Enantiomeric Ratio of Amino Acids as a Tool for Determination of Aging and Disease Diagnostics by Chromatographic Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. d/l Amino Acid Ratio as a Tool for the Determination of Age of Humans
3. d-Amino Acids as Biomarkers of Diseases/Disorders
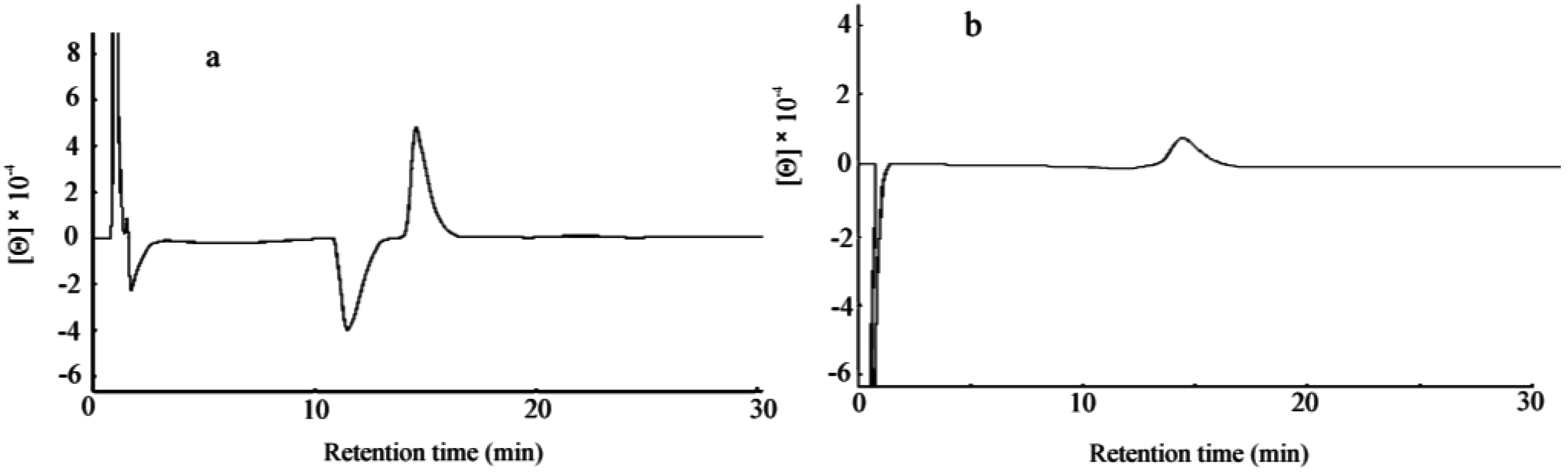
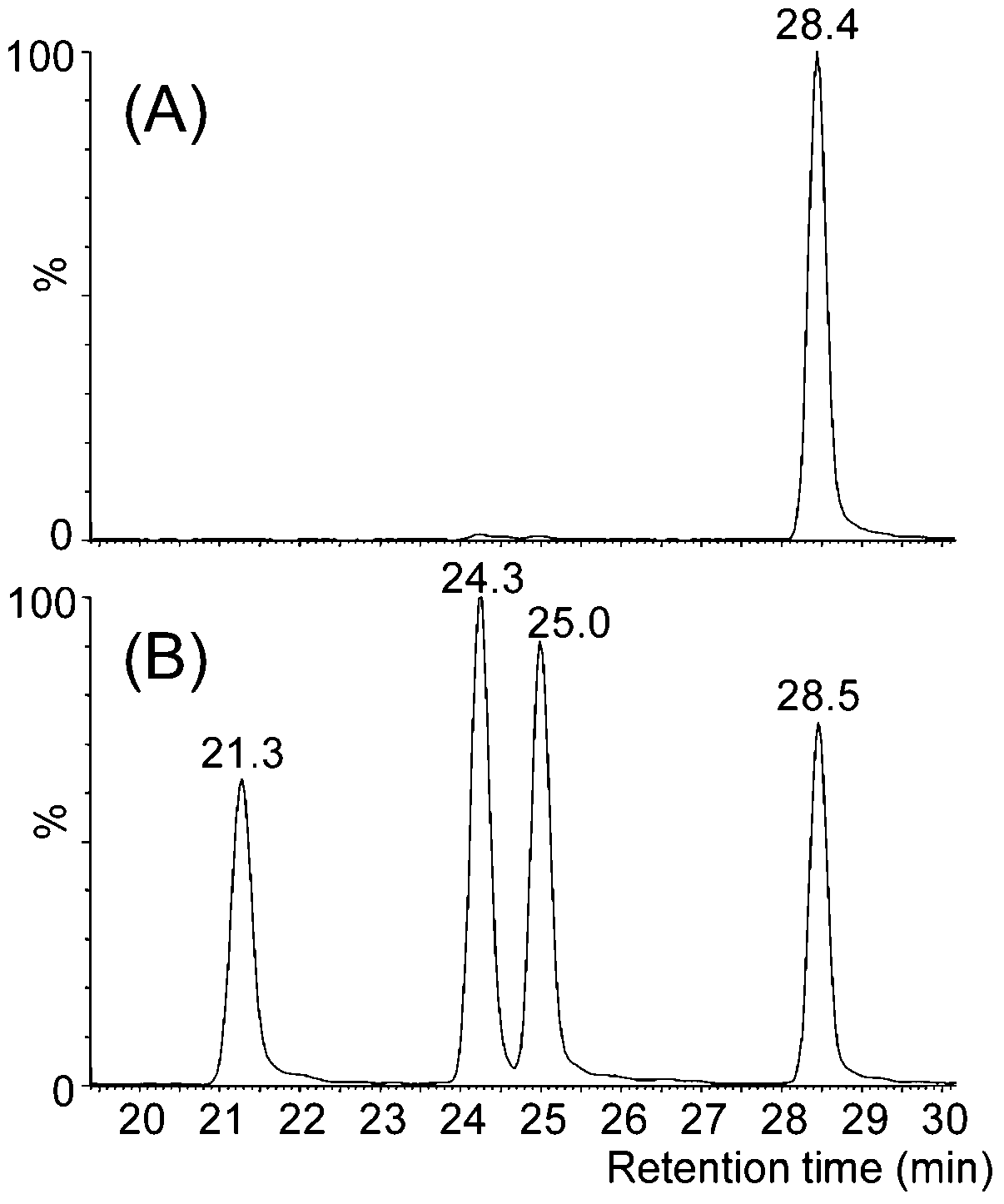
3.1. Chromatographic Methods for AA Determination in Biological Samples
3.2. Chromatographic Determination of AAs as Possible Biomarkers of Diseases/Disorders
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | amino acid |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| MEKC | micellar electrokinetic chromatography |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| UPLC | ultra performance liquid chromatography |
| MP | mobile phase |
| OPA-NAC | o-phthaldialdehyde-N-acetyl-l-cysteine |
| SIM | selective ion monitoring |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CBF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| LIF | laser-induced fluorescence |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SDC | sodium deoxycholate |
| 2D | two dimensional |
| NBD-F | 4-fluoro-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole |
| CSP | chiral stationary phase |
| ODS | octadecylsilica |
| IRI | renal ischemia-reperfusion injury |
| (S)-NIFE | N-(4-nitrophenoxycarbonyl)-l-phenylalanine 2-methoxyethyl ester |
| MeOH | methanol |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| CE SPE | cationic exchange solid phase extraction |
| l-PGA-OSu | l-pyroglutamic acid succinimidyl ester |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| CD | cyclodextrin |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| AAR | AA racemization |
| AAI | AA isomerization |
| CCD-UPLC-MS/MS | covalent chiral derivatized ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| RP | reversed-phase |
| ESI | electrospray ionization |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| SRM | selected reaction monitoring |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
| CRPS | complex regional pain syndrome |
References
- Helfman, P.M.; Bada, J.L. Aspartic acid racemization in dentine as a measure of aging. Nature 1976, 262, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka, S.; Fujii, N.; Ueda, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Satoh, K.; Harada, K. Racemization of aspartic acid in αA-crystallin of bovine lens. Biomed. Res. 1991, 12, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lida, T.; Santa, T.; Toriba, A.; Imai, K. Amino acid sequence and D/L configuration determination methods for d-amino acid-containing peptides in living organisms. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2001, 15, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Yekkala, R.; Meers, C.; Van Schepdael, A.; Hoogmartens, J.; Lambrichts, I.; Willems, G. Racemization of aspartic acid from human dentin in the estimation of chronological age. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 159, S89–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akihiko, S.; Haruka, O.; Takeshi, S.; Fujii, N. Tryptophanase-catalyzed l-tryptophan synthesis from d-serine in the presence of diammonium hydrogen phosphate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar]
- Iadarola, P.; Ferrari, F.; Fumagalli, M.; Viglio, S. Determination of amino acids by micellar EKC: Recent advances in method development and novel applications to different matrices. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanwar, S.; Bhushan, R. Enantioresolution of amino acids: A decade’s perspective, prospects and challenges. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 1113–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, A.; Aturki, Z.; Fanali, S. Chiral separations in food analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalíková, K.; Riesová, M.; Tesařová, E. Recent chiral selectors for separation in HPLC and CE. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 10, 450–471. [Google Scholar]
- König, W.A.; Rahn, W. Gas chromatographic separation of diastereoisomeric amino acid derivatives on glass capillaries: The use of pentafluoropropionyl-amino acid (+)-3-methyl-2-butyl esters. J. Chromatogr. 1977, 133, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurig, V. Gas chromatographic enantioseparation of derivatized α-amino acids on chiral stationary phases—Past and present. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3122–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.; Strasdeit, H.; Haasmann, S.; Brückner, H. Gas chromatographic separation of stereoisomers of non-protein amino acids on modified gamma-cyclodextrin stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1411, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilisz, I.; Péter, A.; Lindner, W. State-of-the-art enantioseparations of natural and unnatural amino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 81, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisz, I.; Aranyi, A.; Péter, A. Chiral derivatizations applied for the separation of unusual amino acid enantiomers by liquid chromatography and related techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1296, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šlechtová, T.; Kalíková, K.; Tesařová, E. Stanovení enantiomerů theaninu pomocí HPLC, porovnání metod detekce. Chem. Listy 2013, 107, 228–232. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Baghdady, Y.Z.; Schug, K.A. Review of in situ derivatization techniques for enhanced bioanalysis using liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, R.A.; Bada, J.L. Glacial-postglacial temperature difference deduced from aspartic acid racemization in fossil bones. Science 1973, 182, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K., Jr.; Bada, J.L. Effect of in situ leaching on amino acid racemisation rates in fossil bone. Nature 1979, 281, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsu’ura, S.; Ueta, N. Fraction dependent variation of aspartic acid racemization age of fossil bone. Nature 1980, 286, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Muraoka, S.; Harada, K. Purification and characterization of a protein containing d-aspartic acid in bovine lens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 999, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Muraoka, S.; Satoh, K.; Hori, H.; Harada, K. Racemization of aspatic acids at specific sites in αA-crystallin from aged human lens. Biomed. Res. 1991, 12, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, E.H.; Sandhouse, M.E.; Burg, J.; Fisher, G.H. Accumulation of d-aspartic acid with age in the human brain. Science 1983, 220, 1407–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, S. Estimation of age from dentin by utilizing the racemization of aspartic acid: Influence of pH. Forensic Sci. Int. 1995, 75, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-J.; Fan, C.-C.; Song, H.-W.; Wei, F.-Q. Age estimation using a modified HPLC determination of ratio of aspartic acid in dentin. Forensic Sci. Int. 1995, 73, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Ohtani, S. Novel chiral selectors anchored on polydimethylsiloxane as stationary phases for separation of derivatized amino acid enantiomers by capillary gas chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benešová, T.; Hozátko, A.; Pilín, A.; Votruba, J.; Flieger, M. A modified HPLC method for the determination of aspartic acid racemization in collagen from human dentin and its comparison with GC. J. Sep. Sci. 2004, 27, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobberstein, R.C.; Huppertz, J.; von Wurmb-Schwark, N.; Ritz-Timme, S. Degradation of biomolecules in artificially and naturally aged teeth: Implications for age estimation based on aspartic acid racemization and DNA analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 179, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Kubota, K. A trial to determine d-amino acids in tissue proteins of mice. Amino Acids 1993, 4, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Sekine, M.; Ogawa, T.; Hidaka, M.; Homma, H.; Masaki, H. Origin of d-amino acids detected in the acid hydrolysates of purified Escherichia coli β-galactosidase. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 116, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, H.; Woiwode, W.; Nicholson, G.J.; Bayer, E. Determination of optical purity of amino acids in proteins. In Stable Isotopes; Kein, E., Kein, P.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt, J.; Nicholson, G.J. Unambiguous determination of the optical purity of peptides via GC-MS. In Peptides: Chemistry, Structure and Biology; Hodges, R.S., Smith, J.A., Eds.; Escom Science Publishers BV: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Liardon, R.; Ledermann, S.; Ott, U. Determination of d-amino acids by deuterium labelling and selected ion monitoring. J. Chromatogr. A 1981, 203, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokihara, K.; Gerhardt, J. Development of an improved automated gas-chromatographic chiral analysis system: Application to non-natural amino acids and natural protein hydrolysates. Chirality 2001, 13, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfman, P.F.; Bada, J.L. Aspartic acid racemization in tooth enamel from living humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 2891–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, M.B.; Aaslo, P.; Egsgaard, H.; Lund, T. Determination of d/l-amino acids by zero needle voltage electrospray ionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCudden, C.R.; Kraus, V.B. Biochemistry of amino acid racemization and clinical application to musculoskeletal disease. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 1112–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chervyakov, A.V.; Gulyaeva, N.V.; Zakharova, M.N. d-amino acids in normal ageing and pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem. J. 2011, 5, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Kaji, Y.; Fujii, N. d-Amino acids in aged proteins: Analysis and biological relevance. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Takata, T.; Fujii, N.; Sakaue, H.; Nirasawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Sasaki, H.; Fujii, N. Rapid survey of four Asp isomers in disease-related proteins by LC-MS combined with commercial enzymes. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N.; Takata, T.; Fujii, N.; Aki, K. Isomerization of aspartyl residues in crystallins and its influence upon cataract. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denoroy, L.; Zimmer, L.; Renaud, B.; Parrot, S. Ultra high performance liquid chromatography as a tool for the discovery and the analysis of biomarkers of diseases: A review. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 927, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Fukushima, T.; Santa, T.; Homma, H.; Hamase, K.; Sakai, K.; Kato, M. Analytical chemistry and biochemistry of d-amino acids. Biomed. Chromatogr. 1996, 10, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamase, K.; Morikawa, A.; Zaitsu, K. d-Amino acids in mammals and their diagnostic value. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 781, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamase, K. Sensitive two-dimensional determination of small amounts of d-amino acids in mammals and the study on their functions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Koga, R.; Oyama, T.; Han, H.; Ueno, K.; Masuyama, K.; Itoh, Y.; Hamase, K. HPLC analysis of naturally occurring free d-amino acids in mammals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Oyama, T.; Itoh, Y.; Hamase, K. Enantioselective two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of amino acids; analysis and physiological significance of d-amino acids in mammals. Chromatography 2014, 35, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Takata, T.; Fujii, N. Quantitative analysis of isomeric (L-α-, L-β-, D-α-, D-β-) aspartyl residues in proteins from elderly donors. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 116, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.H.; D’Aniello, A.; Vetere, A.; Padula, L.; Cusano, G.P.; Man, E.H. Free d-aspartate and d-alanine in normal and Alzheimer brain. Brain Res. Bull. 1991, 26, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, A.; Lee, J.M.; Petrucelli, L.; Fiore, M.M.D. Regional decreases of free d-aspartate levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 250, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.; Lorenzo, H.; Abe, H.; Fujita, E.; Frey, W.H.; Emory, C.; Fiore, M.M.D. Free d-and l-amino acids in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid from Alzheimer and normal subjects. Amino Acids 1998, 15, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouinard, M.L.; Gaitan, D.; Wood, P.L. Presence of the N-methyl-d-aspartate-associated glycine receptor agonist, d-serine, in human temporal cortex: Comparison of normal, Parkinson, and Alzheimer tissues. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumashiro, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Nishikawa, T. Free d-serine in post-mortem brains and spinal cords of individuals with and without neuropsychiatric diseases. Brain. Res. 1995, 681, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Masui, R.; Akino, T. The presence of free d-serine, d-alanine and d-proline in human plasma. Experientia 1992, 48, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Santa, T.; Homma, H.; Nagatomo, R.; Imai, K. Determination of d-amino acids in serum from patients with renal dysfunction. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, H.; Hausch, M. Gas chromatographic characterization of free d-amino acids in the blood serum of patients with renal disorders and of healthy volunteers. J. Chromatogr. 1993, 614, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, S.A.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M.; de Barse, M.M.J.; Roeleveld, M.W.; Hendriks, M.; Dorland, L.; Klomp, L.W.J.; Berger, R.; de Koning, T.J. Two mass-spectrometric techniques for quantifying serine enantiomers and glycine in cerebrospinal fluid: Potential confounders and age-dependent ranges. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlett, D.R.; Abuaf, P.A.; Savage, P.A.; Kowalski, K.A.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Tolan, J.W.; Corkum, N.; Goldstein, G.; Crowther, J.B. Peptide chiral purity determination: Hydrolysis in deuterated acid, derivatization with Marfey’s reagent and analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 707, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsén, G.; Bergquist, J. Chiral separation of amino acids in biological fluids by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 745, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.L.; Shulman, Y.; Tibbo, P.; Hampson, D.R.; Baker, G.B. Determination of d-serine and related neuroactive amino acids in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 844, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Morikawa, A.; Ohgusu, T.; Lindner, W.; Zaitsu, K. Comprehensive analysis of branched aliphatic d-amino acids in mammals using an integrated multi-loop two-dimensional column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic system combining reversed-phase and enantioselective columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1143, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Nimura, N.; Adachi, M.; Sekine, M.; Hanai, T.; Kubo, H.; Homma, H. Determination of d- and l-aspartate in cell culturing medium, within cells of MPT1 cell line and in rat blood by a column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic method. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 761, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.W.; Gasper, M.P.; Lee, S.H.; Ercal, N.; Zukowski, J. Factors controlling the level and determination of d-amino acids in the urine and plasma of laboratory rodents. Amino Acids 1993, 5, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Ueno, K.; Han, H.; Hirano, J.; Morikawa, A.; Mita, M.; Kaneko, T.; Lindner, W.; Zaitsu, K. Simultaneous determination of hydrophilic amino acid enantiomers in mammalian tissues and physiological fluids applying a fully automated micro-two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatographic concept. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasabe, J.; Suzuki, M.; Miyoshi, Y.; Tojo, Y.; Okamura, C.; Ito, S.; Konno, R.; Mita, M.; Hamase, K.; Aiso, S. Ischemic acute kidney injury perturbs homeostasis of serine enantiomers in the body fluid in mice: Early detection of renal dysfunction using the ratio of serine enantiomers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, A.; Hamase, K.; Zaitsu, K. Determination of d-alanine in the rat central nervous system and periphery using column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 312, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Wu, H.-H.; Wang, H. Establishment and application of an automated chiral two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography method for bio-analysis of d-acidic amino acids. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 42, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, W.F.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Ophoff, R.; Bakker, S.; Klomp, L.W.; Berger, R.; de Koning, T.J. A sensitive and simple ultra-high-performance-liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry based method for the quantification of d-amino acids in body fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7130–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, C.; Rafii, M.; Ball, R.O.; Pencharz, P. The significance of d-isomers in stable isotope studies in humans is dependent on the age of the subject and the amino acid tracer. Metabolism 2010, 59, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischl, R.J.; Hartmanova, L.; Carrozzo, M.; Huszar, M.; Frühauf, P.; Lindner, W. Chemoselective and enantioselective analysis of proteinogenic amino acids utilizing N-derivatization and 1-d enantioselective anion-exchange chromatography in combination with tandem mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8379–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilisz, I.; Grecsó, N.; Misicka, A.; Tymecka, D.; Lázár, L.; Lindner, W.; Péter, A. Comparison of the separation performances of Cinchona alkaloid-based zwitterionic stationary phases in the enantioseparation of β2- and β3-amino acids. Molecules 2015, 20, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakawa, S.; Shimbo, K.; Yamada, N.; Mizukoshi, T.; Miyano, H.; Mita, M.; Lindner, W.; Hamase, K. Simultaneous analysis of d-alanine, d-aspartic acid, and d-serine using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to the rat plasma and tissues. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 115, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K.; Jingu, S.; Yamaguchi, J. A surrogate analyte method to determine d-serine in mouse brain using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 432, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, H.; Kakehi, M.; Jinno, F. Bioanalytical method for the simultaneous determination of d- and l-serine in human plasma by LC/MS/MS. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 487, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, H.; Kakehi, M.; Jinno, F. Method development for the determination of d- and l-isomers of leucine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry and its application to animal plasma samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7889–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, T.; Todoroki, K.; Inoue, K.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T. Isotopic variants of light and heavy l-pyroglutamic acid succinimidyl esters as the derivatization reagents for dl-amino acid chiral metabolomics identification by liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 811, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, T.; Takayama, T.; Todoroki, K.; Inoue, K.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T. Towards the chiral metabolomics: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based dl-amino acid analysis after labeling with a new chiral reagent, (S)-2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl-1-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate, and the application to saliva of healthy volunteers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 875, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Péter, A.; Grecsó, N.; Tóth, G.; Fülöp, F.; Lindner, W.; Ilisz, I. Ultra-trace analysis of enantiomeric impurities in proteinogenic N-Fmoc-amino-acid samples on cinchona alkaloid-based chiral stationary phases. Isr. J. Chem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Fukushima, T.; Shimizu, E.; Komatsu, N.; Watanabe, H.; Shinoda, N.; Nakazato, M.; Kumakiri, C.; Okada, S.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Decreased serum levels of d-serine in patients with schizophrenia. Evidence in support of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor hypofunction hypothesis of schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Ohba, H.; Iwayama-Shigeno, Y.; Toyoshima, M.; Okuno, A.; Takao, H.; Toyota, T.; Minabe, Y.; et al. Identification of multiple serine racemase (SRR) mRNA isoforms and genetic analyses of SRR and DAO in schizophrenia and d-serine levels. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsén, G.; Bergquist, J.; Westlind-Danielsson, A.; Josefsson, B. Stereoselective determination of amino acids in β-amyloid peptides and senile plaques. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Fukushima, T.; Shimizu, E.; Okada, S.; Komatsu, N.; Okamura, N.; Koike, K.; Koizumi, H.; Kumakiri, C.; Imai, K.; et al. Possible role of d-serine in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 28, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Lee, J.-A.; Korenaga, T.; Ichihara, H.; Kato, M.; Imai, K. Simultaneous detemination of d-lactic acid and 3-hydroxybutyric acid in rat plasma using a column-switching HPLC with fluorescent derivatization with 4-nitro-7-piperazino-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD-PZ). Biomed. Chromatogr. 2001, 15, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samakashvili, S.; Ibáñez, C.; Simó, C.; Gil-Bea, F.J.; Winblad, B.; Cedazo-Mínguez, A.; Cifuentes, A. Analysis of chiral amino acids in cerebrospinal fluid samples linked to different stages of Alzheimer disease. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Hosaka, D.; Mochizuki, N.; Akatsu, H.; Tsutsumiuchi, K.; Hashizume, Y.; Matsukawa, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Toyo’oka, T. Simultaneous determination of post-translational racemization and isomerization of N-terminal amyloid‑β in Alzheimer’s brain tissues by covalent chiral derivatized ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, T.; Mochizuki, T.; Todoroki, K.; Min, J.Z.; Mizuno, H.; Inoue, K.; Akatsu, H.; Noge, I.; Toyo’oka, T. A novel approach for LC-MS/MS-based chiral metabolomics fingerprinting and chiral metabolomics extraction using a pair of enantiomers of chiral derivatization reagents. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 898, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Cui, Y. Simultaneous determination of 18 d-amino acids in rat plasma by an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method: Application to explore the potential relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and d-amino acid level alterations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Alexander, G.M.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Singh, N.; Torjman, M.C.; Goldberg, M.E.; Wainer, I.W.; Moaddel, R. Development and validation of a sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the determination of d-serine in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 89, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moaddel, R.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Xie, Y.; Villaseñor, A.; Brutsche, N.E.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Lorenzo, M.P.; Garcia, A.; Bernier, M.; et al. d-serine plasma concentration is a potential biomarker of (R,S)-ketamine antidepressant response in subjects with treatment-resistant depression. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Kawai, J.; Imai, K.; Toyo’oka, T. Simultaneous determination of d- and l-serine in rat brain microdialysis sample using a column-switching HPLC with fluorimetric detection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Engberg, G.; Shimizu, E.; Nordin, C.; Lindström, L.H.; Iyo, M. Reduced d-serine to total serine ratio in the cerebrospinal fluid of drug naive schizophrenic patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Engberg, G.; Shimizu, E.; Nordin, C.; Lindström, L.H.; Iyo, M. Elevated glutamine/glutamate ratio in cerebrospinal fluid of first episode and drug naive schizophrenic patients. BMC Psychiatry 2005, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pålsson, E.; Jakobsson, J.; Södersten, K.; Fujita, Y.; Sellgren, C.; Ekman, C.-J.; Ågren, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Landén, M. Markers of glutamate signaling in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with bipolar disorder and healthy controls. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deáková, Z.; Ďuračková, Z.; Armstrong, D.W.; Lehotay, J. Two-dimensional high performance liquid chromatography for determination of homocysteine, methionine and cysteine enantiomers in human serum. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1408, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deáková, Z.; Ďuračková, Z.; Armstrong, D.W.; Lehotay, J. Separation of enantiomers of selected sulfur-containing amino acids by using serially coupled achiral-chiral columns. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 2015, 38, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhier, M.C.; Dettmer, K.; Gruber, M.A.; Oefner, P.J. Comparison of derivatization and chromatographic methods for GC-MS analysis of amino acid enantiomers in physiological samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.Z.; Hatanaka, S.; Yu, H.; Higashi, T.; Inagaki, S.; Toyo’oka, T. First detection of free d-amino acids in human nails by combination of derivatization and UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1233–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.Z.; Hatanaka, S.; Yu, H.; Higashi, T.; Inagaki, S.; Toyo’oka, T. Determination of dl-amino acids, derivatized with R(−)-4-(3-isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-yl)-7-(N,N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, in nail of diabetic patients by UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3220–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, M.P.; Dudzik, D.; Varas, E.; Gibellini, M.; Skotnicki, M.; Zorawski, M.; Zarzycki, W.; Pellati, F.; García, A. Optimization and validation of a chiral GC-MS method for the determination of free d-amino acids ratio in human urine: Application to a Gestational Diabetes Mellitus study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Hamase, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Yasuda, K.; Mita, M.; Rakugi, H.; Hayashi, T.; Isaka, Y. Chiral amino acid metabolomics for novel biomarker screening in the prognosis of chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Nagano, M.; Ishigo, S.; Ito, Y.; Hashiguchi, K.; Hishida, N.; Mita, M.; Lindner, W.; Hamase, K. Chiral amino acid analysis of Japanese traditional Kurozu and the developmental changes during earthenware jar fermentation processes. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 966, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| d-AAs | Disease | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| d-Ala | Alzheimer’s disease | brain | [48] |
| d-Asp | brain | [48,49] | |
| cerebrospinal fluid | [50] | ||
| d-Ser | Parkinson’s disease | brain | [51] |
| Schizophrenia | brain | [52] | |
| d-Ala | Renal disease | plasma | [53] |
| serum | [54] | ||
| d-Asx | serum | [55] | |
| d-Pro | serum | [53] | |
| d-Ser | plasma, serum | [53,55] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalíková, K.; Šlechtová, T.; Tesařová, E. Enantiomeric Ratio of Amino Acids as a Tool for Determination of Aging and Disease Diagnostics by Chromatographic Measurement. Separations 2016, 3, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations3040030
Kalíková K, Šlechtová T, Tesařová E. Enantiomeric Ratio of Amino Acids as a Tool for Determination of Aging and Disease Diagnostics by Chromatographic Measurement. Separations. 2016; 3(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations3040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalíková, Květa, Tereza Šlechtová, and Eva Tesařová. 2016. "Enantiomeric Ratio of Amino Acids as a Tool for Determination of Aging and Disease Diagnostics by Chromatographic Measurement" Separations 3, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations3040030
APA StyleKalíková, K., Šlechtová, T., & Tesařová, E. (2016). Enantiomeric Ratio of Amino Acids as a Tool for Determination of Aging and Disease Diagnostics by Chromatographic Measurement. Separations, 3(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations3040030