Abstract
Development of a rapid approach for universal microbial detection is required in the healthcare, food and environmental sectors to aid with medical intervention, food safety and environmental protection. This research investigates the use of enzymatic hydrolysis of a substrate by a microorganism to generate a volatile organic compound (VOC). One such enzyme activity that can be used in this context is nitroreductase as such activity is prevalent across a range of microorganisms. A study was developed to evaluate a panel of 51 microorganisms of clinical interest for their nitroreductase activity. Two enzyme substrates, nitrobenzene and 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene, were evaluated for this purpose with evolution, after incubation, of the VOCs aniline and 2-fluoroaniline, respectively. Detection of the VOCs was done using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS) with obtained limits of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.17 and 0.03 µg/mL for aniline and 2-fluoroaniline, respectively. The results indicated that both enzyme substrates were reduced by the same 84.3% of microorganisms producing the corresponding volatile anilines which were detected using HS-SPME-GC-MS. It was found that nitroreductase activity could be detected after 6–8 h of incubation for the selected pathogenic bacteria investigated. This approach shows promise as a rapid universal microbial detection system.
1. Introduction
The design and application of enzyme substrates, which facilitate the detection of specific enzymatic activities in pathogenic microorganisms have been widely exploited in diagnostic microbiology by many sectors of the economy including the health-care sector (e.g., hospitals), the food industry (e.g., food quality control) and the environmental sector (e.g., monitoring of water contamination) [1,2,3,4]. We have recently been interested in detecting hydrolytic enzymatic activities in pathogenic microorganisms using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), a technique that is amenable to automation [5,6,7]. In our previous work, the focus has been on identifying specific bacteria (e.g., Salmonella [5] and Pseudomonas aeruginosa [7]) and the ability to differentiate Gram-positive from Gram-negative bacteria [6] using the exogenous VOCs detected from esterase [5] and aminopeptidase [6,7] activities, i.e., phenols and anilines, respectively. The focus of this paper is on selecting a more universal enzyme system, but still based on exogenous VOC evolution and detection, for rapid screening of microorganisms of clinical interest.
The action of nitroreductase enzymes on appropriate nitroaromatic substrates also produces anilines [8]. Our research has been using enzyme substrates to liberate exogenous VOCS that can be analysed using HS-SPME-GC-MS; this approach would seem ideal for the detection of bacterial nitroreductase activity. Normally, the detection of enzyme activity in microorganisms is done using off-the-shelf or synthesized enzyme substrates that cleave, in the presence of the specific enzyme, liberating either a chromophore or fluorophore [4]. Our focus is on the same process, the major difference being that the enzyme substrate is cleaved liberating a VOC that can be easily and rapidly detected at low concentration. Microbial nitroreductase activity was first identified in Escherichia coli in 1957 [9] and its presence was later reported across a wide range of microorganisms [10] including Salmonella [11], Klebsiella [12], Pseudomonas [13] and Bacillus [14]. In view of the known nitroreductase activity across a range of microorganisms, the HS-SPME-GC-MS method might find potential use as a rapid universal microbial detection system for which the primary healthcare application is the detection of microorganisms in blood (known as bacteraemia or fungemia). An automated system such as the BacT alert system incubates patients’ blood samples in the presence of a pH indicator and monitors a pH-induced colour change resulting from an increase in acidity caused by the release of CO2 as a microbial respiration by-product [15], with median time to detection ranging between 10 and 23 h amongst the most commonly encountered (nonfastidious) bacteraemia/fungemia pathogens [16]. In the United Kingdom, more than 200,000 cases annually of sepsis are diagnosed, which are associated with an estimated 52,000 deaths [17].
Following on from our previous VOC-based microbial detection studies using esterase and aminopeptidase substrates [5,6,7], we report in this paper our studies relating to the detection of microbial nitroreductase activity within a panel of clinically important pathogenic microorganisms using HS-SPME-GC-MS. Nitrobenzene and 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene were chosen as the nitroreductase substrates, as they are readily available at low cost and high purity, in order to generate the VOCs aniline and 2-fluoroaniline, respectively. The selection of the exogenous VOCs is done to try and avoid false positives in the data generated; earlier research on the use of HS-SPME-GC-MS for the analysis of bacteria, in broth, indicated that VOCs with specific functionality, e.g., an amino group, and additionally a fluorine were unlikely to naturally occur [18]. We note that incomplete reduction in these nitroaromatics to the relatively involatile hydroxylamines may also occur in some microorganisms [19]. The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate a method for universal detection of clinically important bacteria and yeasts in blood cultures by monitoring VOC release from a novel nitroreductase substrate.
2. Materials and Reagents
All bacteria and fungi used in this study were supplied by the Freeman Hospital Microbiology Department, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. Nitrobenzene (CAS number: 98-95-3; purity 99%), 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene (1493-27-2; 99%), aniline (62-53-3; 99%), 2-fluoroaniline (348-54-9; >99%) and 85 μm polyacrylate (PA) fibres were purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, UK. N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (872-50-4; 99+%) was purchased from Alfa Aesar, Morecambe, UK. Brain heart infusion (BHI) agar (CM1136) and brain heart infusion powder (CM1135) was purchased from Oxoid (Basingstoke, UK). Deionised water (18.2 MΩ cm) was obtained using a Milli-Q Integral 3 water purification system (Merck Millipore, Watford, UK). Brain heart infusion (BHI) broth was prepared following manufacturer’s instructions, by dissolving 37 g of the preprepared BHI broth powder in 1 L of Milli-Q water and sterilising the mixture via autoclave at 121 °C for 15 min.
2.1. Instrumentation
The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analyses were performed using a ThermoFinnigan Trace GC Ultra paired with a Polaris Q ion trap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Loughborough, UK) with Xcalibur 1.4 SR1 software package (Thermo Fisher). Separation of aniline and 2-fluoroaniline was done using an Agilent Technologies (Wokingham, UK) DB-5MS column (30 m × 0.25 mm internal diameter × 0.25 µm film thickness), using the temperature program: initial oven temperature 50 °C (hold 2 min) and then a ramp to 250 °C @ 12.5 °C/min, followed by a final hold time of 2 min. The mass spectrometer was set to full scan mode, scanning a mass range of 33–200 m/z, with a scan event time of 0.31 s. The ion source temperature was maintained at 260 °C, and the mass transfer line was maintained at 250 °C. Identification of aniline and 2-fluoroaniline was done using the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reference library (NIST Mass spectral library, version 2.0a, 2001) as well as authentic standards.
All samples and standards were maintained at 37 °C, using a temperature-controlled hotplate, during SPME sampling with an 85 µm polyacrylate fibre (Sigma-Aldrich, Poole, UK). SPME was done using a manual holder, and exposure to the headspace above all standards and samples was done for 10 min. Following the adsorption of the VOCs, the fibre was immediately retracted inside the needle and transported directly to the inlet of the GC-MS. Desorption of aniline and 2-fluoroaniline was carried out by exposing the fibre within the split-splitless GC injection port at 250 °C for 2 min. The inlet was set to split mode with a split ratio of 1:10, with the helium carrier gas flow rate set to 1 mL/min. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) for HS-SPME-GC-MS were determined by calculating the standard deviation (n = 7) of the background noise from the same retention time as the analyte. The LOD was determined by multiplying the standard deviation by 3, and the LOQ determined by multiplying by 10. Calibration curves were determined by running known concentrations of each VOC standard ranging from 0 to 100 µg/mL, giving a y = mx + c value for sample concentration calculations. Due to variability of adsorptive efficiency within the fibres, a new calibration for each analyte was required each time a new fibre was used.
2.2. Nitroreductase Activity Study across 51 Microorganisms
Microorganisms were selected to represent a wide range of pathogens responsible for a variety of infections including blood stream infections and gastroenteritis. For the most common pathogenic species encountered in bloodstream infections (such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), more than one example of each was included. All bacteria and fungi used in this study were subcultured overnight on to brain heart infusion agar plates and incubated at 37 °C. Following overnight incubation, the fresh bacterial/fungal colonies were inoculated into sterile brain heart infusion broth. The sample inocula were set by adjusting the absorbance of the broth suspensions to 0.132 at 600 nm (equivalent to 0.5 McFarland units) giving approximately 1 × 108 CFU/mL. Using this 108 CFU/mL suspension, 100 μL was dispensed into a sterile 20 mL glass vial containing 9.9 mL sterile brain heart infusion broth and 100 μg/mL of the desired nitroreductase substrate, thereby giving a final substrate concentration of 100 µg/mL and a preincubation inoculum of 1 × 106 CFU/mL. Samples were incubated at 37 °C. All samples were analysed in duplicate for the presence of the VOCs using HS-SPME-GC-MS.
2.3. Incubation Time Study
The 6 bacteria used for this study were inoculated into sterile BHI broth containing 100 µg/mL 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene at a preincubation inoculum of 1 × 10 CFU/mL. All samples were then analysed via HS-SPME-GC-MS and immediately placed into an incubator set to 37 °C. All samples were then analysed in duplicate for VOC production following 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h of incubation. All samples were returned to the incubator between sampling times and were immersed in a 37 °C water bath during sampling in order to maintain sample temperature. Samples were prepared in staggered time slots to ensure VOC analysis occurred following the correct incubation period. Bacterial growth was monitored using a duplicate set of vials to monitor absorbance.
2.4. Initial Inoculum Study
The 2 bacteria used in this study were inoculated into sterile BHI broth containing 100 µg/mL 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene at the following preincubation inocula: 1 × 101, 1 × 102, 1 × 10 3, 1 × 104, 1 × 105 and 1 × 106 CFU/mL. The sample inocula were set by adjusting the absorbance of an initial broth stock to 0.132 at 600 nm (equivalent to 0.5 McFarland units), approximately 1 × 108 CFU/mL, and diluting to the appropriate inoculum using sterile BHI broth. Once samples had been adjusted to the appropriate parameters, they were incubated overnight at 37 °C prior to having their headspaces analysed in duplicate using HS-SPME-GC-MS for the presence of 2-fluoroaniline.
3. Results and Discussion
Calibration curves were constructed for aniline and 2-fluoroaniline so that the amount of these VOCs produced could be measured and their limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantification (LOQ) determined (Table 1). A panel of 51 microorganisms with a preincubation inoculum of 1 × 106 CFU/mL were grown between 18 and 24 h in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth at 37 °C in the presence of either nitrobenzene or 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene (100 µg/mL). The headspaces of the sample vials were then analysed in duplicate for the presence of either aniline or 2-fluoroaniline (Table 2).

Table 1.
Analytical figures of merit for volatile organic compound (VOC) quantitation.

Table 2.
VOC production of various microorganisms in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth following overnight incubation at 37 °C with an inoculum of 1 × 106 CFU/mL and a substrate concentration of 100 µg/mL.
Precise positive responses were produced by both nitroaromatic substrates with 43 of the 51 (84.3%) panel of microorganisms exhibiting nitroreductase activity as indicated by the detection of the appropriate aniline. Eight microorganisms did not generate any detectable VOCs (Yersinia enterocolitica (NCTC 11176), Providencia rettgeri (NCTC 7475), Providencia stuartii (NCTC 10318), Burkholderia cepacia (ATCC 25416), Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC 19606), Corynebacterium diphtheriae (NCTC 10356), Candida albicans (ATCC 90028) and Candida glabrata (NCPF 3943)) (Table 2). To further contextualise the results, within 49 bacteria evaluated, 43 (87.8%) produced the appropriate aniline. Furthermore, 31 out of 36 Gram-negative bacteria and 12 out of 15 Gram-positive bacteria produced anilines thus giving detection rates of 86.1% and 92.3%, respectively. None of the fungi tested (C. albicans and C. glabrata) exhibited detectable nitroreductase activity, however, it is important to note that only 2 fungal organisms were evaluated in this study and therefore work on a wider selection of these microorganisms would be required before any reliable inferences could be made. Furthermore, the choice of growth medium is optimized for bacteria rather than fungi.
When nitrobenzene was employed as the substrate, the highest concentration of aniline liberated was recorded for E. coli (NCTC 12241), which produced a mean of 55.9 µg/mL. The lowest concentration of aniline produced was associated with P. aeruginosa (NCIMB 8295), which produced an average of 1.8 µg/mL. Despite both P. aeruginosa strains generating relatively small amounts of aniline in comparison with the majority of the other microorganisms, the average concentrations were well above the LOQ (0.17 µg/mL). An interesting observation was the disparity between the two members of the Yersinia genus. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (NCTC 10275) produced an average aniline concentration of 15.1 µg/mL, whereas no aniline production could be detected for Yersinia enterocolitica. Many species of the same genus were part of our panel of 51 microorganisms, and the disparity between members of the same genus only occurred with members of Yersinia, with Escherichia, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Shigella, Proteus, Providencia, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Bacillus, Streptococcus and Candida all displaying intragenus concurrence regardless of whether aniline could be detected or not.
The same microorganisms, which produced aniline from nitrobenzene also generated 2-fluoroaniline from 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene. Interestingly, there was a substantial increase in the amount of 2-fluoroaniline that was liberated when 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene was used as the substrate with the exception of 3 microorganisms where nitrobenzene produced the highest VOC concentrations. These microorganisms were Staphylococcus epidermidis NCTC 11047 (liberating an average of 13.0 µg/mL of 2-fluoroaniline and 15.3 µg/mL of aniline), Enterococcus faecium NCTC 7171 (producing an average of 5.1 µg/mL of 2-fluoroaniline and of 7.9 µg/mL of aniline) and Streptococcus agalactiae (generating an average of 8.8 µg/mL of 2-fluoroaniline and 9.8 µg/mL of aniline). In all instances, the amount of 2-fluoroaniline measured was at least 133 times its LOQ (0.03 µg/mL) with the lowest concentration (4.0 µg/mL) produced by Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 12973.
It is interesting to note that for some of 8 microorganisms that did not generate VOCs, nitroreductase activity has been demonstrated using other substrates. For example, in our previous work using fluorogenic 2-(2-nitrophenyl)benzothiazole and 2-(2-nitrophenyl)benzoxazole derivatives as nitroreductase substrates, P. rettgeri, B. cepacia and A. baumannii generally produced strong fluorescent responses in Columbia agar medium [20]. Thus, the absence of VOC production does not infer the absence of nitroreductase enzymes.
Following the encouraging results observed with 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene, it was of interest to establish the minimum time required for microorganism detection. In addition to following 2-fluoroaniline production, bacterial growth was also monitored by measuring absorbance at 600 nm. An initial bacterial inoculum of 1 × 106 CFU/mL prior to incubation was used with a substrate concentration of 100 µg/mL and an incubation temperature of 37 °C. We selected a subpanel of 6 bacteria from our original panel of 51 microorganisms. The 6 bacteria were chosen according to their previously described nitroreductase activities with 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene such that (i) a range of relative nitroreductase activities would be profiled (as determined by the quantities of 2-fluoroaniline liberated), (ii) a selection of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria would be represented and (iii) no two members of same genus were tested. The Gram-negative bacteria selected for this study were E. coli (NCTC 12241 with relatively high 2-fluoroaniline production), S. typhimurium (NCTC 74 with moderate 2-fluoroaniline production) and P. aeruginosa (NCIMB 8295 with relatively poor 2-fluoroaniline production). The Gram-positive bacteria selected were B. subtilis (NCTC 8236 with relatively high 2-fluoroaniline production), S. aureus (NCTC 11939 with moderate 2-fluoroaniline production) and E. faecium (NCTC 7171 with relatively poor 2-fluoroaniline production).
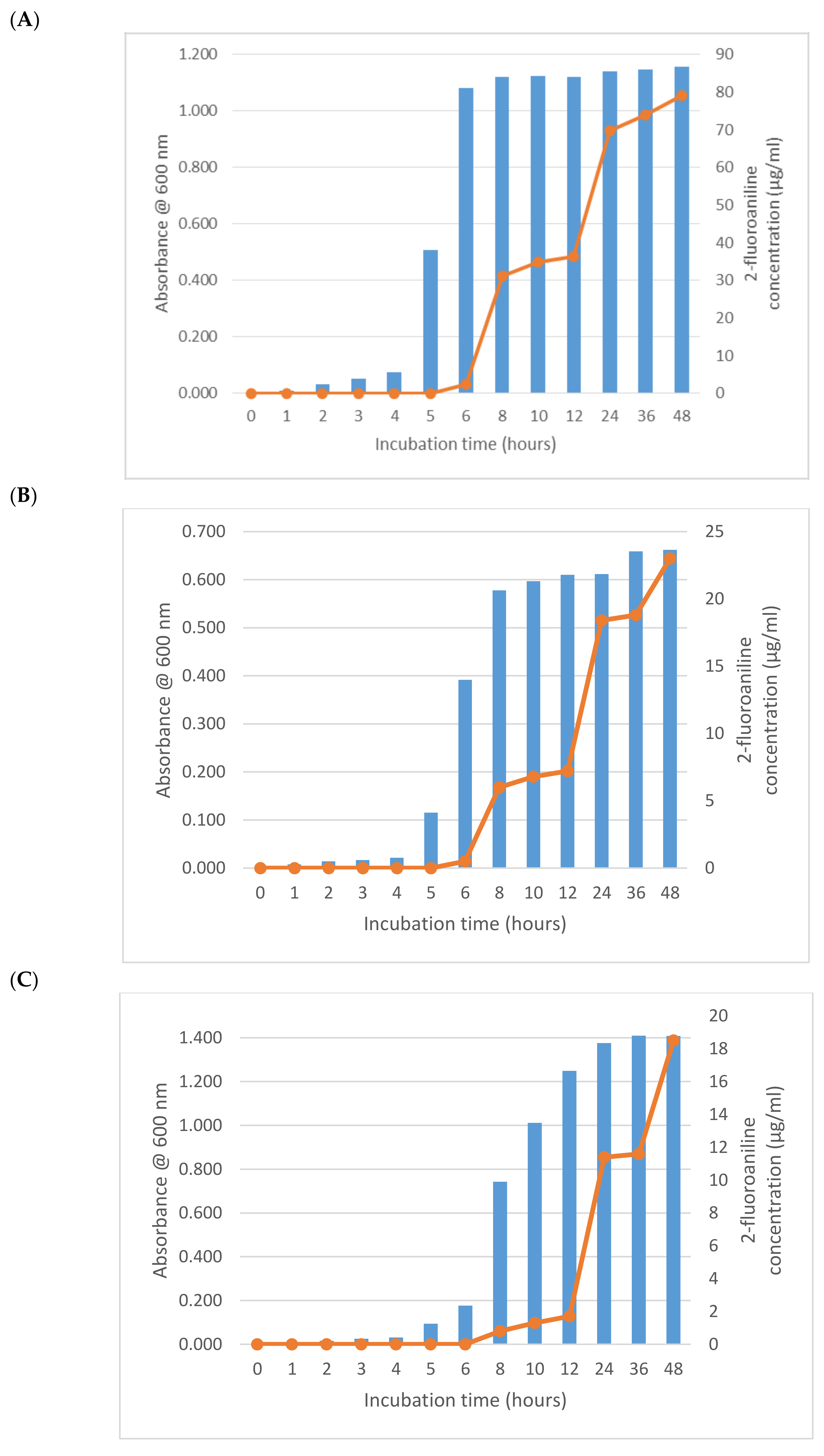
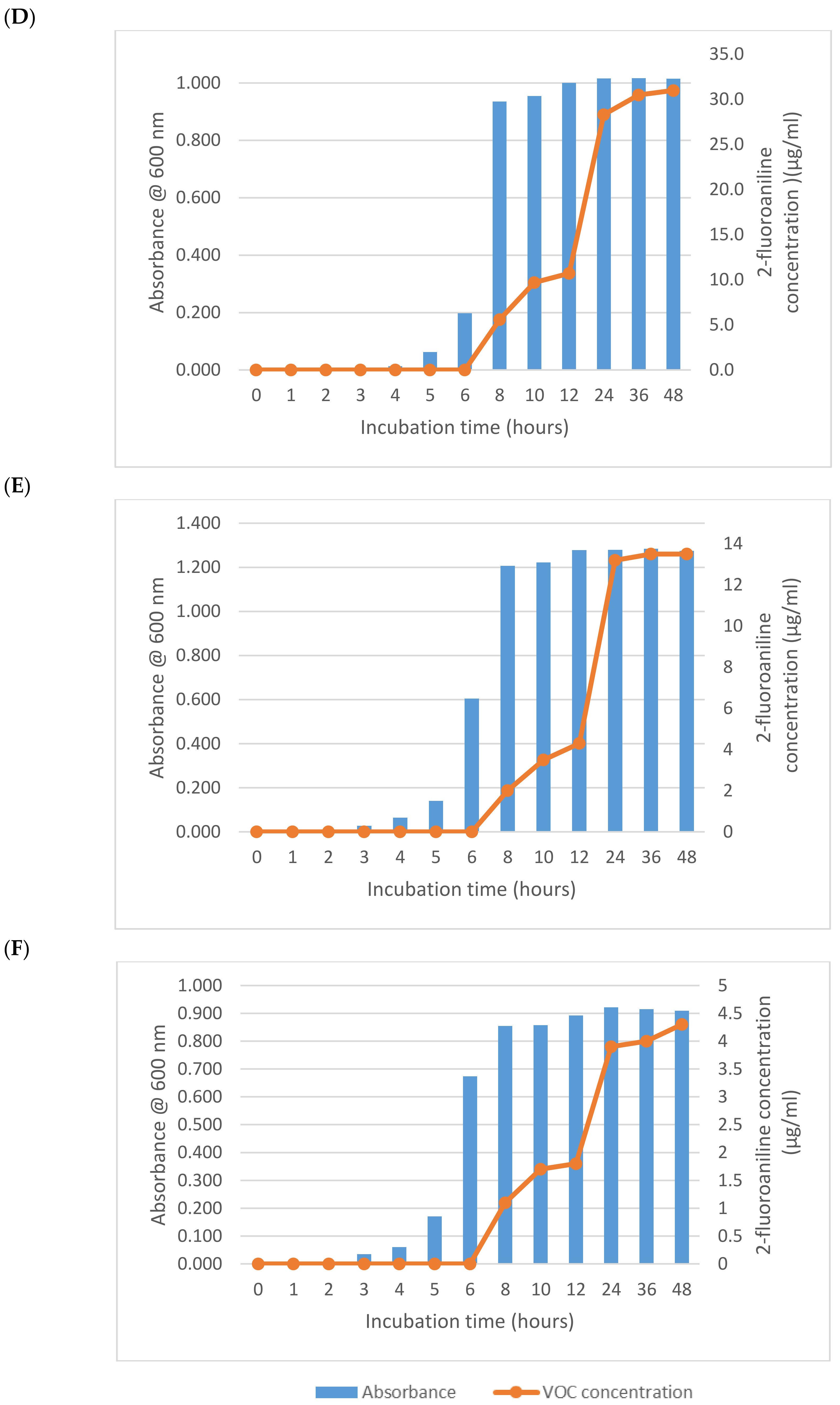
As expected from its previously described activity, E. coli (NCTC 12241) began reducing 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene after 6 h producing a mean of 2.3 µg/mL of 2-fluoroaniline (Figure 1A). Increasing growth of this microorganism after 2 h was apparent from the absorbance measurements, which had almost reached its maximum value after 6 h thus demonstrating a significant lag (>ca 5 h) in 2-fluoroaniline production. Interestingly, after a further 2 h of incubation (8 h in total), the amount of 2-fluoroaniline produced by this microorganism increased notably to a mean 31.3 µg/mL. Following this period of incubation, there was a small plateau in the concentration of 2-fluoroaniline produced and an eventual increase to 36.4 µg/mL at 12 h. At the end of the study (48 h), the average concentration of 2-fluoroaniline had steadily increased reaching 79.2 µg/mL. Broadly similar growth and 2-fluoroaniline production profiles were observed for the other bacteria (i.e., S. typhimurium NCTC 74, P. aeruginosa NCIMB 8295, B. subtilis NCTC 8236, S. aureus NCTC 11939 and E. faecium NCTC 7171) evaluated (Figure 1B–F) with 2-fluoroaniline detection possible within 6–8 h.
Figure 1.
Growth and 2-fluoroaniline production for selected bacteria at 37 °C in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth. Initial inoculum 1 × 106 CFU/mL, 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene concentration 100 µg/mL. (A) E. coli (NCTC 12241), (B) S. typhimurium NCTC 74, (C) P. aeruginosa NCIMB 8295, (D) B. subtilis NCTC 8236, (E) S. aureus NCTC 11939 and (F) E. faecium NCTC 7171.
To determine the minimum preincubation inoculum required to achieve a detectable response, we conducted a study using E. coli (NCTC 12241) and B. subtilis (NCTC 8236). Samples were prepared containing 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene (100 µg/mL) and preincubation inocula ranging from 10 (1 × 101) to 1,000,000 CFU/mL (1 × 106) (Table 3). All samples were analysed in duplicate for 2-fluoroaniline following overnight incubation at 37 °C.

Table 3.
The 2-fluoroaniline concentrations detected from various inocula following overnight incubation at 37 °C with 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene (100 µg/mL).
The results from this study were encouraging with nitroreductase activity detectable in every instance, even at a preincubation inoculum of just 10 CFU/mL. The lowest recorded average value for 2-fluoroaniline production (1.8 µg/mL) was predictably obtained from B. subtilis at a preincubation inoculum of 10 CFU/mL. Although this concentration is relatively low, especially for this microorganism, it is still within the detection capabilities of our VOC method and is 60 times higher than our calculated LOQ (0.03 µg/mL). Of the 2 microorganisms tested, E. coli was the more prolific in terms of 2-fluoroaniline liberation, and this was expected given the previous results described earlier.
As already mentioned, one of the most attractive applications that might be possible using this approach is the detection of microorganisms causing bloodstream infections. Various attempts have been made over the last 40 years to analyse the headspace of blood cultures for VOCs to determine bacterial growth or to attempt to rapidly identify bacterial species [21,22,23,24,25]. Allardyce et al. utilized selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) to detect VOCs in the headspaces of conventional BacT/ALERT blood culture bottles that had been artificially infected with 5 bacterial strains [22]. They reported that growth and species identification could be determined after 6 h incubation by measuring a panel of 9 VOC products. In a more recent study, Drees et al. applied gas chromatography coupled to ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) to analyse the headspace of blood cultures artificially inoculated with S. aureus, E. coli and P. aeruginosa [23]. They concluded that GC-IMS headspace analyses allowed faster recognition of bacterial growth than the standard colorimetric indicator and differentiation between the three investigated species was possible after 6 h of incubation. Finally, Dolch et al. examined the headspace of 282 positive blood cultures using an ion-molecule reaction mass spectrometer (IMR-MS). VOC analysis allowed them to differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in anaerobic bottles but not using aerobic bottles [24]. Using the same technique, the same group were able to demonstrate differentiation of four common Gram-positive species (S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. faecalis and E. faecium) using VOC analysis after a 24 h incubation period [25].
We have described here a novel approach that differs from all previous approaches by the incorporation of a synthetic substrate that is reduced to generate a unique VOC that is not generated by growth in unsupplemented standard culture media. This approach proved to be successful with some important limitations as we were unable to detect growth of some important pathogens including A. baumannii and C. albicans. As these species are known to demonstrate nitroreductase activity, we speculate that changing the substrate may improve sensitivity and enable us to create a genuinely universal detection system.
4. Conclusions
Nitroreductase activity was detected by 84.3% of the panel of 51 selected microorganisms when using nitrobenzene or 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene as enzyme substrates. The determined concentration of VOC was generally greater when 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene was utilised as the substrate, with detection of 2-fluoroaniline by HS-SPME-GC-MS. No detectable nitroreductase activity was observed for the 2 fungi included in this study. On that basis, 87.8% of the 49 bacteria exhibited nitroreductase activity. Nitroreductase activity could be reliably detected within a subpanel of the selected bacteria after 6–8 h. This approach shows promise as a universal microbial detection system, based on nitroreductase enzyme activity. The preferred enzyme substrate is 1-fluoro-2-nitrobenzene with detection of the exogenous VOC, 2-fluoroaniline. Further research is required to extend the number of bacteria investigated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D.P., S.P.S., J.R.D. with R.T.; Analysis, R.T.; Methodology, R.T., J.D.P., S.P.S. and J.R.D.; Writing—original draft, R.T.; Writing—review & editing, S.P.S., J.D.P., J.R.D. with R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded under the Northumbria University Collaborative Doctoral Studentship programme with bioMerieux SA (R&D/0079).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Northumbria University and bioMérieux.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Orenga, S.; James, A.L.; Manafi, M.; Perry, J.D.; Pincus, D.H. Enzymatic substrates in microbiology. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 79, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, M. New developments in chromogenic and fluorogenic culture media. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 60, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, M.; Kneifel, W.; Bascomb, S. Fluorogenic and chromogenic substrates used in bacterial diagnostics. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Váradi, L.; Luo, J.L.; Hibbs, D.E.; Perry, J.D.; Anderson, R.J.; Orenga, S.; Groundwater, P.W. Methods for the detection and identification of pathogenic bacteria: Past, present, and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahroun, N.H.; Perry, J.D.; Stanforth, S.P.; Dean, J.R. Use of exogenous volatile organic compounds to detect Salmonella in milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1028, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Guízar, S.; Sykes, H.; Perry, J.D.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Stanforth, S.P.; Perez-Perez, M.C.I.; Dean, J.R. A chromatographic approach to distinguish Gram-positive from Gram-negative bacteria using exogenous volatile organic compound metabolites. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1501, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.; Stephenson, D.; Sykes, H.E.; Perry, J.D.; Stanforth, S.P.; Dean, J.R. Detection of β-alanyl aminopeptidase as a biomarker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the sputum of patients with cystic fibrosis using exogenous volatile organic compound evolution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10634–10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, M.D.; Pérez-Reinado, E.; Castillo, F.; Moreno-Vivián, C. Reduction of polynitroaromatic compounds: The bacterial nitroreductases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 474–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnis, R.E. The reduction of Furacin by cell-free extracts of Furacin-resistant and parent-susceptible strains of Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1957, 66, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.L.; Perry, J.D.; Jay, C.; Monget, D.; Rasburn, J.W.; Gould, F.K. Fluorogenic substrates for the detection of microbial nitroreductases. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 33, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokhbeh, M.; Boroumandi, S.; Pokorny, N.; Koziarz, P.; Paterson, E.; Lambert, I.B. Identification and characterization of SnrA, an inducible oxygen-insensitive nitroreductase in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium TA1535. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2002, 508, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Bennett, G.N.; Song, H.-G. Degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by Klebsiella sp. isolated from activated sludge. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, C.C.; Nishino, S.F.; Spain, J.C. Purification and characterization of nitrobenzene nitroreductase from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes JS45. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 3837–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlezark, G.M.; Vaughan, T.E.; Fashola-Stone, E.; Michael, N.P.; Murdoch, H.; Sims, M.A.; Stubbs, S.; Wigley, S.; Minton, N.P. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens orthologue of Bacillus subtilis ywrO encodes a nitroreductase enzyme which activates the prodrug CB 1954. Microbiology 2002, 148, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Totty, H.; Ullery, M.; Spontak, J.; Viray, J.; Adamik, M.; Katzin, B.; Dunne, W.M.; Deol, P. A controlled comparison of the BacT/ALERT® 3D and VIRTUO™ microbial detection systems. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congestrì, F.; Pedna, M.F.; Fantini, M.; Samuelli, M.; Schiavone, P.; Torri, A.; Bertini, S.; Sambri, V. Comparison of ‘time to detection’ values between BacT/ALERT VIRTUO and BacT/ALERT 3D instruments for clinical blood culture samples. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 62, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UK Sepsis Trust. Sepsis Manual, 5th ed.; The UK Sepsis Trust: Birmingham, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-9928155-0-9. Available online: www.sepsistrust.org (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Tait, E.; Perry, J.D.; Stanforth, S.P.; Dean, J.R. Identification of volatile organic compounds produced by bacteria using head space—Solid phase microextraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS). J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 52, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koder, R.L.; Haynes, C.A.; Rodgers, M.E.; Rodgers, D.W.; Miller, A.-F. Flavin Thermodynamics Explain the Oxygen Insensitivity of Enteric Nitroreductases. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 14197–14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellier, M.; Gignoux, A.; James, A.L.; Orenga, S.; Perry, J.D.; Robinson, S.N.; Stanforth, S.P.; Turnbull, G. 2-(Nitroaryl)benzothiazole and benzoxazole derivatives as fluorogenic substrates for the detection of nitroreductase activity in clinically important microorganisms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5694–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, L.; Mårdh, P.A.; Odham, G.; Carlsson, M.L. Diagnosis of bacteraemia by automated head-space capillary gas chromatography. J. Clin. Pathol. 1982, 35, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allardyce, R.A.; Langford, V.S.; Hill, A.L.; Murdoch, D.R. Detection of volatile metabolites produced by bacterial growth in blood culture media by selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS). J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 65, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drees, C.; Vautz, W.; Liedtke, S.; Rosin, C.; Althoff, K.; Lippmann, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Legler, T.J.; Yildiz, D.; Perl, T.; et al. GC-IMS headspace analyses allow early recognition of bacterial growth and rapid pathogen differentiation in standard blood cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9091–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolch, M.E.; Janitza, S.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Graßmann-Lichtenauer, C.; Praun, S.; Denzer, W.; Schelling, G.; Schubert, S. Gram-negative and -positive bacteria differentiation in blood culture samples by headspace volatile compound analysis. J. Biol. Res. 2016, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dolch, M.E.; Hornuss, C.; Klocke, C.; Praun, S.; Villinger, J.; Denzer, W.; Schelling, G.; Schubert, S. Volatile organic compound analysis by ion molecule reaction mass spectrometry for Gram-positive bacteria differentiation. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).