Green Protein Extraction from Hazelnut Press Cake: Yield, Efficiency, and Secondary Structure Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Proximate Composition of HPCF
2.3. Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Preparation
2.4. Protein Extraction from HPCF
2.4.1. Acid–Alkali (ALKIS) Extraction
2.4.2. Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Extraction
2.4.3. Determination of Protein Yield and Extraction Rate
2.4.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance–Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR)
2.4.5. Protein Secondary Structure Quantification
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Proximate Composition HPCF
3.2. Protein Yield and Extraction Rate
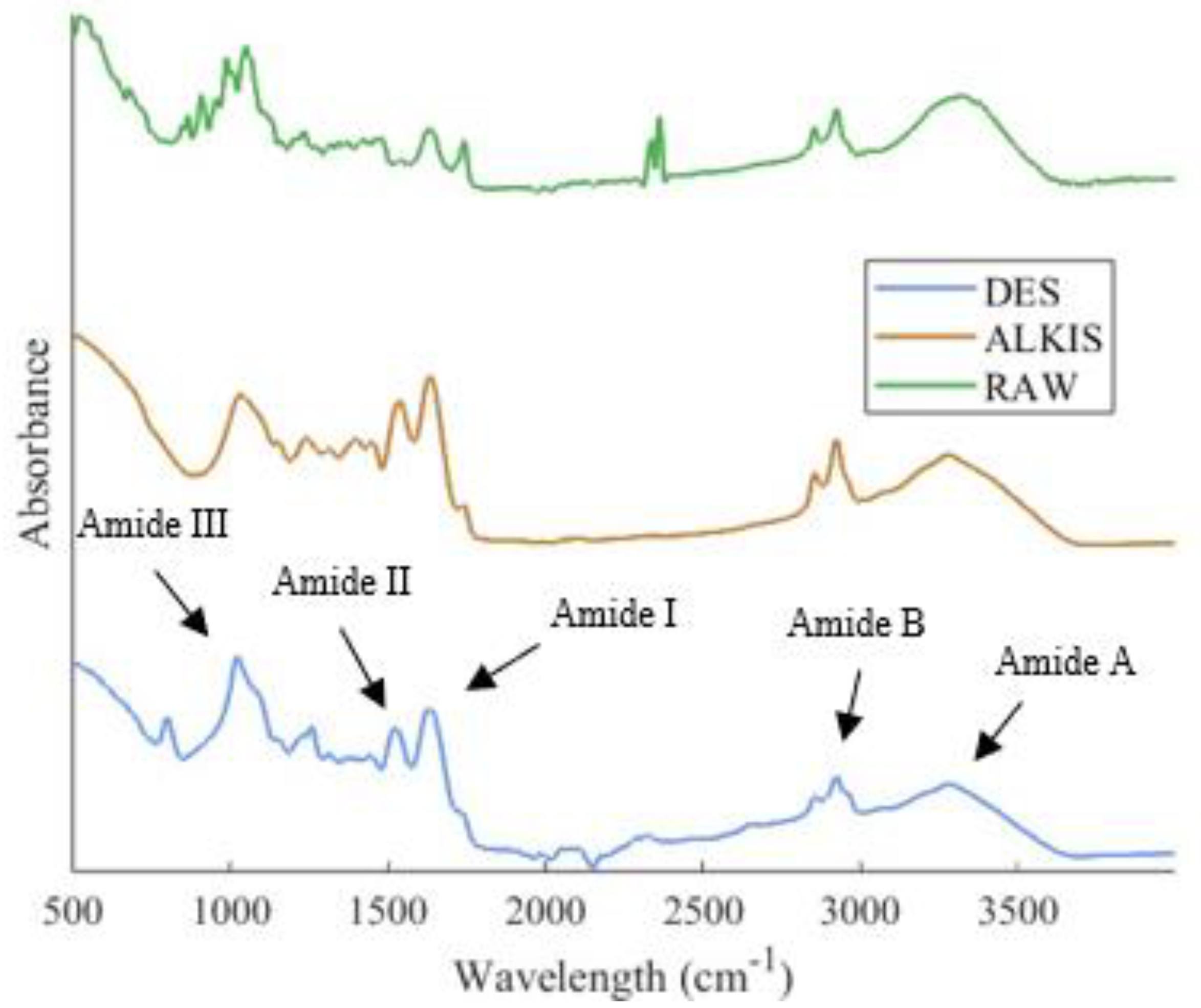
3.3. Protein Secondary Structure Analysis Via ATR-FTIR
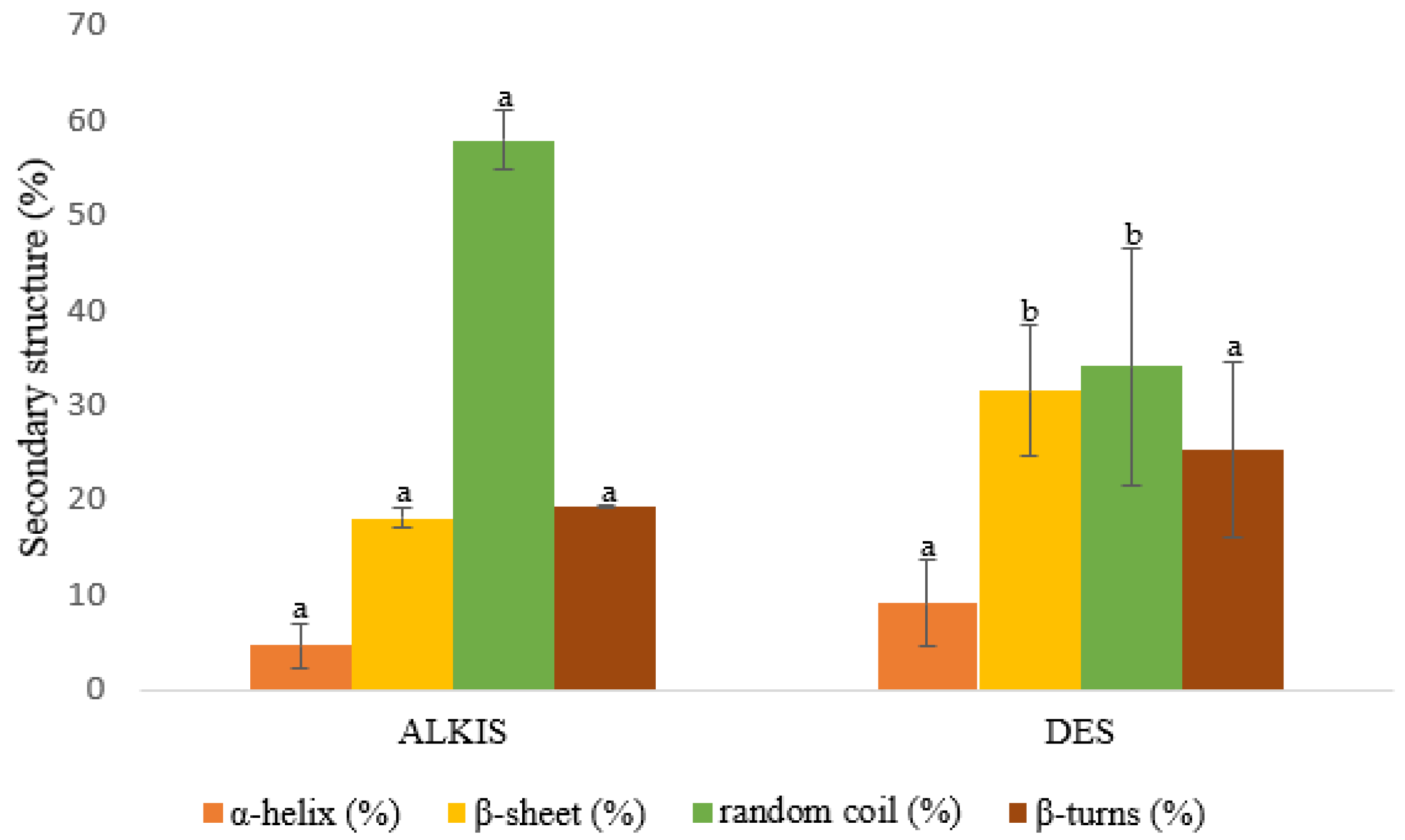
3.4. Secondary Structure of Protein: Amide I Deconvolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture Towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012; pp. 1–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, H.; Lin, Z. Hazelnut and its by-products: A comprehensive review of nutrition, phytochemical profile, extraction, bioactivities and applications. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nera, E.; Paas, W.; Reidsma, P.; Paolini, G.; Antonioli, F.; Severini, S. Assessing the Resilience and Sustainability of a Hazelnut Farming System in Central Italy with a Participatory Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobhal, K.; Singh, N.; Semwal, A.; Negi, A. A brief review on: Hazelnuts. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2018, 9, 23680–23684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, A.; Salvaneschi, P.; Schirone, B.; Cianfaglione, K.; Michele, A.D. Multipurpose plant species and circular economy: Corylus avellana L. as a study case. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursa, K.; Toker, O.S.; Palabiyik, I.; Yaman, M.; Kian-Pourd, N.; Konar, N.; Kilicli, M. Valorization of hazelnut cake in compound chocolate: The effect of formulation on rheological and physical properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 139, 110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, K.; Gantner, M.; Piotrowska, A. The Quality Characteristic and Fatty Acid Profile of Cold-Pressed Hazelnut Oils during Nine Months of Storage. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.B.; Kılıçarslan, E.; Demir, H.; Koca, E.; Salum, P.; Berktaş, S.; Çam, M.; Erbay, Z.; Aydemir, L.Y. Upgrading the Bioactive Potential of Hazelnut Oil Cake by Aspergillus oryzae under Solid-State Fermentation. Molecules 2024, 29, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Potkule, J.; Verma, R.; Punia, S.; Mahapatra, A.; Belwal, T.; Dahuja, A.; Joshi, S.; Berwal, M.K.; et al. Advances in the plant protein extraction: Mechanism and recommendations. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, J.; Ngadi, M. Ultrasound-assisted processing: Science, technology and challenges for the plant-based protein industry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgüç, A.; Özer, P.; Yılmaz, F.M. Microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction of plant protein with antioxidant compounds from the food waste sesame bran: Comparative optimization study and identification of metabolomics using LC/Q-TOF/MS. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 44, e14304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyüz, A.; Ersus, S. Optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction of protein from the sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) leaves for alternative plant protein concentrate production. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green chemistry: Principles and practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Hadinoto, K. Deep Eutectic Solvent as Green Solvent in Extraction of Biological Macromolecules: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Chan, Y.S.; Nandong, J.; Chin, S.F.; Ho, B.K. Formulation of choline chloride/ascorbic acid natural deep eutectic solvent: Characterization, solubilization capacity and antioxidant property. LWT 2020, 133, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, S.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Costanzo, P.; Maiuolo, L.; Tallarico, S.; Nardi, M. Natural deep eutectic solvent as extraction media for the main phenolic compounds from olive oil processing wastes. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ran, L.; Chen, N.; Fan, X.; Ren, D.; Yi, L. Polarity-dependent extraction of flavonoids from citrus peel waste using a tailor-made deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, S.; Gerçek, Y.C.; Kutlu, N.; Bayram, S.; Kırkıncı, S.; Bayram, N.E. Ultrasonic assisted extraction of water-soluble vitamins from minor components of bee pollen with deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as green solvent. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Deep eutectic solvent assists Bacillus australimaris to transform alkali lignin waste into small aromatic compounds. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Ma, L. Exploring carbohydrate extraction from biomass using deep eutectic solvents: Factors and mechanisms. iScience 2023, 26, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsirichot, P.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; Winterburn, J. Holistic valorization of rapeseed meal utilizing green solvents extraction and biopolymer production with Pseudomonas putida. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.H.; Zhang, C.X.; Ma, Y.X.; Yu, Y.M.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, X.D.; Zheng, Y.Z. Extraction of protein from sesame meal: Impact of deep eutectic solvents on protein structure and functionality. LWT 2023, 187, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Bhowmik, P.; Yang, T.C.; Samaranayaka, A.; Chen, L. Extraction of canola protein via natural deep eutectic solvents compared to alkaline treatments: Isolate characteristics and protein structural and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 152, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudniewska, A.; de Melo, E.M.; Chan, A.; Gniłka, R.; Boratyński, F.; Matharu, A.S. Enhanced protein extraction from oilseed cakes using glycerol–choline chloride deep eutectic solvents: A biorefinery approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14842–14850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, E.; La Nasa, J.; Ribechini, E.; Petri, A.; Piccolo, O. Extraction of proteins and residual oil from flax (Linum usitatissimum), camelina (Camelina sativa), and sunflower (Helianthus annuus) oilseed press cakes. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 13, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C.; Wang, W. Deep eutectic solvents and alkaline extraction of protein from seabuckthorn seed meal: A comparison study. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helstad, A.; Forsén, E.; Ahlström, C.; Mayer Labba, I.-C.; Sandberg, A.-S.; Rayner, M.; Purhagen, J.K. Protein extraction from cold-pressed hempseed press cake: From laboratory to pilot scale. J. Food Sci. 2021, 87, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermoula, P.; Virgili, C.; Ortega, R.G.; Mullen, A.M.; Álvarez, C.; O’Brien, N.M.; O’Flaherty, E.A.A.; O’Neill, E.E. Functional protein rich extracts from bovine and porcine hearts using acid or alkali solubilisation and isoelectric precipitation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-R.; Peng, N.; Li, Y.-Q.; Liang, Y.; Guo, Z.-W.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, X. Physicochemical properties, structural characteristics, and protein digestibility of pea protein-wheat gluten composited meat analogues prepared via high-moisture extrusion. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, B.; Qoms, M.S.; Wan Ibadullah, W.Z.; Saari, N. Innovative deep eutectic solvent approach vs. conventional alkaline for kenaf seed protein extraction: A comprehensive comparison of structural, thermal, nutritional and techno-functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 102, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldes, D.; Requejo, P.F.; Vega, M.; Bolado, S.; Wijffels, R.H.; Kazbar, A. Protein extraction from seaweed Saccharina latissima with deep eutectic solvents. Microchem. J. 2024, 205, 111275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tintor, Đ.; Ninković, K.; Milošević, J.; Polović, N.Đ. Gaining insight into protein structure via ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2024, 134, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, F.D.; Adrar, N.; Günal-Köroğlu, D.; Gültekin Subaşı, B.; Capanoglu, E. Combined Neutrase–Alcalase Protein Hydrolysates from Hazelnut Meal, a Potential Functional Food Ingredient. ACS Omega 2022, 8, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.Z.; He, J.X.; Mo, H.Z. Physicochemical, Functional and Antioxidant Properties of Mung Bean Protein Enzymatic Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Prevost, S.; Wahlgren, M. Deep eutectic solvents for the preservation of concentrated proteins: The case of lysozyme in 1:2 choline chloride:glycerol. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4437–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Yang, H.; Qin, S.; Hong, L.; Pu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Study of the molecular structure of proteins in fermented maize-soybean meal-based rations based on FTIR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, S.; Maruyama, N.; Satoh, R.; Adachi, M. Structure–function relationships of soybean proteins revealed by using recombinant systems. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, F.S.; Xue, W.T.; Lee, L. FTIR spectra studies on the secondary structures of 7S and 11S globulins from soybean proteins using AOT reverse micellar extraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Proximate Composition (%) | Mean Value (%) | ± |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture (% w/w, wet HPCF basis) | 11.82 | 0.01 |
| Proteins (% w/w, dry HPCF basis) | 42.44 | 2.85 |
| Carbohydrates (% w/w, dry HPCF basis) | 24.69 | 2.96 |
| Lipids (% w/w, dry HPCF basis) | 18.87 | 0.73 |
| Ashes (% w/w, dry HPCF basis) | 2.18 | 0.32 |
| Wavelength Range (cm−1) | Secondary Structure | Peak Number |
|---|---|---|
| 1650–1660 | α-helix | Peak 1 |
| 1600–1640 | β-sheet | Peak 2 |
| 1640–1650 | random coils | Peak 3 |
| 1660–1700 | β-turns | Peak 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anzà, B.; Fraterrigo Garofalo, S.; Lapolla, A.; Fino, D. Green Protein Extraction from Hazelnut Press Cake: Yield, Efficiency, and Secondary Structure Analysis. Separations 2025, 12, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030063
Anzà B, Fraterrigo Garofalo S, Lapolla A, Fino D. Green Protein Extraction from Hazelnut Press Cake: Yield, Efficiency, and Secondary Structure Analysis. Separations. 2025; 12(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnzà, Bruna, Silvia Fraterrigo Garofalo, Alessandro Lapolla, and Debora Fino. 2025. "Green Protein Extraction from Hazelnut Press Cake: Yield, Efficiency, and Secondary Structure Analysis" Separations 12, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030063
APA StyleAnzà, B., Fraterrigo Garofalo, S., Lapolla, A., & Fino, D. (2025). Green Protein Extraction from Hazelnut Press Cake: Yield, Efficiency, and Secondary Structure Analysis. Separations, 12(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030063






