Prediction of Bleeding via Simulation of Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
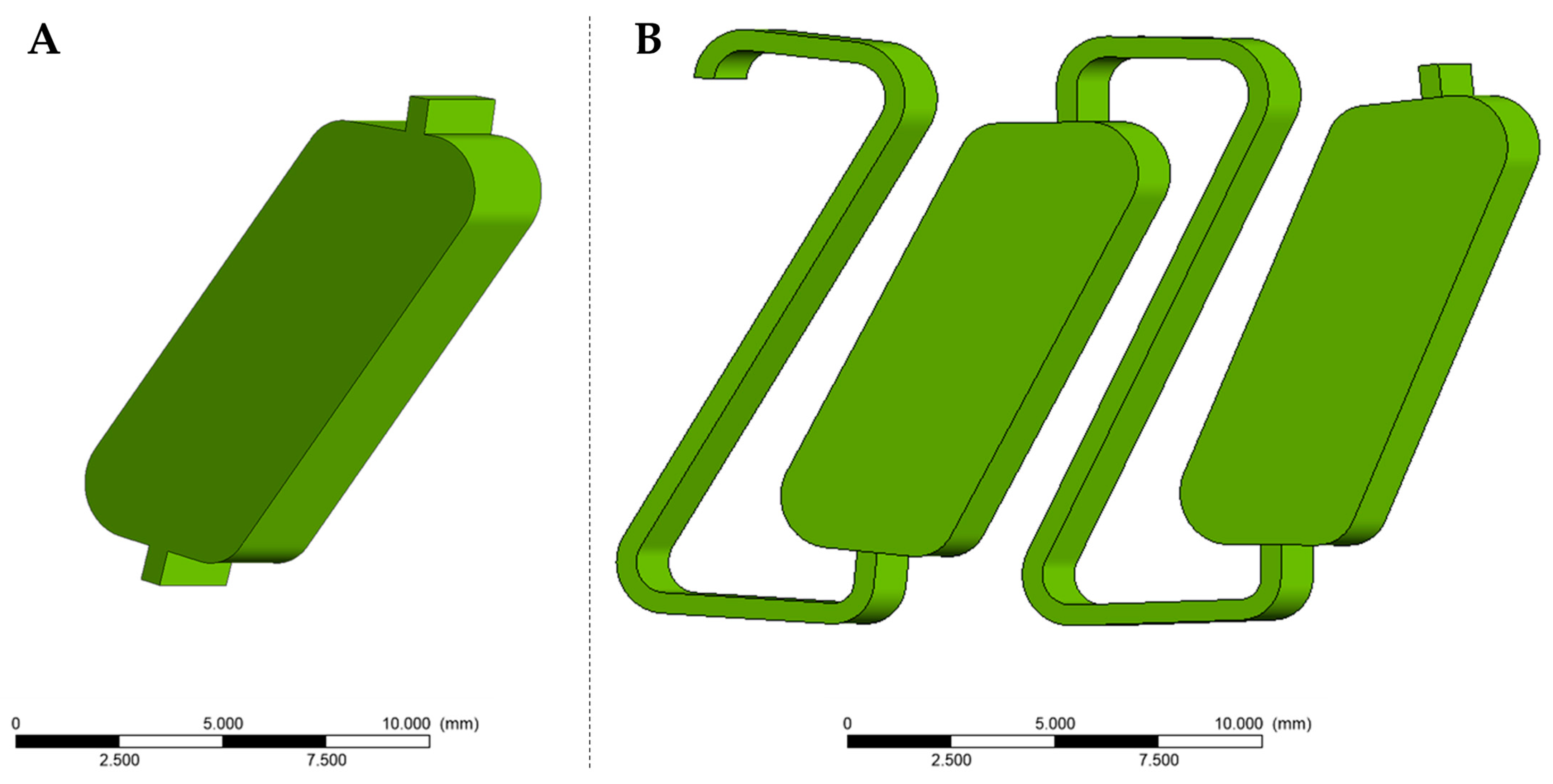
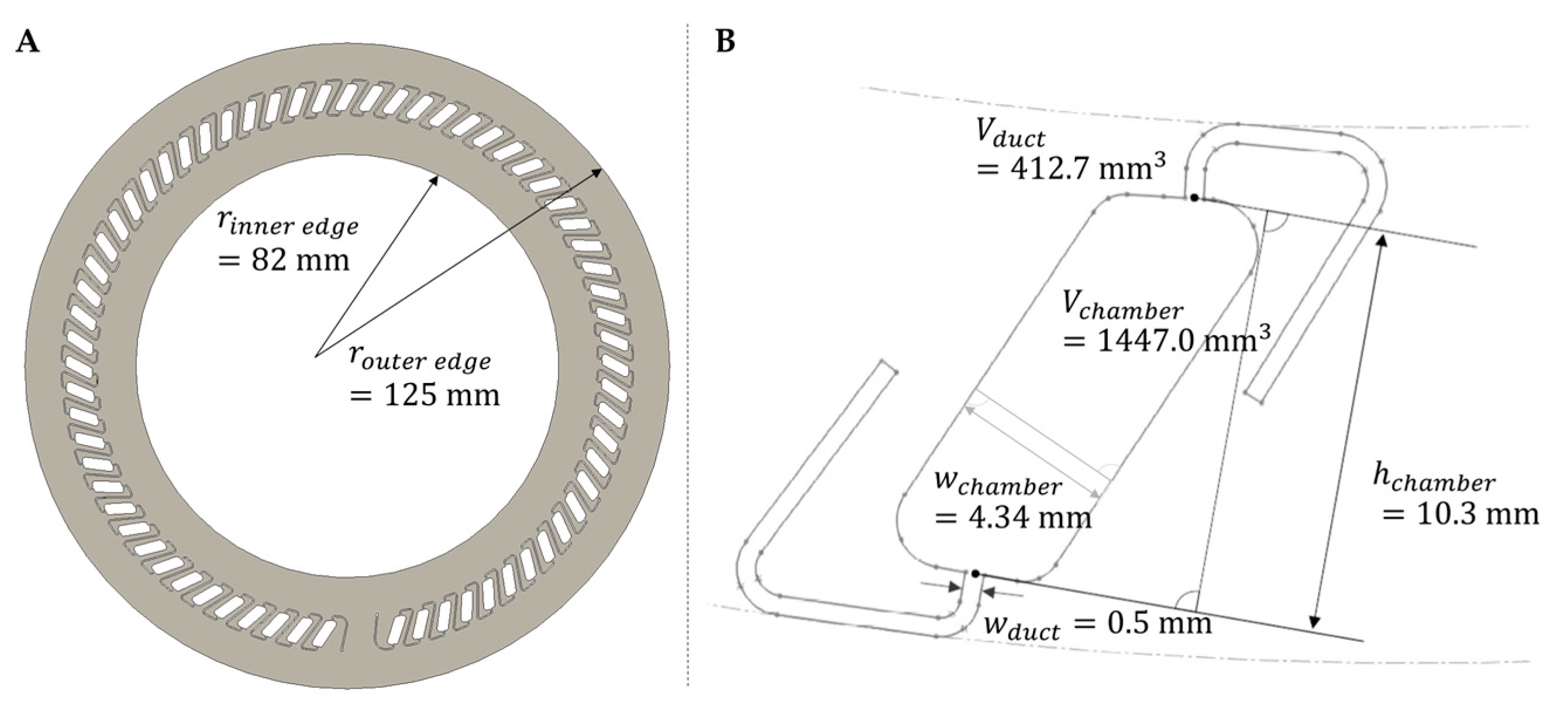
2.1. Model Generation
2.2. Phase System and Operating Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contact Angle
3.2. CFD Model Validation
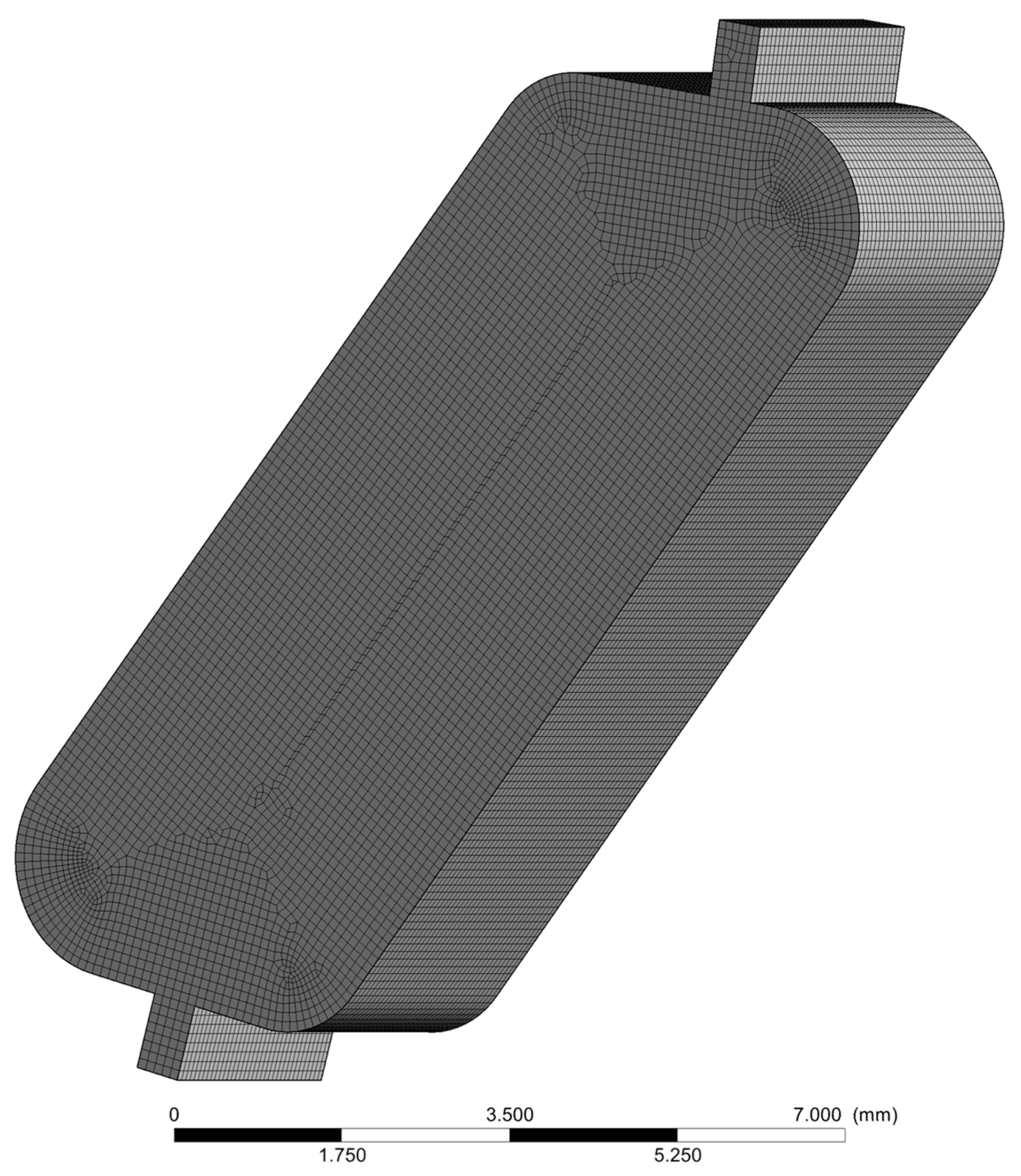
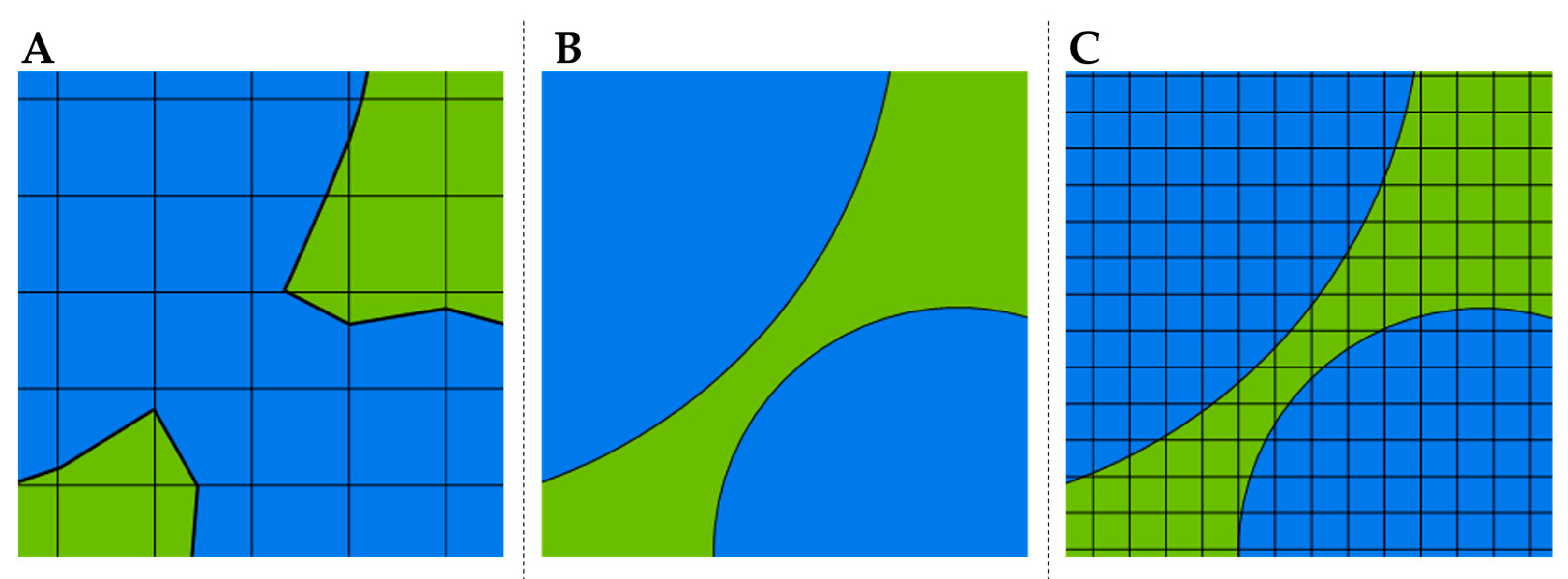
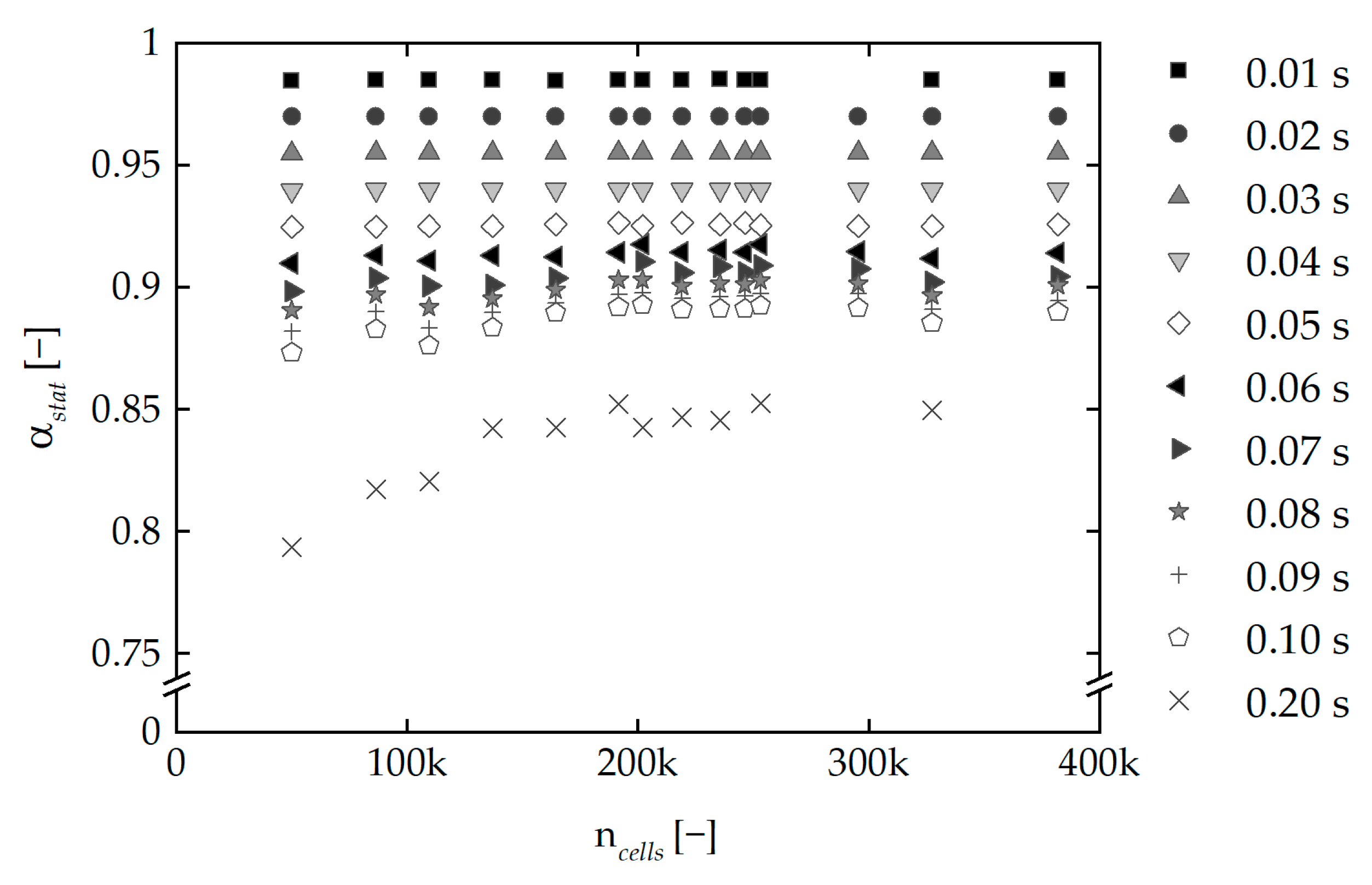
3.3. Mesh Independence Study
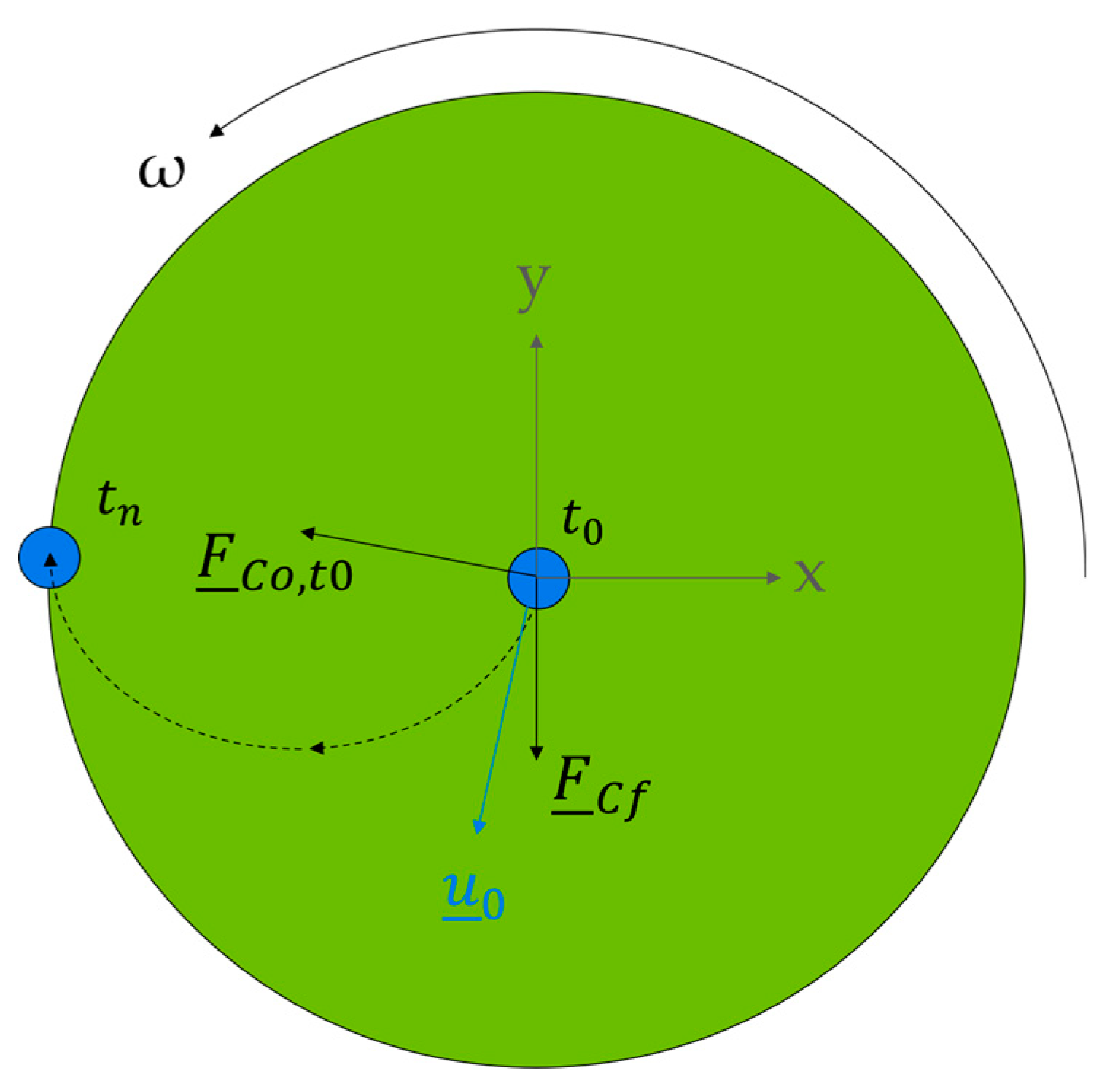
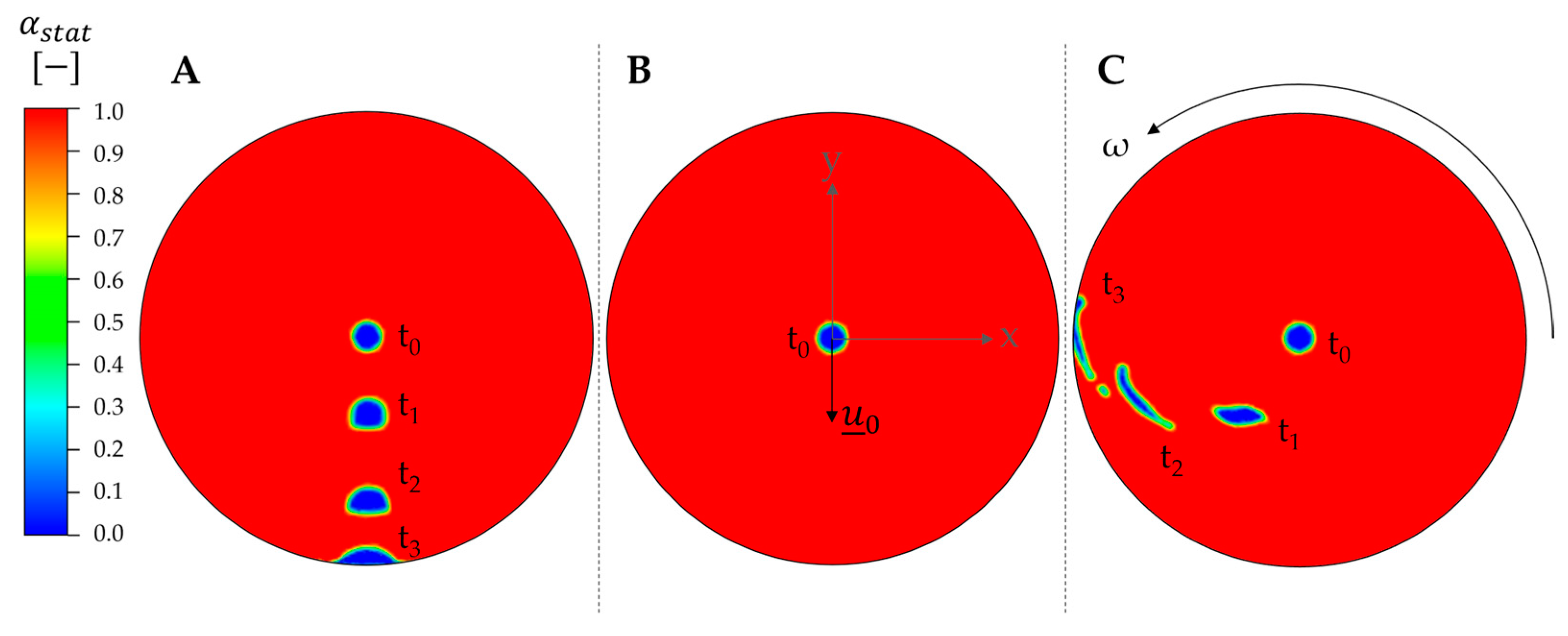
3.4. Rotational Forces in Single CPC Chambers
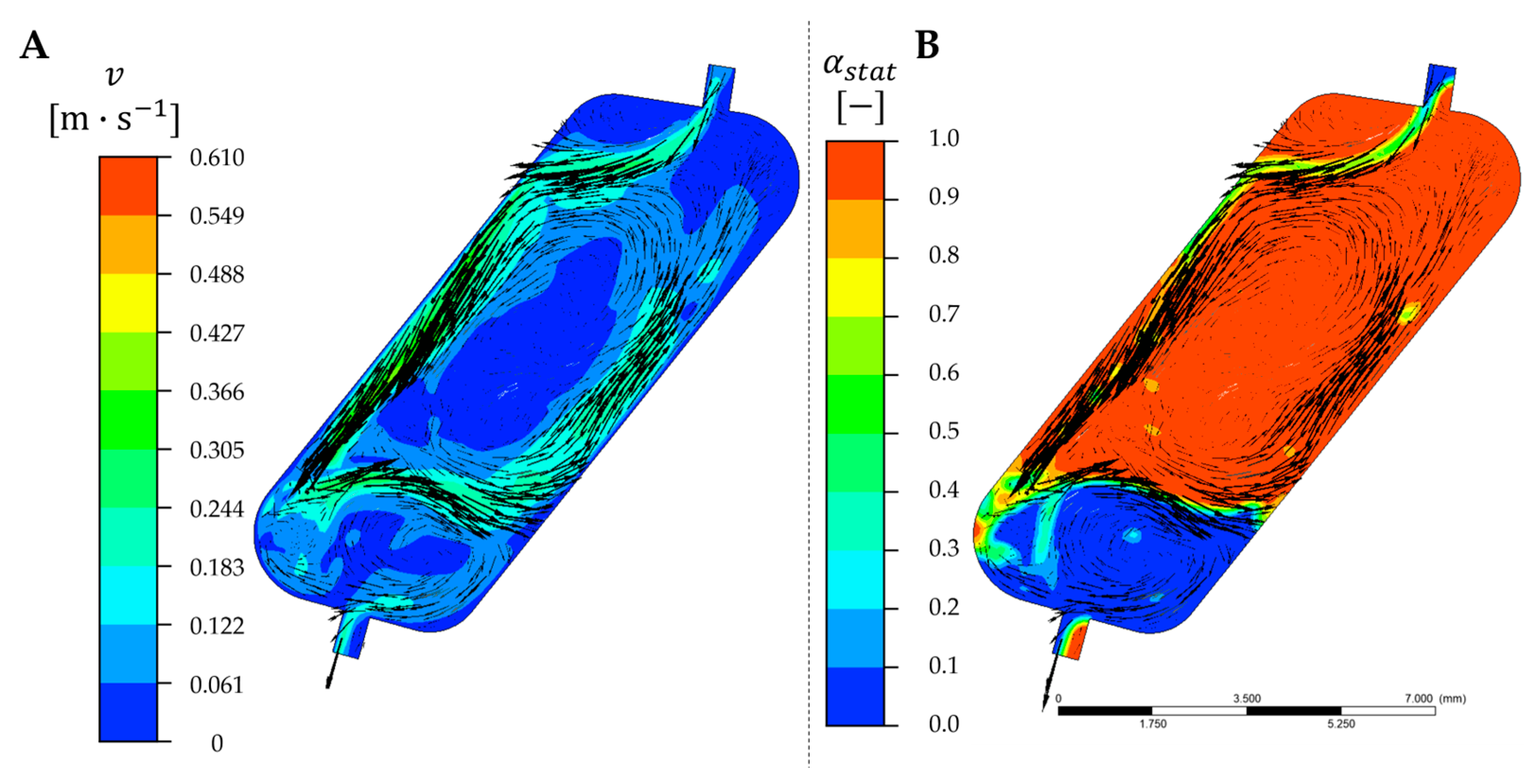
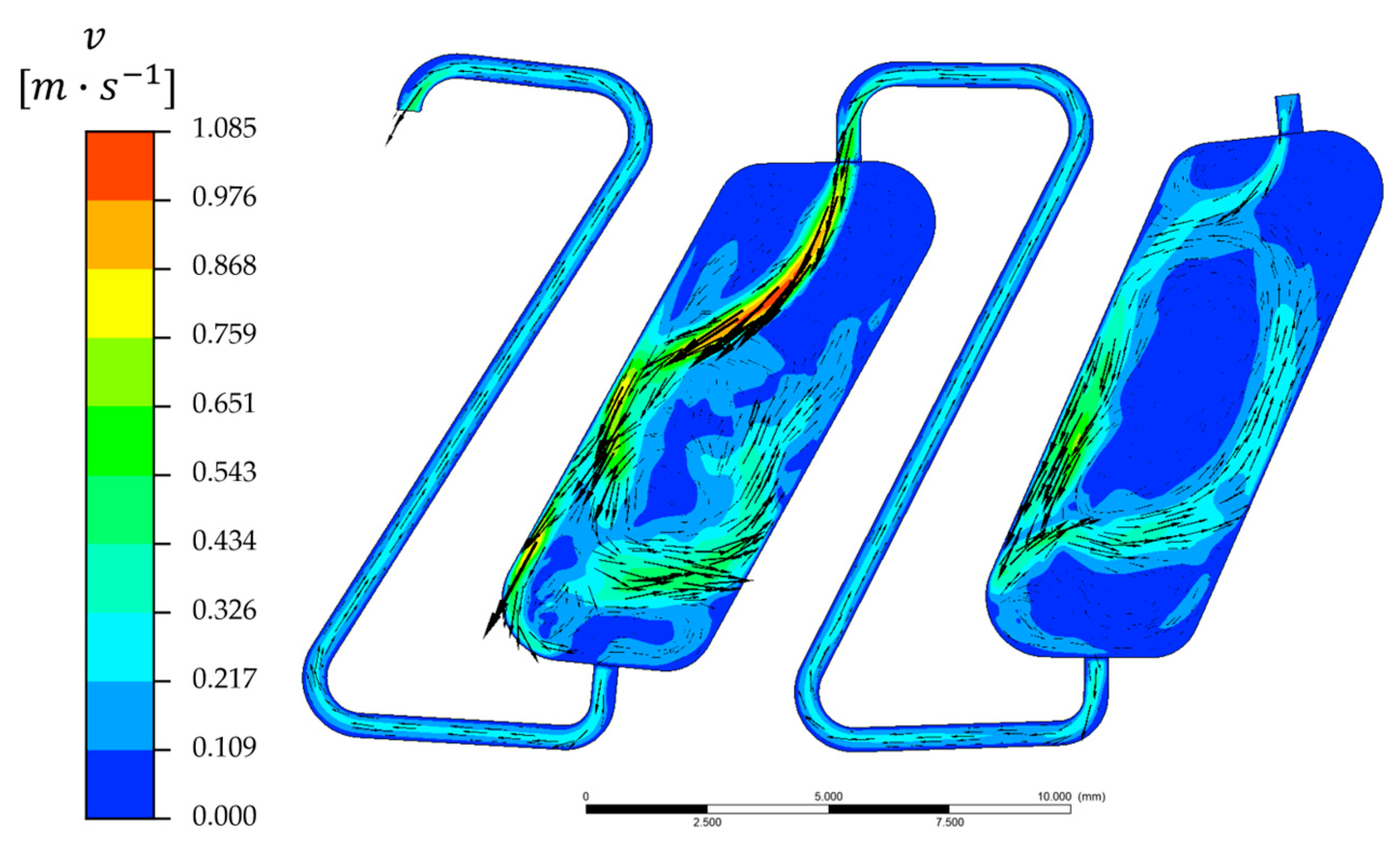
3.5. Velocity Field in Single CPC Chambers
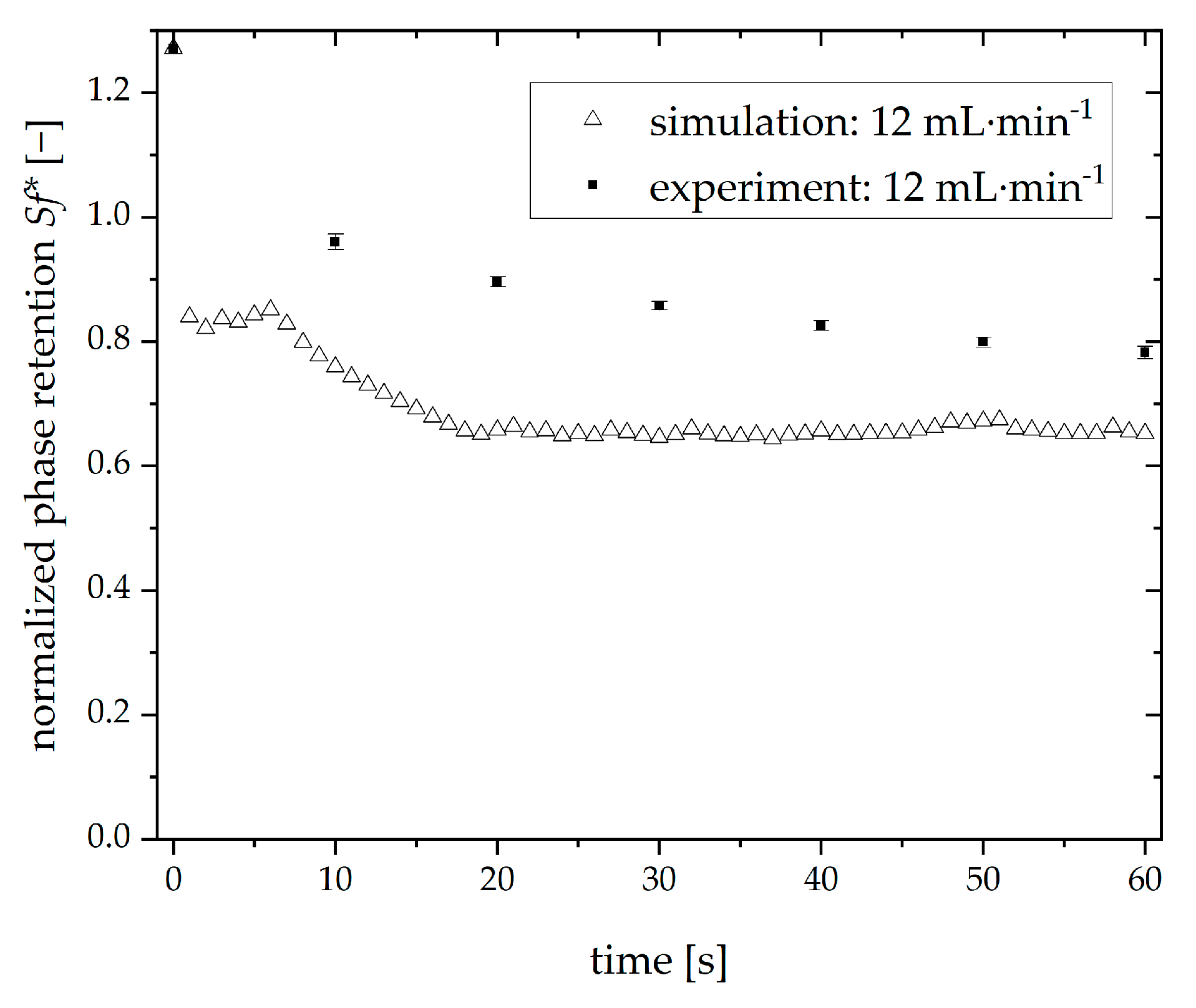
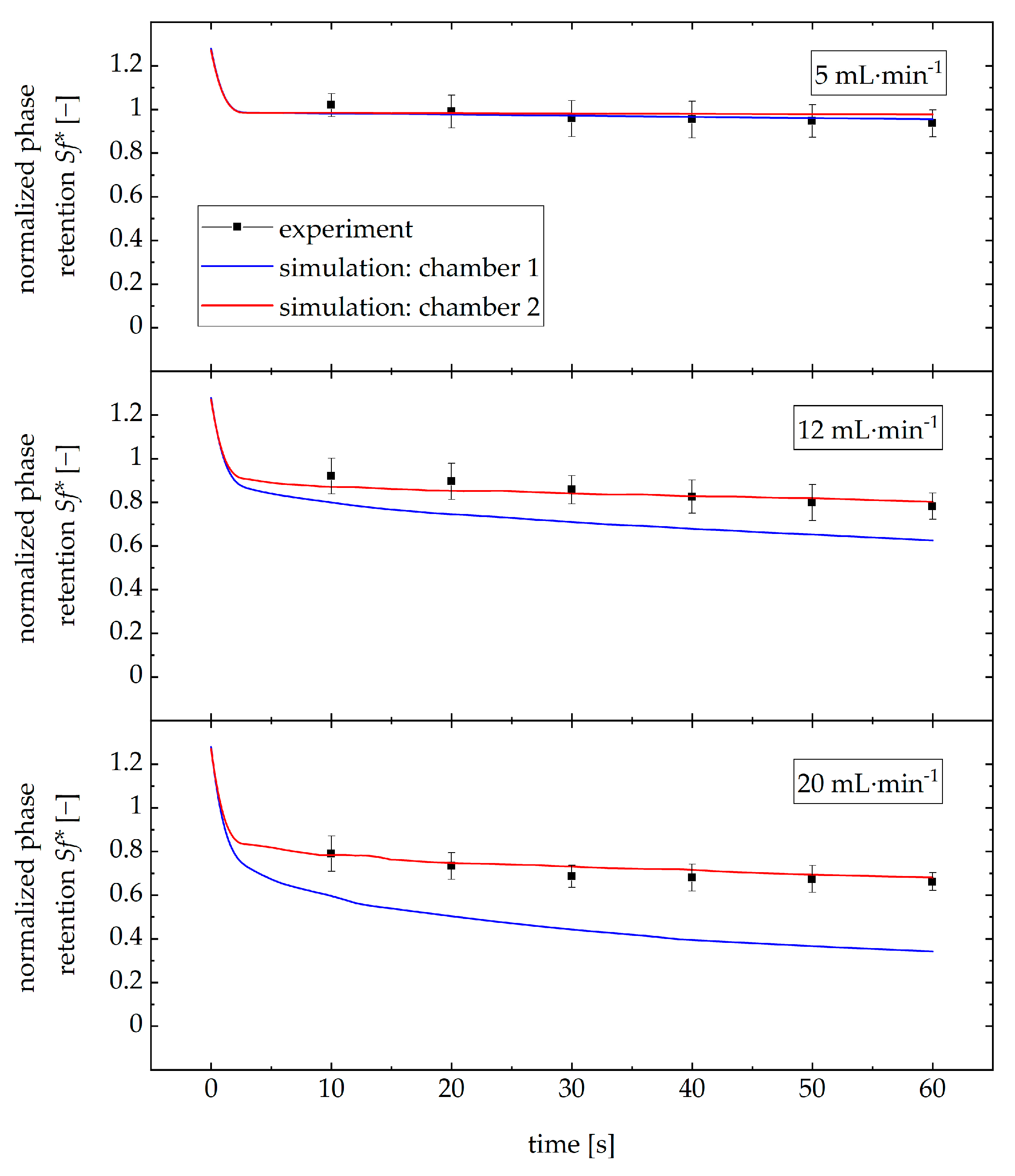
3.6. Comparison of Simulated and Experimental Retention Values in Single CPC Chambers
3.7. Simulation of Two Chambers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 0.10 | 20 | 11 | 0.09 | 30 | 20 | 0.20 | 35 | 5 |
| 0.10 | 25 | 14 | 0.08 | 30 | 25 | 0.15 | 35 | 9 |
| 0.10 | 30 | 16 | 0.07 | 30 | 33 | 0.09 | 35 | 24 |
| 0.10 | 35 | 19 | 0.08 | 35 | 30 | |||
| 0.10 | 40 | 22 | 0.07 | 35 | 38 | |||
| 0.10 | 45 | 25 |



References
- Chmiel, H. (Ed.) Bioprozesstechnik, 3rd ed.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; ISBN 9783827424778. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Traub, H.; Schulte, M.; Seidel-Morgenstern, A. (Eds.) Preparative Chromatography, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2020; ISBN 978-3-527-34486-4. [Google Scholar]
- Foucault, A.P. (Ed.) Centrifugal Partition Chromatography; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780824792572. [Google Scholar]
- Marchal, L.; Foucault, A.P.; Patissier, G.; Rosant, J.-M.; Legrand, J. Chapter 5 Centrifugal Partition Chromatography: An Engineering Approach. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry: Countercurrent Chromatography; Berthod, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 115–157. ISBN 0166-526X. [Google Scholar]
- Kotland, A.; Chollet, S.; Diard, C.; Autret, J.-M.; Meucci, J.; Renault, J.-H.; Marchal, L. Industrial case study on alkaloids purification by pH-zone refining centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1474, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A. (Ed.) Countercurrent Chromatography: The Support-Free Liquid Stationary Phase; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; ISBN 9780444507372. [Google Scholar]
- Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Countercurrent Separation of Natural Products: An Update. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1765–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, E.; Arlt, W.; Minceva, M. Solvent system selection in counter-current chromatography using conductor-like screening model for real solvents. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.; Hopmann, E.; Minceva, M. Selection of Biphasic Liquid Systems in Liquid-Liquid Chromatography Using Predictive Thermodynamic Models. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Weinberger, M.E.; Minceva, M. Computational solvent system screening for the separation of tocopherols with centrifugal partition chromatography using deep eutectic solvent-based biphasic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, E.; Frey, A.; Minceva, M. A priori selection of the mobile and stationary phase in centrifugal partition chromatography and counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1238, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.F. Biocatalytic Conversions in a Centrifugal Partition Chromatograph; Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2017; ISBN 9783843934688. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, M.R.; Ferreira, F.; Domingues, P.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Towards the purification of IgY from egg yolk by centrifugal partition chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Oeldorf, T.; Schembecker, G.; Merz, J. Enzymatic hydrolysis in an aqueous organic two-phase system using centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1391, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Merz, J. Comparison of enzymatic hydrolysis in a centrifugal partition chromatograph and stirred tank reactor. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1504, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, A.; Ruiz-Ángel, M.J.; Carda-Broch, S. Recent advances on ionic liquid uses in separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1559, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Minceva, M. A water-free solvent system containing an L-menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for centrifugal partition chromatography applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1587, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Roehrer, S.; Minceva, M. Ionic Liquids as Modifying Agents for Protein Separation in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Goll, J.; Minceva, M. Study of the applicability of non-conventional aqueous two-phase systems in counter-current and centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1388, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopilovic, B.; Valente, A.I.; Ferreira, A.M.; Almeida, M.R.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Towards the sustainable extraction and purification of non-animal proteins from biomass using alternative solvents. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 1314–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, A. Enzyme Separation Using Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction: Experiment, Model and Simulation; Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- van Buel, M.J.; van Halsema, F.E.D.; van der Wielen, L.A.M.; Luyben, K.C.A.M. Flow regimes in centrifugal partition chromatography. AICHE J. 1998, 44, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, G.; Zhao, D. (Eds.) Sustainable Separation Engineering: Materials, Techniques and Process Development; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; ISBN 9781119740087. [Google Scholar]
- Schwienheer, C.; Merz, J.; Schembecker, G. Investigation, comparison and design of chambers used in centrifugal partition chromatography on the basis of flow pattern and separation experiments. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1390, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, A.; Fischer, C.; Klump, D.; Schembecker, G. Correlating the phase settling behavior of aqueous-organic solvent systems in a centrifugal partition chromatograph. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1620, 461005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, A.; Fischer, C.; Keine, K.; Schembecker, G. Characterization and correlation of mobile phase dispersion of aqueous-organic solvent systems in centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1620, 460990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, S.; Marchal, L.; Jérémy, M.; Renault, J.-H.; Legrand, J.; Foucault, A. Methodology for optimally sized centrifugal partition chromatography columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1388, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelmann, S.; Schwienheer, C.; Schembecker, G. Multiphase flow modeling in centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6092–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys®. Fluent; Ansys: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cushman-Roisin, B. Introduction to Geophysical Fluid Dynamics: Physical and Numerical Aspects, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; ISBN 9780080916781. [Google Scholar]
- Berthod, A.; Hassoun, M.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J. Alkane effect in the Arizona liquid systems used in countercurrent chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaessen, G. Predicting Catastrophic Phase Inversion in Emulsions. Ph.D. Thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Paschedag, A. CFD in der Verfahrenstechnik: Allgemeine Grundlagen und mehrphasige Anwendungen; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 9783527603855. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarze, R. CFD-Modellierung: Grundlagen und Anwendungen bei Strömungsprozessen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-642-24378-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fromme, A. Systematic Approach Towards Solvent System Selection for Ideal Fluid Dynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography; Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2020; ISBN 9783843916110. [Google Scholar]
- Lomax, H.; Pulliam, T.H.; Zingg, D.W.; Kowalewski, T.A. Fundamentals of Computational Fluid Dynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, B61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, A.; Funke, F.; Merz, J.; Schembecker, G. Correlating physical properties of aqueous-organic solvent systems and stationary phase retention in a centrifugal partition chromatograph in descending mode. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1615, 460742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelmann, S.; Schembecker, G. Influence of physical properties and operating parameters on hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5401–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelmann, S. On Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography; Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783843916110. [Google Scholar]
- Buthmann, F.; Pley, F.; Schembecker, G.; Koop, J. Automated Image Analysis for Retention Determination in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Separations 2022, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, J.-I.; Shinomiya, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ohshima, H.; Kitanaka, S.; Ito, Y. Effect of Coriolis force on counter-current chromatographic separation by centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1025, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwienheer, C. Advances in Centrifugal Purification Techniques for Separating (Bio-)chemical Compounds; Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783843929165. [Google Scholar]


| Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| organic phase | 748.4 2.2 | 0.3755 0.0017 | 2.9717 0.1776 |
| aqueous phase | 928.1 10.8 | 1.4632 0.0047 |
| Fluid 1 | Fluid 2 | Solid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| upper phase | saturated vapor | stainless steel | 10 | 0.0 |
| lower phase | saturated vapor | stainless steel | 3.3 | 0.0 |
| upper phase | saturated vapor | seal (FEP) | 1.7 | 0.1 |
| lower phase | saturated vapor | seal (FEP) | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| lower phase | upper phase | stainless steel | 5.7 | 0.1 |
| lower phase | upper phase | seal (FEP) | 3.4 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buthmann, F.; Volpert, S.; Koop, J.; Schembecker, G. Prediction of Bleeding via Simulation of Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Separations 2024, 11, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010016
Buthmann F, Volpert S, Koop J, Schembecker G. Prediction of Bleeding via Simulation of Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Separations. 2024; 11(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleButhmann, Felix, Sophia Volpert, Jörg Koop, and Gerhard Schembecker. 2024. "Prediction of Bleeding via Simulation of Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography" Separations 11, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010016
APA StyleButhmann, F., Volpert, S., Koop, J., & Schembecker, G. (2024). Prediction of Bleeding via Simulation of Hydrodynamics in Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. Separations, 11(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11010016







