Fly Ash-Derived Mesoporous Silica–Alumina Aerogel via an Optimized Water-Acid Leaching Process for Effective Methylene Blue Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Raw Materials
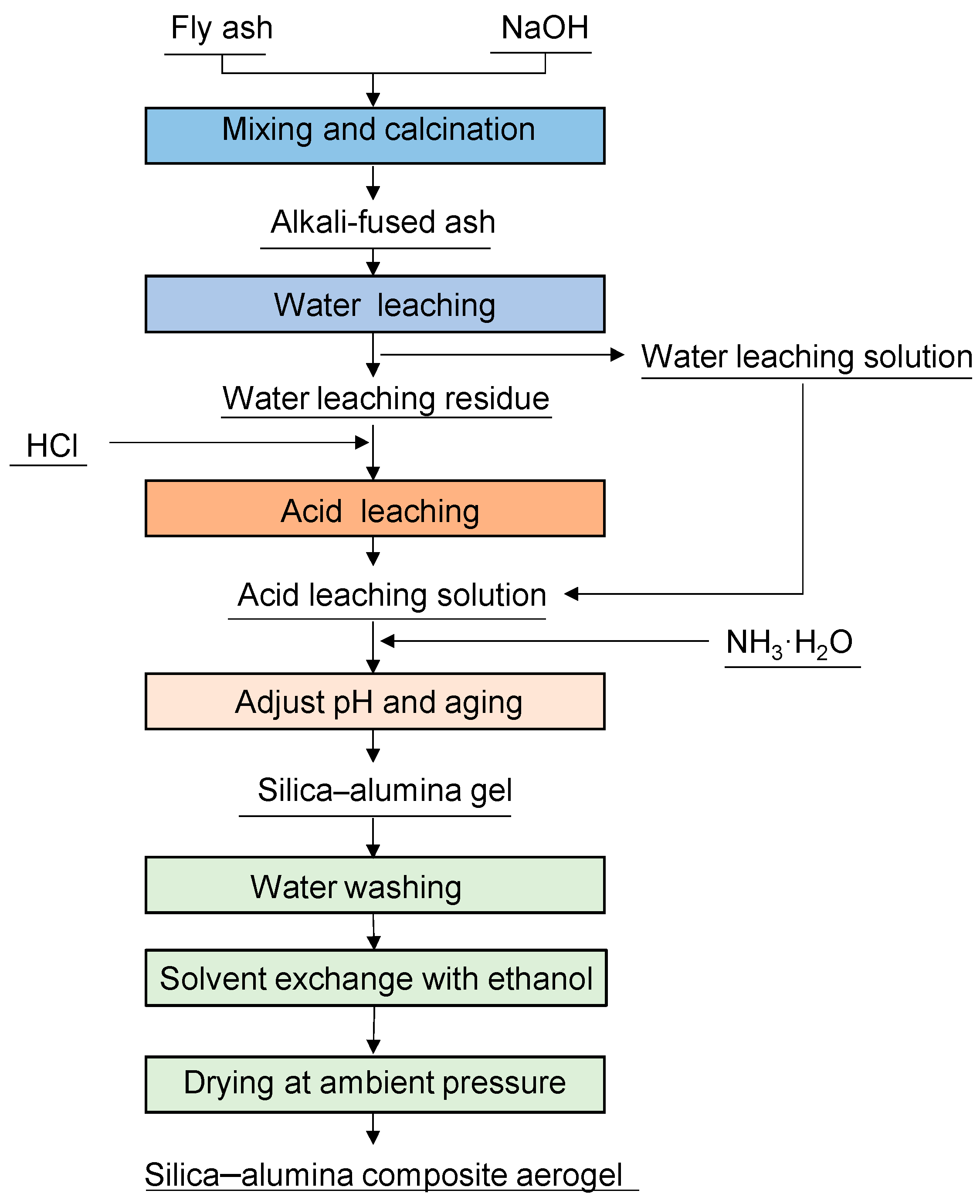
2.2. Preparation of FA-Derived Silica–Alumina Composite Aerogel
2.3. Adsorption Test
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
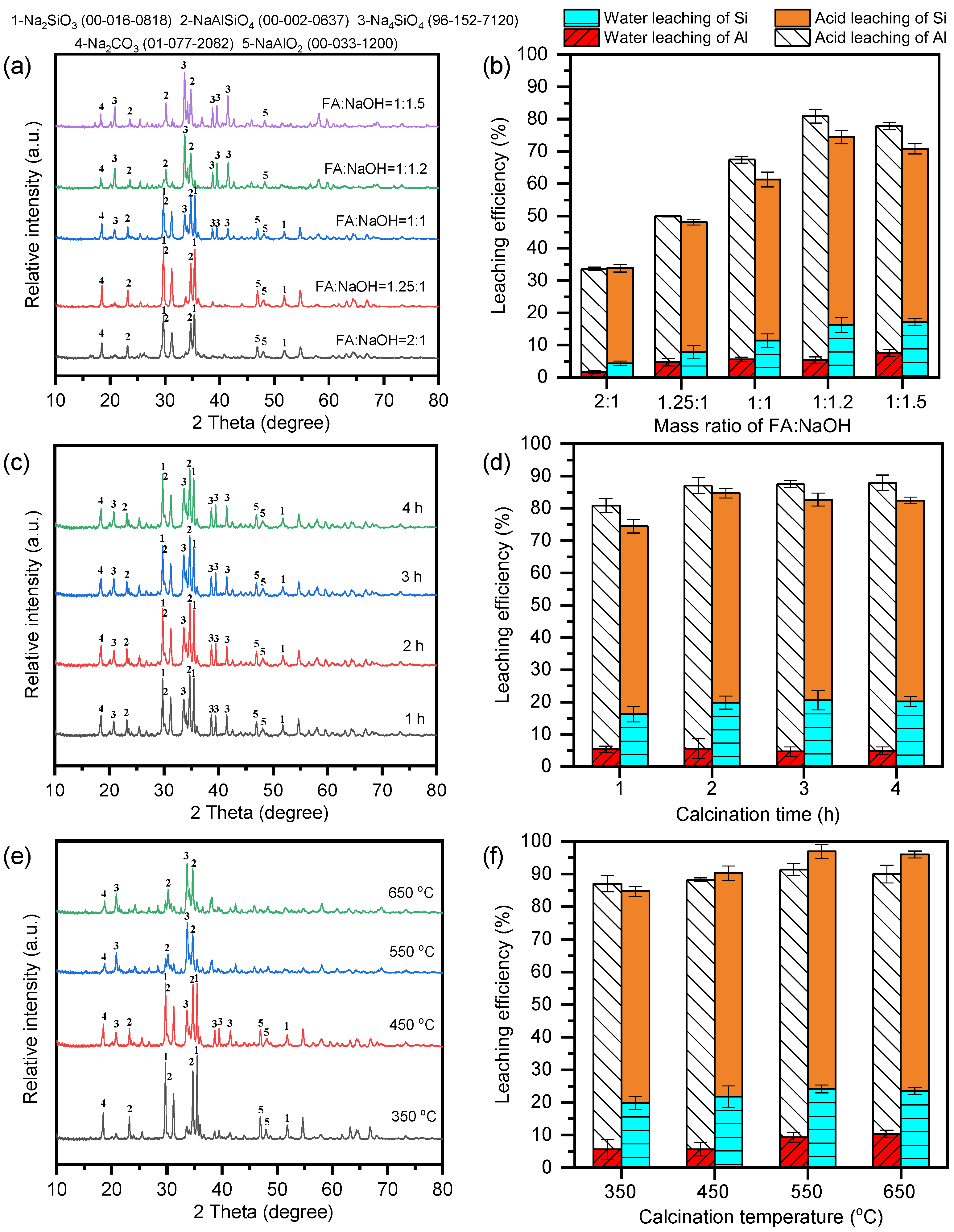
3.1. Optimization of the Alkali Fusion Conditions of FA
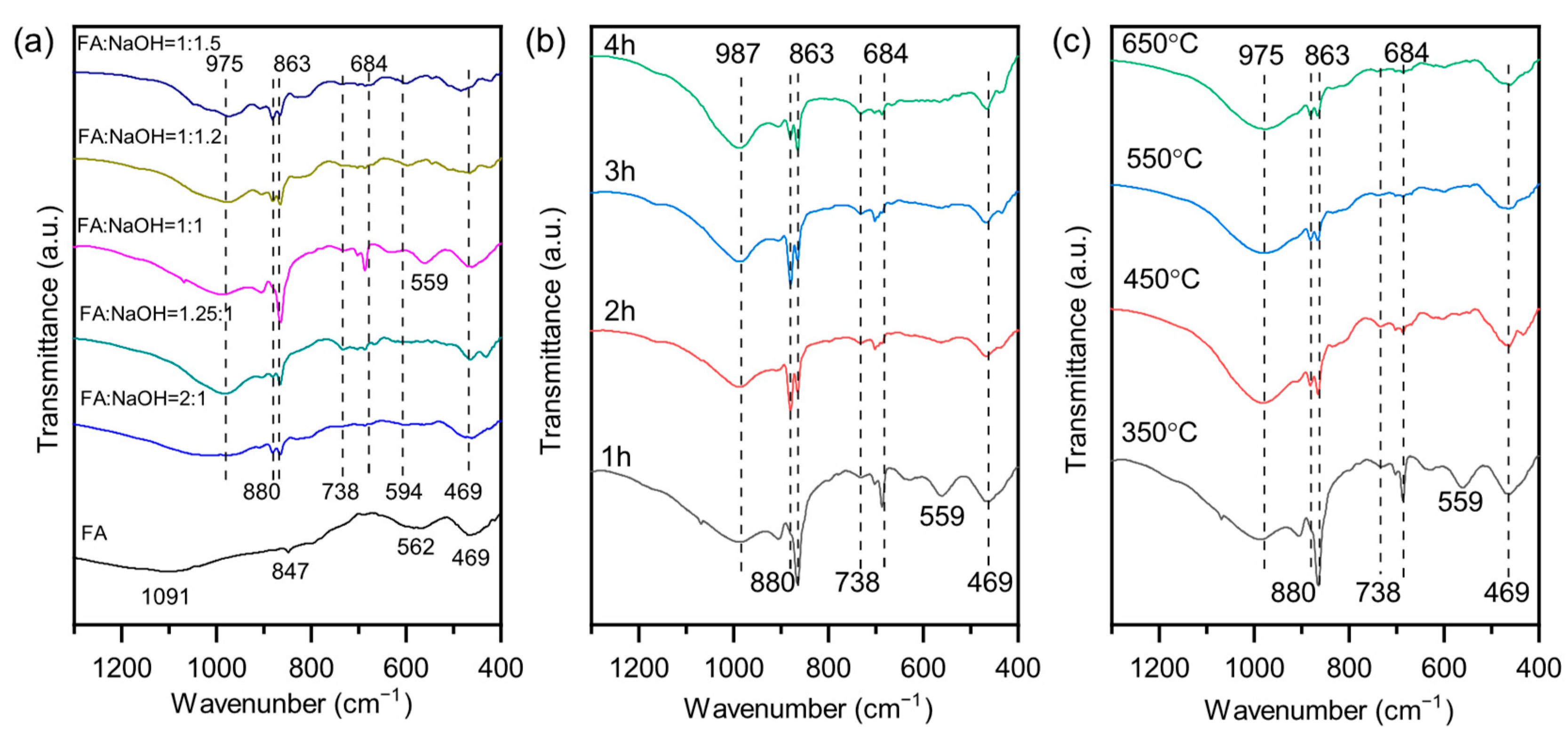
3.2. Phase Transformation During Alkali Activation of Fly Ash
3.3. Optimization of the Sol–Gel Reaction Conditions of FA-Derived Aerogel
3.4. Adsorption Performance of the FA-Derived Silica–Alumina Composite Aerogel
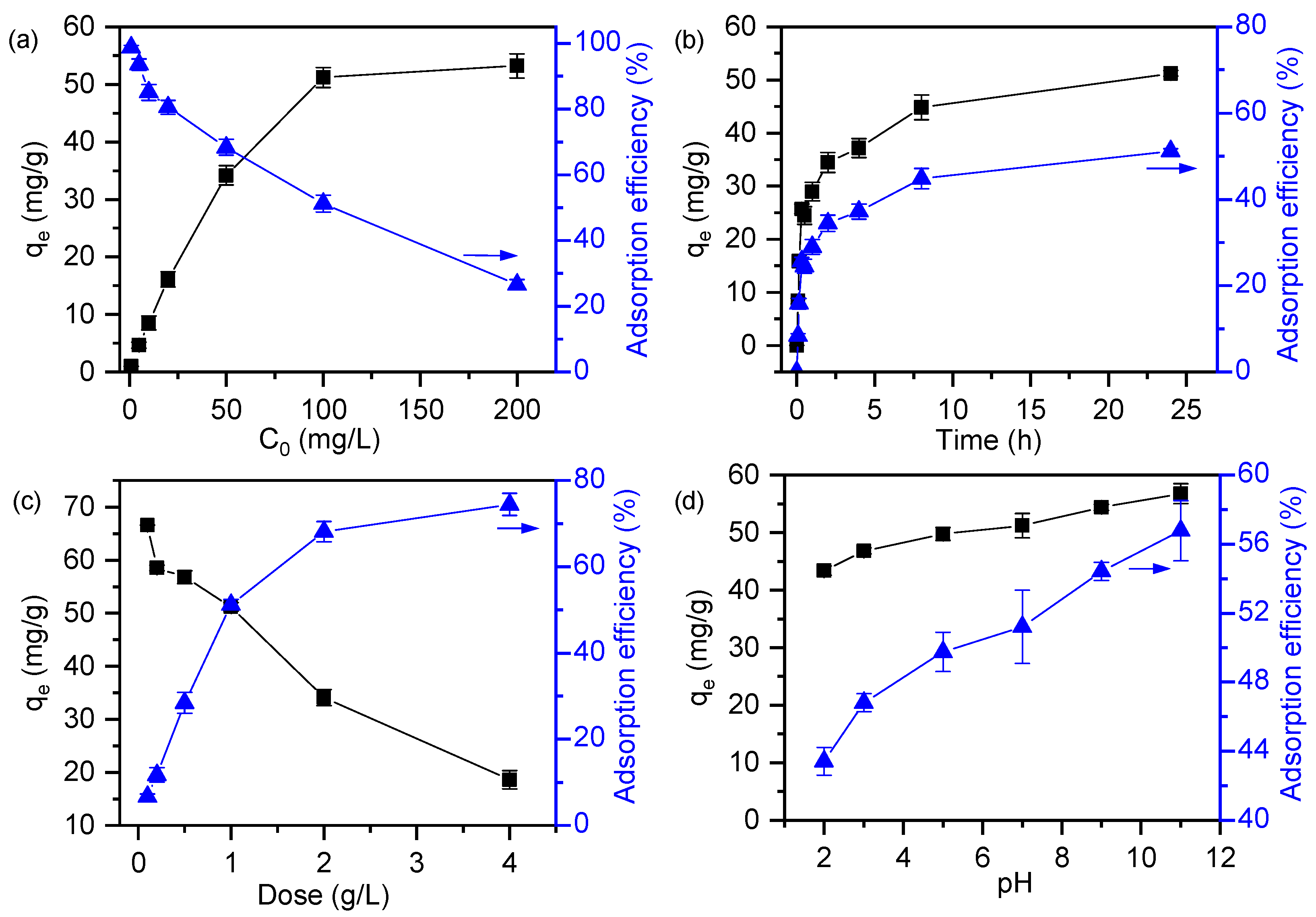
3.4.1. Effect of Adsorption Parameters
3.4.2. Adsorption Mechanism Study
3.4.3. Adsorption Cycle Test
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Agricultural peels for dye adsorption: A review of recent literature. J. Mol. Liquids 2014, 200, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mu, B.; Yang, Y. Feasibility of industrial-scale treatment of dye wastewater via bio-adsorption technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 277, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruna, K.; Nasreen, S.; Begum, S.; Kumari, U.R. A review on modified sugarcane bagasse biosorbent for removal of dyes. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Aguilar, D.M.; Natividad-Rangel, R.; Martínez-Rosales, M.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue in Carbon Nanotubes: A Review with Bibliometric Analysis. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Shao, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. Phase change solvents for post-combustion CO2 capture: Principle, advances, and challenges. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswara Rao, A.; Kalesh, R.R.; Pajonk, G.M. Absorption and desorption of organic liquids in elastic superhydrophobic silica aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 305, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.M.R.; Silva, C.F.; Marques, J.O.; Costa, L.P.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A.; Lira, H.L. An overview on alumina-silica-based aerogels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, X.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Y. Zeolite greenly synthesized from fly ash and its resource utilization: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, M.; Liang, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Resource utilization of solid waste for the collaborative reduction of pollution and carbon emissions: Case study of fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Basu, J.K.; Jana, A.K. Alumina-silica nano-sorbent from plant fly ash and scrap aluminium foil in removing nickel through adsorption. Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chang, L.; Xie, K. Experiment and regeneration kinetic model study on CO2 adsorbent prepared from fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ran, Y.; Xi, J.; Wang, J. Atmospheric drying preparation and microstructure characterization of fly ash aerogel thermal insulation material with superhydrophobic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 303, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y. Synthesis of SiO2-Al2O3 composite aerogel from fly ash: A low-cost and facile approach. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 93, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Gui, L.Z.; Liao, D.C.; Sun, K.; Liang, S.; Duan, H.B.; Yang, J.K. Advances in high-value utilization of fly ash from coal-fired power plants. Energy Environ. Prot. 2023, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Mu, Y.; Feng, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. In-situ Fe/Ti doped amine-grafted silica aerogel from fly ash for efficient CO2 capture: Facile synthesis and super adsorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 138945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Lei, Z.; Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. A study on preparation and properties of fly ash-based SiO2 aerogel material. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 684, 133016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y. Zeolite Synthesized from coal fly ash produced by a gasification process for Ni2+ removal from water. Minerals 2018, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Mid-infrared spectroscopic studies of alkali-activated fly ash structure. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 86, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panias, D.; Giannopoulou, I.P.; Perraki, T. Effect of synthesis parameters on the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Sitarz, M. Vibrational spectra of aluminosilicate ring structures. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 614, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Q. Synthesis and strength optimization of one-part geopolymer based on red mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Habibi Rezaee, M. Synthesis and characterization of silica aerogel as a promising drug carrier system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttakin, M.; Mitra, S.; Thu, K.; Ito, K.; Saha, B.B. Theoretical framework to evaluate minimum desorption temperature for IUPAC classified adsorption isotherms. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, A.; Sato, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Geus, J.W. Pore structure development of silica particles below the isoelectric point. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 267, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cha, Y.C.; Hwang, H.J.; Moon, J.W.; Han, I.S. The effect of pH on the physicochemical properties of silica aerogels prepared by an ambient pressure drying method. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3130–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Qin, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Yi, D.; Wang, B. Improvement of thermal insulation and compressive performance of Al2O3-SiO2 aerogel by doping carbon nanotubes. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 16290–16299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Synthesis of alumina aerogels by ambient drying method and control of their structures. J. Porous Mater. 2005, 12, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Thermal stability of Al-modified silica aerogels through epoxide-assisted sol-gel route followed by ambient pressure drying. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Dai, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Gao, S.; Wang, C. A novel mesoporous Fe-silica aerogel composite with phenomenal adsorption capacity for malachite green. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of methylene blue in water onto activated carbon by surfactant modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Güneş, K.; Gürses, M.S. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using by untreated lignite as potential low-cost adsorbent: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium approach. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 2, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yang, L.; Tao, G.; Dai, J. Adsorption of methylene blue on adsorbent materials produced from cotton stalk. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, E.; Tombácz, E. The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 295, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Chauhan, G.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Reddy, N.S. Novel cellulose nanowhiskers-based polyurethane foam for rapid and persistent removal of methylene blue from its aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.L.; Lau, B.F.; Show, P.L.; Ong, H.C.; Ling, T.C.; Chen, W.H.; Ng, E.P.; Chang, J.S. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic Congo red dyes using wet-torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 272, 115986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, J.; Asadpour, S. Thermodynamics’ study of the adsorption process of methylene blue on activated carbon at different ionic strengths. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2007, 39, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xie, J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto hydrophobic/hydrophilic silica aerogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 509, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, Ö.; Selen, V.; Başgöz, Ö.; Safa, H.; Yahia, I.S. Adsorption properties and synthesis of silica aerogel-hollow silica microsphere hybrid (sandwich) structure. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2021, 100, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Guan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y. Super-assembled highly compressible and flexible cellulose aerogels for methylene blue removal from water. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, M. A TiO2 coated carbon aerogel derived from bamboo pulp fibers for enhanced visible light photo-catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konggidinata, M.I.; Chao, B.; Lian, Q.; Subramaniam, R.; Zappi, M.; Gang, D.D. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of BTEX onto Ordered Mesoporous Carbon (OMC). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujih, M.N.; Ismail, N.; Othman, F. Kinetics, equilibrium and mechanisms of Ni (II) and Pb (II) ion biosorption using biosorbent mixture of Rhizophora apiculate sp. and Elaeis guineensis sp. J. Teknol.-Sci. Eng. 2019, 81, 83–90. [Google Scholar]



| Temperature (°C) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF (L/mg) | R2 | |
| 15 | 51.21 | 0.10 | 0.9973 | 18.0 | 4.48 | 0.9543 |
| 25 | 55.42 | 0.17 | 0.9960 | 37.9 | 7.71 | 0.9833 |
| 35 | 65.35 | 0.33 | 0.9989 | 25.1 | 11.15 | 0.9620 |
| Raw Material | Products | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Adsorption Conditions | Adsorption Capacity of MB (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl orthosilicate | Hydrophobic SiO2 aerogel | 880.5 | Initial MB concentration 250 mg/L, dose1 g/L, 24 h, 298 K, pH 7.0 | 59.78 | [38] |
| Ethyl orthosilicate | Hydrophilic SiO2 aerogel | 628.5 | Initial MB concentration 250 mg/L, dose1 g/L, 24 h, 298 K, pH 7.0 | 41.08 | [38] |
| Ethyl orthosilicate | SiO2 aerogel/hollow silica microsphere composites | 213.0 | Initial MB concentration: 40 mg/L, dose 2 g/L, 2 h, 303 K, pH 10.0 | 29.20 | [39] |
| Cellulose | Cellulose aerogel | — | Initial MB concentration 20 mg/L, dose 4 g/L, 2 h, 298 K, pH 7.0 | 2.28 | [40] |
| Bamboo cellulose fiber | TiO2 coated carbon aerogel | — | Initial MB concentration 20 mg/L, 48 h, 298 K | 18.50 | [41] |
| Fly ash | Silica–alumina composite aerogel | 661.3 | Initial MB concentration 100 mg/L, dose1 g/L, 24 h, 298 K, pH 7.0 | 52.22 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gui, L.; Chen, Z.; Liang, S. Fly Ash-Derived Mesoporous Silica–Alumina Aerogel via an Optimized Water-Acid Leaching Process for Effective Methylene Blue Removal. Separations 2025, 12, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090234
Sun K, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Xu J, Yu J, Zhang J, Gui L, Chen Z, Liang S. Fly Ash-Derived Mesoporous Silica–Alumina Aerogel via an Optimized Water-Acid Leaching Process for Effective Methylene Blue Removal. Separations. 2025; 12(9):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090234
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ke, Yike Liu, Zhiming Zhang, Jiayu Xu, Jiajing Yu, Jiankuan Zhang, Lianzheng Gui, Zhuo Chen, and Sha Liang. 2025. "Fly Ash-Derived Mesoporous Silica–Alumina Aerogel via an Optimized Water-Acid Leaching Process for Effective Methylene Blue Removal" Separations 12, no. 9: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090234
APA StyleSun, K., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, J., Yu, J., Zhang, J., Gui, L., Chen, Z., & Liang, S. (2025). Fly Ash-Derived Mesoporous Silica–Alumina Aerogel via an Optimized Water-Acid Leaching Process for Effective Methylene Blue Removal. Separations, 12(9), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12090234






