Abstract
Wastewater analysis is an important area in analytical and environmental chemistry. It can be performed with both the classic wet methods and instrumental techniques. The development of new methods, and modification of the existing ones, constitute a major task for researchers. Ion chromatography plays a predominant role in ion determinations with the instrumental methods. It offers several advantages over the conventional methods, such as simultaneous determinations of alkali and alkaline earth cations and ammonia. Ammonium ions cannot be determined by spectroscopic methods. Ion chromatography has been accepted world-wide as a reference method for analyzing anions and cations in water and wastewater due to the fact that it enables the replacement of several individual wet chemistry methods for common ions with one instrumental technique. The following article describes the principles of ion chromatography, such as stationary phases, eluents, detectors, and sample preparation methods. Moreover, the applications of ion chromatography in wastewater analyses and international standards are presented.
1. Introduction
The monitoring of the wastewater quality parameters is currently a subject of growing research interest due to the requirements of the environmental protection and introduction of new technologies. Many directives and recommendations put pressure on the wastewater treatment industry to fulfill specific requirements. Substances present in various types of wastewater may be classified as chemical, physical, biological, or radiological ones. Anions and cations were routinely analyzed with the traditional wet chemical methods, including titration, photometry, or colorimetry methods. Unfortunately, many of these techniques suffered from interferences and limited accuracy. They could also be labor-intensive and difficult to automate. Thus, it was necessary to develop more effective, repeatable, and cheaper methods that could be available in ordinary laboratories. In this respect, ion chromatography has become an alternative to the classic wet methods, especially for laboratories that need to analyze inorganic and organic ions in a large number of samples (i.e., wastewater).
Chromatography was discovered in 1903 by Mikhail Semyonovich Tswett, a Russian botanist who worked at the University of Warsaw in Poland [1]. Recently, chromatographic methods have been used at both the preparative and analytical stages. At first, gas chromatography (GC), thin layer chromatography (TLC) and liquid chromatography (LC) were applied mostly to the separation and determination of organic substances. The challenge was to apply the chromatographic methods for inorganic analyses (mainly for ionic substances). In 1975, Small et al. [2] described a new ion-exchange chromatographic method for the separation and conductometric detection of anions and cations. In September 1975, Dionex Corporation presented the first commercially available ion chromatograph (Dionex DX 10) [3].
The key problem in the ion chromatography evolution was developing a suppression method for the eluent conductivity. It was a significant challenge to determine separated analytes against the background of the eluent ions because the eluent is also an electrolyte. In 1980s, Gjerde et al. [4] used the ion chromatography system without the suppression device for the first time. They also used eluents with very low conductivity. They created a new type of ion chromatography, i.e., the non-suppressed ion chromatography. Both the suppressed and non-suppressed ion chromatography modes can be applied to examine various sample matrices. However, when it comes to anion analyses, the application of the suppressed ion chromatography is much more popular.
Although the ion exchange remains a prevailing separation mode in ion chromatography [5,6], other related methods, such as ion-exclusion (IEC) [7], ion-pairing chromatography (IPC) [8], and reversed phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) [9], can also be employed. A short overview of ion chromatography and related methods (with consideration for separation mechanism, eluents, and detectors) is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Separation methods and their applications in ion chromatography.
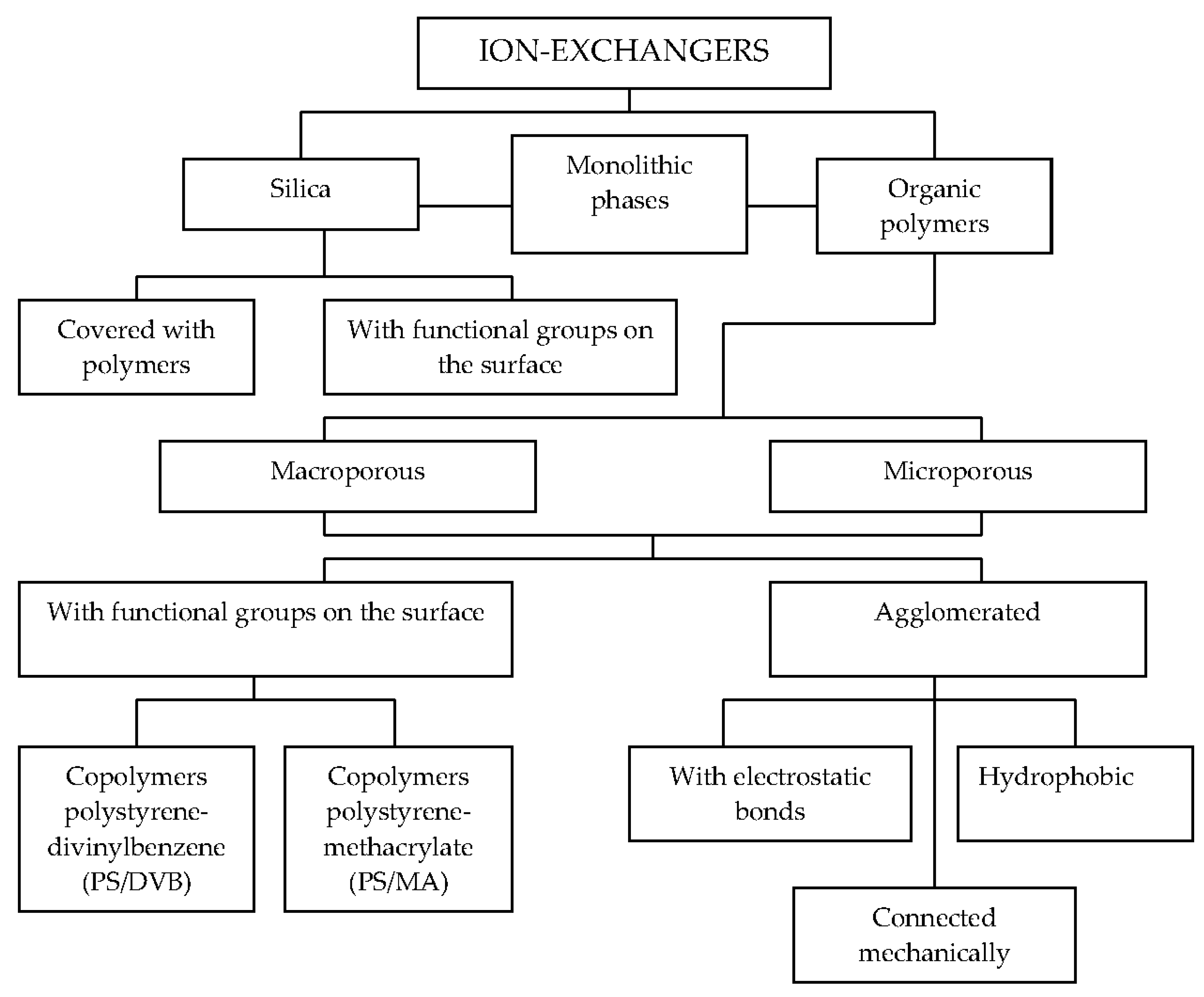
The obtaining of reliable results in ion chromatography depend on many factors, such as types of eluents and stationary phases, detection modes, and sample preparation methods. The applications of ion-exchangers in the chemical analysis were described by Qureshi and Varshney [10]. The stationary phases used in the ion-exchange chromatography columns can be classified according to their applications and ion-exchange capacities. An overview of stationary phases used for ion chromatography is given by Weiss and Jensen [11]. Figure 1 shows a list of selected stationary phases used in ion chromatography.
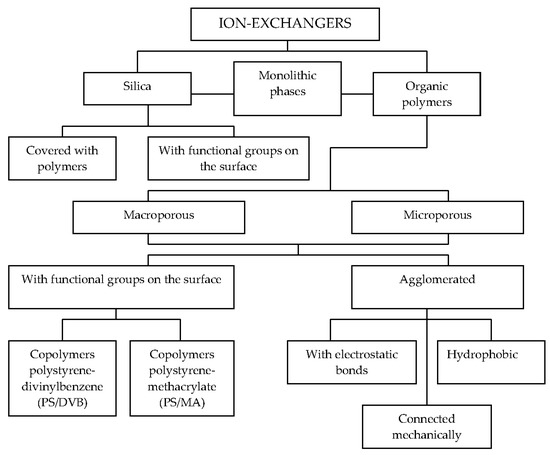
Figure 1.
Stationary phases used in ion chromatography.
In ion chromatography, organic polymers are often used as stationary phases, because they have much higher stability over an extreme pH range when compared to the silica-based materials. These copolymers can be divided into the surface aminated polystyrene-divinylbenzene (PS/DVB) and surface aminated ethylenovinylbenzene-polystyrene-divinylbenzene (EVB/DVB) copolymers. There are also the methacrylate-based stationary phases with quaternary amine functional groups stable at pH = 1–12, and macroporous polyvinyl resins stable at pH = 0–14 [12].
A special type of a peculiar anion exchanger (called latex-based) was introduced in 1975 [13]. In comparison with organic polymers, silica-based stationary phases have the advantage of higher mechanical stability. However, they can only be used with eluents in the pH range between 2 and 8 [14]. Inorganic and organic anions can be separated on cross-linked polymers modified with cyclic ethers, but the number of applicable crown ethers is limited [15] or cryptand-based phases [16].
Similarly to the anion exchangers, cation exchangers are divided into: polymer-based cation exchangers (PS/DVB, EVB/DVB, polyvinyl, and polymethacrylate copolymers), latex-agglomerated cation exchangers, silica-based, and others (e.g., crown ethers, Al2O3). Simultaneous separations of alkali- and alkaline earth metals and aliphatic amines are possible with acid cation exchangers with carboxylic groups. Organic polymers are usually applied for cation-exchange chromatography. In some cases, silica-based exchangers [17] as well as cross-linked polymers modified with cyclic ethers [18] are also used. Moreover, zwitterionic ion-exchangers demonstrate unique separation selectivities for simultaneous separations of anions and cations [19]. Recently, monolithic columns have been used in different types of ion chromatography [20,21].
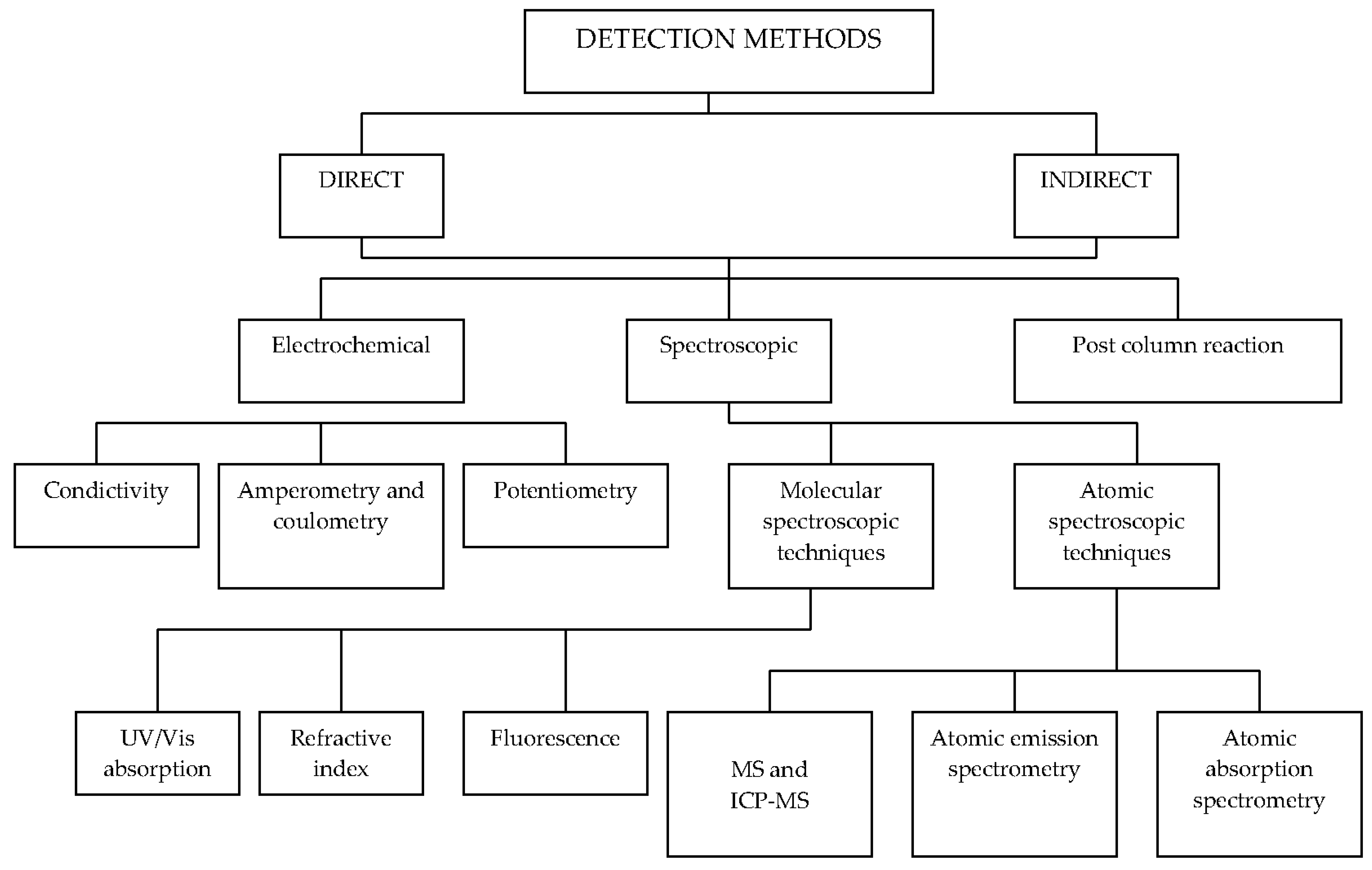
The eluent (its type, concentration, pH, and flow rate) constitutes another important factor affecting the separation efficiency and selectivity. It also depends on the stationary phase. Typical eluents applied in anion-exchange chromatography are: Na2CO3, NaHCO3, NaHCO3 + Na2CO3 NaOH/KOH, and Na2B4O7. For cation-exchange chromatography, diluted water solutions of HNO3, HNO3, HCl, DPA (dipicolinic acid), tartaric acid, and oxalic acid are used. Carbonate and bicarbonate eluents are commonly applied in the anion-exchange ion chromatography. However, hydroxide seems the perfect eluent as it forms water that has virtually zero conductances after suppression. Unfortunately, the hydroxide eluents are difficult to use, because they absorb CO2 from ambient air and form carbonates. The selectivity can be modified through the selection of the stationary phase and eluent composition, which has to be compatible with the detection system. The conductivity detector is still the most popular, but other types of detection modes (e.g., UV-VIS, amperometric, spectrometric ones) can also be applied for different analytes [22]. An overview of detection methods is given in Table 2. Figure 2 shows a division of detection methods used in ion chromatography [23].

Table 2.
Detection methods applied in ion chromatography.

Figure 2.
Division of detection methods for ion chromatography.
The most popular conductometric detector can be applied to determine all anions and cations of strong acids and bases (e.g., F−, Cl−, NO3−, PO43−, SO42−, Na+, K+, NH4+, Mg2+, Ca2+).
The UV-VIS detection is a popular detection mode for high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), but its application in ion chromatography is limited because only a few inorganic ions have an appropriate chromophore [24]. The UV-VIS detection methods can be divided into direct and indirect modes. For the direct UV-VIS detection, the molar absorption of co-ions should be zero. The direct UV-VIS detection is applied for determinations of NO2− and NO3−, as well as Br− and I− in the presence of high Cl− concentrations. Moreover, sulfide, chromate, thiocyanate, thiosulfate, and selected metal chloro- and cyano-complexes can be determined in wastewater with this detection method [25]. The UV-VIS detection with post-column reactions is a versatile technique that combines enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for specific applications [26].
The chemiluminescence detection is generally performed in a post-column reaction mode [27]. In ion chromatography, the fluorescence detection is rarely used as a detection method, because only few ions fluoresce [28]. Furthermore, the amperometric detection can be used for samples with pK values > 7. The amperometric detection method application helps in determining ions such as I−, S2−, S2O32−, SCN−, CN−, or heavy and transition metals [29,30]. Due to the poor selectivity and sensitivity, the refractive index detection is very rarely used in ion chromatography [31]. The most powerful detection method (used not only in ion chromatography) is mass spectrometry [32,33]. Although this detection method is helpful in wastewater analysis, it is not popular in ordinary laboratories due to the high apparatus cost and complex requirements to be met by the method operator [34].
2. Sample Preparation
The sample preparation procedure is necessary before the ion chromatography analysis so as to protect the analytical columns and obtain reliable and repeatable results [35]. A sample that is not properly prepared can cause increased column back pressures and change their performances. The most important reasons why sample preparation in ion chromatography is necessary include the following aspects: analytes concentrations are too high or too low; analytes concentrations differ primarily; and the presence of compounds that may cause interference by peak overlapping [36]. Usually, the choice of the sample preparation method depends on the physical state of the sample and the sample matrices, as well as availability of the apparatus configurations [37]. The typical sample preparation methods for ion chromatography analyses are: filtration, dilution, pH adjustment, derivatization, liquid–liquid extraction, solid-phase extraction, distillation, and membrane separations [38].
The wastewater samples for the ion chromatography analysis should be collected in plastic containers made of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Glass containers can cause ionic contamination when performing trace analysis. Most wastewater samples often require only dilution and filtration to bring the interesting analytes into the working range of the method. For filtration, membrane filters with a pore size of 0.45 μm are strongly recommended. For biologically active samples, sterile filters with a pore size of 0.2 μm should be used. Recently, membrane separation techniques such as micro- and ultra-filtration have gained great importance in the sample preparation for ion chromatography [39]. Many wastewater samples contain high concentrations of chloride, sulfate, and sodium ions. Fully-sulfonated exchangers are available with a variety of counter-ions, such as Ag+, Ba2+, and H+ [40]. Several manufacturers offer ready-to-use cartridges as well as devices for passing the sample solution through special sorbents.
3. Wastewater Analysis with Ion Chromatography
Wastewater is a dynamic system containing organic and inorganic compounds, dissolved compounds, and insoluble substances. Moreover, the composition of samples can change dramatically during or after the sampling [41]. Therefore, analyses require available, reliable, and fully-automatic methods for simultaneous determinations of several analytes. Ion chromatography offers several advantages over the classic wet methods for determinations of inorganic and organic ions in wastewater, such as: short time of analysis (≈10–15 min); high sensitivity and selectivity in samples with complex matrices (e.g., if the ratio of Na+:NH4+ or Cl−:NO2− is 10,000:1); simple sample pre-treatment (usually filtration with a filter with a 0.45-μm pore of is enough); possibilities of simultaneous separation and determination of anions and cations; species analysis (e.g., NO2−/NO3−/NH4+ or Cr3+/Cr6+); use of different detection modes (e.g., conductivity, UV-VIS, amperometry); and safe, cheap, and environmentally friendly chemicals (e.g., diluted water solution of Na2CO3/NaHCO3 or HCl, HNO3). Moreover, ion chromatography is a direct method for the simultaneous determinations of alkali and alkaline earth cations and ammonia. The majority of applications of ion chromatography in wastewater analysis concern determinations of inorganic anions and cations [42,43].
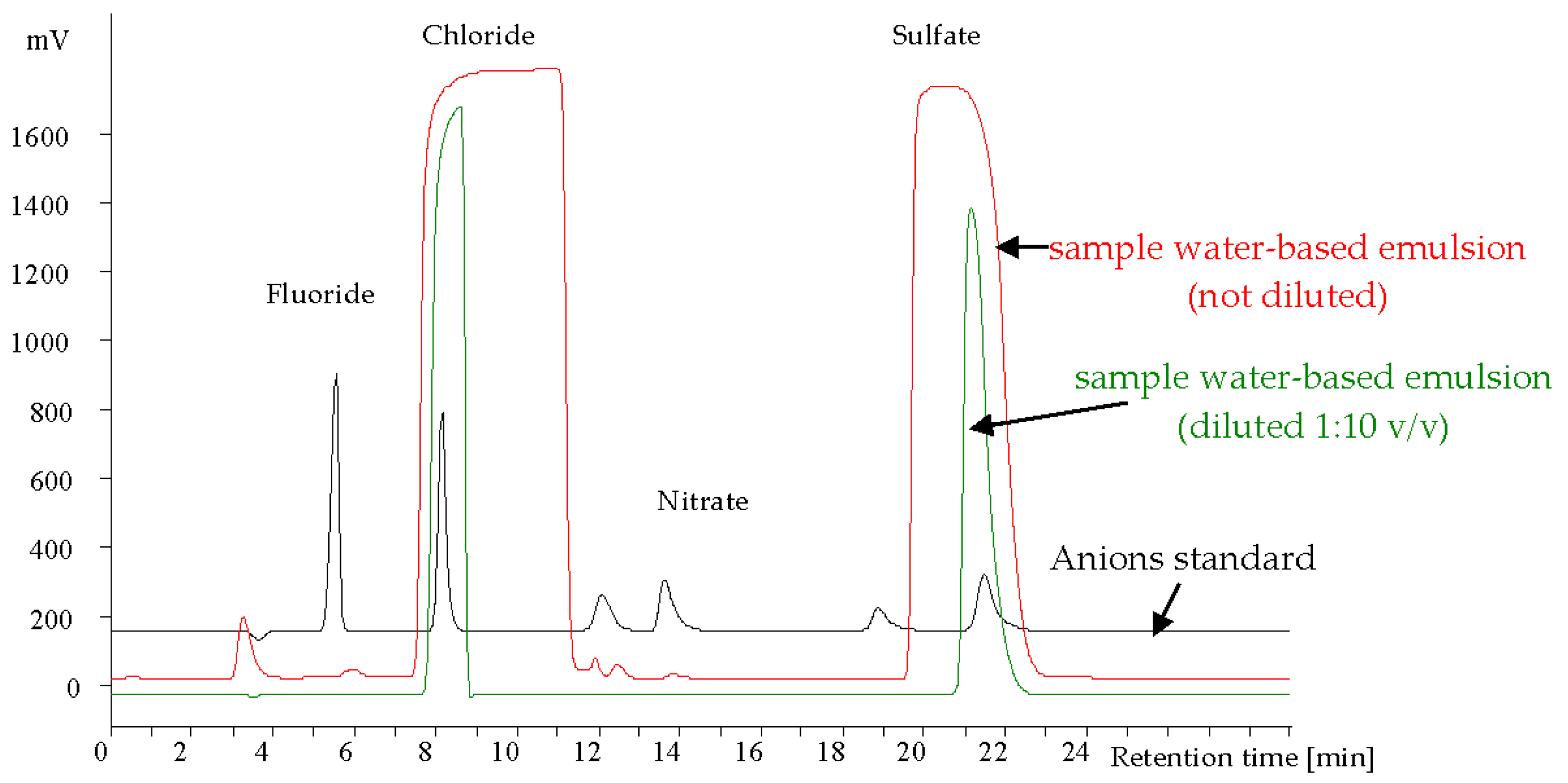
Examples of anion chromatograms for a standard sample and industrial wastewater (emulsion sample) are given in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Chromatograms of anions standard + sample of water-based emulsion (not diluted and diluted 1:10 v/v). Separation condtions: column: Metrohm Metrosep A Supp 3 (250 × 4.6 mm); eluent: 1.7 mM Na2CO3 + 1.6 mM NaHCO3; eluent flow rate: 0.85 mL/min injection volume: 20 μL; detection: suppressed conductivity detection.
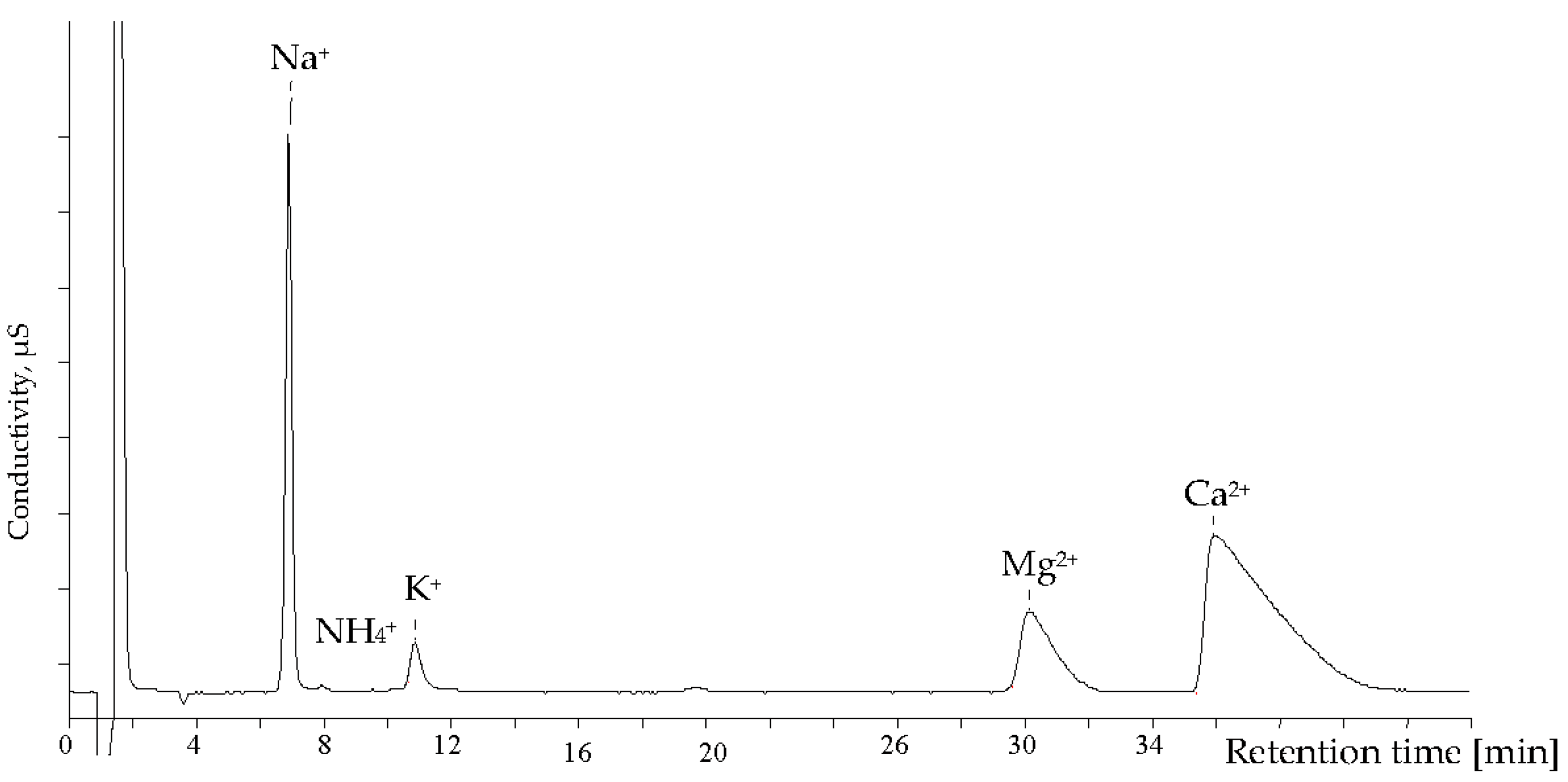
The simultaneous analysis of alkali and alkaline-earth metals and ammonium ions is another important ion chromatographic application in the field of wastewater analysis. An example chromatogram is given in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Chromatogram of cations in a municipal waste water sample. Separation conditions: analytical column: Metrohm Metrosep C2 (250 × 4.6 mm); eluent: 4 mM tartaric acid + 0.75 mM DPA; detection: non-suppressed conductivity.
The samples with low levels of ammonium/nitrite in matrices and high concentrations of sodium/chloride are a typical case. Unfortunately, these pairs of ions (NH4+/Na+ and Cl−/NO2−) have similar selectivities for common stationary phases. The application of ion chromatography for the analysis of waste water with high ion concentrations is given by Singh et al. [44].
Another important example is determination of toxic cyanide in various wastewater samples. Thanks to ion chromatography, ions such as cyanides and sulfides can be separated and determined simultaneously [45]. Moreover, the chelating agents, such as nitriltriacetate acid (NTA) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and polyphosphates can be analyzed in wastewater [46]. In addition to common inorganic ions, some metals and metalloids can be determined in wastewater with ion chromatography. For instance, toxic hexavalent chromium must be monitored in industrial wastewater [47].
From the toxicological data, the chemical form of a specific element or its oxidation state is usually more important for living organisms than its total quantity. Ion chromatography as a separation method plays an important role in hyphenated techniques used for species analysis [48,49]. There is a large number of ion chromatography methods applied for the determination of metal and metalloids [50]. These methods can be divided into off-line and on-line ones. In the case of the off-line method, metal complexes are formed before the separation to create stable complexes and to avoid decomposition during separation, or a ligand must be added to the eluent. In the on-line method, the metal complexation is carried out in the separation column with adding the proper ligand to the eluent (e.g., oxalic acid, pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDCA), or EDTA) [51].
4. Standard Methods Based on Ion Chromatography
The ideal methods for anion and cation determinations should meet the following criteria: determination of target ions within a limit of determination of 25% (or even 10% in some cases) of maximum acceptable concentration; short analysis time; simple sample pre-treatment; low cost of a single analysis; and method availability. Ion chromatography methods meet these requirements. Hence, they are used for routine applications in wastewater laboratories. Thanks to many advantages ion chromatography has when compared to the manual wet methods, it quickly became accepted world-wide as a reference method for the analysis of anions and cations in water and wastewater [52].
Ion chromatography was quickly accepted by many other organizations, such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), or National Institute for Occupational Safety and Heath (NIOSH), as a reference method for water and wastewater analysis. After the publications of the international standard methods based on ion chromatography, the number of laboratories applying this technique increased rapidly. In 1993, the USEPA published Method 300.0, the first USEPA method widely accepted as the standard for common inorganic anions [53]. Many regulatory agencies use the same methodology as the USEPA Method 300.0. During the standardization process, the draft standard methods have to be validated in the range of (at least) accuracy, precision, recovery, and inter-laboratory trials. The normative part of an analytical standard method usually includes: scope, principles, normative references, requirements, chemicals, instruments, interferences, performance of the separation column, sampling and sample pre-treatment procedures, calculation, expression of results and, finally, test reports. However, each agency can use a unique method format and style, as well as a quality control mode. Standard methods are usually adopted as recommended on a voluntary basis by any laboratory around the world. The governments can incorporate the existing standards into their national standards. The overview of selected international standard methods for the determination of selected ions in wastewater is given in Table 3.

Table 3.
An examples of ion chromatography methods for inorganic and organic ions analysis in waste water established by ISO, US EPA, ASTM and NISOH.
5. Conclusions
Wastewater samples can be analyzed with different methods, including classic and instrumental techniques. Due to its many advantages (such as: good accuracy and precision; a broad range of applications, many detection modes; high selectivity, speed, and separation efficiency; well-developed hardware and low cost of consumables), ion chromatography is more and more popular in wastewater analysis. Nevertheless, challenges related to its development and application include: improving the speed and selectivity of analyzed ions; elaborating new sample preparation methods; lowering the limits of detection and quantification; developing new standard methods; extending the range of the analysis with a new group of substances; and introducing portable, fully automatic ion chromatographs for on-line wastewater analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that there is not conflict of interests.
References
- Tswett, M.S. Physikalisch-Chemische Studien Uber das Chlorophyll. Die Adsorptionen. Ber. Bot. Ges. 1906, 24, 316–332. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H.; Stevens, T.S.; Bauman, W.C. Novel Ion Exchange Chromatographic Method Using Conductometric Detection. Anal. Chem. 1975, 47, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.; Bowman, B. Ion Chromatography: A Historical Perspective. Am. Lab. 1998, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerde, D.T.; Fritz, J.S.; Schmuckler, G. Anion Chromatography with Low-Conductivity Eluents. J. Chromatogr. A 1978, 186, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerde, D.T.; Fritz, J. Ion Chromatography; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.; Haddad, P.R. Ion Chromatography: Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, J.S. Principles and applications of ion-exclusion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 546, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, T. Ion-Pair Chromatography and Related Techniques. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1732. [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro, M.C.; Angelino, S. Separation and determination of inorganic anions by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 789, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereshi, M.; Varshney, K.G. Inorganic Ion Exchangers in Chemical Analysis; CRC Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, J.; Jensen, D. Modern stationary phases for ion chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.E.; Pohlandt, C. Advances in stationary phase development in suppressed ion chromatography. Trend. Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.E.; Weigert, C.; Pohl, C.A.; Saini, C. Determination of inorganic anions in environmental waters with a hydroxide-selective column. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 884, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokhin, O.V.; Smolenkov, A.D.; Svintsova, N.V.; Obrezkov, O.N.; Shipgun, O.A. Modified silica as a stationary phase for ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 706, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auler, L.M.; Silva, C.R.; Collins, K.E.; Collins, C.H. New stationary phase for anion-exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1073, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, C.-S.; Shih, J.-S. Fullerene C60-cryptand chromatographic stationary phase for separations of anions/cations and organic molecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 416, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Shan, Z.L.; Zhu, P.L. Preparation of silica-based cation-exchangers for use in ion chromatography. Chromatographia 1989, 27, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K. Indirect ultraviolet spectrophotometric detection in the ion chromatography of common mono- and divalent cations on an aluminum adsorbing silica gel column with tyramine-containing crown ethers as eluent. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 884, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, P.N.; Elefterov, A.I.; Tarasenko, D.A.; Shpigun, O.A. Selectivity of chemically bonded zwitterion-exchange stationary phases in ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 706, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C. Recent developments in ion-exchange and low molecular weight molecules. LC-GC 2003, 28, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, B.; Nesterenko, P.N. New possibilities in ion chromatography using porous monolithic stationary-phase media. Trend Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R. Detection in Ion Chromatography. In Encyclopedia of Chromatography, 3rd ed.; Cazes, J., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, UK; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume I, pp. 576–580. ISBN 978-1-4200-8459-7. [Google Scholar]
- Buchberger, W.W. Detection techniques in ion chromatography of inorganic ions. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, D.; Paull, B. Fast separation of UV absorbing anions using ion-interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 917, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmarkar, S.V. Anion-exchange chromatography of metal cyanide complexes with gradient separation and direct UV detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 956, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, P.K. Postcolumn techniques: A critical perspective for ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1989, 27, 422–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, M.; Lamberty, A.; Gardiner, P.H. Optimization of the simultaneous determination of Cr(VI) and Cr(VI) by ion chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Chem. 1999, 19, 4203–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, Y.; Hatakeyama, M.; Hosino, T.; Haddad, P.R. Rapid ion chromatography of l-ascorbic acid, nitrite, sulfite, oxalate, iodide and thiosulfate by isocratic elution utilizing a postcolumn reaction with cerium(IV) and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 956, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumalesh, K. Simultaneous determination of bromide and nitrate in contaminated waters by ion chromatography using amperometry and absorbance detectors. Talanta 2008, 74, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldini, P.L.; Cavalli, S.; Mevoli, A.; Sharma, J.L. Ion chromatographic and voltamperometric determination of heavy and transition metals in honey. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Jandik, P.; Jones, W.R.; Haganaars, A. Ion chromatography of polyphosphates with direct refractive index detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1987, 389, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwiener, C.; Frimmel, F.H. LC-MS analysis in the aquatic environment and in water treatment—A critical review—Part I: Instrumentation and general aspects of analysis and detection. Anal. Biochem. Chem. 2004, 378, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalski, R.; Jablonska, M.; Szopa, S.; Łyko, A. Application of Ion Chromatography with ICP-MS or MS Detection to the Determination of Selected Halides and Metal/Metalloids Species. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 41, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.R.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Buchberger, W. Recent developments and emerging directions in ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1184, 456–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R. Before the injection—modern methods of sample preparation for separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saubert, A.; Frenzel, W.; Schafer, H.; Bogenschutz, G.; Schafer, J. Sample Preparation Techniques for Ion Chromatography; Metrohm: Herisau, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Slingby, R.; Kaiser, R. Sample treatment techniques and methodologies for ion chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, W.; Michalski, R. Sample Preparation Techniques for Ion Chromatography. In Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental Research; Michalski, R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 210–266. ISBN 9781118862001. [Google Scholar]
- Miro, M.; Frenzel, W. The potential of microdialysis as an automatic sample-processing technique for environmental research. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari-Nordhaus, R.; Nair, L.M.; Anderson, J.M. Elimination of matrix interferences in ion chromatography by the use of solid phase extraction discs. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 671, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.J.; Hand, D.W.; Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Tchobanoglous, G. Principles of Water Treatment; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-470-40538-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.E. Ion chromatography in environmental analysis. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 2779–2801. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, J. Handbook of Ion Chromatography, Fourth, Completely Revised and Enlarged Edition; Wiley-VCH, Verlag GmbH&Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Volumes 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Abbas, N.M.; Smesko, S.A. Suppressed ion chromatography analysis of anions in environmental waters containing high salt concentration, J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 733, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otu, E.O.; Byerley, J.J.; Robinson, C.W. Ion chromatography of cyanide and metal cyanide complexes: A review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1996, 63, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Calero, V.; Galceran, M.T. Ion chromatographic separations of phosphorus species: A review. Talanta 2005, 66, 376–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalski, R. Trace Level Determination of Cr(III)/Cr(VI) in Water Samples Using Ion Chromatography with UV Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 2849–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.A.; Roberts, D.J. Chromatographic and hyphenated methods for elemental speciation analysis in environmental media. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 774, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R. (Ed.) Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental Research; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–269, ISBN 9781118862001 (cloth). ISBN 9781119085478 (epub). [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, M.J.; Haddad, P.R. The determination of trace metal pollutants in environmental matrices using ion chromatography. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarzanini, C.; Bruzzoniti, M.C. Metal species determination by ion chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R. Ion Chromatography as a Reference Method for The Determination of Inorganic Ions in Water and Waste water. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R. Application of ion chromatography for the determination of inorganic cations. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 39, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).