A Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent with High Interfacial Interaction for Lithium Recovery from Brine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Hydrophilic Modification of LTO
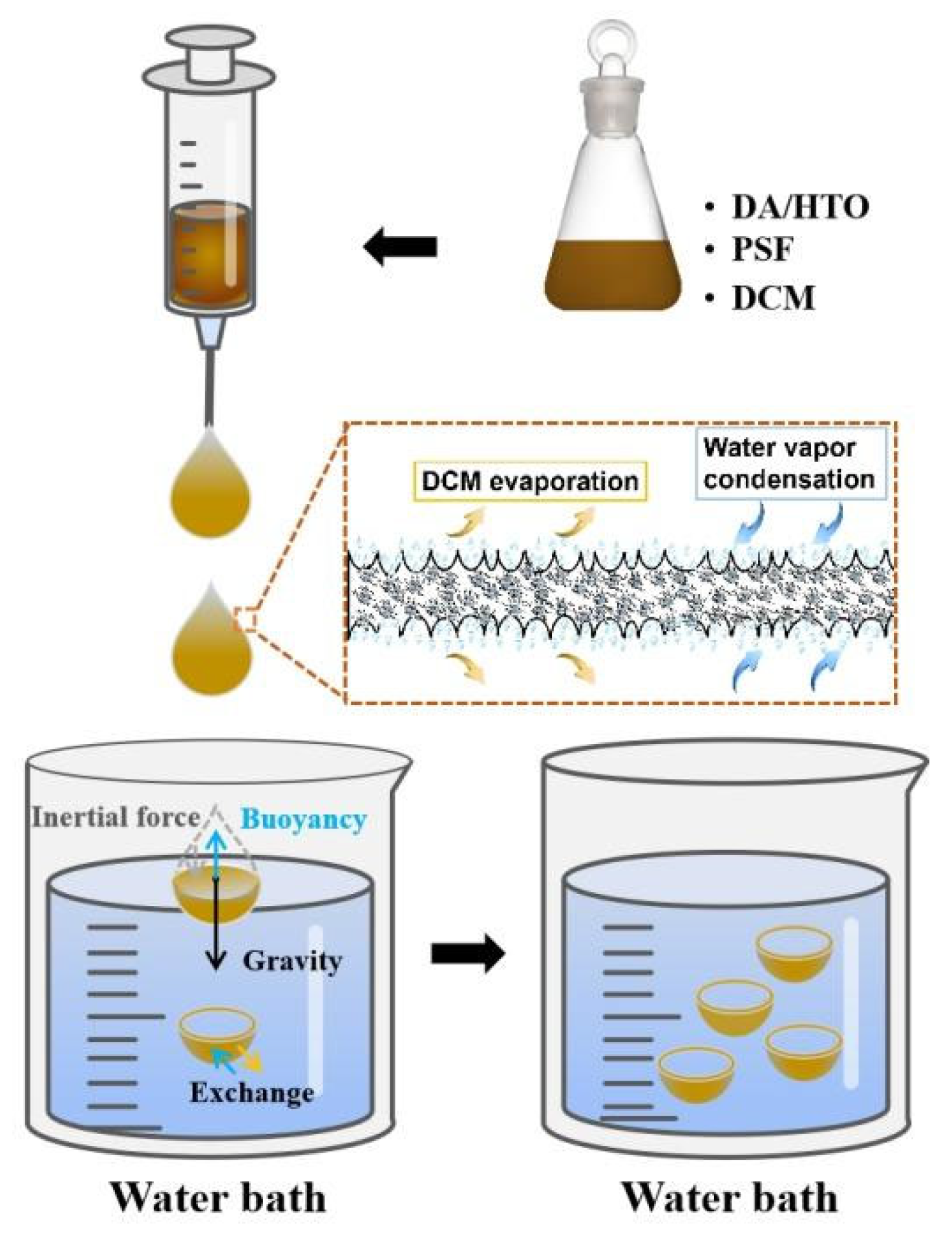
2.3. Preparation of Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent (H-LIS)
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Li+ Adsorption Performance of H-LIS
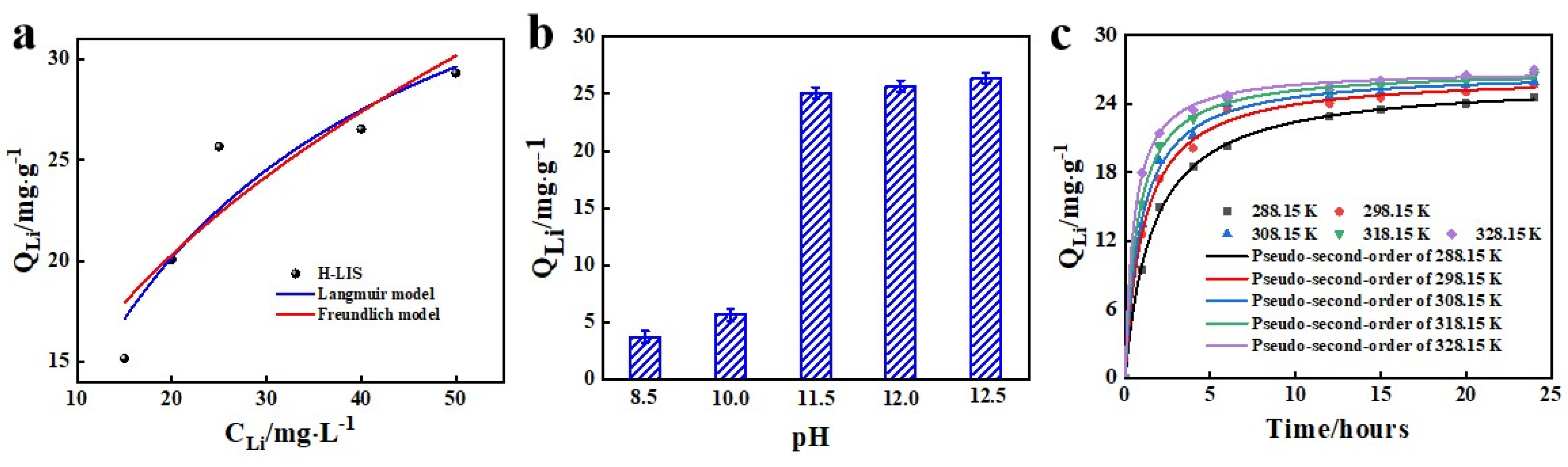
2.5.1. Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity
2.5.2. Adsorption Kinetic Simulation
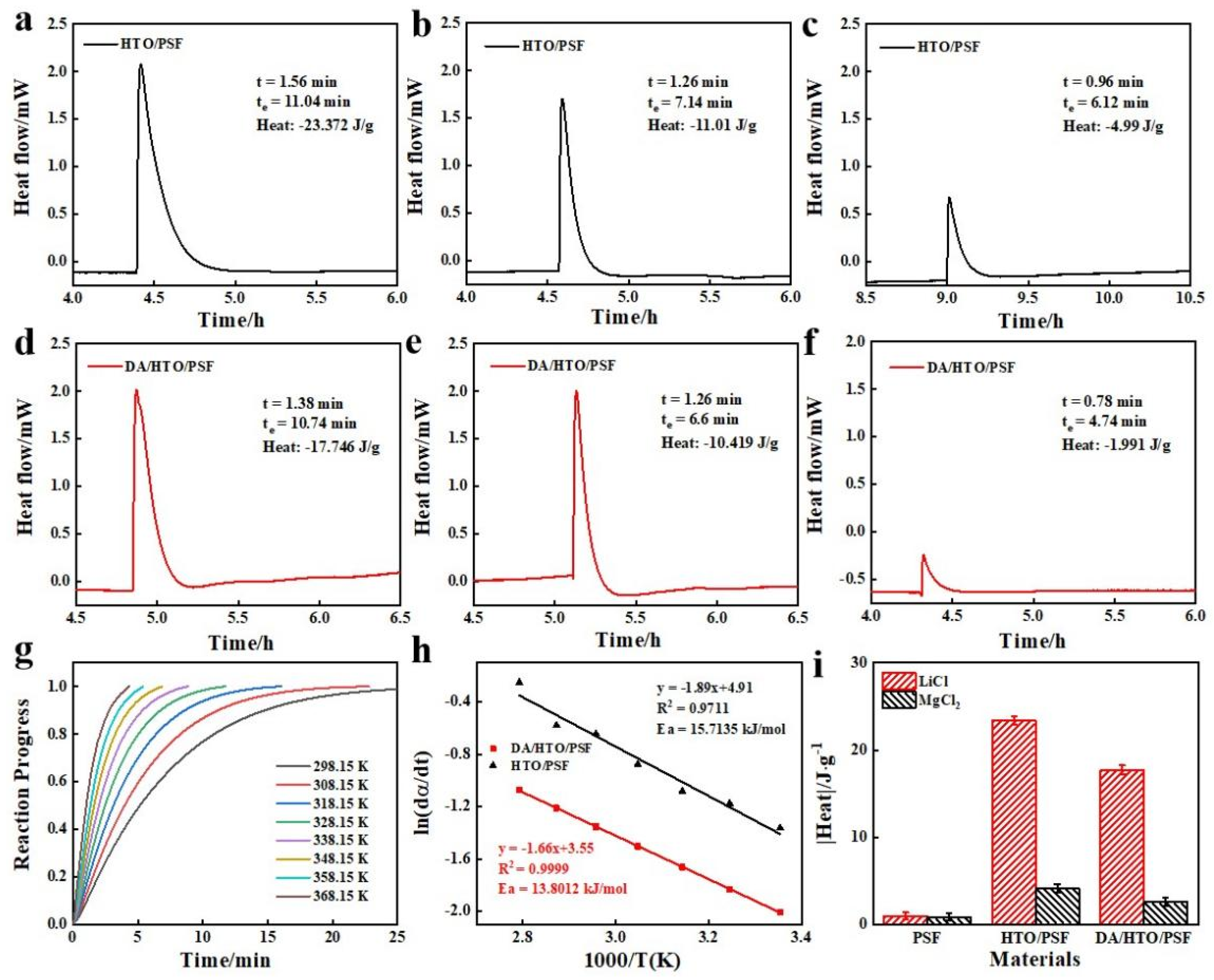
2.5.3. Calorimetry Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization of H-LIS Adsorbent
3.2. Structure Optimization and Adsorption Performance of H-LIS Adsorbent
3.3. Optimization of Adsorption Conditions
3.4. Comparison of Li+ Adsorption Performance with the Current Composite Adsorbent Materials
3.5. Forming Mechanism of H-LIS
3.6. Interfacial Interaction Mechanism Based on Mussel-Bioinspired Surface Chemistry
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crawford, A.; Seefeldt, J.; Kent, R.; Helbert, M.; Guzmán, G.; González, A.; Chen, Z.; Abbott, A. Lithium: The big picture. One Earth 2021, 4, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, A.Z.; Hackl, L.; Akuzum, B.; Pohlman, G.; Magnan, J.F.; Kostecki, R. How to make lithium extraction cleaner, faster and cheaper-in six steps. Nature 2023, 616, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desaulty, A.-M.; Climent, D.M.; Lefebvre, G.; Cristiano-Tassi, A.; Peralta, D.; Perret, S.; Urban, A.; Guerrot, C. Tracing the origin of lithium in Li-ion batteries using lithium isotopes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ouyang, M.; Hao, H. Surging lithium price will not impede the electric vehicle boom. Joule 2022, 6, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lv, S.; Song, S.; Galván, H.J.O.; Quintana, M.; Zhao, Y. Adsorbents for lithium extraction from salt lake brine with high magnesium/lithium ratio: From structure-performance relationship to industrial applications. Desalination 2024, 579, 117480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Dallas, J.; Casanova, S.; Pelech, T.; Bournival, G.; Saydam, S.; Canbulat, I. Towards a low-carbon society: A review of lithium resource availability, challenges and innovations in mining, extraction and recycling, and future perspectives. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Gopan, G. A comprehensive review of lithium extraction: From historical perspectives to emerging technologies, storage, and environmental considerations. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2024, 30, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, N.; Franco, D.; Gubernat, S.; Georgin, J.; Şenol, Z.; Ciğeroğlu, Z.; Allouss, D.; Hajam, M. Advances and future perspectives of water defluoridation by adsorption technology: A review. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin, J.; Franco, D.; Meili, L.; Petriciolet, A.; Kurniawan, T.; Imanova, G.; Demir, E.; Ali, I. Environmental remediation of the norfloxacin in water by adsorption: Advances, current status and prospects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 324, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.; Messaoudi, N.; Ciğeroglu, Z.; Miyah, Y.; Arslanoğlu, H.; Bağlam, N.; Kaya, E.; Kaur, P.; Georgin, J. Removal of food dyes using biological materials via adsorption: A review. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Hou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, W. Self-assembled layered lithium manganese oxide shows ultra-large adsorption capacity and high selectivity for lithium. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, S. Research progress of lithium extraction from salt lake brine by adsorption. Chem. Eng. 2023, 51, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Boroumand, Y.; Razmjou, A. Adsorption-type aluminium-based direct lithium extraction: The effect of heat, salinity and lithium content. Desalination 2024, 577, 117406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthi, R.; Asgar, H.; Gadikota, G.; Smith, Y.R. On the structure and lithium adsorption mechanism of layered H2TiO3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 8361–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mo, Y.; Qing, W.; Shao, S.; Tang, C.Y.; Li, J. Membrane-based technologies for lithium recovery from water lithium resources: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T.; Yu, X. Synthesis of granulated H4Mn5O12/chitosan with improved stability by a novel cross-linking strategy for lithium adsorption from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, P. Synthesis of H2TiO3-PVC lithium-ion sieves via an antisolvent method and its adsorption performance. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 30127–30134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hai, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Synthesis and performance estimation of a granulated PVC/PAN-lithium ion-sieve for Li+ recovery from brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhu, G.; Song, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Meng, C.; Gao, C. Fabrication of polyacrylonitrile-Li1.6Mn1.6O4 composite nanofiber flat-sheet membranes via electrospinning method as effective adsorbents for Li+ recovery from salt-lake brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Tong, B.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Xie, Y.; Deng, T. Synthesis of porous fiber-supported lithium ion-sieve adsorbent for lithium recovery from geothermal water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 131423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Guo, R. An ion-sieve-tailored biomimetic porous nanofiber as an efficient adsorbent for extraction of lithium from brine. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 4187–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, K.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T.; Yu, X. Recovery of lithium from brine with different degrees of mineralization by resorcinol/urea-formaldehyde foam-supported H2TiO3. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tao, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Guo, R.; Chen, L. Preparation and characterization of lithium ion sieves embedded in a hydroxyethyl cellulose cryogel for the continuous recovery of lithium from brine and seawater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 229, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, Y. Macroporous lithium adsorbent monolith prepared via high internal phase emulsion technique. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Li4Mn5O12 doped cellulose acetate membrane with low Mn loss and high stability for enhancing lithium extraction from seawater. Desalination 2021, 506, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L. Preparation of PVC-LMZO membrane and its lithium adsorption performance from brine. Desalination 2023, 561, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Meng, Z.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Hou, X.; Cheng, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Self-intercepting interference of hydrogen-bond induced flexible hybrid film to facilitate lithium extraction. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Zhao, K.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.; Xie, Y.; Deng, T. Novel LIS-doped mixed matrix membrane adsorbent with high structural stability for sustainable lithium recovery from geothermal water. Desalination 2022, 527, 115570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Duo, J.; Deng, T. A novel Co-doped H2TiO3 spinning composite for efficient lithium recovery from alkaline lithium precipitation mother liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, O.; Lu, M.; Cai, M.; Liu, J.; Qiu, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, C.; Qian, Y. Mussel-bioinspired lignin adhesive for wearable bioelectrodes. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2407129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.; Deng, T. LIS-doped thin-film nanocomposite membrane adsorbent with low shielding effect for effective lithium recovery from geothermal water. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 20910–20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Sun, W.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Li, Z. High specific surface crown ether modified chitosan nanofiber membrane by low-temperature phase separation for efficient selective adsorption of lithium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajestani, M.B.; Moheb, A.; Masigol, M. Simultaneous optimization of adsorption capacity and stability of hydrothermally synthesized spinel ion sieve composite adsorbents for selective removal of lithium from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 12207–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawagon, C.P.; Nisola, G.M.; Cuevas, R.A.I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.P.; Chung, W.J. Development of high capacity Li+ adsorbents from H2TiO3/polymer nanofiber composites: Systematic polymer screening, characterization and evaluation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T.; Yu, X. Selective recovery of lithium from geothermal water by EGDE cross-linked spherical CTS/LMO. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Yuan, F.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T. Separation of magnesium from high Mg/Li ratio brine by extraction with an organic system containing ionic liquid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 229, 116019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ge, H.; Yan, L.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Belzile, N.; Deng, T. Readily regenerated porous fiber-supported metal tin sulfide for rapid and selective removal of cesium from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Shan, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. Novel thin-film composite membranes via manipulating the synergistic interaction of dopamine and m-phenylenediamine for highly efficient forward osmosis desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7920–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Zhao, C.; An, M.; Li, L. Porous polyvinyl alcohol/polyacrylamide hydrogels loaded with HTO lithium-ion sieves for highly rapid and efficient Li+ extraction. Desalination 2024, 580, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.W.; He, T. Composite flat-sheet membrane adsorbent of Li2TiO3-Ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol (LTO-EVAL) for lithium extraction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Sui, K.; Liu, Y.; Qi, P. Hollow laminar Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers with polycrystalline property facilitate super-high and ultrafast extraction of lithium ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
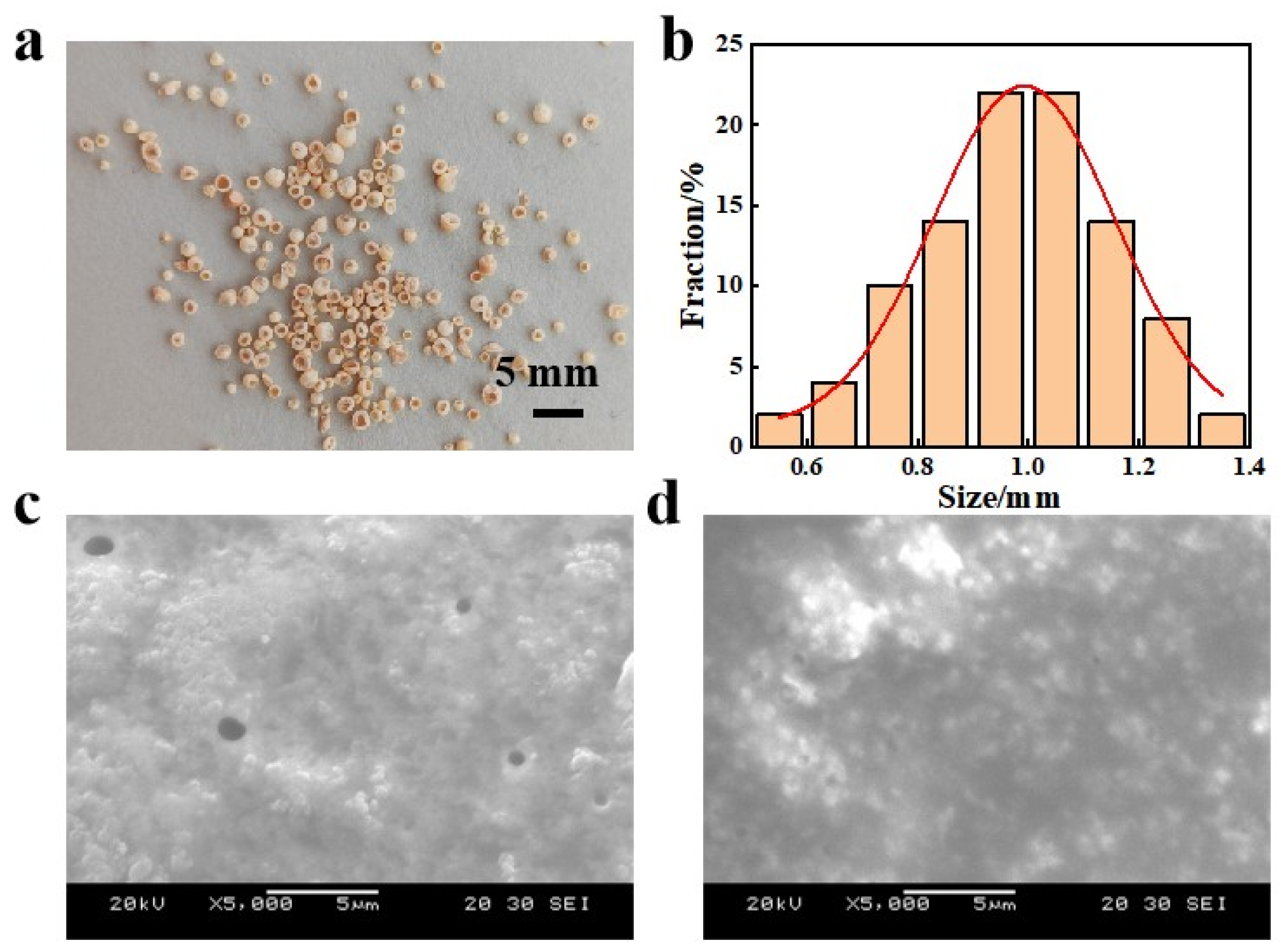
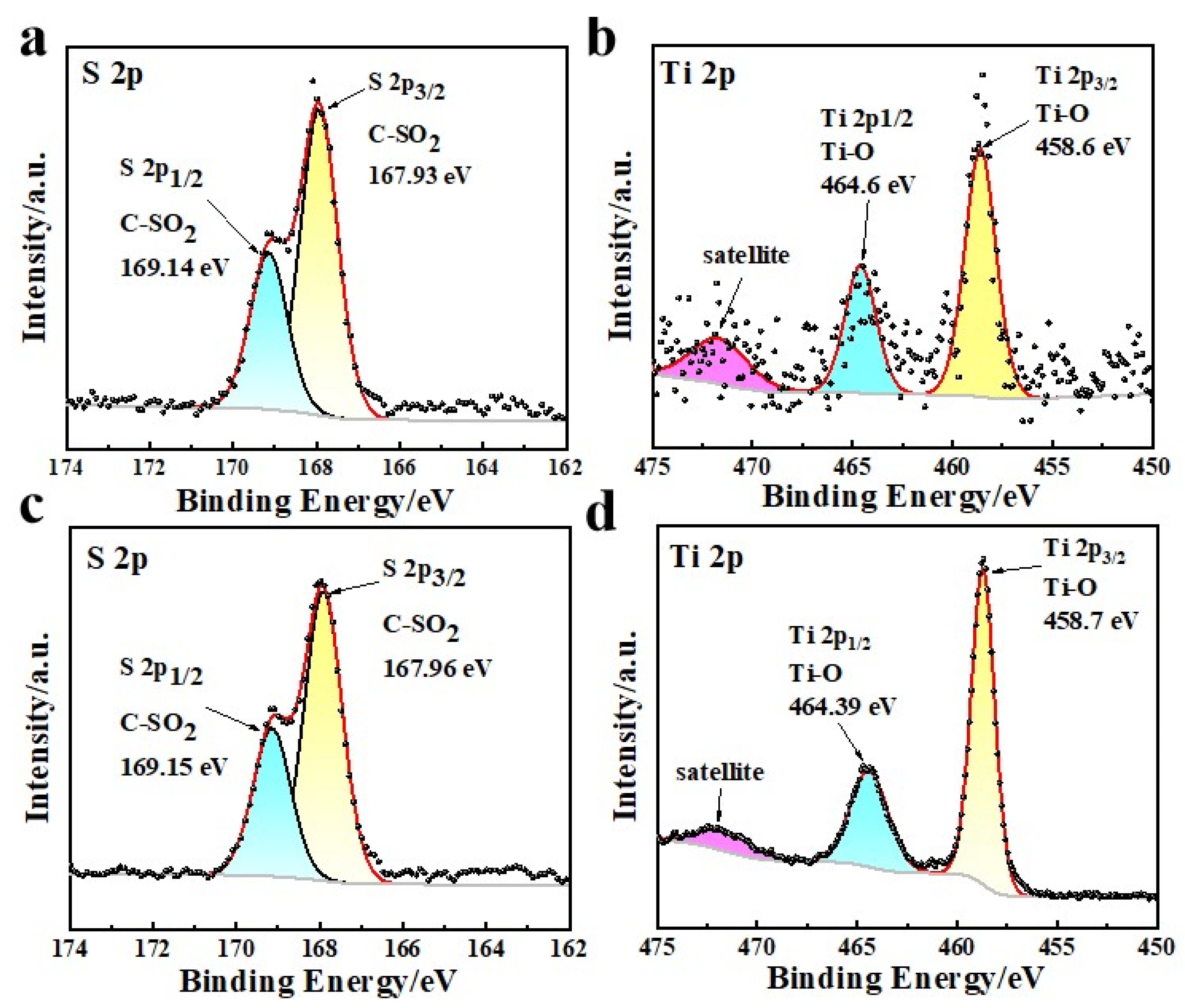
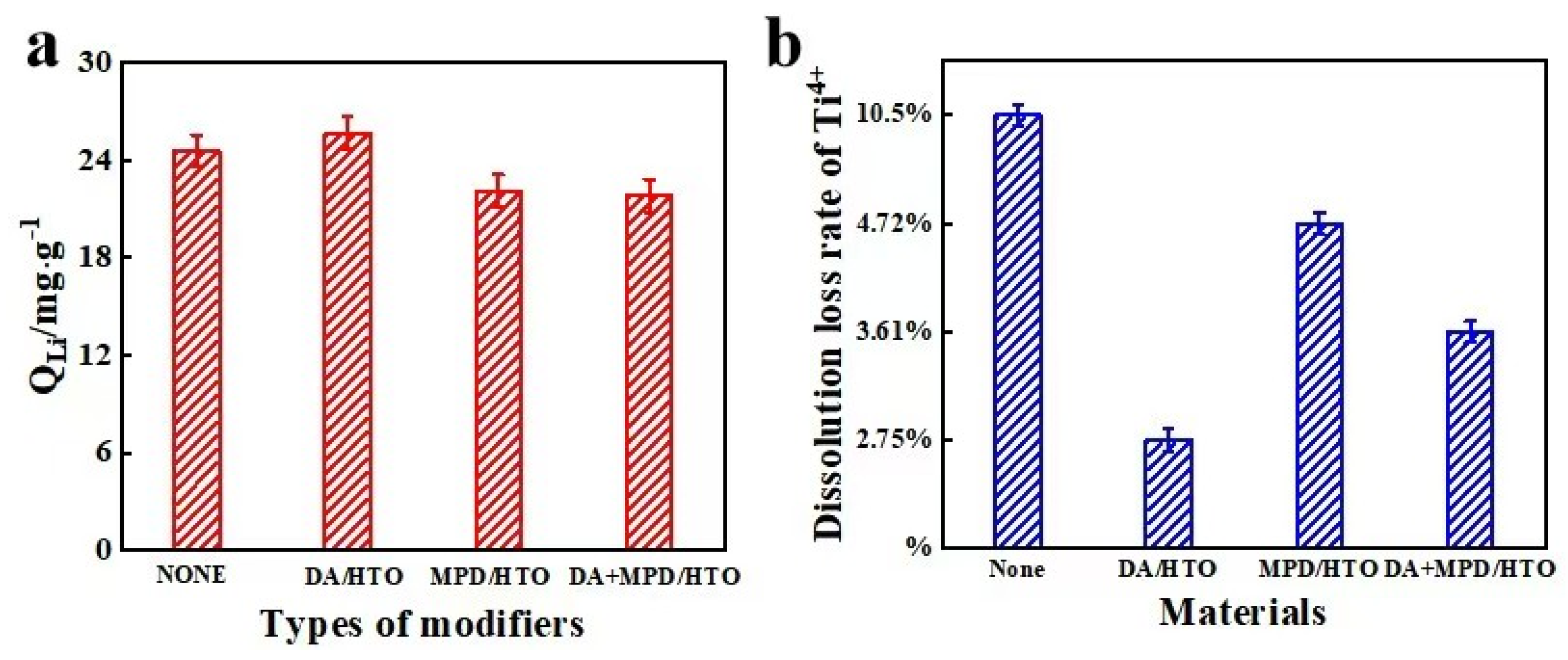
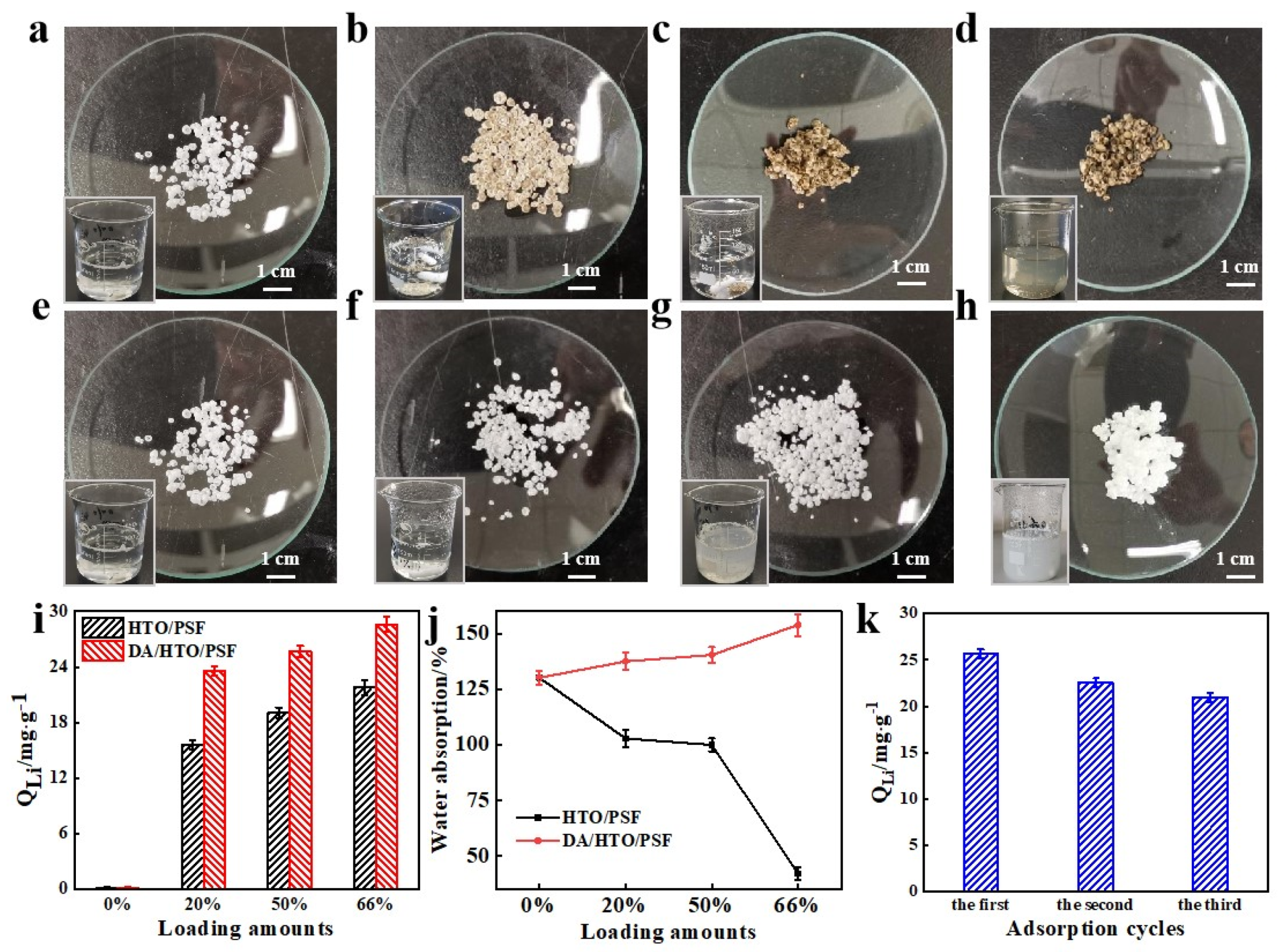
| Types of H-LIS | C (%) | N (%) | O (%) | S (%) | Ti (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA/HTO/PSf | 78.89 | 2.27 | 16.02 | 2.11 | 0.71 |
| HTO/PSf | 72.62 | 0 | 20.59 | 2.36 | 4.45 |
| Samples | S 2p | Ti 2p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (eV) | Species | (%) | Energy (eV) | Species | (%) | |
| DA/HTO/PSF | 167.93 | C-SO2 (2p3/2) | 49.98 | 458.6 | Ti-O (2p3/2) | 42.68 |
| 169.14 | C-SO2 (2p1/2) | 50.02 | 464.6 | Ti-O (2p1/2) | 47.46 | |
| - | - | - | 471.67 | Satellite | 9.86 | |
| HTO/PSF | 167.96 | C-SO2 (2p3/2) | 68.55 | 458.7 | Ti-O (2p3/2) | 60.56 |
| 169.15 | C-SO2 (2p1/2) | 31.45 | 464.39 | Ti-O (2p1/2) | 30.10 | |
| - | - | - | 471.64 | Satellite | 9.34 | |
| Material | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg·g−1) | KL (L·mg−1) | R2 | n | KF (L·mg−1) | R2 | |
| DA/HTO/PSF | 43.1033 | 0.0440 | 0.8878 | 2.3127 | 5.5589 | 0.9929 |
| T (K) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg·g−1) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg·g−1) | K2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | R2 | |
| 288.15 | 23.38 | 0.4572 | 0.9865 | 26.04 | 0.0237 | 0.9988 |
| 298.15 | 24.40 | 0.6161 | 0.9841 | 26.55 | 0.0345 | 0.9967 |
| 308.15 | 24.85 | 0.7050 | 0.9867 | 26.84 | 0.0402 | 0.9971 |
| 318.15 | 25.24 | 0.8483 | 0.9887 | 26.98 | 0.0510 | 0.9985 |
| 328.15 | 25.54 | 1.0800 | 0.9836 | 26.99 | 0.0709 | 0.9987 |
| Materials | Powdery LIS | Shapes | QLi (mg∙g−1) | Equilibrium Time (h) | Ti4+/Mn4+ Loss | qloss % * | Adsorption Condition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-LIS | Li2TiO3 | Hollow helisphere | 25.68 | 4.00 | 2.75% | 4.82% | 25.00 mg·L−1 Li+ in LiCl; pH = 12.0; T = 298.15 K | This work |
| MMMs | Li2TiO3 | Membrane | 25.01 | 6.00 | 1.1% | 3.10% | 25.78 mg·L−1 Li+ in geothermal water; pH = 12.0; T = 328.15 K | [28] |
| TFN | Li2TiO3 | Membrane | 24.38 | 4.00 | - | 5.50% | 25.78 mg·L−1 Li+ in geothermal water; pH = 12.0, T = 328.15 K | [31] |
| HTO-PVA/PAAm | Li2TiO3 | Hydrogel | 31.31 | 1.00 | - | 0.42% | 100 mg·L−1 Li+ in LiCl; pH = 12.0; T = 298.15 K | [39] |
| PVC-LMZO | Zr-doped Li1.6Mn1.6O4 | Membrane | 18.33 | 6.00 | 0.33% | 26.80% | 130 mg·L−1 Li+ in LiCl; pH = 6.05; T = 298.15 K | [26] |
| LTO-EVAL | Li2TiO3 | Membrane | 31.00 | 5.00 | 0.60% | 4.00% | 200 mg·L−1 Li+ in LiCl; pH = 12.0; T = 333.15 K | [40] |
| HTO-A | H4Ti5O12 | Hollow nanofibers | 60.80 | 0.33 | 4.63% | - | 900 mg·L−1 Li+ in LiCl; pH = 13.0; T = 298.15 K | [41] |
| PSF@HTO-1/32 Co-S2 | Co-doped Li2TiO3 | Fibers | 40.02 | 2.00 | 0.43% | 33.24% | 1.51 g·L−1 Li+ in lithium precipitation mother liquor; pH ≈ 12.0, T = 298.15 K | [29] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Han, S.; Deng, T. A Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent with High Interfacial Interaction for Lithium Recovery from Brine. Separations 2024, 11, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100301
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Wang L, Wang S, Xu L, Han S, Deng T. A Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent with High Interfacial Interaction for Lithium Recovery from Brine. Separations. 2024; 11(10):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100301
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yuyang, Yifei Zhang, Lin Wang, Shiqiang Wang, Lina Xu, Senjian Han, and Tianlong Deng. 2024. "A Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent with High Interfacial Interaction for Lithium Recovery from Brine" Separations 11, no. 10: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100301
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Wang, S., Xu, L., Han, S., & Deng, T. (2024). A Hollow Hemispherical Mixed Matrix Lithium Adsorbent with High Interfacial Interaction for Lithium Recovery from Brine. Separations, 11(10), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11100301







