QuEChERS-Based Method for the Determination of Fipronil in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Baits and Vespa velutina LARVAE Samples
2.2. Quality Control (QC) Samples Preparation
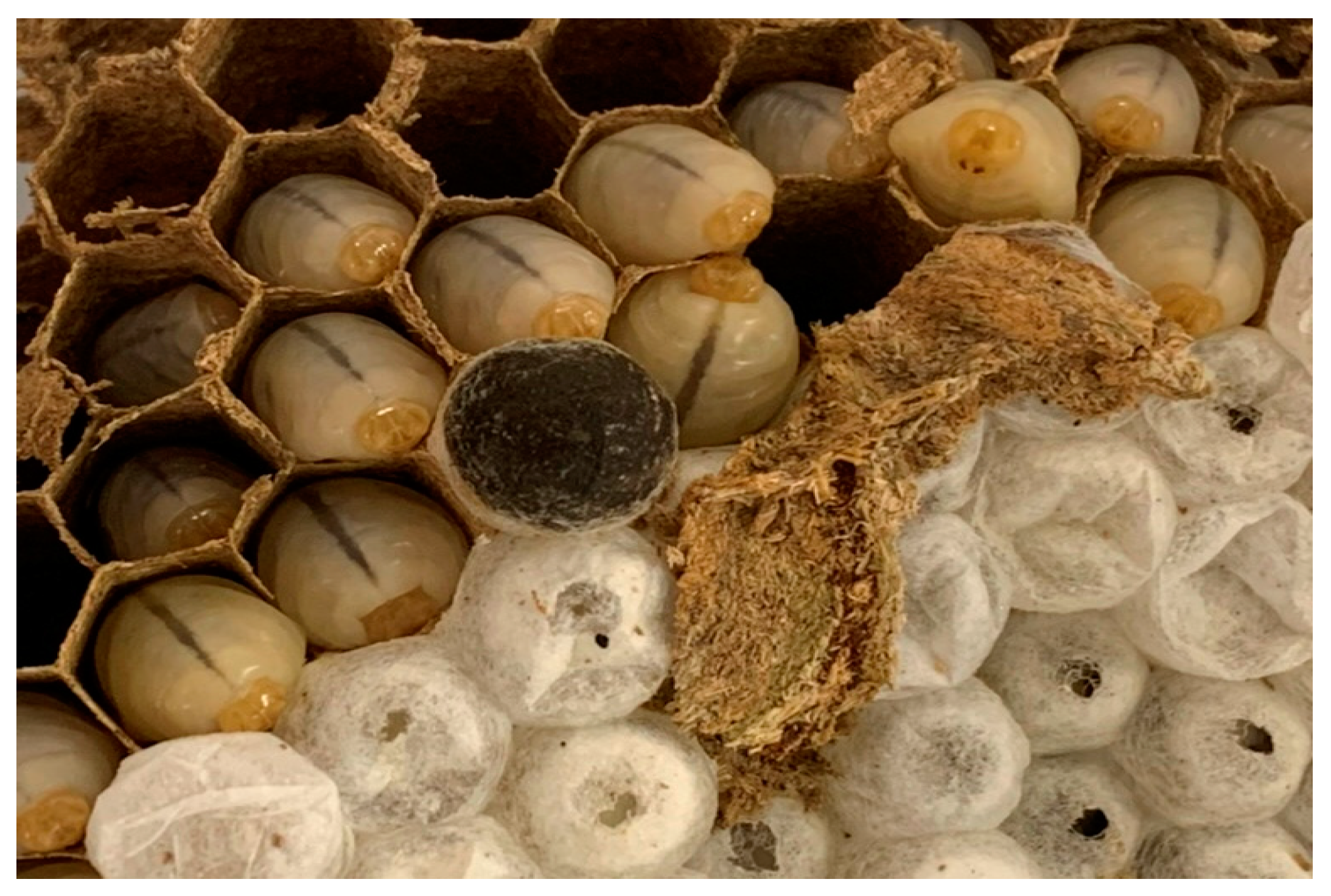
2.3. In Vivo Assays with Larvae
2.4. Sample Treatment
2.5. Chromatographic System and Conditions
2.5.1. HPLC-PDA
2.5.2. GC-MS
2.6. Recovery of the Sample Treatment
2.7. HPLC-PDA Analytical Method Validation
2.7.1. Selectivity
2.7.2. Matrix Effect and Linear Concentration Range
2.7.3. Limits of Detection and Quantification
2.7.4. Repeatability and Accuracy
2.8. Fipronil Content in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-PDA
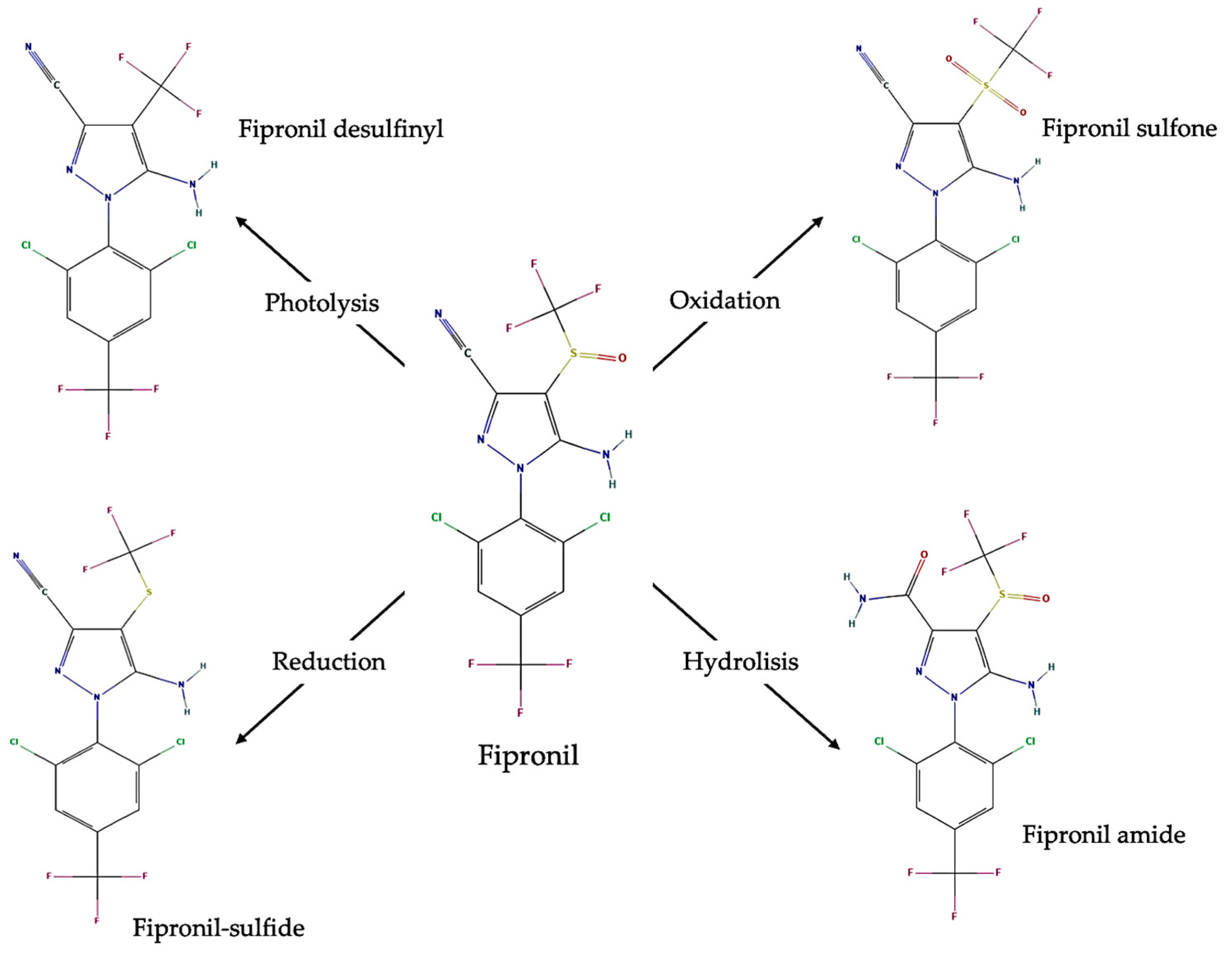
2.9. Metabolism of Fipronil in Vespa velutina Larvae
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In Vivo Assasys with Larvae
3.2. Recovery of the Sample Treatment
3.3. HPLC-PDA Analytical Method Validation
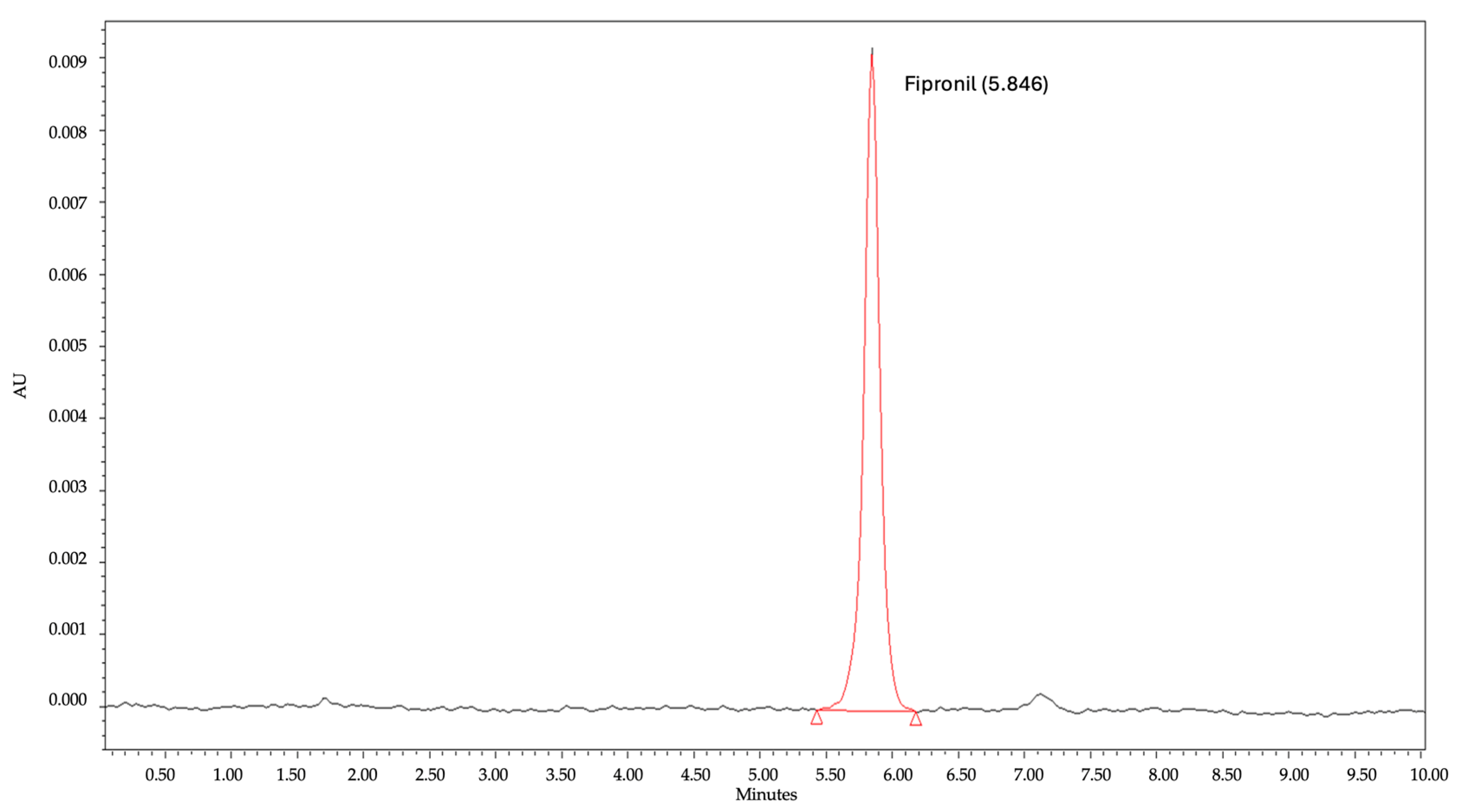
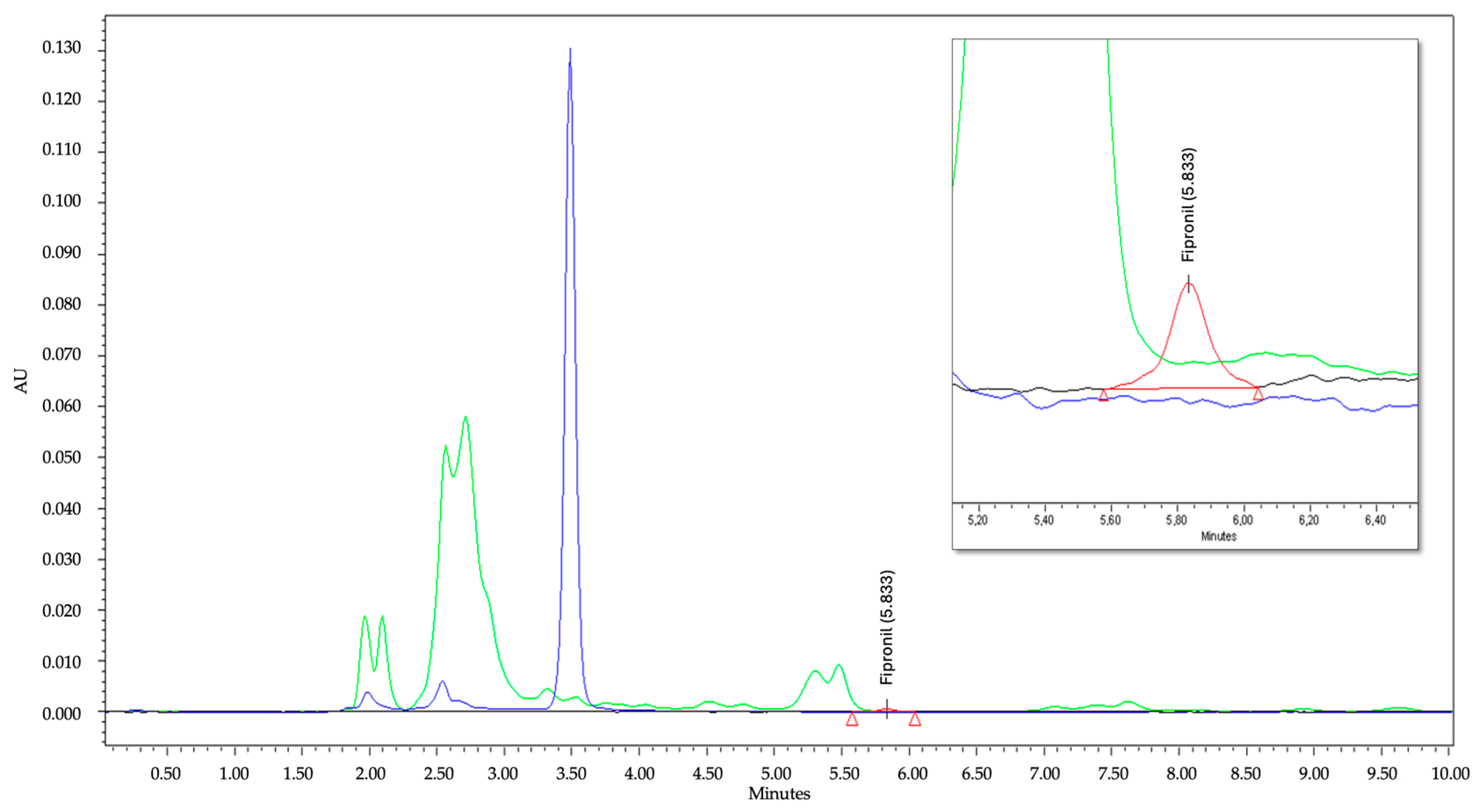
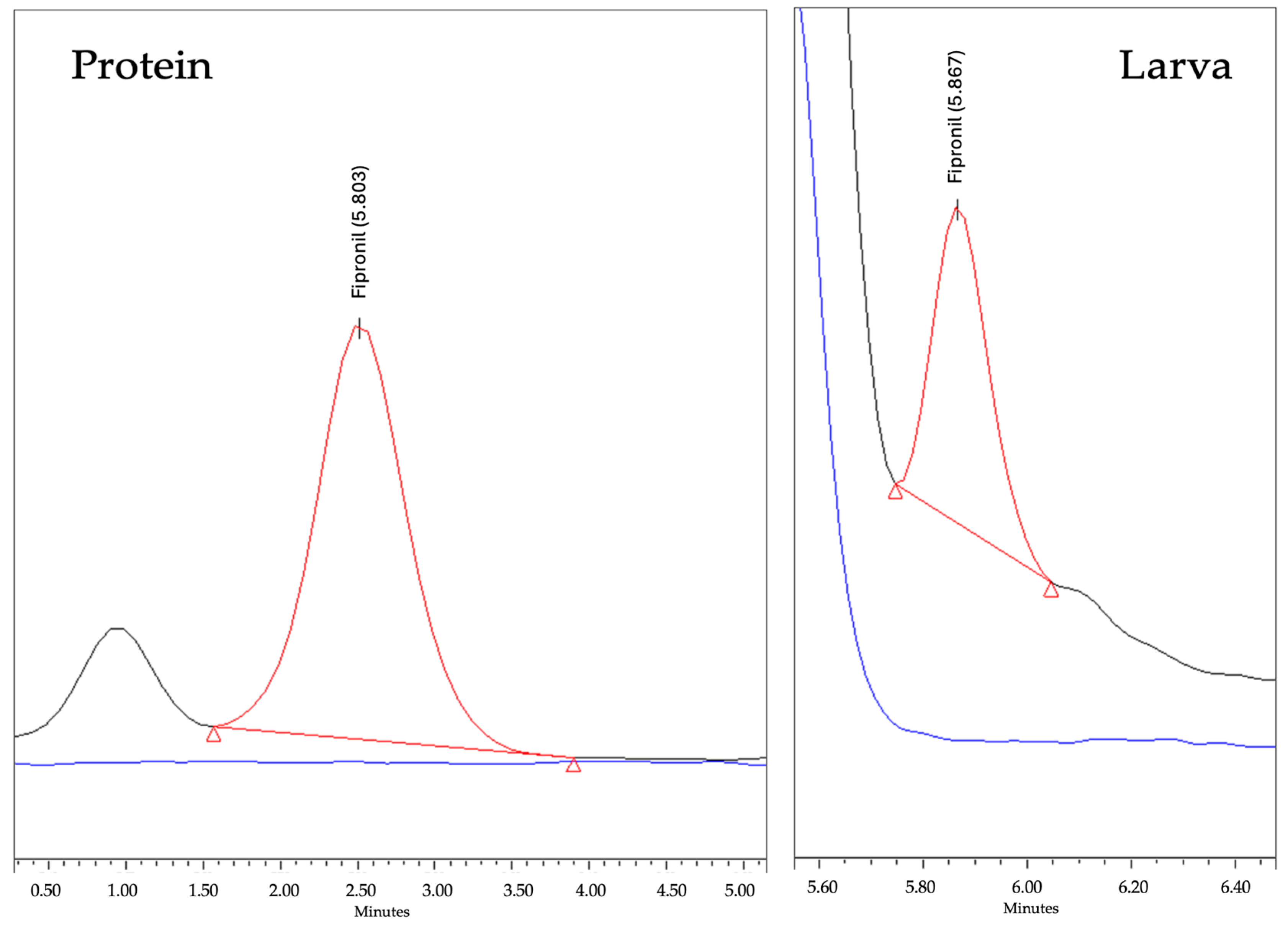
3.3.1. Selectivity
3.3.2. Matrix Effect and Linear Concentration Range
3.3.3. Limits of Detection and Limits of Quantification
3.3.4. Repeatability and Accuracy
3.4. Fipronil Content in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-PDA
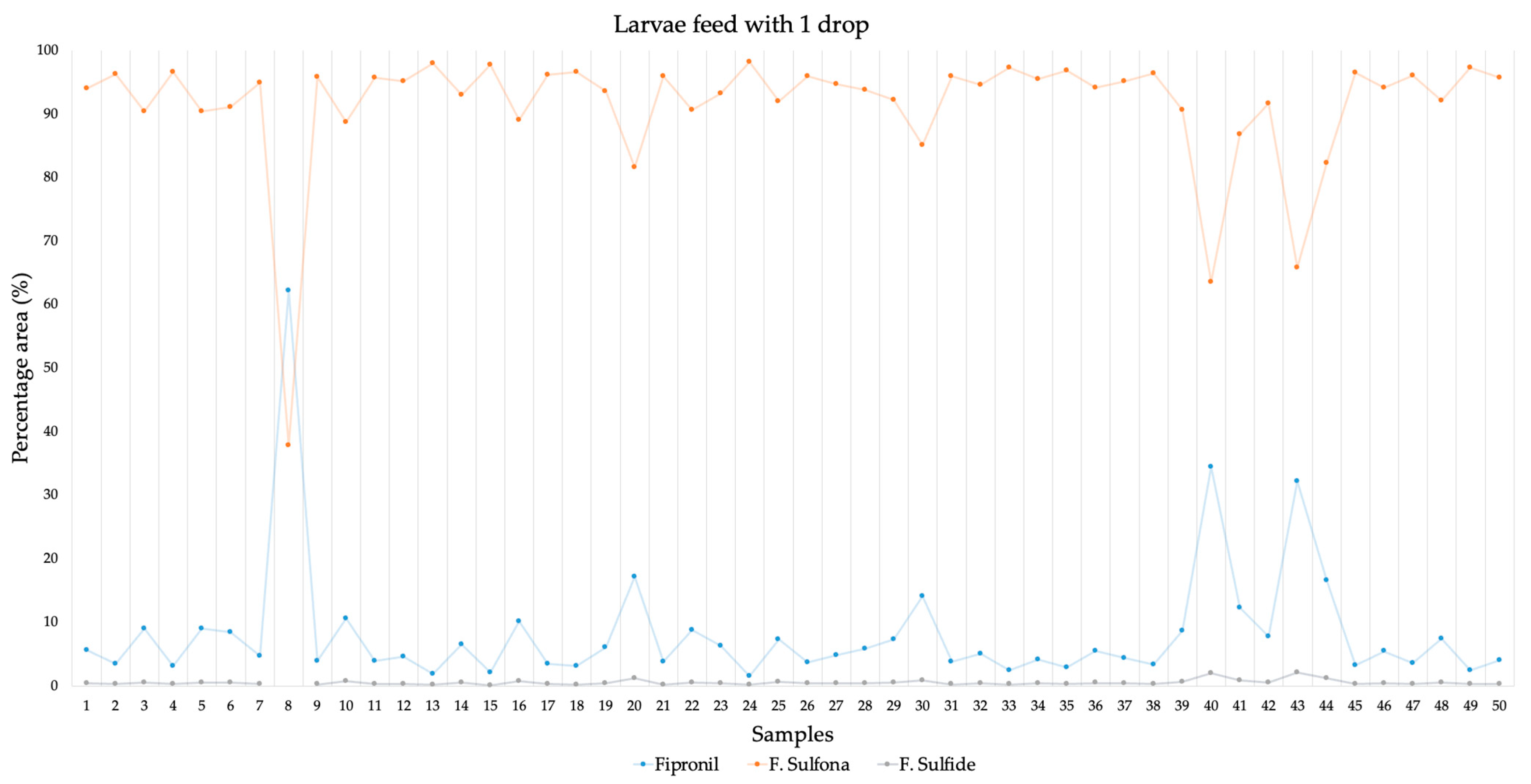
3.5. Metabolism of Fipronil in Vespa velutina Larvae
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villemant, C.; Haxaire, J.; Streito, J. Premier Bilan de l’invasion de Vespa velutina Lepeletier En France (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2006, 111, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauzat, M.-P.; Martin, S. A Foreigner in France: The Asian Hornet. Biologist 2009, 2, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Monceau, K.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Vespa velutina: A New Invasive Predator of Honeybees in Europe. J. Pest. Sci. 2013, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurino, D.; Lioy, S.; Carisio, L.; Manino, A.; Porporato, M. Vespa velutina: An Alien Driver of Honey Bee Colony Losses. Diversity 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillane, E.; Hayden, R.; O’Hanlon, A.; Butler, F.; Harrison, S. The First Recorded Occurrence of the Asian Hornet (Vespa Velutina) in Ireland, Genetic Evidence for a Continued Single Invasion across Europe. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2022, 93, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemant, C.; Barbet-Massin, M.; Perrard, A.; Muller, F.; Gargominy, O.; Jiguet, F.; Rome, Q. Predicting the Invasion Risk by the Alien Bee-Hawking Yellow-Legged Hornet Vespa velutina nigrithorax across Europe and Other Continents with Niche Models. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, S.; González, M.; Goldarazena, A. Vespa velutina Lepeletier, 1836 (Hymenoptera: Vespidae): First Records in Iberian Peninsula. Bull. OEPP/EPPO 2011, 41, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Pagola-Carte, S. Vespa velutina Lepeletier, 1836 (Hymenoptera:Vespidae), Recolectada En La Península Ibérica. Heteropterus Rev. Entomol. 2010, 10, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lioy, S.; Bergamino, C.; Porporato, M. The Invasive Hornet Vespa velutina: Distribution, Impacts and Management Options. CABI Rev. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, S. The Asian Hornet Handbook; Bunker, S., Ed.; Psocid Press: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.J. The Asian Hornet: Threats, Biology & Expansion; IBRA and Northern Bee Books: Mytholmroyd, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leza, M.; Herrera, C.; Marques, A.; Roca, P.; Sastre-Serra, J.; Pons, D.G. The Impact of the Invasive Species Vespa velutina on Honeybees: A New Approach Based on Oxidative Stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Nossa, S.V.; Calviño-Cancela, M. The Invasive Hornet Vespa velutina Affects Pollination of a Wild Plant through Changes in Abundance and Behaviour of Floral Visitors. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rome, Q.; Muller, F.J.; Touret-Alby, A.; Darrouzet, E.; Perrard, A.; Villemant, C. Caste Differentiation and Seasonal Changes in Vespa velutina (Hym.: Vespidae) Colonies in Its Introduced Range. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 139, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feás, X. Human Fatalities Caused by Hornet, Wasp and Bee Stings in Spain: Epidemiology at State and Sub-State Level from 1999 to 2018. Biology 2021, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haro, L.; Labadie, M.; Chanseau, P.; Cabot, C.; Blanc-Brisset, I.; Penouil, F. Medical Consequences of the Asian Black Hornet (Vespa velutina) Invasion in Southwestern France. Toxicon 2010, 55, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cristi, I.; Berville, L.; Darrouzet, E. Characterizing Thermal Tolerance in the Invasive Yellow-Legged Hornet (Vespa velutina Nigrithorax): The First Step toward a Green Control Method. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, T.; Álvarez-Figueiró, P.; Cortés-Vázquez, J.A.; Jácome, M.A.; Servia, M.J. Of Fears and Budgets: Strategies of Control in Vespa velutina Invasion and Lessons for Best Management Practices. Environ. Manag. 2022, 70, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leza, M.; Herrera, C.; Picó, G.; Morro, T.; Colomar, V. Six Years of Controlling the Invasive Species Vespa velutina in a Mediterranean Island: The Promising Results of an Eradication Plan. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioy, S.; Laurino, D.; Capello, M.; Romano, A.; Manino, A.; Porporato, M. Effectiveness and Selectiveness of Traps and Baits for Catching the Invasive Hornet Vespa velutina. Insects 2020, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galartza, E. Manual Para La Gestión de La Avispa Asiática (Vespa velutina) 2016 Medio Natural; Euskadi.Eus: Vitoria, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas-Nossa, S.V.; Novoa, N.; Serrano, A.; Calviño-Cancela, M. Performance of Baited Traps Used as Control Tools for the Invasive Hornet Vespa velutina and Their Impact on Non-Target Insects. Apidologie 2018, 49, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.P.; Geist, J.; Jeschke, J.M.; Kühn, L. Invasive Species in Europe: Ecology, Status, and Policy. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2011, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefond, L.; Paute, S.; Andalo, C. Testing Muzzle and Ploy Devices to Reduce Predation of Bees by Asian Hornets. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Nossa, S.V.; Dasilva-Martins, D.; Mato, S.; Bartolomé, C.; Maside, X.; Garrido, J. Effectiveness of Electric Harps in Reducing Vespa velutina Predation Pressure and Consequences for Honey Bee Colony Development. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 5142–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barandika, J.F.; de la Hera, O.; Fañanás, R.; Rivas, A.; Arroyo, E.; Alonso, R.M.; Alonso, M.L.; Galartza, E.; Cevidanes, A.; García-Pérez, A.L. Efficacy of Protein Baits with Fipronil to Control Vespa velutina nigrithorax (Lepeletier, 1836) in Apiaries. Animals 2023, 13, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Hera, O.; Quintanilla-Casas, B.; Bro, R.; Fañanas, R.; Alonso, R.M. Volatile Organic Compound Profile for the Search of Rejection Markers in Protein Baits Used as Vespa velutina Control Method. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, E.D.; Woolly, E.F.; McLellan, R.M.; Keyzers, R.A. Non-Detection of Honeybee Hive Contamination Following Vespula Wasp Baiting with Protein Containing Fipronil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, P.J.; Beggs, J.R. Invasion Success and Management Strategies for Social Vespula Wasps. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poché, D.M.; Franckowiak, G.; Clarke, T.; Tseveenjav, B.; Polyakova, L.; Poché, R.M. Efficacy of a Low Dose Fipronil Bait against Blacklegged Tick (Ixodes Scapularis) Larvae Feeding on White-Footed Mice (Peromyscus Leucopus) under Laboratory Conditions. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.C.; Wibowo, D.; Yang, G.Z.; Hui, Y.; Middelberg, A.P.J.; Zhao, C.X. Evaluation of Baiting Fipronil-Loaded Silica Nanocapsules against Termite Colonies in Fields. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, E.; Toft, R.; Joice, N.; Westbrooke, I. The Efficacy of Vespex® Wasp Bait to Control Vespula Species (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in New Zealand. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2017, 63, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasac Control Vespugard 1,5 DP. Available online: https://www.anasaccontrol.cl/website/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/vespugard15dp.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Harper, G.A.; Joice, N.; Kelly, D.; Toft, R.; Clapperton, B.K. Effective Distances of Wasp (Vespula vulgaris) Poisoning Using Clustered Bait Stations in Beech Forest. N. Z. J. Ecol. 2015, 40, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingle, C.C.D.; Rother, J.A.; Dewhurst, C.F.; Lauer, S.; King, W.J. Fipronil: Environmental Fate, Ecotoxicology, and Human Health Concerns. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 176, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Castilhos, D.; Dombroski, J.L.D.; Bergamo, G.C.; Gramacho, K.P.; Gonçalves, L.S. Neonicotinoids and Fipronil Concentrations in Honeybees Associated with Pesticide Use in Brazilian Agricultural Areas. Apidologie 2019, 50, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robea, M.A.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G.; Strugaru, S.A.; Ciobica, A. Fipronil: Mechanisms of Action on Various Organisms and Future Relevance for Animal Models Studies. J. Surv. Fish Sci. 2018, 5, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yeh, J.Z.; Salgado, V.L.; Narahashi, T. Fipronil Is a Potent Open Channel Blocker of Glutamate-Activated Chloride Channels in Cockroach Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlamento Europeo y el Consejo de la Unión Europea. Reglamento de Ejecución (UE) No 540/2011 Por El Que Se El Reglamento (CE) No 1107/2009 Del Parlamento y Del Consejo En Lo Que Respecta a La Lista de sustancias Activas Autorizadas. D. Union Eur. 2011, L153, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Carrão, D.B.; Habenchus, M.D.; de Albuquerque, N.C.P.; da Silva, R.M.; Lopes, N.P.; de Oliveira, A.R.M. In Vitro Inhibition of Human CYP2D6 by the Chiral Pesticide Fipronil and Its Metabolite Fipronil Sulfone: Prediction of Pesticide-Drug Interactions. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 313, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.S.; Sharma, R.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, D.K. A Comprehensive Review of Environmental Fate and Degradation of Fipronil and Its Toxic Metabolites. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes Júnior, O.; Batista, L.L.; Ueira-Vieira, C.; Sousa, R.M.F.; Starling, M.C.V.M.; Trovó, A.G. Degradation Mechanism of Fipronil and Its Transformation Products, Matrix Effects and Toxicity during the Solar/Photo-Fenton Process Using Ferric Citrate Complex. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, A.S.; Truong, T.; Goh, K.S.; Spurlock, F.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Environmental Fate and Toxicology of Fipronil. J. Pestic. Sci. 2007, 32, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez–Beltrán, D.A.; Pérez Montes, J.E.; Villar, D. Impacto Ecológico Del Insecticida Fipronil: Valoración de Riesgos En Humanos. Rev. Fac. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2023, 70, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Martínez, M.A.; Wu, Q.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Yuan, Z. Fipronil Insecticide Toxicology: Oxidative Stress and Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 876–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, C.; Foote, D.; Kremen, C. Short- and Long-Term Control of Vespula Pensylvanica in Hawaii by Fipronil Baiting. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.E.; Wall, R.; Howard, J.J.; Strong, L.; Marchiondo, A.A.; Jeannin, P. In Vitro Insecticidal Effects of Fipronil And-Cyfluthrin on Larvae of the Blowfly Lucilia Sericata. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 88, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aajoud, A.; Ravanel, P.; Tissut, M. Fipronil Metabolism and Dissipation in a Simplified Aquatic Ecosystem. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Hernández, J.; Velázquez-Manzanares, M.; Colunga-Urbina, E.M.; De La Garza-Rodríguez, I.M.; Reyes-Sánchez, E.E. QuEChERS En La Determinación de Fipronil y Sus Compuestos de Degradación. Rev. Iberoam. Cienc. 2018, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, M.R.F.; Tomasini, D.; Cardoso, L.V.; Caldas, S.S.; Primel, E.G. Determination of Pesticide Residues in Sugarcane Honey by QuEChERS and Liquid Chromatography. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Domínguez, G.; Nieto-García, A.J.; Romero-González, R.; Frenich, A.G. Application of QuEChERS Based Method for the Determination of Pesticides in Nutraceutical Products (Camellia sinensis) by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. A Review of Recent Developments and Trends in the QuEChERS Sample Preparation Approach. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 980–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-curbelo, M.Á.; Varela-martínez, D.A.; Riaño-herrera, D.A. Pesticide-Residue Analysis in Soils by the QuEChERS Method: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Z. Determination of Residual Fipronil and Its Metabolites in Food Samples: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Huo, N. Multi-Residue Analysis of Fipronil and Its Metabolites in Eggs by SinChERS-Based UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Du, P.; Wei, D.; Zheng, Y. Residue Analysis and Persistence Evaluation of Fipronil and Its Metabolites in Cotton Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatographytandem Mass Spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toffoli, A.L.; da Mata, K.; Bisinoti, M.C.; Moreira, A.B. Development, Validation, and Application of a Method for the GC-MS Analysis of Fipronil and Three of Its Degradation Products in Samples of Water, Soil, and Sediment. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2015, 50, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.D.; Tzimou-Tsitouridou, R.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Papageorgiou, M. Development and Validation of an HPLC-DAD Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Most Common Rice Pesticides in Paddy Water Systems. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European comisión. Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. In SANTE/11312/2021; European Comisión: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- USA Food and Drug Administration. Guidelines for the Validation of Chemical Methods in Food, Cosmetics, and Veterinary Products; USA Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, ML, USA, 2019.
- de Lima, O.J.; de Araújo, D.T.; Marçal, L.; Crotti, A.E.M.; Machado, G.S.; Nakagaki, S.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J. Photodegradation of Fipronil by Zn-AlPO4 Materials Synthesized by Non-Hydrolytic Sol–Gel Method. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.Z.; Puel, S.; Toutain, P.L.; Viguié, C. Quantification of Fipronil and Its Metabolite Fipronil Sulfone in Rat Plasma over a Wide Range of Concentrations by LC/UV/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, J.G.; Birolli, W.G.; Porto, A.L.M. Biodegradation of the Pesticides Bifenthrin and Fipronil by Bacillus Isolated from Orange Leaves. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 3295–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, G.; Pan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Qiu, J. Toxic Effects of Fipronil and Its Metabolites on PC12 Cell Metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, M.E.; Siegfried, B.D.; Meinke, L.J.; Chandler, L.D. Fipronil Metabolism, Oxidative Sulfone Formation and Toxicity among Organophosphate-and Carbamate-Resistant and Susceptible Western Corn Rootworm Populations. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2000, 56, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, E.W.; Siegfried, B.D.; Scharf, M.E. In Vivo and in Vitro Metabolism of Fipronil by Larvae of the European Corn Borer Ostrinia nubilalis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

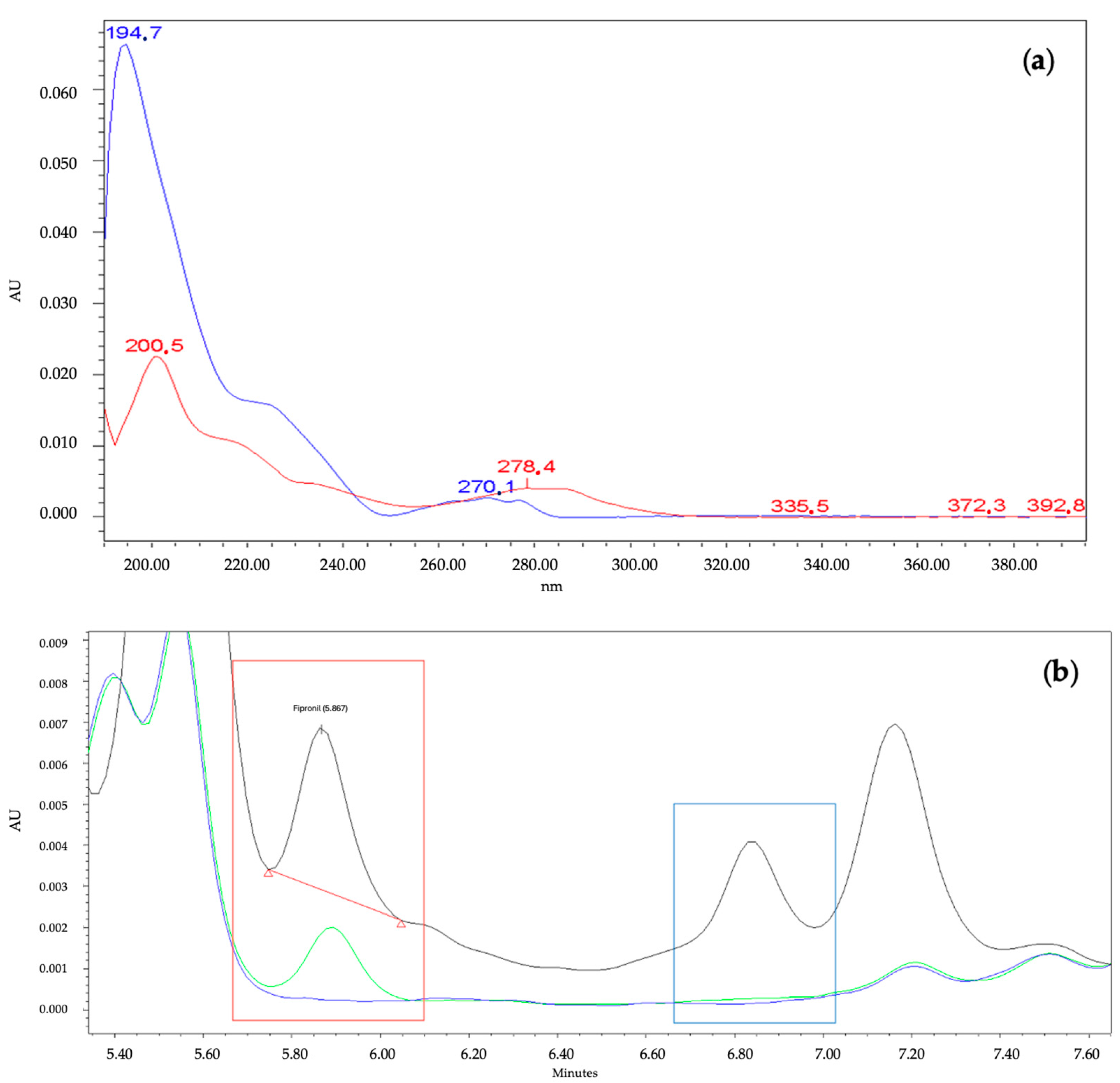


| Parameter | Conditions |
|---|---|
| Column | HPLC C18 ABZ+Plus (25 cm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) |
| Column temperature (°C) | 40 |
| Elution mode | Isocratic |
| Flow rate (mL/min) | 1 |
| Injection volume (µL) | 10 |
| Mobile phase | 35% aqueous phase (A) (H2O, 0,01% TFA) 65% organic phase (B) (100% ACN) |
| Autosampler temperature (°C) | 4 |
| Analysis time (min) | 12 |
| Wavelength (nm) | 277 |
| Parameter | Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| GC | Carrier gas Column Injection temperature (°C) | Helium 1 mL/min (constant flow) HP-5MS UI (30 m × 0.25 mm ID × 0.25 µm) 280 |
| Temperature gradient | Initial temp.: 100 °C for 1 min Ramp: 10 °C/min to 150 °C; 25 °C /min to 175 °C; 10 °C /min to 250 °C and hold 4 min | |
| Scan time (min) | 17.5 | |
| MS | Transfer line temperature (°C) | 300 |
| Solvent delay (min) | 3 | |
| Mode | SCAN (range: 40 to 400 m/z) | |
SIM m/z ions:
| ||
| Dwell time (ms) | 50 | |
| Detector temperature (°C) | 300 |
| Calibration Method | Linear Concentration Range (mg/L) | Regression Equations | Slope Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| External | 0.5–16 | 6851x − 1812; R2 = 0.999 | 0.94 |
| Protein-matched | 6458x + 86; R2 = 0.999 | ||
| External | 0.5–4 | 7745x + 747; R2 = 0.999 | 0.95 |
| Larvae-matched | 7352x − 1586; R2 = 0.998 |
| Protein Baits | Vespa velutina Larvae | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLOQ | MLOQ | ULOQ | LLOQ | MLOQ | ULOQ | ||
| Fipronil concentration (mg/L) | 0.5 | 8 | 16 | 0.5 | 2 | 4 | |
| RSD% | Intra-day | 5.0 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| Inter-day | 5.2 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 7.6 | 2.9 | 2.7 | |
| ER% | Intra-day | 18.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 16.3 | 4.7 | 4.3 |
| Inter-day | 19.0 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 16.7 | 4.8 | 4.4 | |
| RSD % SANTE criteria | ≤20 | ≤15 | ≤20 | ≤15 | |||
| ER % FDA criteria | |||||||
| Bait Samples | % of Fipronil/g Bait |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0104 ± 0.0004 |
| 2 | 0.0102 ± 0.0004 |
| 3 | 0.0102 ± 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Hera, O.; Izaguirre, A.; Rivas, A.; Alonso, R.M. QuEChERS-Based Method for the Determination of Fipronil in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS. Separations 2024, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110317
de la Hera O, Izaguirre A, Rivas A, Alonso RM. QuEChERS-Based Method for the Determination of Fipronil in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS. Separations. 2024; 11(11):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110317
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Hera, Omaira, Aritza Izaguirre, Arrate Rivas, and Rosa María Alonso. 2024. "QuEChERS-Based Method for the Determination of Fipronil in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS" Separations 11, no. 11: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110317
APA Stylede la Hera, O., Izaguirre, A., Rivas, A., & Alonso, R. M. (2024). QuEChERS-Based Method for the Determination of Fipronil in Protein Baits and Vespa velutina Larvae by HPLC-DAD and GC-MS. Separations, 11(11), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11110317






