Abstract
Wastewater treatment plants generally lack a specialized design for the efficient removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX), a toxic and bio-resistant compound. In this study, secondary effluent from a Beijing wastewater reclamation treatment plant was spiked with SMX and used to investigate the filtration performance and fouling mechanisms of thermo-responsive membranes. Thermo-responsive materials were prepared using polyvinylidene fluoride, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), and graphene oxide through Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization. The results showed that the removal of SMX and COD reached 42% and 92%, respectively, with a NIPAM dosage of 1 g, and the removal of UV254 reached its highest value at 57.9%. Additionally, the filtration flux was higher at a temperature of 35 °C with a NIPAM dosage of 1 g. The fluorescence intensity of the organic matter from the secondary effluent spiked with SMX and decreased after the thermo-responsive membranes were implemented, and filtration with the membrane containing 1 g of NIPAM achieved a lower intensity at a value of 3074.6, according to the analysis of three-dimensional fluorescence excitation–emission spectroscopy. According to the extended Derjaguin–Laudau–Verwey–Overbeek theory analysis, the interfacial free energies of the thermo-responsive membrane with a 1 g dose of NIPAM were higher than the others during filtration.
1. Introduction
In recent years, sulfamethoxazole (SMX) has garnered significant attention as an emerging micro-pollutant due to its relatively stable structure and anti-biodegradability [1,2,3]. SMX has been frequently detected in raw municipal wastewater at concentrations ranging from ng/L to tens of μg/L [4,5] and even up to mg/L in individual household wastewater [6]. SMX concentrations in wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) effluents typically range from ng/L to μg/L and can even be found in surface water receiving WWTP effluent at ng/L concentrations [7,8]. Consequently, the effective removal of SMX in WWTPs is crucial to mitigating its environmental impact.
A multitude of technologies have been explored for the removal of SMX, including adsorption, advanced oxidation, activated sludge, and membrane separation [9,10,11]. Adsorption needs an analytical process, which is expensive in real applications. Advanced oxidation usually generates toxic by-products that lead to secondary pollution. Activated sludge treatment requires assessing the biodegradability of the substance environment for activated sludge treatment. Among the various methods of removal, membrane separation has garnered significant attention because it is an environmentally friendly approach that prevents secondary pollution [10]. Gomes et al. used a nanofiltration membrane for the removal of SMX in a mixture containing raw water, and the results showed that pH was the operating variable that most affected membrane performance and contaminant rejection [12]. Zhang et al. blended dopamine with a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for SMX treatment using a membrane bioreactor and found that the removal rate of SMX increased rapidly after 15 days of acclimation [13]. However, in a real-world application of the membrane for SMX removal, they ignored the removal of pollutants via membrane filtration and the membrane fouling mechanism during filtration. Temperature was an easy index to control in real water treatment.
In this study, secondary effluent from a Beijing wastewater reclamation treatment plant spiked with SMX (10 mg/L) was used to investigate the filtration performance and fouling mechanism of thermo-responsive membranes. In our previous study, thermo-responsive materials were prepared using polyvinylidene fluoride, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), and graphene oxide (GO) through Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization [14]. The performance of the thermo-responsive membranes was evaluated by assessing the flux changes and retention of SMX, COD, and UV254, determining the molecular weight distribution and performing three-dimensional fluorescence excitation–emission spectroscopy. The anti-fouling properties of the thermo-responsive membranes were also discussed, and the interaction energy between the pollutant and the membrane surface was calculated using extended Derjaguin–Laudau–Verwey–Overbeek (XDLVO) theory.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
SMX (purity > 98%) was purchased from J&K Scientific. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was purchased from China Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The thermo-responsive materials were prepared using polyvinylidene fluoride, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), and graphene oxide via Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization. Thermo-responsive membranes were prepared via non-solvent-induced phase separation in our previous study [14]. The concentration of NIPAM was controlled by adding 0 g, 1 g, 2 g, and 3 g of NIPAM to produce membranes referred to as PNG0, PNG1, PNG2, and PNG3, respectively. The properties of the thermo-responsive membranes are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.

Table 1.
Properties of thermo-responsive membranes.
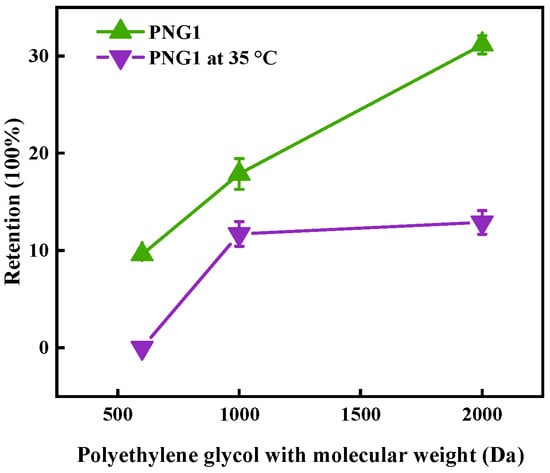
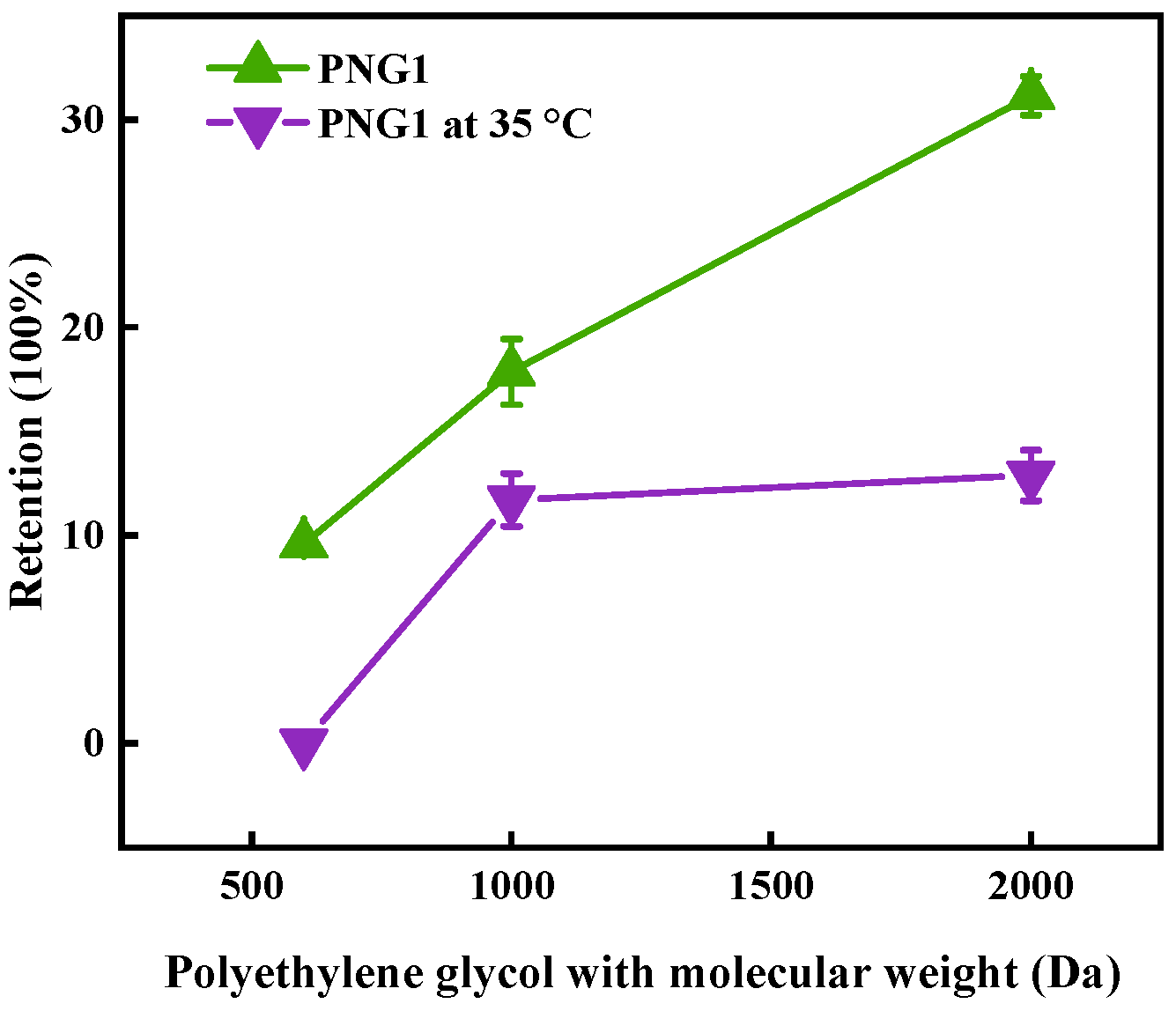
Figure 1.
Retention of polyethylene glycol by PNG1 membrane under different temperatures.
2.2. Thermo-Responsive Membrane Filtration Experiments
Secondary effluent from the Beijing wastewater reclamation treatment plant, with SMX added at 10 mg/L, was used as experimental water, named RW. The water quality is shown in Table 2. The temperature of RW varied according to the water bath (TAISITE, DK-98-II, Luoyang, China) at 25 °C and 35 °C. Our previous study confirmed that the thermo-responsive temperature was 35 °C. The raw water flux was measured at 0.1 MPa through an ultra-filter cup (Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA) 200 mL) and calculated using Equation (1):
where J (LMH) is the water flux, V (L) is the volume of filter water, A is the effective membrane area (m2), and t (s) is filtration time.

Table 2.
Characterization of the secondary effluent with 10 mg/L SMX.
2.3. Analysis of Thermo-Responsive Membrane Performance
The concentration of SMX in the solution was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (2487, Waters, Milford, MA, USA). The analytical system consisted of an HPLC unit equipped with a UV–vis detector, and separation was achieved using a Zorbax-SB C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 µm). Chromatographic separation was performed under gradient elution conditions, where mobile phase A was methanol and mobile phase B was a 0.1% phosphoric acid solution. The gradient program for the mobile phase was as follows: mobile phase A was maintained at 10% during the initial 0–1 min, it was then gradually increased to 50% over a period of 1–6 min, and finally, it was reduced back to 10% within 10–15 min. The detection wavelength was set at 254 nm. The rejection rate of the thermosensitive membrane for SMX was calculated based on the difference in the SMX concentration before and after membrane separation.
RW and the permeation were measured using a UV spectrophotometer at 254 nm, COD, a molecular weight (MW) instrument (2487, Waters, Milford, MA, USA), and 3D-EEM (F-7000, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The MW distribution was assessed through high-performance size-exclusion chromatography, employing a sophisticated Waters liquid chromatography setup. This system consisted of a Waters 2487 Dual λ Absorbance Detector and a 1525 pump. Three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix (3D-EEM) spectra were collected by sequentially recording the NOM source over an excitation (EX) range from 200 to 600 nm and an emission (EM) range from 220 to 550 nm, with a 5 nm step size. The instrument settings included a 5 nm excitation and emission slit width, a 0.01 s response time, and a scan speed of 2000 nm/min for optimal data acquisition. The fluorescence value of the organic matter could be determined by the 3D-EEM spectra.
2.4. Anti-Fouling Properties of Thermo-Responsive Membranes
The anti-fouling characteristics of the thermo-responsive membranes were systematically evaluated through the measurement of irreversible (Rir) and reversible (Rr) resistance, which could be determined as follows [15]:
where Jrf, Jf, and Jp were the recovery flux, raw water flux, and pure water flux, respectively.
NaOH at 0.01 moL/L was used to clean the membrane. The flux recovery (FR) was employed to assess the anti-fouling abilities of the thermo-responsive membranes, where it was defined as follows:
XDLVO Theory for Membrane Fouling Behavior
The XDLVO theory, a fundamental concept in surface science, decomposes the total interaction energy between a pollutant and a membrane surface as the sum of Van der Waals (LW), acid–base (AB), and electrostatic (EL) interactions, as shown in Equation (5) [16]:
where , , , and are the total interaction energy, LW interaction term, EL interaction term, and AB interaction term, respectively.
The interfacial free energies , , and are expressed in mJ/m2 and can be calculated as follows:
where γLW, γ+, and γ− are the LW surface tension component, electron acceptor component, and the electron donor, respectively. The surface tension parameters (, , and ) for the pollutant and membrane can be calculated using the extended Young equation, given as follows:
where is the contact angle, and , and can be obtained from the literature [16]. The surface tension of the membrane and foulants was calculated according to the contact angle of the three liquids (ultrapure water, glycerol, and diiodomethane) with known surface tension [17].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Thermo-Responsive Membranes
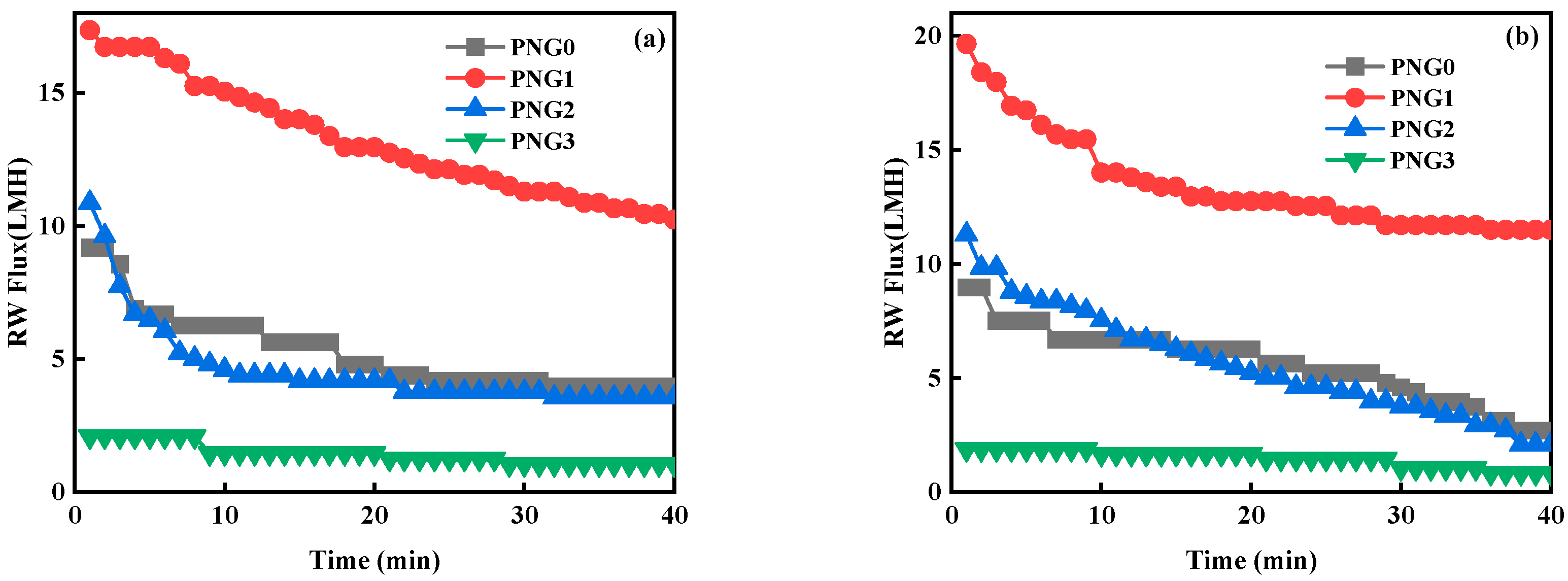
The change in water flux during the filtration process is a critical indicator of the membrane’s performance. As shown in Figure 2, the RW flux through the membranes exhibited a decline with increasing filtration time. This phenomenon is due to the complex contaminant in the secondary effluent, which led to membrane fouling. Additionally, the RW flux was higher at a temperature of 35 °C than Saadat et al. reported when the NIPAM dosage was 1 g [18]. This phenomenon occurred because the NIPAM underwent a reversible phase transition when heated or cooled, switching from a hydrophilic coiled state to a hydrophobic globular state at 35 °C [19,20]. Additionally, the flux decline rate reached from 19.7 LMH to 11.5 LMH, which is higher than what Russo et al. reported [21]. This indicates that controlling the temperature could increase flux when using thermo-responsive membranes in real filtration applications. Thermo-responsive membrane materials were synthesized through Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization, which is a more convenient and safe method of preparing polymer-functionalized materials and enlarging them from milligram scale to gram level for application than coating and grafting [22,23].
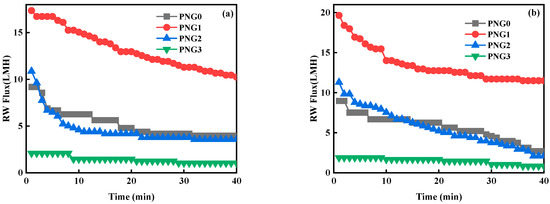
Figure 2.
Performance of thermo-responsive membranes during the filtration of RW under different temperatures: (a) 25 °C and (b) 35 °C.
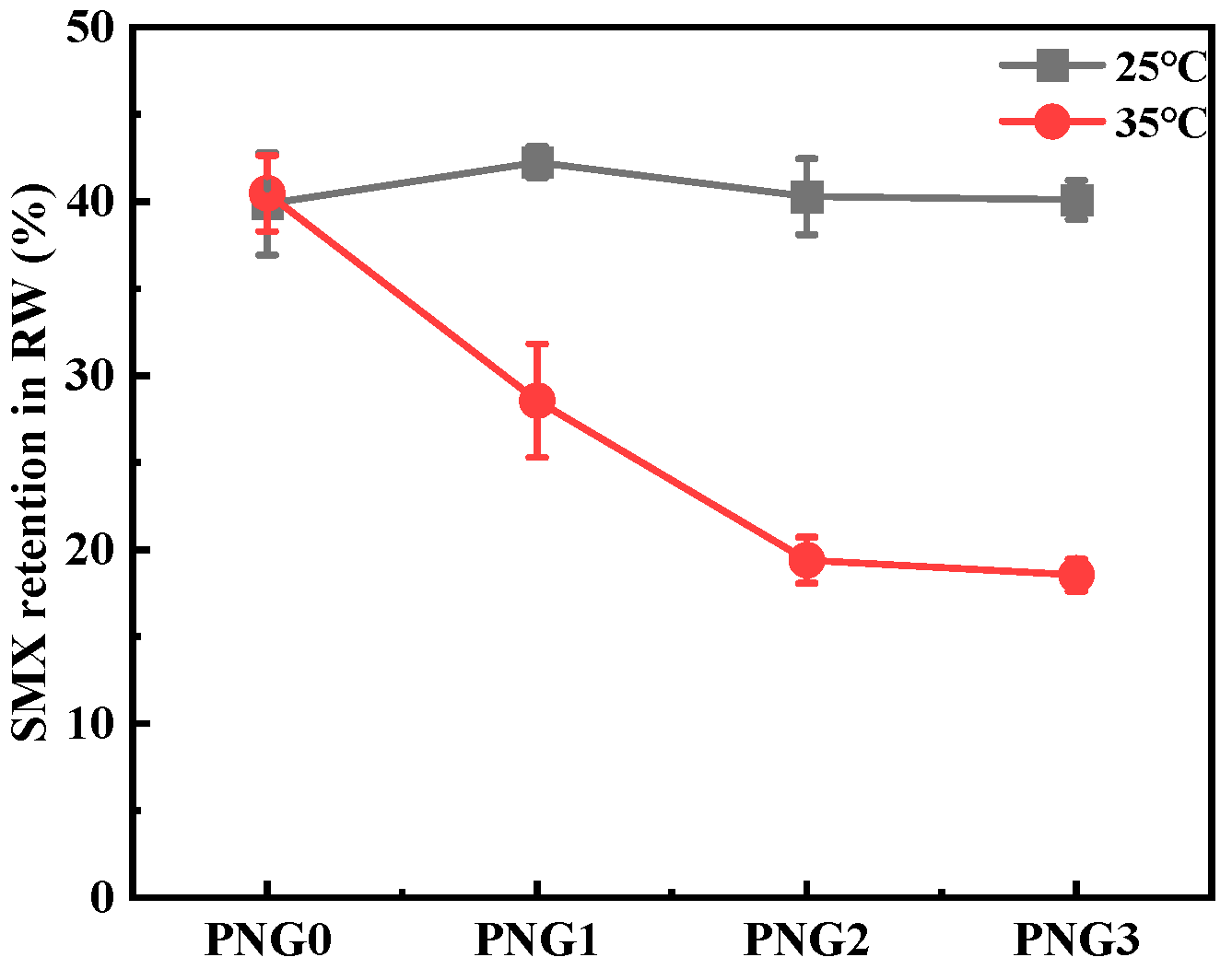
The retention of SMX under various temperatures is illustrated in Figure 3. As displayed in Figure 3, the removal of SMX at 42% occurred at of 25 °C. According to recent research [24,25,26], the removal rate of SMX by membrane separation technology alone had increased 2.3–32.0%. If we combined the photocatalysis or powder-activated carbon with membrane separation, the removal rate of SMX could be further enhanced. It was noticed that the removal rate of SMX was higher at a NIPAM dosage of 1 g than that the other dosages for the membrane. This enhancement might be due to the interaction between SMX and the contaminant in secondary effluent with membranes. The result of the retention of polyethylene glycol by the PNG1 membrane showed that the membrane pore would open below 35 °C. This decline occurred because the NIPAM underwent a reversible phase transition when heated or cooled and switched from a hydrophilic coiled state to a hydrophobic globule state at a temperature of 35 °C. Additionally membranes pores in an “open” state resulted in reduced removal efficiency, as previously reported [27].
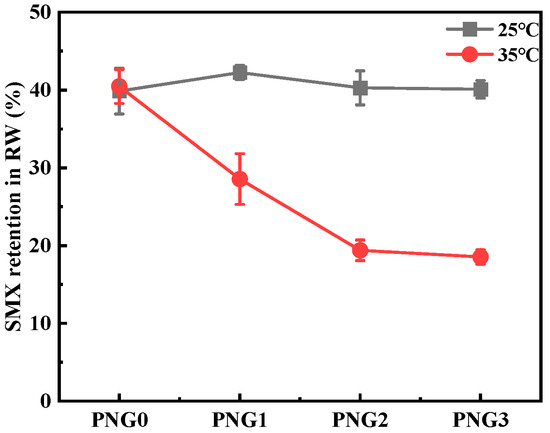
Figure 3.
Retention of SMX by thermo-responsive membrane filtration under different temperatures.
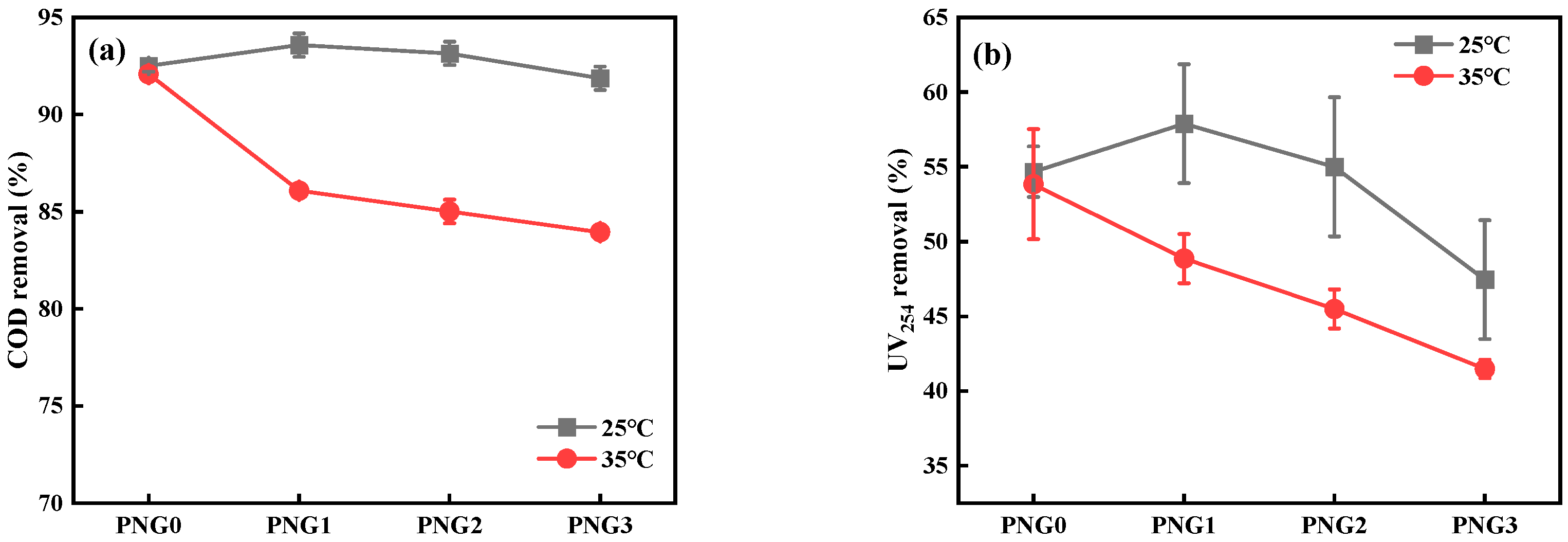
COD and UV254 removal were employed to assess the general water treatment capability of the thermo-responsive membranes. The COD and UV254 absorbance values of RW were 23.150 mg/L and 0.124 cm−1, respectively. Figure 4 shows the removal of COD and UV254 during the RW filtration by the thermo-responsive membranes. The removal of COD was maintained at 92% at a temperature of 25 °C. However, it decreased with the addition of NIPAM, a result similar to the rejection of SMX at a temperature of 35 °C. Moreover, the removal of UV254 reached its highest value at 57.9% when the PNG1 membrane was under a temperature of 25 °C. This phenomenon might be attributed to the interfacial reaction between the negatively charged dissolved organic matter in RW and the negative functional groups of the membrane. It is known that the interfacial reaction played a significant role in the rejection of dissolved organic matter during membrane filtration [28]. In addition, the water quality met the discharge standard of water pollutants for municipal wastewater (DB11/890-2012) by the PNG1 membrane at 35 °C. This indicated that the thermo-responsive membranes could increase the product flux in wastewater reclamation treatment.
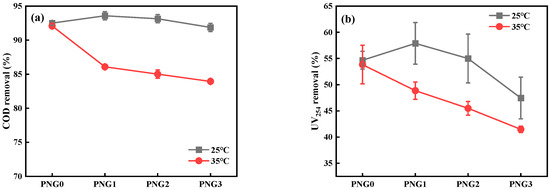
Figure 4.
The removal of COD and UV254 during filtration for RW with thermo-responsive membranes: (a) the removal of COD and (b) the removal UV254.
3.2. Identifying the Contaminant During Thermo-Responsive Membrane Filtration
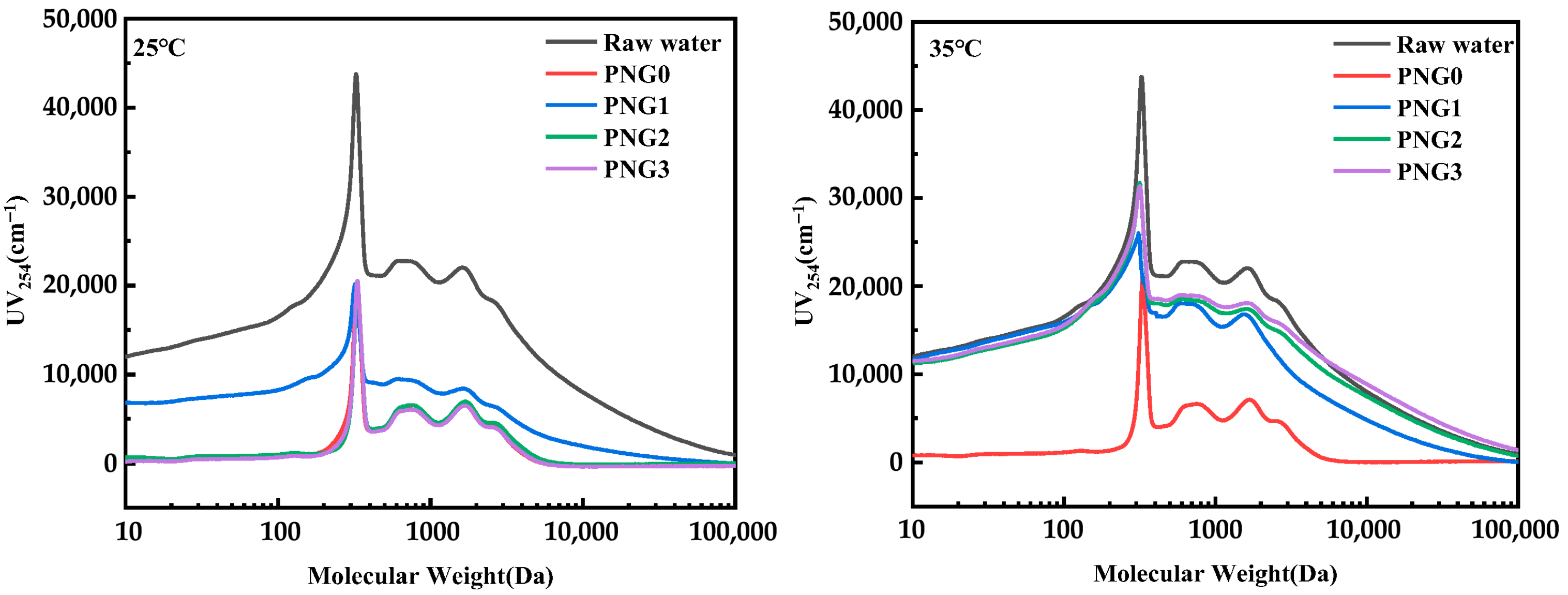
Figure 5 demonstrates the MW distribution after the thermo-responsive membrane filtration of RW at different temperatures. Figure 5 illustrates that there were three main dominant peaks in the water, which were SMX at 253 Da and contaminant from the secondary effluent at 712 Da and 1660 Da, respectively. As depicted in Figure 5, the peak intensity of SMX and the contaminant from the secondary effluent dramatically decreased during thermo-responsive membrane filtration at a temperature of 25 °C. This phenomenon was attributed to the addition of GO and NIPAM, which could increase the rejection of pollutants by the membrane. However, the peak intensity of SMX and the contaminant from the secondary effluent declined slowly with the addition of NIPAM, and the use of PNG1 resulted in lower pollutant removal. This phenomenon is due to the huddling together effect of NIPAM, which caused an “open” pore state, resulting in reduced removal efficiency [27].
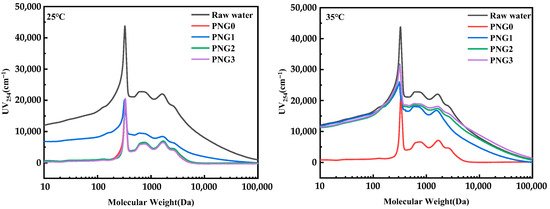
Figure 5.
Changes in MW distribution after thermo-responsive membrane filtration for RW at different temperatures.
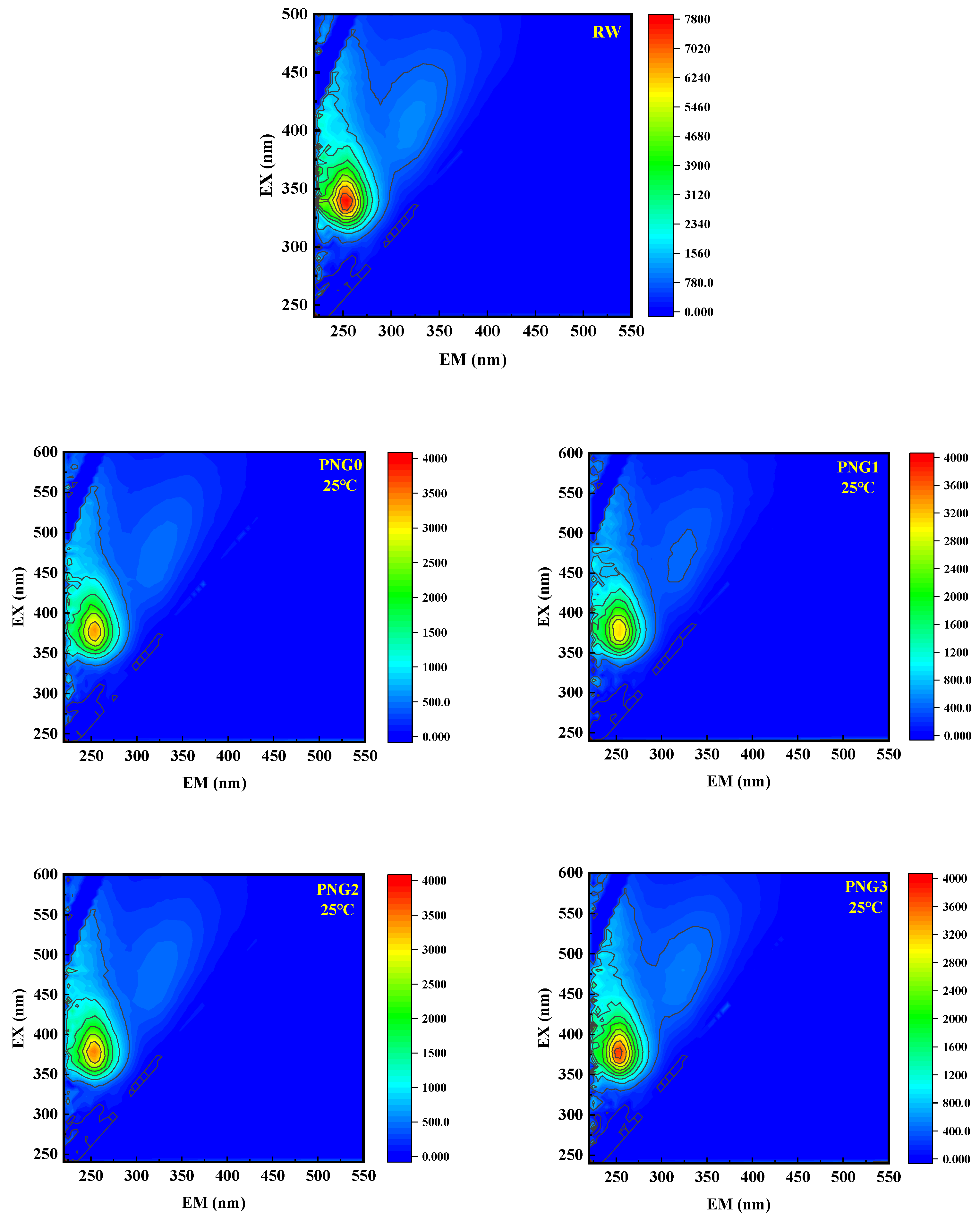
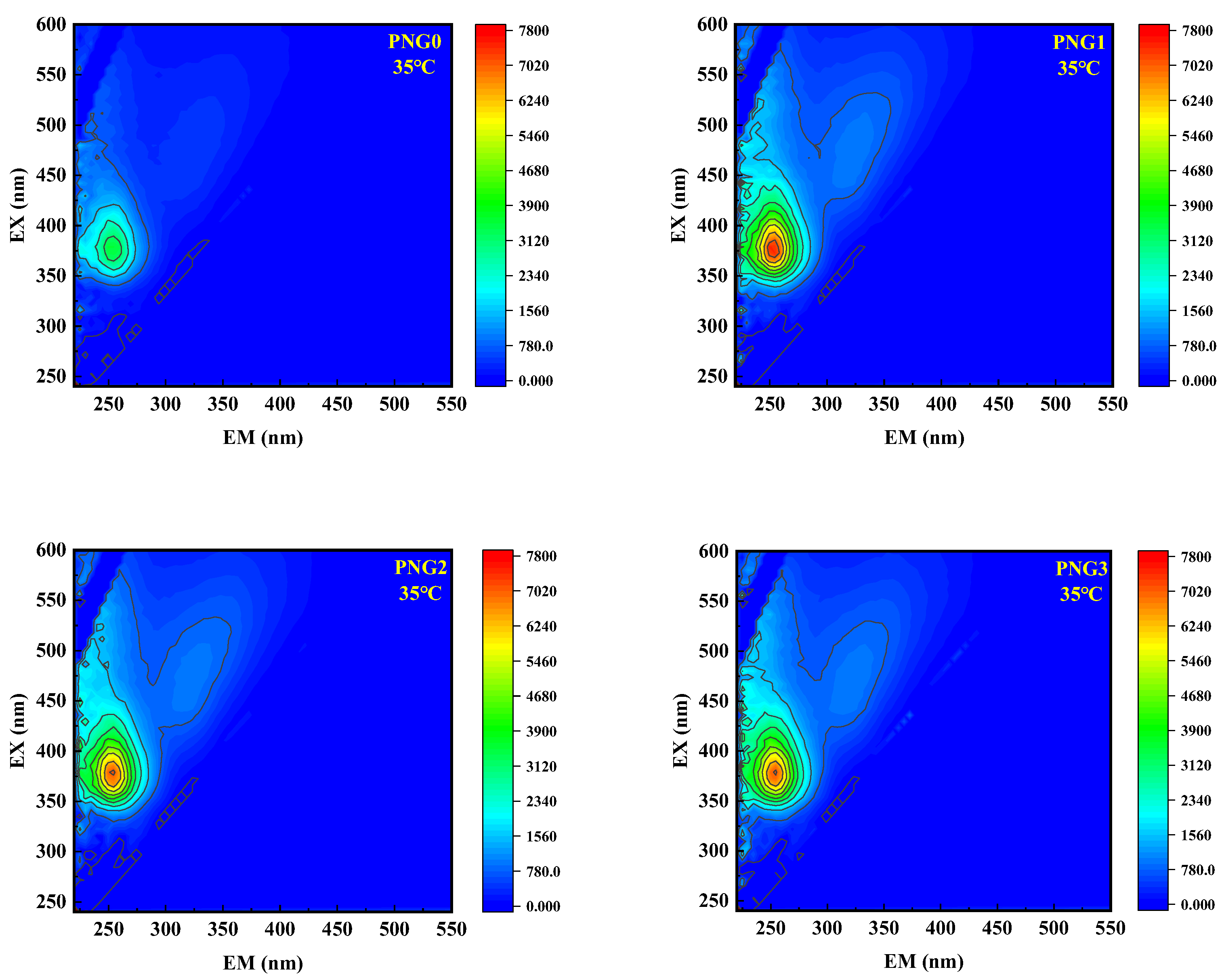
EEM was employed to investigate the alterations in the dissolved natural organic matter (NOM) of the raw water samples during membrane filtration. The fluorescence peaks in the EEM spectra were classified as soluble microbial products at EX > 250 nm and EM = 280–380 nm [29]. Figure 6 shows the changes in 3D-EEM fluorescence spectra in the water samples after thermo-responsive membrane filtration for the RW. As shown in Figure 6, there was one remarkable area in the EEM spectra, representing soluble microbial products (SMPs). The peak intensity of SMPs in the secondary effluent spiked with SMX was 7723.4, and the peak intensity of the SMPs decreased following treatment by the thermo-responsive membranes at a temperature of 25 °C. However, the peak intensity of the SMPs decreased slowly at a temperature of 35 °C. The EEM spectra results were consistent with the outcome of SMX retention. In addition, Table 3 shows the change in fluorescence intensity in the RW samples following the thermo-responsive membrane treatment process. As depicted in Table 3, the fluorescence intensities for the organic matter from RW decreased after the thermo-responsive membrane process, and the PNG1 membrane achieved the lowest intensity at a value of 3074.6 under a temperature of 25 °C. The results were consistent with the outcome for UV254, which is due to interfacial interaction between the SMPs in RW and the functional groups of the membrane. Additionally, the fluorescence intensity increased with the introduction of NIPAM, as the temperature increased from 25 °C to 35 °C.
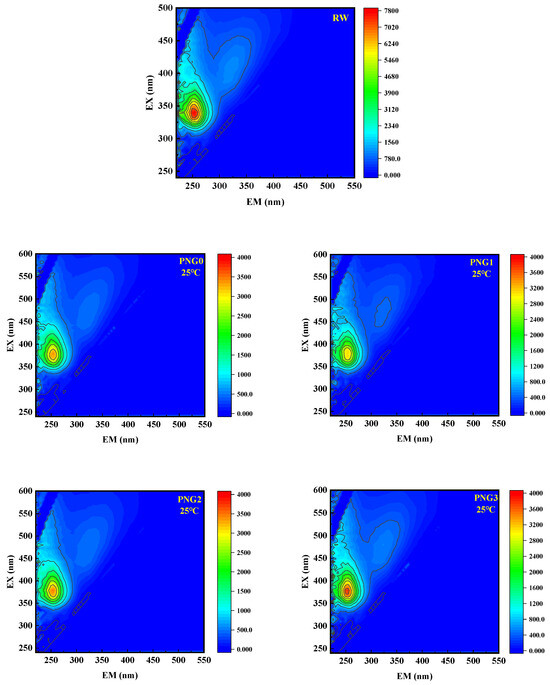
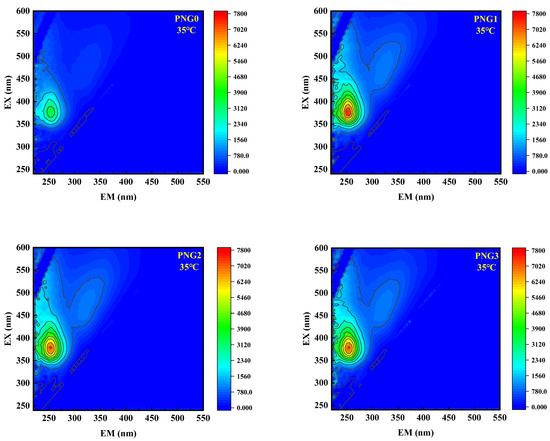
Figure 6.
Changes of 3D-EEM fluorescence spectra in the water types after thermo-responsive membrane filtration for RW.

Table 3.
Transformation of fluorescent intensities in the water samples with the thermo-responsive membranes process for RW.
3.3. The Anti-Fouling Properties of the Thermo-Responsive Membranes
Rr, Rir, and FR were employed to further analyze the anti-fouling abilities of the thermo-responsive membranes in detail. The anti-fouling properties of the thermo-responsive membranes during RW filtration under different temperatures are shown in Table 4. The FR of PNG1 reached higher values of 0.699 and 0.585 under temperatures of 25 °C and 35 °C, respectively, and the Rr of PNG1 reached higher values of 0.271 and 0.105 under temperatures of 25 °C and 35 °C, respectively. The Rr of PNG1 was shown to be higher than the polyethersulfone membrane by comparing its results with the literature [30]. Additionally, the Rir of PNG1 was shown to be lower than the GO-blending PVDF membrane by comparing its results with the literature [31]. The results showed that the PNG membranes containing 1 g of NIPAM exhibited great anti-fouling ability. Moreover, the thermo-responsive membrane could be cleaned using NaOH. These results indicate that the thermo-responsive membranes can be applied in real wastewater reclamation treatment.

Table 4.
Anti-fouling properties of the thermo-responsive membranes during the RW filtration under different temperatures.
3.4. XDLVO Theory for Membrane-Fouling Behavior
Table 5 shows the interfacial free energies between the contaminant and the membrane surface in RW under different temperatures. The absolute values of the AB component of free energy were significantly higher compared with the LW and EL components of free energy in the interfacial free energies of all the PNG membranes. The analysis revealed that AB interaction exhibited a more dominant influence compared with the LW and EL interactions. The for the PNG1 membrane achieved maximum absolute values of −42.921 mJ/m2 and −54.653 mJ/m2, as compared with the other PNG membranes under temperatures of 25 °C and 35 °C. Additionally, the increase at the temperature increase from 25 °C to 35 °C was due to the presence of a complex contaminant in the secondary effluent. Furthermore, reversible fouling led to the formation of a loose filter cake, which can be effectively mitigated through NaOH cleaning [32]. Overall, interactions between the contaminants and the membrane surface determined its adsorption capacity, contributing to the development of reversible fouling. The analysis based on the XDLVO theory provided a sound thermodynamic explanation for the excellent anti-fouling properties exhibited by the PNG membranes containing 1 g of NIPAM in practical applications.

Table 5.
Interfacial free energies between the contaminant and membrane surface in RW filtration under different temperatures.
4. Conclusions
In this study, secondary effluent from a Beijing wastewater reclamation treatment plant spiked with SMX (10 mg/L) was used to investigate the filtration performance and fouling mechanism of thermo-responsive membranes. Thermo-responsive materials were prepared using polyvinylidene fluoride, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), and graphene oxide through Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization. The performance and anti-fouling ability of these thermo-responsive membranes for contaminant removal were investigated. In summary, the following conclusions were drawn:
(1) The removal of SMX and COD reached 42% and 92%, respectively, with a 1 g dosage of NIPAM at 25 °C, and the removal of UV254 reached the highest value in PNG1 at 57.9% at a temperature of 25 °C.
(2) The fluorescence intensities for the organic matter from the secondary effluent spiked with SMX decreased after filtration with the thermo-responsive membranes. A lower intensity of 3074.6 was achieved with the thermo-responsive membrane containing 1 g of NIPAM.
(3) The thermo-responsive membrane with a 1 g dose of NIPAM exhibited great anti-fouling ability at a temperature of 25 °C. According to XDLVO theory analysis, the interfacial free energies of this membrane were higher than those of the other membranes.
Author Contributions
L.Y.: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, resources, funding acquisition; H.Q., L.Z., Y.Y., G.L., P.X. and J.C.: methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation; F.X.: review and editing, software, data curation, visualization; S.Y.: resources, supervision, review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This authors of this study greatly appreciate the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52030003 and 52200003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Jentai Yang Sustainable Environmental Protection and Eco-humanistic Education Fund from Overseas Chinese Environmental Engineers and Scientists Association (OCEESA).
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Lian Yang, Haoran Qiu, Yingjie Yang, Lijun Zhao, Guoliang Liu, and Jiang Chang were employed by the company Beijing Drainage Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Mohapatra, S.; Bhatia, S.; Senaratna, K.Y.K.; Jong, M.-C.; Lim, C.M.B.; Gangesh, G.R.; Lee, J.X.; Giek, G.S.; Cheung, C.; Yutao, L.; et al. Wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 and chemical markers in campus dormitories in an evolving COVID-19 pandemic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.; Tit, D.M.; Behl, T.; Aleya, L.; Zaha, D.C. Aspects of excessive antibiotic consumption and environmental influences correlated with the occurrence of resistance to antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 19, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mehmood, S.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Antibiotics traces in the aquatic environment: Persistence and adverse environmental impact. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, S.; Yargeau, V. Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole: Current knowledge and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and ecotoxicity of sulfonamides in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegglen, C.; Joss, A.; McArdell, C.S.; Fink, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Ternes, T.A.; Siegrist, H. The fate of selected micropollutants in a single-house MBR. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Takada, H.; Mutoh, K.; Hosoda, H.; Harada, A.; Nakada, N. Nationwide monitoring of selected antibiotics: Distribution and sources of sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and macrolides in Japanese rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, A.L.; Kincaid, T.M.; Kostich, M.S.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Olsen, A.R. Evaluating the extent of pharmaceuticals in surface waters of the United States using a National-scale Rivers and Streams Assessment survey. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Bürgmann, H. New insight into effect of antibiotics concentration and process configuration on the removal of antibiotics and relevant antibiotic resistance genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, B.L.; Ong, C.C.; Mohamed Saheed, M.S.; Show, P.-L.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C.; Lam, S.S.; Juan, J.C. Conventional and emerging technologies for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeu, M.; Neves, M.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Almeida, A. Wastewater chemical contaminants: Remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 1573–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.; Cardoso, M.; Martins, R.C.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Removal of a mixture of pharmaceuticals sulfamethoxazole and diclofenac from water streams by a polyamide nanofiltration membrane. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R. Effect and degradation pathway of sulfamethoxazole removal in MBR by PVDF/DA modified membrane. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiu, H.; Liu, G.; Chang, J.; Yang, S.; Xiao, F. Effect of N-isopropylacrylamide and graphene oxide on the microstructure and performance of thermo-responsive membranes by Ce (IV)-induced redox radical polymerization. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 703, 135284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirilargani, M.; Sabetghadam, A.; Mohammadi, T. Polyethersulfone/polyacrylonitrile blend ultrafiltration membranes with different molecular weight of polyethylene glycol: Preparation, morphology and antifouling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, J.A.; Childress, A.E. Assessing short-range membrane–colloid interactions using surface energetics. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 203, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Tian, J. Membrane fouling behaviors of ceramic hollow fiber microfiltration (MF) membranes by typical organic matters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, Y.; Tabatabaei, S.; Kim, K.; Foudazi, R. Thermoresponsive antifouling ultrafiltration membranes from mesophase templating. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 684, 121861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, E.; Chapman, R.G.; Holmlin, R.E.; Takayama, S.; Whitesides, G.M. A Survey of Structure−Property Relationships of Surfaces that Resist the Adsorption of Protein. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5605–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Akasaki, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Aoyagi, T. Stimuli-Responsive Coacervate Induced in Binary Functionalized Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Aqueous System and Novel Method for Preparing Semi-IPN Microgel Using the Coacervate. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9510–9517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Santoro, S.; Galiano, F.; Ursino, C.; Avruscio, E.; Nicolo, E.; Desiderio, G.; Lombardo, G.; Criscuoli, A.; Figoli, A. A luminescent thermosensitive coating for a non-invasive and in-situ study of thermal polarization in hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 685, 121928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Guo, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, D. Hydrothermal treatment to prepare hydroxyl group modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uredat, S.; Gujare, A.; Runge, J.; Truzzolillo, D.; Oberdisse, J.; Hellweg, T. A review of stimuli-responsive polymer-based gating membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Wu, C.; Lichtfouse, E. Removal of antibiotics from black water by a membrane filtration-visible light photocatalytic system. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, T.; Liang, H.; Tang, X. Effects of pre-treatments on the filtration performance of ultra-low pressure gravity-driven membrane in treating the secondary effluent: Flux stabilization and removal improvement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 303, 122122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertkulsak, S.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Itonaga, T.; Yamamoto, K. Removals of pharmaceutical compounds from hospital wastewater in membrane bioreactor operated under short hydraulic retention time. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Zhou, S.; Shi, S.; Xue, A.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xing, W. Anti-fouling and easy-cleaning PVDF membranes blended with hydrophilic thermo-responsive nanofibers for efficient biological wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Mauch, R.; Waite, T.D.; Fane, A.G. Charge Effects in the Fractionation of Natural Organics Using Ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2572–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence Excitation—Emission Matrix Regional Integration to Quantify Spectra for Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Dai, J.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, X. Polyethersulfone membrane modified by zwitterionic groups for improving anti-fouling and antibacterial properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 122, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Yang, L.; Liao, G.; Xia, H.; Xiao, F. Applications of graphene oxide blended poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes for the treatment of organic matters and its membrane fouling investigation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Interaction mechanisms and predictions on membrane fouling in an ultrafiltration system, using the XDLVO approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).