Electrochemical Precipitation of Struvite from Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach for Nitrogen Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Swine Wastewater
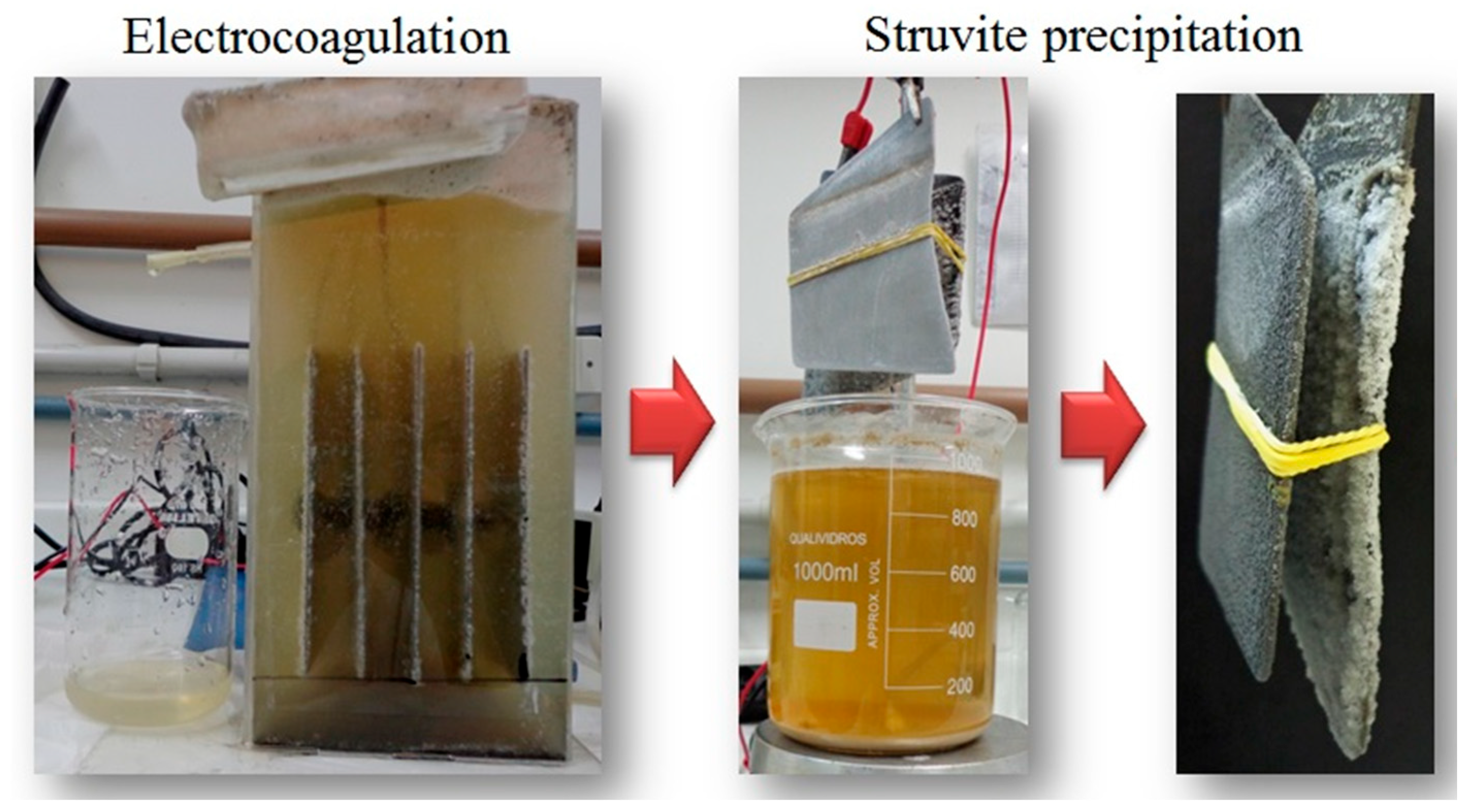
2.2. Electrochemical Precipitation Reactor for Nitrogen Recovery
2.3. Analytical Determinations
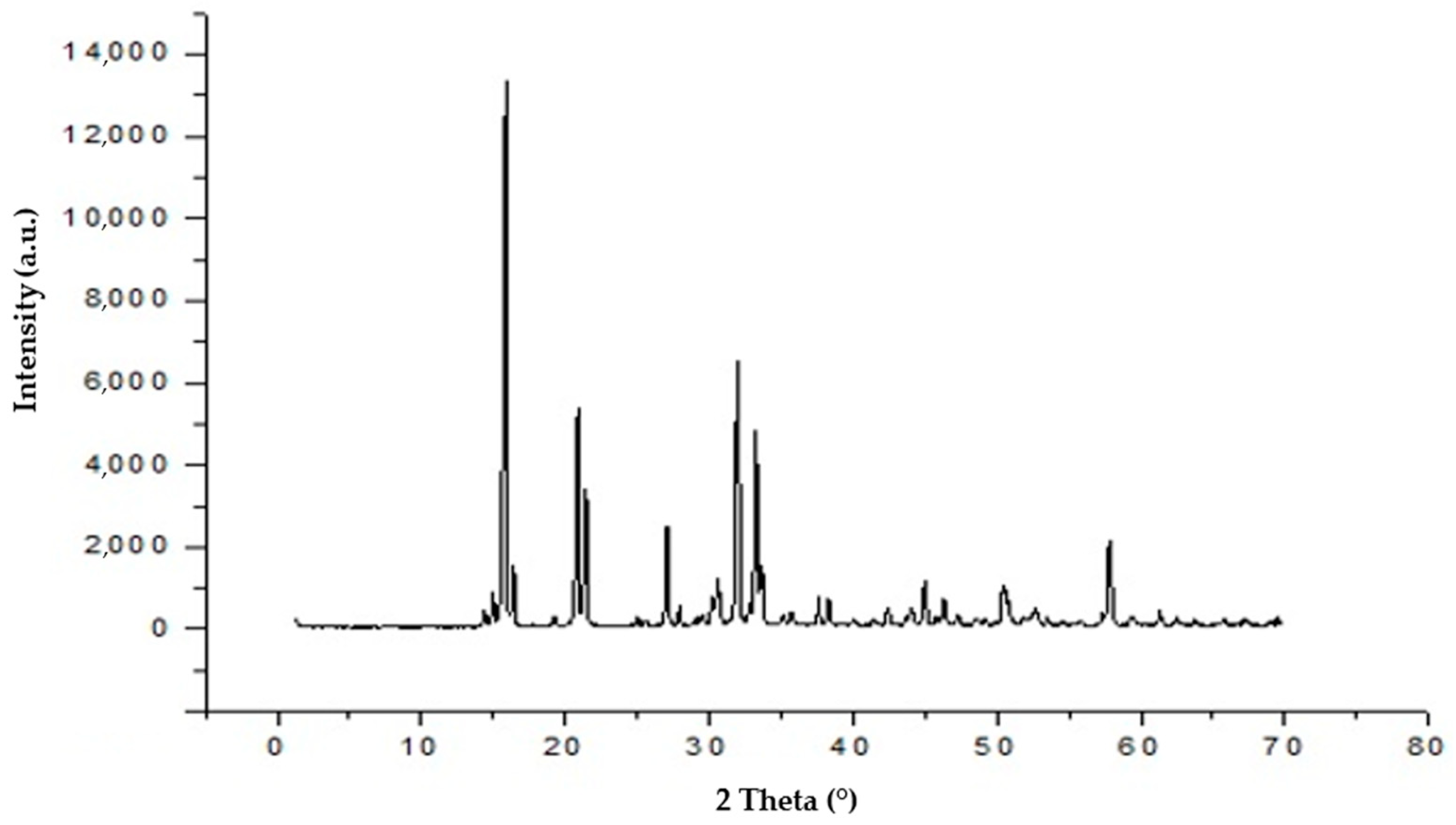
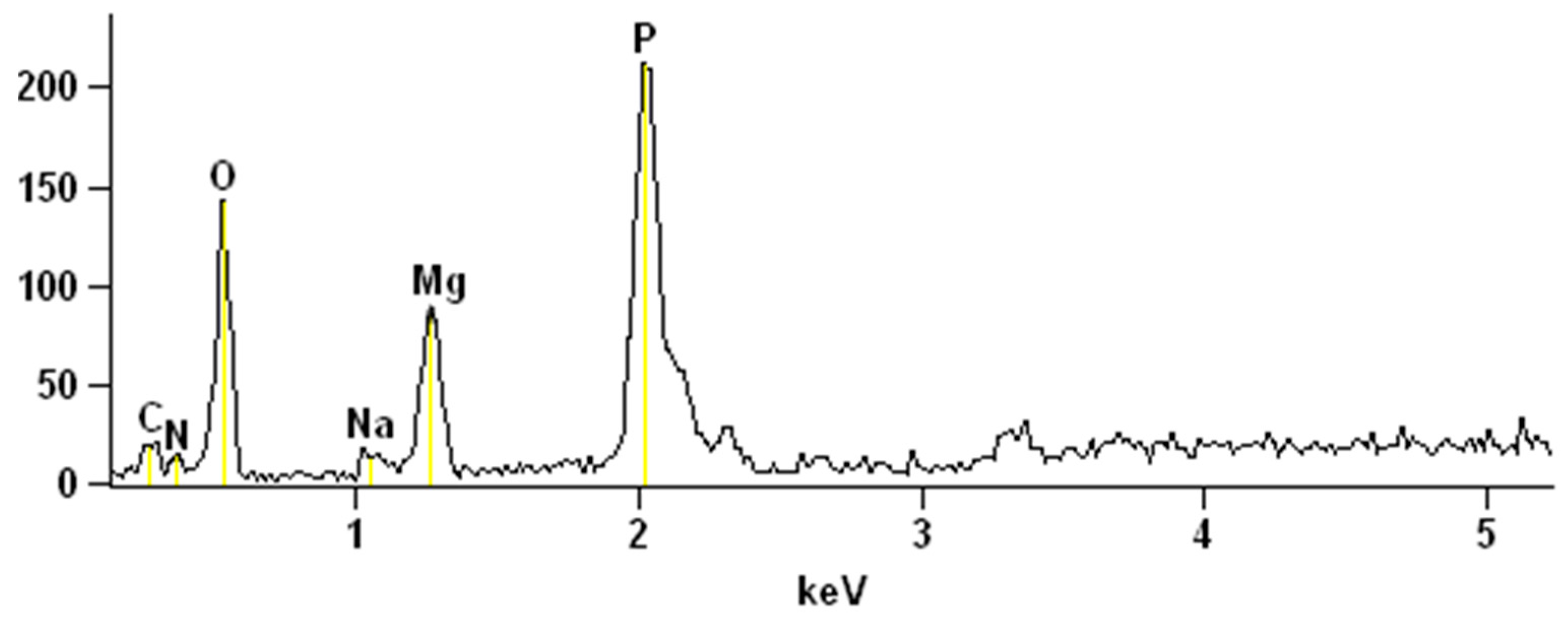
2.4. Struvite Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Electrocoagulation Process
3.2. Electrochemical Struvite Precipitation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ED | Electrode Distance |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
| SOC | Soluble Organic Carbon |
References
- Rahimi, S.; Modin, O.; Mijakovic, I. Technologies for Biological Removal and Recovery of Nitrogen from Wastewater. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, A.K.; Kamei, T.; Amatya, I.M.; Mori, K.; Kazama, F.; Toyama, T. Ammonium-Nitrogen (NH4+-N) Removal from Groundwater by a Dropping Nitrification Reactor: Characterization of NH4+-N Transformation and Bacterial Community in the Reactor. Water 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ali, A.; Su, J.; Huang, T.; Wang, Z. Ammonium Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal by Bacterial-Algal Symbiotic Dynamic Sponge Bioremediation System in Micropolluted Water: Operational Mechanism and Transformation Pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, M.; Zeng, H.; Min, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G. Application of Physicochemical Techniques to the Removal of Ammonia Nitrogen from Water: A Systematic Review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Long, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.M.; Lu, M.; Huang, L.Z. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater by Ceramsite: Adsorption Mechanism, Plant Cultivation and Sustainability Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Zheng, K.; Wan, C.; Li, J. Promising Carbon Utilization for Nitrogen Recovery in Low Strength Wastewater Treatment: Ammonia Nitrogen Assimilation, Protein Production and Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simas, A.; Mores, R.; Steffens, J.; Dallago, R.M.; Kunz, A.; Michelon, W.; Fongaro, G.; Viancelli, A. Electrodisinfection of Real Swine Wastewater for Water Reuse. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Narindri, B.; Chu, H.; Whang, L.M. Recent Advancement on Biological Technologies and Strategies for Resource Recovery from Swine Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwitasari, D.S.; Muryanto, S.; Jamari, J.; Bayuseno, A.P. Kinetics and Morphology Analysis of Struvite Precipitated from Aqueous Solution under the Influence of Heavy Metals: Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddeo, R.; Kolppo, K.; Lepistö, R. Sustainable Nutrients Recovery and Recycling by Optimizing the Chemical Addition Sequence for Struvite Precipitation from Raw Swine Slurries. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.J.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A.A.; García-González, M.C. Enhancing Recovery of Ammonia from Swine Manure Anaerobic Digester Effluent Using Gas-Permeable Membrane Technology. Waste Manag 2016, 49, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Zhao, N.; Guo, G.; Young, B. Influence of Process Parameters on the Heavy Metal (Zn2+, Cu2+ and Cr3+) Content of Struvite Obtained from Synthetic Swine Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Sun, C.; Ma, G.; Zhang, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.Y.; et al. Anaerobic Treatment of Nitrogenous Industrial Organic Wastewater by Carbon–Neutral Processes Integrated with Anaerobic Digestion and Partial Nitritation/Anammox: Critical Review of Current Advances and Future Directions. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 415, 131648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Arya, S.; Kumar, S. Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Current Trends, Bottlenecks, and Best Practices. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, J.Y.; Chang, C.Y. Removal of Ammonia from Wastewater by Air Stripping Process in Laboratory and Pilot Scales Using a Rotating Packed Bed at Ambient Temperature. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 60, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.L.; Chen, L.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Yu, C.P.; Ma, H.W.; Chiang, P.C. Advanced Ammonia Nitrogen Removal and Recovery Technology Using Electrokinetic and Stripping Process towards a Sustainable Nitrogen Cycle: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, I.T.; Park, G.I.; Lee, E.H. Electrochemical Conversion Characteristics of Ammonia to Nitrogen. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, B.M.; Meier, E.A.; Hunt, J.R.; McBeath, T.M.; Llewellyn, R.S. A Modelled Quantification of Reduced Nitrogen Fertiliser Requirement and Associated Trade-Offs from Inclusion of Legumes and Fallows in Wheat-Based Crop Sequences. Field Crops Res. 2024, 307, 109236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhang, H.; Krampe, J.; Muster, T.; Gao, B.; Zhu, N.; Jin, B. Applying a Chemical Equilibrium Model for Optimizing Struvite Precipitation for Ammonium Recovery from Anaerobic Digester Effluent. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Shih, K. Effects of Calcium and Ferric Ions on Struvite Precipitation: A New Assessment Based on Quantitative X-Ray Diffraction Analysis. Water Res. 2016, 95, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Phosphorus Recovery from Wastewater by Struvite Crystallization: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 433–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muryanto, S.; Bayuseno, A.P. Influence of Cu2+ and Zn2+ as Additives on Crystallization Kinetics and Morphology of Struvite. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, L. Characterization of Morphology and Component of Struvite Pellets Crystallized from Sludge Dewatering Liquor: Effects of Total Suspended Solid and Phosphate Concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Han, Z.; Lin, X.; Du, J.; Lei, Z.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, J. Mechanisms of Releasing Magnesium Ions from a Magnesium Anode in an Electrolysis Reactor with Struvite Precipitation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Hu, C. Enhanced Struvite Generation and Separation by Magnesium Anode Electrolysis Coupled with Cathode Electrodeposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.J.; Elektorowicz, M.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Struvite Precipitation and Phosphorus Removal Using Magnesium Sacrificial Anode. Chemosphere 2014, 101, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabe, Y.; Ota, N.; Fujiyama, M.; Okayasu, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Minamiyama, M. Utilisation of Polarity Inversion for Phosphorus Recovery in Electrochemical Precipitation with Anaerobic Digestion Effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mores, R.; Kunz, A.; Steffens, J.; Dallago, R.M.; Benazzi, T.L.; do Amaral, A.C. Swine Manure Digestate Treatment Using Electrocoagulation. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzi, T.L.; Di Luccio, M.; Dallago, R.M.; Steffens, J.; Mores, R.; Do Nascimento, M.S.; Krebs, J.; Ceni, G. Continuous Flow Electrocoagulation in the Treatment of Wastewater from Dairy Industries. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kabdaşli, I.; Parsons, S.A.; Tünay, O. Effect of Major Ions on Induction Time of Struvite Precipitation. Croat. Chem. Acta 2006, 79, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Yetilmezsoy, K.; Ilhan, F.; Kocak, E.; Akbin, H.M. Feasibility of Struvite Recovery Process for Fertilizer Industry: A Study of Financial and Economic Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irdemez, Ş.; Demircioǧlu, N.; Yildiz, Y.Ş.; Bingül, Z. The Effects of Current Density and Phosphate Concentration on Phosphate Removal from Wastewater by Electrocoagulation Using Aluminum and Iron Plate Electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceni, G.; Mores, R.; Demaman Oro, C.E.; Denti, A.F.; Tres, B.P.; Venquiaruto, L.D.; Dallago, R.M.; Steffens, J.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V. Addition of Hydrogen Peroxide in Electrocoagulation of Dairy Liquids. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 5978–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Boiarkina, I.; Young, B.; Yu, W. Quantification and Mitigation of the Negative Impact of Calcium on Struvite Purity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 2354–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutnik, N.; Stanclik, A.; Piotrowski, K.; Matynia, A. Size-Dependent Growth Kinetics of Struvite Crystals in Wastewater with Calcium Ions. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, S.A.; Doyle, J.D. Struvite Formation, Control and Recovery. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3925–3940. [Google Scholar]
- Hug, A.; Udert, K.M. Struvite Precipitation from Urine with Electrochemical Magnesium Dosage. Water Res. 2013, 47, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, R.V.S.S.N.; Chandrasekhar, A.V.; Ramakrishna, C.; Reddy, Y.P. X-Ray Powder Diffraction, Thermal Analysis and IR Studies of Zinc Ammonium Phosphate Hexahydrate. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2010, 4, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tansel, B.; Lunn, G.; Monje, O. Struvite Formation and Decomposition Characteristics for Ammonia and Phosphorus Recovery: A Review of Magnesium-Ammonia-Phosphate Interactions. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagastyo, A.Y.; Anggrainy, A.D.; Khoiruddin, K.; Ursada, R.; Warmadewanthi, I.D.A.A.; Wenten, I.G. Electrochemically-Driven Struvite Recovery: Prospect and Challenges for the Application of Magnesium Sacrificial Anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Wastewater Pre-Treated by UASB | After Electrocoagulation | Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (mS·cm−1) | 11.5 | 8.01 | 30 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 1179.2 | 22.4 | 98 |
| SOC (mg·L−1) | 4001.0 | 1572.5 | 61 |
| P (mg·L−1) | 76.5 | 1.1 | 98 |
| Cu (mg·L−1) | 2.0 | 0.3 | 85 |
| Zn (mg·L−1) | 7.9 | <DL | 100 |
| Fe (mg·L−1) | 7.8 | 19.3 | - |
| Ca (mg·L−1) | 1214.0 | 43.7 | 96 |
| Mg (mg·L−1) | 34.4 | 25.7 | 25 |
| K (mg·L−1) | 609.0 | 480.0 | 21 |
| Alkalinity (mgCaCO3 L−1) | 3414.7 | 2099.3 | 38 |
| Ammonium (mg·L−1) | 1221.0 | 1121.0 | 8 |
| Nitrate (mg·L−1) | <DL * | <DL * | - |
| Nitrite (mg·L−1) | <DL * | <DL * | - |
| 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm | 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) | NH3(mg·L−1) | P (mg·L−1) | NH3(mg·L−1) | P (mg·L−1) | NH3(mg·L−1) | P (mg·L−1) | NH3(mg·L−1) | P (mg·L−1) |
| 0 | 1168 (0%) | 2063 (0%) | 1116 (0%) | 1935 (0%) | 2000 (0%) | 1184 (0%) | 1740 (0%) | 1550 (0%) |
| 2 | 984 (16%) | 1853 (10%) | 1217 (0%) | 1830 (1%) | 1760 (12%) | 948 (20%) | 1800 (0%) | 1326 (14%) |
| 4 | 983 (16%) | 1763 (15%) | 1087 (3%) | 1920 (5%) | 1140 (43%) | 420 (60%) | 1235 (29%) | 1065 (31%) |
| 6 | 891 (24%) | 1725 (16%) | 894 (20%) | 1660 (14%) | 860 (57%) | 469 (65%) | 1079 (38%) | 933 (40%) |
| Yield (g) | 5.12 | 4.33 | 15.19 | 11.32 | ||||
| Elements | 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm | 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg (g/100 g) | 22.16 ± 0.15 | 15.44 ± 0.85 | 17.78 ± 0.15 | 19.25 ± 0.08 |
| N_NH3 (g/100 g) | 1.59 ± 0.25 | 4.49 ± 0.17 | 5.34 ± 0.03 | 4.73 ± 0.14 |
| P (g/100 g) | 14.52 ± 0.19 | 11.48 ± 0.48 | 12.60 ± 0.19 | 11.83 ± 0.36 |
| Compounds | NH4MgPO4·6H2O | Mg3(PO4)2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 245.3 g/mol | 264.0 g/mol | |||
| Elements | Mg | N | P | Mg | P |
| Contribution of mass to the molecular weight of struvite | 24.3 | 14.0 | 31.0 | 72.9 | 62.0 |
| Percentage contribution (%) | 9.9 | 5.7 | 12.6 | 27.6 | 23.5 |
| Stoichiometry | 1.74 | 1.0 | 2.21 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| P/Mg ratio | 1.28 | 0.85 | |||
| Conditions | Mg (g/100 g) | N_NH3 (g/100 g) | P (g/100 g) | Stoichiometry | Linked to Struvite | Not Linked to Struvite | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | N | P | Mg * (%) | P * (%) | Mg * (%) | P * (%) | Relação Mg/P | ||||
| 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 22.16 ± 0.15 | 1.59 ± 0.25 | 14.52 ± 0.19 | 13.92 | 1 | 9.12 | 12.50 | 24.23 | 12.28 | 6.91 | 0.56 |
| 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 1 cm | 15.44 ± 0.85 | 5.34 ± 0.03 | 12.60 ± 0.19 | 2.89 | 1 | 2.36 | 60.17 | 93.65 | 1.25 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| 2.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm | 19.25 ± 0.08 | 4.49 ± 0.07 | 11.48 ± 0.48 | 4.28 | 1 | 2.56 | 40.61 | 86.48 | 2.64 | 0.35 | 0.13 |
| 7.5 mA·cm−2 and 3 cm | 17.78 ± 0.15 | 4.73 ± 0.14 | 11.83 ± 0.36 | 3.76 | 1 | 2.50 | 46.24 | 88.32 | 2.12 | 0.29 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mores, R.; Cunha Junior, A.; Antes, F.G.; Di Luccio, M.; Oro, C.E.D.; Tres, M.V.; Steffens, C.; Steffens, J.; Kunz, A.; Dallago, R.M. Electrochemical Precipitation of Struvite from Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach for Nitrogen Recovery. Separations 2025, 12, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050108
Mores R, Cunha Junior A, Antes FG, Di Luccio M, Oro CED, Tres MV, Steffens C, Steffens J, Kunz A, Dallago RM. Electrochemical Precipitation of Struvite from Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach for Nitrogen Recovery. Separations. 2025; 12(5):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMores, Rúbia, Anildo Cunha Junior, Fabiane Goldschmidt Antes, Marco Di Luccio, Carolina E. Demaman Oro, Marcus V. Tres, Clarice Steffens, Juliana Steffens, Airton Kunz, and Rogério Marcos Dallago. 2025. "Electrochemical Precipitation of Struvite from Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach for Nitrogen Recovery" Separations 12, no. 5: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050108
APA StyleMores, R., Cunha Junior, A., Antes, F. G., Di Luccio, M., Oro, C. E. D., Tres, M. V., Steffens, C., Steffens, J., Kunz, A., & Dallago, R. M. (2025). Electrochemical Precipitation of Struvite from Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach for Nitrogen Recovery. Separations, 12(5), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12050108








