Separating 2-Propanol and Water: A Comparative Study of Extractive Distillation, Salting-Out, and Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Entrainer | Feasibility Evaluation | Literature |
|---|---|---|
| (ChCl:U:LiCl) (1:2:0.44) (ChCl:SnCl2) (1:2) (ChCl:ZnCl2:SnCl2) (1:1:1) (ChCl:U:CaCl2) (1:2:0.36) (U:NaI) (4:1) (ChCl:Gly:CaCl2) (1:2:0.09) (ChCl:Gly:LiCl) (1:2:0.09) | Isobaric VLE was determined experimentally and correlated with NRTL Conceptual design involving partial heat integration and intermediate reboilers was developed in Aspen Plus Energy efficiency, environmental impact, and economic feasibility were evaluated (ChCl:U:CaCl2) (1:2:0.36) was recommended | [24] |
| [EMIM][BF4] (ChCl:Gly) (1:2) (ChCl:EG) (1:2) DMSO | Process modeling and simulation were performed in Aspen Plus VLE was calculated with NRTL A new design with a flash column for regeneration of the entrainer was developed High-purity IPA could be obtained (>99.9 mol %) | [25] |
| 380 ILs Gly, EG, DEG, TEG, DMSO, DMF, NMP | Entrainers were selected based on the VLE and relative volatility evaluation for organic solvents Selectivity of ILs was evaluated by COSMO RS VLE was modeled with UNIFAC Process simulation with EG and [EMIM][DCA] was performed in Aspen Plus | [26] |
| U | Isobaric VLE was determined experimentally and correlated with NRTL 13 mol% of the entrainer was required for breaking the azeotrope | [10] |
| EG | Process simulation was performed in ASPEN Plus High-purity IPA could be obtained (99.974 mol %) | [9] |
| (ChCl:EG) (1:2; 1:4; 1:8) EG | Isobaric VLE was determined experimentally and correlated with NRTL ChCl influenced activity coefficients of H2O and IPA DESs were found better than EG 15.7 wt% of DES was required for breaking the azeotrope | [27] |
| (ChCl:Gly) (1:2) Gly | Isobaric VLE was determined experimentally and correlated with NRTL DES was found better than Gly 14.2 wt% of DES was required for breaking the azeotrope | [28] |
| [EMIM][OAc] [BMIM][OAc] [EMIM][Br] | Isobaric VLE was determined experimentally and correlated with NRTL All tested ILs enhanced relative volatility of IPA to H2O [EMIM][OAc] was the best entrainer | [29] |
| Entrainer | Feasibility Evaluation | Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Na2CO3, K2CO3 | Binodal data were experimentally obtained Effective volume of salts and salting-out coefficient was determined Na2CO3 was better entrainer | [30] |
| K4P2O7, K2HPO4, K3PO4, K2CO3 | Experimental LLE data were determined Recovery of IPA and dehydration ratio were calculated K4P2O7 was the most effective salting-out entrainer IPA/K4P2O7 aqueous system was effective in separating 2,3-butanediol from aqueous solution | [31] |
| Cations: Na+, K+, Ca2+, NH4+ Anions: Cl–, SO42–, CO32–, NO3– | Experimentally obtained LCST and minimum salt concentration for phase splitting UNIQUAC and NRTL models were used for equilibrium calculation and simulation in Aspen Plus | [32] |
| NaCl, KCl, CaCl2, Na2CO3, K2CO3, potassium ethanolate | Aqueous salt solution: water:IPA:n-hexane (1:1:1) LLE was determined experimentally IPA distribution coefficient between hexane and aqueous solution was evaluated K2CO3 was the best entrainer Salting-out experiment was performed in RPC | [11] |
| NaCl | Salting-out ability of NaCl was experimentally determined | [12] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Solubility Measurements
2.3. Preparation of DESs
2.4. COSMO-RS Prediction
2.5. Extractive Distillation
2.6. Extraction
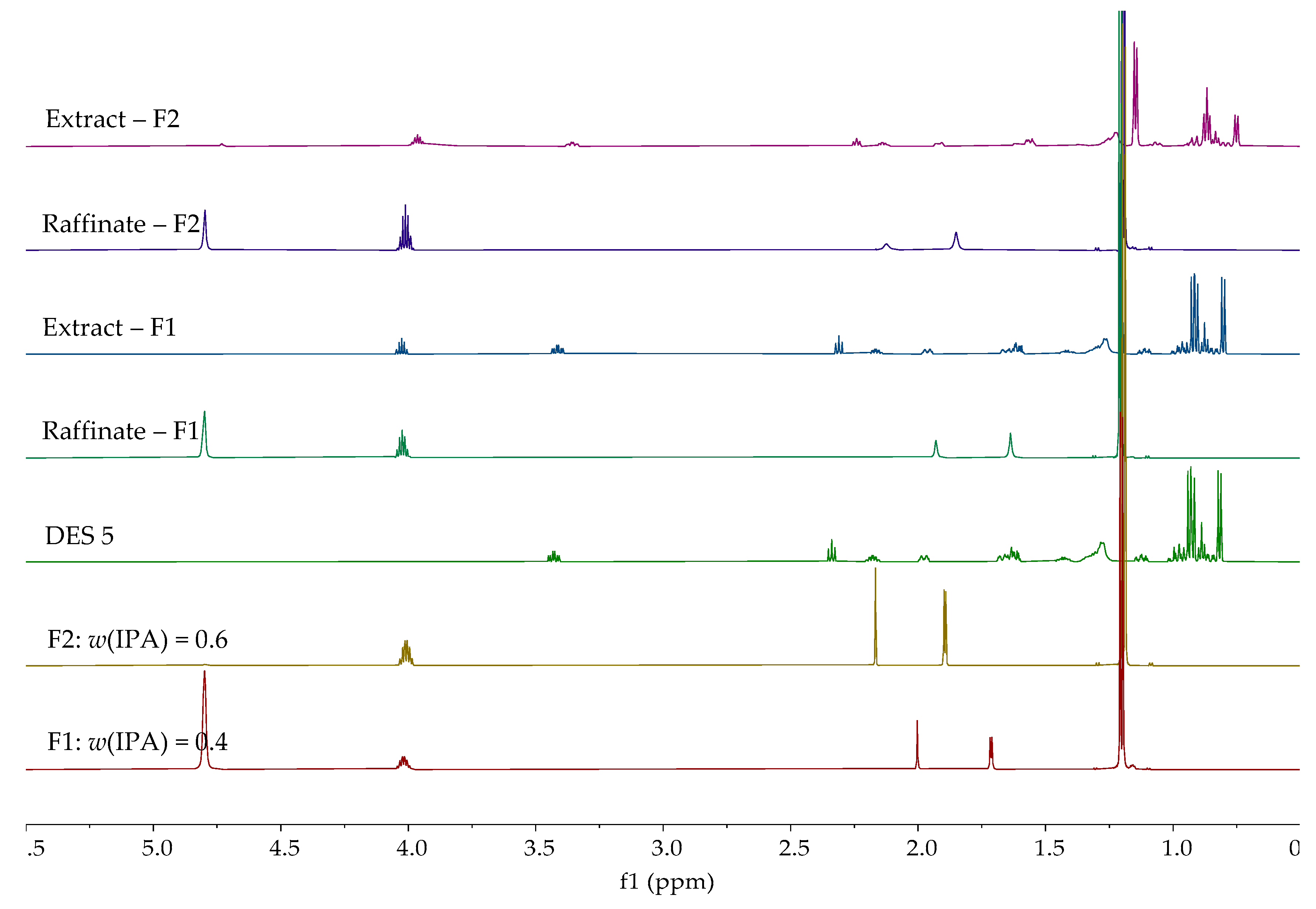
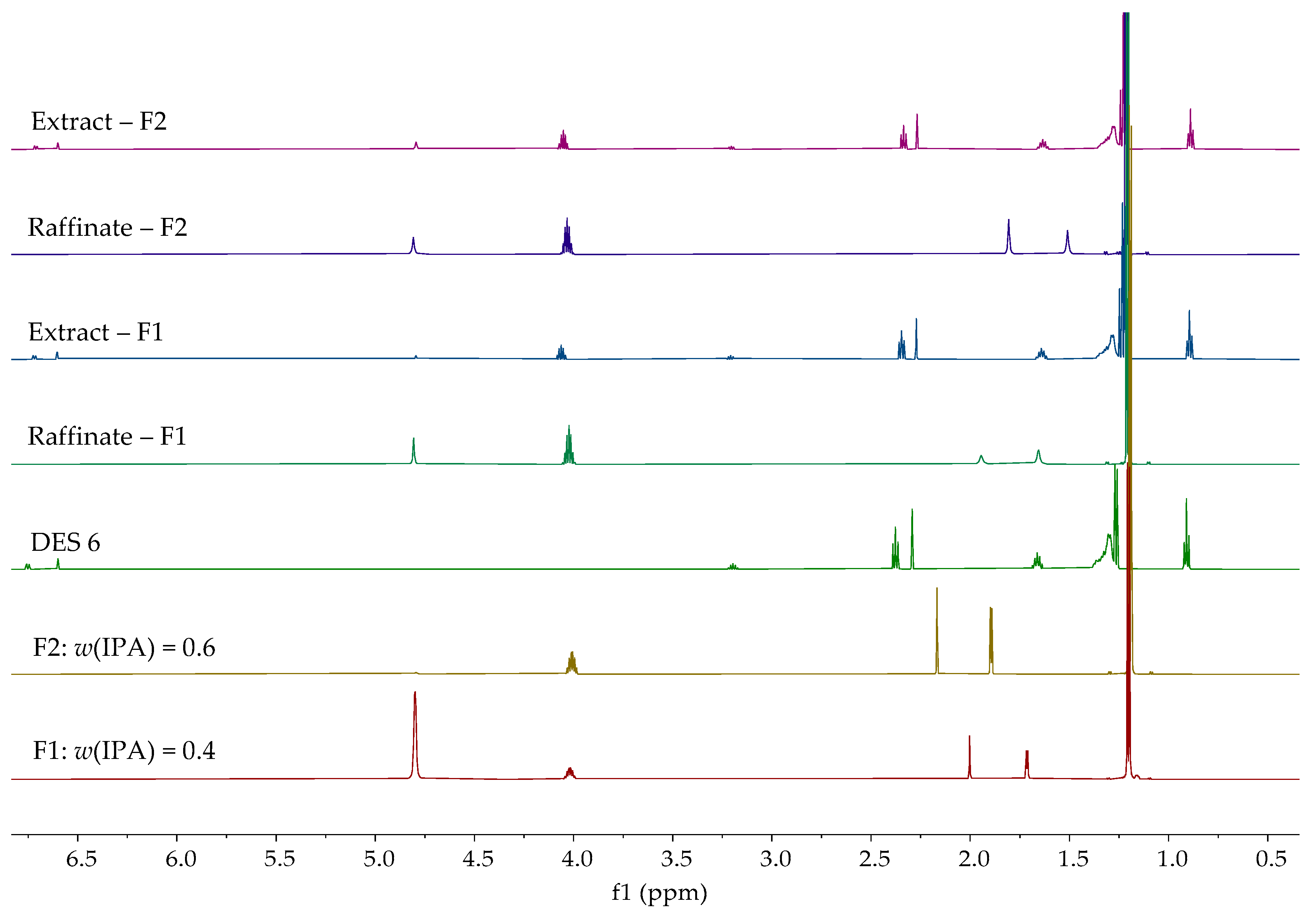
2.7. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Extractive Distillation
3.1.1. COSMO-RS Predictions
3.1.2. Experimental Validation
3.2. Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3.2.1. COSMO-RS Predictions
3.2.2. Experimental Validation
3.2.3. Reusability of DESs and Multistage Extraction
3.3. Salting-Out
3.3.1. COSMO-RS Predictions
3.3.2. Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATPS | aqueous two-phase system |
| CAS | Chemical Abstracts Service |
| ChCl | choline chloride |
| COSMO-RS | conductor-like screening model for real solvents |
| DA | decanoic acid |
| DDA | dodecanoic acid |
| DES | deep eutectic solvent |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EG | ethylene glycol |
| [EMIM][BF4] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [EMIM][DCA] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| Gly | glycerol |
| HBA | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| HBD | hydrogen bond donor |
| HDES | hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| IPA | 2-propanol (isopropanol) |
| LLE | liquid–liquid equilibria |
| M | menthol |
| NRTL | non-random two-liquid activity coefficient model |
| O | 1-octanol |
| PHI-IR | partial heat-integrated intermediate evaporator |
| T | thymol |
| TAC | total annual cost |
| VLE | vapor–liquid equilibria |
References
- Nhien, L.C.; Agarwal, N.; Lee, M. Dehydration of Isopropanol: A Comparative Review of Distillation Processes, Heat Integration, and Intensification Techniques. Energies 2023, 16, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhang, P.; Yang, J.; Xiao, L.; Ye, C. Novel Procedure for Production of Isopropanol by Transesterification of Isopropyl Acetate with Reactive Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 13881–13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, J.; Matsuo, T.; Takemura, K.; Kato, S.; Fujii, T.; Wada, K.; Nakamichi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Aoi, Y.; Morita, T.; et al. Isopropanol Production via the Thermophilic Bioconversion of Sugars and Syngas Using Metabolically Engineered Moorella Thermoacetica. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2024, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sallee, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Kumar, S. Electrochemical Hydrogenation of Acetone to Produce Isopropanol Using a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Reactor. Energies 2018, 11, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.B.; Dwivedi, M.; Jha, D.; Kumar, R.; Marriyappan Sivagnanam, B. Azeotropic Separation of Isopropanol-Water Using Natural Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.M.; Gorri, E.D.; Ortiz, I. Pervaporative Recovery of Isopropanol from Industrial Effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guido, G.; Monticelli, C.; Spatolisano, E.; Pellegrini, L.A. Separation of the Mixture 2-Propanol + Water by Heterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation with Isooctane as an Entrainer. Energies 2021, 14, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shi, X.; Guang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Comparison of Pressure-Swing Distillation and Heterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation for Recovering Benzene and Isopropanol from Wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 122, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, S.; Upadhyaya, S.; Singh, K.; Dohare, R.K.; Agarwal, M. A Case Study on Separation of IPA-Water Mixture by Extractive Distillation Using Aspen Plus. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. 2016, 3, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, R.; Jain, T.; Singh, N.; Kushwaha, J.P.; Sharma, B. Using Diaminomethanal as an Entrainer for the Separation of Isopropanol + Water Mixture. J. Solut. Chem. 2020, 49, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigang, T.; Rongqi, Z.; Zhanting, D. Separation of Isopropanol from Aqueous Solution by Salting-out Extraction. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Kumamoto, M.; Nishimoto, J. Chemical Properties of Water-Miscible Solvents Separated by Salting-out and Their Application to Solvent Extraction. Anal. Sci. 1994, 10, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. (Liquid + Liquid) Extraction of 2-Propanol from Aqueous Solutions Using Extracting Agents Ethyl Butyrate and n-Pentyl Acetate at Three Temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2020, 144, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, A.A. Liquid-Liquid Equilibria of Some Water + 2-Propanol + Solvent Ternaries. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1991, 36, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Separation of Isopropanol from Water by Pervaporation Using Silicone-Based Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 74, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-Y.; Lin, L.-C. Pervaporation Separation of Isopropanol/Water Using Zeolite Nanosheets: A Molecular Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 128, 8546–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurşun, F. The Separation Characteristics of an Isopropyl Alcohol/Water Azeotrope Using Evapomeation and Temperature-Difference Controlling Evapomeation Methods with PVA/NaY Membranes. Int. J. Environ. Geoinform. 2021, 8, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Xie, H. Economically and Thermodynamically Efficient Pressure-Swing Distillation with Heat Integration and Heat Pump Techniques. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 218, 119389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, Y.; Santoso, H.; Hartanto, Y. Process Control for Isopropanol-Water Separation via Azeotropic Distillation with Dividing Wall. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Instrumentation, Control, and Automation (ICA), Bandung, Indonesia, 31 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Han, Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, D.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Liquid-Liquid Equilibrium Data for Ternary Mixtures (Water + Isopropanol + 1-Pentanol/1-Hexanol/1-Heptanol) at 298.15 K: Measurement, Correlation and Prediction. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2022, 174, 106871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Su, Y.-H.; Chen, C. Recovery and Repurposing of Waste Isopropanol with CO2-Switchable Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audeh, D.J.S.A.; Carniel, A.; Borges, C.P.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Buarque, F.S.; Ribeiro, B.D. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Ethanol, Propan-1-Ol, and Propan-2-Ol Recovery from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2024, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. Separation of Isopropanol from Its Aqueous Solution with Deep Eutectic Solvents: Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Measurement and Thermodynamic Modeling. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Duan, W.; He, Y.; Tang, S.; Fu, T. Energy-Saving Extractive Distillation Using Salt-Based DESs as an Entrainer for Separating 2-Propanol and Water Mixture. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 72, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomey, A.K.; Tripathi, M.M.; Haider, M.B.; Kumar, R. Comparative Analysis of Isopropyl Alcohol Dehydration Using Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Ion. Liq. 2023, 3, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, R.; Lei, Z. Extractive Distillation for Separation of Isopropanol-n-Propanol-Water Ternary System: Mechanism Analysis and Process Design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 200, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lan, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Vapor–Liquid Equilibria for 2-Propanol Dehydration through Extractive Distillation Using Mixed Solvent of Ethylene Glycol and Choline Chloride. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, D.; Lan, M. 2-Propanol Dehydration via Extractive Distillation Using a Renewable Glycerol–Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvent: Vapor–Liquid Equilibrium. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, D.; Pan, F.; Dai, S.; Li, W. Separation of 2-Propanol and Water Azeotropic System Using Ionic Liquids as Entrainers. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 412, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Yan, Y.; Guan, W. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium of Potassium/Sodium Carbonate + 2-Propanol/Ethanol + Water Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Correlation at 298.15 K. Calphad 2009, 33, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Yin, S.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Fang, J. A Novel Isopropanol Salt Aqueous Two-Phase System and Its Applications for 2, 3-Butanediol Extraction. Desalination 2021, 520, 115234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, A.; García-Cano, J.; Font, A.; Gomis, V. Operational Limits in Processes with Water, Salt, and Short-Chain Alcohol Mixtures as Aqueous Two-Phase Systems and Problems in Its Simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerson, A.S. Measurement of Solubility. In Handbook of Industrial Crystallization; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 15–16. ISBN 978-0-7506-7012-8. [Google Scholar]
- Klamt, A.; Jonas, V.; Bürger, T.; Lohrenz, J.C.W. Refinement and Parametrization of COSMO-RS. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 5074–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Rogošić, M.; Vezjak Fluksi, A.; Frljak, L.; Petračić, A.; Parlov Vuković, J. Evaluation of Different Methods for the Separation of Acetonitrile and Water. Part 1: Extractive Distillation and Distillation under Reduced Pressure. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 429, 127576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Rogošić, M.; Slivar, A.; Žuteg, B. Separation of Hydrocarbons by Means of Liquid-Liquid Extraction with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2016, 34, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Petračić, A.; Parlov Vuković, J.; Husinec, L. From Coffee to Biodiesel—Deep Eutectic Solvents for Feedstock and Biodiesel Purification. Separations 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Petračić, A.; Zokić, I.; Vrsaljko, D. Scaling up Extractive Deacidification of Waste Cooking Oil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivendra; Kumar Singh, V.; Kumar Kaushal, R. Separation of IPA Water Azeotrope by Extractive Distillation. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2022, 11, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Petračić, A.; Rogošić, M.; Župan, M.; Frljak, L.; Cvetnić, M. Feasibility of Different Methods for Separating N-Hexane and Ethanol. Separations 2024, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, M.; Takebayashi, S.; Taguchi, M.; Kasahara, Y.; Minami, H.; Matsuzawa, H. Dynamical Dimer Structure and Liquid Structure of Fatty Acids in Their Binary Liquid Mixture: Decanoic/Octadecanoic Acid and Decanoic/Dodecanoic Acid Systems. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2005, 133, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A. COSMO-RS for Aqueous Solvation and Interfaces. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 407, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiao, C.; Song, K.; Jiang, S.; Yao, J. Hofmeister Effect on the Viscosity Properties of Gelatin in Dilute Solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Namboodiri, V.; Singh, A.K.; Mondal, J.A.; Sarkar, S.K. How Ions Affect the Structure of Water: A Combined Raman Spectroscopy and Multivariate Curve Resolution Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 16479–16485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Che, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Effect of Na2CO3 on the Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties and Mechanism Analysis of PVA/CMC Composite Film. Polymers 2020, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, A. Density, Refractive Index, Electrical Conductivity, pH, and FT-IR and UV–Vis Spectra of Potassium Carbonate–Potassium Bicarbonate–Water System. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2025, 70, 766–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, A.; Muruganand, S.; Palaniswamy, M. Vibrational studies of Na2SO4, K2SO4, NaHSO4 and KHSO4 crystals. RASĀYAN J. Chem. 2009, 2, 981–989. [Google Scholar]
- Gabelica, Z. Structural Study of Solid Inorganic Thiosulfates by Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 1980, 60, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


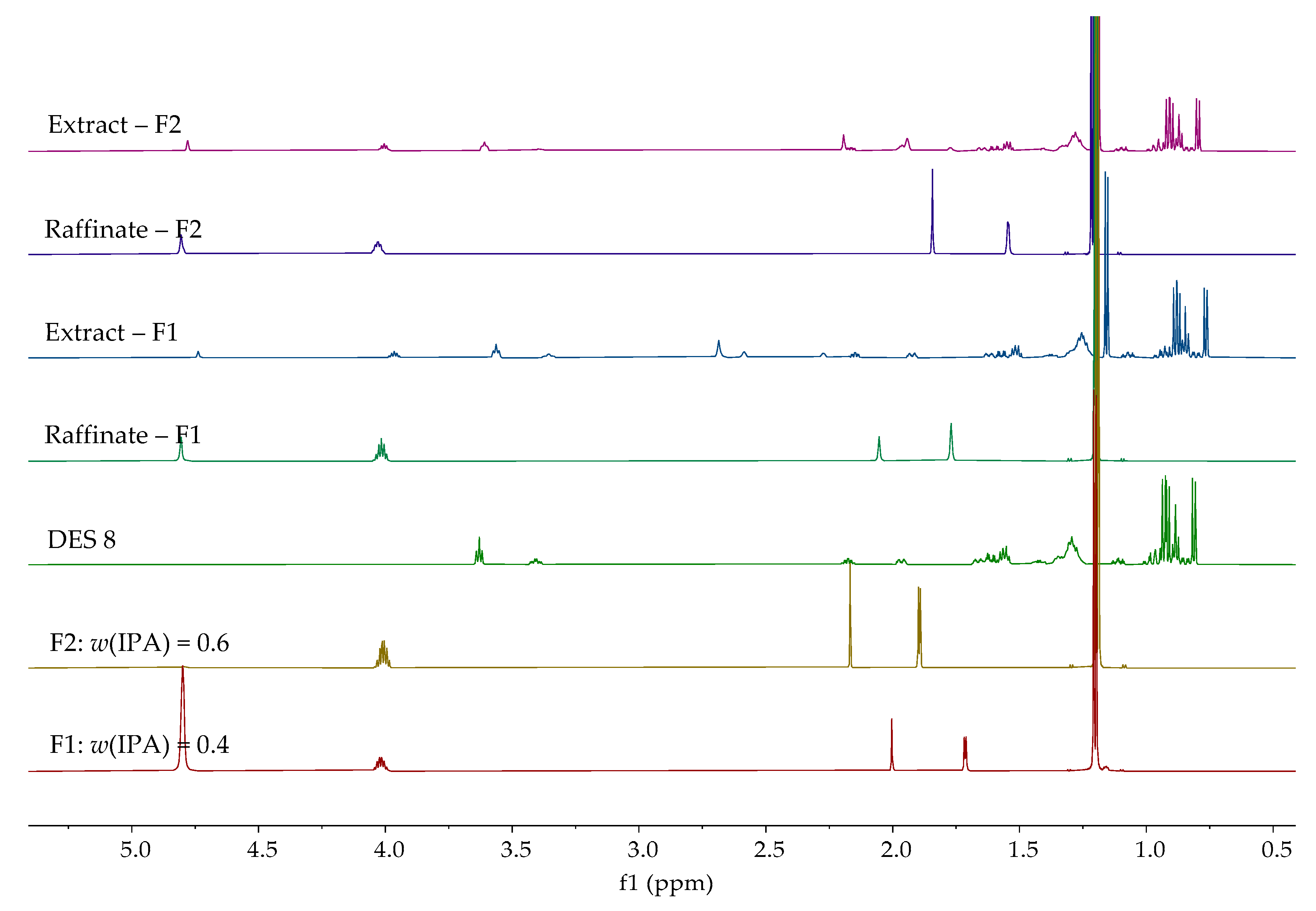
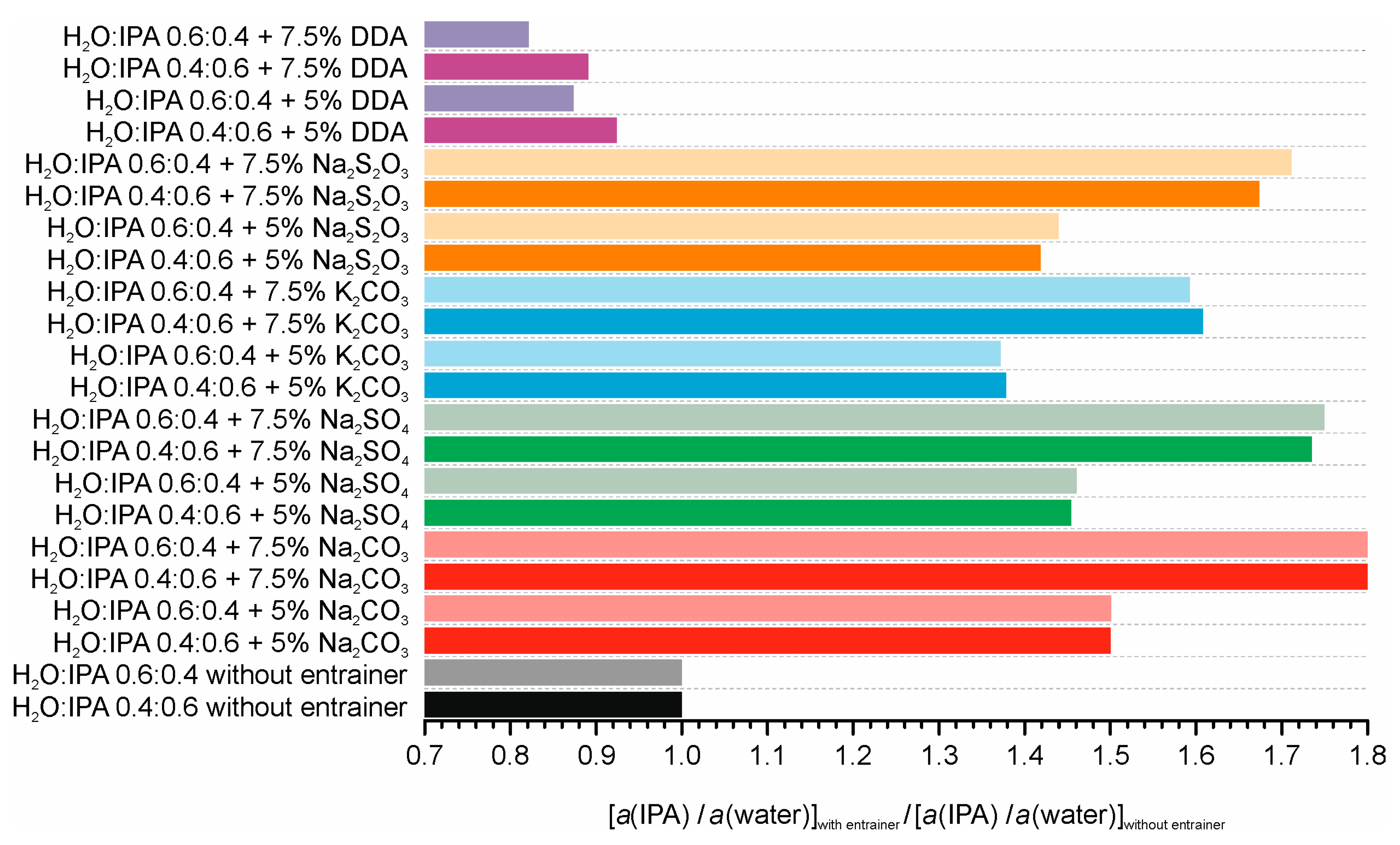
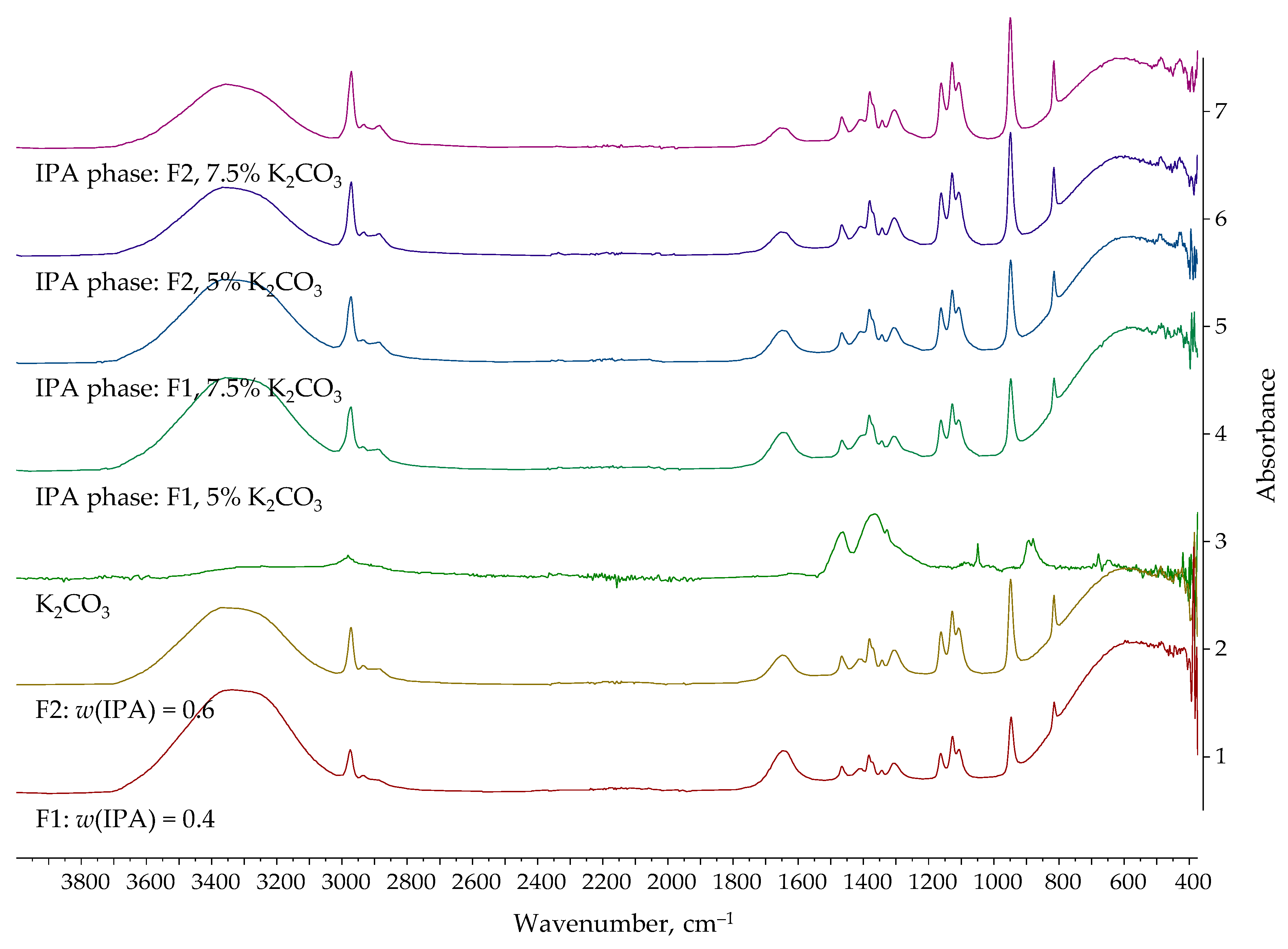
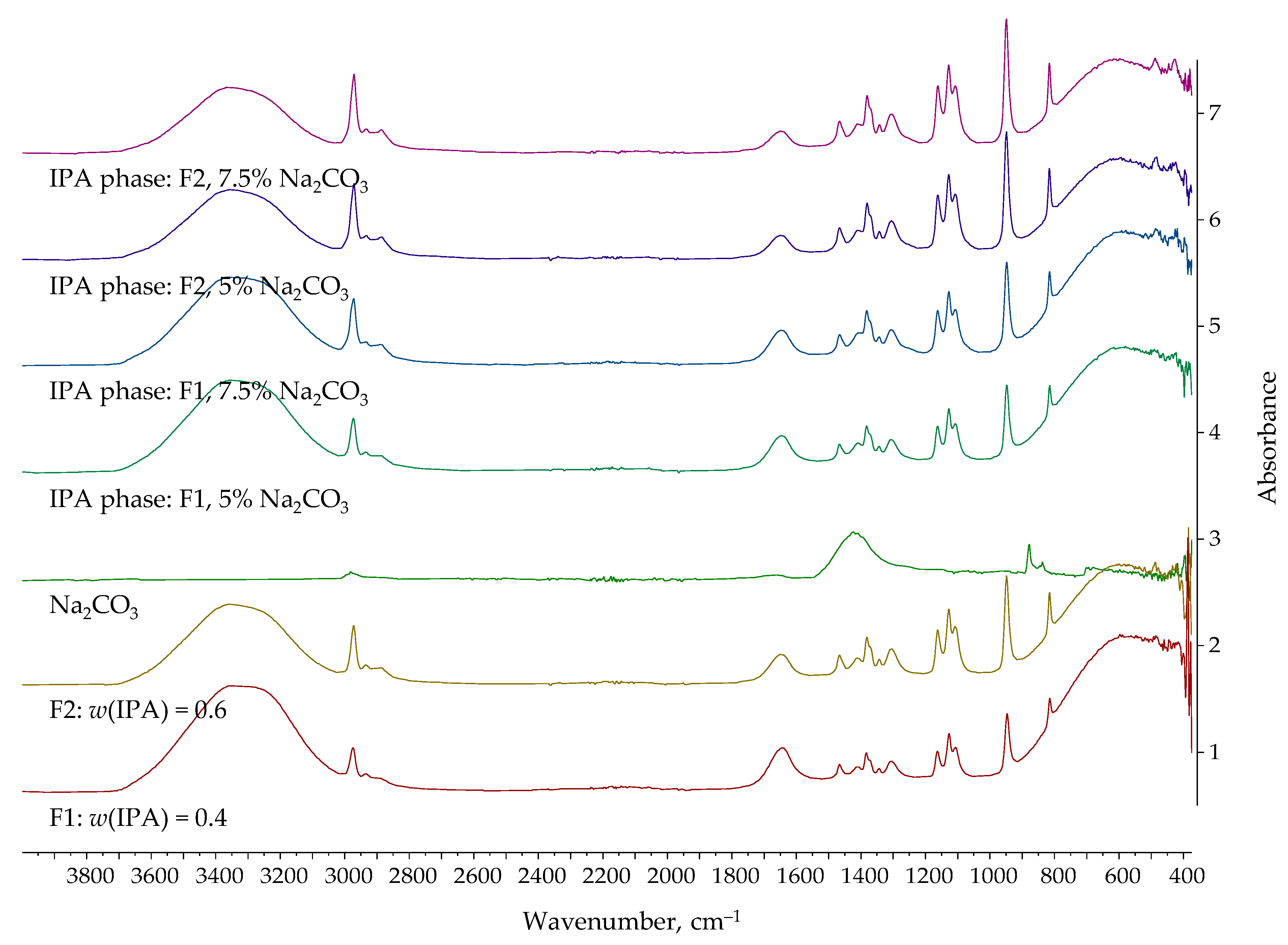
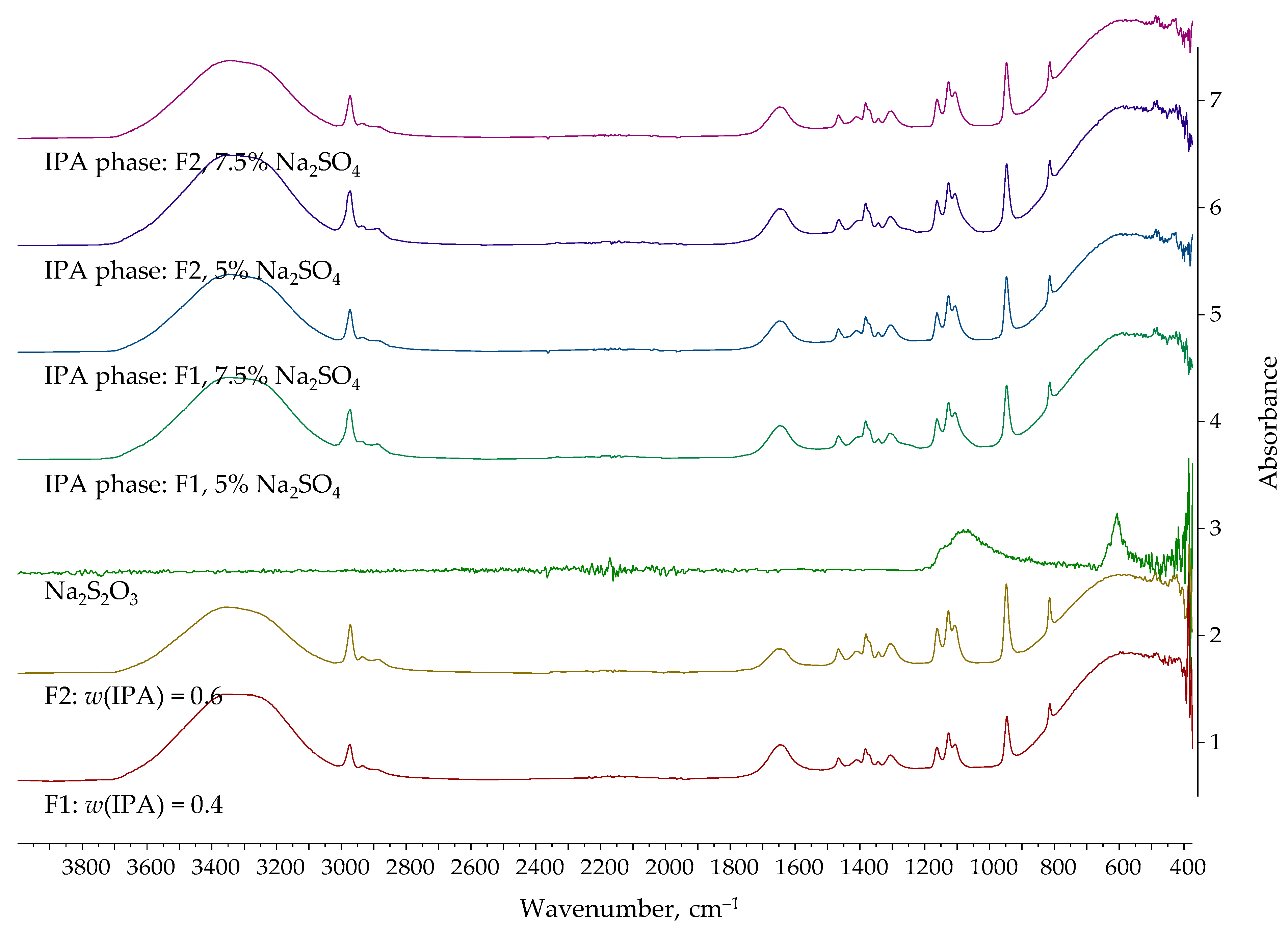
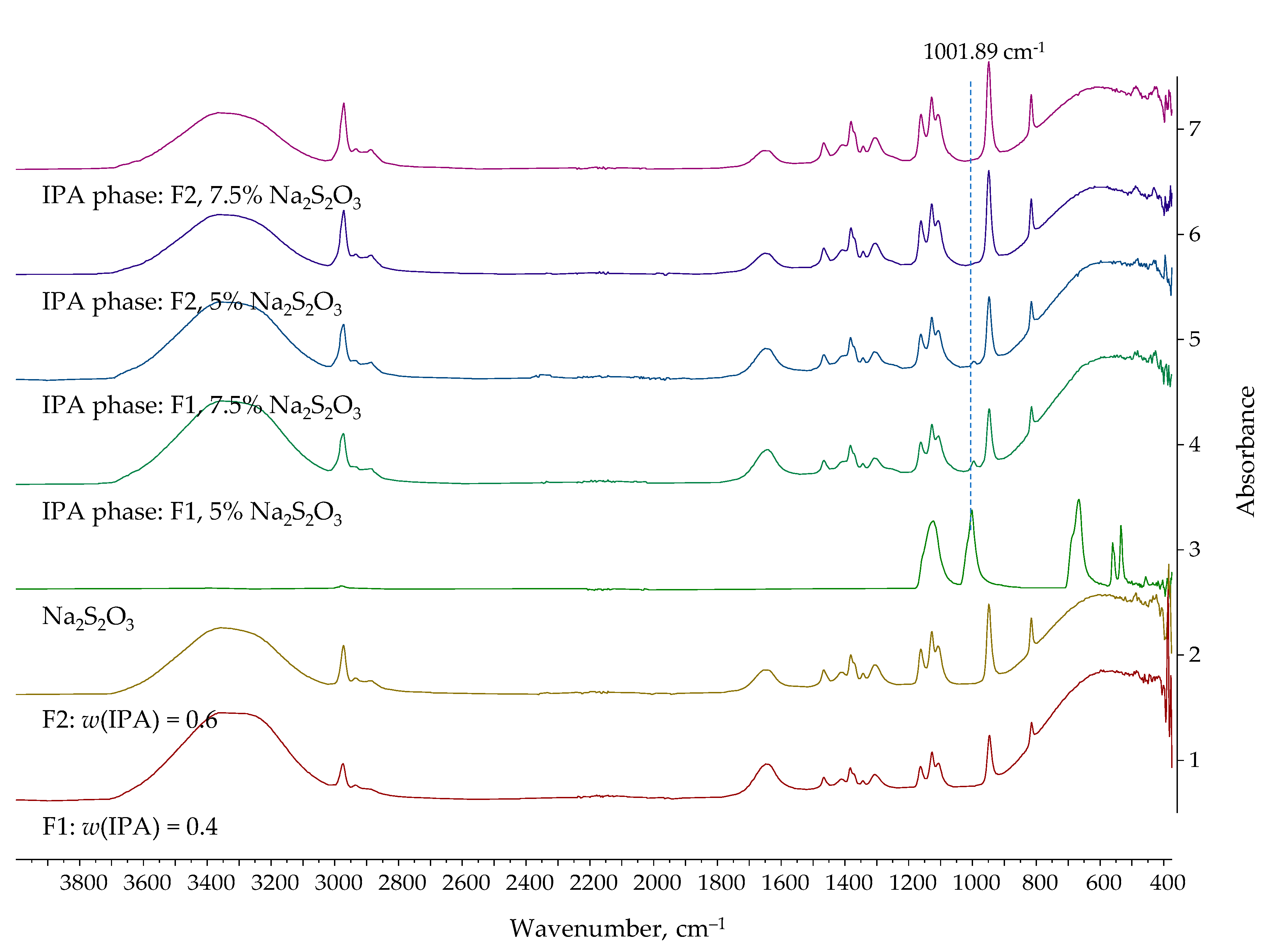
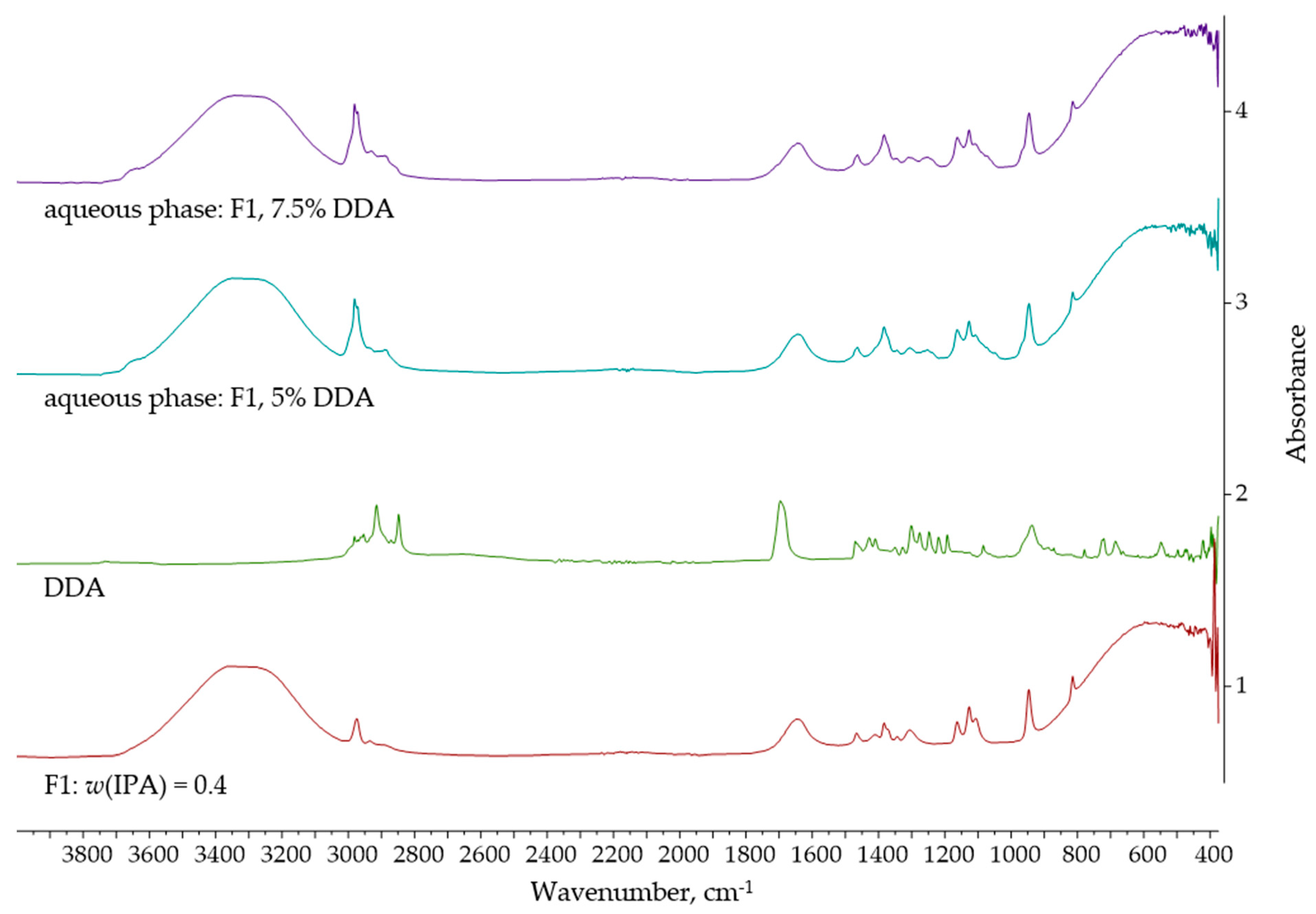
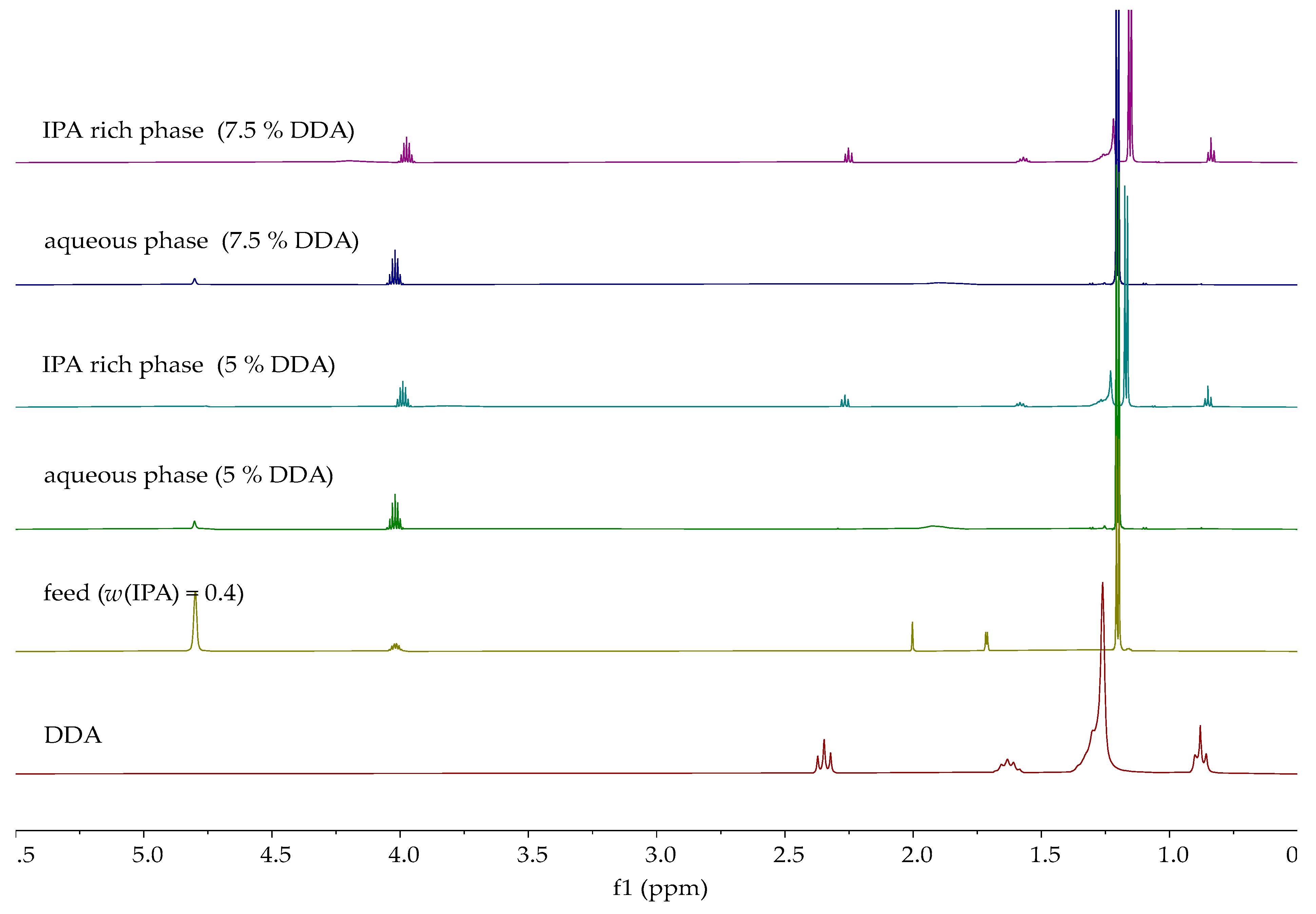
| Entrainer | Feasibility Evaluation | Literature |
|---|---|---|
| 1-pentanol, 1-hexanol, 1-heptanol | LLE determined experimentally, predicted with UNIFAC and COSMO-UNIFAC, and correlated with NRTL and UNIQUAC 1-Heptanol was the best entrainer, based on separation factors and partition coefficients determined | [20] |
| CO2-switchable DESs (molar ratio 1:1): (MEA:BuOH), (MEA:PrOH), (MEA:2-meth), (MEA:3-meth), (MEA:4-meth) hydrophobic DESs (molar ratio 1:1): (T:DA), (DDA:DA] | Liquid–liquid extraction The best entrainer selected based on the distribution coefficient of IPA CO2 switchable (MEA)-based DESs were better than hydrophobic ones | [21] |
| (M:DDA) (2:1), (M:DA) (1:1), (DA:MA) (5:1), (DA:PA) (8:1), (DA:DDA) (3:1) | LLE experimentally determined and correlated with NRTL Selectivity of all DESs was high | [5] |
| HBD:10-undecenoic acid HBA:carvacrol, terpineol, thymol, fenchol, DL-menthol, L-menthol HBD:HBA (1:2; 1:1; 2:1) | Experimental SLE for HDESs Liquid–liquid extraction Efficiency explained by the hydrophobicity of HBA The best HDES was one with DL-menthol as HBA The best molar ratio (HBA:HBD) was (2:1) | [22] |
| Trioctyl ammonium chloride: 1-hexanol Trioctyl ammonium chloride: 1-decanol | LLE experimentally determined and correlated with NRTL trioctyl ammonium chloride:1-decanol was found better, based on determined distribution ratio and separation factor | [23] |
| Ethyl butyrate n-pentyl acetate | LLE was experimentally determined and correlated with modified and extended UNIQUAC Distribution ratio and separation factor were determined | [13] |
| Chemical | Manufacturer | CAS Number |
|---|---|---|
| Isopropyl alcohol, HPLC grade | Fisher Chemical | 67-63-0 |
| Ethanol absolute, p.a. | Alkaloid Skopje | 64-17-5 |
| Choline chloride, 99% | Acros Organics | 67-48-1 |
| Ethylene glycol, p.a. | Lach-Ner | 107-21-1 |
| Glycerol anhydrous | Lach-Ner | 56-81-5 |
| DL-menthol, >98% | Thermo Scientific | 89-78-1 |
| Potassium carbonate, p.a. | Lach-Ner | 584-08-7 |
| Decanoic acid, >98% | TCI | 334-48-5 |
| Dodecanoic acid, >98% | TCI | 143-07-7 |
| Thymol, >98.5% | Gram Mol | 89-83-8 |
| 1-octanol, 99% | Thermo Scientific | 111-87-5 |
| Chemical | Manufacturer | CAS Number |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | VWR | 58-08-2 |
| Glycine | VWR | 56-40-6 |
| Piperine | VWR | 94-62-2 |
| Pentaerythritol | Acros Organics | 115-77-5 |
| Potassium carbonate | Lach-Ner | 584-08-7 |
| Potassium chloride | Kemika d.d. | 7447-40-7 |
| Potassium iodide | VWR | 7681-11-0 |
| Potassium sulfate | Kemika d.d. | 7778-80-5 |
| Sodium carbonate | Lach-Ner | 497-19-8 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Lach-Ner | 144-55-8 |
| Sodium chloride | Kemika d.d. | 7647-14-5 |
| Sodium sulfate | Kemika d.d. | 7757-82-6 |
| Sodium thiosulfate | VWR | 7772-98-7 |
| Sorbitol | VWR | 50-70-4 |
| DES Type | Label | DES |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophilic DESs | DES 1 | ChCl–EG (1:2.5) |
| DES 2 | ChCl–Gly (1:2) | |
| DES 3 | K2CO3–Gly (1:6) | |
| DES 4 | K2CO3–EG (1:10) | |
| Hydrophobic DESs | DES 5 | M–DA (2:1) T–DA (1:1) DA–DDA (2:1) M–O (1:1) |
| DES 6 DES 7 DES 8 |
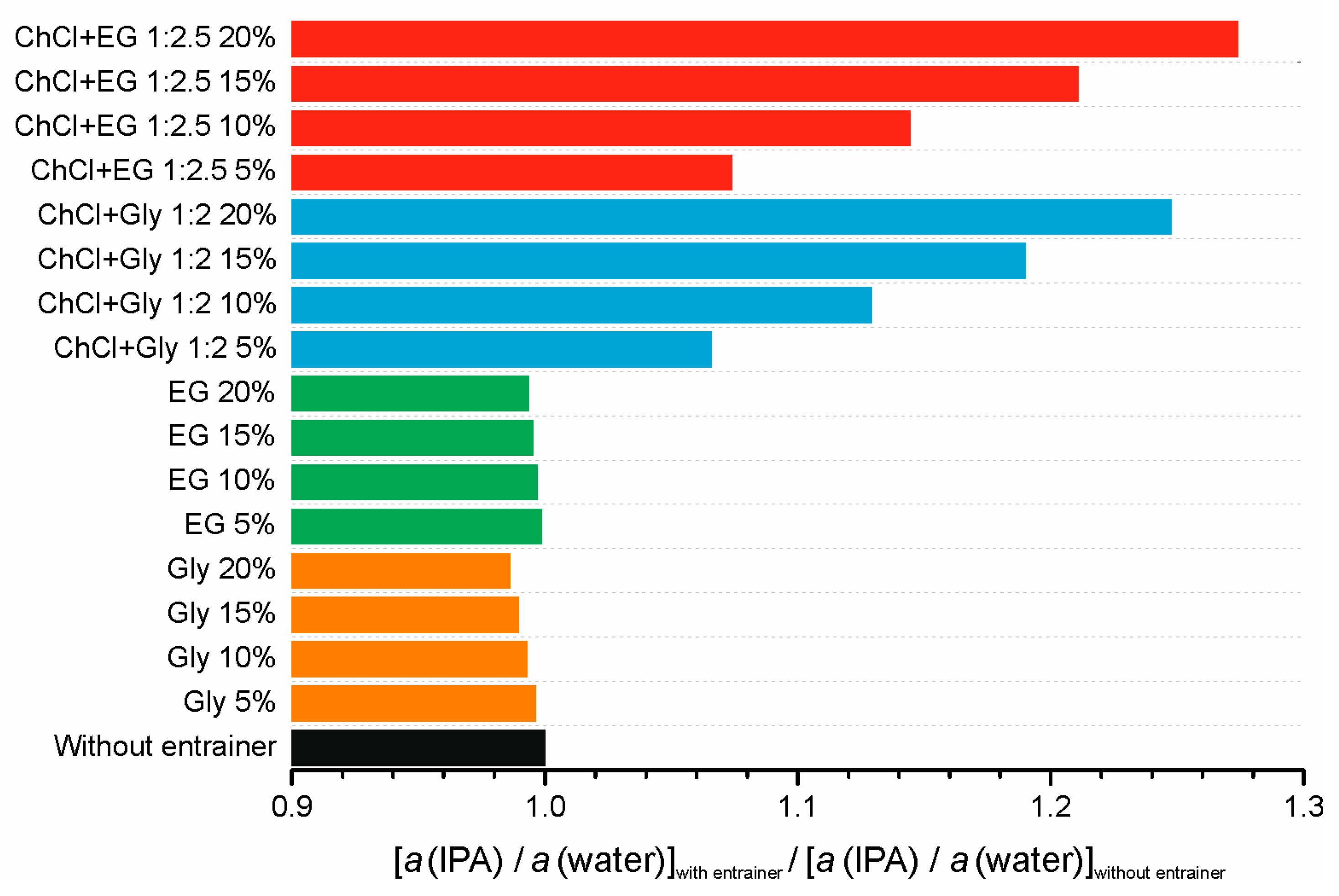
| Entrainer | n(DES)/n(Feed), mol/mol | w(Entrainer), % | w(IPA), % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | 82.29 | - |
| Glycerol | 0.016 | 5 | 82.03 | −0.316 |
| 0.033 | 10 | 83.47 | 1.434 | |
| 0.053 | 15 | 84.14 | 2.248 | |
| 0.075 | 20 | 82.29 | 0 | |
| Ethylene glycol | 0.023 | 5 | 65.39 | −20.537 |
| 0.049 | 10 | 65.20 | −20.768 | |
| 0.079 | 15 | 67.21 | −18.325 | |
| 0.112 | 20 | 77.73 | −5.541 | |
| DES 1 | 0.017 | 5 | 84.94 | 3.220 |
| 0.037 | 10 | 86.40 | 4.995 | |
| 0.058 | 15 | 84.94 | 3.220 | |
| 0.082 | 20 | 82.42 | 0.158 | |
| DES 2 | 0.014 | 5 | 82.68 | 0.474 |
| 0.029 | 10 | 85.35 | 3.719 | |
| 0.045 | 15 | 86.59 | 5.225 | |
| 0.064 | 20 | 85.93 | 4.423 |
| Entrainer | w(IPA)F, % | w(IPA), % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| DES 5 | 0.4 | 16.55 | 58.64 |
| 0.6 | 16.12 | 73.14 | |
| DES 6 | 0.4 | 14.62 | 63.46 |
| 0.6 | 18.26 | 69.57 | |
| DES 7 | 0.4 | 16.97 | 57.57 |
| 0.6 | 20.87 | 65.22 | |
| DES 8 | 0.4 | 16.12 | 59.71 |
| 0.6 | 21.54 | 64.11 |
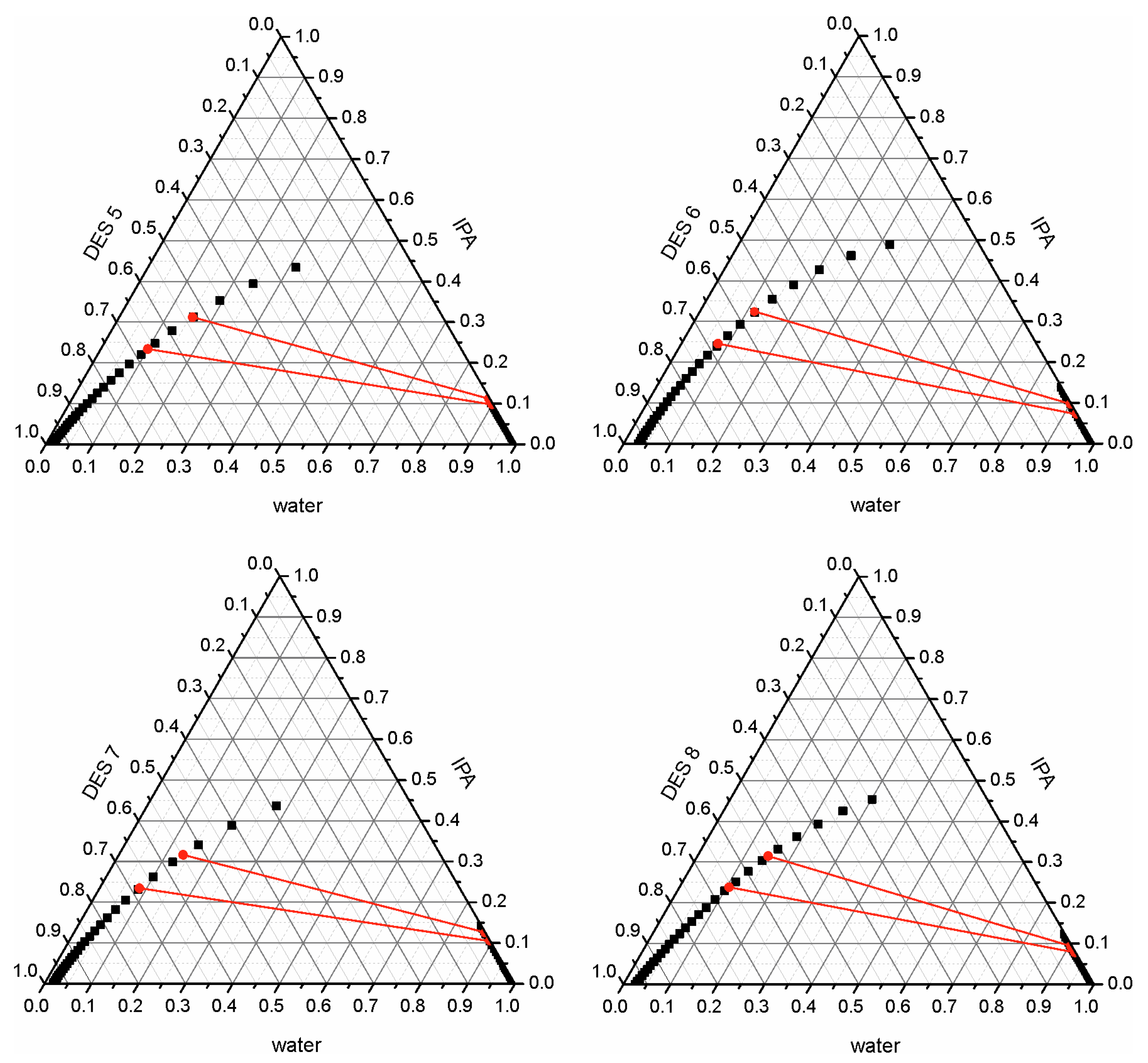
| Entrainer | w(IPA)F, % | Cycle | w(IPA), % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES 5 | 0.6 0.6 | 1 2 | 33.52 - | 44.13 - |
| DES 6 | 0.4 0.4 | 1 2 | 22.67 33.67 | 43.90 15.81 |
| Entrainer | w(IPA)F, % | Stage | w(IPA), % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES 5 | 0.6 | 1 2 3 | 33.52 18.04 10.88 | 44.13 69.93 81.86 |
| DES 6 | 0.4 | 1 2 3 | 22.21 11.11 5.08 | 43.90 72.23 87.30 |
| Entrainer | X (Solubility), g/g | |
|---|---|---|
| Water | IPA | |
| Caffeine | 0.0248 | 0.0382 |
| Glycine | 0.2564 | 0.0031 |
| Piperine | 0.0002 | 0.0415 |
| Pentaerythritol | 0.0786 | 0.0172 |
| Potassium carbonate | 1.8008 | 0.0009 |
| Potassium chloride | 0.3582 | 0.0067 |
| Potassium iodide | 1.4964 | 0.1089 |
| Potassium sulfate | 0.1245 | 0.0005 |
| Sodium carbonate | 0.2163 | 0.0004 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.0566 | 0.0013 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.3611 | 0.0070 |
| Sodium sulfate | 0.2779 | 0.0011 |
| Sodium thiosulfate | 0.8870 | 0.0002 |
| Sorbitol | 1.3181 | 0.0623 |
| Dodecanoic acid | 0.0041 | 1.2000 |
| Choline chloride | 4.3661 | 0.1638 |
| Entrainer | w(IPA)F, % | w(Entrainer), % | w(IPA), % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2CO3 | 40 | 5.0 | 63.24 | 38.73 |
| 7.5 | 70.59 | 50.99 | ||
| 60 | 5.0 | 82.44 | 56.09 | |
| 7.5 | 87.84 | 69.59 | ||
| Na2CO3 | 40 | 5.0 | 65.00 | 41.67 |
| 7.5 | 66.82 | 44.69 | ||
| 60 | 5.0 | 85.48 | 63.71 | |
| 7.5 | 90.25 | 75.63 | ||
| Na2SO4 | 40 | 5.0 | 57.69 | 29.49 |
| 7.5 | 61.52 | 35.87 | ||
| 60 | 5.0 | 80.95 | 52.38 | |
| 7.5 | 79.49 | 48.73 | ||
| Na2S2O3 | 40 | 5.0 | 66.21 | 43.68 |
| 7.5 | 69.31 | 48.85 | ||
| 60 | 5.0 | 81.69 | 54.23 | |
| 7.5 | 85.48 | 63.71 | ||
| Dodecanoic acid | 40 | 5.0 | 36.88 | 7.79 |
| 7.5 | 33.98 | 15.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sander, A.; Rogošić, M.; Frljak, L.; Vasiljević, D.; Blažević, I.; Parlov Vuković, J. Separating 2-Propanol and Water: A Comparative Study of Extractive Distillation, Salting-Out, and Extraction. Separations 2025, 12, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080196
Sander A, Rogošić M, Frljak L, Vasiljević D, Blažević I, Parlov Vuković J. Separating 2-Propanol and Water: A Comparative Study of Extractive Distillation, Salting-Out, and Extraction. Separations. 2025; 12(8):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080196
Chicago/Turabian StyleSander, Aleksandra, Marko Rogošić, Leonarda Frljak, Daniela Vasiljević, Iva Blažević, and Jelena Parlov Vuković. 2025. "Separating 2-Propanol and Water: A Comparative Study of Extractive Distillation, Salting-Out, and Extraction" Separations 12, no. 8: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080196
APA StyleSander, A., Rogošić, M., Frljak, L., Vasiljević, D., Blažević, I., & Parlov Vuković, J. (2025). Separating 2-Propanol and Water: A Comparative Study of Extractive Distillation, Salting-Out, and Extraction. Separations, 12(8), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080196







