Abstract
This study investigated the adsorption properties of graphene oxide in a magnetic-assisted adsorber for the depollution of water containing heavy metals. Two samples of graphene oxide with different surface chemistry were synthetized and assessed using the magnetic-assisted adsorption systems. One graphene oxide sample exhibited a dual magnetic behavior presenting both diamagnetic and ferromagnetic phases, while the other graphene oxide was diamagnetic. The adsorption properties of these graphene oxide samples for removing Pb2+ and Cu2+ were tested and compared with and without a magnetic field exposure. The results showed that the Pb2+ removal increased using both graphene oxide samples in the magnetic-assisted configuration, while Cu2+ adsorption was less sensitive to the application of the magnetic field. A monolayer model was used to simulate all the heavy metal adsorption isotherms quantified experimentally. It was concluded that the adsorption mechanism designed to remove Pb2+ and Cu2+ using tested graphene oxide samples was mainly multi-ionic where two metallic cations could interact with one active site (i.e., oxygenated functional groups) from the adsorbent surface. The oxygenated surface functionalities of graphene oxide samples played a relevant role in determining the impact of magnetic field exposure on the heavy metal removal efficacy. Magnetic-assisted adsorption using graphene oxide is an interesting alternative to reduce the concentration of Pb2+ in polluted effluents, and it can also be applied to improve the performance of adsorbents with a limited concentration of oxygenated functional groups, which usually show poor removal of challenging water pollutants such as toxic heavy metals.
1. Introduction
Drinking water constitutes 3% of Earth’s total water, with 0.01% accessible for human utilization. Unfortunately, this finite fundamental resource is increasingly threatened by urbanization, industrialization, and global environmental changes [1,2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), climate change is anticipated to restrict clean water accessibility to approximately 50% of the global population. A recent report from the United Nations revealed that three out of ten individuals lack access to potable water because of contamination associated with toxic compounds [3]. The escalating concern for water pollution has generated new technological challenges worldwide because organic (dyes, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals) and inorganic (heavy metals) pollutants are continuously discharged into aqueous reservoirs from anthropogenic activities. This phenomenon is attributable to the rapid progression of industrial activities and profound urban expansion, which progressively compromise the quality of water sources [4,5].
Environmental degradation, particularly the impact of heavy metal pollution on human health, has substantial detrimental consequences [5,6,7]. The worldwide concern regarding the presence of diverse heavy metals in water resources and industrial effluents has intensified mainly because of their non-biodegradability, toxicity [8,9], and bioaccumulation in the environment [10,11]. For example, the WHO and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have determined that exposure of children to a low concentration (5 mg/L) of lead (Pb2+) via drinking water has adverse effects on both the central and peripheral nervous systems [8]. Copper (Cu2+) is another relevant example of toxic water pollutants. This metal is a highly prized mineral worldwide and is used in various industrial applications [12,13,14,15,16,17]. Cu2+ is also an essential trace element in the human body, but its chronic exposure via water consumption has been associated with hypoglycemia, cramps, Wilson’s disease, Menkes syndrome, Alzheimer disease, diabetes, liver and kidney diseases, mental disorders, osteoporosis, and even cancer [15,16,17,18].
To overcome the critical problem of water depollution associated with toxic heavy metals, including Cu2+ and Pb2+, numerous purification technologies have been investigated and implemented. They include membrane-based filtration, ion exchange, precipitation, reverse osmosis, permeable reactive barriers, flocculation, adsorption, and electrodialysis [4,5,6,7,8,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Adsorption is a physicochemical treatment that separates organic and inorganic pollutants from fluids [5]. This method is a commercially consolidated technology because of its low-cost operation, minimal secondary pollution, and straightforward equipment requirements [6,8]. Several adsorbents have been documented for the removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ from water, such as clays, activated carbons, chalcogenides, zeolites, layered double hydroxides, polymeric materials, and magnetic materials [20,26,27]. However, the utilization of carbonaceous porous materials is a common approach for depolluting water containing heavy metals [28]. These materials are characterized by diverse allotropic forms, microstructures, and morphologies, and include carbon nanotubes, graphene, graphdiyne, activated carbon, and carbon nanospheres, which can exhibit a wide spectrum of surface properties [8,29].
Graphene and its oxidized versions have been explored and tested as prospective next-generation adsorbents for water depollution due to their distinctive physicochemical characteristics, including a high specific surface area (up to >2000 m2/g), mechanical flexibility, and thermal and chemical stabilities [17,20,21]. Graphene has a two-dimensional honeycomb structure formed by the bonding of sp2-hybridized carbon atoms [30], while graphene oxide (GO) is characterized by its content of epoxy, hydroxyl, and carboxyl groups distributed across both edges and planes. The functionalized surface of GO allows for an effective sequestration of cations such as Cu2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, Co2+, and U6+ from aqueous solutions [1,23,24,27,28,31]. Herein, it is convenient to indicate that GO can be easily prepared via a variety of low-cost routes, including mechanical exfoliation and other improved approaches [26,29,32,33], offering additional advantages for large-scale industrial applications.
On the other hand, magnetic-assisted adsorption processes have been introduced as strategies to intensify water purification where an enhanced removal efficacy can be obtained if the best operating conditions are applied [34]. This improved performance can be ascribed to various factors associated with the properties of a solution or material under the influence of a magnetic field [33]. The spin and orbital motions of electrons within an object can respond to the application of an external magnetic field, which is known as magnetization. This phenomenon has been exploited in different fields including the application of magnetism for the separation of pollutants from aqueous solutions, showing its potential benefits in terms of environmental sustainability, safety, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness [35,36]. Various mechanisms have been discussed to elucidate the potential impact of magnetic fields on adsorption processes [37]. The predominant mechanism associated with the influence of the magnetic field on the adsorption is the Lorentz force. This force alters the orientation of the pollutant ions in the solution, guiding them towards the adsorbent surface. The exposure to a magnetic field also affects the adsorbent properties (e.g., leading to a reduced zeta potential), the water properties, and the water–adsorbent interface via the formation of hydrogen bonds and a reduction in the surface tension [37].
The magnetic properties of graphene, GO, and their derivatives have attracted special attention because of their promising applications in spintronics [38]. The extended spin diffusion lengths and coherent times, resulting from the weak spin–orbit and hyperfine interactions in graphene, create favorable conditions for coherent spin manipulation. Graphene-based materials can exhibit interesting carrier mobility, and it has been predicted that the introduction of approximately one Bohr magneton (μB) can occur with a single hydroxyl group in graphene, and ferromagnetism may be induced by the epoxy groups in graphene nanoribbons [39]. However, the intrinsic magnetic properties of GO have not yet been properly characterized and explained. In fact, the limited experimental findings on the magnetic properties of GO can be contradictory and show significant differences, probably due to its nonstoichiometric atomic composition, which depends on the initial graphite material and oxidative conditions [40,41]. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, magnetic-assisted adsorption processes to remove water pollutants with GO have also not been assessed.
The present study focuses on the utilization of GO in magnetic-assisted batch adsorption systems for the removal of toxic heavy metal ions from water. The adsorption properties of two GO samples for the separation of Cu2+ and Pb2+ cations from water with and without the presence of a magnetic field were characterized, modeled, and discussed. The results indicate that this intensified purification strategy using GO can be applied for the depollution of water containing heavy metal ions, mainly Pb2+, with the aim of protecting human health and ecosystems in a world that seeks innovative and sustainable solutions to address environmental contamination problems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide
Two variants of GO, labeled samples GO2 and GO3, were synthesized in this study to compare the impact of magnetic field exposure on their adsorption properties to remove Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions from water. Sample GO2 was prepared with a mass-to-volume ratio of 8 g/mL, corresponding to 4 g of graphite and 0.5 mL of neutral industrial surfactant, and 400 mL of deionized water. The mechanical exfoliation [42,43] was carried out using a commercial blender (Oster, WI, USA) model 6800–6889 at 60 Hz and 450 W, maintaining a speed of 18,000 rpm for 45 min. Subsequently, the suspension was filtered with a commercial filter paper, followed by Topscien Spinplus-6 centrifugation for 45 min at 150 rpm. The final product was then dried in an oven at 80 °C for 48 h. Sample GO3 was obtained via a similar methodology but using 10 g of graphite and 1.25 mL of alkaline industrial surfactant to obtain an 8 g/mL mass-to-volume ratio, and 100 mL of deionized water was required for its synthesis. The mechanical exfoliation was performed in a blender for 60 min at 16,000 rpm. The suspension was filtered and centrifuged for 45 min at 150 rpm, and the final solid was dried at 80 °C for 24 h. These synthesis conditions ensured the formation of GO samples with different surface chemistries.
2.2. Characterization of GO Samples
Samples GO2 and GO3 were characterized using FT-IR spectroscopy, RAMAN spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XDR), and a Physical Property Measurement System (PPMS, Quantum Design Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The transformations in terms of the surface chemistry of graphite during the oxidation process were identified and studied using FTIR spectroscopy. A Thermo Scientific Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) instrument (model IS10) (Thermo Scientific, Kansas City, MO, USA) with ATR was used for this analysis. Special attention was paid to the spectral interpretation of the characteristic absorption bands associated with the vibrations of the C-C and C=C bonds and the oxygenated groups present in GO, which were related to the graphite oxidation process. On the other hand, the characterization of graphite and GO samples by Raman spectroscopy focused on the identification and assessment of the characteristic peaks of these materials. In its basal form, graphite exhibits a characteristic Raman spectrum with vibrational modes associated with the hexagonal carbon structure. However, substantial changes in the bond configuration can be observed during the oxidation process to obtain GO, which affect the vibrational modes detected by Raman spectroscopy. Therefore, this analysis focused on the “D” and “G” Raman peaks that reflect the vibrations of the C-C and C-O bonds in graphite and GO. Raman results were used to discuss the presence of oxygenated groups in GO, as well as alterations in the crystal lattice of graphite. A micro-Raman system with an excitation laser (632.8 nm) was used for the measurements. Raman spectra of tested samples were obtained under right-handed polarization, with 60 s captures and a power of 5 mW. The crystalline structures of the GO samples were determined by X-ray diffraction. The sample diffractograms were obtained with PANalytical Empyrean X-ray equipment using the Bragg–Brentano configuration with Cu Kα radiation. The X-ray tube was operated at 45 kV and 40 mA, where the diffraction angle 2θ was varied from 10° to 80° with a step size of 0.0262°. The X’Pert HighScore Plus software (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands, Westborough, MA, USA) and the database PDF2 were used to identify the crystalline structures of the samples. The pH at the point of zero charge for both GO samples was determined following the procedures reported in [44]. Finally, the magnetic properties of the GO samples were analyzed via magnetic field intensity versus magnetization per unit mass. These measurements were obtained with a vibrating sample magnetometer (PPMS DYNACOOL, Quantum Design Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) using a measurement interval of −10,000 to 10,000 Oe at 300 K.
2.3. Heavy Metal Adsorption Studies with and without the Presence of a Magnetic Field
All adsorption experiments were performed in batch systems using reactive grade nitrate salts of Pb2+ and Cu2+. The heavy metal concentrations were quantified using an atomic absorption spectrometer (Thermo Scientific iCE 3000, Kansas City, MO, USA) with linear calibration curves. Individual stock solutions were prepared for Pb2+ (7.2 mmol/L) and Cu2+ (15.7 mmol/L). These solutions were diluted to generate a set of adsorbate solutions of known concentrations that were used in the adsorption experiments. All batch adsorption tests were carried out at a mass-to-volume ratio of 2 g/L, 30 °C, constant solution pH = 5, and equilibrium time of 24 h. Heavy metal adsorption isotherms were quantified with and without the influence of a magnetic field using both GO samples. This approach allowed the comparison and analysis of the impact of GO properties and heavy metal ion type on the removal performance of the tested adsorption systems with and without magnetic field exposure. Magnetic-assisted experiments were performed with a nominal magnetic flux density of 5T and a monopole electronic configuration. The adsorption capacities of GO samples (qe, mmol/g) were calculated for each heavy metal using Equation (1) [45,46,47]:
where Co and Ce are the initial and equilibrium concentrations (mmol/L) of Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions, respectively, V (L) is the adsorbate solution volume, and m (g) is the GO sample mass. All the adsorption experiments were performed by triplicate using the mean results in data analysis. The results of the equilibrium adsorption studies were modeled using statistical physics theory [48]. It was assumed that the heavy metal adsorption process on the GO samples was a monolayer process where the oxygenated functionalities were the active sites for the removal of these pollutants. The selection of the statistical physics model was supported by the characterization results of the GO samples, as described below.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of GO Samples
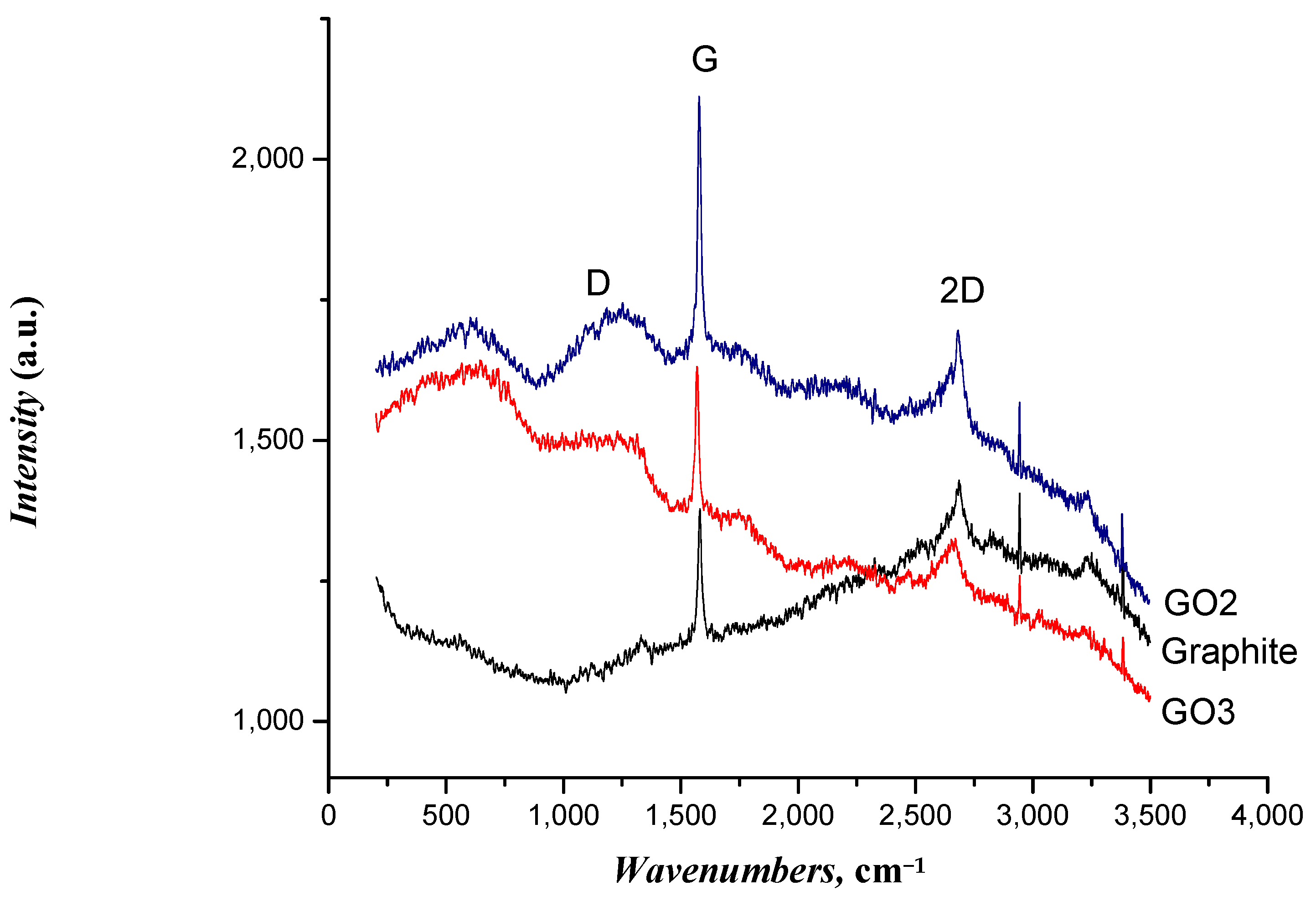
The Raman spectroscopy results for the graphite and GO samples are shown in Figure 1. The peaks D and G, which are associated with the deformation and vibration of the carbon–carbon bonds in the hexagonal lattice, were observed in the Raman spectrum of graphite. G and D peaks for the graphite, GO2, and GO3 samples were located at ~1583 and 1251 cm−1, respectively. The peak at ~1583 cm−1 was related to the sp2 vibration of carbon atoms bonded in a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice in a graphite layer [49], while the peak at ~1333 cm−1 was associated with the disordered sp3 vibration in the bonded carbon atoms [50,51]. For the GO samples, these peaks shifted and broadened, indicating changes in the crystal structure due to the incorporation of oxygenated groups. A significant increase in the intensities of peaks D and G was observed for the GO samples. This increase in the intensity of peak D suggests the presence of structural defects induced by the introduction of oxygenated functionalities during the oxidation process. In addition, the increase in the peak G intensity could be caused by changes in the crystal structure due to functionalization with oxygen-containing groups [43]. Similar findings have been reported in other studies on graphite oxidation [51,52,53]. The relationship between the intensities of the D and G peaks in Raman spectroscopy was utilized as a measure of changes in the structure of graphene during its transformation into GO [45,50,54,55]. The ID/IG ratio of GO3 = 0.9203 indicates a higher structural defect/disorder than the other samples; that is, GO2 = 0.8215 and graphite = 0.417. It was concluded that the GO3 sample was the most oxidized material obtained by graphene exfoliation.
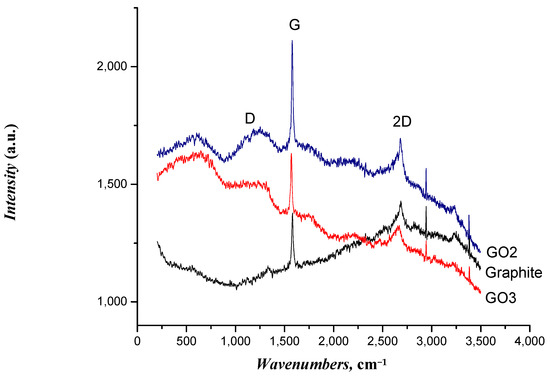
Figure 1.
Results of Raman spectroscopy for graphite and GO samples.
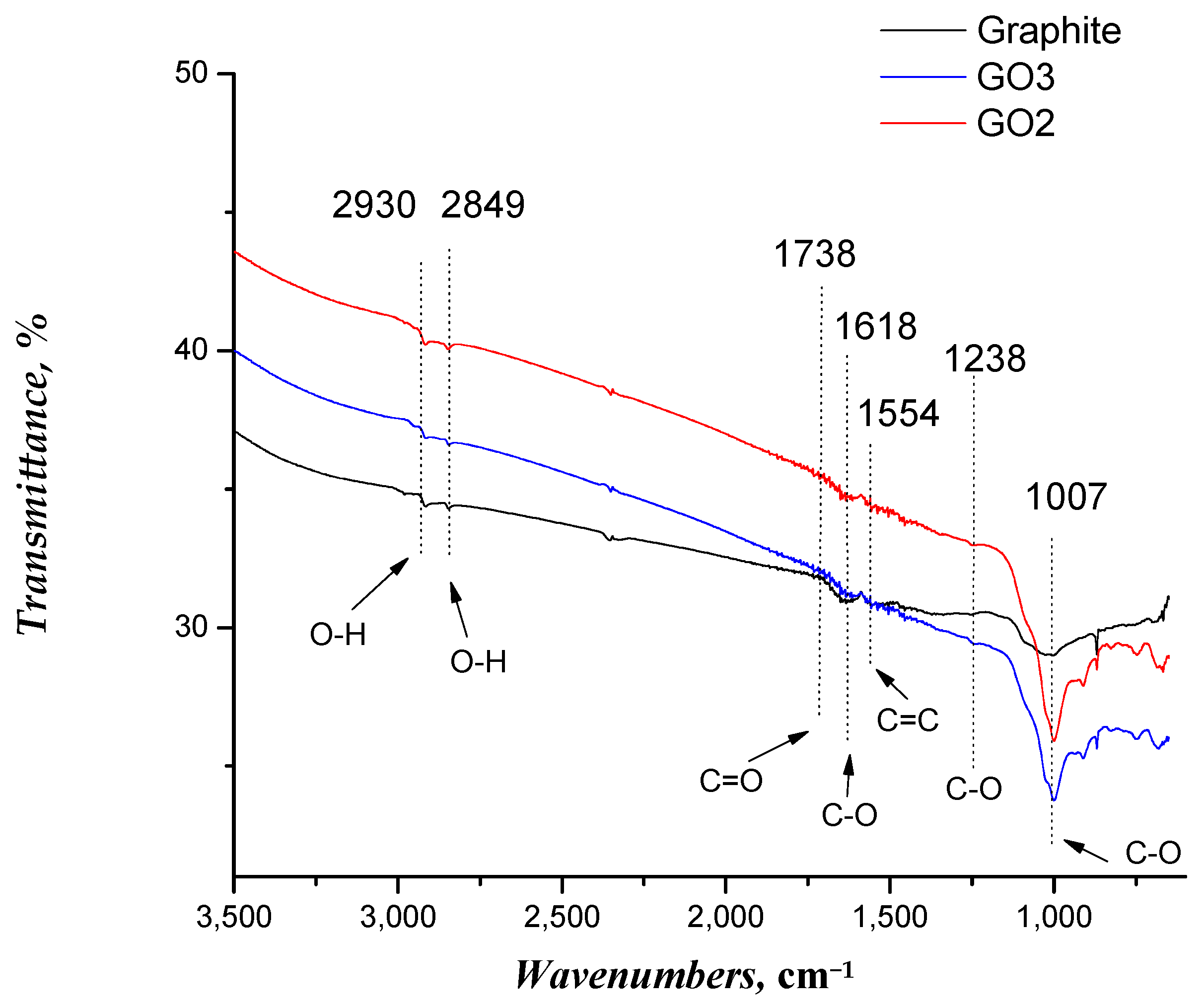
FTIR spectra of the graphite, GO2, and GO3 samples are reported in Figure 2. In the case of graphite, absorption bands corresponding to the vibrations of sp2 bonds were observed, highlighting the characteristic hexagonal structure [51]. On the other hand, new absorption bands emerged in the GO sample spectra that were related to the introduction of oxygen-containing functional groups, such as epoxide, hydroxyl, and carboxyl [46,47]. Specifically, the following functional groups were identified: O-H bond at 2930 and 2849 cm−1, C=O carbonyl group at 1738 cm−1, C-O bond at 1618, 1238, and 1007 cm−1, and C=C double bond at 1554 cm−1, respectively. These results confirmed the successful functionalization of pristine graphene to obtain GO2 and GO3.
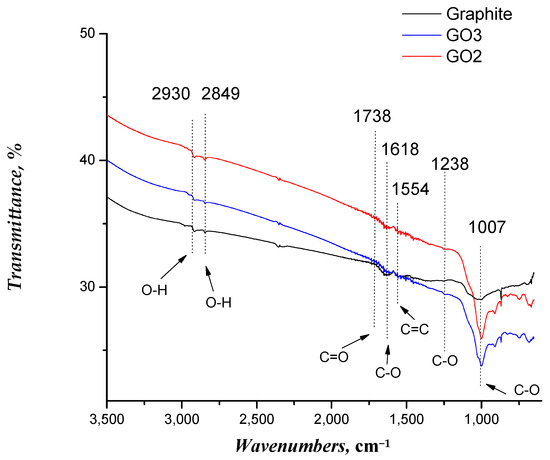
Figure 2.
Results of FTIR spectroscopy for graphite and GO samples.
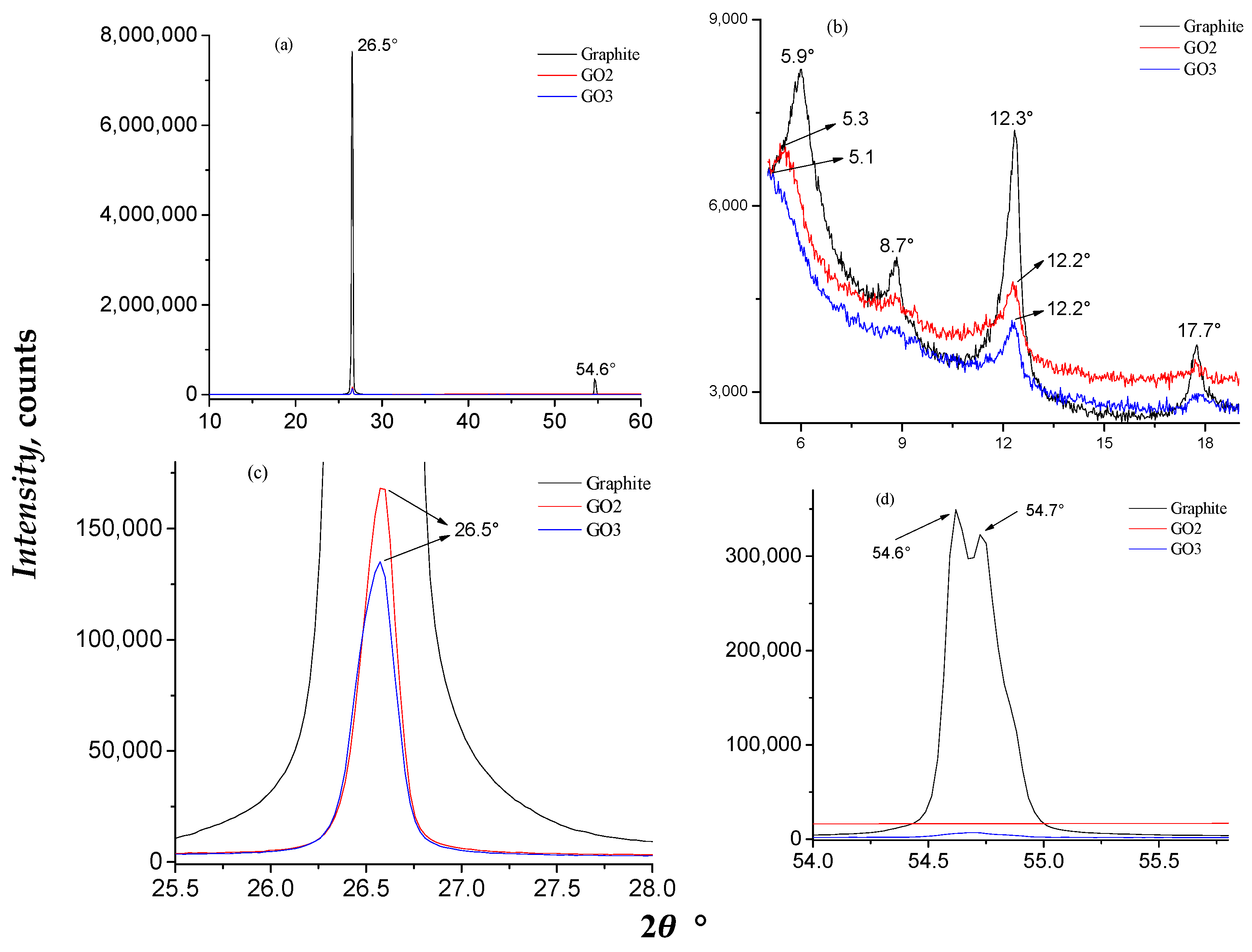
The results of XRD analysis are shown in Figure 3. The diffractogram of pristine graphite revealed a distinct diffraction peak at 2θ = 26.57° [42], implying the presence of a well-defined hexagonal crystalline structure, which is characteristic of this material. After mechanical exfoliation, a broader diffraction peak was observed at 2θ = 12.26° in the diffraction pattern of the GO samples, confirming the introduction of oxygen into the interlayer spaces of the graphite (Figure 3b). A distinct diffraction peak was observed at 2θ = 54.72°, aligned with the (100) and (004) reflection planes, suggesting a slight crystallinity of the GO samples (Figure 3d) [54,56].
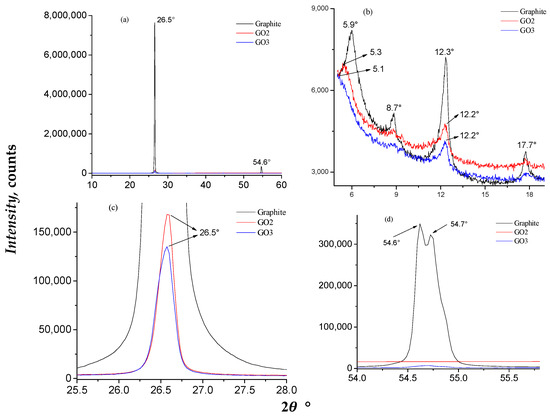
Figure 3.
Results of XRD for graphite and GO samples. (a) XRD patterns of graphite, GO2, and GO3 samples, and their enlargement at (b) 2θ = 5–19°, (c) 2θ = 25.5–28°, and (d) 2θ = 54–56°.
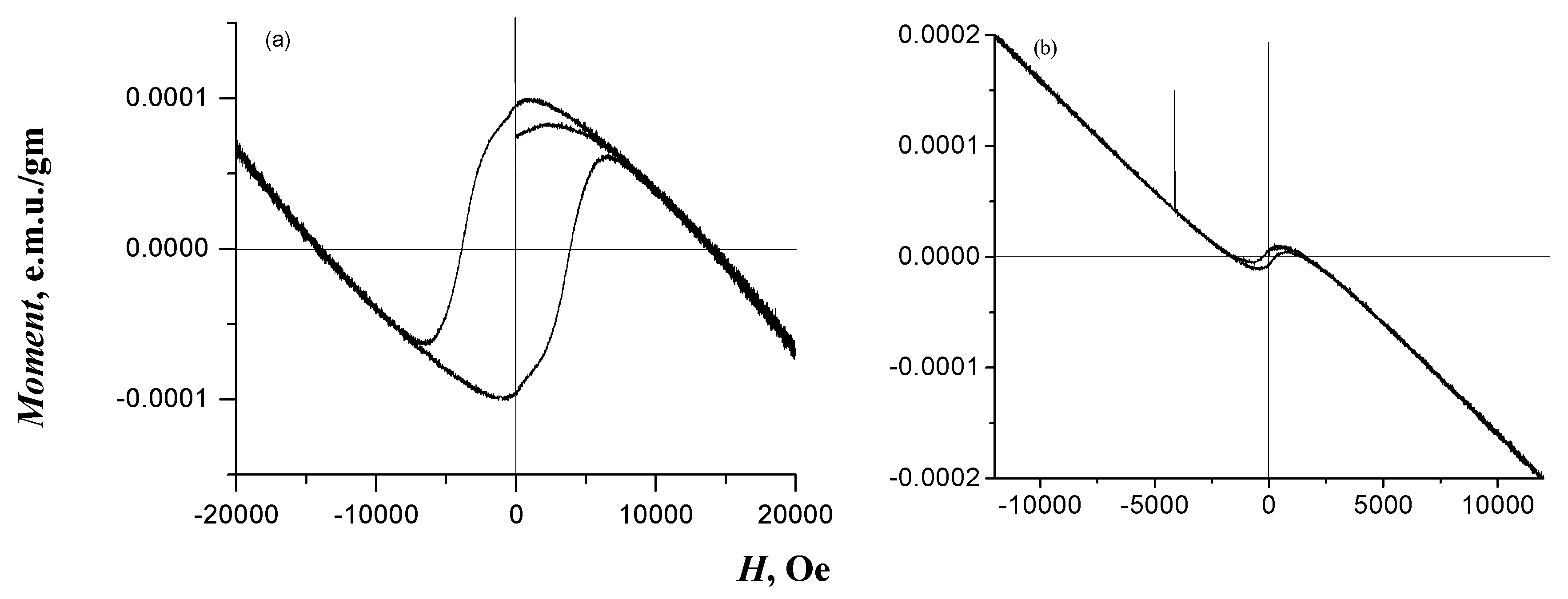
The results of the magnetic characterization indicated that GO2 exhibited dual magnetic behavior, presenting both diamagnetic and ferromagnetic phases (Figure 4a). The diamagnetic phase was identified in the low-magnetization region, where this sample exhibited a negative response to an applied magnetic field, indicating slight repulsion. In contrast, the ferromagnetic phase was identified in the high-magnetization region, where the material exhibited a strong attraction to the applied magnetic field, which proved the presence of magnetic moments aligned in the same direction [57]. GO3 was characterized as a diamagnetic material at 300 K based on the experimental data (Figure 4b) and theoretical results (Figure S1). The diamagnetic property of GO3 is attributed to its graphene or graphite-based structure, which is intrinsically diamagnetic because of its electronic configuration and the absence of unpaired spins, resulting in repulsion against the applied magnetic field [58]. This behavior is characteristic of graphene-derived materials such as graphite, which do not exhibit permanent magnetic moments [58].
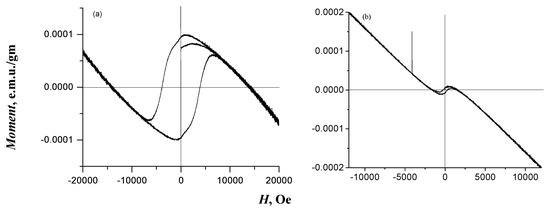
Figure 4.
Diagrams of magnetic field intensity versus magnetization at 300 K for (a) GO2 and (b) GO3 samples.
3.2. Adsorption Properties of GO Samples to Remove Pb2+and Cu2+ with and without Magnetic Field
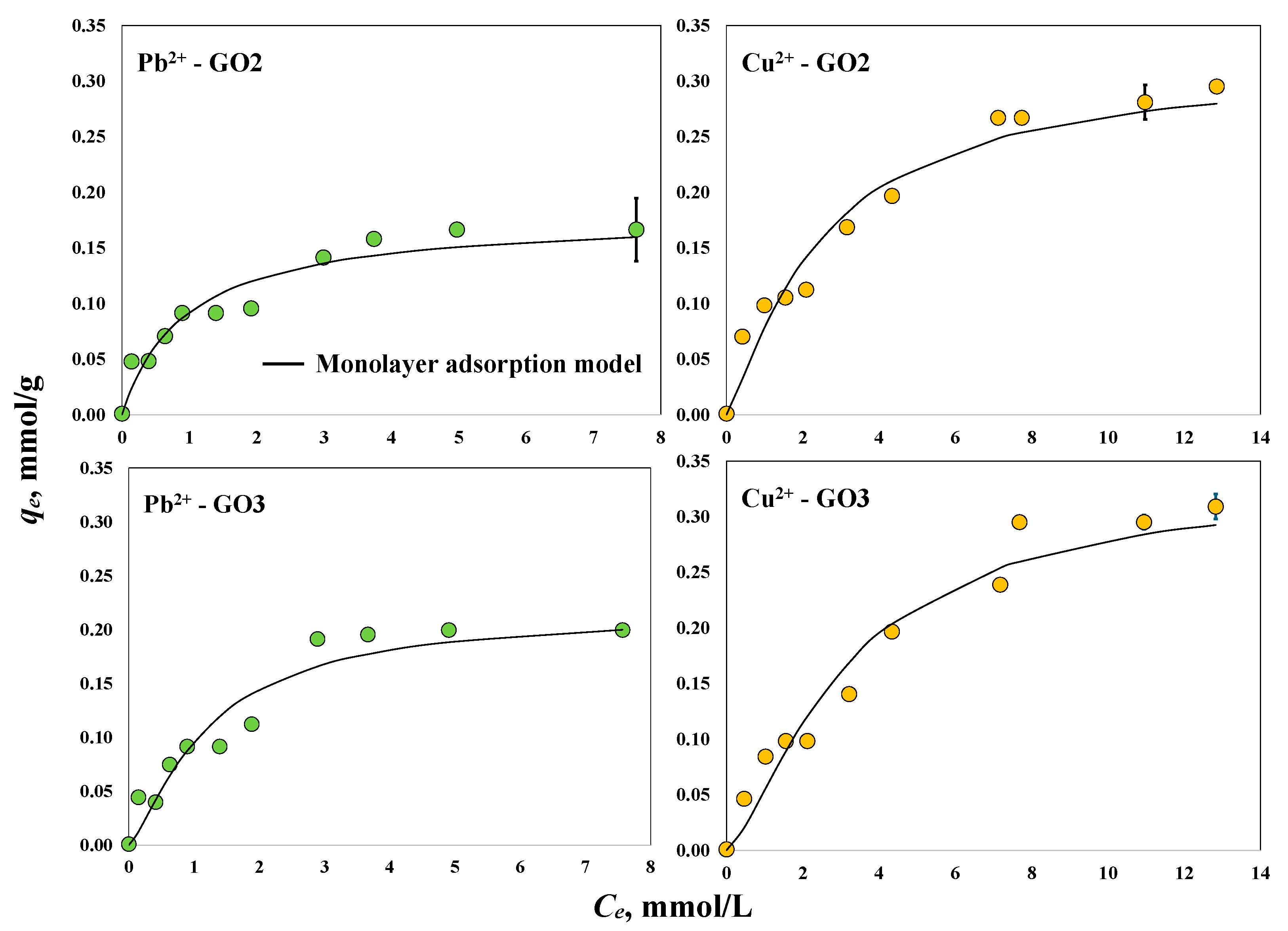
The experimental isotherms for the adsorption of heavy metals using the GO samples in the absence of a magnetic field are shown in Figure 5. The maximum experimental adsorption capacities for Pb2+ and Cu2+ using GO2 were 0.17 and 0.30 mmol/g, respectively. In the experiments using GO3, the maximum adsorption capacities were 0.20 and 0.31 mmol/g. Overall, GO3 showed better performance in removing Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions, where its adsorption capacities were higher by 18 and 3%, respectively, than those obtained for the GO2 sample. The improved adsorption properties of GO3 agreed with the surface characterization results, which indicated a more oxidized (i.e., functionalized) surface for this material. These oxygenated functionalities interact with heavy metal ions during adsorption [59]. The adsorption capacities of both GO2 and GO3 followed the order Cu2+ > Pb2+ where the removal of Cu2+ was higher than that of Pb2+ by 76 and 55% using GO2 and GO3, respectively. Note that the differences in the adsorption properties of GO samples without a magnetic field were related mainly to their synthesis conditions, especially the industrial surfactant used [60,61]. The utilization of an alkaline surfactant favored the adsorption properties of GO3, especially for Pb2+ removal, due to the promotion of more oxygenated functionalities on the adsorbent surface.
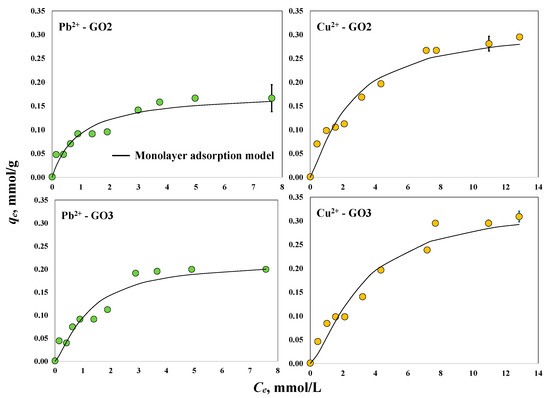
Figure 5.
Experimental isotherms for the adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ on GO samples at pH 5 and 30 °C.
Table 1 displays a comparison of the adsorption capacities reported in the literature with those obtained in the present study using the GO2 and GO3 samples without the application of a magnetic field. This table provides an overview of the adsorption properties of different materials used for the depollution of water containing heavy metal ions. These results indicated that the GO2 and GO3 samples showed a competitive performance in removing the tested pollutants, even in comparison with other adsorbents that have been prepared with different technologies and subjected to additional chemical treatments. These results highlight the potential application of both the GO2 and GO3 samples for depolluting fluids containing toxic heavy metals such as Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions.

Table 1.
Comparisons of adsorption capacities for the removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ using different adsorbents.
In terms of the adsorption mechanism, note that GO2 and GO3 contained oxygenated surface functionalities and π-conjugated structure that participated in the removal process. At tested pH conditions, the GO2 and GO2 surfaces were negatively charged because their values of pH at the point of zero charge (3.5–4) were lower than the solution pH, causing electrostatic attraction forces to promote the adsorption of these heavy metal ions. Additionally, GO2 and GO3 showed a π-conjugated system derived from the sp2-hybridized carbon atoms in the graphene structure. This conjugated π-electron system can interact with heavy metal ions via π–π interactions.
A monolayer adsorption model was used to simulate the heavy metal adsorption isotherms of the GO samples. The characterization results indicated the presence of epoxide, carboxyl, and hydroxyl functional groups in the GO samples, which are expected to be responsible for heavy metal adsorption. Therefore, it was assumed that these active sites were the main oxygenated functionalities involved in the adsorption of the metallic cations. Therefore, the following isotherm equation was applied to correlate the experimental data, assuming a monolayer process with the participation of oxygen-containing active sites to bind the metallic cations:
where nIon is the number of cations adsorbed per oxygenated functional group from the GO surface, DGO-Ion is the concentration (mmol/g) of oxygenated functionalities from the GO surface involved in heavy metal adsorption, and C1/2 is the half-saturation concentration (mmol/L) to form a monolayer on the GO surface. The results of the data modeling of the experimental isotherms were utilized to compare the calculated physicochemical parameters for the adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ on the tested GO samples. The monolayer model showed R2 values of 0.94 to 0.97 for these adsorption systems and its calculated parameters for each adsorption system are reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
Calculated monolayer adsorption parameters for the removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ using the GO2 and GO3 samples with and without the exposure to the magnetic field.
It was calculated that the adsorption of Pb2+ ions on the GO2 surface was a mono-ionic process (nPb-GO2 ≅ 1) involving a concentration of active sites (DGO2-Pb) of 0.18 mmol/g, while the Cu2+ removal using this GO sample was a combination of mono- and multi-ionic processes (nCu-GO2 = 1.22) where the oxygenated functionalities could adsorb one or two heavy metal ions per active site. The estimated concentration of GO2 active sites participating in the Cu2+ adsorption process was DGO2-Cu = 0.26 mmol/g where 78% of these active sites adsorbed one Cu2+ cation and the remaining 22% adsorbed two Cu2+ cations. For the GO3 sample, the adsorption of both Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions was multi-ionic (i.e., nPb-GO3 = 1.34 and nCu-GO3 = 1.43) where the concentrations of actives sites involved in the cation removal were DGO2-Pb = 0.16 mmol/g and DGO2-Cu = 0.23 mmol/g, respectively. Note that 66% of the GO3 active sites adsorbed one Pb2+ ion, whereas 34% interacted simultaneously with two Pb2+ cations. In the case of Cu2+ adsorption, 57% of the GO3 active sites adsorbed one cation, while the remaining 43% adsorbed two ions. Overall, the active sites involved in Cu2+ adsorption were 44% higher than those involved in Pb2+ adsorption for both GO samples.
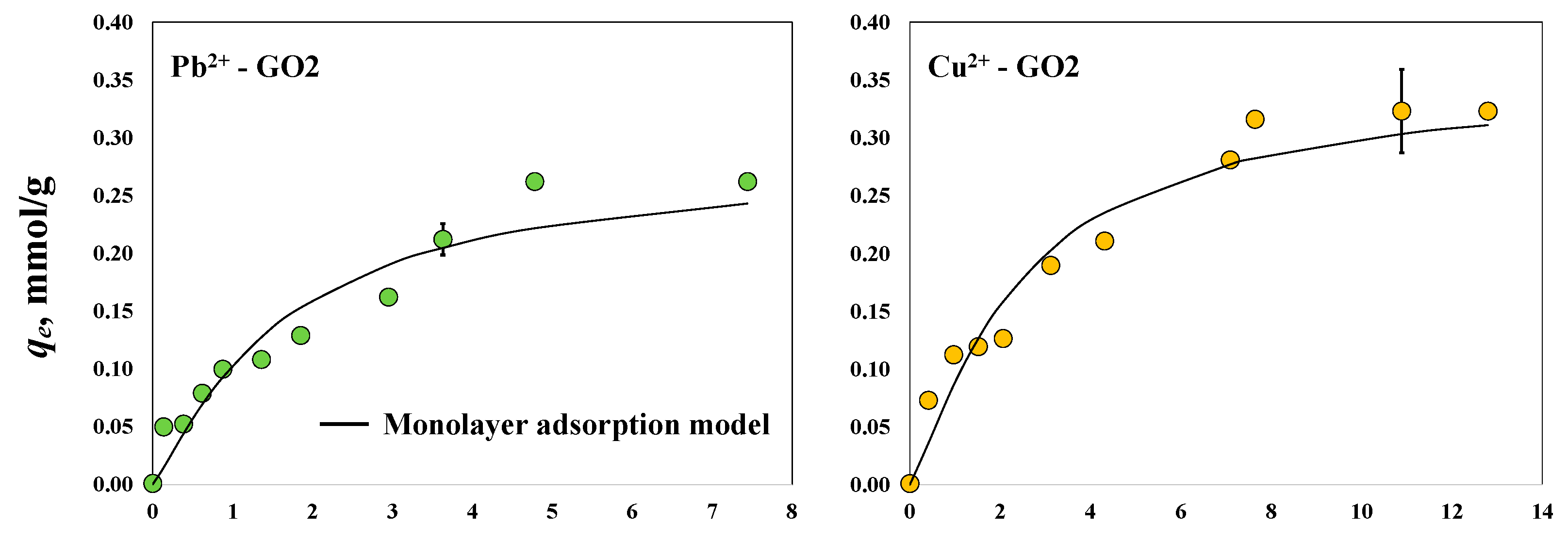
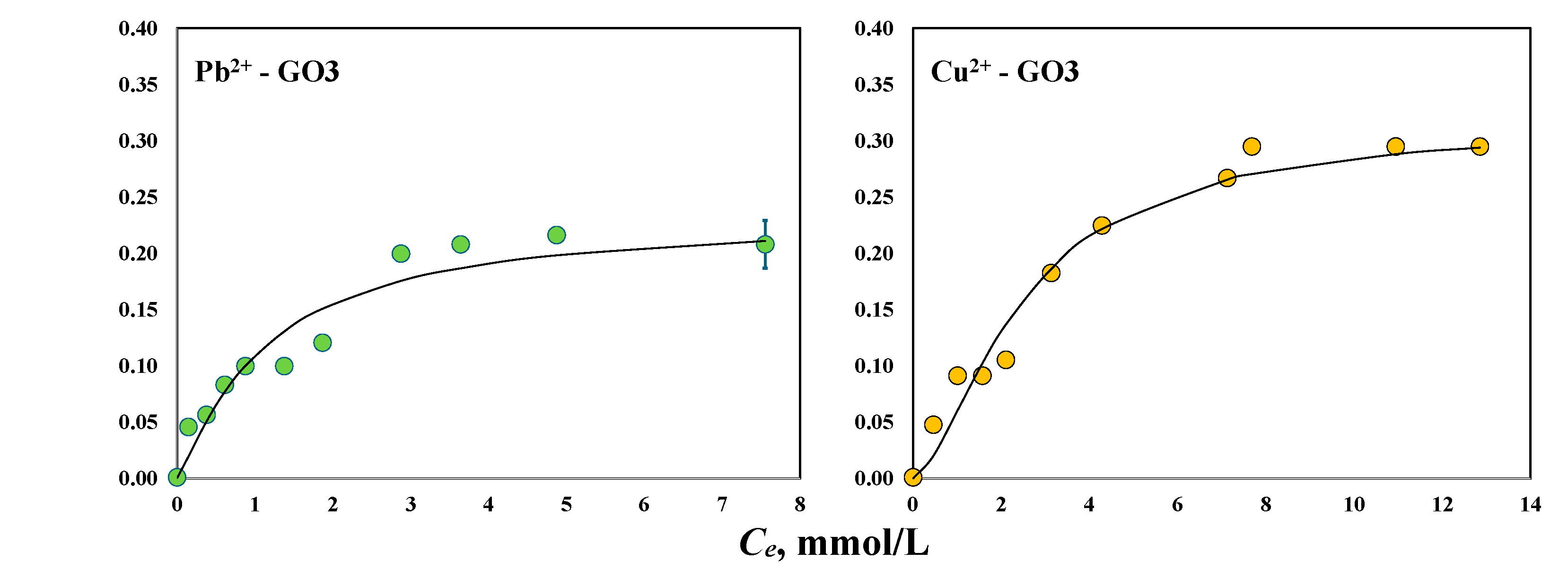
The isotherms for the magnetic-assisted removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ using GO2 and GO3 are shown in Figure 6. The maximum experimental adsorption capacities of GO2 and GO3 to separate Pb2+ under the presence of the magnetic field were 0.26 and 0.22 mmol/g, respectively. These materials showed maximum adsorption capacities of 0.32 and 0.30 mmol/g, respectively, to remove Cu2+ ions in the magnetic-assisted system. The same trend was observed for the adsorption properties of both GO samples to remove these heavy metals from aqueous solutions with and without the magnetic field; that is, Cu2+ adsorption > Pb2+ adsorption. However, the results prove that the intensified adsorber improved the removal performance of the tested GO samples, particularly for Pb2+ separation. The adsorption capacities in the magnetic-assisted systems for removing Pb2+ increased by 53 and 10% for GO2 and GO3, respectively, while Cu2+ adsorption was slightly affected by the magnetic field using both GO samples with a maximum improvement of 7% for GO2. The magnetic-assisted adsorption of both metals using GO3 was outperformed by GO2, where the most significant removal increments were obtained for this material due to the magnetic field.
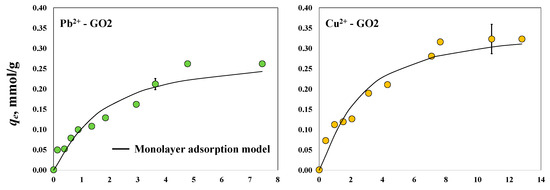
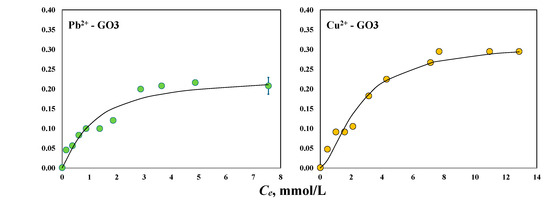
Figure 6.
Experimental isotherms for the magnetic-assisted adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ using the GO samples at pH 5 and 30 °C.
The increments in the adsorption capacities of the GO samples in the magnetic-assisted systems suggested a possible interaction between the magnetic moments of electrons and metal ions adsorbed on the material surface. This interaction can facilitate the capture and retention of metallic cations, thus accelerating the adsorption rate and increasing the overall adsorption capacity of the adsorbent [71]. These results also highlight that the impact of the magnetic field on the adsorption capacity of GO depends on the type of metallic ions and adsorbent surface chemistry. As stated, the magnetic characterization analysis revealed that GO2 exhibited dual magnetic behavior compared to GO3, which showed a diamagnetic nature. This difference in magnetic response could be related to the differences observed for the structure and defect distributions between these materials.
On the other hand, the statistical physics modeling (R2 = 0.93–0.97) indicated that the magnetic-assisted adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions was a multi-ionic process using GO2 and GO3 (i.e., nPb-GO2 = 1.18, nCu-GO2 = 1.23, nPb-GO3 = 1.18, nCu-GO3 = 1.59). The estimated concentrations of oxygenated functionalities involved in the magnetic-assisted Pb2+ adsorption on GO2 and GO3 were DGO2-Pb = 0.24 mmol/g and DGO3-Pb = 0.20 mmol/g, respectively, while DGO2-Cu = 0.29 mmol/g and DGO3-Cu = 0.20 mmol/g were calculated for the Cu2+ adsorption with the magnetic field. It was concluded that 82% of the active sites from the GO2 and GO3 surfaces interacted with one Pb2+ cation, while the remaining sites adsorbed two Pb2+ ions. In contrast, 41–77% of the oxygenated functional groups of these GO samples were involved in the mono-ionic interaction of Cu2+, and 23–59% corresponded to the adsorption of two Cu2+ ions. Overall, it was observed that the application of the magnetic field caused an increment of 25–33% in the concentration of the active sites of GO2 and GO3 that participated in the removal process, mainly for Pb2+. For Cu2+ removal, the application of a magnetic field did not generate a significant increase in the concentration of oxygenated functionalities participating in the adsorption process. These calculations suggest that the magnetic field can play the role of an external activator of GO surface functionalities to enhance the adsorption properties, but its impact depends on the pollutant to be removed. Note that the magnetic field was more effective at improving the adsorption capacities of the GO2 sample, which showed the lowest concentration of oxygenated functionalities. This result opens the possibility that the magnetic-assisted adsorption equipment could be an alternative for adsorbents with a limited concentration of surface functionalities, which usually show a limited performance to remove challenging adsorbates such as toxic heavy metal ions.
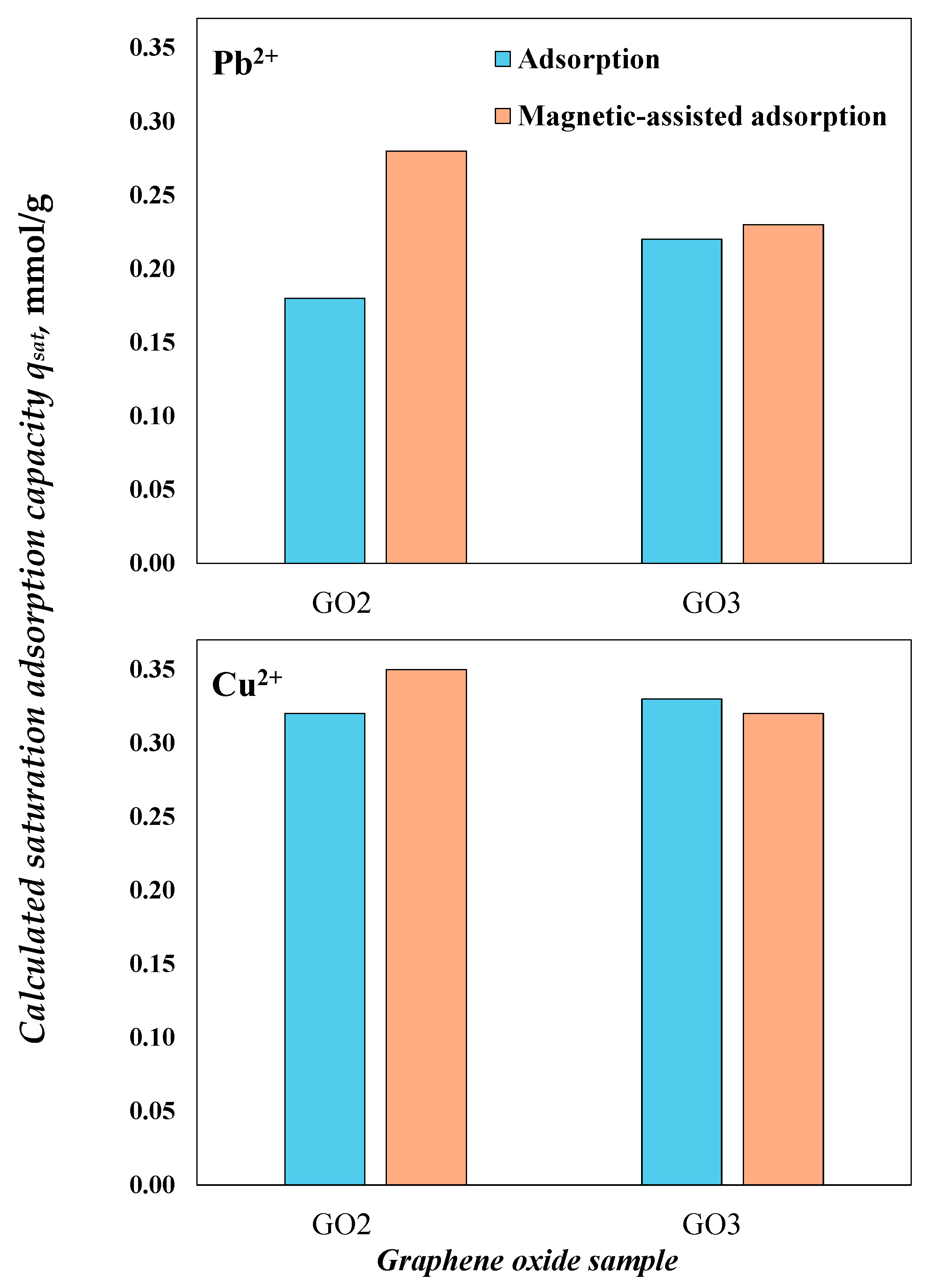
The calculated saturation adsorption capacities of GO samples (with and without the magnetic field) are reported in Figure 7, which were calculated by qsat = nIon · DGO-Ion. These theoretical values clearly indicate that GO2 significantly improved its removal performance with the magnetic field exposure, especially for Pb2+ ions. In contrast, the adsorption properties of GO3 did not change significantly in the magnetic-assisted system.
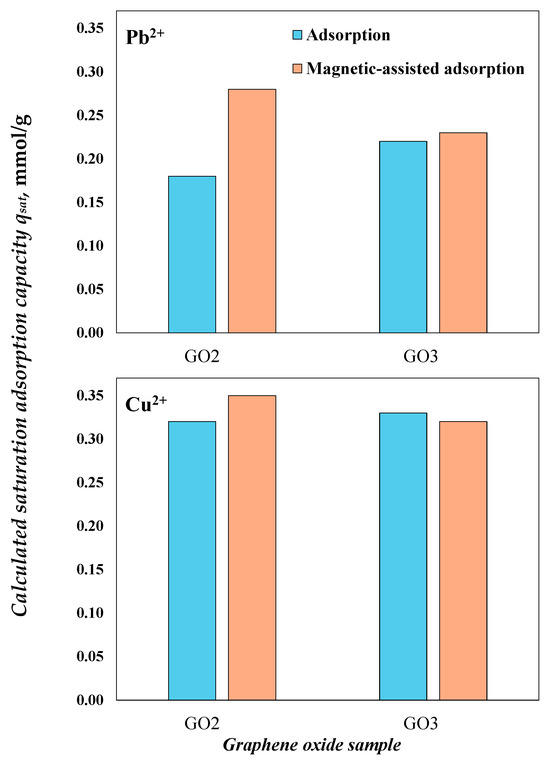
Figure 7.
Calculated saturation adsorption capacities for the removal of Pb2+ and Cu2+ using the GO samples at pH 5 and 30 °C.
Interaction energies (E, kJ/mol) for both GO samples in tested adsorber configurations were estimated with the monolayer model using the following expression:
where Cs (mmol/L) is the solubility of tested heavy metals in water, T (K) is the temperature used in the adsorption experiments, and R is the universal ideal gas constant. The calculated E values for Pb2+ and Cu2+ adsorption without the magnetic field for the GO samples were 18.3–18.9 kJ/mol and 20.6–21.2 kJ/mol, respectively. For the case of the magnetic-assisted adsorption systems, these energies were estimated in 17.6–18.5 k/J/mol for Pb2+ and 21.0–21.2 k/J/mol for Cu2+.
4. Conclusions
The adsorption properties of graphene oxide samples to remove heavy metal ions in magnetic-assisted systems were analyzed. It was proven that the surface chemistry of graphene oxide and heavy metal ion type determined the magnitude and impact of the magnetic field exposure on the removal process performance. Magnetic-assisted Pb2+ adsorption on graphene oxide showed a significant increase in the removal efficacy, while Cu2+ adsorption on this adsorbent was less sensitive to the magnetic field exposure. The characterization results indicated that the oxygenated functionalities of graphene oxide were involved in the separation of the tested metallic cations. It appeared that these oxygen-containing functional groups were activated by the magnetic field mainly for Pb2+ removal from water. Overall, it was concluded that the graphene oxide samples, with or without magnetic field exposure, showed better adsorption properties to remove Cu2+ than Pb2+. A multi-ionic monolayer adsorption process was expected to occur for the removal of these heavy metals from water using the graphene oxide samples where the oxygen-containing functional groups could interact with two cations. These results confirm the potential of sintered graphene oxide materials to purify water contaminated by toxic heavy metals using magnetic-assisted adsorption systems. However, the analysis and characterization of the effects of the magnetic field on the adsorption capacity of graphene-based adsorbents are fundamental for optimizing the performance of this intensified scheme for water treatment. The results reported in this study could have important implications for the design and intensification of heavy metal removal systems, where the application of magnetic fields can be considered an effective strategy to enhance the separation efficacy and performance of carbonaceous adsorbents.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations11100294/s1, Figure S1: Theoretical diamagnetic material [72].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.M.-V.; Methodology, E.L.O.; Investigation, A.P.M.-D.; Writing original draft preparation, A.P.M.-D. and M.R.M.-V.; Software, O.F.G.-V.; Writing-review and editing, H.E.R.-Á. and A.B.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Tecnológico Nacional de México: 18499.23-P.
Data Availability Statement
No new data has been generated.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by Tecnológico Nacional de México (TecNM) and the MatPore—Porous Materials National Laboratory.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict interest.
References
- Ain, Q.U.; Farooq, M.U.; Jalees, M.I. Application of Magnetic Graphene Oxide for Water Purification: Heavy Metals Removal and Disinfection. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Bai, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Magnetic-responsive CNT/chitosan composite as stabilizer and adsorbent for organic contaminants and heavy metal removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdoub, M.; Amedlous, A.; Anfar, Z.; Jada, A.; El Alem, N. Engineering of amine-based binding chemistry on functionalized graphene oxide/alginate hybrids for simultaneous and efficient removal of trace heavy metals: Towards drinking water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, V.N.; Rajkumar, M.; Mobika, J.; Sibi, S.P.L. Adsorption of As (V) ions from aqueous solution by carboxymethyl cellulose incorporated layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Safari, E.; Baghdadi, M.; Janmohammadi, M. Enhanced adsorption of heavy metals in groundwater using sand columns enriched with graphene oxide: Lab-scale experiments and process modeling. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Chen, J. Preparation of dialdehyde cellulose graftead graphene oxide composite and its adsorption behavior for heavy metals from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 212, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, A. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by chitosan-based magnetic composite flocculants. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 108, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuma, S.; Mishra, P.; Bhat, B.R. Polypyrrole functionalized Cobalt oxide Graphene (COPYGO) nanocomposite for the efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal pollutants from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.G.; Mu, X.; Wu, D.B.; Ye, W.M. Graphene oxide-modified organic Gaomiaozi bentonite for Yb(III) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 274, 125176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, L.; Beyou, E.; El Ghali, A.; Baouab, M.H.V. Comparative studies on the adsorption of metal ions from aqueous solutions using various functionalized graphene oxide sheets as supported adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Impact of synthesis conditions on Pb(II) removal efficiency from aqueous solution by green tea extract reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ihsanullah, I.; Younas, M.; Shah, M.U.H. Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibebunjo, K.; El Ouardi, Y.; Bediako, J.K.; Iurchenkova, A.; Repo, E. Functionalization of recycled polymer and 3D printing into porous structures for selective recovery of copper from copper tailings. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 286, 119664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Wu, W.K.; Chen, B.; Kong, Q.P.; Lian, J.J. Co-adsorption of tetracycline and copper by the thiourea-modified porous sodium alginate microspheres. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidli, A.; Huang, Y.; Rejeb, Z.B.; Zaoui, A.; Park, C.B. Sustainable and efficient technologies for removal and recovery of toxic and valuable metals from wastewater: Recent progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyen, L.T.; Bac, B.H. Adsorption–desorption behavior of halloysite clay for Cu2+ ions and recovery of copper by electrodeposition method. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, S.; Vetrivelan, V.; Muthu, S.; Al-Saadi, A.A. Computational analysis of anti-cancer drug hydroxyurea adsorption on nanocages of gold, silver and copper: SERS and DFT assessment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.-X.; Yang, J.; Yoon, K.-B. Silicone-modified black peanut shell (BPS) biochar adsorbents: Preparation and their adsorptions for copper(II) from water. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, Y. Cross-linked sulfydryl-functionalized graphene oxide as ultra-high capacity adsorbent for high selectivity and ppb level removal of mercury from water under wide pH range. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Amino-assisted AHMT anchored on graphene oxide as high performance adsorbent for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Hg(II) from aqueous solutions under wide pH range. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.Y.; Lau, S.Y.; Pan, S.; Lam, M.K. 3D graphene-based adsorbents: Synthesis, proportional analysis and potential applications in oil elimination. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Fan, X.W.; Li, Y.Z. Efficient removal of a low concentration of Pb(II), Fe(III) and Cu(II) from simulated drinking water by co-immobilization between low-dosages of metal-resistant/adapted fungus Penicillium janthinillum and graphene oxide and activated carbon. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Yadav, A.; Bagotia, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S. Adsorptive potential of modified plant-based adsorbents for sequestration of dyes and heavy metals from wastewater—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, A.; Alduaij, O.; Al-Bahir, A.; Alshammari, D.A.; Alqarni, N.; Eldesoky, A.; Farag, A.A.; Toghan, A. A comparative study of pyridine and pyrimidine derivatives based formamidine for copper corrosion inhibition in nitric acid: Experimental and computational exploration. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, A.M.; Utra, U.; Yussof, N.S.; Bashir, M.J.K. Advancements in Adsorption Techniques for Sustainable Water Purification: A Focus on Lead Removal. Separations 2023, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Hiew, B.Y.Z.; Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Gan, S. Environmental application of three-dimensional graphene materials as adsorbents for dyes and heavy metals: Review on ice-templating method and adsorption mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 174–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaabane, L.; Beyou, E.; Baouab, M.H.V. Preparation of a novel zwitterionic graphene oxide-based adsorbent to remove of heavy metal ions from water: Modeling and comparative studies. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 2502–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.S.; Konwar, K.; Ghosh, T.N.; Mondal, B.; Sarkar, S.K.; Deb, P. Multifunctional Iron oxide embedded reduced graphene oxide as a versatile adsorbent candidate for effectual arsenic and dye removal. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 39, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, F.; Yu, T.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, D.; Wei, C. Strategies to improve the adsorption properties of graphene-based adsorbent towards heavy metal ions and their compound pollutants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.H.; Mubarak, M.F.; El-Sabban, H.A.; Kang, J.; El Shahawy, A.; Alshwyeh, H.A.; Hemdan, M. Exploring the sustainable synthesis pathway and comprehensive characterization of magnetic hybrid alumina nanoparticles phase (MHAl-NPsP) as highly efficient adsorbents and selective copper ions removal. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 34, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Selvaraj, M.; Zain, J.; Banat, F.; Haija, M.A. Polyethylenimine modified graphene oxide hydrogel composite as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, S.F.; Virgen, M.M.; Montoya, V.H.; Morán, M.M.; Gómez, R.T.; Vázquez, N.R.; Cruz, M.P.; González, M.E. Effect of an external magnetic field applied in batch adsorption systems: Removal of dyes and heavy metals in binary solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, O.F.G.; Virgen, M.d.R.M.; Montoya, V.H.; Gómez, R.T.; Flores, J.L.A.; Cruz, M.A.P.; Morán, M.A.M. Adsorption of Heavy Metals in the Presence of a Magnetic Field on Adsorbents with Different Magnetic Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9323–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Khasnabis, S.; Kumar, V.; Nath, B.; Adiga, V.; Naik, T.S.K.; Subramanian, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; et al. Sustainable removal of Cr(VI) using graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanohybrid: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Huang, Z. Magnetic dithiocarbamate functionalized reduced graphene oxide for the removal of Cu(II), Cd(II), Pb(II), and Hg(II) ions from aqueous solution: Synthesis, adsorption, and regeneration. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J. Magnetic field assisted adsorption of pollutants from an aqueous solution: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Feng, Q.; Tang, N.; Du, Y. Identifying the magnetic properties of graphene oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 123104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Ahmed, M.; Mukadam, M.D.; Yusuf, S.M. Investigation of Graphite Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Magnetic Properties Revisited. Asian J. Mater. Chem. 2016, 1, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, S.; Jehan, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Graphene oxide-based materials for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Swami, S.; Shrivastava, V.; Nair, R.; Shrivastava, R. Graphene oxide and functionalized graphene oxide: Robust, 2d material as heterogeneous green catalyst for heterocyclic synthesis. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrla, E.; Paton, K.R.; Backes, C.; Harvey, A.; Smith, R.J.; McCauley, J.; Coleman, J.N. Turbulence-assisted shear exfoliation of graphene using household detergent and a kitchen blender. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11810–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Álvarez, D.T.; Davies, P.; Stafford, J. Foam flows in turbulent liquid exfoliation of layered materials and implications for graphene production and inline characterisation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes on activated carbons with different surface chemistries. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, H.; Eslami-Farsani, R.; Torabian, M.; Amousa, N. Recent advances in one-pot functionalization of graphene using electrochemical exfoliation of graphite: A review study. Synth. Met. 2020, 269, 116549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, A.S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Ha, S.K.; Hong, C.K. An Efficient Water Saving Step During the Production of Graphene Oxide via Chemical Exfoliation of Graphite. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 21, 1749–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anurag, K.; Kumar, S.R. Synthesis of graphene through electrochemical exfoliation technique in aqueous medium. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 2695–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrhar, O.; El Gana, L.; Mobarak, M. Calculation of adsorption isotherms by statistical physics models: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4519–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Upadhyay, S.; Balachandran, M. Exploration of Graphene Layers in Various Carbon Materials by Raman Spectroscopic Techniques. Mapana J. Sci. 2021, 20, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cai, W.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, L.; Yu, H.; Song, L.; Gui, Z.; Hu, Y. One-pot exfoliation and synthesis of hydroxyapatite-functionalized graphene as multifunctional nanomaterials based on electrochemical approach. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasuli, H.; Rasuli, R.; Alizadeh, M.; BoonTong, G. Microwave-assisted exfoliation and tearing of graphene oxide in the presence of TiO2 nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyurnina, A.V.; Morton, J.A.; Subroto, T.; Khavari, M.; Maciejewska, B.; Mi, J.; Grobert, N.; Porfyrakis, K.; Tzanakis, I.; Eskin, D.G. Environment friendly dual-frequency ultrasonic exfoliation of few-layer graphene. Carbon 2021, 185, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Manickam, S.; Lester, E.; Wu, T.; Pang, C.H. Synthesis of graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots from miscanthus via ultrasound-assisted mechano-chemical cracking method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Perez-Page, M.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Holmes, S. One step electrochemical exfoliation of natural graphite flakes into graphene oxide for polybenzimidazole composite membranes giving enhanced performance in high temperature fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, C.J.; Manikandan, R.; Thondaiman, P.; Sivakumar, P.; Savariraj, A.D.; Cho, W.-J.; Kim, B.C.; Jung, H. Sonoelectrochemical exfoliation of graphene in various electrolytic environments and their structural and electrochemical properties. Carbon 2021, 184, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudiki, A.; Matrouf, M.; Azriouil, M.; Farahi, A.; Lahrich, S.; Bakasse, M.; El Mhammedi, M. Preparation of graphene samples via electrochemical exfoliation of pencil electrode: Physico-electrochemical Characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Crisóstomo, C.E.; Pal, U.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Shelyapina, M.G.; Shmyreva, A.A. Local-field effect on the hybrid ferromagnetic-diamagnetic response of opals with Ni nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 514, 167102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Li, Q.; Shaikh, M.S.; Li, Z. The pure paramagnetism in graphene oxide. Results Phys. 2021, 26, 104407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Ajaj, Y.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; Ghadir, G.K.; Alani, Z.K.; Hussein, M.M.; Hussein, S.A.; Karim, M.M.; Al-Khalidi, A.; Abbas, J.K.; et al. Adsorption of heavy metal ions use chitosan/graphene nanocomposites: A review study. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Siddiqui, W.A.; Ahmad, T. Synthesis, Characterization of Silica Nanoparticles and Adsorption Removal of Cu2+ Ions in Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2017, 7, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Yang, B.; Vincent, T.; Faur, C.; Guibal, E. Selenium(VI) and copper(II) adsorption using polyethyleneimine-based resins: Effect of glutaraldehyde crosslinking and storage condition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Han, H.; Han, R. Adsorption properties of lead and zinc ions onto iminodiacetic acid functionalized loofah from solution. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 253, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.K.S.; Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Study of binary and single biosorption by the floating aquatic macrophyte salvinia natans. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Z.; Yu, Q.J.; El Hanandeh, A. Removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution using date seed-derived biochar: Batch and column studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, X.; Liao, X.P.; Shi, B. Adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using collagen-tannin resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmita, H.; Karthikeyan, K.G.; Pan, X.J. Copper and cadmium sorption onto kraft and organosolv lignins. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6183–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhang, B.H. Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption of copper(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqueous solution using sawdust xanthate modified with ethanediamine. Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, X.; Lu, J. Competitive Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Cu2+ onto Citric Acid Modified Pine Sawdust. Clean 2015, 43, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Do, H.; Yusuf, A.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Ren, Y.; He, J. Camellia oleifera shell–reduced graphene oxide for adsorption of copper(II). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 314, 128818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Y. Non-covalent interactions of graphene surface: Mechanisms and applications. Chem 2022, 8, 947–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basem, A.; Jasim, D.J.; Majdi, H.S.; Mohammed, R.M.; Ahmed, M.; Al-Rubaye, A.H.; Kianfar, E. Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater by chitosan: A review. Engineering 2024, 23, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).