Removal of Inorganic Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Operational Principle of EC
1.2. The Merits of EC
- There is no possibility of secondary contamination occurring via side reactions of high chemical concentrations, as no chemicals were added [54].
- Pollutants can be removed more readily by floating on the surface of the solution due to the gas bubbles created by EC [54].
- Due to the simplicity of the equipment, full process automation is achievable [55].
- Clear, colorless, and odorless water is produced through EC treatment of wastewater [55].
- Due to the ability of the electric current to speed up, impact, and promote coagulation, EC may eliminate even the smallest colloidal particles [54].
2. Inorganic Contaminants
2.1. Hydrated Silica and Related Minerals
2.2. Silver (Ag)
2.3. Arsenic (As)
2.4. Cadmium (Cd)
2.5. Manganese (Mn)
2.6. Calcium (Ca)
2.7. Phosphorus (P)
2.8. Nitrogen (N)
| NO. | Removed Element | Anode | Cathode | Gap (cm) | Conc. (mg/L) | η (%) | pH | Time (min) | Power (A/m2) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | NO3 | Al | Al | ---- | 100 | 88–94 | 7.25 | 120 | ---- | [105] |
| 3 | NO3 | Al | Al | ---- | 100 | 94 | 7 | ---- | ---- | [106] |
| 5 | NO3 | Al | Al | ---- | 2500 | 87 | 7, | 100 | 29.4–1030 | [107] |
| 7 | fluoride | Al | Al | 1.8 | 100 | 88, | 5.94 | 180 | 90.9 | [108] |
| NO3 | 42 | |||||||||
| 8 | N | Fe | Fe | 2.5 | ---- | 80 | 6.72–7.25 | ---- | ---- | [109] |
2.9. Zinc (Zn)
2.10. Boron (B)
2.11. Chromium (Cr)
2.12. Iron (Fe)
2.13. Fluoride (F)
2.14. Mercury (Hg)
2.15. Lead (Pb)
2.16. Selenium (Se)
| NO. | Removed Element | Anode | Cathode | Gap (cm) | Conc. (mg/L) | η (%) | pH | Time (min) | Power (A/m2) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ag | Graphite | Al | 1 | 20 | 97 | 5.4 | 20 | 50 | [66] |
| 4 | As(V) | ZVI-PVDF | ---- | ---- | 5.12 | 99 | 7 | 120 | ---- | [146] |
| 7 | Ni (II) | Fe sheets | Ti | ---- | 100 | 99. | 7 | 25 | 7 | [147] |
| 8 | Cr(VI), | Al | Al | 3 | 50 | ~95, | 5 | 60 | 250 | [132] |
| Ni(II) | ~96, | |||||||||
| Cu(II) | ~100 | |||||||||
| 9 | Boron | Fe-based | 304 SS | 1 | ---- | 6–13 | 7.5 | 600 | [127] | |
| 10 | Zn, | Al | Al | 0.7 | 0.096, | 95 for Heavy metals and 97 for microplastics | 6 | 20 | 120 | [148] |
| Ni, | 0.022, | |||||||||
| Cu, | 0.045, | |||||||||
| Cr, | 0.036, | |||||||||
| Pb, | 0.003, | |||||||||
| microplastics | 48.1 | |||||||||
| 11 | As | SS | SS | ---- | 0.01 | 92 | ---- | ---- | ---- | [75] |
| 12 | As | Fe2+ | Fe2+ | ---- | 0.1, 0.3, 0.4, and 1 | ---- | 7–8 | 60 | 20.83 | [149] |
| 13 | Ni(II) | platinum-coated titanium mesh | nickel plate | ---- | 325 | 97 | 4.5 | 120 | 50 | [150] |
| 14 | Fe, | Al | Al | ---- | 100 | 99, | ---- | 5, 90, 150, 45, 150, +435, +435 | 200 | [77] |
| Zn, | 99, | |||||||||
| Mn, | 99, | |||||||||
| Cu, | 99, | |||||||||
| Ni, | 98, | |||||||||
| Cd, | 96, | |||||||||
| Cr | 88 | |||||||||
| 15 | Cu-EDTA | RuO2–IrO2/Ti | Al | ---- | 50 | 99 | 7 | 60 | 102.9 | [151] |
| 17 | Pb, | Fe | Fe | 1 | 18, 451, 17 | 99, | 5 | 40 | 140 | [12] |
| Cr, | 94, | |||||||||
| Cd | 99 | |||||||||
| 18 | Fe | Al | Al | ---- | 10–30 | 99 | ---- | 10–50 | 15–45 | [139] |
| 19 | Fluoride | Fe | Fe | ---- | ---- | ---- | 6 | 75.44 | [152] | |
| 20 | Ca(II) (COD) | Al, Mg, and Fe | Ti | 5 | ---- | 64, 75 | 7.5 | 60 | 115 | [153] |
| 21 | Zn, | steel anode with polypyrrole modification | SS-Al | 2 | ---- | 99, | 4 | 70 | 300 | [154] |
| Ni | 80 | |||||||||
| 22 | Fluoride | Al | Al | ---- | 1.37–48 | 90 | 4–9 | ---- | ---- | [155] |
| 23 | As | Fe | Fe | ---- | 15.2–41.5 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 3 | [156] |
| 24 | Cu | Al | Al | 1 | ---- | 95 | ---- | 10 | 40 | [157] |
| 25 | Cr (VI) | Fe | ---- | ---- | 1, 5, and 10 | ---- | ---- | ---- | 13 | [158] |
| 27 | Fluoride | Al | ---- | ---- | 61 | ---- | 4.8–5 | ---- | 50 | [159] |
| 28 | NO3, | Al3+ or Fe2+ | H2 | ---- | ---- | 62, | 7 | 240 | 100 | [160] |
| C−, | 30, | |||||||||
| SO42−, | 42, | |||||||||
| K(I), | 29, | |||||||||
| Mg(II), | 83, | |||||||||
| Ca(II), | 31, | |||||||||
| Na(I) | 27, | |||||||||
| F- | 69 | |||||||||
| 29 | Fluoride | Al | ---- | ---- | 7.35 | 86 | ---- | 10 | 100 | [161] |
| 30 | Sb(V) and Co(II) | Fe | SS | 1 | 60 | 95 | ---- | 20 | 50 | [162] |
| 31 | Na, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Ni | Al | H2 | 0.5–20 | 10.2 | 85–98 | 3.6–8.7 | 20 | 20–80 | [163] |
| 32 | Boron | Al | H2 | ---- | ---- | 70 | 7.35 | ---- | 187.5 | [124] |
| 33 | Fe(II) | Al | SS | 1 | 330 | ---- | 6.34 | 45 | 20 | [164] |
| 34 | Ca(II), | Mg | SS | 1 | ---- | 52, | 8 | 60 | 142.9 | [165] |
| Mg(II) | 94 | |||||||||
| 35 | Sb(V) | Fe | Fe | ---- | > 4.0 | 99 | 30 | ---- | [166] | |
| 36 | fluoride and HS | AL | Al | ---- | 4.08, 90 | 96 | 7.38 | ---- | 40–70 | [167] |
| 38 | Fe, | Al, Fe | Fe, Al | 1 | ---- | 99, | 7.09 | 60 | 68.50 | [80] |
| Cr, | 99, | |||||||||
| Pb, | 99, | |||||||||
| Mn, | 98, | |||||||||
| Cu | 73 | |||||||||
| 39 | Br-, Cl-, TDS, and SO42− | Al | Al | ---- | ---- | 84 | 8 | 10 | 20 | [168] |
| 40 | Ca, Mg, silica and dissolved organic matter | Ti | SS | ---- | 17–25 | 60–65 | 11.5 | ---- | 220 | [169] |
3. Operating Parameters Affecting the EC Process
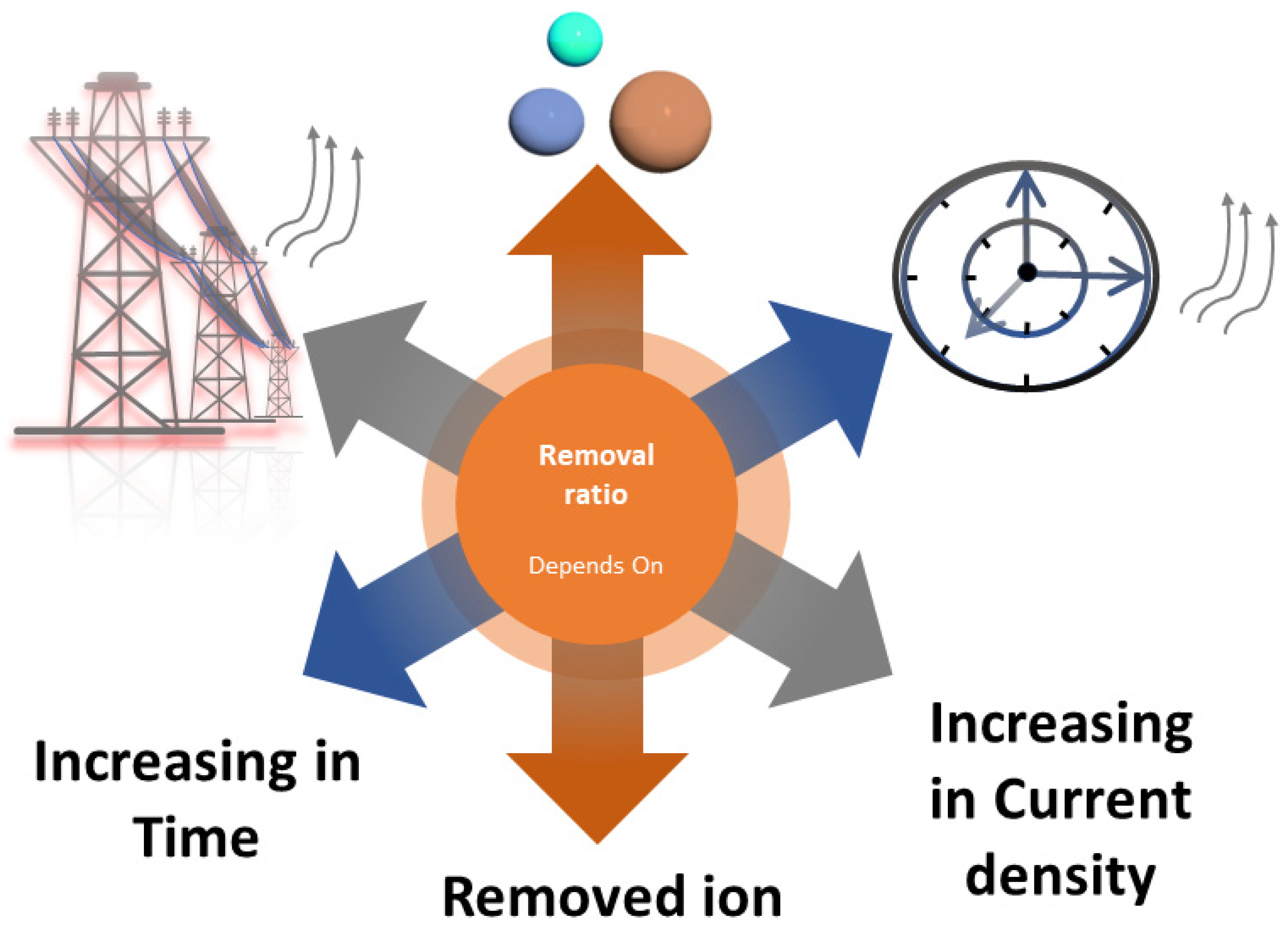
3.1. pH Value
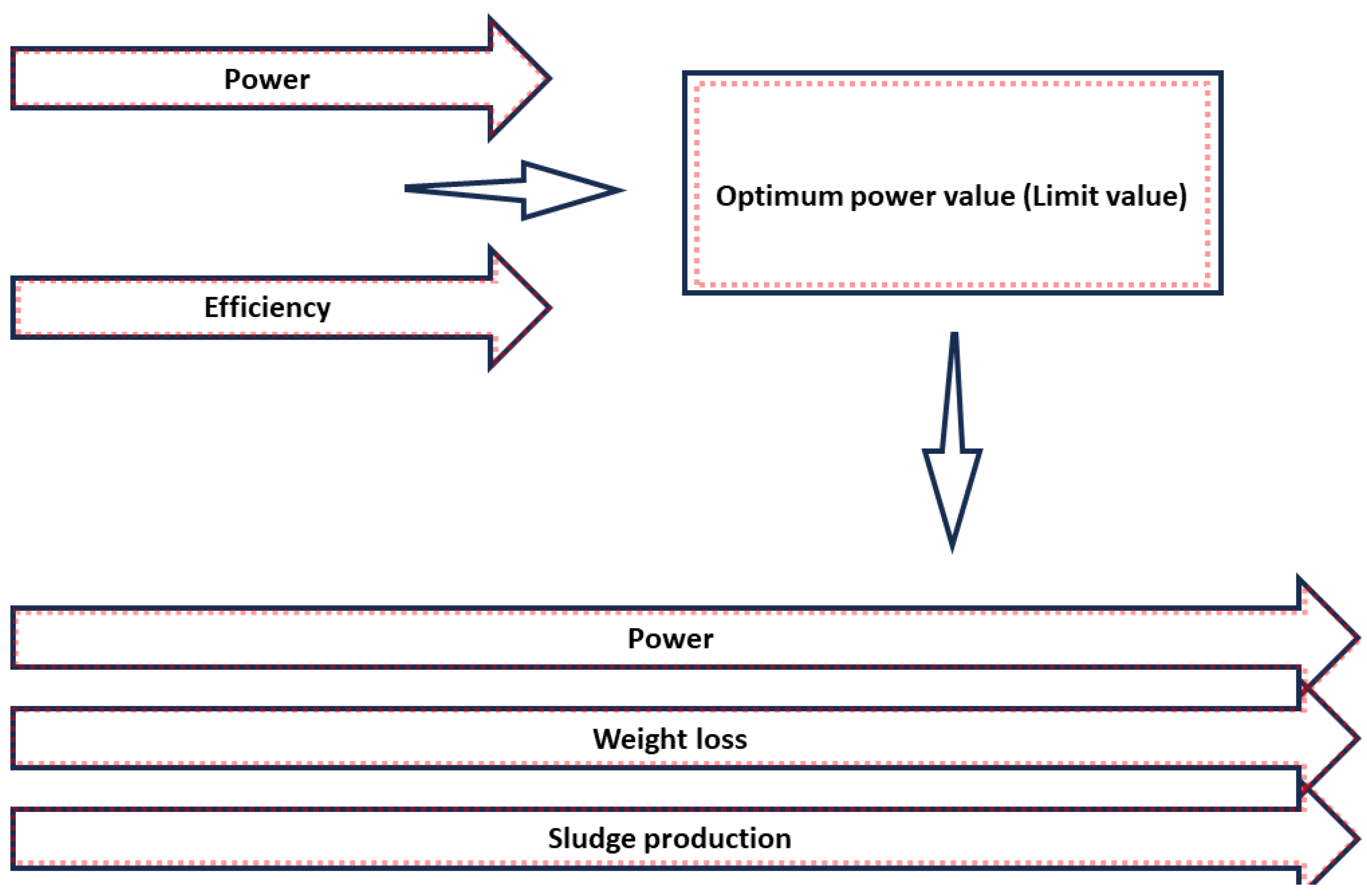
3.2. Applied Power
3.3. Time
3.4. Electrode Spacing
3.5. Concentration of Contaminants
3.6. Anode Material
4. Limitations and Opportunities of the Low-Cost EC Process
4.1. Drawbacks of the EC Process
- The electrode produces gas, while the flocculant is a result of wear, necessitating regular plate replacement [148].
- The using of electricity and electrode passivation may raise energy consumption and cost [191].
- Excessive electrolyte concentrations might result in the creation of hazardous compounds, so pretreatment is necessary in some cases before the EC [148].
- Formation of sludge.
4.2. New Developments and Opportunities
| NO. | Removed Substance | Removal Technique (1) | Removal Technique (2) | Energy Consumption/Cost (1) | Energy Consumption/Cost (2) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PE | EC | --- | 0.91 USD·L−1 | --- | [148] |
| 2 | MPs | EC | --- | 0.03 and 3.85 USD/m3 | --- | [197] |
| 3 | COD | EC | --- | 31.9 kWh/m3 and 20.4 kWh/kg | --- | [198] |
| 4 | Acid Red 18 | EC | --- | 3 USD/Kg | --- | [199] |
| 5 | Cobalt | EC | --- | 0.204 kWh | --- | [200] |
| 6 | Cr | EC | --- | 137.2 KWh m−3 | --- | [201] |
| 7 | Cr, P, COD, and turbidity contents | EC | --- | 2.21 kWh/m3 | --- | [202] |
| 8 | azo dyes | EC | --- | 1.5925 KWh m−3 | --- | [203] |
| 9 | oxytetracycline hydrochloride | EC | --- | 0.0014 kWh/L and 0.19 kWh/L | --- | [204] |
| 10 | Pb, Cd, and Cu | EC | --- | 12.71 kWh/m3 | --- | [205] |
| 11 | Blue dye | EC | photo-assisted chemical oxidation | 0.0481 USD and 0.6418 USD | 1.0267 USD and 1.04337 USD | [206] |
| 12 | Dye | EC | Ozonation | 1.58 kWh/m3 | 8.41 kWh/m3 | [207] |
| 13 | Dye | EC | Fenton | 1.58 kWh/m3 | 4.71 kWh/m3 | [207] |
| 14 | Dye | EC | Photo-Fenton | 1.58 kWh/m3 | 11.2 kWh/m3 | [207] |
| 15 | Boron | EC | chemical coagulation | 0.8 $/kg | 1.8 USD/kg | [208] |
| 16 | COD | EC | Photo-electrocoagulation | 65.06 kWh/kg | 119.34 kWh/kg | [209] |
| 17 | COD | EC | Peroxi-electrocoagulation | 65.06 kWh/kg | 32.14 kWh/kg | [209] |
| 18 | COD | EC | Peroxi-photoelectrocoagulation | 65.06 kWh/kg | 77.55 kWh/kg | [209] |
| 19 | COD | EC | Chemical coagulation | 1.336 USD/kg | 0.591 USD/kg | [210] |
| 20 | COD | EC | Chemical coagulation | 1.336 USD/kg | 0.318 USD/kg | [210] |
| 21 | COD | EC | Ultrafiltration | 1.336 USD/kg | 0.044 USD/kg | [210] |
| 22 | Dye | EC | Chemical coagulation | 0.34–0.52 US$/kg | 0.32 USD/kg | [211] |
| 23 | COD | EC | Electrochemical Fenton | 2.73 kWh/kg | 3.38 kWh/kg | [212] |
| 24 | COD | EC | Electro-Fenton | 2.73 kWh/kg | 63.64 kWh/kg | [212] |
| 25 | COD | EC | Peroxi-coagulation | 2.73 kWh/kg | 23.19 kWh/kg | [212] |
| 26 | TOC, COD, TP, and color | EC | electro-Fenton | 1.27 EUR/m3 | 1.42 EUR/m3 | [213] |
5. Summary and Path Forward
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Raad, A.A.; Hanafiah, M.M. Removal of inorganic pollutants using electrocoagulation technology: A review of emerging applications and mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, T.K.; Jasim, N.A. A comparison study between chemical coagulation and electro-coagulation processes for the treatment of wastewater containing reactive blue dye. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1946–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, H.; Hanafiah, M.M. A review of sustainable e-waste generation and management: Present and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, F. Impacts of Metals on Aquatic Ecosystems and Human Health. Environ. Communities 2008.
- Corcoll, N.; Bonet, B.; Leira, M.; Guasch, H. Chl-a fluorescence parameters as biomarkers of metal toxicity in fluvial biofilms: An experimental study. Hydrobiologia 2011, 673, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N.; More, N.; Yadav, A.; Zainith, S.; Mani, S.; Chowdhary, P. Heavy metal contamination: An alarming threat to environment and human health. In Environmental Biotechnology: For Sustainable Future; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 103–125. [Google Scholar]
- Onakpa, M.M.; Njan, A.A.; Kalu, O.C. A Review of Heavy Metal Contamination of Food Crops in Nigeria. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, C.E.; Guirardello, R.; Silva, E.A.; Veit, M.T.; Tavares, C.R.G. Removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous solution by biosorption in a fixed bed column: Experimental and theoretical breakthrough curves. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 30, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Xiong, W.; Ahmad, K. Electrocoagulation treatment of arsenic in wastewaters: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, A.T.; Minasse, F.A.; Guilherme, M.R.; Reis, A.V.; Muniz, E.C.; Nozaki, J. Novel adsorbent based on silkworm chrysalides for removal of heavy metals from wastewaters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, L.S.; Baghel, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Parmar, H.; Varma, A.K.; Mondal, P. Simultaneous removal of lead, chromium and cadmium from synthetic water by electrocoagulation: Optimization through response surface methodology. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 72, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Jankar, J.S. A Comparative Study of Chromium: Therapeutic Uses and Toxicological Effects on Human Health. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2022, 13, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health hazards of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) and its microbial reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezami, L.; Capart, R. Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbons: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, S.; Oh, S. A review on microbial-integrated techniques as promising cleaner option for removal of chromium, cadmium and lead from industrial wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwikima, M.M.; Mateso, S.; Chebude, Y. Potentials of agricultural wastes as the ultimate alternative adsorbent for cadmium removal from wastewater. A review. Sci. Afr. 2021, 13, e00934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegane, S.A.; Kangale, K. A Review on Removal of Heavy Metals by Using Low Cost Adsorbents with Reference to Electroplating Industry. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Res. Technol. 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Xiao, X.; Luo, S. Advances in microbial remediation for heavy metal treatment: A mini review. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2021, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, P.; Nayak, S.; Samantaray, S.M. Microalgal bioremediation of toxic hexavalent chromium: A review. Environ. Agric. Microbiol. Appl. Sustain. 2021, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Macias-Garbett, R.; Malacara-Becerra, A.; Iqbal, H.M.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Environmental impact of emerging contaminants from battery waste: A mini review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouida, L.; Rafatullah, M.; Kerrouche, A.; Qutob, M.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Alorfi, H.S.; Hussein, M.A. A Review on Cadmium and Lead Contamination: Sources, Fate, Mechanism, Health Effects and Remediation Methods. Water 2022, 14, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, E.D.H.; Chau, J.H.F.; Lai, C.W.; Khe, C.S.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Siengchin, S.; Sanjay, M.R. GO/TiO2-Related Nanocomposites as Photocatalysts for Pollutant Removal in Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís–Rodríguez, R.; Pérez–Garibay, R.; Alonso–González, O.; Mendieta–George, D.; Alvarado–Gómez, A. Vanadium removal by electrocoagulation with anodes of zinc. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Primary Drinking Water Regulations, National Primary Drinking Water Regulations|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Aziz, N.I.H.A.; Hanafiah, M.M. Application of life cycle assessment for desalination: Progress, challenges and future directions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajda, M.; Aleksander-Kwaterczak, U. Wastewater Treatment Methods for Effluents from the Confectionery Industry—An Overview. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Kusmayadi, A.; Yen, H.W.; Dong, C.D.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Current advances in biological swine wastewater treatment using microalgae-based processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pal, D.B.; Mohammad, A.; Alhazmi, A.; Haque, S.; Yoon, T.; Srivastava, N.; Gupta, V.K. Biological remediation technologies for dyes and heavy metals in wastewater treatment: New insight. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; Kot, P.; Zubaidi, S.L.; Alwash, R.; Al Khaddar, R.; Shaw, A.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Aljefery, M.H. Energy efficient electrocoagulation using baffle-plates electrodes for efficient Escherichia coli removal from wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.; Meng, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Crittenden, J. Electrochemical degradation of methylisothiazolinone by using Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/α, β-PbO2 electrode: Kinetics, energy efficiency, oxidation mechanism and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Ren, S.; Pooley, S.; Sun, W.; Kowalczuk, P.B.; Gao, Z. Electrocoagulation for industrial wastewater treatment: An updated review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.L.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Abatement of hydrated silica and simultaneous removal of coexisting ions from deep well water by electrocoagulation using an up-flow reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Hu, B. Phosphorus removal and recovery from dairy manure by electrocoagulation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57960–57968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xiao, J.; Gao, F. imultaneous removal of ammonia nitrogen and recovery of phosphate from swine wastewater by struvite electrochemical precipitation and recycling technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. Comparison investigation on phosphate recovery from sludge anaerobic supernatant using the electrocoagulation process and chemical precipitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salbitani, G.; Carfagna, S. Ammonium utilization in microalgae: A sustainable method for wastewater treatment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepova, K.; Fediv, I.; Mažeikienė, A.; Šarko, J.; Mažeika, J. dsorption of Ammonium Ions and Phosphates on Natural and Modified Clinoptilolite: Isotherm and Breakthrough Curve Measurements. Water 2023, 15, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Li, K.; Cao, A.; Wang, J. A novel electrocoagulation-membrane stripping hybrid system for simultaneous ammonia recovery and contaminant removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagastyo, A.Y.; Sidik, F.; Anggrainy, A.D.; Lin, J.L.; Nurhayati, E. The Performance of Electrocoagulation Process in Removing Organic and Nitrogenous Compounds from Landfill Leachate in a Three-Compartment Reactor. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Hong, X.; Wu, K.; Hui, K.S.; Du, Y.; Hui, K.N. Simultaneous removal of ammonia and phosphate by electro-oxidation and electrocoagulation using RuO2–IrO2/Ti and microscale zero-valent iron composite electrode. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyonar, F.; Korkmaz, M.U. Sequential use of the electrocoagulation-electrooxidation processes for domestic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhaede, M.; Ahmed, A.; Wollmann, M.; Wagner, L. Evaluating the effects of hydroxyapatite coating on the corrosion behavior of severely deformed 316Ti SS for surgical implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 50, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benekos, A.K.; Tsigara, M.; Zacharakis, S.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Katsaounis, A.; Vayenas, D.V. Combined electrocoagulation and electrochemical oxidation treatment for groundwater denitrification. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Lin, S.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, X. Influence of key cations and anions on phosphate removal by Fe(0) electrocoagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollas, C.E.; Bolsan, A.C.; Venturin, B.; Bonassa, G.; Tápparo, D.C.; Cândido, D.; Antes, F.G.; Vanotti, M.B.; Szögi, A.A.; Kunz, A. Second-Generation Phosphorus: Recovery from Wastes towards the Sustainability of Production Chains. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibagli, P.; Isik, Z.; Mazmanci, M.A.; Dizge, N. Phosphate recovery from waste fish bones ash by acidic leaching method and iron phosphate production using electrocoagulation method. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attour, A.; Touati, M.; Tlili, M.; Amor, M.B.; Lapicque, F.; Leclerc, J.P. Influence of operating parameters on phosphate removal from water by electrocoagulation using aluminum electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 123, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Barjenbruch, M.; Kabbe, C.; Inial, G.; Remy, C. Phosphorus recovery from municipal and fertilizer wastewater: China’s potential and perspective. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.S.A.; Ramesh, S.T. An experimental study of CI Reactive Blue 25 removal from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using Aluminum sacrificial electrode: Kinetics and influence of parameters on electrocoagulation performance. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinpally, S.; Kolla, A.; Kainthola, J.; Kodali, R.; Vemuri, J. A state-of-the-art review of the electrocoagulation technology for wastewater treatment. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaied, B.K.; Rashid, M.; Nasrullah, M.; Zularisam, A.W.; Pant, D.; Singh, L. A comprehensive review on contaminants removal from pharmaceutical wastewater by electrocoagulation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.; Morkovsky, P.; Gomes, J.A.; Kesmez, M.; Parga, J.; Cocke, D.L. Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 114, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Mohammadi, L.; Ansari-Moghaddam, A.; Mahvi, A.H. Heavy metals removal from aqueous environments by electrocoagulation process– a systematic review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.F.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Arsenic and hydrated silica removal from groundwater by electrocoagulation using an up-flow reactor in a serpentine array. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, M.; Idrus, M.A.M.; Crombie, C.; Jegatheesan, V. Performance of precipitation and electrocoagulation as pretreatment of silica removal in brackish water and seawater. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.; Lee, Y.; Sheikholeslami, R. Silica fouling and cleaning of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2001, 139, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-H.; Chen, S.-S.; Yang, S.-R. In-line coagulation/ultrafiltration for silica removal from brackish water as RO membrane pretreatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, W.; Wang, C.-J. Removal of silica from brackish water by electrocoagulation pretreatment to prevent fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 59, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, G.; Hater, W.; Zum Kolk, C.; Dupoiron, C.; Harrer, T.; Götz, T. Investigations of silica scaling on reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2010, 250, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelich, C.J.; Williams, M.D.; Rahardianto, A.; Franklin, J.C.; Cohen, Y. High-recovery reverse osmosis desalination using intermediate chemical demineralization. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 301, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.F.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Simultaneous removal of arsenic, fluoride, and hydrated silica from deep well water by electrocoagulation using hybrid Al-Fe electrodes. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 166, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, H.; Pham, A.L.-T. Effective removal of silica and sulfide from oil sands thermal in-situ produced water by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Shen, L.; Yao, C.; Wang, Y. In-situ silver recovery for biofouling mitigation with catechol-assisted nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2023, 547, 116233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z. Green capturing of Ag from ultra-low concentration precious metal wastewater by electrodeposition assisted with electrocoagulation: Electrochemical behavior and floc characterization. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 167, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji Yaychi, R.; Manteghian, M. Investigation of effect of electric field on silver nanoparticles in order to separation of them from aqueous medium using electrocoagulation process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, M.S.; Melegari, S.P.; Vicentini, D.S.; Matias, W.G.; Ricordel, C.; Hauchard, D. Synthetic wastewaters treatment by electrocoagulation to remove silver nanoparticles produced by different routes. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, A.; Xu, C.C.; Yang, W. Recovery of arsenic and practical utilization of aqueous phase in hydrothermal liquefaction of hyperaccumulator. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Kong, X.; Yi, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Jiang, W. Synergy of directional oxidation and vacuum gasification for green recovery of As2O3 from arsenic-containing hazardous secondary resources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 859, 160091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qing, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Zeng, L.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Wang, M.; Guan, W. A feasible strategy for deep arsenic removal and efficient tungsten recovery from hazardous tungsten residue waste with the concept of weathering process strengthening. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, X.; He, M.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, F.; Yang, X.; Kong, L. Reductive removal of As(V) and As(III) from aqueous solution by the UV/sulfite process: Recovery of elemental arsenic. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín-Reyes, J.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Concurrent elimination of arsenic and hydrated silica from natural groundwater by electrocoagulation using iron electrodes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 184, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Ulu, F.; Gebologlu, U.; Demirbas, E.; Oncel, M.S. Treatment of potable water containing low concentration of arsenic with electrocoagulation: Different connection modes and Fe–Al electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 77, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.Q.; Loganathan, P.; Dinh, B.K.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.H. Removing arsenate from water using batch and continuous-flow electrocoagulation with diverse power sources. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadikhan, S.; Amooghin, A.E.; Sanaeepur, H.; Shirazi, M.M.A. A critical review on cadmium recovery from wastewater towards environmental sustainability. Desalination 2022, 535, 115815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, M.; Montel, E.; Zissimos, A.; Christoforou, I.; Dermentzis, K.; Agapiou, A. Removal of toxic metals and anions from acid mine drainage (AMD) by electrocoagulation: The case of North Mathiatis open cast mine. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkele, K.; Mpenyana-Monyatsi, L.; Masindi, V. Challenges, advances and sustainabilities on the removal and recovery of manganese from wastewater: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neculita, C.M.; Rosa, E. A review of the implications and challenges of manganese removal from mine drainage. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nandi, B.K. Treatment of iron ore beneficiation plant process water by electrocoagulation. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cao, J.; Teng, M.; Meng, L.; Zhao, L.; Chi, X.; Han, Z.; Tucker, M.E.; Zhao, H. Calcium ion removal at different sodium chloride concentrations by free and immobilized halophilic bacteria. Water Res. 2022, 229, 119438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Electrocoagulation treatment of shale gas drilling wastewater: Performance and statistical optimization. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 794, 148436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Luo, J.; Xie, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.Y. Species, fractions, and characterization of phosphorus in sewage sludge: A critical review from the perspective of recovery. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 786, 147437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janpum, C.; Pombubpa, N.; Monshupanee, T.; Incharoensakdi, A.; In-Na, P. Advancement on mixed microalgal-bacterial cultivation systems for nitrogen and phosphorus recoveries from wastewater to promote sustainable bioeconomy. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 360, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamilya, T.; Majumder, A.; Yadav, M.K.; Ayoob, S.; Tripathy, S.; Gupta, A.K. Nutrient pollution and its remediation using constructed wetlands: Insights into removal and recovery mechanisms, modifications and sustainable aspects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłodowska, I.; Rodziewicz, J.; Janczukowicz, W.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Parszuto, K. Effect of citric acid on the efficiency of the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus compounds during simultaneous heterotrophic-autotrophic denitrification (HAD) and electrocoagulation. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, I.; Estahbanati, M.K.; Carabin, A.; Drogui, P. Coupling electrocoagulation with electro-oxidation for COD and phosphorus removal from industrial container wash water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 119992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azerrad, S.P.; Isaacs, M.; Dosoretz, C.G. Integrated treatment of reverse osmosis brines coupling electrocoagulation with advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omwene, P.I.; Kobya, M.; Can, O.T. Phosphorus removal from domestic wastewater in electrocoagulation reactor using aluminium and iron plate hybrid anodes. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 123, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Lee, J.; Arbelaez, S.; Cohen, N.; Kim, J.Y. Removal of phosphate from surface and wastewater via electrocoagulation. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, J.; Gao, B.; Sillanpää, M. Anaerobic offsite Fe2+ releasing for electrocoagulation in ABMBR: Membrane fouling mitigation, nutrients removal and anodes protection. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Synergistic integration of electrocoagulation and algal cultivation to treat liquid anaerobic digestion effluent and accumulate algal biomass. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Hu, B. A pilot-scale study of electrocoagulation on phosphorus removal from animal manure and the economic analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 219, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Mao, R.; Shi, Y.; Lin, S.; Qiao, M.; Zhao, X. Removal of phosphate in secondary effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plant by iron and aluminum electrocoagulation: Efficiency and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; He, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, W.; Ren, N.; Logan, B.E. Energy efficient electrocoagulation using an air-breathing cathode to remove nutrients from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, V.; Kuokkanen, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U.; Roininen, J. Removal of phosphate from wastewaters for further utilization using electrocoagulation with hybrid electrodes—Techno-economic studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 8, e50–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchamango, S.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Ngameni, E.; Hadjiev, D.; Darchen, A. Treatment of dairy effluents by electrocoagulation using aluminium electrodes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.F.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Simultaneous elimination of hydrated silica, arsenic and phosphates from real groundwater by electrocoagulation using a cascade-shaped up-flow reactor. Electrochimica Acta 2020, 331, 135365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzioli, F.; Bertasini, D.; Bolzonella, D.; Frison, N.; Battista, F. A critical review on the techno-economic feasibility of nutrients recovery from anaerobic digestate in the agricultural sector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guisasola, A.; Baeza, J.A. A review on the integration of mainstream P-recovery strategies with enhanced biological phosphorus removal. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Khadir, A.; M.A.Tehrani, R. Optimization of nitrogen removal from an anaerobic digester effluent by electrocoagulation process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhuo, Q.; Ren, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, K. Treatment of wastewater from adhesive-producing industries by electrocoagulation and electrochemical oxidation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Yousefi, N.; Fatehizadeh, A. Survey efficiency of electrocoagulation on nitrate removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; Al Khaddar, R.; Jasim, N.; Shaw, A.; Phipps, D.; Kot, P.; Pedrola, M.O.; Alattabi, A.W.; Abdulredha, M.; Alawsh, R. Electrocoagulation as a green technology for phosphate removal from river water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarine, M.; Lekhlif, B.; Echaabi, J. Nitrate removal from groundwater in Casablanca region (Morocco) by electrocoagulation. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarine, M.; Lekhlif, B.; Sinan, M.; El Rharras, A.; Echaabi, J. Treatment of nitrate-rich groundwater using electrocoagulation with aluminum anodes. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; El-Ashtoukhy, E.Z.; Zoromba, M.S.; Bassyouni, M.; Sedahmed, G.H. Removal of nitrates from water by electrocoagulation using a cell with horizontally oriented Al serpentine tube anode. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, H.; Chaabane, T.; Omine, K.; Sivasankar, V.; Sano, H.; Hecini, M.; Darchen, A. Electrocoagulation in the dual application on the simultaneous removal of fluoride and nitrate anions through respective adsorption/reduction processes and modelling of continuous process. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qiu, T.; Chen, F.; Zhou, L.; Du, Y.; Sun, J. Nitrogen migration law and recycling strategy in an innovative recirculating aquaculture system: Enhancing performance through electrocoagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.K.; Barton, G.W.; Mitchell, C.A. The future for electrocoagulation as a localised water treatment technology. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wan, J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; Chen, G.; Huang, Z.; He, K.; Cheng, M.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the cytotoxicity of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in Phanerochaete chrysosporium by cellular uptake and oxidative stress. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zeng, G.; Chen, G.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Wan, J.; Chen, A.; Guo, Z.; Yan, M.; Wu, H.; et al. Treatment of landfill leachate using immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium loaded with nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Aji, B.; Yavuz, Y.; Koparal, A.S. Electrocoagulation of heavy metals containing model wastewater using monopolar iron electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pociecha, M.; Lestan, D. Using electrocoagulation for metal and chelant separation from washing solution after EDTA leaching of Pb, Zn and Cd contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dura, A.; Breslin, C.B. Electrocoagulation using stainless steel anodes: Simultaneous removal of phosphates, Orange II and zinc ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ren, P.; Li, T.; Trembly, J.P.; Liu, X. Zinc removal from model wastewater by electrocoagulation: Processing, kinetics and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Demirbas, E.; Dedeli, A.; Sensoy, M.T. Treatment of rinse water from zinc phosphate coating by batch and continuous electrocoagulation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoorian, H.J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jafari, A.J. Removal of lead and zinc from battery industry wastewater using electrocoagulation process: Influence of direct and alternating current by using iron and stainless steel rod electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, S.; Siddique, A.A.; Khursheed, M.S.; Zarei, A.; Alam, I.; Asgari, E.; Changani, F. Removal of heavy metals (Cr, Cu and Zn) from electroplating wastewater by electrocoagulation and adsorption processes. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 179, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najid, N.; Kouzbour, S.; Ruiz-García, A.; Fellaou, S.; Gourich, B.; Stiriba, Y. Comparison analysis of different technologies for the removal of boron from seawater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.Y.; Recepoglu, Y.K.; Karagunduz, A.; Khataee, A.; Yoon, Y. A review of boron removal from aqueous solution using carbon-based materials: An assessment of health risks. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Mahasti, N.N.N.; Huang, Y.H. Recent advances in adsorption and coagulation for boron removal from wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Ribeiro, T.; Grossi, C.D.; Merma, A.G.; dos Santos, B.F.; Torem, M.L. Removal of boron from mining wastewaters by electrocoagulation method: Modelling experimental data using artificial neural networks. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.E.; Boncukcuoğlu, R.; Kocakerim, M.M. An empirical model for parameters affecting energy consumption in boron removal from boron-containing wastewaters by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezechi, E.H.; Isa, M.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Yaqub, A. Boron removal from produced water using electrocoagulation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2014, 92, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Zeng, F.; An, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, T.; Fang, J. Enhancement mechanism for boron removal at high anodic polarization potential during electrocoagulation using iron-based materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Osibote, O.A. A review of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solutions by sorption technique using nanomaterials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambika, S.; Kumar, M.; Pisharody, L.; Malhotra, M.; Kumar, G.; Sreedharan, V.; Singh, L.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Bhatnagar, A. Modified biochar as a green adsorbent for removal of hexavalent chromium from various environmental matrices: Mechanisms, methods, and prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Díaz, C.E.; Lugo-Lugo, V.; Bilyeu, B. A review of chemical, electrochemical and biological methods for aqueous Cr(VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 223–224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Gyawali, D.; Ghimire, K.N.; Paudyal, H. An assessment of the lignocellulose-based biosorbents in removing Cr(VI) from contaminated water: A critical review. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, W.; Xie, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z. A novel electrocoagulation process with centrifugal electrodes for wastewater treatment: Electrochemical behavior of anode and kinetics of heavy metal removal. Chemosphere 2022, 310, 136862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Domínguez, A.; Rivera-Huerta, M.D.L.; Pérez-Castrejón, S.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E.; Villegas-Mendoza, I.E.; Gelover-Santiago, S.L.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G. Chromium removal from drinking water by redox-assisted coagulation: Chemical versus electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Islam, D.T.; Farooqi, I.H.; Ayub, S.; Basheer, F. Hexavalent chromium removal in an electrocoagulation column reactor: Process optimization using CCD, adsorption kinetics and pH modulated sludge formation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 122, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Guan, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Jia, H.; Wu, Y. 3D hierarchically porous NiO/NF electrode for the removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater by electrocoagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Electricity generation from salinity gradient to remove chromium using reverse electrodialysis coupled with electrocoagulation. Electrochimica Acta 2021, 379, 138153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Camcı, S. Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination 2011, 269, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Lakshmi, J.; Sozhan, G. Studies on the Removal of Iron from Drinking Water by Electrocoagulation—A Clean Process. Clean Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhadi, B.; Kot, P.; Hashim, K.; Shaw, A.; Muradov, M.; Al-Khaddar, R. Continuous-flow electrocoagulation (EC) process for iron removal from water: Experimental, statistical and economic study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Solanki, H.; Purkait, M. Removal of Fe(II) from tap water by electrocoagulation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.S.; Shaw, A.; Al Khaddar, R.; Pedrola, M.O.; Phipps, D. Iron removal, energy consumption and operating cost of electrocoagulation of drinking water using a new flow column reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 189, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamjomeh, M.M.; Sivakumar, M. Fluoride removal by a continuous flow electrocoagulation reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibikamal, V.; Torabian, A.; Janpoor, F.; Hoshyaripour, G. Fluoride removal from industrial wastewater using electrocoagulation and its adsorption kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Tchamango, S.R.; Ngom, P.C.; Darchen, A.; Ngameni, E. Mercury(II) removal from water by electrocoagulation using aluminium and iron electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.K.; Peña, S.F.; Gutiérrez, C.; Lazo, A.; Lazo, P.; Ottosen, L.M. Selenium removal from petroleum refinery wastewater using an electrocoagulation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Suib, S.L.; Qiu, G. Removal of As(V) from wastewaters using magnetic iron oxides formed by zero-valent iron electrocoagulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, X.; Xu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Ou, J.; Hu, B.; Xie, Z.; Lei, X.; Yu, G. Effect of iron ion configurations on Ni2+ removal in electrocoagulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Wang, H. Removal of microplastics and attached heavy metals from secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plant using interpenetrating bipolar plate electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, H.; Anantha Singh, T.S.; Sasikumar Jampa, S. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution using combined ultrasonic and electrocoagulation process. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Xie, X.; Sun, L.; Lei, W.; Wang, F. An efficient Two-Chamber Electrodeposition-Electrodialysis combination craft for nickel recovery and phosphorus removal from spent electroless nickel plating bath. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Ai, S.; Dong, S.; Sun, J.; Sun, S. Efficient removal of Cu-EDTA complexes from wastewater by combined electrooxidation and electrocoagulation process: Performance and mechanism study. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandraker, N.; Chaudhari, P.K.; Jyoti, G.; Prajapati, A.; Thakur, R.S. Removal of fluoride from water by electrocoagulation using Mild Steel electrode. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Ma, H.; Li, M.; Zhu, K.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Electrocoagulation pre-treatment to simultaneously remove dissolved and colloidal substances and Ca2+ in old corrugated container wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Wu, P.; Yan, Q.; Vayenas, D.V. Elongation the duration of steel anode with polypyrrole modification during the electrocoagulation treatment process of electroplating wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureth, R.; Machunda, R.; Njau, K.N.; Dodoo-Arhin, D. Assessment of fluoride removal in a batch electrocoagulation process: A case study in the Mount Meru Enclave. Sci. Afr. 2021, 12, e00737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, S.R.; Roy, A.; Gadgil, A.J.; van Genuchten, C.M. Long-term electrode behavior during treatment of arsenic contaminated groundwater by a pilot-scale iron electrocoagulation system. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamović, S.; Prica, M.; Dalmacija, B.; Isakovski, M.K.; Kerkez, Đ.; Rapajić, S.; Adamović, D. Measurement of copper deposition by electrocoagulation/flotation from waste printing developer. Measurement 2019, 131, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitlo, H.A.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. Removal mechanism for chromium (VI) in groundwater with cost-effective iron-air fuel cell electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grich, N.B.; Attour, A.; Mostefa, M.L.P.; Guesmi, S.; Tlili, M.; Lapicque, F. Fluoride removal from water by electrocoagulation: Effect of the type of water and the experimental parameters. Electrochimica Acta 2019, 316, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkani, I.; Belkacem, M.; Trari, M.; Lapicque, F.; Bensadok, K. Assessment of electrocoagulation based on nitrate removal, for treating and recycling the Saharan groundwater desalination reverse osmosis concentrate for a sustainable management of Albien resource. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancor-Abreu, A.; Mena, V.F.; González, S.; Delgado, S.; Souto, R.M.; Santana, J.J. Design and optimization of an electrocoagulation reactor for fluoride remediation in underground water sources for human consumption. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Guo, T.; Zhao, X. Treatment of Sb(V) and Co(II) containing wastewater by electrocoagulation and enhanced Sb(V) removal with Co(II) presence. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changmai, M.; Pasawan, M.; Purkait, M. Treatment of oily wastewater from drilling site using electrocoagulation followed by microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nandi, B.K. Removal of Fe (II) ions from drinking water using Electrocoagulation (EC) process: Parametric optimization and kinetic study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Shoeib, M.A.; El-Khateeb, M.A.; Youssef, A.O.; Hafez, O.M. Electrochemical treatment of industrial cooling tower blowdown water using magnesium-rod electrode. Water Resour. Ind. 2020, 23, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Qiao, M.; Li, A.; Hao, J.; Zhao, X. Advantage of selective production of green rusts for Sb(V) removal in Fe(0) electrocoagulation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2779–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, L.F.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L.; Carreño, G. Removal of fluoride and hydrated silica from underground water by electrocoagulation in a flow channel reactor. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Raad, A.A.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Naje, A.S.; Ajeel, M.A. Optimized parameters of the electrocoagulation process using a novel reactor with rotating anode for saline water treatment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265 Pt B, 115049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AzadiAghdam, M.; Achilli, A.; Snyder, S.A.; Farrell, J. Increasing water recovery during reclamation of treated municipal wastewater using bipolar membrane electrodialysis and fluidized bed crystallization. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampeta, C.; Mastrantonaki, M.; Katsaouni, N.; Frontistis, Z.; Koutsoukos, P.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Treatment of printing ink wastewater using a continuous flow electrocoagulation reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Fan, R.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, D. Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) from acid wastewater by electrocoagulation using sacrificial metal anodes. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Mustafa, F.S.; Ezugwu, O.N.; Gazi, M. Efficient removal of antibiotic in single and binary mixture of nickel by electrocoagulation process: Hydrogen generation and cost analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, A.A.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Removal of brilliant green tannery dye by electrocoagulation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 911, 116223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, C.E.; Pauli, C.S.; Coan, A.S.; Simionatto, E.L.; Koslowski, L.A.D. Investigating the process of electrocoagulation in the removal of azo dye from synthetic textile effluents and the effects of acute toxicity on Daphnia magna test organisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D. Electrocoagulation and electrooxidation for disinfecting water: New breakthroughs and implied mechanisms. Appl. Eng. 2019, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ankoliya, D.; Mudgal, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Patel, V.; Patel, J. Application of electrocoagulation process for the treatment of dairy wastewater: A mini review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 77, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahreen, A.; Jami, M.S.; Ali, F. Role of electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment: A developmental review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D.; Alghamdi, A.; Ghernaout, B. Electrocoagulation process: A mechanistic review at the dawn of its modeling. J. Environ. Sci. Allied Res. 2019, 2, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandegar, V.; Saroha, A.K. Electrocoagulation for the treatment of textile industry effluent—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Khandegar, V.; Saroha, A.K. Removal of Chromium from Electroplating Industry Effluent Using Electrocoagulation. J. Hazardous Toxic Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, E.Ü.; Akarsu, C.; Gönen, Ç.; Özay, Y. Enhancing treatability of tannery wastewater by integrated process of electrocoagulation and fungal via using RSM in an economic perspective. Process. Biochem. 2019, 84, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.; Lim, J.H.; Amr, S.S.A.; Wong, L.P.; Sim, Y.L. Post treatment of palm oil mill effluent using electro-coagulation-peroxidation (ECP) technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Sharma, M.; Purkait, M.K. Recent progress on electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, T.; Velinov, N.; Petrović, M.; Najdanović, S.; Bojić, D.; Radović, M.; Bojić, A. Mechanism of the electrocoagulation process and its application for treatment of wastewater: A review. Adv. Technol. 2021, 10, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Naghdali, Z.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Alizadeh, S.M.; Niaragh, E.K.; Malekmohammadi, S.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Roberts, E.P.; Sillanpää, M.; Emamjomeh, M.M. A systematic diagnosis of state of the art in the use of electrocoagulation as a sustainable technology for pollutant treatment: An updated review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2021, 47, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.; Sheob, M.; Saeed, B.; Khan, S.U.; Shirinkar, M.; Frontistis, Z.; Basheer, F.; Farooqi, I.H. Use of Electrocoagulation for Treatment of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Water/Wastewater: A Review Exploring Opportunities and Challenges. Water 2021, 13, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; He, Y.; Yi, C.; Feng, C. Electrocoagulation coupled with electrooxidation for the simultaneous treatment of multiple pollutants in contaminated sediments. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Lin, D.; Liang, H. Ferrate-enhanced electrocoagulation/ultrafiltration system on municipal secondary effluent treatment: Identify synergistic contribution of coagulant and oxidation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Almatrafi, E.; Hu, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, B.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G. Efficient removal of microplastics from wastewater by an electrocoagulation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorayyaei, S.; Raji, F.; Rahbar-Kelishami, A.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. Combination of electrocoagulation and adsorption processes to remove methyl orange from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangarnokolaei, M.; Ayati, B.; Ganjidoust, H. Novel baffled configuration of electro-coagulation–flotation process for treatment and fate of Direct Blue 71: Sludge characteristics and process optimization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Islam, M.S. Effect of additional Fe(2+) salt on electrocoagulation process for the degradation of methyl orange dye: An optimization and kinetic study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, J.; Moghaddam, M.R.A.; Habibzadeh, S. The role of the current waveform in mitigating passivation and enhancing electrocoagulation performance: A critical review. Chemosphere 2022, 312, 137212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Melhem, K.; Al-Kilani, M.R.; Tawalbeh, M. Evaluation of scrap metallic waste electrode materials for the application in electrocoagulation treatment of wastewater. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, K.S.; Shaw, A.; Al Khaddar, R.; Pedrola, M.O.; Phipps, D. Energy efficient electrocoagulation using a new flow column reactor to remove nitrate from drinking water—Experimental, statistical, and economic approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazlabadi, E.; Moghaddam, M.R.A.; Karamati-Niaragh, E. Simultaneous removal of nitrate and nitrite using electrocoagulation/floatation (ECF): A new multi-response optimization approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Carissimi, E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici Guvenc, S.; Can-Güven, E.; Varank, G. Persulfate enhanced electrocoagulation of paint production industry wastewater: Process optimization, energy consumption, and sludge analysis. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M. Techno-economical aspects of electrocoagulation optimization in three acid azo dyes’ removal comparison. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Rai, S.; Srinivas, R.; Al-Raoush, R.I. Bioinspired modeling and biogeography-based optimization of electrocoagulation parameters for enhanced heavy metal removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.S.; Reddy, A.S.; Thukral, A.K. Electrocoagulation removal of Cr(VI) from simulated wastewater using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukanov, A.; El Allaoui, N.; Omor, A.; Elmadani, F.Z.; Bouayad, K.; Nakabayashi, S. Large-scale removal of colloidal contaminants from artisanal wastewater by bipolar electrocoagulation with aluminum sacrificial electrodes. Results Chem. 2020, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Dong, J.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, F. Continuous flowing electrocoagulation reactor for efficient removal of azo dyes: Kinetic and isotherm studies of adsorption. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariyan, E.; Aghababaei, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of pharmaceutical from water with an electrocoagulation process, effect of various parameters and studies of isotherm and kinetic. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlJaberi, F.Y.; Hawaas, Z.A. Electrocoagulation removal of Pb, Cd, and Cu ions from wastewater using a new configuration of electrodes. MethodsX 2023, 10, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahedi, A.; Darban, A.K.; Taghipour, F.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A.J.C.O.I.E. A review on industrial wastewater treatment via electrocoagulation processes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 22, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, R.; Yasar, A.; Ikhlaq, A.; Nissar, H.; Nizami, A.S. Comparison of ozonation, Fenton, and photo-Fenton processes for the treatment of textile dye-bath effluents integrated with electrocoagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.E.; Boncukcuoğlu, R.; Kocakerim, M.M. A quantitative comparison between electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation for boron removal from boron-containing solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Aminzadeh, B.; Torabian, A.; Khatibikamal, V.; Fard, M.A. Comparison of COD removal from pharmaceutical wastewater by electrocoagulation, photoelectrocoagulation, peroxi-electrocoagulation and peroxi-photoelectrocoagulation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219–220, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavijeh, H.N.; Sadeghi, M.; Kashani, M.R.K.; Moheb, A. Efficient Chemical Coagulation-Electrocoagulation-Membrane Filtration Integrated Systems for Baker’s Yeast Wastewater Treatment: Experimental and Economic Evaluation. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakizimana, J.N.; Gourich, B.; Chafi, M.; Stiriba, Y.; Vial, C.; Drogui, P.; Naja, J. Electrocoagulation process in water treatment: A review of electrocoagulation modeling approaches. Desalination 2017, 404, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. A comparative study of electrocoagulation, electrochemical Fenton, electro-Fenton and peroxi-coagulation for decolorization of real textile wastewater: Electrical energy consumption and biodegradability improvement. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, A.; Can, O.T.; Demirbas, E.; Kobya, M. A comparative study of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton for treatment of wastewater from liquid organic fertilizer plant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 112, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebba, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Alemayehu, E. Investigation on operating parameters and cost using an electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
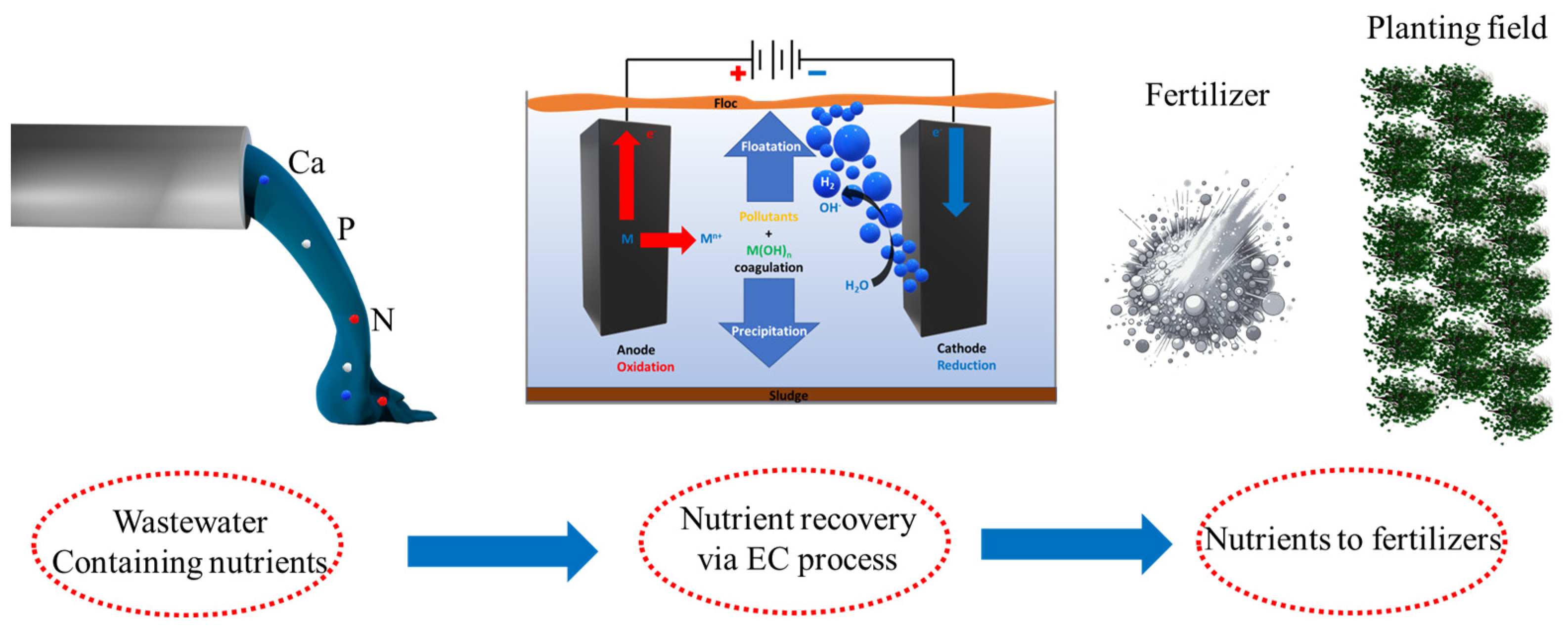
| Contaminant | MCLG (mg/L) | MCL or TT (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Antimony | 0.006 | 0.006 |
| Arsenic | 0.0 | 0.010 as of 01/23/06 |
| Asbestos (fiber > 10 μm) | 7 million fibers per liter (MFL) | 7 MFL |
| Barium | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Beryllium | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Cadmium | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Chromium (total) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Copper | 1.3 | Action Level = 1.3 |
| Cyanide (as free cyanide) | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Fluoride | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Lead | 0.0 | Action Level = 0.015 |
| Mercury (inorganic) | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Nitrate (measured as Nitrogen) | 10 | 10 |
| Nitrite (measured as Nitrogen) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Selenium | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Thallium | 0.0005 | 0.002 |
| NO. | Recovered Substance | Anode | Cathode | Gap (cm) | Concentration (mg/L) | Efficiency η (%) | pH | Time (min) | Power (A/m2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | P | Al-Fe | Ti | --- | --- | 100 | 4 | 80 | 20 | [89] |
| 2 | P | Fe | Graphite | 1 | 22.9 | 97 | 7.9 | 90 | 91 and 136 | [87] |
| 3 | P | Al | Al | 2.5 | 2 | 99 | 5–8.83 | 60 | --- | [90] |
| 4 | P | Fe-Al | SS | 1 | 10 | 98 | 4 | 2–5 | 100 | [94] |
| 5 | P | Al | Activated carbon | 0.5 to 2 | --- | 99 | 7–7.2 | 360 | 6–8 | [95] |
| 6 | P | Al-Fe | Fe-Al | 0.7 | --- | 93 | 5 | 60 | 100 | [96] |
| 7 | P | Al | Al-Fe | --- | --- | 89 | 6.88–7.05 | 15 to 210 | --- | [97] |
| 8 | P | Steel rod | steel pipe | --- | --- | 99 | 6–7 | 60 | --- | [92] |
| 9 | P | Two carbon brushes and 1 Fe plate | carbon felt | --- | 87 | 5.15 | --- | --- | [91] | |
| 10 | P | Fe | Graphite | 1 | 22.9 | 97 | 3–7.2 | 45 | 91 | [87] |
| 11 | PO₄3⁻ | Fe | SS-Al | 1 | 1.3 | 98 ± 2 | 2 | 100 | [94] | |
| 15 | Phosphate | Fe, Al | SS | ---- | 5.5, | 99, | ---- | ---- | 94 | [88] |
| Carbonate | 75, | 88–98 | ||||||||
| DOM | 300 | 40–50 | ||||||||
| 16 | HS, arsenic, and phosphates | Al | Al | ---- | 161, 22 | 40 | 7.6 | ---- | 40–100 | [98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ammar, M.; Yousef, E.; Ashraf, S.; Baltrusaitis, J. Removal of Inorganic Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation: A Review. Separations 2024, 11, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110320
Ammar M, Yousef E, Ashraf S, Baltrusaitis J. Removal of Inorganic Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation: A Review. Separations. 2024; 11(11):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110320
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmmar, Mohamed, Ezz Yousef, Sherif Ashraf, and Jonas Baltrusaitis. 2024. "Removal of Inorganic Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation: A Review" Separations 11, no. 11: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110320
APA StyleAmmar, M., Yousef, E., Ashraf, S., & Baltrusaitis, J. (2024). Removal of Inorganic Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation: A Review. Separations, 11(11), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110320







