Optimizing Membrane Distillation Performance through Flow Channel Modification with Baffles: Experimental and Computational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Membrane Distillation Module
2.2. Porous Membranes
2.3. Preparation of the Baffles in the Flow Channels
2.4. AGMD Tests
3. CFD Simulations
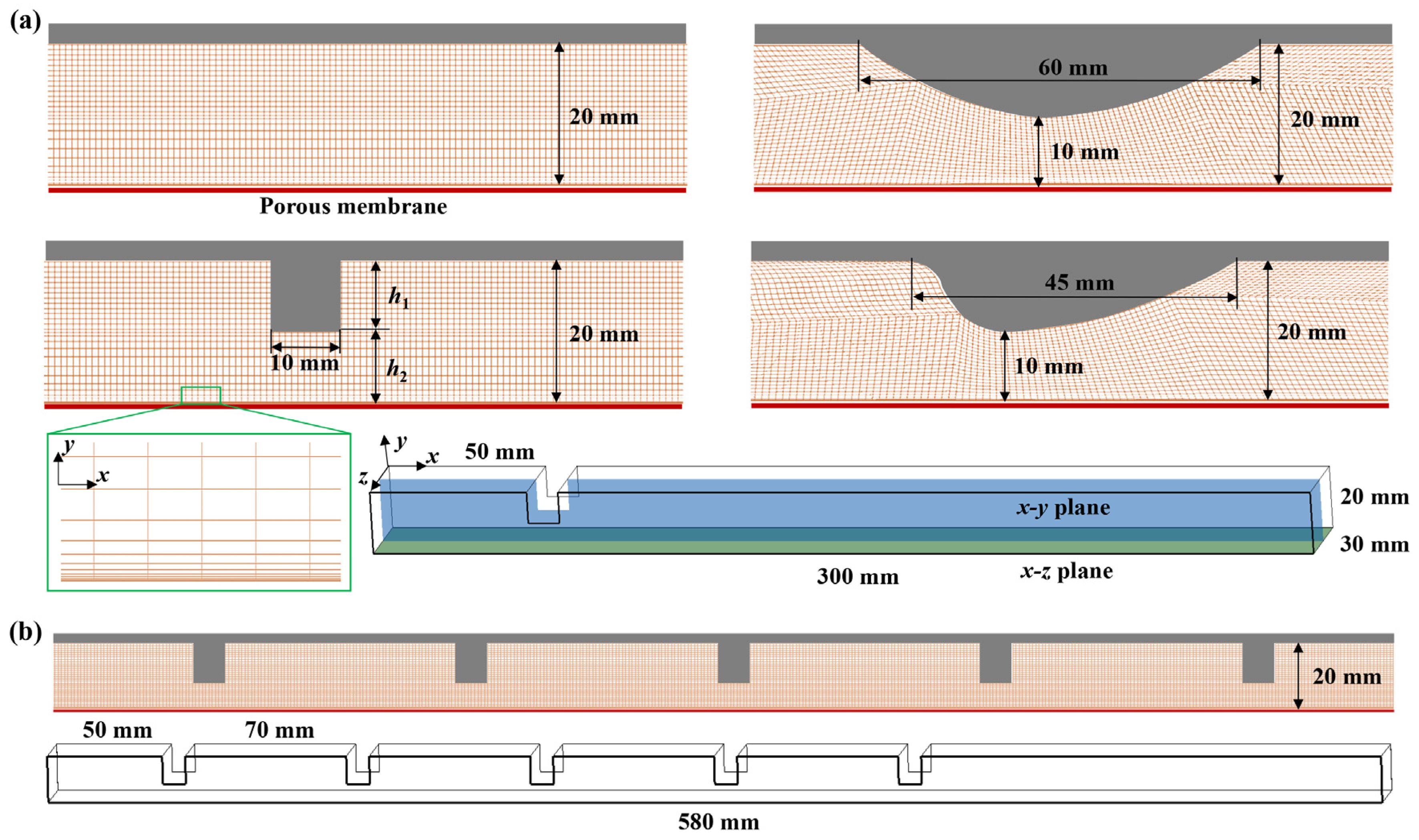
3.1. Geometry Model
3.2. Mesh Generation
3.3. Assumptions and Governing Equations
3.4. Boundary Conditions
3.5. Algorithm and Turbulence Model
4. Results and Discussion
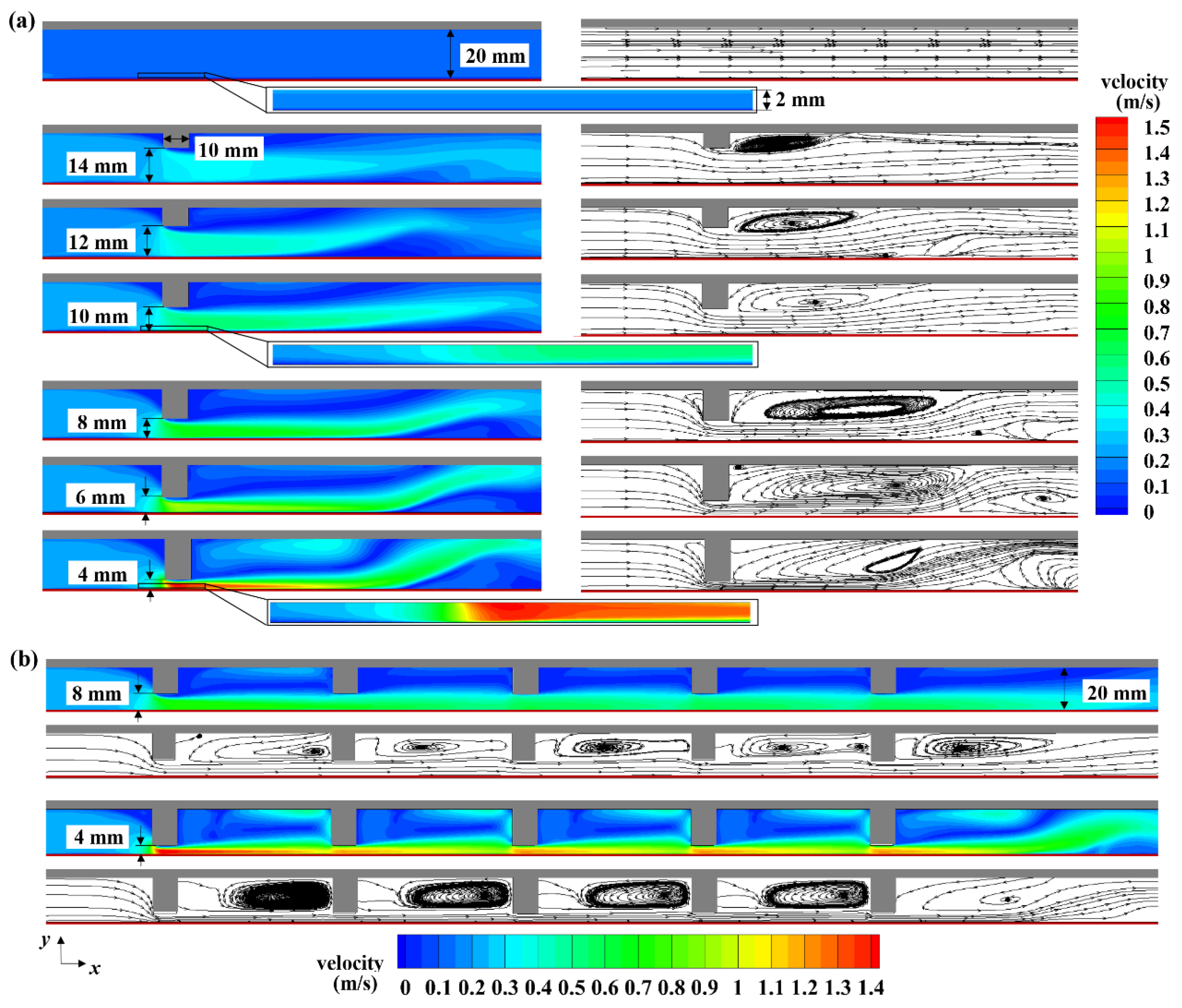
4.1. Flow Disturbance near Membrane Surface by Baffles in the Flow Channel
4.2. Influence of Multiple Baffles in the Flow Channel
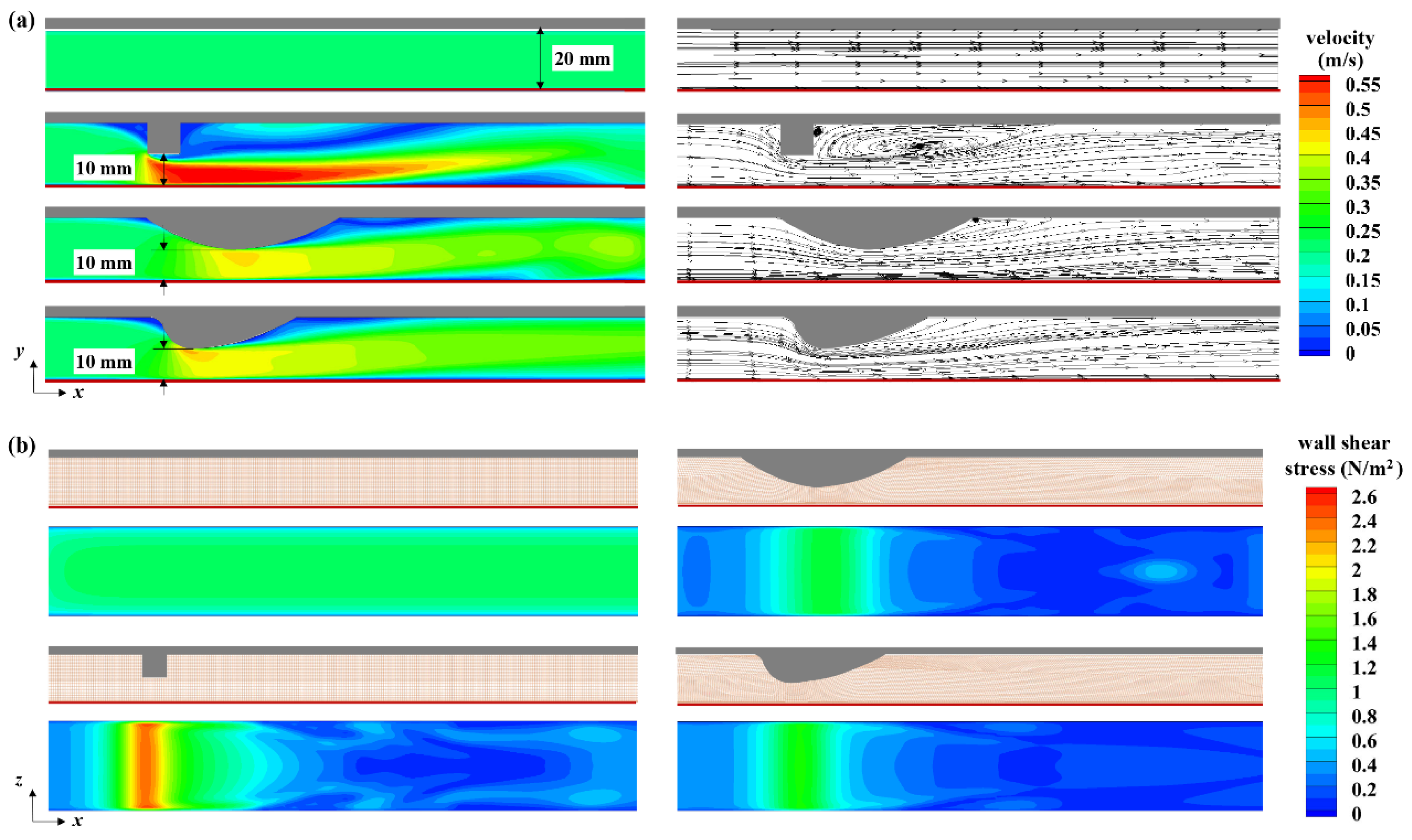
4.3. Influence of Baffle Geometry
4.3.1. Velocity in the Flow Channel
4.3.2. Effect on the Wall Shear Stress of Membrane Surface
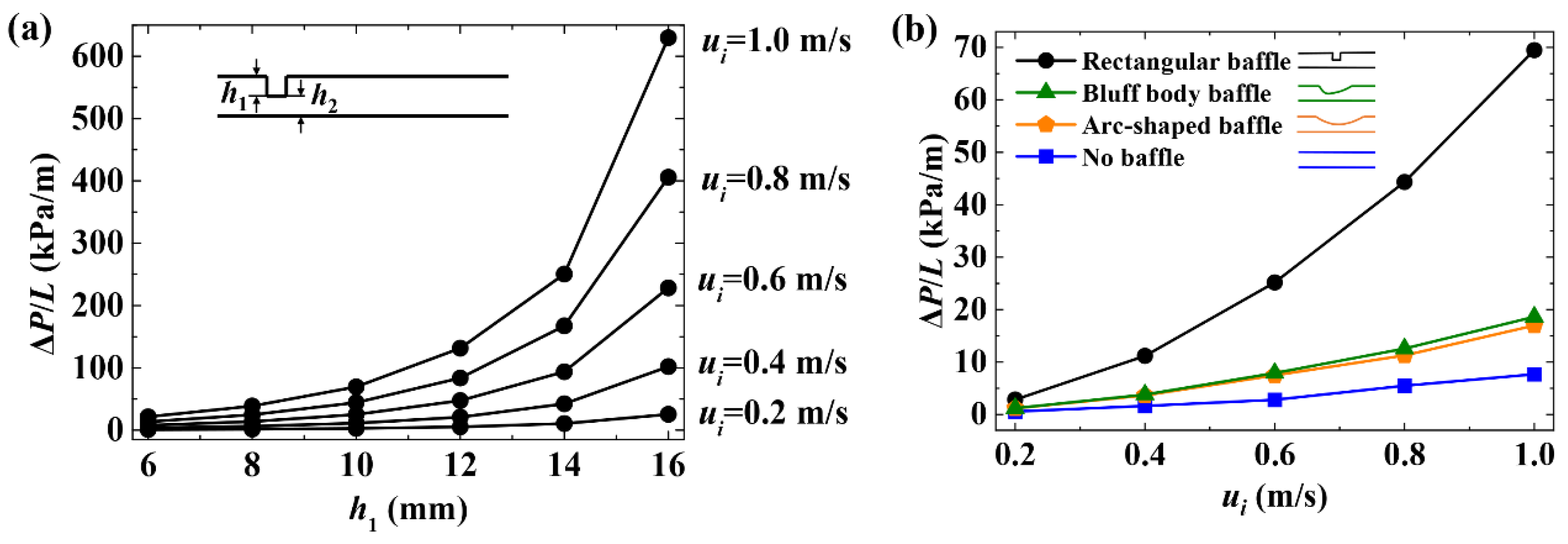
4.4. Effect on Pressure Drop in the Flow
4.4.1. Influence of the Size of the Gap between the Baffle and the Membrane
4.4.2. Influence of Baffle Geometric Structure
4.5. MD Performance
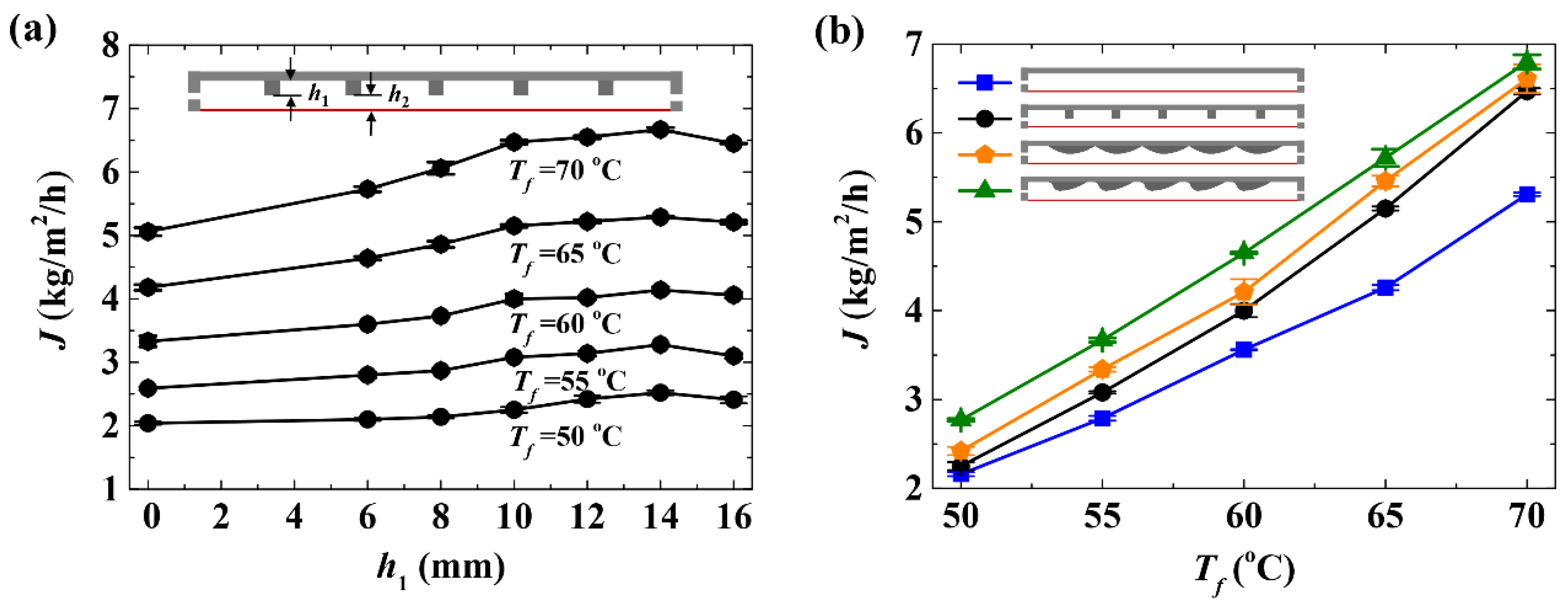
4.5.1. Influence of Baffle Height on Transmembrane Flux
4.5.2. Influence of Baffle Geometric Structure on Transmembrane Flux
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | wetted surface area of the computational domain (m2) |
| cp | specific heat (J/kg/K) |
| dh | hydraulic diameter (m) |
| g | gravitational acceleration (m/s2) |
| h1 | height of the baffle (m) |
| h2 | distance between the baffle and the membrane surface (m) |
| H | height of the computational domain (m) |
| J | transmembrane flux (kg/m2/h) |
| k | thermal conductivity (W/m/K) |
| L | length of computational domain (m) |
| P | pressure (Pa) |
| Tf | feed temperature (°C) |
| uav | mean velocity along the flow direction (m/s) |
| ui | inlet velocity of the CFD simulation (m/s) |
| u, v, w | velocity component along x, y, z (m/s) |
| V | volume of computational domain (m3) |
| W | width of computational domain (m) |
| x, y, z | cartesian coordinates (m) |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| Greek letters | |
| μ | dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| ν | kinematic viscosity (m2/s) |
| ρ | density (kg/m3) |
| ΔP | pressure drop along the flow direction (kPa) |
References
- Qtaishat, M.; Matsuura, T.; Kruczek, B.; Khayet, M. Heat and mass transfer analysis in direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2008, 219, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, S.; Piash, K.P.S.; Sanyal, O. Anti-fouling and anti-wetting membranes for membrane distillation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, F. Membrane distillation using surface modified multi-layer porous ceramics. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 129, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Díez, L.; Vázquez-González, M.I.; Florido-Díaz, F.J. Temperature polarization coefficients in membrane distillation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, H.; Chishti, S.A.A. Thermal osmosis in liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 1976, 1, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Maroto, J.M. On transport resistances in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 295, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Arifin, E.; Dong, G.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Superhydrophobic modification of TiO2 nanocomposite PVDF membranes for applications in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, A.; Azimi Yancheshme, A.; Kekre, K.M.; Ronen, A. State-of-the-art methods for overcoming temperature polarization in membrane distillation process: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisurichan, S.; Jiraratananon, R.; Fane, A.G. Mass transfer mechanisms and transport resistances in direct contact membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz De Zarate, J.M.; Velazquez, A.; Pena, L.; Mengual, J.I. Influence of temperature polarization on separation by membrane distillation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Díez, L.; Vázquez-González, M.I. Temperature and concentration polarization in membrane distillation of aqueous salt solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Shim, W.G.; He, T.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane containing carbon nanotubes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M. Preparation of superhydrophobic PVDF composite membrane via catechol/polyamine co-deposition and Ag nanoparticles in-situ growth for membrane distillation. Desalination 2022, 529, 115649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xu, G.; An, X.; Hu, Y. Robust reduced graphene oxide composite membranes for enhanced anti-wetting property in membrane distillation. Desalination 2022, 526, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafieian, A.; Rizwan Azhar, M.; Khiadani, M.; Kanti Sen, T. Performance improvement of thermal-driven membrane-based solar desalination systems using nanofluid in the feed stream. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 39, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarchi, N.; Shahnia, F. A comprehensive review of solar-driven desalination technologies for off-grid greenhouses. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 1357–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, M.A.; Bamaga, O.A.; Al-beirutty, M.H.; Gzara, L. Separation and purification technology effect of intermittent operation on performance of a solar-powered membrane distillation system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 220, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.I.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Zolkhiflee, N.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Lau, W.J.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Arahman, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Development of a novel corrugated polyvinylidene difluoride membrane via improved imprinting technique for membrane distillation. Polymers 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharraz, J.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A. Flux stabilization in membrane distillation desalination of seawater and brine using corrugated PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, M.; Anqi, A.E.; Oztekin, A. Reverse osmosis desalination modules containing corrugated membranes—Computational study. Desalination 2017, 416, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Q. Preparation of polysulfone membranes via vapor-induced phase separation and simulation of direct-contact membrane distillation by measuring hydrophobic layer thickness. Desalination 2013, 316, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Tong, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, T. Mitigation of gypsum and silica scaling in membrane distillation by pulse flow operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 624, 119107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.H. Spacer optimization strategy for direct contact membrane distillation: Shapes, configurations, diameters, and numbers of spacer filaments. Desalination 2017, 417, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.D.; Francis, L.; Lee, J.G.; Ham, M.G.; Ghaffour, N. Effect of non-woven net spacer on a direct contact membrane distillation performance: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwatban, A.M.; Alshwairekh, A.M.; Alqsair, U.F.; Alghafis, A.A.; Oztekin, A. Performance improvements by embedded spacer in direct contact membrane distillation—Computational study. Desalination 2019, 470, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumée, L.; Zhang, J.; de Li, J.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in membrane distillation for water desalination and purification applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukane, S.; Ghaffour, N. Showerhead feed distribution for optimized performance of large scale membrane distillation modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, M.; Elkady, M.F.; El-Shazly, A.H. Effect of channel height on the overall performance of direct contact membrane distillation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 196, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.; Elhenawy, Y.; Moustafa, G. Experimental evaluation of corrugated feed channel of direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhenawy, Y.; Elminshawy, N.A.S.; Bassyouni, M.; Alhathal Alanezi, A.; Drioli, E. Experimental and theoretical investigation of a new air gap membrane distillation module with a corrugated feed channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Long, R.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Analysis of temperature and concentration polarizations for performance improvement in direct contact membrane distillation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 145, 118724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, F. Investigation of interfacial crystallization fouling behaviors and membrane re-functionalization based on a long-distance membrane distillation module. Desalination 2022, 534, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.B.; Irfan, S.; Lam, S.S.; Sun, X.; Chen, S. 3D printed nanofiltration membrane technology for waste water distillation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.S.; Mohamed, A.M.; Poggio, D.; Walker, M.; Pourkashanian, M. Modelling mass transport within the membrane of direct contact membrane distillation modules used for desalination and wastewater treatment: Scrutinising assumptions. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case | Number of Cells | ui (m/s) | Re | ΔP/L (Pa/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 280,000 | 0.1 | 2392 | 77 |
| Case 2 | 560,000 | 0.1 | 2392 | 78 |
| Case 3 | 1,740,000 | 0.1 | 2392 | 78 |
| Fluid | ρ (kg/m3) | cp (J/(kg·K)) | k (W/(m·K)) | μ (Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water | 998.2 | 4182.1 | 0.613 | 1.003 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Mu, X.; Sun, J.; Guo, F. Optimizing Membrane Distillation Performance through Flow Channel Modification with Baffles: Experimental and Computational Study. Separations 2023, 10, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090485
Zhang Y, Mu X, Sun J, Guo F. Optimizing Membrane Distillation Performance through Flow Channel Modification with Baffles: Experimental and Computational Study. Separations. 2023; 10(9):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090485
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yaoling, Xingsen Mu, Jiaqi Sun, and Fei Guo. 2023. "Optimizing Membrane Distillation Performance through Flow Channel Modification with Baffles: Experimental and Computational Study" Separations 10, no. 9: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090485
APA StyleZhang, Y., Mu, X., Sun, J., & Guo, F. (2023). Optimizing Membrane Distillation Performance through Flow Channel Modification with Baffles: Experimental and Computational Study. Separations, 10(9), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10090485







