Abstract
The application of microsphere molecularly imprinted materials for the targeted extraction and purification of flavonoids derived from agricultural waste has emerged as a prominent area of investigation. An innovative boronate affinity imprinted microsphere (MC-CD@BA-MIP) was successfully synthesized using the Pickering emulsion interfacial assembly strategy for the selective separation of naringin (NRG). The double-bond functionalized covalent organic framework (COF)-based microspheres were synthesized through Schiff–base reaction and secondary interfacial emulsion polymerization. Then, the synthetic mono-(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin (SH-β-CD) was grafted onto the surface of the microspheres (MC) using click chemistry. The 1-allylpyridine-3-boronic acid (APBA) as a functional monomer was grafted onto the initiator (ABIB) through atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). Ultimately, the synthesized boronic acid-imprinted ABIB-BA-MIPs were immobilized onto the COFs microsphere surface through host–guest interactions. As expected, under neutral conditions, the MC-CD@BA-MIPs still exhibited a significant adsorption capacity (38.78 μmol g−1 at 308 K) for NRG. The regenerated MC-CD@BA-MIPs maintained 92.56% of their initial adsorption capacity through six consecutive cycles.
1. Introduction
Agricultural waste pollution has evolved into a critical ecological threat amid global population growth and agricultural intensification. Conventional disposal methods like landfilling and incineration not only inefficiently utilize land resources but also trigger cascading environmental consequences: increased greenhouse gas emissions, soil/groundwater contamination, and biodiversity decline [1]. This challenge is exemplified by China, with 1.5 million metric tons of pomelo peel waste being generated annually [2]. If not managed properly, these organic residues become significant environmental pollutants. Notably, pomelo peels are rich in bioactive compounds, particularly the pharmaceutically valuable flavonoid naringin (NRG). As a prototypical flavonoid, a lot of studies have focused on NRG due to its characteristic cis-diol structure and broad biomedical potential (e.g., analgesic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer activities) [3]. Efficient flavonoid extraction from agricultural waste is pivotal for resource utilization. Current NRG isolation methods primarily include ultrasonic extraction [4], microwave extraction [5], and supercritical CO2 extraction [6]. However, these techniques suffer from some limitations: high organic solvent consumption, substantial energy requirements, and expensive equipment. In contrast, adsorption emerges as the preferred approach for the extraction of bioactive flavonoids from agricultural waste, offering distinct advantages: operational simplicity, cost-effectiveness, high adsorption capacity, and minimal bioactivity impairment of target compounds [7]. In recent years, significant attention has been directed toward boronic acid-based affinity materials due to their efficacy in the selective capture of NRG. This capability stems from the reversible covalent bonding inherent between boronic acid functional groups and cis-diol moieties [8]. The core principle of boronic acid affinity separation lies in the reversible covalent binding between the phenylboronic acid moiety (-B(OH)2) and cis-diol-containing compounds. Under alkaline conditions (pH > pKa), the boronic acid transforms into a negatively charged boronate species (-B(OH)3−), which forms a stable five-membered cyclic ester bond with the cis-diol [9]. Hu et al. [10] developed boronate-functionalized organic/inorganic hybrid copolymers that successfully purified crude NRG with an efficiency of 92.68% via a triple sacrificial cross-linking strategy. Yao et al. [11] fabricated an innovative boronate-functionalized cellulose foam for the specific purpose of glycoprotein enrichment. However, the performance of conventional boronate affinity materials is constrained by multiple factors, including elevated binding energy requirements during operation, diffusion-limited kinetics constrained by low specific surface area, and competitive binding interference from co-existing cis-diol-containing compounds in agricultural waste matrices. Consequently, developing adsorbents featuring high-density recognition sites and superior selectivity constitutes a paramount objective for achieving efficient separation and purification of NRG.
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) constitute a type of highly ordered porous material constructed from organic molecular building blocks linked via robust covalent bonds. They are considered promising candidates for applications in catalysis, separation, and energy storage because of their well-defined periodic architectures and tunable porosity. The density of binding sites in adsorbents is significantly increased by their inherently high specific surface area, while subsequent functionalization is facilitated by their tunable pore sizes and robust chemical stability [12,13]. The inherently tunable porosity and exceptional stability of COFs have driven widespread research into their application for molecular separations over the past decade. For instance, Su et al. [14] prepared surface-imprinted polymers on covalently cross-linked COFs for the selective extraction of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from complex food samples. Wang et al. [15] engineered robust COFs exhibiting exceptional acid stability and tailored porosity to enable selective capture of aryl-organophosphorus flame retardants in water. Liu et al. [16] fabricated a core–shell structured magnetic COF for the efficient extraction and sensitive detection of sulfonamide residues in a meat matrix. Furthermore, novel strategies for NRG enrichment and purification are offered by the microsphere, leveraging its unique encapsulation capability and selective separation potential. The integration of COFs with microspheres effectively addresses critical limitations of powdered COFs in industrial separation processes, namely, equipment clogging and poor recyclability, while simultaneously enhancing mechanical stability under continuous-flow conditions [17]. For instance, Chen et al. [18] synthesized a novel asymmetric mesoporous organosilicon nanosheet with semi-open quasi-spherical mesopores by using the double emulsion directional micellar assembly technology, and transformed it into asymmetric mesoporous organosilicon microspheres (AMOMs) through ultrasonic-controlled emulsification. Among various microspherification techniques, the Pickering emulsion interfacial assembly approach offers distinct advantages. It enables the formation of radially aligned mesochannels through emulsion templating, while facilitating precise control over emulsion monodispersity via adjustable shear rates [19,20,21]. However, the adsorption performance of conventional microspheres is governed by the inherent properties of their COF shell layers, resulting in an inherent lack of molecular recognition capability toward target compounds.
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have garnered significant attention as advanced functional materials due to their capacity for specific molecular recognition, achieved through template molecule-directed formation of three-dimensional complementary cavities [22,23]. Through the strategic combination of boronate affinity and molecular imprinting techniques, the design of molecularly imprinted polymers is made achievable, culminating in simultaneous superior target selectivity, enhanced binding stability, and controllable reversible recognition. Jia et al. [24] fabricated hollow SnO2 microspheres with molecularly imprinted boronate affinity sites for the specific recognition of the cis-diol-containing flavonoid-luteolin (LTL). The synthesized material exhibited a high density of binding sites (0.22 mg m−2). Zhu et al. [25] developed boronate affinity-based molecularly imprinted hollow carbon nanofibers via electrospinning for the selective separation of shikimic acid, achieving an adsorption capacity of 127.8 mg g−1. However, there are certain drawbacks associated with molecularly imprinted polymers, such as unstable grafting, uneven site dispersion, and easy site stacking, which seriously affect the adsorption effect. Host–guest interactions, characterized by their reversibility, tunability, and stimuli-responsiveness, offer an attractive strategy for epitope anchoring [26]. The molecular encapsulation capability of cyclodextrin (CD) stems from its hydrophobic cage-like structure, which permits host–guest interactions with numerous compounds, exemplified by polyethylene glycol (PEG), adamantane (Ad), and azobenzene and its derivatives. Recently, polymers containing CD have shown great potential in the field of selective separation due to ultrafast adsorption and multifunctional modification [27]. For instance, Liu et al. [28] developed a novel porous high-density borate-affinity triblock imprinted copolymer adsorbent with abundant recognition sites for ovalbumin. Tang et al. [29] developed an innovative porous boronate-affinity imprinted hydrogel, which achieved an enhanced NRG adsorption capacity of 56.03 mg/g. Zhang et al. [30] fabricated functionalized cyclodextrin (CD)-scaffolded nanosponges for the rapid removal of boronic acids and organic micropollutants. Thus, by harnessing the synergistic effects of emulsion interfacial polymerization and precision assembly techniques, molecularly imprinted recognition sites can be precisely constructed with uniform alignment at the oil–water interface.
This study introduces a new class of porous boronate affinity-based molecularly imprinted microspheres, which exhibit a high density of specific recognition sites and demonstrate exceptional adsorption capacity. Therefore, compared with the traditional boronate affinity molecularly imprinted polymers, the MC-CD@BA-MIPs molecule has a higher adsorption capacity. Firstly, COF particles with double bonds were synthesized by Schiff–base reaction, and hollow-structured microspheres were prepared through secondary interface polymerization. Boronate ester molecular imprinted polymers were grafted onto Ad initiators and anchored on the surface of microspheres by thiol-functionalized β-cyclodextrin to prepare boric acid affinity imprinted polymers. In addition, MC-CD@BA-MIPs have the following advantages: (1) Tunable pore architecture via emulsion interfacial polymerization enables simultaneous optimization of pore size distribution and microsphere permeability. (2) The material was prepared by the Pickering emulsion template method, which enhanced the structural stability of the adsorbent. (3) Abundant boronate affinity sites and rapid binding kinetics for target molecules in complex matrices are obtained by the enhanced surface functionality, which is facilitated by high specific surface area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde (BTCA, 98%), aniline (99%), triethylamine (TEA, 99%), aniline (99%), acetic acid (98%), naringin (NRG, 98%), pyridine-3-boronic acid (97%), allyl bromide, mono-(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin (SH-β-CD), 1,4-benzenedicarboxaldehyd (DVA), sodium ascorbate, rutin (RT, 95%), hydroquinone (HQ), quercetin (QRCT), alizarin red S (ARS), and acetonitrile (≥99%) were sourced from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Benzaldehyde was obtained from J&K Scientific Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), trichloromethane (CHCl3, ≥99%), hydrochloric acid (HCl, 36.0–38.0%), ethanol (≥99%), tetrahydrofuran (THF, ≥99%), and methanol (HPLC, ≥99%) were provided by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). 1-adamantanol was supplied by Baisheng Jiaye Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Mesitylene, dichloromethane, dimethyl sulfoxide, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene (TAPB, 97%), and 1,4-dioxane were supplied by Macklin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.2. Instruments and Apparatus
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer (FT-IR, NEXUS-470, Nicolet, New York, NY, USA) was used to analyze the composition of functional groups of membrane samples in the wavelength range of 4000 to 400 cm−1. The KSV CM200 contact angle meter (Biolin Scientific AB, Espoo, Finland) measures the contact angle. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM, S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) was used to characterize the materials at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV. The XPS spectra were performed on a thermal ESCALAB 250 with Al Ka radiation at y = 901 for the X-ray sources, and the binding energies were calibrated using the C1s peak at 284.9 eV. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were investigated on a powder X-ray diffractometer (Smart Lab, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) using Cu Ka radiation (λ = 1.5406 A, 40 kV, 40 mA), data from 2θ = 2–40° were collected at a sample rate of 5°/min for phase detection. Zeta potential measurements were carried out using a Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) with a Malvern ZEN3600 Zetasizer Nano instrument (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK) with deionized water as the dispersant at 25 °C. The specific surface area, pore volume, and size analysis were measured through Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) methods, respectively, on a Micromeritics Surface Area & Porosity Gemini VII 2390 system at −196 °C. The static water contact angle was measured by using a KSV CM200 contact angle instrument (Finland).
2.3. Preparation of Double-Bond Functionalized COF (TAPB-BTCA-DVA-COF)
The COF was synthesized following a modified literature procedure [31]. TAPB (35.2 mg, 0.10 mmol), BTCA (8.1 mg, 0.05 mmol), and DVA (8.3 mg, 0.05 mmol) were dispersed in a three-necked flask containing 78 mL of acetonitrile. Subsequently, benzaldehyde (122 μL, 1.2 mmol) and aniline (99 μL, 1.2 mmol) were added, and then the mixture was subjected to ultrasonication at 25 °C for 10 min. Subsequently, 2.0 mL of the acetonitrile solution of 23.6 mg of Sc(OTf)3 was prepared and introduced into the mixture. The reaction was mechanically stirred at 25 °C for 24 h. After washing with acetonitrile, the product was dried under vacuum at 60 °C for 12 h, yielding the final product designated as TAPB-BTCA-DVA-COF.
2.4. Synthesis of Microsphere (MC)
Initially, 1.7 mg of TAPB-BTCA-DVA-COF was dissolved in 4.0 mL of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene. Subsequently, 200 μL of a Sc(OTf)3 solution (7 mg mL−1) was slowly added. The resulting mixture was then subjected to high-speed homogenization at 15,000 rpm for 3 min, yielding a stable oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. Subsequently, 2.0 mL of this emulsion was carefully transferred to a centrifuge tube and diluted with 4 mL of mesitylene. Separately, 3.5 mg of TAPB, 1.6 mg of BTCA, and 1.6 mg of DVA were dissolved in 2.0 mL of chloroform. Then, 12.1 μL of benzaldehyde and 10.8 μL of aniline were added as competitive inhibitors. The mixture was transferred to a 10 mL centrifuge tube and incubated at room temperature for 24 h to facilitate microsphere formation through interfacial polymerization at the aqueous–organic interface. The final microsphere product was designated as MC.
2.5. Synthesis of MC-CD
SH-β-CD (1.0 g) was initially immersed in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 1 mL), and the resultant mixture was transferred into a system containing 3.0 g of MC dispersed in 1,4-dioxane as solvent. The reaction was performed in a nitrogen environment at 120 °C for 12 h. The product obtained was subsequently subjected to purification by washing with acetonitrile and dried under vacuum at 60 °C overnight, yielding the final functionalized material designated as MC-CD.
2.6. Synthesis of 1-Allylpyridinium-3-Boronic Acid (APBA)
The mixture of pyridine-3-boronic acid (200 mg, 1.63 mmol) and allyl bromide (400 mg, 3.31 mmol) was mixed in ethanol (50 mL) under a nitrogen atmosphere. The mixture was heated to 110 °C and kept at this temperature for 24 h. Upon reaction completion, the ethanol and residual allyl bromide were eliminated under reduced pressure.
2.7. Synthesis of Boronic Acid Imprinted Microsphere (MC-CD@BA-MIP)
The mixture of 1-adamantanol (1.522 g, 0.010 mol) and triethylamine (TEA, 0.12 mol) was dispersed in dichloromethane (20 mL). After addition, the mixture was agitated at 0 °C for 2 h, followed by stirring at room temperature for 24 h. After the reaction, precipitated salts were separated via filtration, and the resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude underwent purification via silica gel column chromatography, petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (10:1, v/v) as the eluent solvent. After the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, the final product ABIB was obtained.
BA-MIPs were synthesized through the reaction between APBA and ABIB. Specifically, ABIB (0.015 mol) was dispersed in methanol (20 mL) in a three-necked flask and subjected to ultrasonication at 25 °C for 10 min. Then, APBA (12 mmol), NRG (48 mmol), and a CuCl2–PMDETA catalyst solution (0.0036 mmol CuCl2 and 0.036 mmol PMDETA) were introduced into the mixture. Ascorbic acid (15 mg, 0.084 mmol), pre-dissolved in methanol (1 mL), was injected into the reaction system via syringe. The reaction was executed at 25 °C for 24 h under a nitrogen environment. After the reaction, the mixture was centrifuged to collect the solid product. The obtained BA-MIPs were thoroughly washed with methanol and acetic acid/methanol (1:9, v/v) until NRG was no longer detected in the washing solution. The resulting material was dried under vacuum at 40 °C for 24 h. For control experiments, non-imprinted polymers (MC-CD@BA-NIPs) were synthesized following an identical procedure but performed in the absence of NRG.
2.8. Binding Experiments
In the pH binding experiment, 5.0 mg of either MC-CD@BA-MIPs or MC-CD@BA-NIPs was added to 5.0 mL of NRG solution (35 mg L−1) at varying pH conditions (5.0–9.0, in 1.0 pH unit increments). The experiment was conducted under controlled shaking using a constant temperature shaking bed. The adsorption process was carried out at 35 °C for a duration of 360 min. After the adsorption was completed, the residual concentration of NRG was quantified by UV-Vis spectroscopy, and the adsorption amount was calculated by Equation (1) [32,33]:
where C0 and Ce (mg L−1) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of NRG, m (mg) represents the mass of the adsorbent, and V (mL) corresponds to the volume of NRG solution.
In the adsorbent dose experiment, different doses of MC-CD@BA-MIPs (1.0 mg–9.0 mg, in increments of 2.0 mg) were added to 5.0 mL of NRG solution (35 mg/L, pH = 7.4). The remaining conditions were identical to those in the pH binding experiment.
Adsorption kinetics experiments were performed to evaluate and compare the adsorption capacities of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs for NRG. In the experiment, 5.0 mg of MC-CD@BA-MIPs or MC-CD@BA-NIPs was added to 5.0 mL of NRG buffer solution (pH = 7.4, concentration of 35 mg L−1) and stirred at 35 °C for 5 to 360 min. Subsequently, the temporal evolution of NRG adsorption was monitored by measuring residual concentrations at predetermined intervals using UV-Vis spectroscopy. The adsorption isotherm experiments were conducted under identical conditions, except that the concentration of NRG buffer solution was 10, 15, 25, 35, and 50 mg L−1, and the temperature was set at 25 °C, 30 °C, and 35 °C, respectively.
To further study the regeneration performance of MC-CD@BA-MIPs or MC-CD@BA-NIPs, the 35 mg L−1 NRG solution was subjected to six sorption–desorption cycles at 35 °C, and the adsorbed MC-CD@BA-MIPs or MC-CD@BA-NIPs were eluted with a mixture of methanol and acetic acid (9:1, v/v) until no NRG molecule was detected in the elution solution.
2.9. Selectivity Study
To systematically evaluate the targeted capture capability of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs for NRG, the specific adsorption of NRG and other compounds (NRG, RT, ARS, QRCT, and HQ) was studied. In the experiment, 5.0 mg of adsorbent was added to a 5.0 mL solution of NRG (35 mg L−1, pH = 7.4) and reacted at 35 °C for 360 min. After the reaction, the supernatant was separated by centrifugation and analyzed by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The specificity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs to NRG was quantitatively assessed through the imprinting factor (IF) calculated according to the following Equation (2) [34]:
where the adsorption capacities of competing molecules on MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs are represented as QMIP and QNIP, respectively.
To comprehensively assess the selectivity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs, binary solutions were prepared containing 35 mg L−1 of NRG along with various structural analogues, including NRG/RT, NRG/ARS, NRG/QRCT, and NRG/HQ. In each case, 5.0 mg of either MC-CD@BA-MIPs or MC-CD@BA-NIPs was placed in 5.0 mL of the respective binary solution and allowed to stand at 30 °C for 6.0 h.
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of MC-CD@BA-MIPs
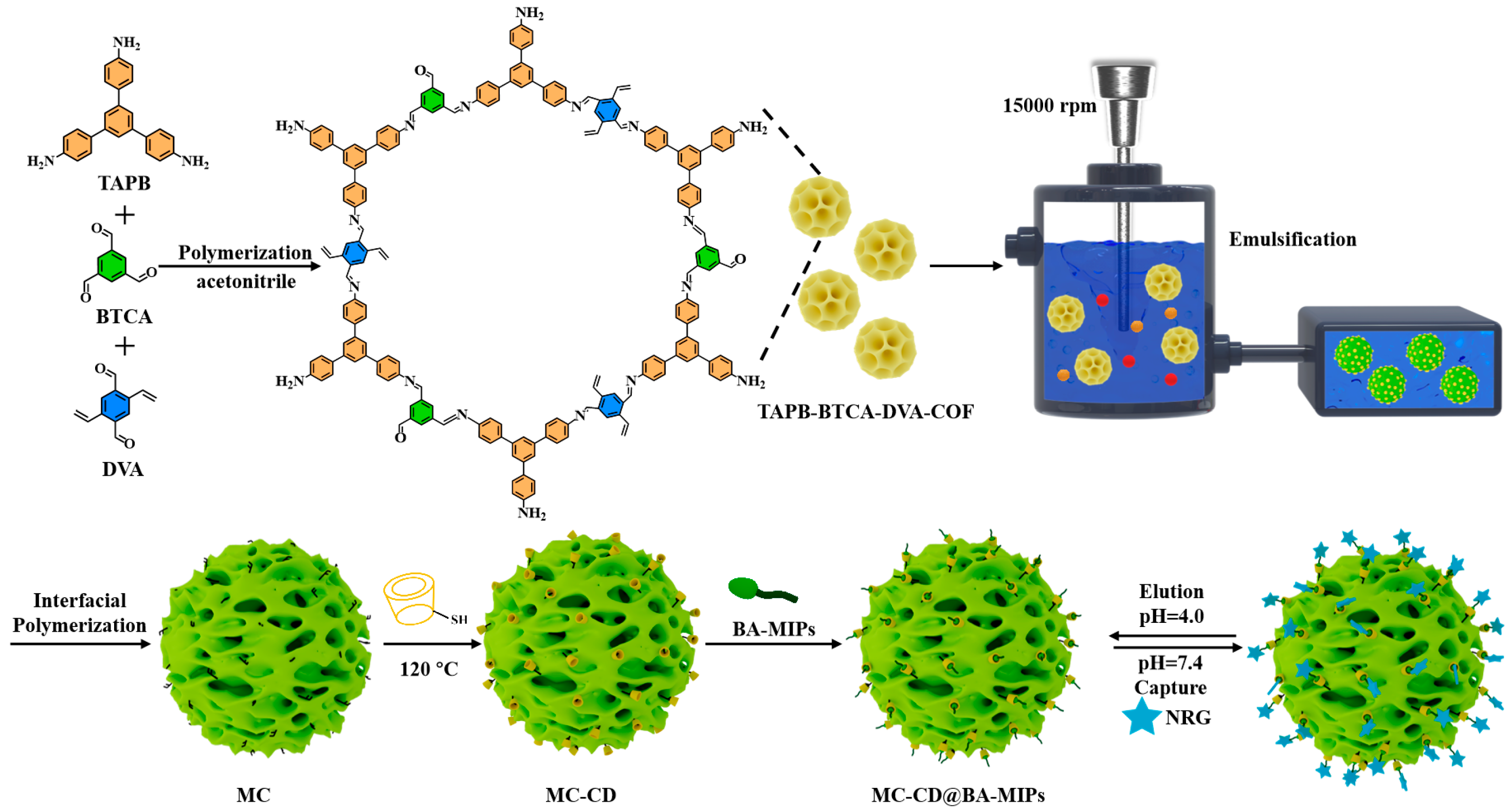
An innovative type of porous boronic acid molecular imprinted microspheres (MC-CD@BA-MIPs), exhibiting a high density of specific recognition sites and enhanced binding capacity, was successfully synthesized via an oil-in-water (O/W) Pickering emulsion interfacial assembly strategy (Scheme 1). Initially, double-bond functionalized TAPB-BTCA-DVA-COF particles were synthesized through Schiff–base reaction, employing TAPB, BTCA, and DVA as the molecular building units. Subsequently, hollow-structured microspheres (MCs) were prepared through secondary interfacial polymerization. The functional monomer 1-allylpyridine-3-boronic acid (APBA) was grafted onto the initiator (ABIB) via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). The adsorption performance was significantly enhanced by the synthesized boronate affinity imprinted polymers (ABIB-BA-MIPs) in biological environments. The resulting imprinted polymers were subsequently immobilized onto the microsphere surface via host–guest interactions, leveraging the specific binding affinity between SH-β-CD and the target structure to achieve precise and stable surface functionalization. The flux of the imprinted microspheres is enhanced by the porous architecture generated through the emulsion template strategy, and the selectivity of the sorbent is effectively improved by the construction of homogeneous recognition cavities via the interfacial assembly.
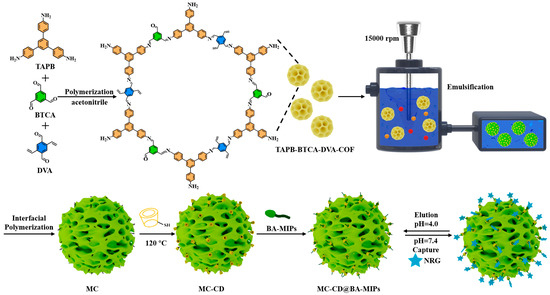
Scheme 1.
Schematic illustration of the preparation of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and binding/dissociation behavior for NRG.
3.2. Characterization of MC-CD@BA-MIPs
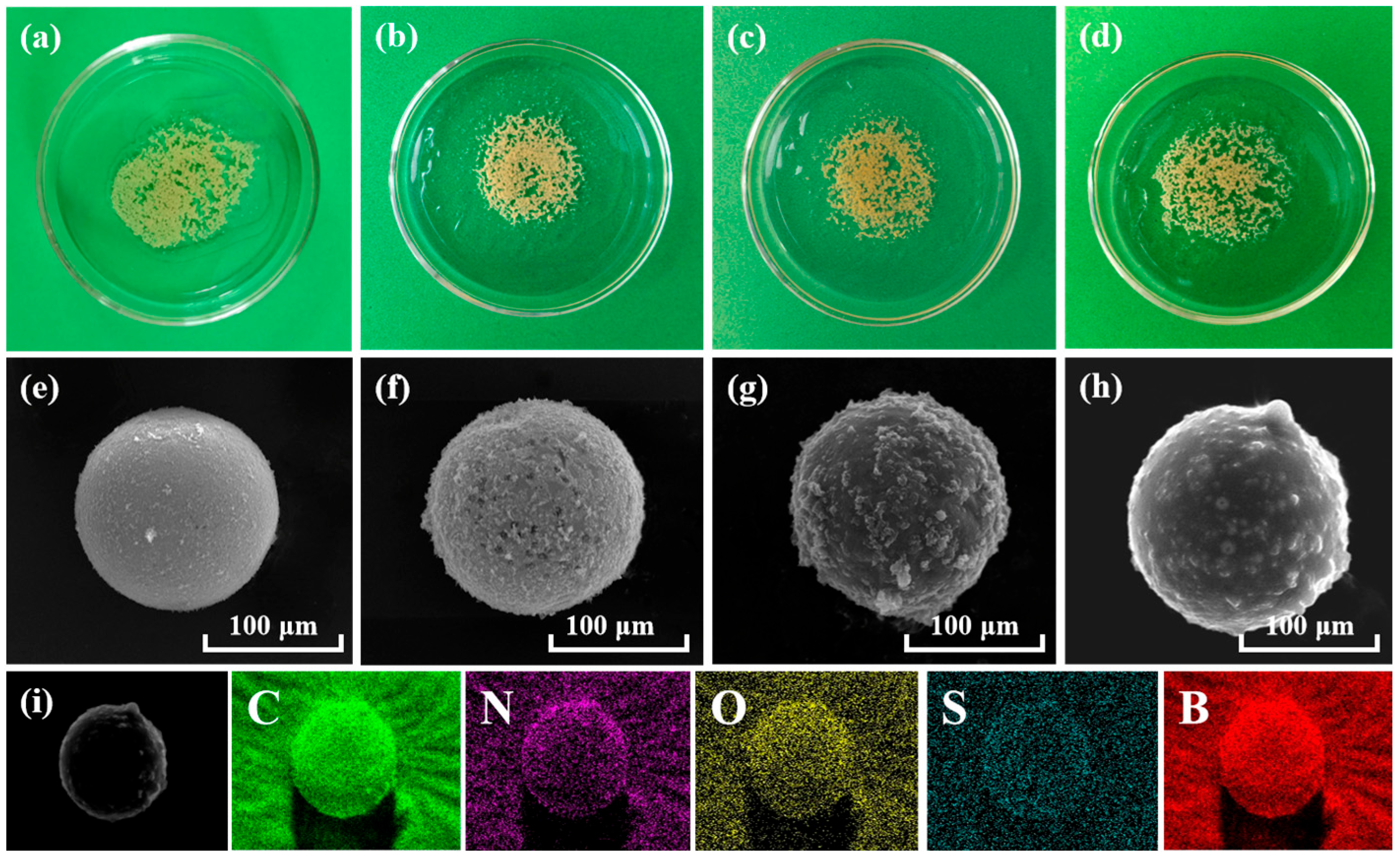
Digital photographs of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs are presented in Figure 1a–d. There are distinctly spherical morphologies across all samples, with a noticeable darkening occurring after SH-β-CD modification. The corresponding scanning electron microscope (SEM) images (Figure 1e–h) show that the structure of the synthesized microspheres is characterized by a continuous and distinct shell structure. A smooth surface and a diameter of 110.51 nm ± 5 nm are exhibited by the original MC. Compared with MC, a rougher surface on MC-CD@BA-MIPs is apparent along with an increase in size of approximately 15 nm (Figure 2b), which is due to the formation of the imprinted shell layer. Figure 1e shows the element distribution data of MC-CD@BA-MIPs. The typical peak energy values of B, C, N, O, and S are 0.12, 0.18, 0.26, 0.51, and 2.24 keV, respectively, corresponding to atomic contents of 4.76%, 77.00%, 7.75%, 9.30%, and 1.17%, respectively. The successful introduction of ABIB-BA-MIPs is confirmed by the appearance of element B [35].
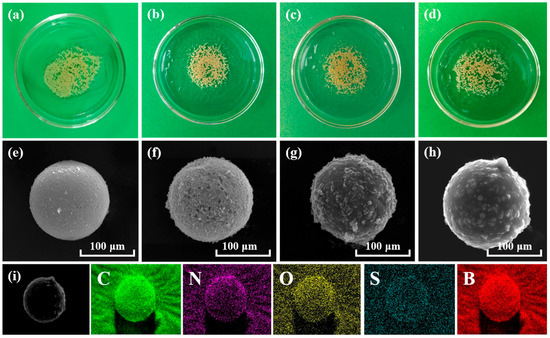
Figure 1.
Photos of the corresponding microspheres of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs (a–d). The SEM images of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs (e–h), the EDS mapping of MC-CD@BA-MIPs (i).
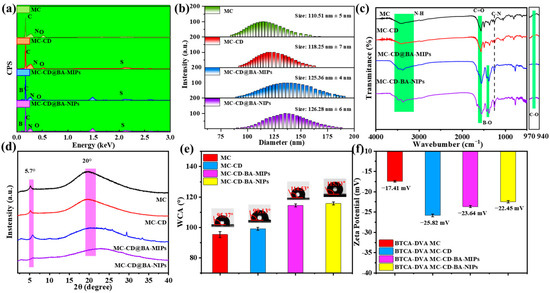
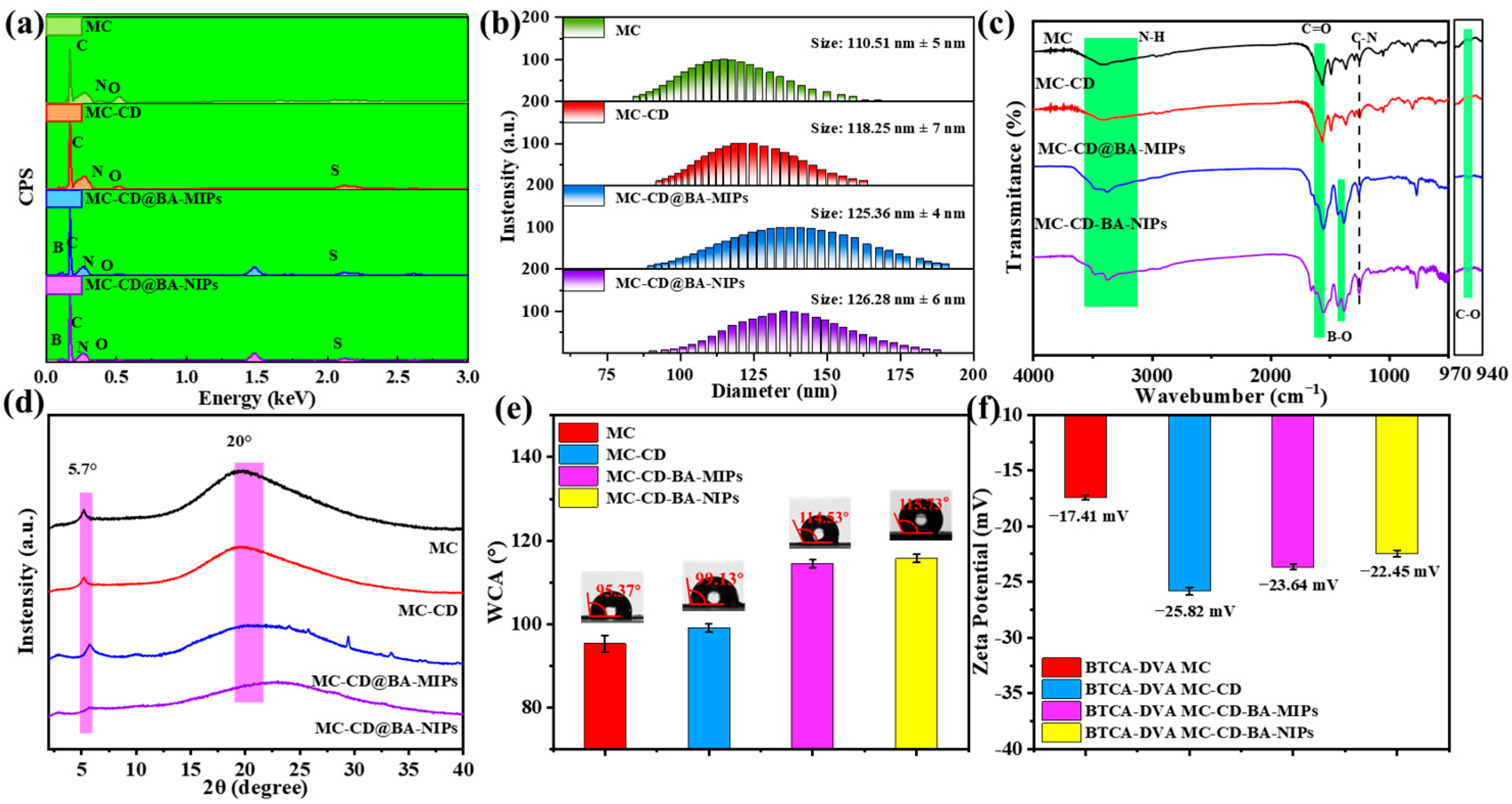
Figure 2.
The responding EDS results (a), the size distribution (b), FT-IR spectrum (c), XRD pattern (d), WCA (e), and zeta potential (f) of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-NIPs, and MC-CD@BA-MIPs.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic (FT-IR) analysis was employed to verify the structural integrity of the synthesized microspheres. Figure 2c shows the FT-IR spectroscopy of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD-NIPs. The peak at 1324 cm−1 corresponds to the C-N stretching vibration. The broad peak at 3365 cm−1 relates to the N-H stretching vibration. The peak at 1600 cm−1 can be attributed to the overlap of N-H bending and C=O stretching vibrations [36]. It is noteworthy that a distinct B-O stretching vibration peak appeared at approximately 1385 cm−1 in the FT-IR spectra of both MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs, further confirming the effective incorporation of boronate affinity sites [37]. The MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD-NIPs exhibit broad diffraction peaks around 20° and sharp diffraction peaks at 5.7°, which suggests the successful preparation of COF microspheres via the emulsion interface polymerization. As shown in Figure 2d, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, MC-CD@BA-NIPs, MC-CD, and MC exhibit the same characteristic diffraction peaks in the range of 2–40°. These results demonstrated the successful preparation of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and the excellent chemical stability of MC-CD@BA-MIPs [38,39]. To further study the hydrophilicity of microsphere adsorbents, we tested the contact angles of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs in aqueous solutions at different time points, and their values were 95.37°, 99.13°, 114.53°, and 115.73°, respectively (Figure 2e). Compared to the unmodified MC, there was a measurable increase in the water contact angle subsequent to the successful grafting of SH-β-CD onto the surface (MC-CD). After grafting microspheres with boric acid imprinted sites, the contact angle further increased, indicating that the incorporation of boronate affinity groups enhanced the hydrophobicity of the adsorbent.
To examine the host–guest interactions between MC-CD and ABIB-BA-MIPs, zeta potential measurements were conducted in ethanol suspension. The successful incorporation of boronate affinity molecular imprinted cavities on the microsphere surface resulted in more negative zeta potentials, with values of −23.03 mV for MC-CD@BA-MIPs and −22.87 mV for MC-CD@BA-NIPs, respectively (Figure 2f). This trend confirms the enhanced surface charge properties arising from functional imprinting. This is due to the action of the -OH on the boronic acid functional groups present on the surface of the surface-imprinted layer [40]. The specific surface area and porosity of the fabricated materials were characterized by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). The permanent porosities of various materials were examined using the N2 sorption isotherms obtained at −196 °C. The Rapid N2 uptakes at the relatively lower pressure range (P/P0 < 0.1) indicate that the characteristic type-V reversible isotherms [41]. As shown in N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms (Figure S3a,b), the specific surface areas for MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs were determined to be 473.54, 386.48, 281.88, and 266.05 m2/g, respectively. The average pore diameters of the functionalized materials, as derived by the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH), were 8.35 nm, 6.49 nm, 5.44 nm, and 5.32 nm, respectively. The progressive reduction in both specific surface area and pore dimensions observed in MC-CD@BA-MIPs is attributed to sequential surface modification and functionalization processes during material fabrication. Table S5 shows that the microporous volumes of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs are 0.012 cm3 g−1, 0.028 cm3 g−1, 0.018 cm3 g−1, and 0.017 cm3 g−1, respectively, while their mesoporous volumes are 0.090 cm3 g−1, 0.062 cm3 g−1, 0.117 cm3 g−1, and 0.109 cm3 g−1, respectively. Notably, the sum of micropore volume and mesopore volume is largest for MC-CD@BA-MIPs, which is advantageous for its adsorption capacity [42].
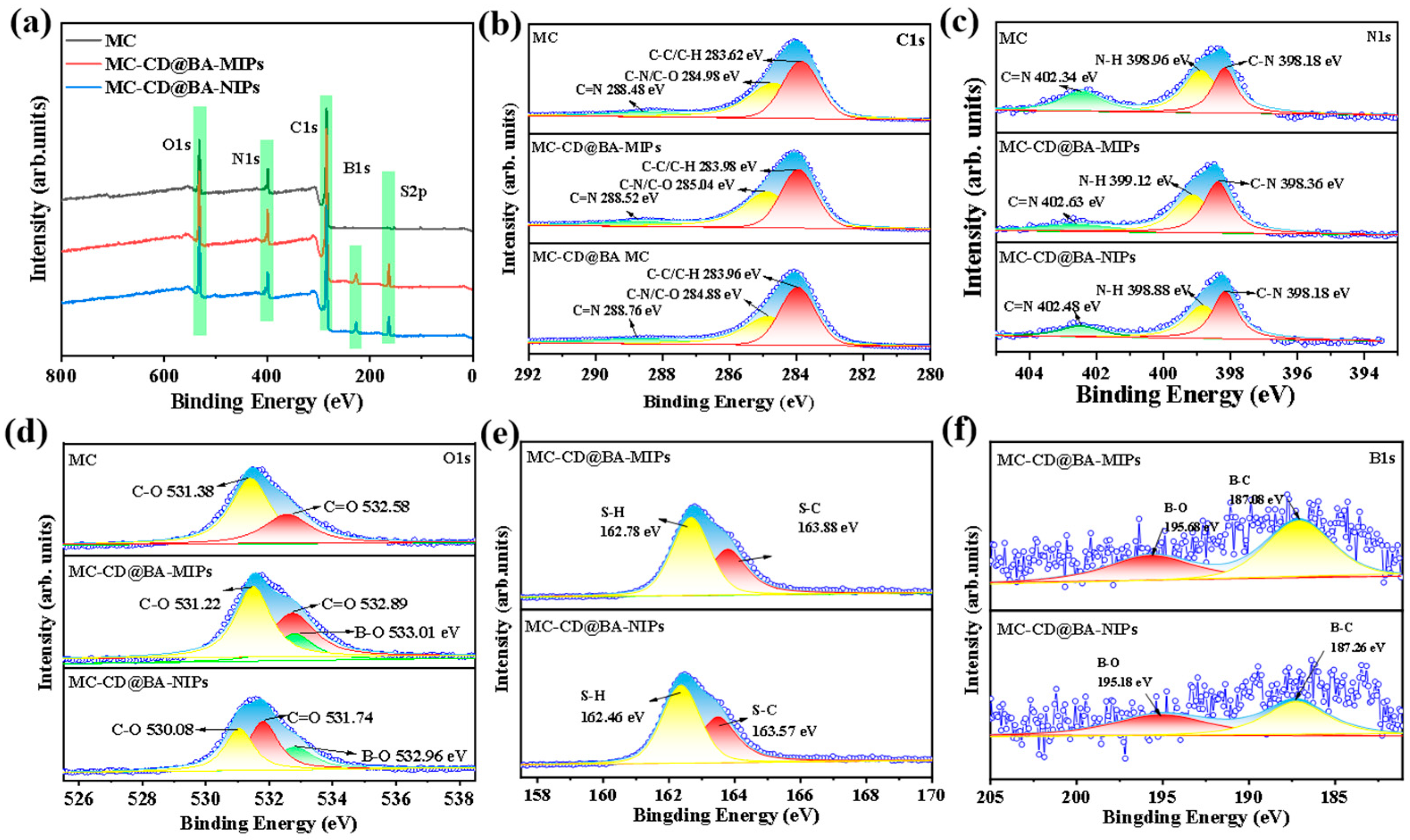
The chemical evolution process of MC-CD@BA-MIPs was systematically monitored using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The corresponding results are shown in Figure 3a. Characteristic peaks of C1s, N1s, O1s, and S2p can be observed in the full-range XPS spectra of 284.00 eV, 398.00 eV, and 531.00 eV. Compared with MC-CD, the B element appears in MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MD-CD@BA-NIPs, which is due to the effective functionalization of borate affinity MIPs (BA-MIPs). The high-resolution C1s spectra of Figure 3b show that C-C, C-O, C=O, C-N, and C=N bonds exist in all three materials. The high-resolution N1s spectrum of MC-CD@BA-MIPs in Figure 3c can be decomposed into three characteristic peaks: 398.18 eV (N-C), 398.96 eV (N-H), and 402.34 eV (C=N). The high-resolution O1s spectra in Figure 3d show that the binding energies of the B-O functional groups of MC-CD@BA-NIPs and MC-CD@BA-MIPs change at 531.74 eV and 533.01 eV, respectively. Furthermore, the new peaks at 195.68 eV and 187.08 eV in the MC-CD@BA-MIPs spectrum (Figure 3f) correspond to the B-O and B-C bonds, confirming the existence of the phenylboronic acid imprinting recognition site. These results indicate the presence of the boric acid group on the surface of the functionalized microspheres, further verifying the feasibility of successfully synthesizing MC-CD@BA-MIPs through the host–guest modification imprinting strategy.
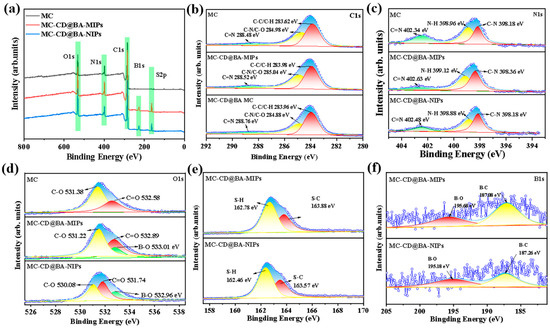
Figure 3.
XPS survey spectra of MC, MC-CD@BA-NIPs, and MC-CD@BA-MIPs (a), high-resolution XPS spectrum of C1s (b), N1s (c), O1s (d), S2p (e), and B1s (f).
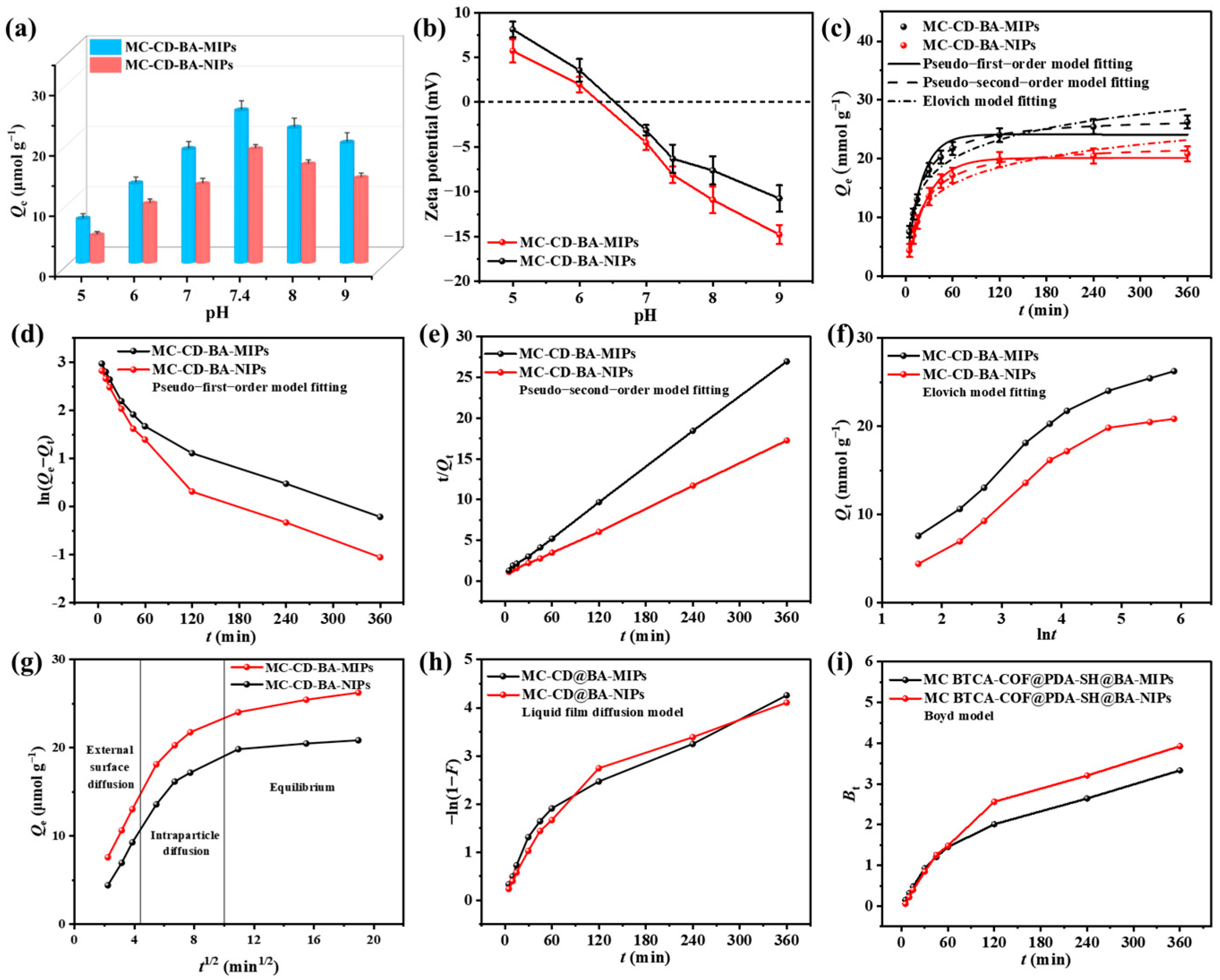
3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dose and pH
The binding of NRG by boronate-affinity molecularly imprinted sorbents is strongly influenced by solution pH, which modulates the reversible covalent interaction with its cis-diol group [43]. Therefore, the binding behaviors of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs toward NRG were systematically investigated across a pH range of 5.0 to 9.0. As illustrated in Figure 4a, MC-CD@BA-MIPs exhibited significantly higher adsorption capacity than MC-CD@BA-NIPs under all tested pH conditions, which can be attributed to the presence of specifically tailored recognition cavities within the imprinted polymer matrix. When the pH was between 5.0 and 7.4, the adsorption capacities of MC-CD@BA-MIPs were 7.34 μmol/g, 13.22 μmol/g, 18.88 μmol/g, and 25.31 μmol/g, respectively. The adsorption capacity reached the optimum when the pH was 8.0. However, as the pH value increased from 7.4 to 9.0, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent gradually decreased. This might be due to the fact that the strongly negative zeta potential exhibited by MC-CD@BA-MIPs in high-pH environments which affects the binding performance of boric acid affinity [44]. The experimental results confirmed that boronate affinity molecularly imprinted recognition sites can improve the selective adsorption of NRG in complex agricultural waste matrices. To investigate the effect of adsorbent dose on adsorption capacity, we used different masses of adsorbent to adsorb the target product and measured the adsorption capacity to determine the optimal dose. The results are presented in Figure S4. As the adsorbent dose increased, the adsorption capacity reached its maximum at 5.0 mg, with subsequent dose increases having little effect on adsorption capacity. Furthermore, at doses of 1.0 mg and 3.0 mg, the small sample sizes led to substantial mass measurement fluctuations, resulting in significant errors. Therefore, we selected 5.0 mg as the optimal adsorbent dose.
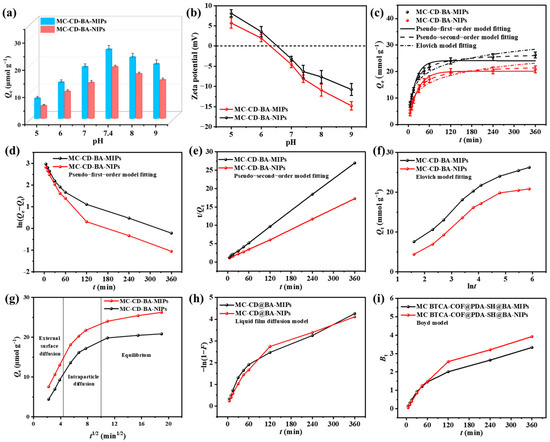
Figure 4.
The pH influence on the adsorption amounts of MC-CD@BA-NIPs and MC-CD@BA-MIPs (a), adsorption kinetics (b–e), Elovich model (f), intraparticle diffusion (g), liquid film diffusion model (h), and the Byod model (i).
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics of MC-CD@BA-MIPs
To investigate the adsorption behavior and elucidate the underlying mechanisms, the adsorption kinetics of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs were systematically evaluated under optimized conditions (30 °C, pH = 7.4). During the initial 60 min, MC-CD@BA-MIPs exhibited a sharp rise in adsorption capacity, owing to the abundant and highly accessible recognition sites on the material surface. As these imprinted cavities became progressively occupied by NRG molecules, the adsorption rate slowed due to increased mass transfer resistance, which hindered further diffusion of NRG toward the remaining internal boronate affinity sites. The saturated adsorption capacity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs reached 26.24 μmol/g, and the adsorption equilibrium was attained at 360 min. Furthermore, the adsorption kinetics results were analyzed by fitting the experimental data to the pseudo-first-order model, pseudo-second-order model, and Elovich models (equations are provided in Table S2). The nonlinear regression curves and fitting results for the pseudo-first-order model, pseudo-second-order model, and Elovich model are presented in Figure 4c and Table 1. The nonlinear fitting results of the pseudo-second-order model demonstrated superior correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.996) than the pseudo-first-order model (R2 = 0.994), and its calculated equilibrium adsorption capacity (Qbe = 27.10 μmol g−1)aligned closely with the experimental value. The linear fitting plots for the pseudo-first-order model, pseudo-second-order model, and Elovich model are shown in Figure 4d, Figure 4e, and Figure 4f, respectively. It is evident that the pseudo-second-order model (R2 = 0.999) provides a significantly better fit than the pseudo-first-order model (R2 = 0.898). Similarly, the adsorption capacity (Qbe = 27.25 μmol g−1) calculated by the linear pseudo-second-order model is also closer to the actual value (Table 1). The kinetic fitting results suggest that the adsorption kinetics are primarily governed by chemisorption, specifically through boronate affinity interactions between the adsorbent and NRG [45]. The α value (5.305 μmol g−1 min−1) of the Elovich model is higher than the β value (0.211 μmol g−1 min−1), indicating that the adsorption process proceeds rapidly with limited desorption interference. Therefore, the adsorption process is feasible [46]. Meanwhile, the adsorption kinetics of NRG were well described by the Elovich model (RN2 = 0.963), further indicating that chemical adsorption plays a leading role throughout the adsorption process. The diffusion mechanisms of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs were studied by using the Weber–Morris model fitted based on the dynamic data in Table S3. As shown in Figure 4g, the multi-linear profile of the kinetic curve suggests a multi-stage adsorption process. The initial phase is characterized by rapid surface adsorption, driven by the migration of NRG molecules from the water phase toward the adsorbent surface. This is followed by a slower phase dominated by intraparticle diffusion, where NRG interacts with boronate affinity-based imprinting recognition sites within MC-CD@BA-MIPs, reflected by the shallower slope of the curve. The final stage approaches adsorption equilibrium, where the uptake rate declines due to saturation of accessible binding sites and increased steric hindrance, ultimately leading to stabilization of the adsorption capacity.

Table 1.
Nonlinear kinetic parameters obtained in the adsorption of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs.
The fitted linear plot for the adsorbent does not intersect the origin, suggesting that both internal and external surface sites participate in the adsorption of NRG, as summarized in Table S3. Moreover, the intraparticle diffusion rate constants (kid) for MC-CD@BA-MIPs across the three stages exhibit a progressive decrease: kid1 = 3.329 μmol−1·g·min−1/2 > kid2 = 1.605 μmol−1·g·min−1/2 > kid3 = 0.279 μmol−1·g·min−1/2. This decline implies that intraparticle diffusion is not the exclusive rate-limiting step, and the adsorption of NRG likely involves a multi-mechanism diffusion process. Additionally, neither the liquid film diffusion model (Figure 4h) nor the Boyd model plot (Figure 4i) passes through the origin, further supporting that film diffusion and internal particle diffusion collectively govern the overall mass transfer of NRG molecules.
3.5. Adsorption Isotherms
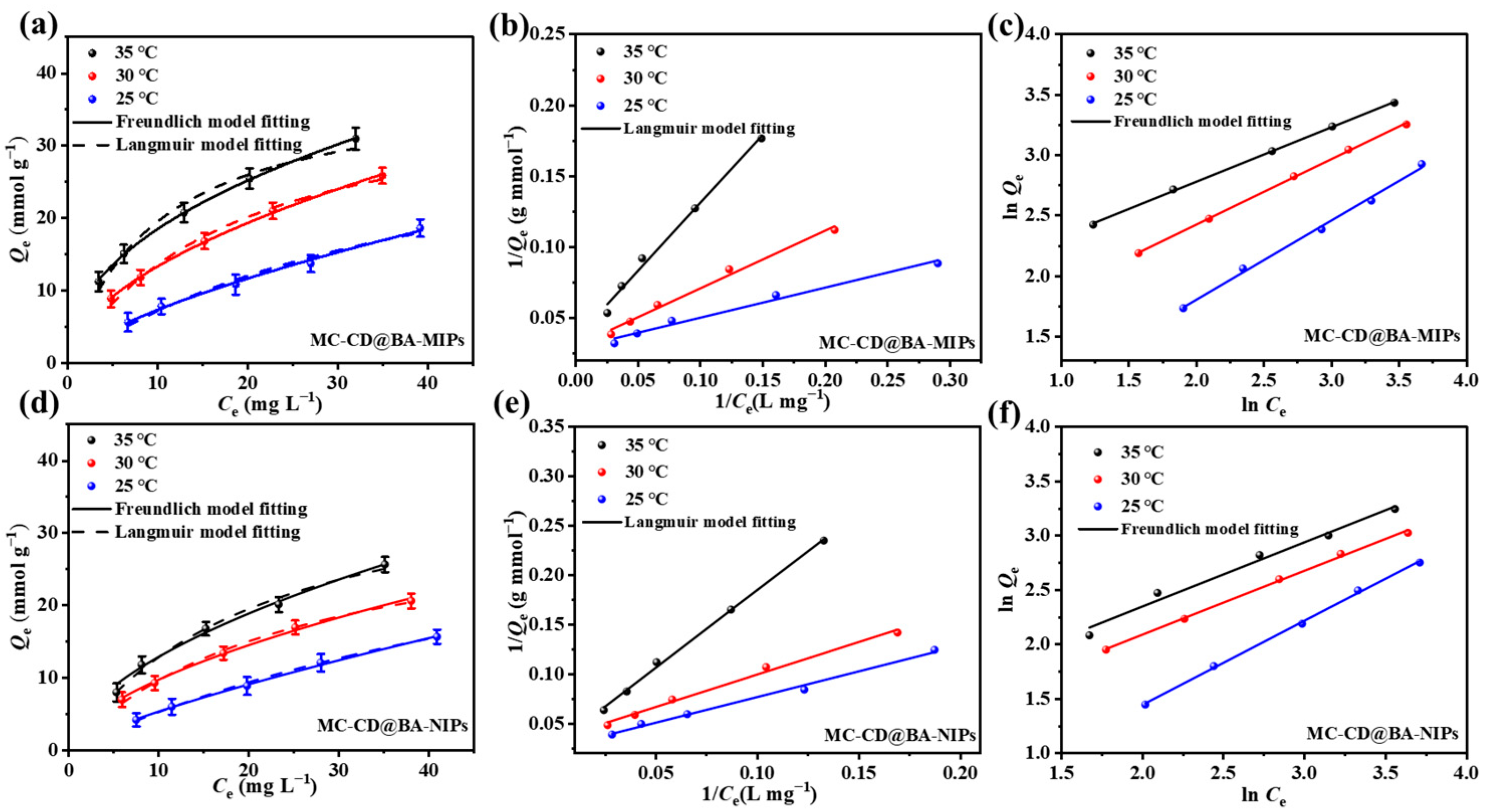
To elucidate the adsorption mechanism of the materials, adsorption isotherms were employed to investigate the equilibrium binding behaviors of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs toward NRG over a range of initial concentrations. The adsorption data were modeled using the Langmuir and the Freundlich isothermal adsorption models, and the key fitting parameters are summarized in Table 2. Figure 5a shows the results of the nonlinear fitting for the Langmuir and the Freundlich models. The adsorption capacity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs exhibits a positive correlation with increasing temperature. The corresponding adsorption capacities from the nonlinear fitting results in Table 2 are Qm,25°C = 31.82 μmol g−1, Qm,30°C = 34.85 μmol g−1, and Qm,35°C = 38.78 μmol g−1, respectively. Figure 5b,c present the linear fitting plots for the Langmuir and the Freundlich models of MC-CD@MIPs, respectively. The corresponding adsorption capacities from the linear fitting results in Table 2 are Qm,25°C = 28.25 μmol g−1, Qm,30°C = 33.01 μmol g−1, and Qm,35°C = 34.42 μmol g−1, respectively. This suggests that the adsorption of NRG onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs is an endothermic process. Furthermore, the nonlinear regression analysis revealed that the Freundlich isotherm model exhibited higher correlation coefficients (R225°C = 0.992, R230°C = 0.998, R235°C = 0.999) compared to the Langmuir model (R225°C = 0.975, R230°C = 0.989, R235°C = 0.971) across all tested temperatures. This indicated that the adsorption of NRG onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs presents a multilayer adsorption mechanism [47]. Moreover, the value of the Freundlich constant (1/n) is less than 1.0 (Table 2), confirming that the adsorption of NRG onto the surface of MC-CD@BA-MIPs is feasible. To further evaluate the adsorption performance of MC-CD@BA-MIPs, we adopted the Scatcherd model for calculation. The calculation results of the binding constant (Ka, μmol L−1) and the maximum binding capacity (Nmax, μmol g−1) conform to the relationship shown in Equation (3) [48].
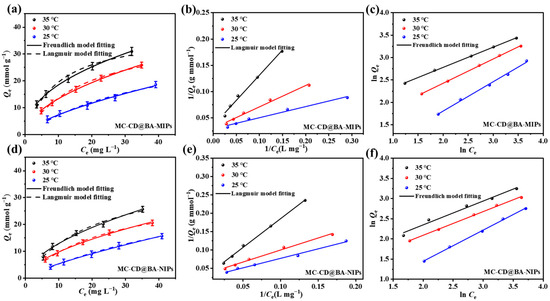
Figure 5.
The adsorption isotherms for model fitting curves for NRG (a,d), linear Langmuir (b,e), and the Freundlich model (c,f) of the experimental data of MC-CD@BA-NIPs and MC-CD@BA-MIPs.
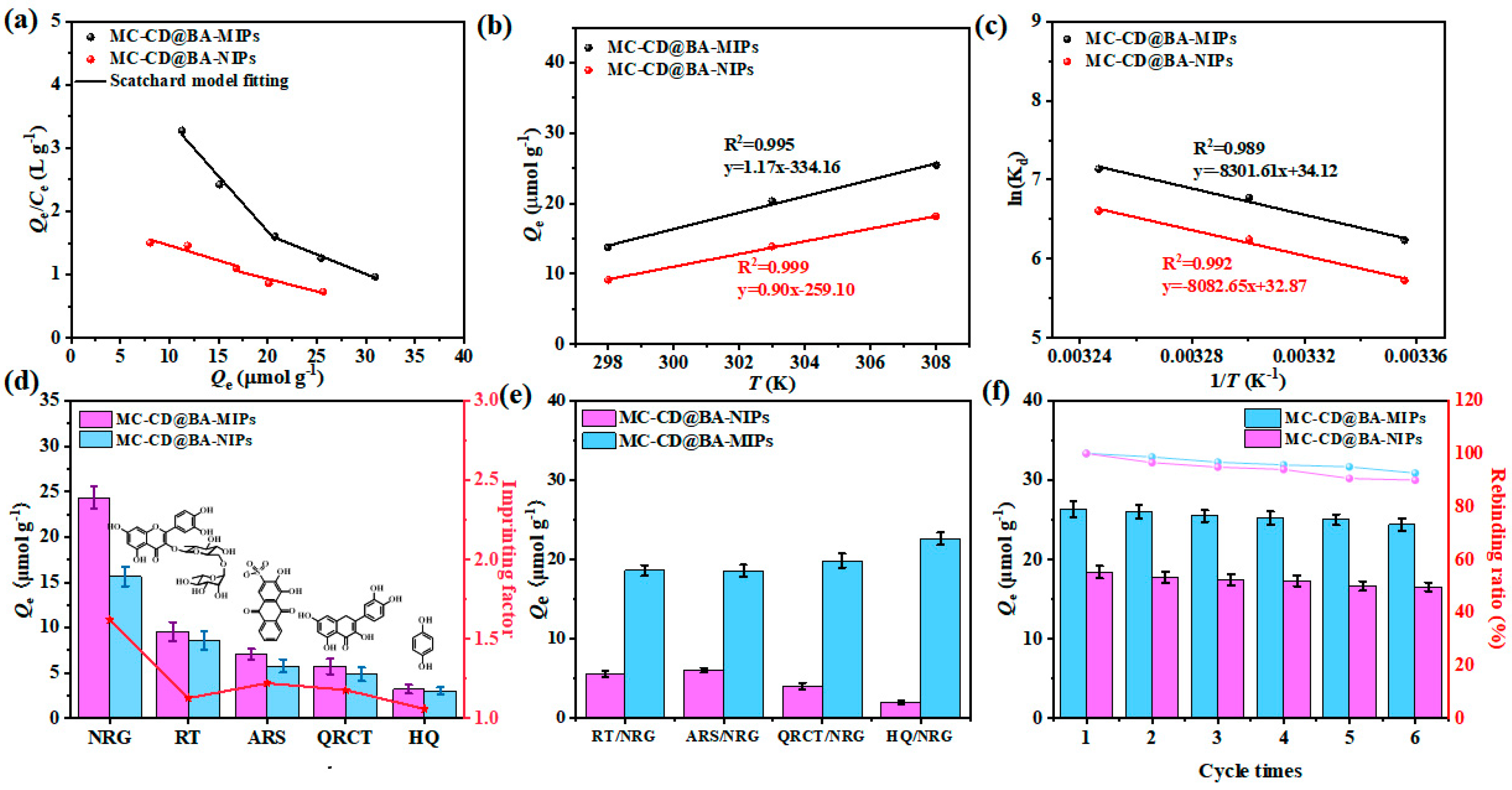
The enrichment mechanism of NRG on MC-CD@BA-MIPs is divided into two stages: enrichment mediated by high-affinity binding sites and enrichment mediated by low-affinity binding sites (Figure 5a). It was determined that the binding constant Ka of MC-CD@BA-MIPs was 24.91 μmol/L, and the maximum binding capacity Nmax was 46.31 μmol/g. In addition, the calculated density value of the high-affinity binding site was 0.52 μmol/m2 (Table S4). These results indicated that the high-affinity binding sites originate from the borate ester structure formed between NRG and functional monomers, which explains why MC-CD@BA-MIPs have enhanced adsorption capacity and specificity for NRG.

Table 2.
Linear and nonlinear adsorption equilibrium constants for Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm equations onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs.
Table 2.
Linear and nonlinear adsorption equilibrium constants for Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm equations onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs.
| Adsorption Isotherm Models | Constants | Nonlinear Form | Linear Form | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | ||
| Langmuir model | R2 | 0.975 | 0.989 | 0.971 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| Qm (µmol g−1) | 31.82 | 34.85 | 38.78 | 28.25 | 33.01 | 34.42 | |
| KL (Lμmol−1) | 0.024 | 0.054 | 0.101 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.013 | |
| RL | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.37 | |
| Freundlich model | R2 | 0.992 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.995 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| KF (μmol1−n g−1 Ln) | 1.59 | 3.91 | 6.62 | 6.53 | 3.82 | 1.64 | |
| 1/n | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.65 | |
3.6. Adsorption Thermodynamics and Adsorption Mechanism
The thermodynamic behavior of the adsorption process was evaluated by determining the changes in entropy (ΔS, J mol−1 K−1), enthalpy (ΔH, kJ mol−1), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG, kJ mol−1). The formulas used for these calculations are as follows (Equations (4)–(6)) [49,50,51]:
where R denotes the universal gas constant (8.314 J K−1 mol−1) and Kd represents the equilibrium constant (L/g).
As shown in Figure 5b,c, there is a positive correlation between temperature and adsorption capacity. The enthalpy change ΔH for MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs was found to be 69.01 kJ·mol−1 and 67.20 kJ·mol−1, respectively (Table 3). The positive values of ΔH confirm that the adsorption of NRG onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs is an endothermic process, requiring input of thermal energy to facilitate binding. The Gibbs free energy change ΔG for MC-CD@BA-MIPs at various temperatures (25 °C, 30 °C, 35 °C) was determined to be −15.45 kJ/mol, −17.07 kJ/mol, and −18.28 kJ/mol, respectively. The negative ΔG values suggested that the adsorption process is thermodynamically spontaneous under the experimental conditions applied. Furthermore, the entropy change ΔS values for MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs were found to be 0.283 kJ·mol−1 K−1 and 0.273 kJ·mol−1 K−1, respectively. This suggests that the solid–liquid interface is characterized by randomness throughout the adsorption process.

Table 3.
Thermodynamic parameters at different testing temperatures.
3.7. Adsorption Selectivity and Competitive
To estimate the binding specificity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs toward NRG, competitive adsorption experiments were carried out using structural analogs—including RT, ARS, QRCT, and HQ-under competitive conditions at 35 °C. The results of these selectivity studies are presented in Figure 6d. The adsorption capacities of MC-CD@BA-MIPs for NRG, RT, ARS, QRT, and HQ are 24.34 μmol/g, 9.56 μmol/g, 7.06 μmol/g, 5.72 μmol/g, and 3.21 μmol/g, respectively. Meanwhile, NRG extracted by MC-CD@BA-MIPs significantly exceeded that of MC-CD@BA-NIPs, demonstrating the critical role of both the molecularly imprinted cavities and the boronate affinity binding sites in the specific capture and concentration of NRG. In addition, the imprinting factors (IF) for NRG, RT, ARS, QRCT, and HQ were calculated as 1.62, 1.13, 1.22, 1.80, and 1.06, respectively, which fully confirmed their excellent selectivity for NRG. Based on these results, the distribution coefficient (Kd), selectivity coefficient (k), and relative selectivity coefficient (K′) of NRG and its structural analogs (RT, ARS, QRCT, and HQ) were calculated according to Equations (7)–(9) [52].
where C0 (mg L−1) and Ce (mg L−1) represent the initial concentration of NRG in the solution and the equilibrium concentration of NRG after adsorption. x refers to other competitor molecules present in the system during selectivity experiments.
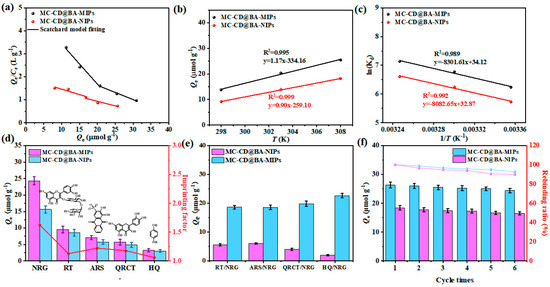
Figure 6.
The Scatchard model (a), the effect of temperature on the enrichment of NRG of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs (b) and relationship between ln Kd and 1/T (c), selective adsorption capacity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs (d), adsorption study on MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs in binary solution (e), the six adsorption–desorption cycles of MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs (f).
The calculated values of Ce, Kd, k, and K′ are summarized in Table 4. The relative selectivity coefficients (K′) for the structural analogs were determined to be 2.45, 2.21, 2.33, and 2.65, respectively. All values exceed 1.0, confirming the outstanding selectivity of MC-CD@BA-MIPs, which is attributable to the synergy interaction of molecularly imprinted recognition and boronate affinity. Furthermore, adsorption performance was evaluated in binary component systems including RT/NRG, ARS/NRG, QRCT/NRG, and HQ/NRG (Figure 5e). Even in the presence of competing interferents, MC-CD@BA-MIPs demonstrated significantly higher affinity toward NRG relative to other compounds. This remarkable selectivity is ascribed to the well-defined three-dimensional imprinted cavities created through the emulsion interfacial imprinting strategy, which provides both shape complementarity and specific chemical affinity for the target molecule.

Table 4.
Distribution coefficient and selectivity coefficient data for MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs.
3.8. Reusability Results
The recyclability and stability of adsorbents are critical parameters for assessing their long-term practical applicability and potential for industrial adoption [53]. Through six continuous adsorption–desorption regeneration cycles, the adsorption capacity Q values of NRGNRG for MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs in each cycle were calculated. As shown in Figure 6f, after six cycles, the adsorption capacity of NRG by MC-CD@BA-MIPs decreased by only 7.44%. These results indicate that MC-CD@BA-MIPs have remarkable stability and reusability, and have broad application prospects. In conclusion, this material has good application potential in the field of NRG-specific recognition. Furthermore, compared to other borate-affinity materials reported in the literature (Table 5) [54,55,56,57,58], the MC-CD@BA-MIPs exhibit the highest adsorption capacity, shorter adsorption time, and faster NRG adsorption rate, demonstrating broad application potential in separation fields.

Table 5.
Comparison of the results developed in this work with other homologous materials.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a novel boronate affinity molecularly imprinted material, designated as MC-CD@BA-MIP, was successfully developed for the target-specific extraction and refinement of high-value flavonoids. The incorporation of SH-β-CD into the microsphere structure resulted in improved uniformity and enhanced accessibility of the molecularly imprinted binding sites, thereby substantially improving the adsorption selectivity and recognition performance of the material. Under neutral conditions, the material reached saturation within 360 min with an adsorption capacity of 38.78 μmol·g−1, attributed to a high number of high-affinity binding sites. Furthermore, the adsorbent exhibited excellent selectivity, with adsorption selectivity factors of 2.45, 2.21, 2.33, and 2.65, respectively. This innovative approach not only significantly improves the purification efficiency of cis-diol-containing flavonoids through highly specific molecular recognition but also establishes an environmentally sustainable pathway for obtaining high-purity NRG with potential applicability in green separation processes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations12100267/s1: Table S1: Elementary analyses of MC-CD@BA-MIPs. Table S2: Several kinds of adsorption kinetic models [59,60,61,62,63,64]. Table S3: Intraparticle diffusion and liquid film diffusion models parameters obtained in the adsorption of NRG onto MC-CD@BA-MIPs and MC-CD@BA-NIPs. Table S4: Scatchard analysis of the binding isotherms. Table S5: The textural properties of MC, MC-CD, MC-CD@BA-MIPs, and MC-CD@BA-NIPs. Figure S1: The 1H NMR spectra of APBA in CD3OD (a) and ABIB in CDCl3 (b). Figure S2: Photos of the corresponding stable emulsions of TAPB-BTCA-DVA-COF (a) and using an optical microscope (b,c). Figure S3: The N2 adsorption and desorption isotherms (a) and corresponding pore size distribution (b) of various materials. Figure S4: Adsorption capacity of adsorbents at different dosages.
Author Contributions
J.L.: Writing—original draft preparation, visualization, formal analysis, conceptualization, methodology. X.Z.: Visualization, supervision, investigation. J.X.: Software, validation, resources. X.F.: Data curation, visualization. S.L.: Writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22008093), the Postdoctoral Fund of China (No. 2023 M731820), and the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX25_2464).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jincheng Xu, Xi Feng, and Shucheng Liu were employed by the company Nantong Sunshine Graphite Equipment Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, R.R.; Wen, Z.L.; Zheng, B.; Yang, J.X.; Wang, M.; Ding, X.F.; Shi, L.J.; Hu, H.; Chen, T.Q.; Xiao, S.T.; et al. Targeted design of three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with full exposure of functional adsorption sites for efficient iodine capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 370, 133234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ye, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.H. Utilization of pomelo peels to manufacture value-added products: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qi, Q.L.; Wang, M.T.; Li, Q.Y. Therapeutic potential of naringin: An overview. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaiden, E.E.; Kahia, H.E.; Nasser, B.; Moustaid, K.; Qarah, N.; Boukcim, H.; Hirich, A.; Kouisni, L.; Kharrassi, Y.E. Deep eutectic solvent-ultrasound assisted extraction as a green approach for enhanced extraction of naringenin from Searsia tripartita and retained their bioactivities. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1193509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Qiao, L.; Gu, H.Y.; Yang, F.J.; Yang, L. Development of Brönsted acidic ionic liquid based microwave assisted method for simultaneous extraction of pectin and naringin from pomelo peels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Dandekar, D.V.; Toledo, R.T.; Singh, R.K.; Patil, B.S. Supercritical fluid extraction of limonoids and naringin from grapefruit (Citrus paradisi Macf.) seeds. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Liu, C.K.; Wen, H.; Raza, S. Polyamide-based membranes with nanoscale homogeneity and asymmetric structure for ultrafast ion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 685, 121921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: Structure, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8097–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.X.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, H.J.; Zhang, R.G.; Chen, L.X.; Yang, X.L. Boronate affinity material-based sensors for recognition and detection of glycoproteins. Analyst 2020, 145, 7511–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, S.C.; Tang, N.N.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.M. Hierarchically porous MOFs selfsupporting copolymers for ultrafast transport and precise recognition of flavonoids: A triple interfacial crosslinking strategy based on microreactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 326, 124819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, S.F.; Qian, L.W.; Du, M. Dendrimer-assisted boronate affinity cellulose foams for the efficient and selective separation of glycoproteins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Li, J.K.; Wang, R.; Zhao, S.N.; Zang, S.Q.; Mak, T. Construction of core-shell MOF@COF hybrids with controllable morphology adjustment of COF shell as a novel platform for photocatalytic cascade reactions. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.T.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Liao, X.J.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, J.; et al. Strategy of fusion covalent organic frameworks and molecularly imprinted polymers: A surprising effect in recognition and loading of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8751–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.H.; Qian, H.L.; Yang, C.; Wang, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yan, X.P. Surface imprinted-covalent organic frameworks for efficient solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in food samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Deng, S.; Ren, L.; Li, D.; Wang, W.; Vakili, M.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Stable covalent organic frameworks as efficient adsorbents for high and selective removal of an aryl-organophosphorus flame retardant from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30265–30272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.M.; Lv, S.W.; Yuan, X.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, S. Facile construction of magnetic core-shell covalent organic frameworks as efficient solid-phase extraction adsorbents for highly sensitive determination of sulfonamide residues against complex food sample matrices. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14247–14253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.C.; Xiao, F.Y.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, N. Sulfhydryl-functionalized covalent organic frameworks microspheres supported Au nanoparticles for continuous flow-through catalysis. Water Process. Eng. 2025, 77, 108357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hung, C.T.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.; Li, P.F. Asymmetric monolayer mesoporous nanosheets of regularly arranged semi-opened pores via a dual-emulsion-directed micelle assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27708–27717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Feng, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, X. Preparation of Mono-Dispersed Polyurea-Urea Formaldehyde Double Layered microspheres. Polym. Bull. 2008, 60, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Liang, Q.F.; Karim, A.; Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M.; Rasheed, H.A.; Virk, M.S.; Qayyum, A.; Suleria, H.; Ren, X.F. Pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by biopolymeric particles: From production to high-performance applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wan, X.; Duan, Y.Q.; Hu, K.; Cai, M.H.; Zhang, H.H. Tuning the binding process of rapeseed protein with quercetin for stabilizing high internal phase emulsions. Food Chem. 2025, 488, 144829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Mao, Z.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.D.; Guo, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, C.Y. Ultrasonic assisted water-in-oil emulsions encapsulating macro-molecular polysaccharide chitosan: Influence of molecular properties, emulsion viscosity and their stability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 64, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.F.; Jacob, K.I.; Lu, J.W.; Guo, L. Facile fabrication of surface imprinted polymers based on nanofibrous aerogels for specific capture of lysozyme form egg white. Food Chem. 2025, 484, 144449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Ma, Y.; Peng, Y.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, W.L. Selective recognition and separation of luteolin based on the molecular imprinted hollow SnO2 and boronate affinity. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.H.; Pan, Z.Y.; Rong, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.Y.; Pan, J.M.; Qiu, F.X. Teamed boronate affinity-functionalized Zn-MOF/PAN-Derived molecularly imprinted hollow carbon electrospinning nanofibers for selective adsorption of shikimic acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 27294–27308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, B.L.; Tian, L.; Ali, Z.; Zhang, Q.Y. Fabrication and characterization of glutathione-imprinted polymers on fibrous SiO2 microspheres with high specific surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.T.; Jia, Q. Epitope molecularly imprinted polymers based on host-guest interaction: Specific recognition of CD59. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1755, 466056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, N.N.; Ou, H.X.; Pan, J.M. Selective separation of target glycoproteins using boronate affinity imprinted copolymers: Precise identification and increase the number of recognition sites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 326, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.N.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.Y.; Lu, R.H.; Luo, H.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, H.T.; Liu, S.C. Hyperbranched porous boronate affinity imprinted hydrogels for specific separation of flavonoids under physiological pH: A emulsion interfacial assembly imprinted strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.H.; Li, W.; Liu, P.W.; Wang, W.J. Hierarchical assembly of two-dimensional polymers into colloidosomes and microcapsules. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Guo, D.Z.; Mao, Y.Y.; Bai, B.; Li, Z.J. Emulsion interfacial synthesis of hierarchically porous covalent organic framework microcapsules with multilayered boronic acid binding sites for specific molecular separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 635, 157695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, R.H.; Cui, C.Y.; Tian, C.B.; Yang, G.Y. Designed assembly of heterometallic cluster organic frameworks based on anderson-type polyoxometalate clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6462–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X.M.; Yin, H.B.; Liu, W.M. Separation and purification of polyprenols from Ginkgo biloba leaves by silver ion anchored on imidazole-based ionic liquid functionalized mesoporous MCM-41 sorbent. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Ni, X.; Xia, J.; Suo, H.; Yan, L.; Zou, B. Immobilized lipase based on SBA-15 adsorption and gel embedding for catalytic synthesis of isoamyl acetate. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.R.; Chen, L.W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.H. Improving performance of cell imprinted PDMS by integrating boronate affinity and local post-imprinting modification for selective capture of circulating tumor cells from cancer patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 223, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.Z.; Bai, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.C.; Liu, S.C. Hyperbranched imprinted hydrogel with covalent organic frameworks-based precisely design hyperbranched sites for the coupling engineering of flavoniods separation and environmental remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Pan, Z.H.; Rong, J.; Mao, K.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.C.; Qiu, F.X.; Pan, J.M. Boronate affinity surface imprinted polymers supported on dendritic fibrous silica for enhanced selective separation of shikimic acid via covalent binding. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.X.; Fang, Y.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Wei, J.; Jiao, T.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Guo, Z.Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.M. Molecularly imprinted polymers-coated magnetic covalent organic frameworks for efficient solid-phase extraction of sulfonamides in fish. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 141007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Bai, B.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Y.Y.; Guo, D.Z. Fabrication of rod-like boronate affinity imprinted covalent organic frameworks (COFs) interconnected with polyHIPEs for selective high-flux separation of flavoniods. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Cao, J.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Hu, X.P.; Zhao, X.H.; Song, X.L.; Chen, L.X. Simultaneous magnetic purification and detection of transferrin in human serum using an imprinting-based fluorescence sensor by boronate affinity and secondary signal amplification assay. Analyst 2025, 150, 2410–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttersack, C. Modeling of type IV and V sigmoidal adsorption isotherms. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 5614–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batonneau-Gener, I.; Sachse, A. Determination of the Exact Microporous Volume and BET Surface Area in Hierarchical ZSM-5. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 4235–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lin, R.X.; Zhang, K.C.; Yan, J.M.; Ma, F.G.; Zhen, J.J.; Pan, J.M. Discontinuous cooperative imprinting idea based on MXene-nanocomposite membrane for high structurally stable recognition and separation of shikimic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.X.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, W.Y.; Xu, H.; Ling, Q.F.; Yang, J.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, K.X.; Zheng, X.L.; He, S.R.; et al. Iron and nitrogen co-doping biochar for simultaneous and efficient adsorption of oxytetracycline and norfloxacin from wastewater. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 226, 120646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Mu, Y.Y.; Ma, H.L.; Qu, W.J. Functional Magnetic Nanoparticles for Highly Efficient Cholesterol Removal. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wang, H. Water-in-water emulsions stabilized by silica Janus nanosheets. Small 2023, 19, 2206215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.C.; Ma, F.G.; Wu, Y.Y. Construction of anchor points in metal-organic framework-based membranes for high flux separations and high-efficient anticancer drug intermediates capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Xie, H.H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.H.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, Y.T.; Wang, H.L.; Hao, C. High-performance polyethylenimine-functionalized lignin/silica porous composite microsphere for the removal of hexavalent chromium, phosphate and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 194, 116289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Yang, P.P.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Xie, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.T.; Guo, Z.H. Graphene oxide based dopamine mussel-like cross-linked polyethylene imine nanocomposite coating with enhanced hexavalent uranium adsorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16902–16911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.Y.; Xing, C.R.; Xue, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, P. Selective removal of Pb(II) from yellow rice wine using magnetic carbon-based adsorbent. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6929–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, J.Y.; Dong, C.Y.; Shi, H.X.; Han, Y.R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, R.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, J.J. Surface molecular imprinted membranes as a “gate” for selective transdermal release of chiral drug amlodipine. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 664, 121059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Pan, Z.Y.; Dai, Y.T.; Rong, J.; Zhang, T.; Xue, S.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Qiu, F.X. Fabrication of sustainable boronate affinity membrane derived from rape pollen biomass and cellulose acetate for the selective separation of shikimic acid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.D.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.L.; Li, H.; Luo, J.Q.; Pan, J.M. Hybrid hydrogel microspheres loading single-hole hollow imprinted particles for fast and selective uptake of 2′-deoxyadenosine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.Z.; Sun, Y. Hu, Z. Liu, S.C.; Yu, Q.W.; Li, Z.J. Formation of boronate-based macroporous copolymer via emulsion-assisted interface self-assembly method for specific enrichment of naringin. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.M.; Liu, S.C.; Hu, Z.; Yan, X.C.; Geng, S.B.; Zhao, X.; Ou, H.X. Separation and purification of target flavonoids using covalently connected MOFs@boronic acidfunctionalized-COFs magnetic hybrids: Precise identification and enhanced stability. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124061. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.Z.; Mao, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, B.; Yan, X.C.; Liu, S.C. Hierarchically porous boronic acid functioned copolymers fabricated from HIPEs microreactor for ultrafast transport and specific recognition of flavonoids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, S.C. Water-compatible imprinted polymers based on CS@SiO2 particles for selective recognition of naringin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ren, Y.M.; Li, G. Detection of naringin by fluorescent polarization molecularly imprinted polymer. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.F.; Mao, Y.L.; Ni, L.; Xie, X.Q. Preparation of temperature-sensitive magnetic microspheres for separation and purification of bromelain. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 114, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.N.; Shi, B.Q.; Hu, X.T.; Shi, Y.Q.; Wang, T.X.; Huang, X.W.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y. Simultaneous adsorption and fluorescent sensing of ampicillin based on a trimetallic metal-organic framework. Food Chem. 2025, 472, 142891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.Y.; Huang, W.; Zhu, F.G.; Geng, F.; Tian, M.M. A new boronate-afffnity hollow solid phase extraction sorbent for the enrichment of cis-diol-containing isoffavones in soybean milk samples. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S. Peroxymonosulfate-activated molecularly imprinted bimetallic MOFs for targeted removal of PAHs and recovery of biosurfactants from soil washing effluents. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Sun, Y.; Guo, D.Z.; Lu, R.H.; Mao, Y.Y.; Ou, H.X. Porous boronate imprinted microsphere prepared based on new RAFT functioned cellulose nanocrystalline with multiple H-bonding at the emulsion droplet interface for highly specific separation of Naringin. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Ma, W.; Dan, O.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Su, H.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z. Thiol functionalized covalent organic framework for highly selective enrichment and detection of mercury by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-fight mass spectrometry. Analyst 2021, 146, 2991–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).