.0 g of Caulis Sinomenii medicinal powder and a certain amount of 0.3 mol/L of hydrochloric acid were placed into a beaker to swell for 1 h. Then the mixture was transferred into a percolation tube to immerse for 12 h. Finally, about 800 mL Caulis Sinomenii extract was obtained using a percolation process with 0.3 mol/L of hydrochloric acid as the solvent solution at a flow rate of 4 mL/min.
2.2.2. Preparation of Semen Aesculi Extract
About 100.0 g of Semen Aesculi powder was extracted using 200.0 g of ether at room temperature with stirring for 3 h. After filtration, 200.0 g of ether was added to the filter residue to continue the extraction with stirring for 3 h. After filtration, 300.0 g of 60% ethanol was added to the filter residue to allow for extraction with stirring for 12 h. After filtration, the filtrates were concentrated to an appropriate amount at 40 °C. The Semen Aesculi extract was obtained via drying in a vacuum drying oven at 65 °C.
2.2.3. Preparation of the Flos Lonicerae, Radix Scutellariae, and Radix Astragali Extracts
A total of 40.0 g of Flos Lonicerae and 500 mL of water were mixed to allow for reflux extraction for 3 h at room temperature. The Flos Lonicerae extract was obtained after filtration. A total of 40.0 g of Radix Scutellariae and 1000 mL of water were mixed to allow for boiling extraction for 2 h. The Radix Scutellariae extract was obtained after filtration. A total of 50.0 g of Radix Astragali and 800 mL of water were mixed and decocted for 4 h. The Radix Astragali extract was obtained after filtration.
2.3. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Extraction Experiment
2.3.1. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Experiment of Caulis Sinomenii
About 30 g of Caulis Sinomenii extract and 30 g of organic extractant were placed into each Erlenmeyer flask with different amounts of NaOH solution being added to adjust the pH value, which was measured using a pH meter (S40, Mettler-Toledo Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Erlenmeyer flasks were placed in a constant temperature water bath oscillator (DSHZ-300, Taicang City Experimental Equipment Factory, Taicang, China) at 30 °C and shaken at 110 rpm for 12 h. Then, the organic and aqueous phases in the mixed solution were separated using a centrifuge (5804R, Eppendorf, Shanghai, China) at 4200 rpm for 15 min. The pH value of the aqueous phase was then measured. The aqueous phase was diluted with 0.3 mol/L of hydrochloric acid and the organic phase was diluted with methanol. After filtering with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane (Fitmax Syringe Filter 13 mm 0.22 μm Nylon 100/pk, Dikma, Beijing, China), the subsequent filtrate was taken out for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (FL5090, Zhejiang Fuli Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd., Taizhou, China) analysis. Experiments were carried out in different extraction systems, where the experimental conditions are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Liquid–liquid equilibrium extraction system.
2.3.2. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Experiment Using Semen Aesculi
About 0.25 g of Semen Aesculi extract, 30.0 g of water, and 30 g of 1-butanol were added to each Erlenmeyer flask with different amounts of 1% hydrochloric acid and 1% NaOH solution added to adjust the pH value. Then, Erlenmeyer flasks were placed in a constant-temperature water bath oscillator at 30 °C and shaken at 140 rpm for 12 h. After centrifugation, the organic and aqueous phases in the mixture were separated, and the pH value of the aqueous phase was measured. The two phases were diluted with methanol separately. These solutions were filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane and analyzed using HPLC.
2.3.3. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Experiment Using Flos Lonicerae
A total of 15 mL of Flos Lonicerae extract and 10 mL of 1-octanol were placed into each Erlenmeyer flask. Different amounts of 1% hydrochloric acid solution were used to adjust the pH value. Then, Erlenmeyer flasks were placed in a constant temperature water bath oscillator at 30 °C and shaken at 140 rpm for 12 h. The solution was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 20 min to separate the two-phase solution, and the pH value of the aqueous phase was measured. The concentrations of the neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid B, isochlorogenic acid A, and isochlorogenic acid C in each phase were determined using HPLC (1100, Agilent Technology, Beijing, China).
2.3.4. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Experiment Using Radix Scutellariae
A total of 15 mL of the Radix Scutellariae extract and 10 mL of 1-octanol were added to each Erlenmeyer flask, and different amounts of 1% hydrochloric acid solution were used to adjust the pH value. Then, Erlenmeyer flasks were shaken for 10 h at 140 rpm at 30 °C. The aqueous and organic phases were separated via centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min. After being filtered with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane, the solution was analyzed using HPLC to determine the concentrations of baicalin and wogonoside in each phase.
2.3.5. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Experiment Using Radix Astragali
A total of 15 mL of Radix Astragali extract and 10 mL of 1-octanol were added to each Erlenmeyer flask. Different amounts of 1% hydrochloric acid solution or 0.02 g/mL of NaOH solution were used to adjust the pH value. The Erlenmeyer flasks were shaken for 10 h at 140 rpm in a 30 °C constant-temperature oscillator. The aqueous and organic phases were separated via centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min. After being filtered with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane, the solution was analyzed using HPLC to determine the concentrations of isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and calycosin-7-glucoside in each phase.
2.4. Analysis Method
2.4.1. Analysis Method of Sinomenine in Caulis Sinomenii
The method was performed on a Fuli HPLC system using an Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) at 25 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.25% ethylenediamine–water (A) and 0.25% ethylenediamine–methanol (B) using (50/50, v/v) gradient program. The flow rate was 1 mL/min and the volume of the sample injection was 10 μL. The detector wavelength was set to 262 nm. The detection time was 30 min. A typical chromatogram of the Caulis Sinomenii system is shown in Figure A1 in the Appendix A.
2.4.2. Analysis Method of Aescins in Semen Aesculi
The concentrations of aescin A, aescin B, aescin C, and aescin D were determined using HPLC analysis according to the method published by Cao et al. [17]. The method was performed on a Fuli HPLC system using an Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) at 35 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.2% phosphoric acid–water (A) and acetonitrile (B) using a 63/37 (v/v) gradient program. The flow rate was 1 mL/min, and the injection volume was 10 μL. The detector wavelength was set to 220 nm. The detection time was 30 min. A typical chromatogram of Semen Aesculi is shown in Figure A2 in the Appendix A.
2.4.3. Analysis Method of Phenolic Acids in Flos Lonicerae
The concentrations of chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acids A, B, and C, and cryptochlorogenic acid were determined using HPLC analysis according to the method published by Wang et al. [18]. The method was performed on an Agilent HPLC system using an Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) at 30 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.1% phosphoric acid–water (A) and acetonitrile (B) using the following gradient program: 8–10% B from 0 to 10 min, 10–15% B from 10 to 20 min, 15–15% B from 20 to 30 min, 15–25% B from 30 to 40 min, and 25–100% B from 40 to 60 min. The flow rate was 1 mL/min and the volume of the sample injection was 10 μL. The detector wavelength was set to 325 nm. The detection time was 30 min. A typical chromatogram of Flos Lonicerae is shown in Figure A3 in the Appendix A.
2.4.4. Analysis Method of Flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae
The concentrations of baicalin and wogonoside were determined using HPLC analysis according to the method published by Zhu et al. [19]. The method was performed on an Agilent HPLC system using an Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) at 25 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.2% phosphoric acid–water(A) and methanol (B) using the following gradient program: 45–45% B from 0 to 10 min and 45–70% B from 10 to 55 min. The flow rate was 1 mL/min and the injection volume was 10 μL. The detector wavelength was set to 274 nm. The detection time was 30 min. A typical chromatogram of Radix Scutellariae is shown in Figure A4 in the Appendix A.
2.4.5. Analysis Method of Flavonoids in Radix Astragali
The concentrations of calycosin-7-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside were determined using HPLC analysis according to the method published by Chen et al. [20]. The method was performed on an Agilent HPLC system using a Diamonsil C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) at 35 °C. The mobile phase consisted of 0.05% formic acid–water (A) and acetonitrile (B) using the following gradient program: 15–29% B from 0 to 40 min, 29–40% B from 40 to 50 min, 40–40% B from 50 to 60 min, and 40–90% B from 60 to 70 min. The flow rate was 1 mL/min and the volume of the sample injection was 10 μL. The detector wavelength was set to 210 nm. The detection time was 30 min. A typical chromatogram of Radix Astragali is shown in Figure A5 in the Appendix A.
2.5. Data Processing
2.5.1. pKa Fitting of the Active Ingredients in Semen Aesculi, Flos Lonicerae, Radix Scutellariae, and Radix Astragali
For active ingredients in Semen Aesculi, Flos Lonicerae, Radix Scutellariae, and Radix Astragali, the nonlinear fitting formulas for and derived by Gong et al. [10] were used to fit the , as shown in Formulas (1)–(3).
where is the apparent distribution coefficient, (mg/L) refers to the concentration of the target component, and the subscripts org and aq refer to the organic phase and the water phase, respectively.
where is the distribution coefficient of the molecule, and is the distribution coefficient of the first-order dissociated ion. When fitting, the logarithms of both sides of the formula were taken to get the following formula:
where and are the base 10 logarithms of and , respectively.
2.5.2. pKa Fitting of Sinomenine
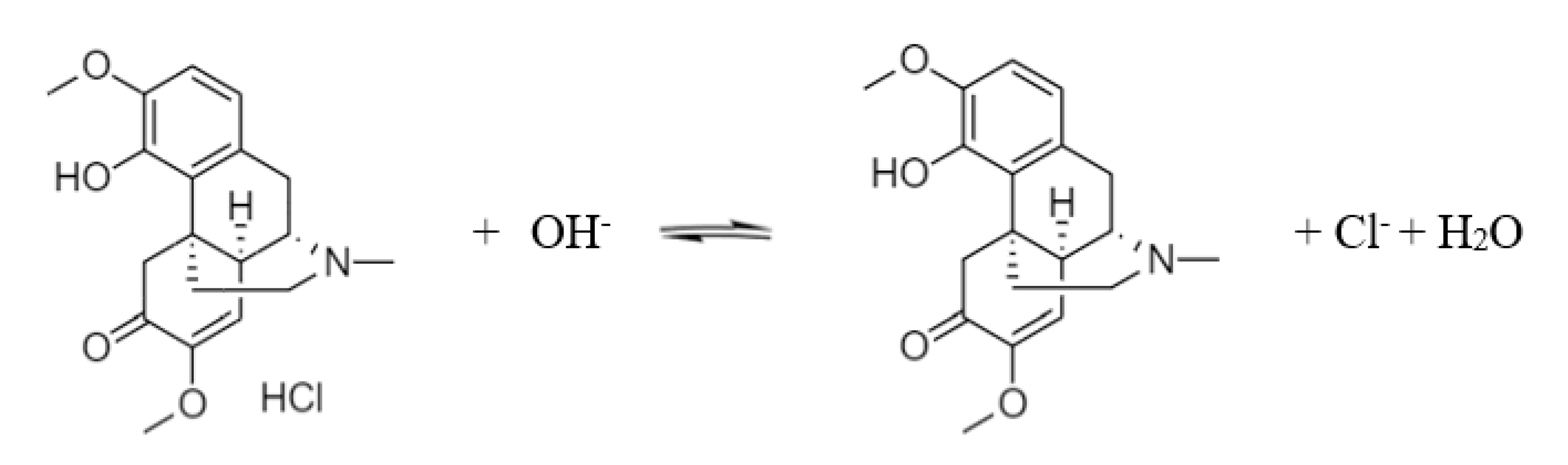
Sinomenine is an alkaloid and its structural formula is shown in Figure 1. It shows that the dissociable groups of sinomenine are mainly tertiary amino groups and phenolic hydroxyl groups. When 0.3 mol/L of hydrochloric acid was used to extract Caulis Sinomenii, the tertiary amino group on sinomenine reacted with hydrochloric acid to form sinomenine hydrochloride salt. When exposed to alkali, the sinomenine hydrochloride salt removes the hydrochloric acid to generate sinomenine molecules. The reaction equation is shown in Scheme 1.
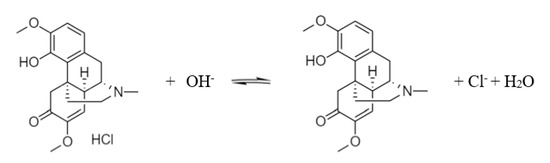
Scheme 1.
Dissociation of sinomenine hydrochloride.
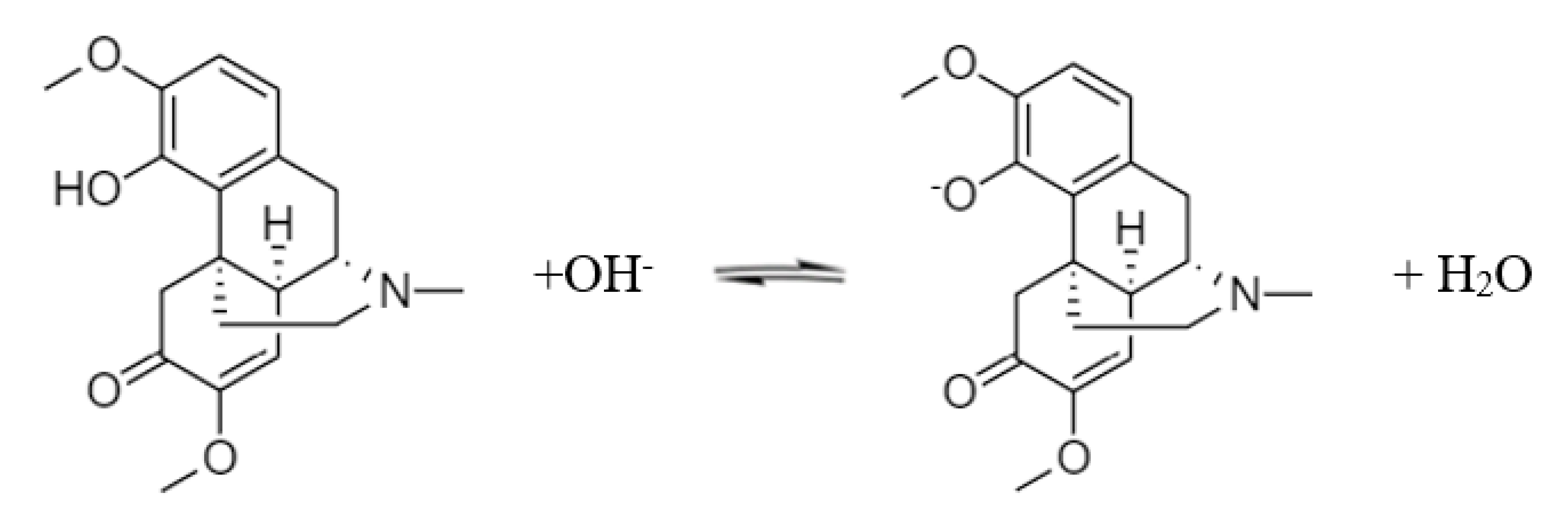
With further exposure to an alkali, the phenolic hydroxyl group on the sinomenine molecule ionizes to form a salt. The sodium salt of sinomenine is soluble in water. The reaction equation is shown in Scheme 2.
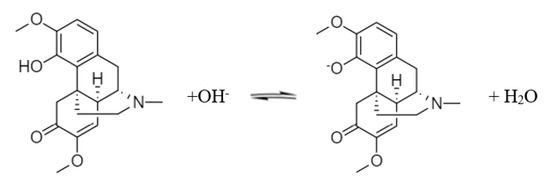
Scheme 2.
Dissociation of sinomenine.
Sinomenine hydrochloride can be regarded as a dibasic acid when the two pKa values of sinomenine were fitted simultaneously. The hydrochloric acid is completely removed during the first dissociation, and the phenolic hydroxyl group is ionized during the second dissociation. Based on Gong et al. [10], Formula (4) was used for the data fitting:
where is the distribution coefficient of sinomenine after the secondary dissociation, is the first dissociated (the of sinomenine hydrochloride), and is the of the secondary dissociation (the of the phenolic hydroxyl group). When fitting, the logarithm of both sides of the formula was also taken to obtain Formula (5):
where is the base 10 logarithm of . If a value of , , or was less than −20, the corresponding distribution coefficient was considered to be extremely small. In order to facilitate the fitting of other parameters, the value of the extremely small , , or was set to −20.
3. Results and Discussion
In this work, the extracts of the medicinal herbs were prepared and extracted with organic solvents. After reaching liquid–liquid equilibrium, the concentrations of the active ingredients in the two phases were determined. The values were calculated and fitted using Formula (3) or (5) to obtain the value.
3.1. Dapp and pKa of Sinomenine
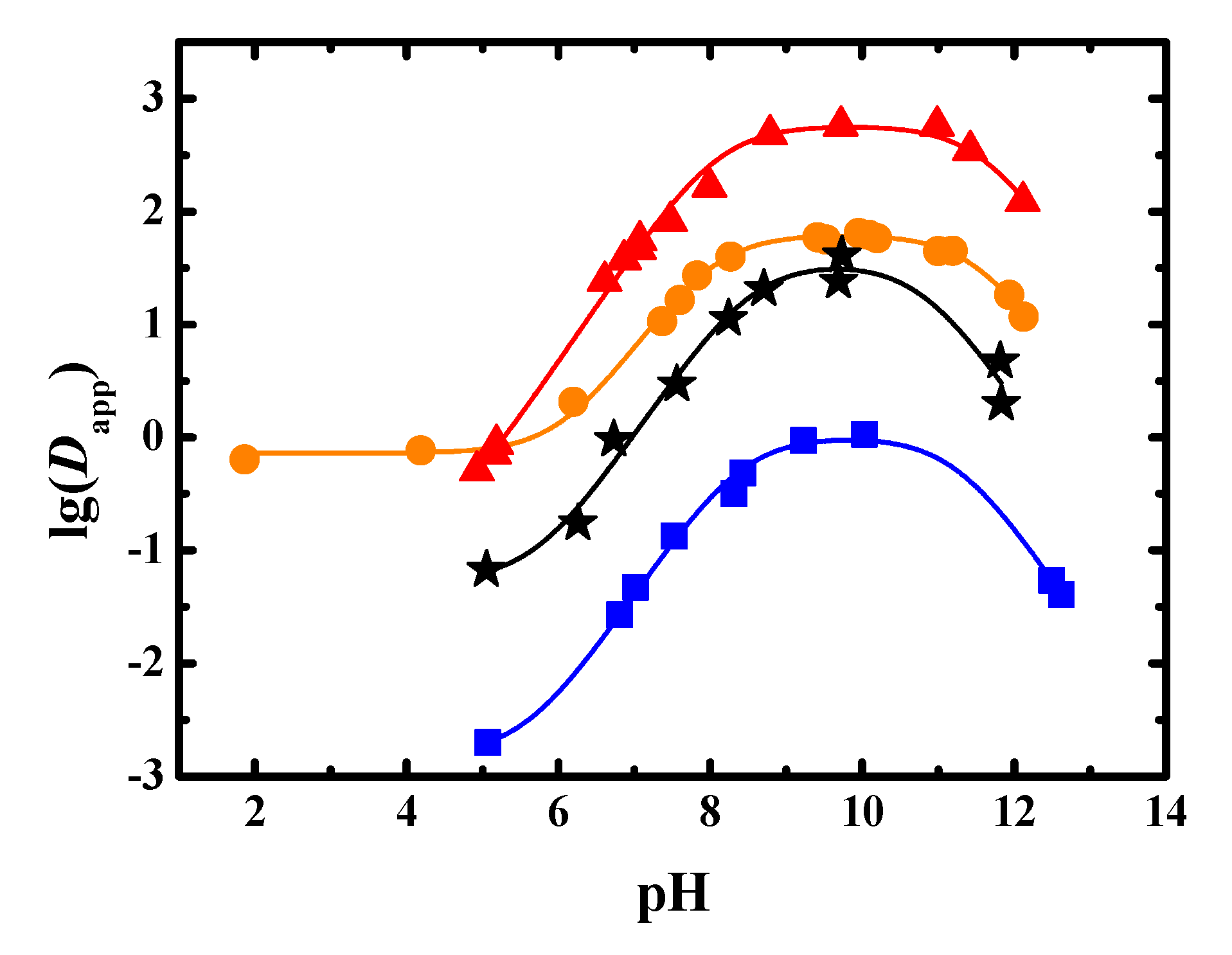
The Dapp of sinomenine at different pH values in the 1-butanol-water, trichloromethane–water, methyl isobutyl ketone–water, and 1-octanol–water systems were found, as seen in Table A1. The results are shown in Figure 2.
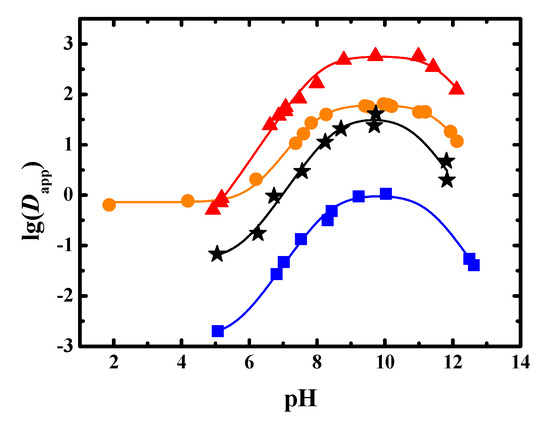
Figure 2.
Experimental and fitted results of Dapp of sinomenine obtained in four extraction systems (●: 1-butanol, ▲: trichloromethane, ■: methyl isobutyl ketone, ★: 1-octanol, solid line: fitted results).
As shown in Figure 2, when the pH value of the system was less than 10 in the four liquid–liquid equilibrium systems, the Dapp value increased as the pH value increased. When the pH value of the system was greater than 10, the Dapp value decreased as the pH value increased. When the pH value was low, such as less than the pKa of the amine group, the proportion of sinomenine in molecular form increased as the pH value increased. Therefore, the Dapp value of the liquid–liquid extraction was observed to increase. When the pH value increased to be higher than the pKa of phenolic hydroxyl ionization, the proportion of sinomenine in the salt form increased. Therefore, the Dapp value of sinomenine decreased. The maximum Dapp of sinomenine in 1-butanol–water system was more than 60. The maximum Dapp in trichloromethane–water system was more than 500, indicating that the extraction capacity of trichloromethane was very large. The maximum Dapp in methyl isobutyl ketone–water system was less than 1.1, indicating that the extraction capacity of the methyl isobutyl ketone was small. The maximum Dapp in 1-octanol–water system was about 40, which was a little lower than that of the 1-butanol system.
The experimental results were fitted using Origin software (2018, OriginLab, MA, USA) and are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2. The distribution coefficient of sinomenine salt after ionization of the phenolic hydroxyl group was too small; thus, d2 was set to −20 for the fitting. It can be seen from Table 2 that the R2adj values that were obtained by fitting the data from the four extraction systems of 1-butanol–water, trichloromethane–water, methyl isobutyl ketone–water, and 1-octanol–water were 0.996, 0.992, 0.992, and 0.969, respectively, which showed that the fitting results were in good agreement with the measured values. From the fitting results, the pKa,1 values of sinomenine conjugate acid were 8.01, 8.10, 8.40, and 8.53, respectively. The pKa,2 values of the phenolic hydroxyl dissociation of sinomenine were 11.52, 11.59, 11.25, and 10.81, respectively. The distribution coefficients of the sinomenine molecules in the 1-butanol–water, trichloromethane–water, methyl isobutyl ketone–water, and 1-octanol–water systems were 62.4, 575, 1.01, and 35.2, respectively. The distribution coefficients of sinomenine hydrochloride in the above four systems were 7.26 × 10−1, 1.20 × 10−1, 1.53 × 10−3, and 5.32 × 10−2, respectively, indicating that the four solvents had poor extraction capacities for sinomenine hydrochloride salt in water. Because 1-octanol was applied as the extractant, the logP values of sinomenine and sinomenine hydrochloride were 1.55 and −1.27, respectively.

Table 2.
The pKa fitting results for sinomenine.
3.2. Dapp and pKa of Aescins
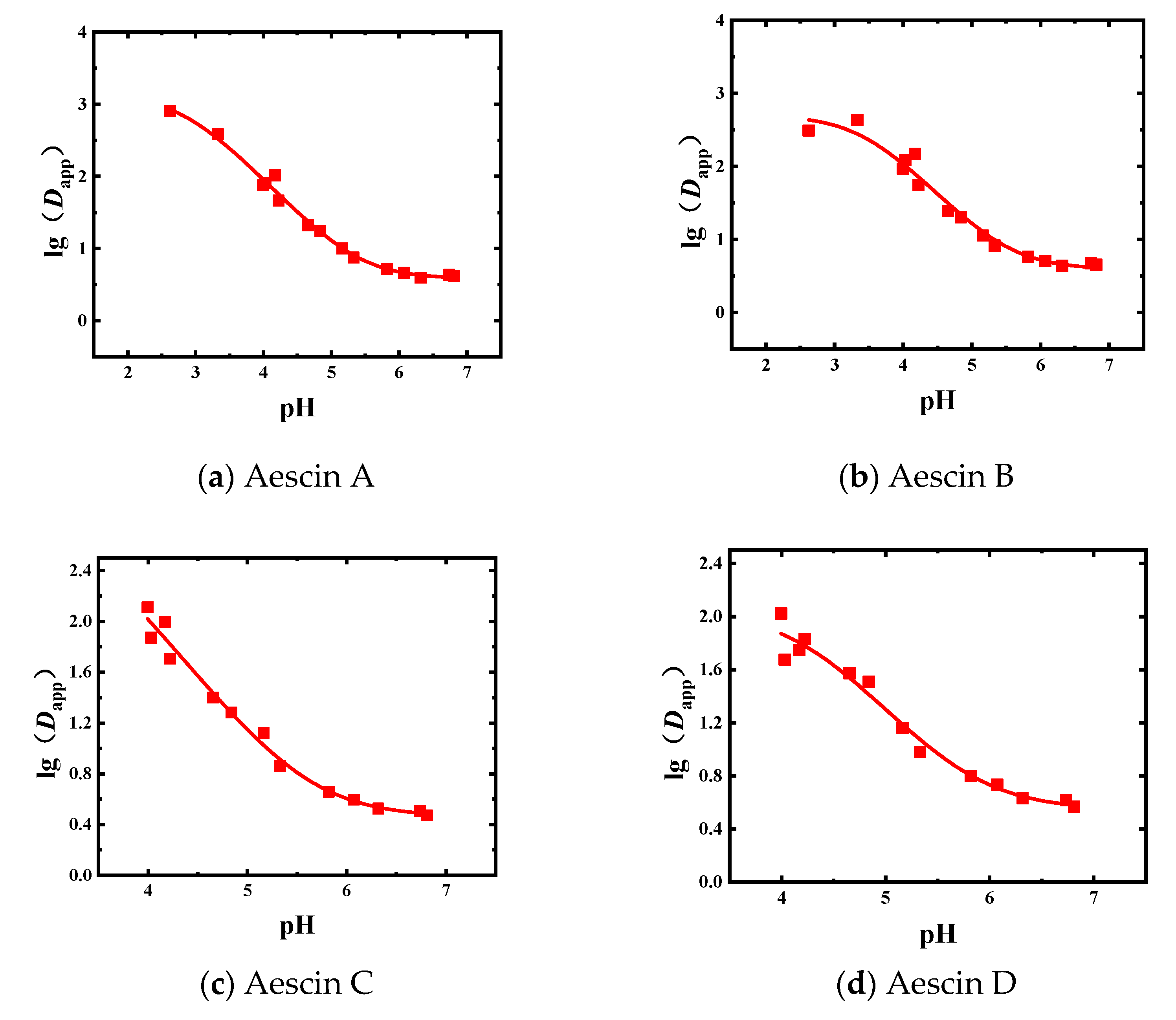
The liquid–liquid equilibrium experiments of the Semen Aesculi extract were carried out with 1-butanol as the extractant. The experimental results of Dapp of aescins are shown in Figure 3 and Table A2.
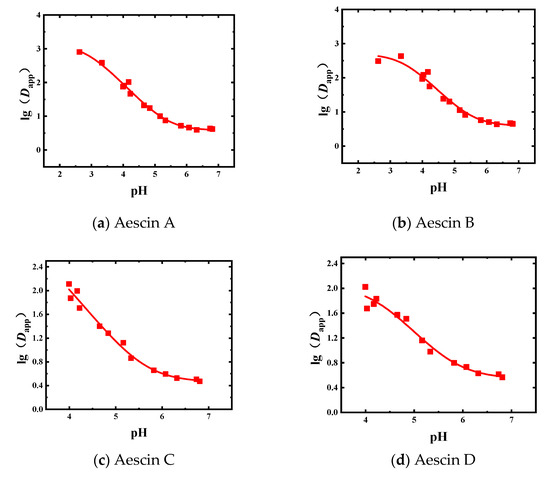
Figure 3.
Experimental and fitted results for the Dapp of the four aescins obtained in the 1-butanol system (■: experimental results, solid line: fitted results); (a) Aescin A; (b) Aescin B; (c) Aescin C; (d) Aescin D.
In the 1-butanol equilibrium system, the change trends of the Dapp values of the four aescins were roughly the same. When the pH value increased, the Dapp value gradually decreased. The Dapp value changed rapidly between pH 3.0 and 5.0. The data obtained in the 1-butanol system was fitted, and the initial values of d0, d1, and pKa were adjusted to make the fitted curve better coincide with the actual data points. The fitting results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 3.

Table 3.
The pKa fitting results of aescins.
It can be seen from Table 3 that the Dapp results of aescins A, B, C, and D in the 1-butanol system were fitted well, with R2 values greater than 0.97. The value of d0 was higher than that of d1 because the solubility of the molecules in the organic phase was higher than that of the ions. Overall, the d0 values of the four ingredients were greater than 2.00, that is, the distribution coefficients of the molecular forms of the aescins were greater than 100. The d1 values were in the range of 0–1, which means that the distribution coefficients of the ionic form of the aescins were in the range of 1–10. This shows that the solubility of the aescins in the 1-butanol phase was quite large. In the 1-butanol system, the calibrated pKa values of aescins A, B, C, and D were 2.83, 3.42, 3.10, and 4.24, respectively.
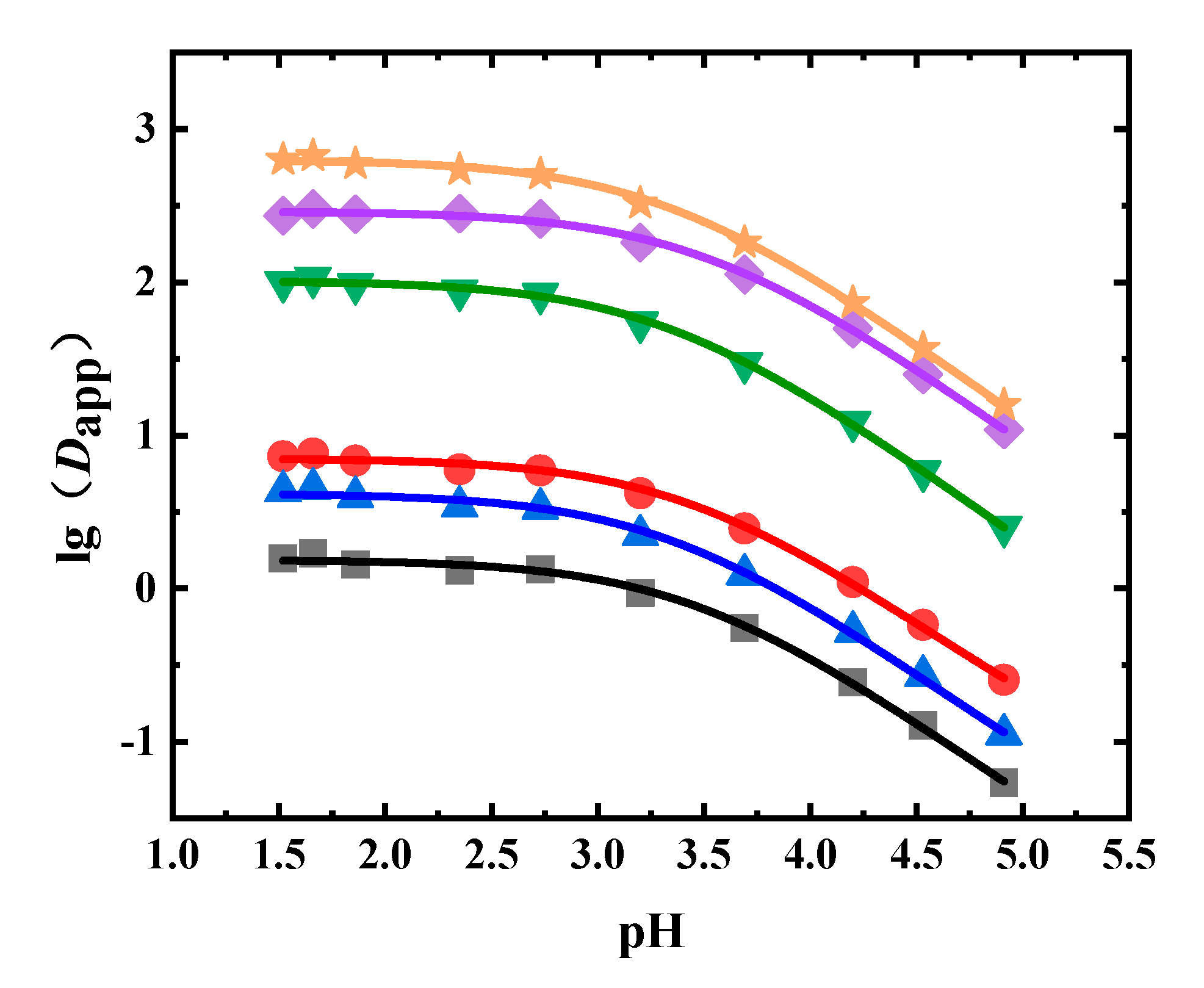
3.3. Dapp and pKa of the Phenolic Acids in Flos Lonicerae
In the liquid–liquid equilibrium experiments using the Flos Lonicerae extract, 1-octanol was the extractant. The Dapp values of neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid A, isochlorogenic acid B, and isochlorogenic acid C at different pH values are shown in Figure 4 and Table A3. It can be seen from Figure 4 that as the pH value decreased, the Dapp value increased. The Dapp value of isochlorogenic acid C was the largest, while the Dapp value of neochlorogenic acid was the lowest at the same pH value. The Dapp values of isochlorogenic acids A, B, and C in the 1-octanol system could reach more than 100. The Dapp values of neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, and cryptochlorogenic acid were below 10.
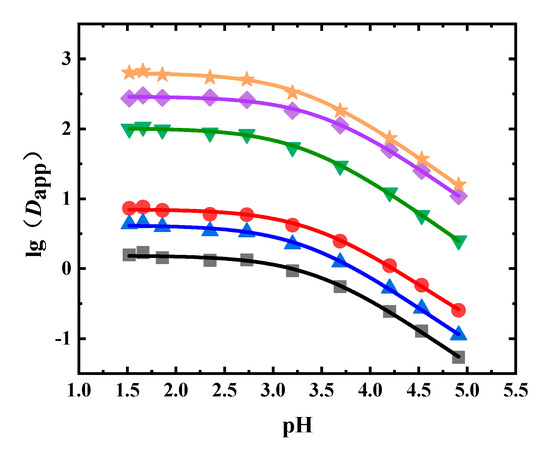
Figure 4.
Experimental and fitted results of Dapp of six phenolic acids in Flos Lonicerae (■: neochlorogenic acid, ●: chlorogenic acid, ▲: cryptochlorogenic acid, ◆: isochlorogenic acid A, ▼: isochlorogenic acid B, ★: isochlorogenic acid C, solid line: fitted results).
The obtained Dapp values were fitted, where the fitting results are shown in Table 4. It can be seen from Table 4 and Figure 4 that the fitting results agreed well with the experimental results, with R2 values higher than 0.99. The pKa values of all six phenolic acids were between 3.3 and 3.5. The logP values of chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid A, isochlorogenic acid B, and isochlorogenic acid C were 0.85, 0.19, 0.62, 2.46, 2.01, and 2.80, respectively.

Table 4.
The pKa fitting results of six phenolic acid ingredients of Flos Lonicerae.
3.4. Dapp and pKa of Flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae
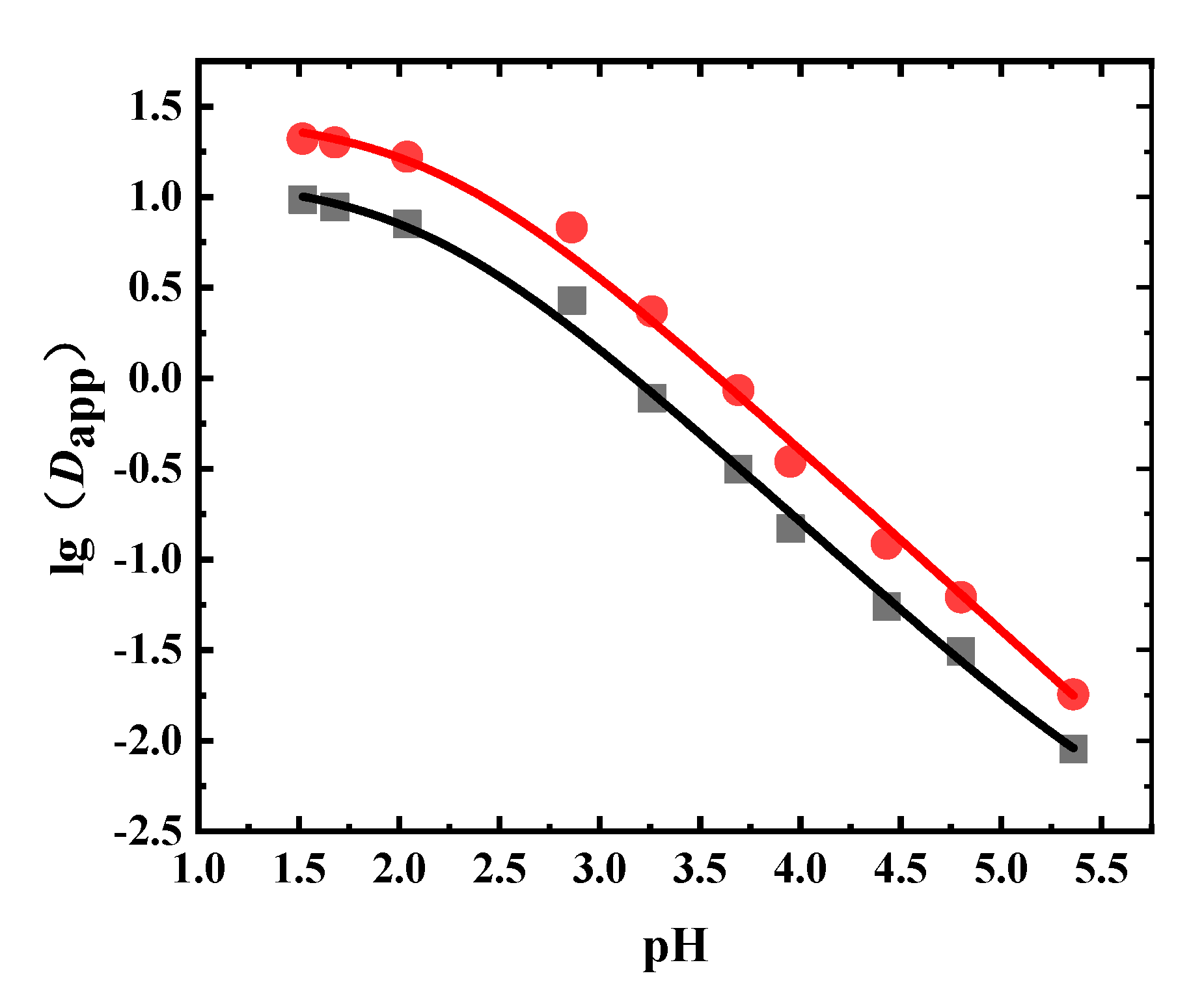
1-Octanol was the extractant in the liquid–liquid equilibrium extraction experiment using the Radix Scutellariae extract. The Dapp values of wogonoside and baicalin under different pH values are shown in Figure 5 and Table A4. It can be seen that the Dapp changing trends of baicalin and wogonoside were very similar. As the pH value increased, the Dapp values of wogonoside and baicalin decreased. The Dapp value of wogonoside was higher than that of baicalin, which means that the extraction capacity of wogonoside in 1-octanol was larger.
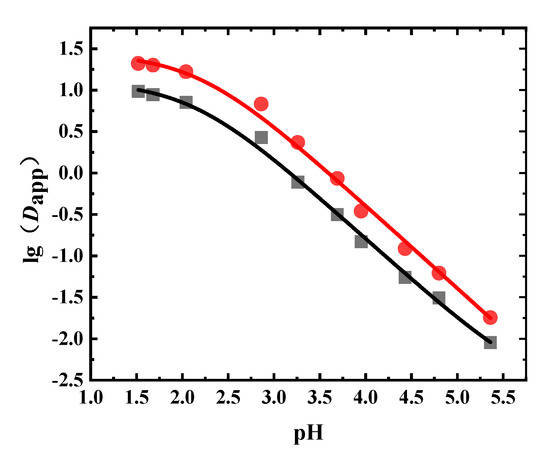
Figure 5.
Experimental and fitted results of the Dapp of flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae (●: wogonoside, ■: baicalin, solid line: fitted results).
The obtained Dapp values were fitted, where the fitting results are shown in Table 5 and Figure 5. From Table 5, it can be seen that the fitting results agreed well with experimental results, with R2 values greater than 0.99. Since these two flavonoids contain carboxyl groups, the pKa values obtained were both around 2.1. The logP values of baicalin and wogonoside were 1.10 and 1.44, respectively.

Table 5.
The pKa fitting results of flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae.
3.5. Dapp and pKa of Glycosides in Radix Astragali
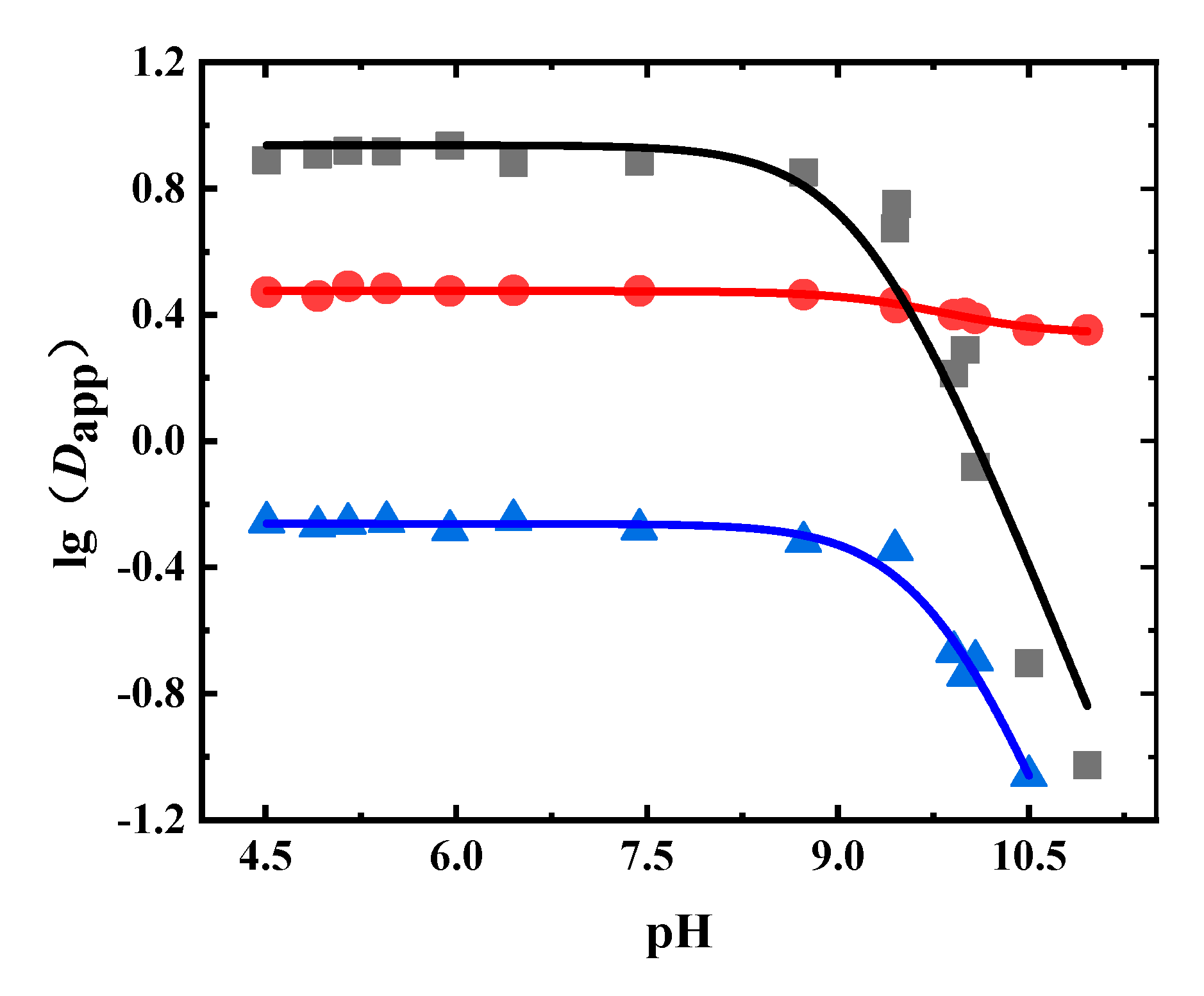
1-Octanol was the extractant in the liquid–liquid equilibrium extraction experiment using the Radix Astragali extract. The Dapp values of astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, and calycosin-7-glucoside at different pH values are shown in Figure 6 and Table A5. It can be seen that the Dapp values of astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside and isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside were less than 10, but the Dapp values of calycosin-7-glucoside were less than 1. When the pH value was greater than 8.0, the Dapp of calycosin-7-glucoside and isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside significantly decreased.
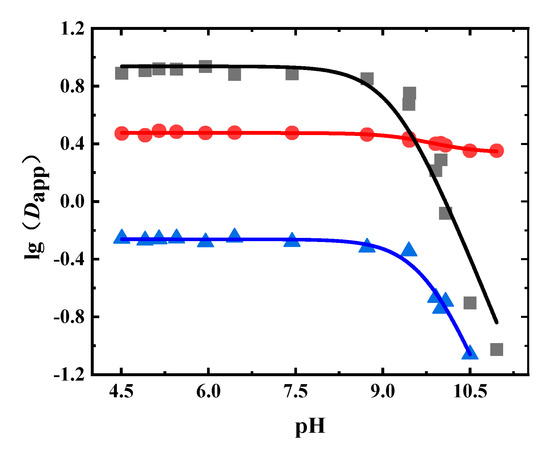
Figure 6.
Experimental and fitted results of the Dapp of glycosides in Radix Astragali. (●: astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, ■: isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, ▲: calycosin-7-glucoside, solid line: fitted results).
The obtained Dapp values were fitted, where the fitting results are shown in Table 6. The pKa value obtained by this fitting corresponds to the ionization of the phenolic hydroxyl group. From Table 6, it can be seen that the Dapp fitting results of isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and calycosin-7-glucoside in the Radix Astragali extract were also satisfactory, with R2 values greater than 0.94. The pKa values were between 9.1–9.8. The logP values of isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and calycosin-7-glucoside were 0.94, 0.48, and −0.26, respectively.

Table 6.
The pKa fitting results of glycosides in Radix Astragali.
3.6. Comparison between the Experimental Values and Literature Values
In order to check the reliability of the test results, the logP and pKa values were predicted using Discovery Studio (V3.1, BIOVIA, Paris, France), which is widely used in ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity), QSAR (Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship), pharmacophore model prediction, and virtual screening [21,22,23,24]. In addition, we also compared the pKa results with those reported in the literature. The comparison between the pKa results found in this work, the prediction value from the software, and those in the literature are listed in Table 7.

Table 7.
The comparison between the pKa results of this work, the prediction values using software (Discovery Studio V3.1), and those in the literature.
In Table 7, the pKa values obtained in this work are close to the reported values, which indicates that the results obtained in this work are relatively reliable. The prediction values from Discovery Studio were also close to the results from experiments on most occasions. For many organic acids, the predicted pKa values were a little lower than those reported in this work.
The comparison between the logP results of this work and the prediction values of Discovery Studio can be seen in Table 8. The logP values of sinomenine were very close. However, for the logP values of other ingredients, the deviation was remarkable.

Table 8.
The comparison between the logP results of this work and the prediction values using software.
The determination method used in this work also has certain limitations. For example, in different solvents, the measured pKa values will have certain differences. When the extraction capacity of the solvent is too large, the concentration of the ingredient in the aqueous phase will be too low, which usually leads to difficulties in making concentration measurements.
3.7. Suitable Mobile Phase for the HPLC Analysis of Each Ingredient
Because the pH value of the mobile phase influences the dissociation of these ingredients, the pKa value of each active ingredient can be used as a reference when choosing a mobile phase for HPLC analysis. It is suggested that the pH value of the mobile phase should be smaller than the pKa when analyzing organic acids using reversed-phase HPLC [31]. Some suitable mobile phases for the HPLC analysis for these active ingredients are listed in Table 9. It can be seen from Table 9 that the pH value of the mobile phase for analyzing sinomenine was 9.0. According to the results in Table 2, most sinomenine was in its molecular form at a pH value of 9.0. The pH values of other mobile phases listed in Table 9 were measured. Most of the mobile phase was present at a low pH value, which can inhibit the dissociation of these active ingredients.

Table 9.
Some of the reported high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis conditions of each ingredients.
4. Conclusions
This study mainly determined the Dapp and pKa of 16 active ingredients in medicinal herbs, namely, sinomenine in Caulis Sinomenii, aescins in Semen Aesculi, phenolic acids in Flos Lonicerae, flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae, and glycosides in Radix Astragali. The pKa,1 value of sinomenine was between 8.0 and 8.6, while the pKa,2 value was between 10.8 and 11.6. Trichloromethane had the largest extraction capacity for sinomenine, with a maximum Dapp of more than 500. The pKa values of aescins A, B, C, and D were similar, which were all between 2.8 and 4.3. The pKa values of six phenolic acids in Flos Lonicerae were all in the range of 3.3–3.5. The Dapp values of isochlorogenic acids A, B, and C in 1-octanol could reach more than 100, while the Dapp values of neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, and cryptochlorogenic acid were below 10. The pKa of baicalin and wogonoside in Radix Scutellariae were both about 2.1. The pKa values obtained by fitting the three ingredients of isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, and calycosin-7-glucoside in Radix Astragalus were all between 9.10 and 9.80. The pKa and Dapp values of the 16 active ingredients examined in this work can be used in the development of the extraction process and analytical methods for these ingredients.
Author Contributions
Investigation, W.W., B.Z. and P.L.; data curation, W.W., B.Z., J.W. and W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W. and B.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.G.; supervision, X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the National S&T Major Project of China (2018ZX09201011-002), Student Research Training Program of Zhejiang University (X20200244), and the National Project for Standardization of Chinese Materia Medica (ZYBZH-C-GD-04).
Data Availability Statement
We have listed all the data in the Appendix A.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Feng Zhu for his help in the calculations of pKa and logP by Discovery Studio.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
HPLC diagram of the Caulis Sinomenii aqueous phase.
Figure A1.
HPLC diagram of the Caulis Sinomenii aqueous phase.

Table A1.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of sinomenine that were obtained in four liquid–liquid equilibrium systems.
Table A1.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of sinomenine that were obtained in four liquid–liquid equilibrium systems.
| 1-Butanol | Trichloromethane | Methyl Isobutyl Ketone | 1-Octanol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Dapp | pH | Dapp | pH | Dapp | pH | Dapp |
| 1.871 | 0.636 | 4.925 | 0.510 | 5.071 | 0.002 | 5.053 | 0.068 |
| 4.188 | 0.769 | 5.156 | 0.717 | 6.804 | 0.027 | 6.258 | 0.175 |
| 6.197 | 2.073 | 5.180 | 0.871 | 7.015 | 0.047 | 6.729 | 0.961 |
| 7.366 | 10.70 | 6.609 | 24.36 | 7.520 | 0.134 | 7.562 | 2.981 |
| 7.596 | 16.54 | 6.862 | 37.69 | 8.309 | 0.317 | 8.236 | 11.28 |
| 7.826 | 27.13 | 7.062 | 46.37 | 8.429 | 0.483 | 8.703 | 20.63 |
| 8.264 | 39.87 | 7.071 | 55.50 | 9.226 | 0.939 | 9.688 | 24.05 |
| 9.413 | 59.42 | 7.471 | 82.10 | 10.03 | 1.067 | 9.730 | 40.90 |
| 9.523 | 56.52 | 7.990 | 165.5 | 12.50 | 0.054 | 11.82 | 4.769 |
| 9.954 | 64.25 | 8.788 | 481.2 | 12.63 | 0.041 | 11.83 | 2.005 |
| 10.08 | 62.42 | 9.723 | 574.3 | - | - | - | - |
| 10.20 | 57.92 | 10.99 | 571.7 | - | - | - | - |
| 11.00 | 44.59 | 11.42 | 348.2 | - | - | - | - |
| 11.19 | 44.88 | 12.11 | 123.6 | - | - | - | - |
| 11.94 | 18.30 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 12.13 | 11.74 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Figure A2.
HPLC diagram of the Semen Aesculi organic phase (1: aescin A, 2: aescin B, 3: aescin C, 4: aescin D).
Figure A2.
HPLC diagram of the Semen Aesculi organic phase (1: aescin A, 2: aescin B, 3: aescin C, 4: aescin D).

Table A2.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of aescins in Semen Aesculi obtained in a 1-butanol system.
Table A2.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of aescins in Semen Aesculi obtained in a 1-butanol system.
| pH | Aescin A | Aescin B | Aescin C | Aescin D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.624 | 801.4 | 309.0 | - | - |
| 3.332 | 383.5 | 431.1 | - | - |
| 3.995 | 75.03 | - | 130.0 | 105.5 |
| 4.030 | 80.79 | 121.3 | 74.50 | - |
| 4.171 | - | 148.2 | 99.03 | - |
| 4.223 | 46.28 | 55.71 | 50.88 | 67.76 |
| 4.654 | 21.11 | 24.25 | 25.16 | 37.42 |
| 4.839 | 17.48 | 20.06 | 19.16 | 32.24 |
| 5.162 | 10.04 | 11.25 | 13.23 | 14.47 |
| 5.331 | 7.489 | 8.220 | 7.279 | 9.521 |
| 5.819 | 5.210 | 5.745 | 4.554 | 6.298 |
| 6.073 | 4.608 | 5.036 | 3.940 | 5.390 |
| 6.317 | 3.942 | 4.349 | 3.357 | 4.269 |
| 6.737 | 4.321 | 4.712 | 3.207 | 4.121 |
| 6.811 | 4.185 | 4.501 | 2.954 | 3.685 |
Figure A3.
HPLC diagram of the Flos Lonicerae organic phase (1: neochlorogenic acid, 2: chlorogenic acid, 3: cryptochlorogenic acid, 4: isochlorogenic acid B, 5: isochlorogenic acid A, 6: isochlorogenic acid C).
Figure A3.
HPLC diagram of the Flos Lonicerae organic phase (1: neochlorogenic acid, 2: chlorogenic acid, 3: cryptochlorogenic acid, 4: isochlorogenic acid B, 5: isochlorogenic acid A, 6: isochlorogenic acid C).

Table A3.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of phenolic acids in Flos Lonicerae obtained in the 1-octanol system.
Table A3.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of phenolic acids in Flos Lonicerae obtained in the 1-octanol system.
| pH | Neochlorogenic Acid | Chlorogenic Acid | Cryptochlorogenic Acid | Isochlorogenic Acid B | Isochlorogenic Acid A | Isochlorogenic Acid C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.910 | 0.054 | 0.254 | 0.112 | 2.527 | 10.89 | 15.80 |
| 4.530 | 0.128 | 0.581 | 0.270 | 5.800 | 25.00 | 37.02 |
| 4.200 | 0.245 | 1.104 | 0.524 | 12.24 | 49.84 | 73.58 |
| 3.690 | 0.552 | 2.474 | 1.241 | 29.51 | 112.3 | 181.5 |
| 3.200 | 0.935 | 4.201 | 2.228 | 54.28 | 181.7 | 326.9 |
| 2.730 | 1.339 | 5.905 | 3.326 | 83.89 | 259.9 | 506.8 |
| 2.350 | 1.314 | 6.009 | 3.444 | 87.93 | 281.2 | 545.1 |
| 1.860 | 1.435 | 6.852 | 3.971 | 97.22 | 278.2 | 594.8 |
| 1.660 | 1.699 | 7.606 | 4.507 | 106.7 | 300.3 | 669.1 |
| 1.520 | 1.572 | 7.310 | 4.337 | 100.0 | 271.6 | 632.7 |
Figure A4.
HPLC diagram of the Radix Scutellariae organic phase (1: baicalin, 2: wogonoside).
Figure A4.
HPLC diagram of the Radix Scutellariae organic phase (1: baicalin, 2: wogonoside).

Table A4.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae obtained in the 1-octanol system.
Table A4.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of flavonoids in Radix Scutellariae obtained in the 1-octanol system.
| pH | Baicalin | Wogonoside |
|---|---|---|
| 5.360 | 0.009 | 0.018 |
| 4.800 | 0.031 | 0.062 |
| 4.430 | 0.055 | 0.122 |
| 3.950 | 0.148 | 0.347 |
| 3.690 | 0.315 | 0.861 |
| 3.260 | 0.777 | 2.337 |
| 2.860 | 2.678 | 6.800 |
| 2.040 | 7.073 | 16.67 |
| 1.680 | 8.796 | 19.99 |
| 1.520 | 9.658 | 20.98 |
Figure A5.
HPLC diagram of the Radix Astragali organic phase (1: calycosin-7-glucoside, 2: astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, 3: isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside).
Figure A5.
HPLC diagram of the Radix Astragali organic phase (1: calycosin-7-glucoside, 2: astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-glucoside, 3: isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside).

Table A5.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of flavonoids in Radix Astragali obtained in the 1-octanol system.
Table A5.
Experimental results of the Dapp values of flavonoids in Radix Astragali obtained in the 1-octanol system.
| pH | Isomucronulatol 7-O-Glucoside | Astraisoflavan-7-O-β-D-Glucoside | Calycosin-7-Glucoside |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.96 | 0.094 | 2.249 | - |
| 10.500 | 0.198 | 2.245 | 0.087 |
| 10.08 | 0.828 | 2.449 | 0.202 |
| 10.00 | 1.947 | 2.538 | 0.181 |
| 9.910 | 1.635 | 2.513 | 0.215 |
| 9.460 | 5.632 | 2.645 | 1.030 |
| 9.450 | 4.724 | 2.753 | 0.452 |
| 8.730 | 7.099 | 2.914 | 0.480 |
| 7.440 | 7.681 | 2.990 | 0.526 |
| 6.450 | 7.594 | 3.001 | 0.564 |
| 5.950 | 8.639 | 2.987 | 0.522 |
| 5.450 | 8.294 | 3.042 | 0.556 |
| 5.150 | 8.320 | 3.094 | 0.549 |
| 4.910 | 8.095 | 2.882 | 0.537 |
| 4.510 | 7.764 | 2.964 | 0.554 |
References
- Alexovic, M.; Dotsikas, Y.; Bober, P.; Sabo, J. Achievements in robotic automation of solvent extraction and related approaches for bioanalysis of pharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1092, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.C.; Kuminek, G.; Cardoso, S.G.; Rodriguez-Hornedo, N. The role of pH and dose/solubility ratio on cocrystal dissolution, drug supersaturation and precipitation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Lins, P.V.; Henrique, D.C.; Ide, A.H.; da Silva Duarte, J.L.; Dotto, G.L.; Yazidi, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Erto, A.; de Paiva e Silva Zanta, C.L.; Meili, L. Adsorption of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug onto MgAl/LDH-activated carbon composite-Experimental investigation and statistical physics modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, A.L.P.; Wood, B.; Faisal, W.; Farag, F.; Garvie-Cook, H.; Glennon, B.; Vucen, S.; Crean, A.M. Application of percolation threshold to disintegration and dissolution of ibuprofen tablets with different microcrystalline cellulose grades. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, E.; Gebauer, D.; Cölfen, H. Potentiometric titration method for the determination of solubility limits and pK(a) values of weak organic acids in water. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9511–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebier, M.; Kocak, E.; Dogan, A.; Altinoz, S.; Basci, N.E. Investigating the physicochemical properties of phenazopyridine hydrochloride using high-performance liquid chromatography and UV-visible spectrophotometry. J. Res. Pharm. 2018, 22, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Su, X.; Bo, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, K. Determination of dissociation constants of ten alkaloids by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2003, 26, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. pK(a) determination of oxysophocarpine by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Springerplus 2013, 2, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Read, A.J. Ionization-constants of aqueous ammonia from 25 to 250 °C and to 2000 bar. J. Solut. Chem. 1982, 11, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Huang, S.; Jiao, R.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Qu, H. The determination of dissociation constants for active ingredients from herbal extracts using a liquid liquid equilibrium method. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 409, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, K.; Kozka, G.; Winiarski, M.; Piekoszewski, W. A Simple, Fast, and Green Oil Sample Preparation Method for Determination of Cannabidioloic Acid and Cannabidiol by HPLC-DAD. Separations 2020, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J. Research progress on anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects of sinomenine. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2015, 31, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Sirtori, C.R. Aescin: Pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic profile. Pharmacol. Res. 2001, 44, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, C.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q. Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematic review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, P. Traditional uses, ten-years research progress on phytochemistry and pharmacology, and clinical studies of the genus Scutellaria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Teng, J.; Xin, D.; Li, J.; Kong, X. Effect of Astragali Radix Membranaceus in promoting blood circulation and its modern pharmacology research. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2020, 26, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Yang, G. Comparison of Different Extraction Methods of β-aescin A, B from Three Different Aesculi Semens in Wudang Area. J. Hubei Univ. Med. 2018, 37, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.N.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Q. Simultaneous determination of eight Bioactive components in lonicerae japonicae flos by quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, J.; Li, F. A quantitative method for simultaneous assay of four flavones with one marker in Radix Scutellariae. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 3229–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Tan, X.; Wang, P.; Bi, K. RP-HPLC simultaneous determination of six flavonoids in Radix Astragali. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2009, 29, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Kong, D.; Xu, W. The discovery of a novel and selective inhibitor of PTP1B over TCPTP: 3D QSAR pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, synthesis, and biological evaluation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Mou, M.; Lu, Y.; Chen, K.; Xue, J.; Luo, Y.; Fu, J.; He, X.; et al. INTEDE: Interactome of drug-metabolizing enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1233–D1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.B.; Chhabria, M.T.; Desai, P.R. Rational Discovery of Novel Squalene Synthase Inhibitors through Pharmacophore Modelling. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2018, 14, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, H. Pharmacophore-based drug design for the identification of novel butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 54, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tian, S.; Gu, H.; Wu, Z.; Nyagblordzro, M.; Feng, G.; He, X. In vitro-in vivo predictive dissolution-permeation-absorption dynamics of highly permeable drug extended-release tablets via drug dissolution/absorption simulating system and pH alteration. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S. Degradation Mechanism and Mateiral Behaviors Analysis of the Inclusion Complexes of Sinomenine to Cyclodextrins. Master’s Thesis, Jishou University, Jishou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Xu, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Three Phenolic Acid in Pugongying Granules by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chemistry 2008, 71, 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Moridani, M.Y.; Scobie, H.; Jamshidzadeh, A.; Salehi, P.; O’Brien, P.J. Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, and dihydrocaffeic acid metabolism: Glutathione conjugate formation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; Liao, X.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Li, H. Multispectroscopic and docking studies on the binding of chlorogenic acid somers to human serum albumin: Effects of esteryl position on affinity. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zuo, G.; Wang, X.; Kim, H.Y.; Zhao, S.; Sun, W.; Tong, S.; Lim, S.S. Retention mechanism of pH-peak-focusing in countercurrent chromatographic separation of baicalin and wogonoside fromScutellaria baicalensisGeorgi. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 3806–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chang, J.; Wang, W. Study on Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation Condition and Determination Method of Organic Acids. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2001, 19, 260. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Ma, S. RP-HPLC determination of sinomenine in Caulis Sinomenii. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2006, 26, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, X. Quantified analysis of triterpenoid saponins in Semen Aesculi by HPLC. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2007, 38, 767–770. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Meng, J.; Fu, X.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Determination of eight components in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos by HPLC. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2014, 45, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).