Effect of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Substrate Configuration on Cadmium Removal in Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
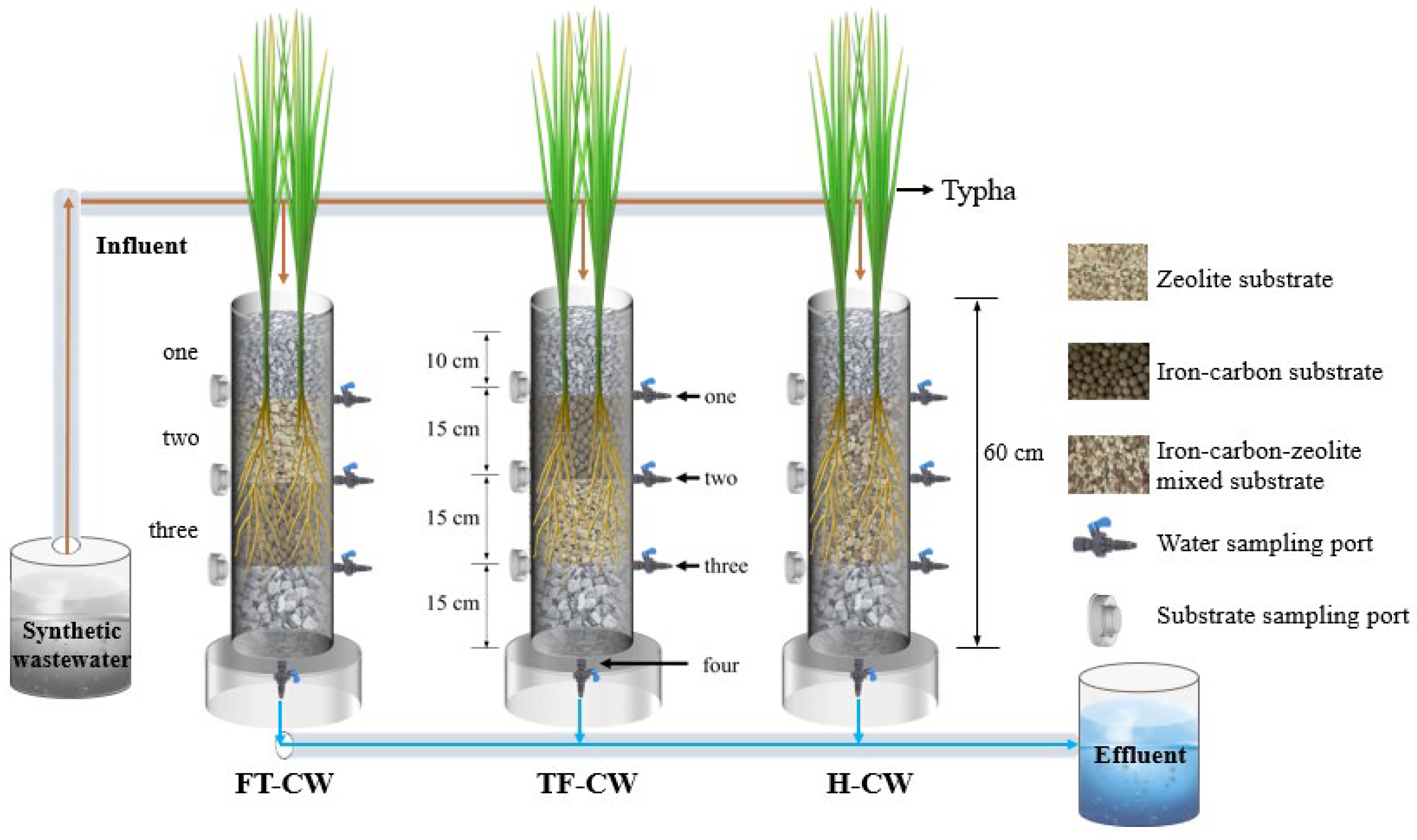
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Operation of Constructed Wetland Systems
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Water Sample Collection and Detection
2.3.2. Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.3.3. Substrate Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.4. Microbial Sample Collection and Analysis
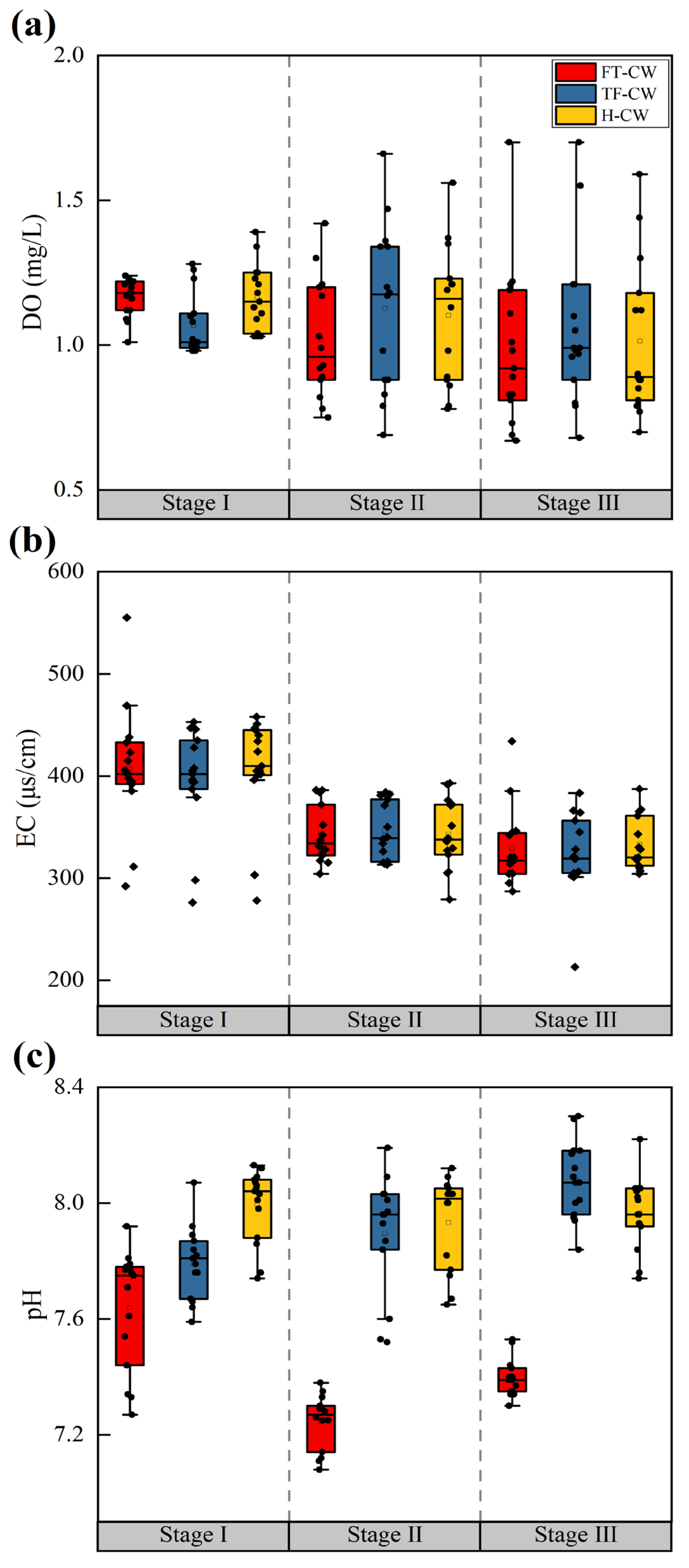
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Cadmium on the Pollutant Removal Performance of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Constructed Wetlands
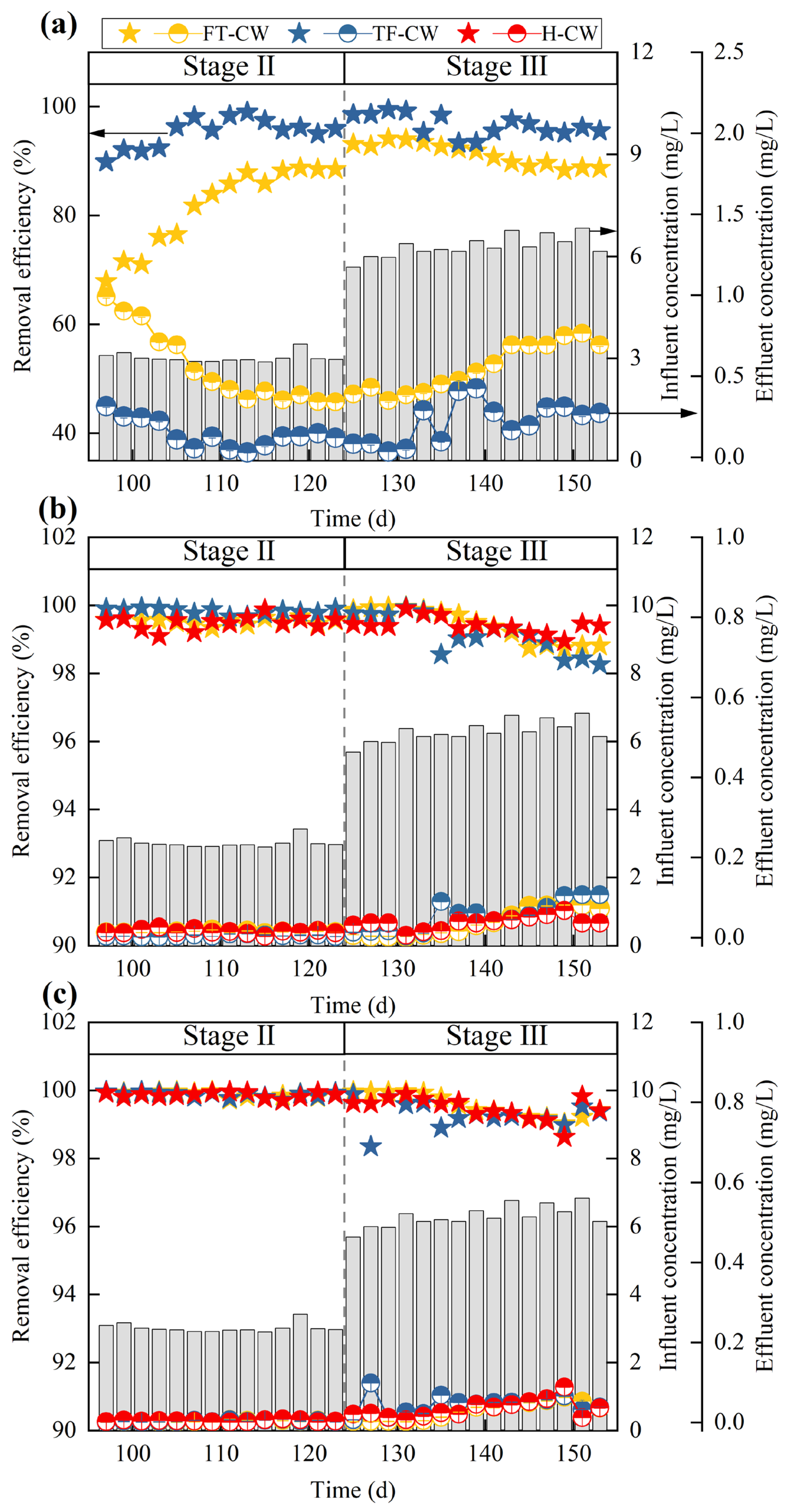
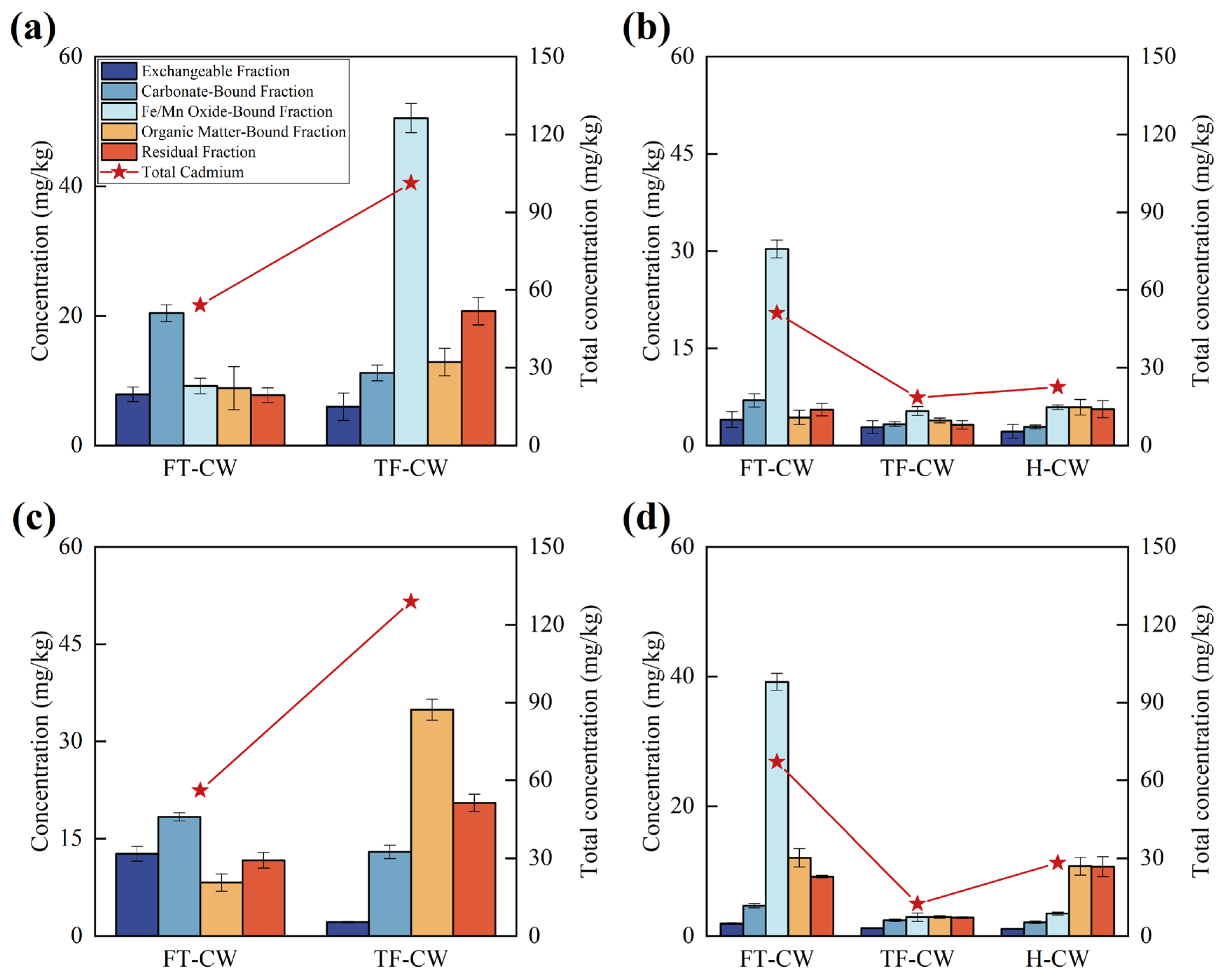
3.1.1. Cd2+ Removal Efficiency and Mechanisms
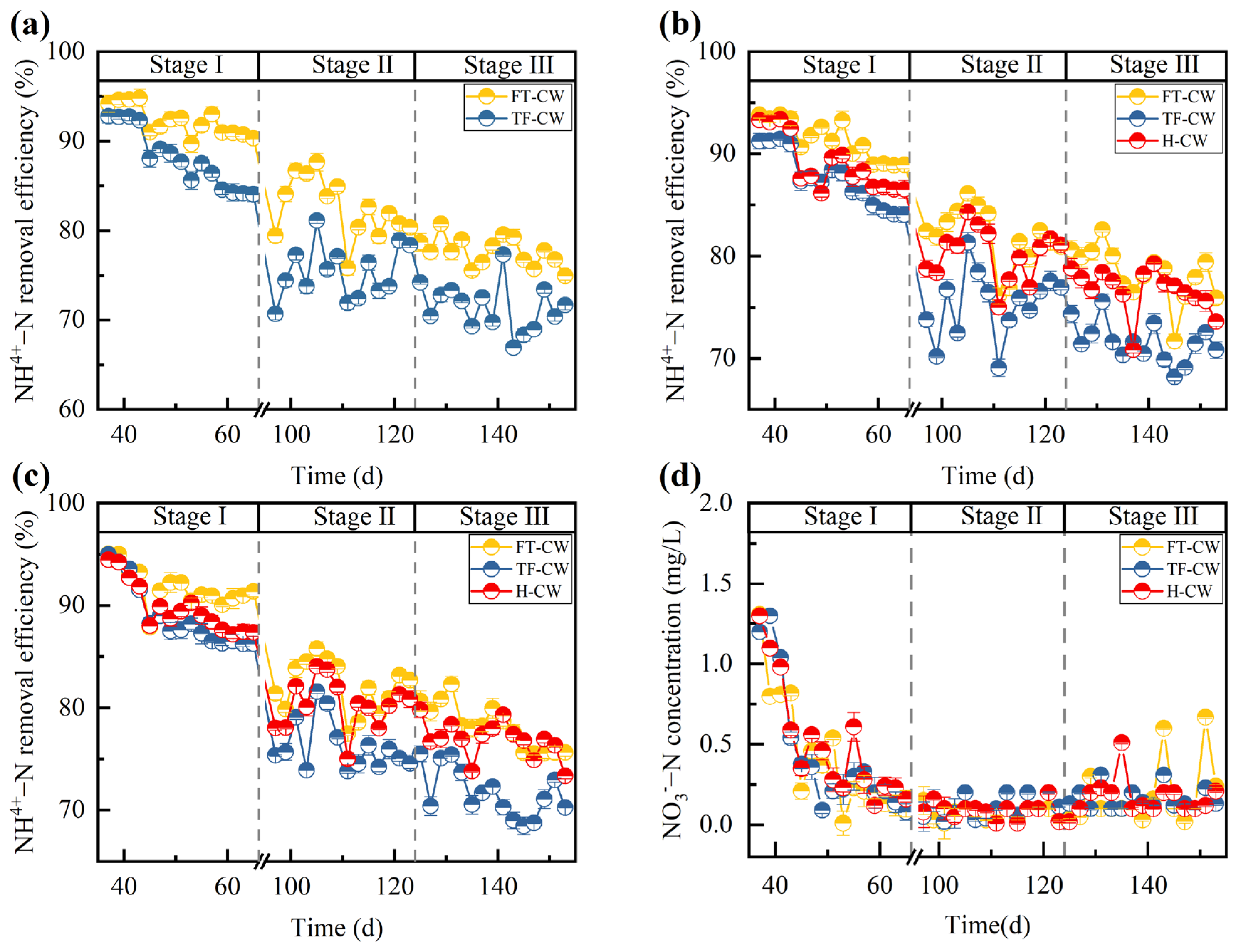
3.1.2. NH4+-N Removal
3.1.3. Nitrate Nitrogen Accumulation
3.2. Effects of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Constructed Wetlands on the Plant Response Under Cadmium Stress
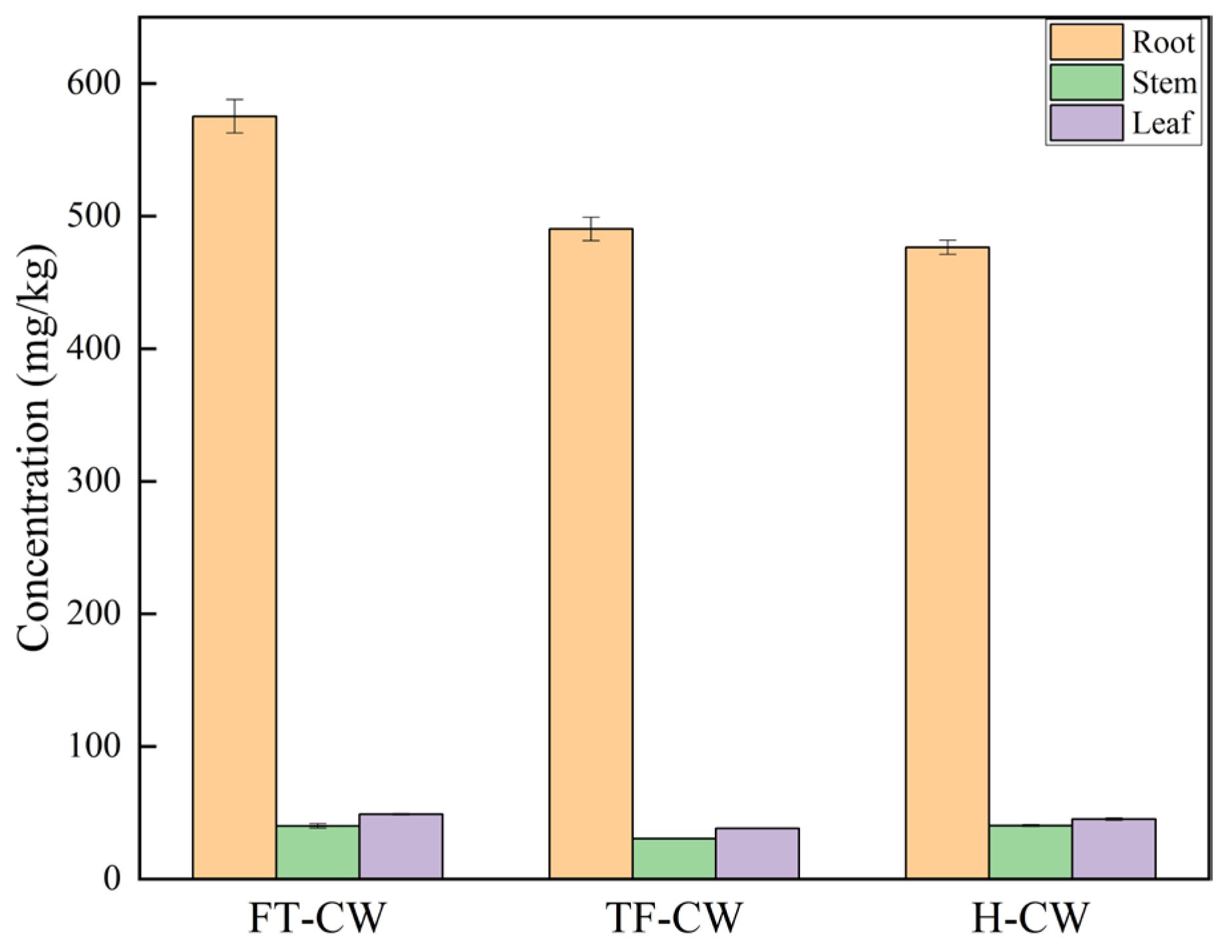
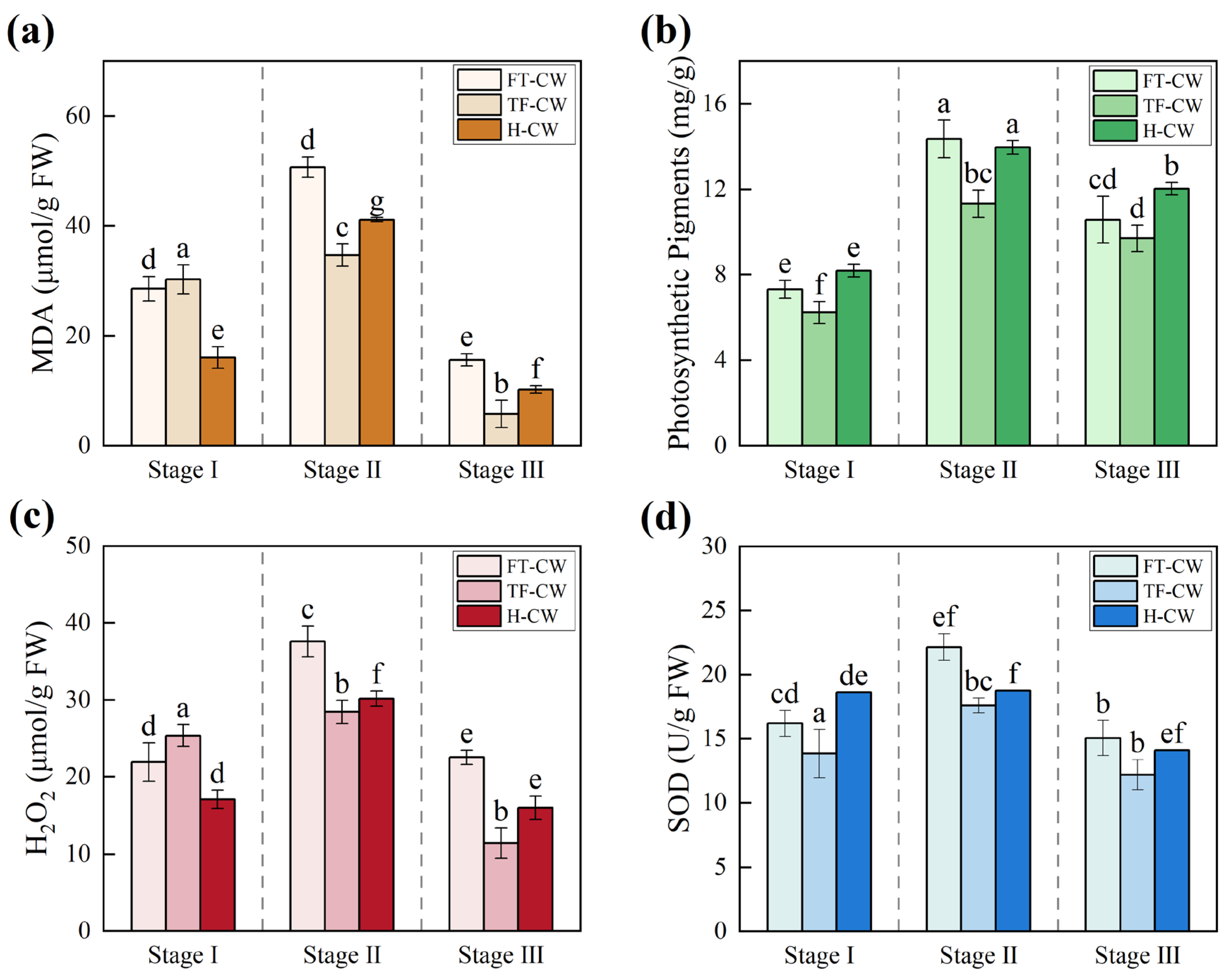
Cadmium Accumulation and Antioxidant Regulation
3.3. Effects of Cadmium on Microorganisms in Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Constructed Wetlands
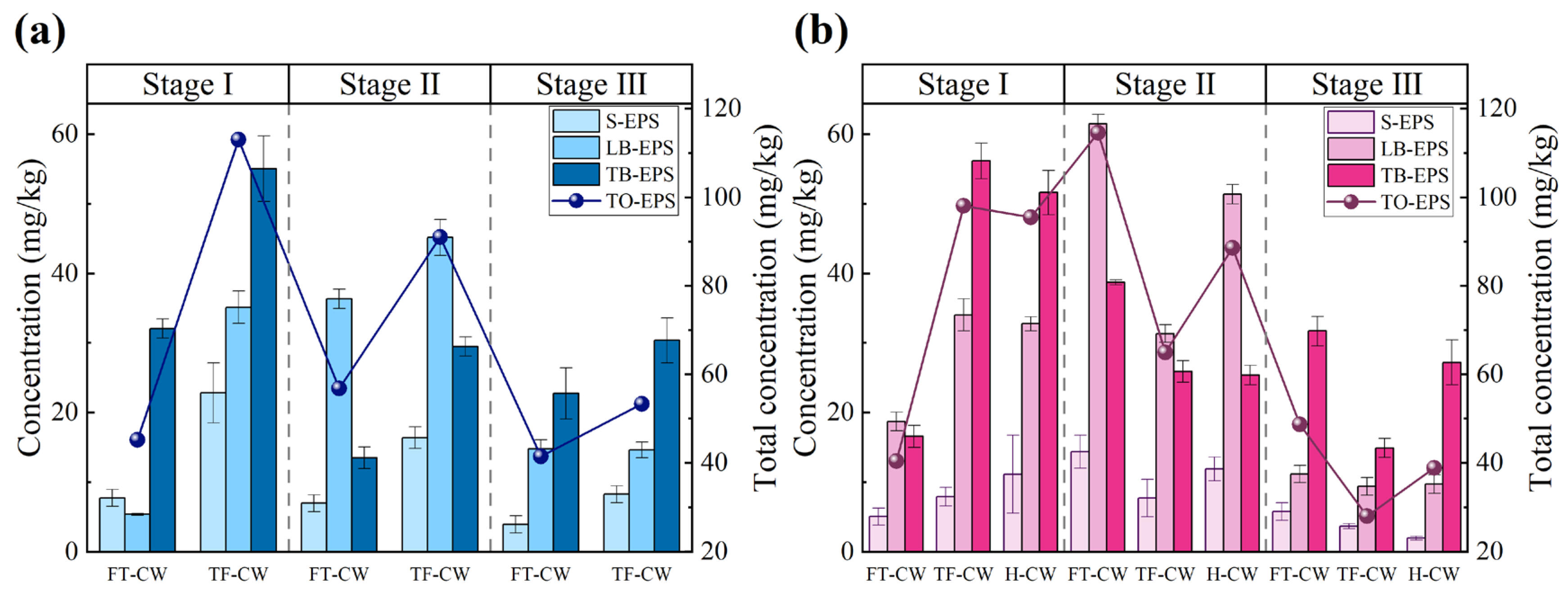
3.3.1. EPS Secretion and Biofilm Formation
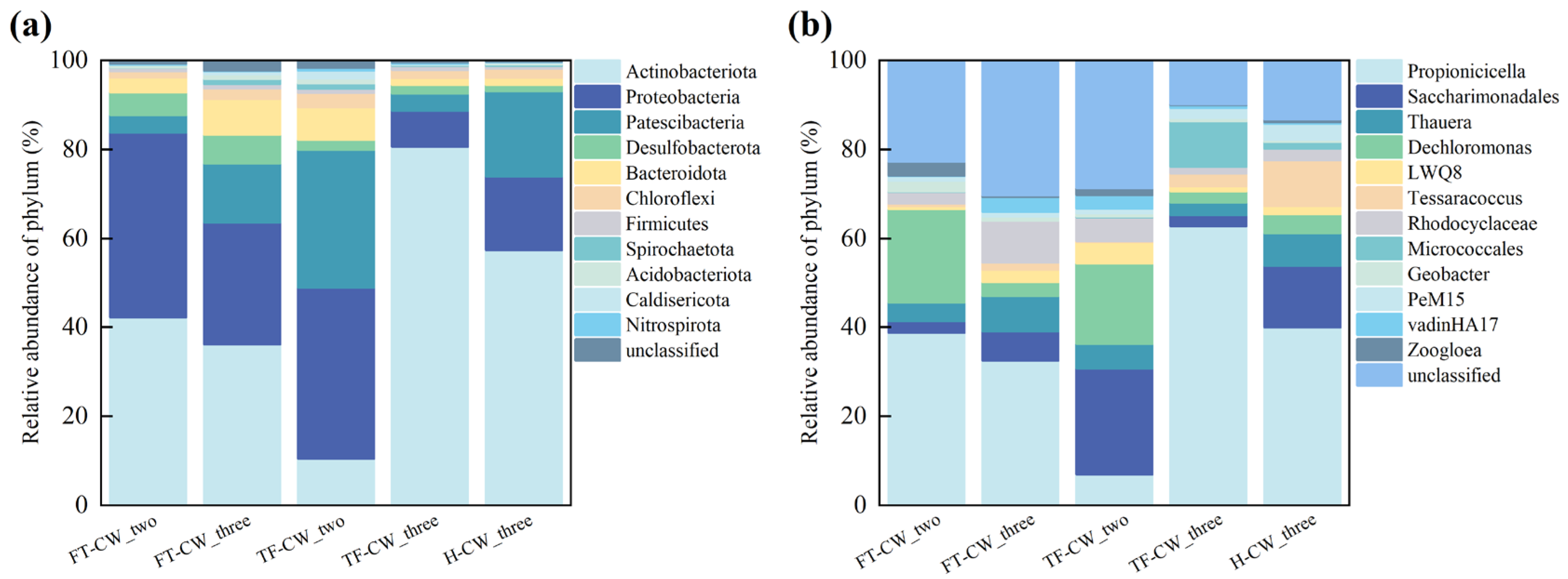
3.3.2. Microbial Community Structure Analysis
3.4. Substrate Configuration Optimization Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotnala, S.; Tiwari, S.; Nayak, A.; Bhushan, B.; Chandra, S.; Medeiros, C.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Impact of heavy metal toxicity on the human health and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 987, 179785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhi, D.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Yang, Y. Effects of seed priming with different concentrations and forms of silicon on germination and growth of rice under cadmium stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 207, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Horiguchi, H.; Matsukawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Omori, Y.; Oguma, E.; Komatsuda, A. A suspected case of “itai-itai disease” in a cadmium-polluted area in akita prefecture, Japan. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2024, 29, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Long, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, S. Enhanced nitrogen removal through aerobic denitrifying bacteria in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Influencing factors and microbial community structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, H. Can we use mine waste as substrate in constructed wetlands to intensify nutrient removal? A critical assessment of key removal mechanisms and long-term environmental risks. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Ai, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, F.; Cheng, K. Synergistic enhancement of cadmium immobilization and soil fertility through biochar and artificial humic acid-assisted microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Dong, L.; Zhai, T.; Gao, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Enhanced effect and mechanism of nano fe-ca bimetallic oxide modified substrate on Cu(II) and Ni(II) removal in constructed wetland. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yu, G.; Chi, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Q.; et al. Insights into the enhanced effect of biochar on cadmium removal in vertical flow constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreto, F.; Velikova, V. Isoprene produced by leaves protects the photosynthetic apparatus against ozone damage, quenches ozone products, and reduces lipid peroxidation of cellular membranes. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Reprint of: Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 726, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.R.C.; Bewley, J.D. Lipid peroxidation associated with accelerated aging of soybean axes. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bódog, I.; Polyák, K.; Csikós-Hartyányi, Z.; Hlavay, J. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of elements in fly ash samples. Microchem. J. 1996, 54, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, D.; Ferrante, M.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Milani, M.; Sacco, A.; Licciardello, F.; Cirelli, G.L. Metal removal processes in a pilot hybrid constructed wetland for the treatment of semi-synthetic stormwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, A.A.H.; Taha, D.S.; Hassan, W.H.; Lakhera, S.K.; Ansar, S.; Pradhan, S. Subsurface flow constructed wetlands for treating of simulated cadmium ions-wastewater with presence of canna indica and typha domingensis. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Zheng, D. Cadmium removal by constructed wetlands containing different substrates: Performance, microorganisms and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, L.; Su, J.; Liu, S.; Ali, A.; Zhang, P.; Cao, S. Denitrification driven by additional ferrous (Fe2+) and manganous (Mn2+) and removal mechanism of tetracycline and cadmium (Cd2+) by biogenic Fe–Mn oxides. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zeng, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-G.; Zhang, X.; Ji, A.-M.; Kang, L.-L.; Ji, R.; Yu, Q.; Gao, D.; et al. Highly efficient removal of hexavalent chromium by magnetic Fe-C composite from reed straw and electric furnace dust waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 33737–33755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Tang, S.; Zhou, J.; Pan, W.; Ma, Q.; Wu, L. Nano zero-valent iron-induced changes in soil iron species and soil bacterial communities contribute to the fate of cd. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salem, D.; Yahiaoui, K.; Bernardo, M.; Gatica, J.M.; Ouakouak, A.; Touahra, F.; Saad Eltaweil, A.; Tran, H.N. Insights into cadmium adsorption characteristics and mechanisms by new granular alginate hydrogels reinforced with biochar: Important role of cation exchange. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 383, 125407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zong, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Mei, S.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Y.; et al. Highly efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by waste cation exchange resin-based activated carbons: Performance, mechanism, and theoretical calculation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, T.; Yuan, R.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bian, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Joseph, S.; Li, L.; et al. Enhancing soil redox dynamics: Comparative effects of Fe-modified biochar (N–Fe and S–Fe) on Fe oxide transformation and cd immobilization. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Nitrite accumulation stability evaluation for low-strength ammonium wastewater by adsorption and biological desorption of zeolite under different operational temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Luo, X.; Hu, Y. Activated carbon as an insoluble electron shuttle to enhance the anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with Fe(III) reduction process. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, J.; Rodríguez, C.; Serrano, J.; Leiva, E. Study of the key biotic and abiotic parameters influencing ammonium removal from wastewaters by Fe3+-mediated anaerobic ammonium oxidation (feammox). Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Song, B.; Lin, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xue, G. Tuning pH to motivate chain reaction of iron release with extracellular polymeric substances formation for long lasting Fe0-driven autotrophic denitrification. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Li, T.; Ren, T.; Zang, Y.; Sun, S.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; He, S. Heterotrophic denitrification enhancement via effective organic matter degradation driven by suitable iron dosage in sediment. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Hou, R.; Yang, P.; Qian, S.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Yuan, R.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B. Application of external carbon source in heterotrophic denitrification of domestic sewage: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, H. Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.; Su, G.; Guo, Y.; Yin, Y.; Jiao, W.; Cai, Y.; et al. Low-molecular weight organic acids can enhance the microbial reduction of iron oxide nanoparticles and pollutants by improving electrons transfer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 137123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cui, J.; Song, J.; Ji, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Jia, H.; Yin, X. Transport of polystyrene nanoplastics with different functional groups in goethite-coated saturated porous media: Effects of low molecular weight organic acids and physicochemical properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 653, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, L.; Mench, M.; Jacob, D.L.; Otte, M.L. Metal and metalloid removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of plants and standardized measurements: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yao, Y.; Xing, C.; Guo, Y.; Cai, L.; Yan, J.; Wu, X.-L.; Cai, M. Effects of zeolite imidazole frameworks on rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.): Phytotoxicity, transformation, and bioaccumulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 144, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Liu, H.; Kong, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, S.; Wu, H. Interactions of high-rate nitrate reduction and heavy metal mitigation in iron-carbon-based constructed wetlands for purifying contaminated groundwater. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.B.; Song, J.L.; Yao, Q.J.; Chen, Z.X.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.L.; Wang, M.X.; Wang, B.J.; Zhou, J.M. Effects of dissolved oxygen on the sludge dewaterability and extracellular polymeric substances distribution by bioleaching. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, H. Impacts of aeration and biochar addition on extracellular polymeric substances and microbial communities in constructed wetlands for low C/N wastewater treatment: Implications for clogging. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, H. Optimizing agricultural biomass application to enhance nitrogen removal in vertical flow constructed wetlands for treating low-carbon wastewater. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hua, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xue, H. The addition of iron-carbon enhances the removal of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in constructed wetlands. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Cao, S.; Yu, X.; Wu, N. Deciphering retention effect of extracellular polymeric substances to typical heavy metals and their interaction with key inner enzymes of Candidatus Kuenenia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: An overview. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. Potential application of novel cadmium-tolerant bacteria in bioremediation of cd-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The Diversity and Biogeography of Soil Bacterial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/epdf/10.1073/pnas.0507535103 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. Microbial interspecific interaction and nitrogen metabolism pathway for the treatment of municipal wastewater by iron carbon based constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, T.; Feng, Y. Intensified nitrogen and phosphorus removal and mechanism revelation in constructed wetlands amended with iron-carbon based substrate towards low C/N ratio wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Xu, W.; He, F.; Peng, F.; Zhu, X.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Functional genera for efficient nitrogen removal under low C/N ratio influent at low temperatures in a two-stage tidal flow constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Yang, S.; Kou, X.; Sun, S. Removal Mechanisms of Single and Combined Pollutants of Cadmium and Antibiotics by Wetland Plants. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 19, 127–149. [Google Scholar]
| Stage | Influent Concentration (mg/L) | pH | DO (mg/L) | EC a (μs/cm) | Duration (d) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH4+-N | TP | Cd2+ | |||||
| I | 60 | 40 | 1 | 0 | 7.65 ± 0.20 | 4.46 ± 0.18 | 458.07 ± 24.98 | 36–66 |
| II | 60 | 40 | 1 | 3 | 7.53 ± 0.10 | 4.46 ± 0.21 | 363.14 ± 33.50 | 96–124 |
| III | 60 | 40 | 1 | 6 | 7.60 ± 0.07 | 4.57 ± 0.20 | 355.80 ± 22.18 | 124–153 |
| Analysis Parameter | Analysis Item | Detection Wavelength (nm) | Calculation Formula | Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthetic Pigments | Chl 2 a, Chl b, The total amounts of carotenoids | 470, 649, 665 | Ca = 13.95A665 − 6.88A649 Cb = 24.96A649 − 7.32A665 Cx + c = (1000A4702.05Ca × 114.8Cb)/245 | [9] |
| ROS 1 | H2O2 | 390 | / | [10] |
| Lipid Peroxidation | MDA 3 | 532, 600, 450 | C 5 = 6.45 (A532 − A600) − 0.56A450 | [11] |
| Antioxidative Enzymes | SOD 4 | 560 | C 6 = (Ack − Ac) × V/(50% × Ack × W × Vt) | [12] |
| CWs | Substrate Layer | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT-CW | 2 | 678.35 | 650.08 | 2.91 | 0.20 | 0.998 |
| 3 | 793.63 | 791.63 | 3.51 | 0.12 | 0.997 | |
| TF-CW | 2 | 875.36 | 852.69 | 3.64 | 0.09 | 0.997 |
| 3 | 543.80 | 538.33 | 1.92 | 0.41 | 0.998 | |
| H-CW | 3 | 585.22 | 576.04 | 2.68 | 0.19 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, N.; Yu, G. Effect of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Substrate Configuration on Cadmium Removal in Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands. Separations 2025, 12, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080223
Li M, Chen S, Chen J, Zhou N, Yu G. Effect of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Substrate Configuration on Cadmium Removal in Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands. Separations. 2025; 12(8):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengyi, Shiyu Chen, Jundan Chen, Naifu Zhou, and Guanlong Yu. 2025. "Effect of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Substrate Configuration on Cadmium Removal in Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands" Separations 12, no. 8: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080223
APA StyleLi, M., Chen, S., Chen, J., Zhou, N., & Yu, G. (2025). Effect of Iron–Carbon–Zeolite Substrate Configuration on Cadmium Removal in Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetlands. Separations, 12(8), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080223







