A New Affinity Gel Synthesized for Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Isolated from Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Leaf and an Investigation into Its Kinetic Properties †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Partial Purification of Crude PAL Extract Isolated from Red Clover Leaf (RCL-PAL)
2.2.2. Characterization Studies upon RCL-PAL
2.2.3. Determination of Kinetic Constants of RCL-PAL
2.2.4. Studies on Affinity Chromatography of RCL-PAL
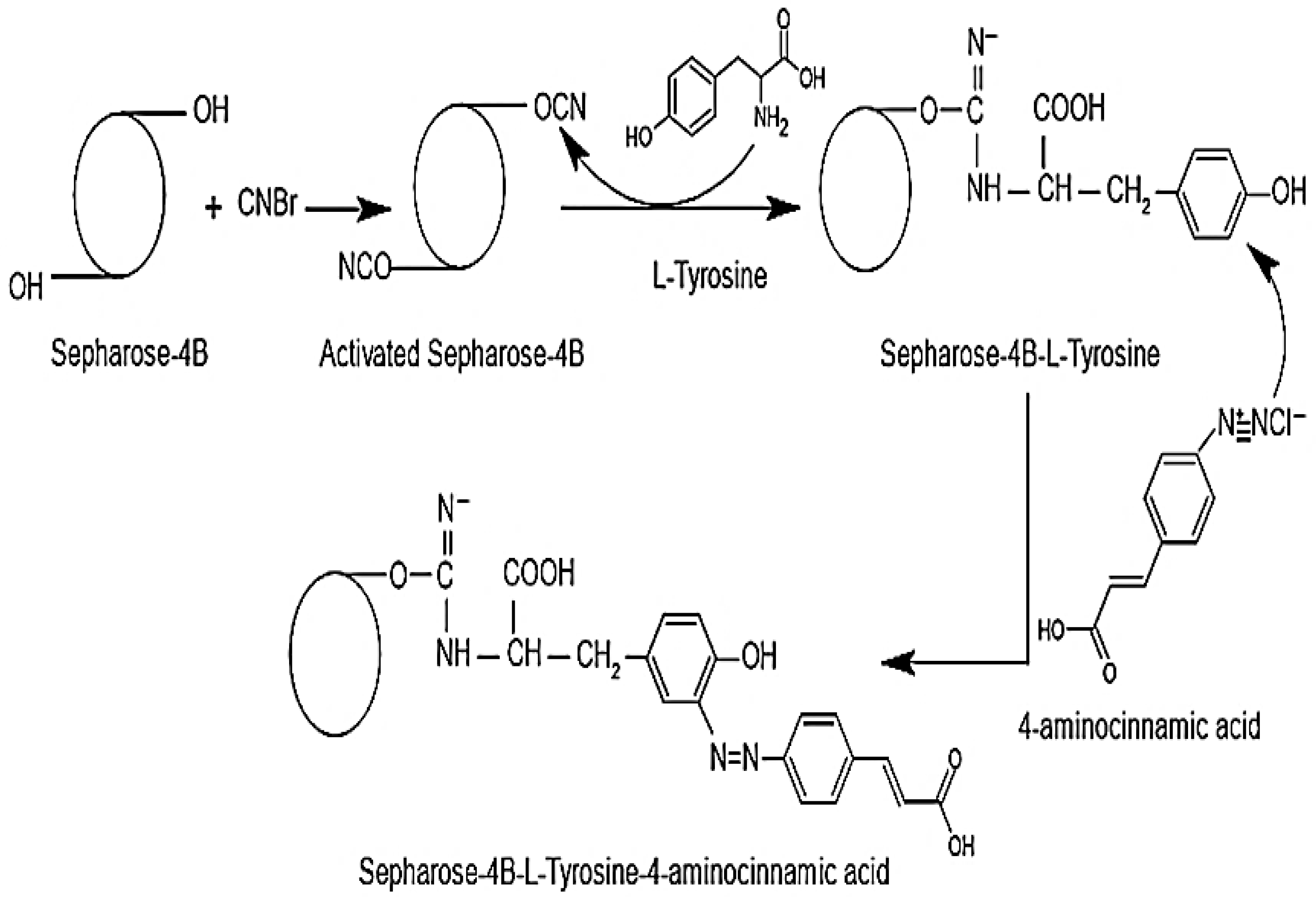
2.2.5. Synthesis of Affinity Gel for RCL-PAL Separation
2.2.6. FT-IR Analysis of the Original S-4B-TACA Affinity Gel
2.2.7. Purification of RCL-PAL by Using the Affinity Gel
2.2.8. Detection of RCL-PAL Amount
2.2.9. Activity Studies of RCL-PAL
2.2.10. Electrophoresis Studies of RCL-PAL
2.2.11. Formation of Purification Table for RCL-PAL
2.2.12. Detection of RCL-PAL Stabilization
2.2.13. Statistical Analysis of RCL-PAL Stability
3. Results and Discussion
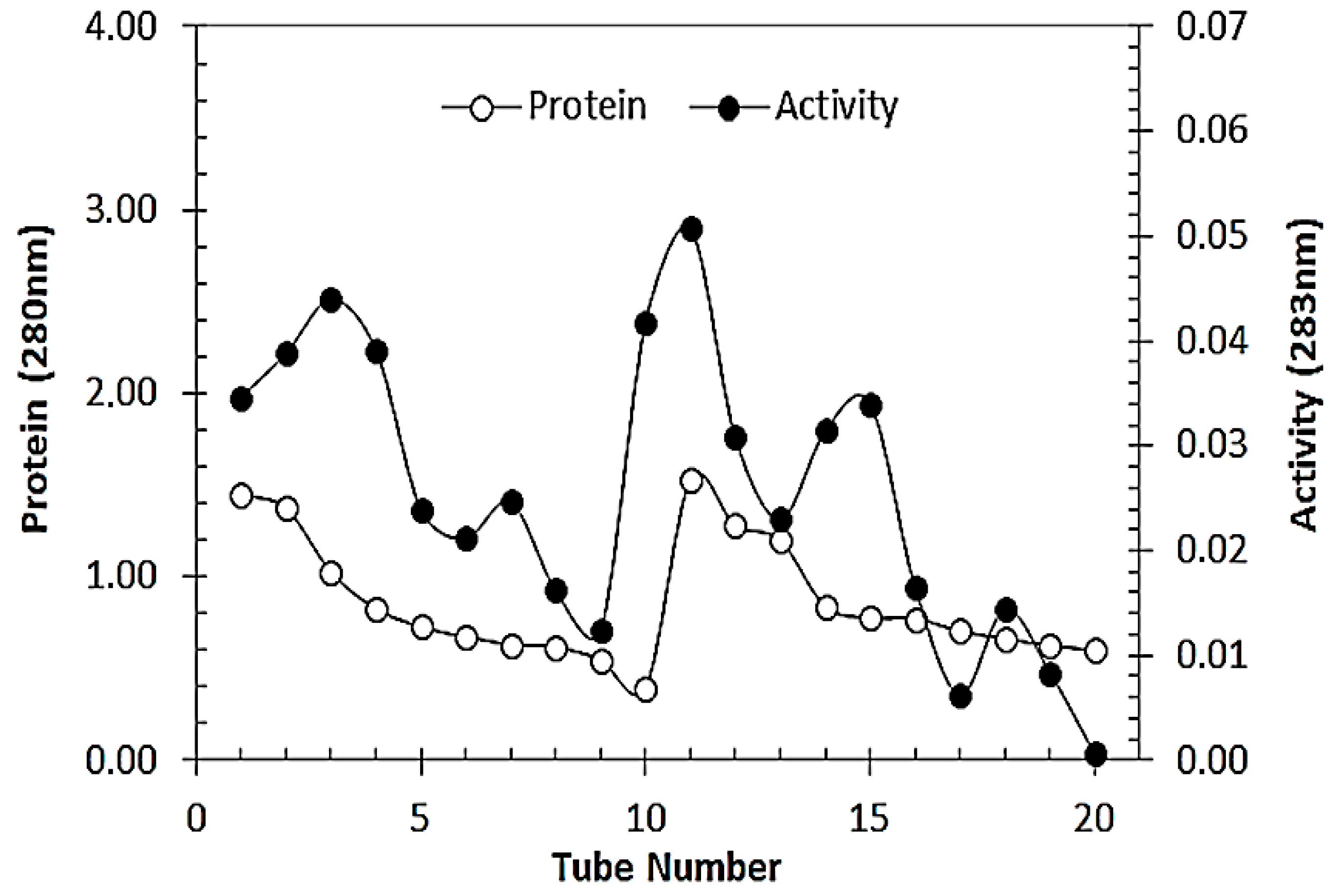
3.1. Partial Purification of RCL-PAL
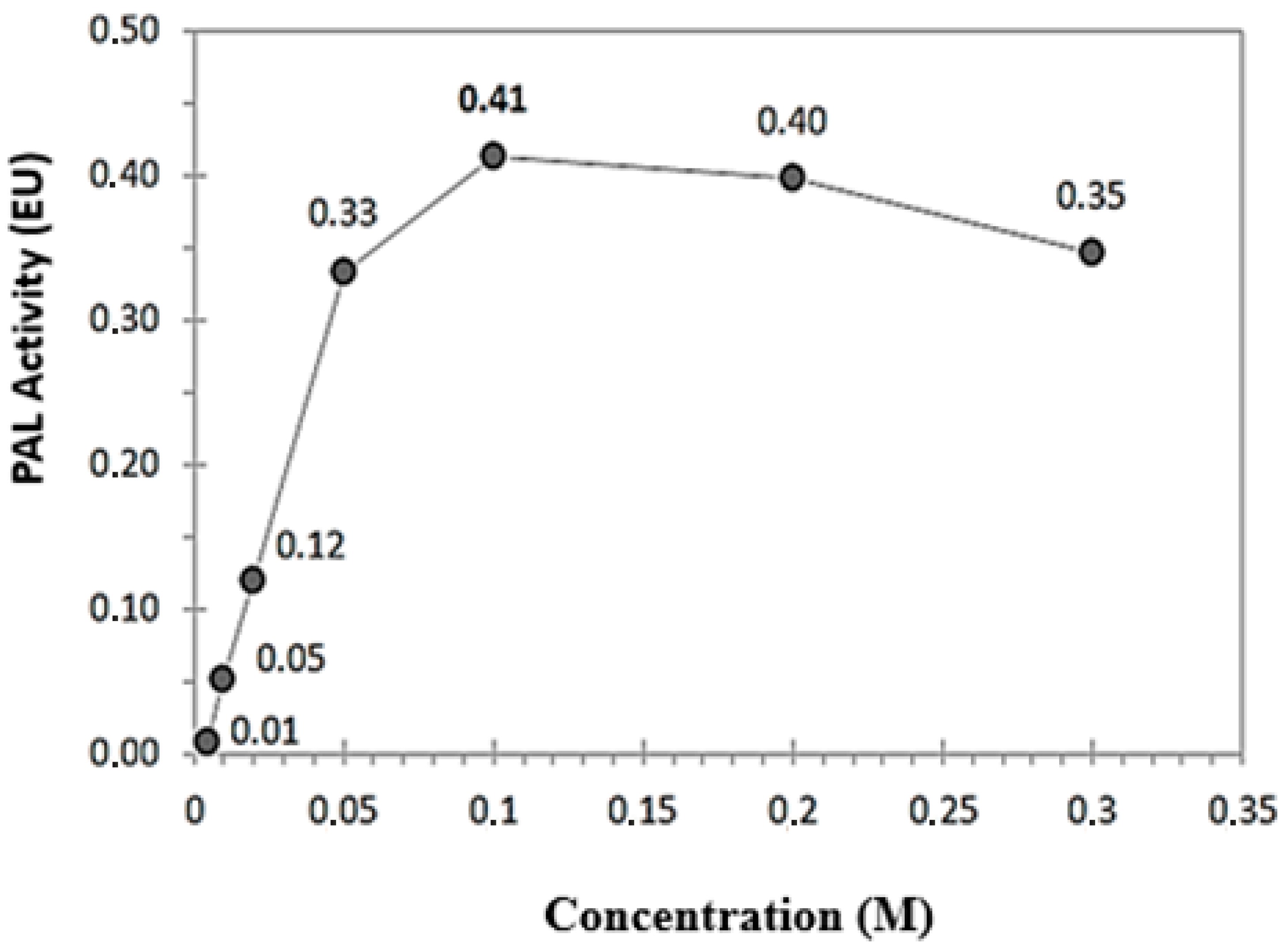
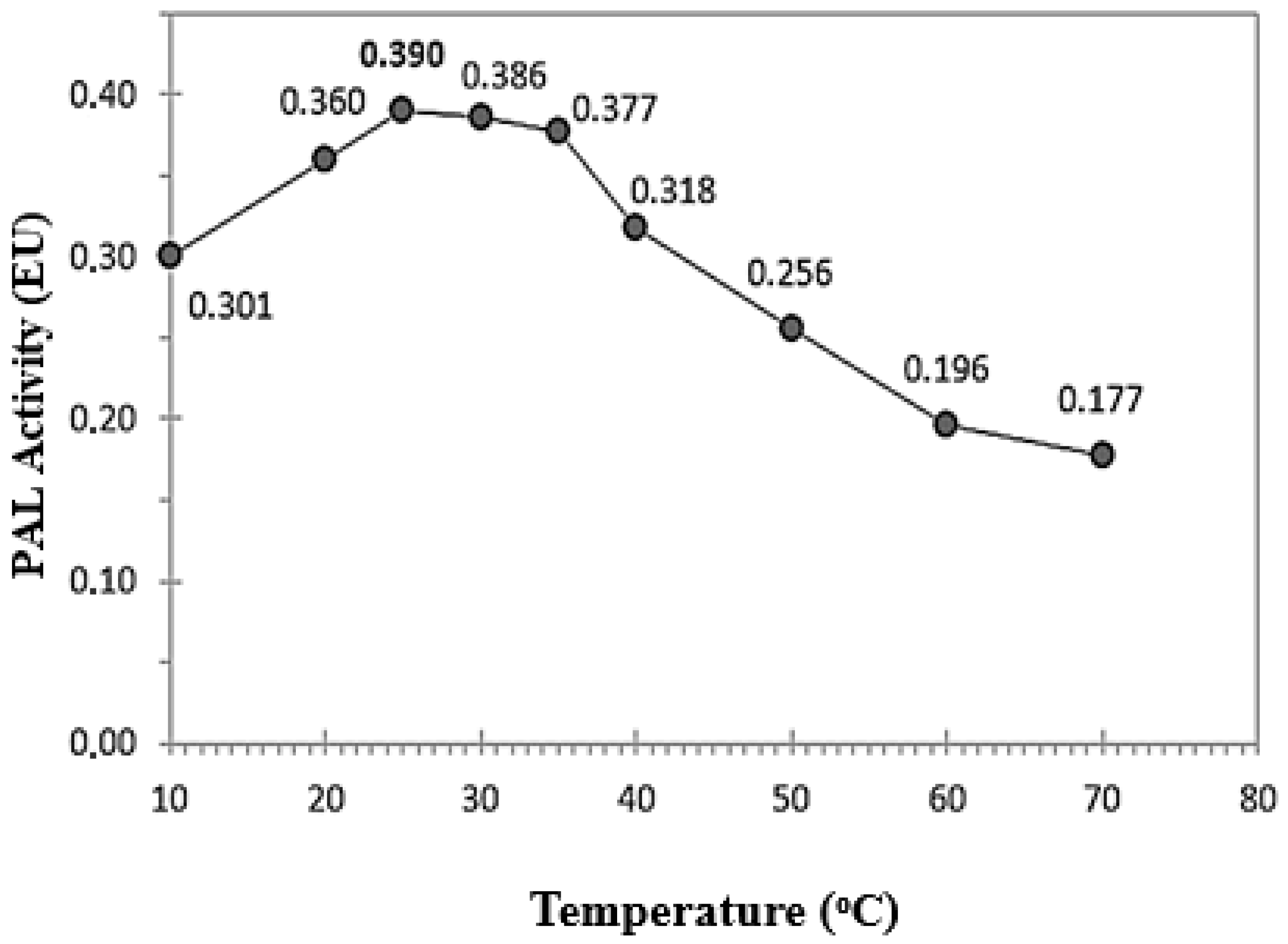
3.2. Characterization Studies of RCL-PAL
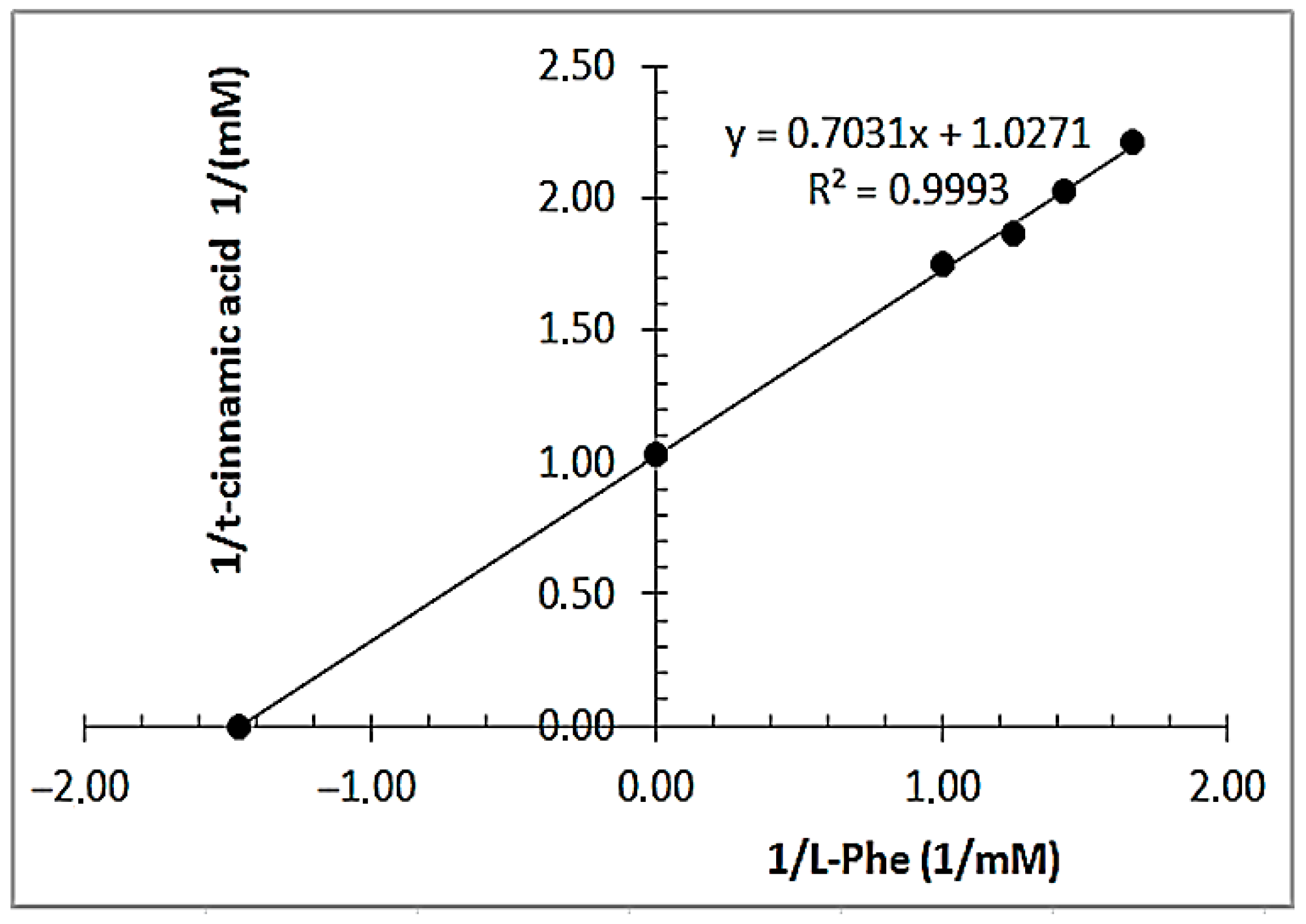
3.3. Determination of Kinetic Constants of RCL-PAL
3.4. FT-IR Analysis of the Original S-4B-TACA Affinity Gel
3.5. Purification of RCL-PAL by Affinity Chromatography
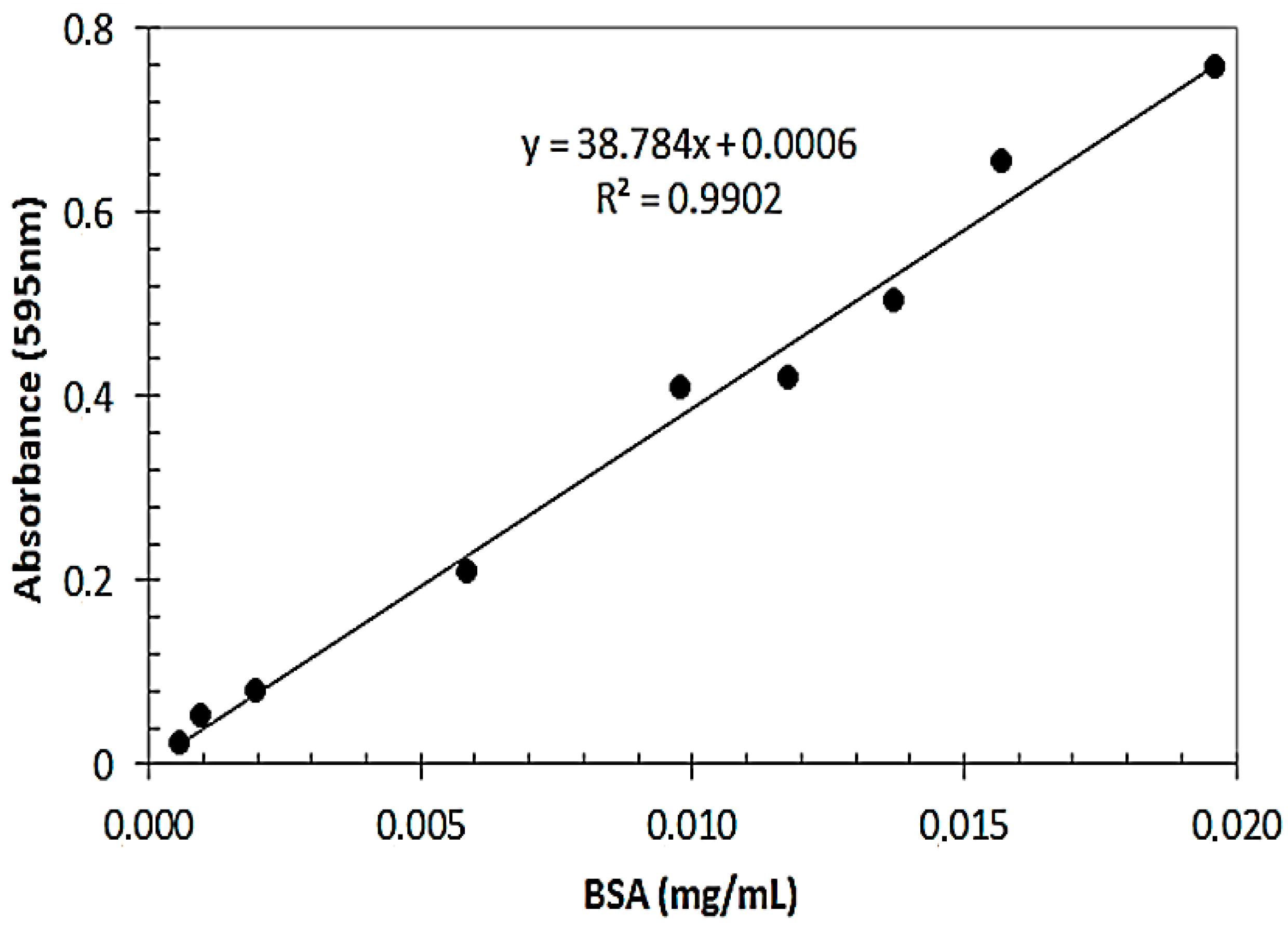
3.6. Determination of Protein Content of RCL-PAL
3.7. Determination of RCL-PAL Activity
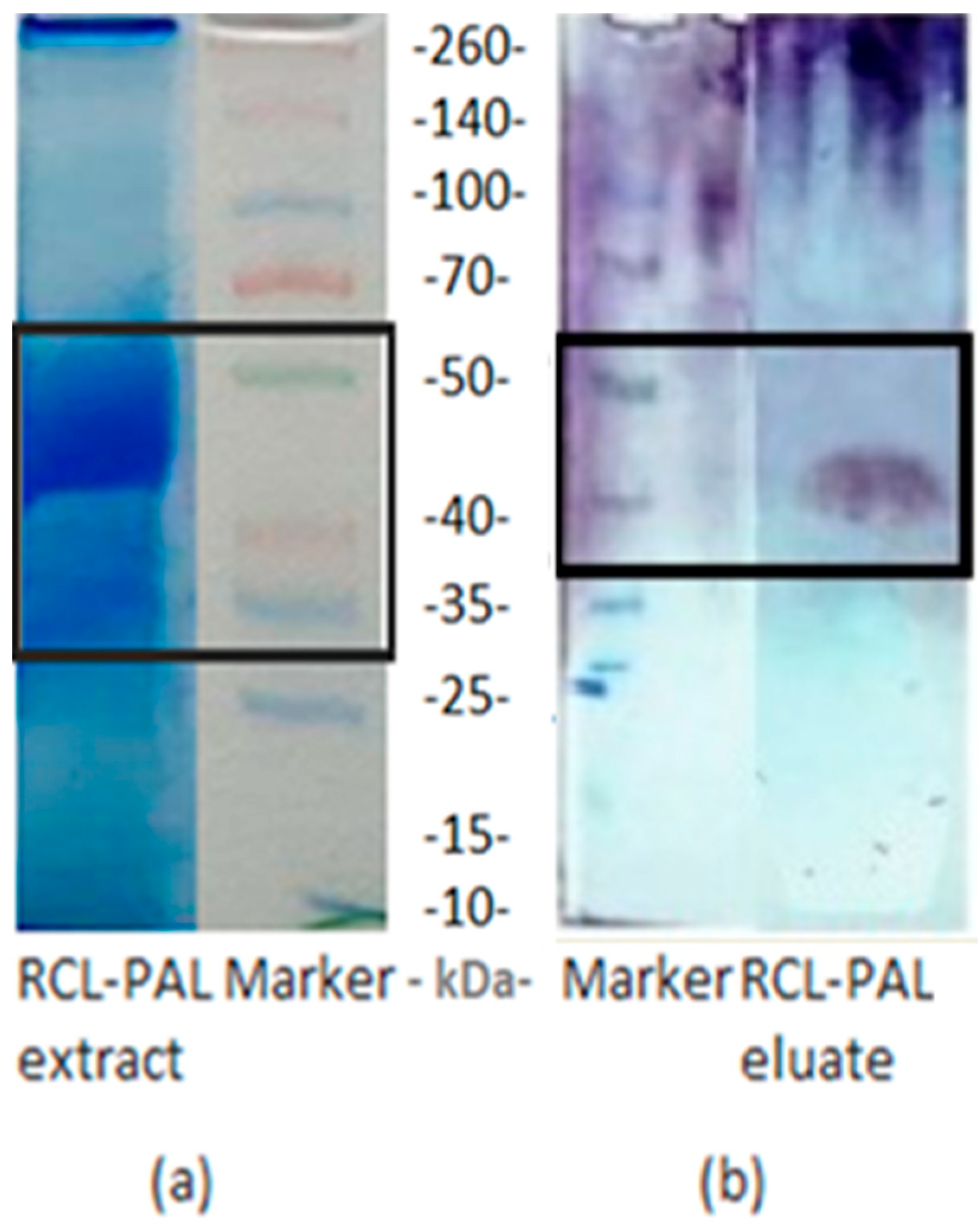
3.8. Determination of the Molecular Weight of RCL-PAL by SDS-PAGE
3.9. Formation of Purification Table of RCL-PAL
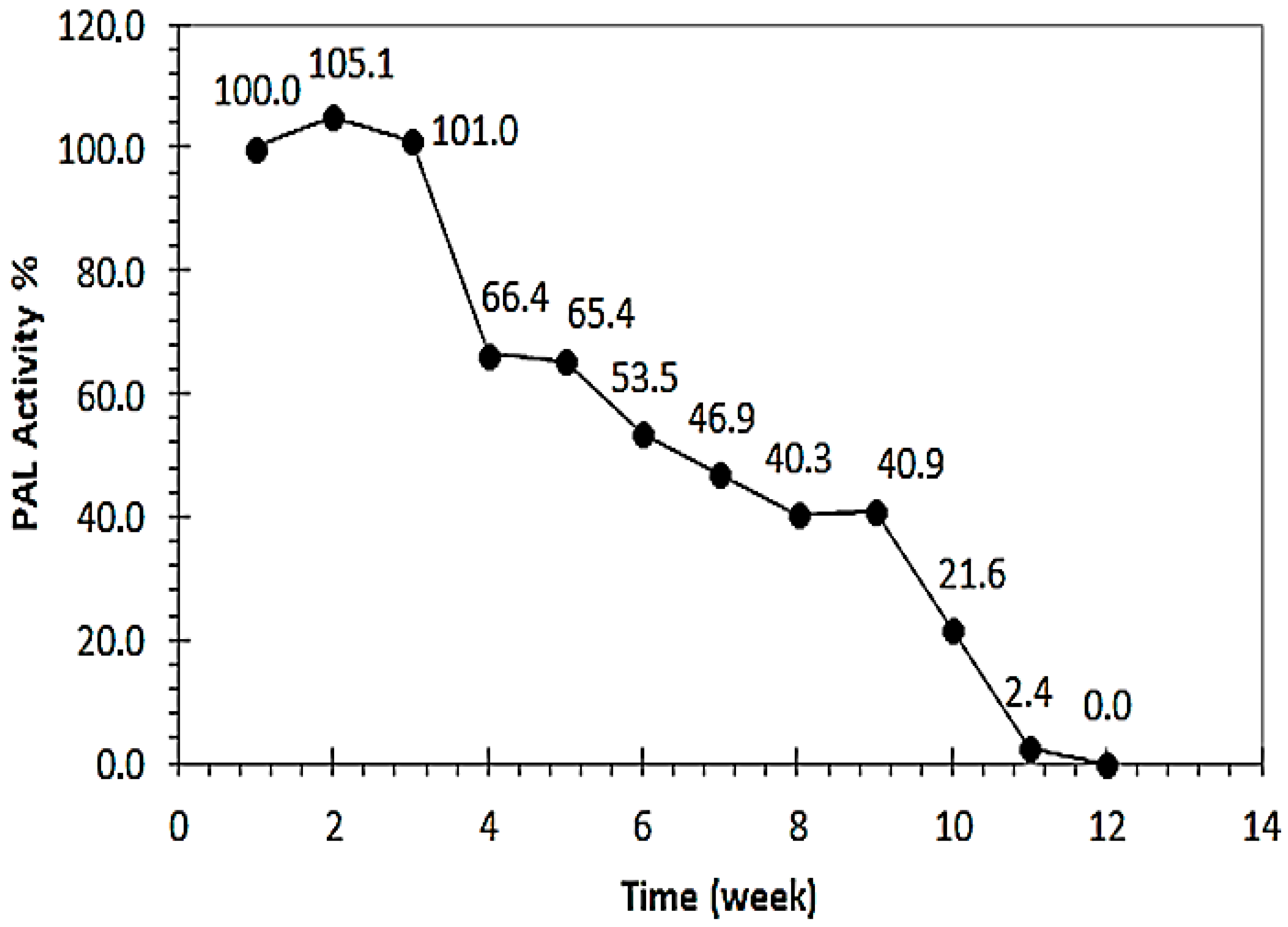
3.10. Determination of RCL-PAL Stabilization
3.11. Statistical Evaluation of RCL-PAL Stabilization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAL | Phenyalanine ammonia lyase |
| RCL | Red clover leaf |
| t-CA | Trans-cinnamic acid |
| L-Phe | L-phenylalanine |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| S-4B-TACA | Sepharose-4B-L-tyrosine-4-aminocinnamic acid |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| MIO | 4-methyldiene-imidazol-5-one |
| APS | Ammonium persulfate |
| TEMED | Tetramethyl ethylene diamine |
| Tris BASE | Tris hydroxymethyl aminomethane |
| CBB | Coomassie brillant blue |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Sabudak, T.; Guler, N. Trifolium L.-A review on its phytochemical and pharmacological profile. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, S.; Cupina, B.; Krstic, D.; Pataki, I.; Katanski, S.; Milosevic, B. Seasonal changes of proteins, structural carbohydrates, fats and minerals in herbage dry matter of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2011, 27, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabudak, T.; Dokmeci, D.; Ozyigit, F.; Isik, E.; Aydogdu, N. Antiinflammatory and antioxidant activities of Trifolium resupinatum var. microcephalum extracts. Asian J. Chem. 2008, 20, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.W.; Khatoon, S. Ethnobotanical studies on some useful herbs of Haramosh and Bugrote valleys in Gilgit, Northern Areas of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2008, 40, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, B.; Hajdari, A.; Krasniqi, F.; Hoxha, E.; Ademi, H.; Quave, C.L.; Pieroni, A. Medical ethnobotany of the Albanian Alps in Kosovo. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2012, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, H.P.; Lu, J.; Booth, N.L.; Yamamura, H.I.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Wang, Z.J. A red clover (Trifolium pratense) phase II clinical extract possesses opiate activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo, A.R. Lignification in plant cell walls. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1997, 176, 87–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Jung, W.J.; Avice, J.C.; Ourry, A.; Kim, T.H. Peroxidases and lignification in relation to the intensity of water-deficit stress in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, G.; Moreno, F.D.; Blanch, G.P.; del Castillo, M.L.R. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, flavanone 3 beta-hydroxylase and flavonol synthase enzyme activity by a new in vitro assay method in berry fruits. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Sonne, C.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals and arsenic stress in food crops: Elucidating antioxidative defense mechanisms in hyperaccumulators for food security, agricultural sustainability, and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, M.L.; Berry, H.M.; Mine, A.; Argueso, C.T.; Tsuda, K. Evolution of Hormone Signaling Networks in Plant Defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Wang, Z.; Wei, C.; Amo, A.; Ahmed, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Phenylpropanoid Pathway Engineering: An Emerging Approach towards Plant Defense. Pathogens 2020, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.C.; Takeno, K. Stress-induced flowering. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukol, J.; Conn, E.E. Metabolism of aromatic compounds in higher plants. IV. Purification and properties of phenylalanine deaminase of Horden vulgare. J. Biol. Chem. 1961, 236, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahlbrock, K.; Scheel, D. Physiology and molecular biology of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1989, 40, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieseberg, T.P.; Dadras, A.; Furst-Jansen, J.M.R.; Ashok, A.D.; Darienko, T.; De-Vries, S.; Irisarri, I.; De-Vries, J. Crossroads in the evolution of plant specialized metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 134, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Guo, J.; Lu, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F.; Yao, C.; Hao, E. Pharmacological Potential of Cinnamic Acid and Derivatives: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.T.; Ding, Y.L. Stories of Salicylic Acid: A Plant Defense Hormone. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.B.; Liu, C.J. Multifaceted Regulations of Gateway Enzyme Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase in the Biosynthesis of Phenylpropanoids. Mol. Plant. 2015, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Tah, A.; Gosset, G. Production of cinnamic and p-hydroxycinnamic acids in engineered microbes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.-Q.; Lin, H.-X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracchi, L.M.; Panahabadi, R.; Barros-Rios, J.; Bartley, L.E.; Sanguinet, K.A. Grass lignin: Biosynthesis, biological, roles, and industrial applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1343097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yin, H. The Flavonoid Biosynthesis Network in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Hu, S.-Y.; Xiao, F.-Y.; Dong, Z.-B.; Ye, J.-H.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Liang, Y.-R.; Lu, J.-L. Dihydrochalcones in Sweet Tea: Biosynthesis. Distribution and Neuroprotection Function. Molecules 2022, 27, 8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, N.; Vinogradova, E.; Chaplygin, V.; Mandzhieva, S.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Seth, C.S.; Burachevskaya, M.; Lysenko, D.; et al. Phenolic Compounds of the Medicinal Plants in an Anthropogenically Transformed Environment. Molecules 2023, 28, 6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, R. Evolution of aromatic amino acid metabolism in plants: A key driving force behind plant chemical diversity in aromatic natural products. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2024, 379, 20230352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, L.H.; Verberne, M.C.; Verpoorte, R. Activities of enzymes involved in the phenylpropanoid pathway in constitutively salicylic acid-producing tobacco plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 40, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaman, M.E.; Copaja, S.V.; Argandona, V.H. Relationships between salicylic acid content, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) activity, and resistance of barley to aphid infestation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2227–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Lai, Z.; Fan, B. Biosynthesis of salicylic acid in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, N.M. Industrial Biotechnology Based on Enzymes From Extreme Environments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 870083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Chen, W.; Ren, T.; Ma, A.; Li, S.; Jia, Y. Characterization of an epilactose-producing cellobiose 2-epimerase from Clostridium sp. TW13 and reutilization of waste milk. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, J. Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J. Simulative Fabrication of Milk Fortified with Sialyloligosaccharides and Its Prospective Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 15835–15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L. Simple phenylpropanoids: Recent advances in biological activities, biosynthetic pathways, and microbial production. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 41, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viniegra-Gonzalez, G.; Favela-Torres, E.; Aguilar, C.N.; Romero-Gomes, S.J.; Diaz-Godinez, G.; Augur, C. Advantages of fungal enzyme production in solid state over liquid fermentation system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, R.; Chandrasekaran, R.; Muthuselvam, M. Microbial biotechnology, rapid advances in an area of massive impact. Adv. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, G.; Goyal, S.; Sooch, B.S. Purification Approaches of Biocatalyst Applied for Cellulosic Biomass Breakdown. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2024, 53, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovbude, S.T.; Sharmeen, S.; Kyei, I.; Olupathage, H.; Jones, J.; Bell, R.J.; Powers, R.; Hage, D.S. Applications of chromatographic methods in metabolomics: A review. J. Chromatogr. B 2024, 1239, 124124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urh, M.; Simpson, D.; Zhao, K. Chapter 26, Affinity Chromatography: General Methods, Methods in Enzymology; Promega Corporation: Madison, WI, USA, 2009; Volume 463, pp. 417–438. ISSN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yan, K.Z.; Huang, S.H.; Pan, S.H.; Chen, G.G.; Liang, Z.Q. A Novel Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Purified from Rhodosporidium paludigenum PT3. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, R.I.; Lara, M.; Lopezmunguia, A. Purification and Stabilization of Phenylalanine Ammonia-lyase from Sporidiobolus-pararoseus. Biotechnol. Tech. 1995, 9, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.G.; Charles, D.J.; Yu, L.L.; Simon, J.E. Purification and Characterization of A Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase from Ocimum basilicum. Phytochemistry 1996, 43, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shore, H.M. Properties of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase from Marrow Cotyledons. Plant Sci. 2002, 162, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Lehninger, A.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry, 7th ed.; Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–2582. ISBN 978-1-4641-2611-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantition of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.U.; Vaidyanathan, C.S. A New Simple Spectrophotometric Assay of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase. Curr. Sci. 1986, 55, 391–393. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24089938 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Laemmli, D.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basic and Advanced Molecular Biology Methods, Genomic and Proteomic Analyses, 2nd ed.; Temizkan, G., Arda, N., Eds.; Nobel Medicine Bookstore: Istanbul, Turkey, 2021; ISBN 978-605-335-362-1. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, K.N.; Carey, P.M. Data Analysis with Microsoft Excel: Updated for Office 2007; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 0-495-39178-6. [Google Scholar]
- Şirin, S.; Aydaş, S.B.; Aslım, B. Biochemical Evaluation of Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase from Endemic Plant Cyathobasis fruticulosa (Bunge) Aellen for the Dietary Treatment of Phenylketonuria. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-W.; Parkl, S.-S.; Lim, C.-J. Purification and Properties of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase from Leaf Mustard. Mol. Cells 1997, 7, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydaş, S.B.; Şirin, S.; Aslim, B. Biochemical analysis of Centaurea depressa phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) for biotechnological applications in phenylketonuria (PKU). Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, H.A.; Ibrahim, W.A. Kinetics of phenylalanine and tyrosine ammonia-lyase enzymes activity of banana fruit (Musa cavendishii L., cv. Enana). Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 680–689. [Google Scholar]
- Whetten, R.W.; Sederoff, R.R. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from loblolly pine: Purification of the enzyme and isolation of complementary DNA clones. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, M.J.; D’Cunha, G.B. A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Song, C.; Manzoor, M.A.; Li, D.; Cao, Y.; Cai, Y. Functional and kinetics of two efficient phenylalanine ammonia lyase from Pyrus bretschneideri. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Perez, M.O.; Patience, G.S. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy-FTIR. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 98, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, D.A.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 7th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-305-57721-3. [Google Scholar]
- Amersham Pharmacia Biotech. Affinity Chromatography, Principles and Methods, edition AC 18-1022-29, 2007. Available online: https://b3p.it.helsinki.fi/download/GE_Protein_Purification_Handbooks/Affinity_Chromatography_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Arafa, A.; Abdel-Ghani, A.; El-Dahmy, S.; Abdelaziz, S.; El-Ayouty, Y.; El-Sayed, A. Purification and Characterization of Anabaena flos-aquae Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase as a Novel Approach for Myristicin Biotransformation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldson-Barnaby, A.; Scaman, C.H. Purification and characterization of Phenylalanine ammonia lyase from Trichosporon cutaneum. Enzym. Res. 2013, 2013, 670702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cui, W.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Z. Cloning, expression and characterization of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Rhodotorula glutinis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, A. Purification, characterization and induction of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in Phaseolus vulgaris. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 178, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Component of the Gel | Volume |
|---|---|
| Acrylamide/bisacrylamide (30%, v/v) | 2.80 mL |
| Distilled water | 2.24 mL |
| 1.5 M Tris-HCI (pH: 8.8) buffer solution | 1.82 mL |
| SDS: (10%, w/v) | 0.07 mL |
| TEMED | 7.00 μL |
| APS: (10%, w/v) | 70.00 μL |
| Component of the Sample Buffer | Amount |
|---|---|
| Bromophenol blue, mg | 3.00 |
| 1.0 M Tris BASE (pH: 6.8), mL | 3.75 |
| SDS: (10%, w/v), g | 1.20 |
| Glycerol, mL | 6.00 |
| β-mercaptoethanol, mL | 1.00 |
| Purification Step | Volume (mL) | Activity (* mU/mL) | Total Activity (* mU) | Protein (μg/mL) | Total Protein (μg) | Specific Activity (mU/mg) | Yield % | Purification Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 10.0 | 267.9 | 2679.3 | 67.4 | 673.7 | 3977.2 | 100.0 | 1.0 |
| Affinity Chromatography | 2.0 | 50.8 | 101.6 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 77,341.4 | 3.8 | 19.4 |
| Time Factor (Week) | Number of Measurements | Average ± SD | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0.682 ± 0.008 | 6.3 × 10−5 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.716 ± 0.008 | 6.3 × 10−5 |
| 3 | 3 | 0.688 ± 0.005 | 2.3 × 10−5 |
| 4 | 3 | 0.452 ± 0.047 | 2.2 × 10−3 |
| 5 | 3 | 0.446 ± 0.003 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| 6 | 3 | 0.365 ± 0.017 | 3.0 × 10−4 |
| 7 | 3 | 0.319 ± 0.003 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| 8 | 3 | 0.275 ± 0.006 | 4.0 × 10−5 |
| 9 | 3 | 0.278 ± 0.003 | 1.0 × 10−5 |
| Measurement No | Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Fcalculated | p Value |
| 1 | 0.674 | 0.708 | 0.683 | 1.97 × 10−3 | |
| 2 | 0.689 | 0.724 | 0.693 | 20.95 | |
| 3 | 0.682 | 0.716 | 0.688 | ||
| Measurement No | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Fcalculated | p Value |
| 1 | 0.500 | 0.443 | 0.383 | 1.89 × 10−2 | |
| 2 | 0.405 | 0.449 | 0.348 | 8.25 | |
| 3 | 0.452 | 0.446 | 0.365 | ||
| Measurement No | Week-7 | Week-8 | Week-9 | Fcalculated | p Value |
| 1 | 0.316 | 0.281 | 0.281 | 3.2 × 10−5 | |
| 2 | 0.323 | 0.269 | 0.275 | 91.50 | |
| 3 | 0.319 | 0.275 | 0.278 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toksöz, Y.S.; Bilen, Ç.; Karakuş, E. A New Affinity Gel Synthesized for Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Isolated from Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Leaf and an Investigation into Its Kinetic Properties. Separations 2025, 12, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090241
Toksöz YS, Bilen Ç, Karakuş E. A New Affinity Gel Synthesized for Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Isolated from Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Leaf and an Investigation into Its Kinetic Properties. Separations. 2025; 12(9):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090241
Chicago/Turabian StyleToksöz, Yavuz Selim, Çiğdem Bilen, and Emine Karakuş. 2025. "A New Affinity Gel Synthesized for Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Isolated from Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Leaf and an Investigation into Its Kinetic Properties" Separations 12, no. 9: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090241
APA StyleToksöz, Y. S., Bilen, Ç., & Karakuş, E. (2025). A New Affinity Gel Synthesized for Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase Isolated from Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Leaf and an Investigation into Its Kinetic Properties. Separations, 12(9), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090241







