Synthesis of Isoreticular Metal Organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) Porous Nanostructure and Its Effect on Naphthalene Adsorption: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. IRMOF-3 Synthesis
2.3. IRMOF-3 Characterization
2.4. Sample Preparation and Adsorption Characterization
2.5. Experimental Design Method
3. Results and Discussion
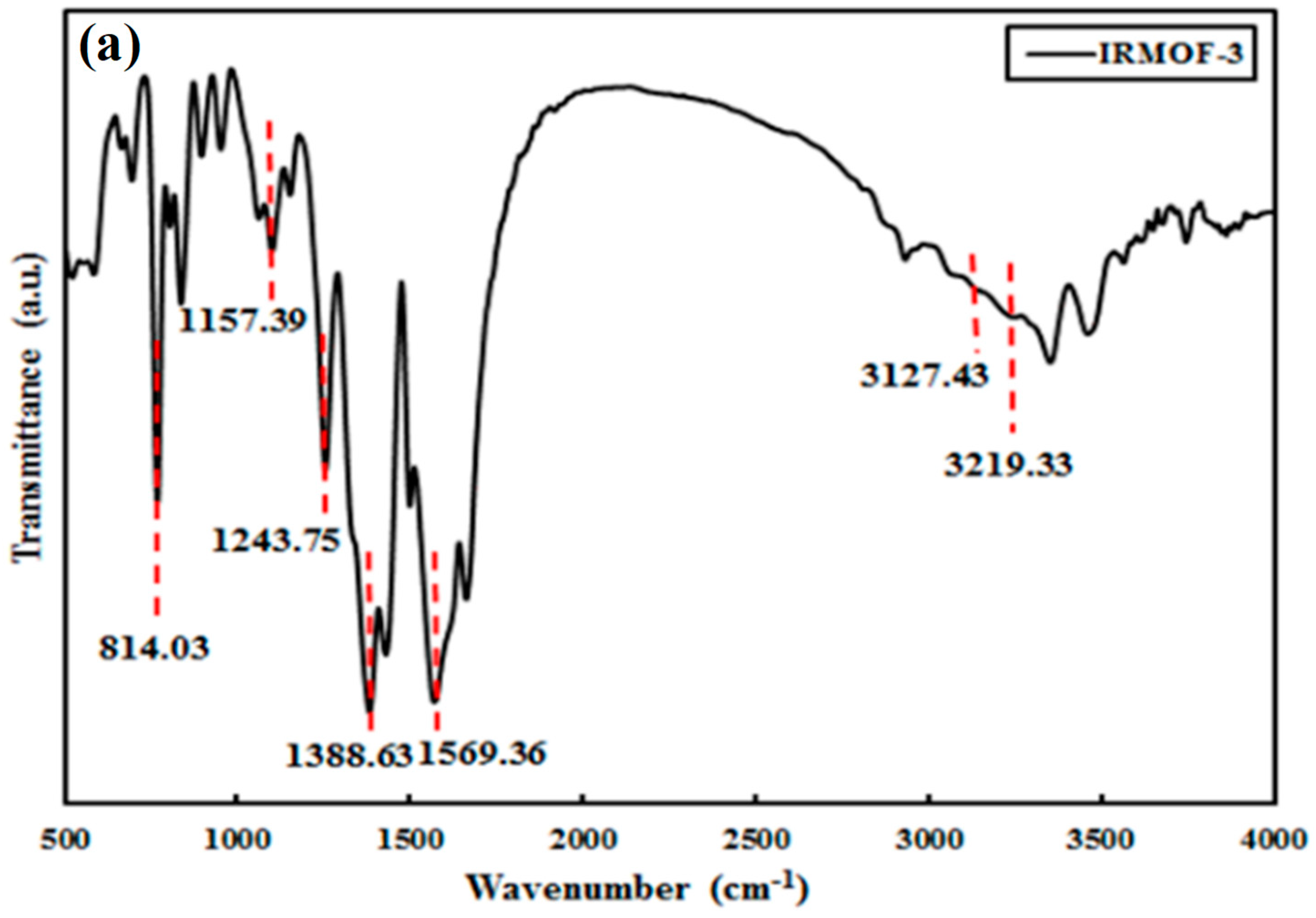
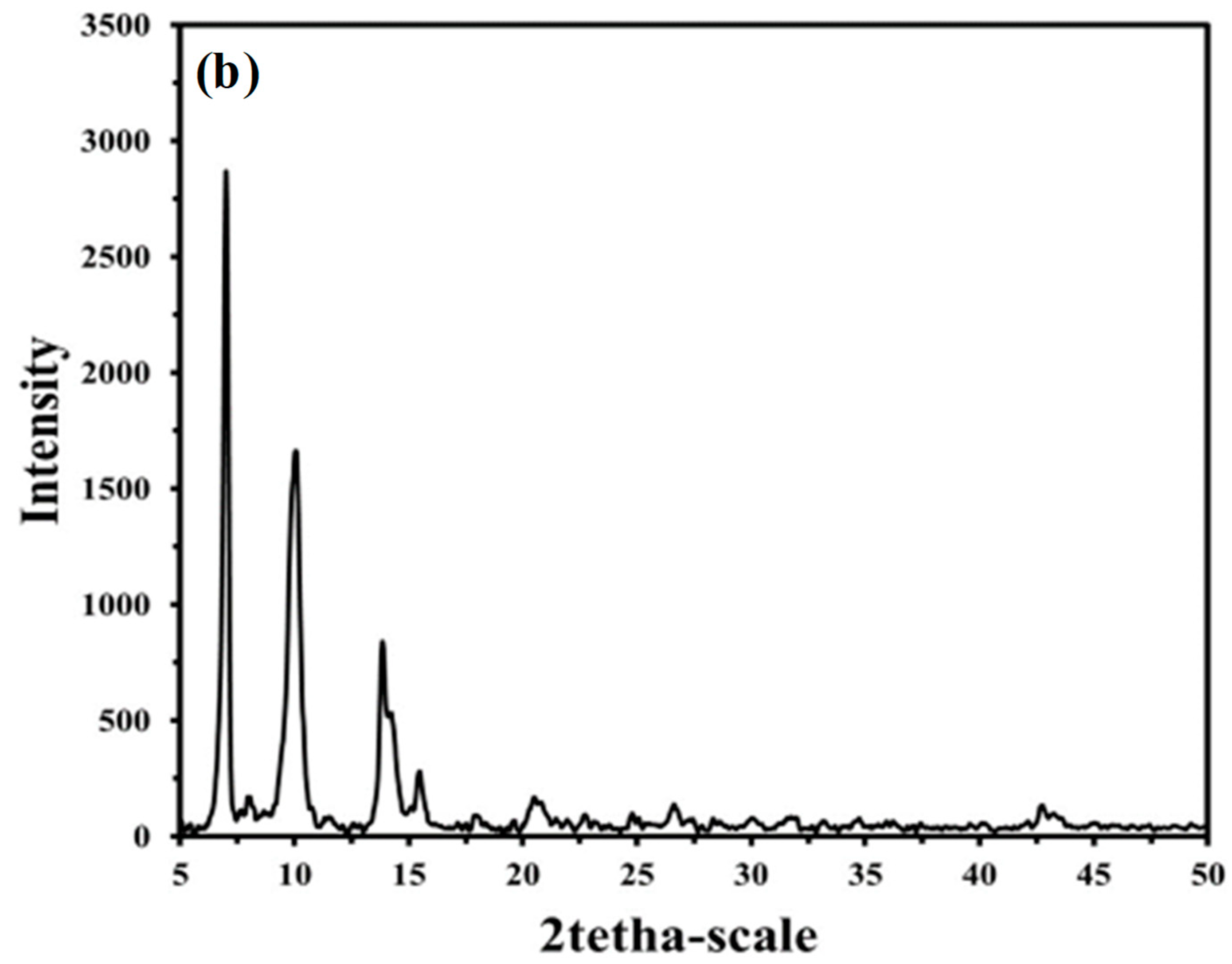
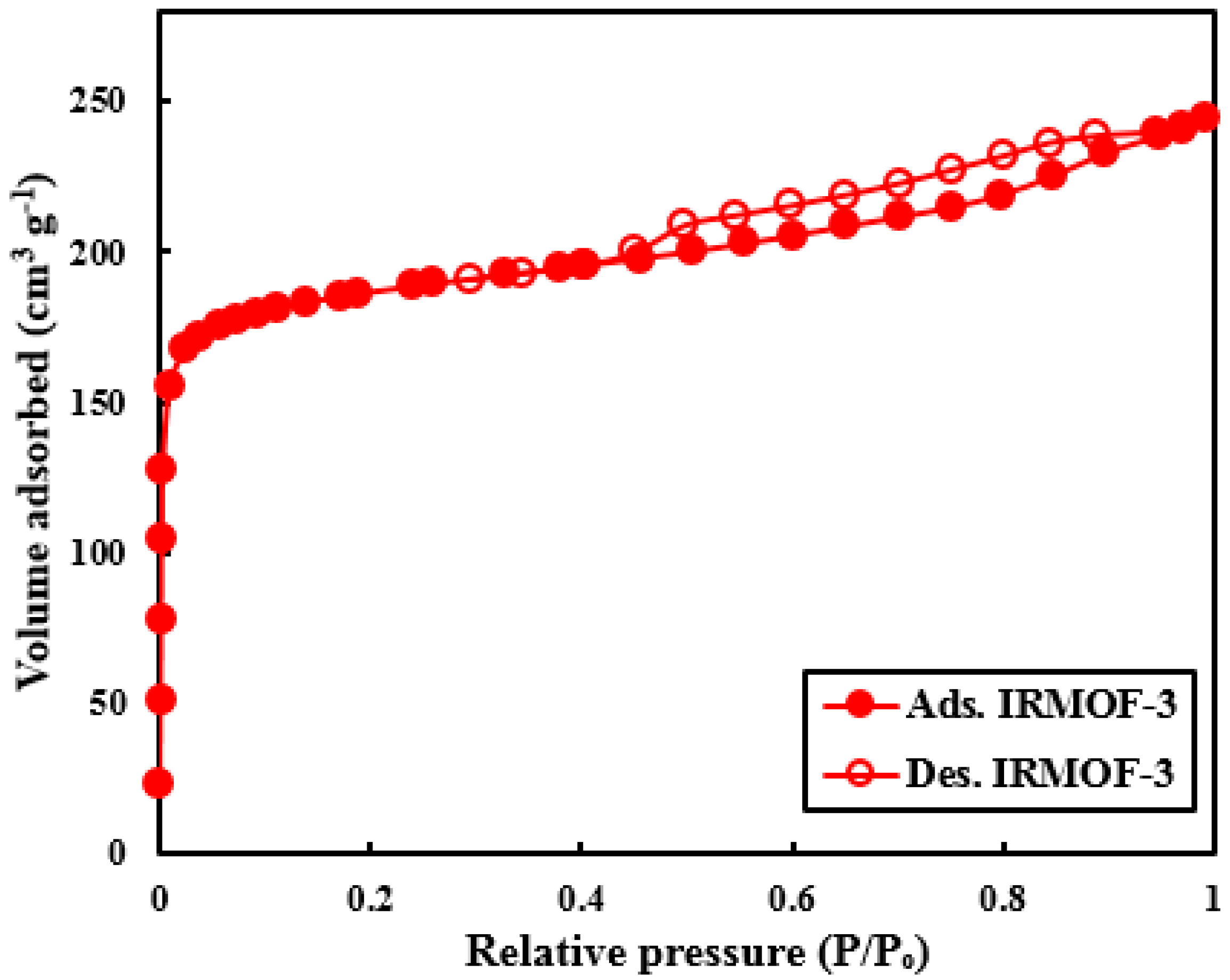
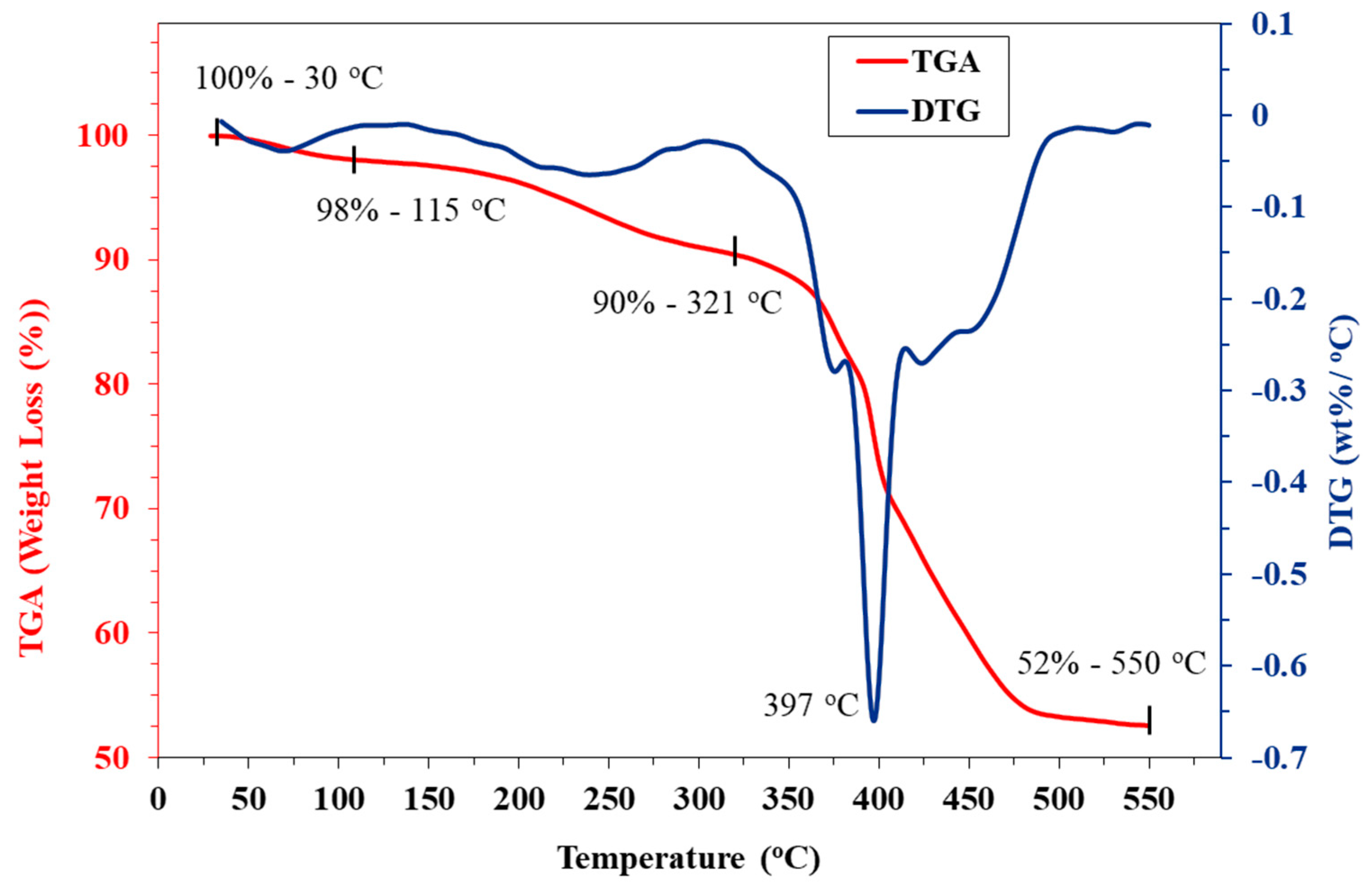
3.1. IRMOF-3 Characterization
3.2. Model Analysis Based on CCD
3.3. Impact of Combination of Variables on Response Levels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montgomery, M.A.; Elimelech, M. Water And Sanitation in Developing Countries: Including Health in the Equation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nanosci. Technol. A Collect. Rev. Nat. J. 2010, 452, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J. China faces up to groundwater crisis. Nature 2010, 466, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Kalashgarani, M.Y. Nano Protein and Peptides for Drug Delivery and Anticancer Agents. Adv. Appl. NanoBio-Technol. 2022, 3, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Rahmanian, V.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Gholami, A.; Omidifar, N.; Chiang, W.-H. Highly Sensitive Flexible SERS-Based Sensing Platform for Detection of COVID-19. Biosensors 2022, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Shahzad, S.; Munir, A.; Nadagouda, M.; Khan, G.S.; Shams, D.F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Rana, U.A. Micelles as Soil and Water Decontamination Agents. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6042–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashgarani, M.Y.; Babapoor, A. Application of nano-antibiotics in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. Adv. Appl. NanoBio-Technol. 2022, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Gholami, A.; Omidifar, N.; Babapoor, A.; Rao, N.V.; Chiang, W.-H. Recent Advances in Plasma-Engineered Polymers for Biomarker-Based Viral Detection and Highly Multiplexed Analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parales, R.E.; Lee, K.; Resnick, S.M.; Jiang, H.; Lessner, D.J.; Gibson, D.T. Substrate Specificity of Naphthalene Dioxygenase: Effect of Specific Amino Acids at the Active Site of the Enzyme. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Omidifar, N.; Bahrani, S.; Rao, N.V.; Babapoor, A.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H. Bioactive Graphene Quantum Dots Based Polymer Composite for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.K.; Flora, J.R.; Ferry, J. Mechanisms for naphthalene removal during electrolytic aeration. Water Res. 2003, 37, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Omidifar, N.; Lai, C.W.; Rao, N.V.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H. The Pivotal Role of Quantum Dots-Based Biomarkers Integrated with Ultra-Sensitive Probes for Multiplex Detection of Human Viral Infections. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, M.; Binazadeh, M.; Baghulifard, N.; Sarani, M. Demulsification of saline-in-crude oil via biocompatible cellulose derivative polymers. Fuel 2022, 311, 122533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ania, M.C.O.; Cabal, B.; Parra, J.B.; Pis, J.J. Importance of the Hydrophobic Character of Activated Carbons on the Removal of Naphthalene from the Aqueous Phase. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2007, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Kurniawan, D.; Gholami, A.; Rahmanian, V.; Omidifar, N.; Chiang, W.-H. Recent Advances in Inflammatory Diagnosis with Graphene Quantum Dots Enhanced SERS Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, A.M.J.; Aitken, M.D. Bacterial Chemotaxis to Naphthalene Desorbing from a Nonaqueous Liquid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5968–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, A.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Pouya, H.; Arash, V. Electric Field Induced Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes: Methodology and Outcomes. In Carbon Nanotubes-Recent Progress; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Rahmanian, V.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H.; Lai, C.W. Biomedical Applications of an Ultra-Sensitive Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Based on Smart MXene Quantum Dots (SMQDs). Biosensors 2022, 12, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, I.; Abu Al-Rub, F.A.; Sheikha, D.; Volesky, B. Biosorption of Naphthalene from Refinery Simulated Waste-Water on Blank Alginate Beads and Immobilized Dead Algal Cells. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2208–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Kurniawan, D.; Gholami, A.; Chiang, W.-H. Bioresource-Functionalized Quantum Dots for Energy Generation and Storage: Recent Advances and Feature Perspective. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko-Malkovskaya, A.; Kirzhner, F.; Zimmels, Y.; Armon, R. Eichhornia crassipes capability to remove naphthalene from wastewater in the absence of bacteria. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Gholami, A.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Rao, N.V.; Omidifar, N.; Hsiao, W.W.-W.; Lai, C.W.; Chiang, W.-H. Plasma-Enabled Smart Nanoexosome Platform as Emerging Immunopathogenesis for Clinical Viral Infection. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binazadeh, M.; Karimi, I.A.; Li, Z. Fast biodegradation of long chain n-alkanes and crude oil at high concentrations with Rhodococcus sp. Moj-3449. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2009, 45, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.M.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Chairez, I.; Tiznado, H.; Poznyak, T. Naphthalene degradation by catalytic ozonation based on nickel oxide: Study of the ethanol as cosolvent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25550–25560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, P.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Nema, A.K. Degradation of Low-Molecular-Weight PAHs: Naphthalene, Acenaphthylene, Phenanthrene, and Fluorene. J. Hazardous, Toxic, Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 04017008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, D.; Pan, B. Co-contaminant effects on ofloxacin adsorption onto activated carbon, graphite, and humic acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23834–23842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, S.; Andreozzi, M.; Micó, M.M.; Alvarez, M.G.; Contreras, S. Produced water treatment by advanced oxidation processes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 666, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M. Effect of bubble based degradation on the physical properties of Single Wall Carbon Nanotube/Epoxy Resin composite and new approach in bubbles reduction. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.M.; Rocha, Q.D.C.; Rocha, P.C.S.; Louvisse, A.M.T.; Lucas, E.F. Removal of naphthalene from aqueous systems by poly(divinylbenzene) and poly(methyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene) resins. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karri, R.R.; Sahu, J. Modeling and optimization by particle swarm embedded neural network for adsorption of zinc (II) by palm kernel shell based activated carbon from aqueous environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Esmaeili, H.; Amani, A.M.; Mojoudi, F. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Modified by Oak Shell for Treatment of Wastewater Containing Ni(II). Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owabor, C.; Agarry, S.; Jato, D. Removal of naphthalene from aqueous system using unripe orange peel as adsorbent: Effects of operating variables. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 48, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younker, J.M.; Walsh, M.E. Impact of salinity and dispersed oil on adsorption of dissolved aromatic hydrocarbons by activated carbon and organoclay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hyun, S. Sorption of ionic and nonionic organic solutes onto giant Miscanthus-derived biochar from methanol-water mixtures. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 615, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyed, M.M. Unsaturated polyester resins modified with cresol novolac epoxy and silica nanoparticles: Processing and mechanical properties. Int. J. Chem. Pet. Sci. (IJCPS) 2016, 5, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z. Impact of metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles on wastewater treatment and anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaedi, M.; Daneshyar, A.; Asfaram, A.; Purkait, M.K. Adsorption of naphthalene onto high-surface-area nanoparticle loaded activated carbon by high performance liquid chromatography: Response surface methodology, isotherm and kinetic study. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 54322–54330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, Ş.S.; Yildiz, M.; Aşçi, Y.S.; Şahin, M.; Bener, M.; Eğlence, S.; Salam, M.A. Rapid adsorptive removal of naphthalene from water using graphene nanoplatelet/MIL-101 (Cr) nanocomposite. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 701, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Amani, A.M.; Saed, H.; Jahandideh, S.; Mojoudi, F. Polyethylene Terephthalate/Acryl Butadiene Styrene Copolymer Incorporated with Oak Shell, Potassium Sorbate and Egg Shell Nanoparticles for Food Packaging Applications: Control of Bacteria Growth, Physical and Mechanical Properties. Polym. Renew. Resour. 2017, 8, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Liang, J.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.-J.; Bag, P.P.; Gao, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cao, R. An Anion Metal–Organic Framework with Lewis Basic Sites-Rich toward Charge-Exclusive Cationic Dyes Separation and Size-Selective Catalytic Reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, A.U.; Trukhan, N.; Müller, U. Industrial applications of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdari, R.; Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Bahrani, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Decorated graphene with aluminum fumarate metal organic framework as a superior non-toxic agent for efficient removal of Congo Red dye from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabushita, M.; Li, P.; Bernales, V.; Kobayashi, H.; Fukuoka, A.; Gagliardi, L.; Farha, O.K.; Katz, A. Unprecedented selectivity in molecular recognition of carbohydrates by a metal–organic framework. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 7094–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Aghili, A.; Hashemi, S.; Goudarzian, N.; Bakhoda, Z.; Baseri, S. Improved Morphology and Properties of Nanocomposites, Linear Low Density Polyethylene, Ethylene-Co-Vinyl Acetate and Nano Clay Particles by Electron Beam. Polym. Renew. Resour. 2016, 7, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binazadeh, M. Cellulose derivative polymers for demulsification of lagoon wastewater-in-crude oil systems: An efficient water reuse strategy. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 211, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic Design of Pore Size and Functionality in Isoreticular MOFs and Their Application in Methane Storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Esmaeili, H.; Arjmand, O.; Karimi, S.; Hashemi, S.A. Biodegradation Study of Nanocomposites of Phenol Novolac Epoxy/Unsaturated Polyester Resin/Egg Shell Nanoparticles Using Natural Polymers. J. Mater. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoyne, A.; Meijboom, R. Knoevenagel Condensation Reactions Catalysed by Metal-Organic Frameworks. Catal. Lett. 2013, 143, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Zarei, M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chiang, W.-H.; Lai, C.W.; Gholami, A.; Omidifar, N.; Shokripour, M. Asymmetric Membranes: A Potential Scaffold for Wound Healing Applications. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-L.; Pan, T.-M. Statistical optimization of medium components for the production of Antrodia cinnamomea AC0623 in submerged cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Bahrani, S.; Koosha, M.; Babapoor, A. Green synthesis of supermagnetic Fe3O4–MgO nanoparticles via Nutmeg essential oil toward superior anti-bacterial and anti-fungal performance. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binazadeh, M.; Li, Z.; Karimi, I.A. Optimization of Biodegradation of Long Chain n-Alkanes by Rhodococcus sp. Moj-3449 Using Response Surface Methodology. Phys. Chem. Res. 2020, 8, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti, R.; Sahai, V. Optimization of compactin production in chemically defined production medium by Penicillium citrinum using statistical methods. Process. Biochem. 2002, 38, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Arjmand, O.; Hashemi, S.; Banaei, N. Modification of the Epoxy Resin Mechanical and Thermal Properties with Silicon Acrylate and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles. Polym. Renew. Resour. 2016, 7, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizavi, A.; Mirbagheri, N.S.; Hosseini, Z.; Chen, P.; Sabbaghi, S. Efficient removal of naphthalene from aqueous solutions using a nanoporous kaolin/Fe3O4 composite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzadkia, M.; Ghorbanian, M.; Biglari, H.; Gholami, M.; Mehrizi, E.A. Application of the central composite design to optimization of petroleum hydrocarbons removal from oilfield water using advanced oxidation process. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2018, 44, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Borousan, F.; Yousefi, F.; Ghaedi, M. Removal of malachite green dye using IRMOF-3–MWCNT-OH–Pd-NPs as a novel adsorbent: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4801–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, C.N.; Karthikeyan, S. Investigation of Naphthalene Removal from Aqueous Solutions in an Integrated Slurry Photocatalytic Membrane Reactor: Effect of Operating Parameters, Identification of Intermediates, and Response Surface Approach. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2021, 41, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqubzadeh, A.; Ahmadpour, A.; Bastami, T.R.; Hataminia, M. Low-cost preparation of silica aerogel for optimized adsorptive removal of naphthalene from aqueous solution with central composite design (CCD). J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2016, 447, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, J.; Szlachetko, J.; Kleymenov, E.; Lothschütz, C.; Nachtegaal, M.; Ranocchiari, M.; Safonova, O.V.; Servalli, M.; Smolentsev, G.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Fine tuning of gold electronic structure by IRMOF post-synthetic modification. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12043–12048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Garg, V.; Kadirvelu, K. Investigation of Cr(VI) adsorption onto chemically treated Helianthus annuus: Optimization using Response Surface Methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaheri, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Hajati, S. Performance of CuS nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon in the adsorption of methylene blue and bromophenol blue dyes in binary aqueous solutions: Using ultrasound power and optimization by central composite design. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V. Optimization of Pb (II) and Cd (II) adsorption onto ZnO nanoflowers using central composite design: Isotherms and kinetics modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 271, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashamiri, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Zare, F.; Wang, S. Multi-response optimization of ultrasound assisted competitive adsorption of dyes onto Cu (OH)2-nanoparticle loaded activated carbon: Central composite design. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Deng, K.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z. Core–Shell Palladium Nanoparticle@Metal–Organic Frameworks as Multifunctional Catalysts for Cascade Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1738–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Chowdhuri, A.R.; Kumari, A.; Sahu, S.K. IRMOF-3: A fluorescent nanoscale metal organic frameworks for selective sensing of glucose and Fe (III) ions without any modification. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuri, A.; Vucetic, N.; Smått, J.-H.; Mansoori, Y.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Murzin, D.Y. Pd Supported IRMOF-3: Heterogeneous, Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Heck Reaction. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, R.A.; Siddiqui, Z.N. Sulfonic acid functionalized metal–organic framework (S-IRMOF-3): A novel catalyst for sustainable approach towards the synthesis of acrylonitriles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15749–15762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamnia, S.; Morsali, A. Size-controlled crystalline basic nanoporous coordination polymers of Zn4O(H2N-TA)3: Catalytically study of IRMOF-3 as a suitable and green catalyst for selective synthesis of tetrahydro-chromenes. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2014, 411, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zango, Z.U.; Ramli, A.; Jumbri, K.; Abdurrahman, M. UiO-66 and ZIF-8 Metal-organic Frameworks for Acenaphthene Adsorption. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Fundamental and Applied Sciences: ICFAS 2020, Kuching, Malaysia, 4–16 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zango, Z.U.; Jumbri, K.; Zaid, H.F.M.; Sambudi, N.S.; Matmin, J. Optimizations and artificial neural network validation studies for naphthalene and phenanthrene adsorption onto NH2-UiO-66(Zr) metal-organic framework. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 842, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, R.N.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Prediger, P.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of naphthalene polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from wastewater by a green magnetic composite based on chitosan and graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, W.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Liang, W.; Nie, Y.; Shen, C.; Ai, S. A novel aminated lignin/geopolymer supported with Fe nanoparticles for removing Cr(VI) and naphthalene: Intermediates promoting the reduction of Cr(VI). Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 866, 161379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, S.; He, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, S.; Liang, J.; Ren, X. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons over CuZnFeAl–LDH modified by sodium dodecyl sulfate. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25623–25632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Whitcomb, P.J. Design of experiments. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Muluh, N.S. Central composite design analysis and optimization of cadmium adsorption from synthetic wastewater by avocado seed activated carbon. Int. J. Adv. Res. Dev. 2017, 5, 652–661. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, S.; Fazilati, M.; Mousavi, S.M.; Nazem, H. Anti-bacterial/fungal and anti-cancer performance of green synthesized Ag nanoparticles using summer savory extract. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2020, 15, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchola, J.; Tang, S.; Hemyari, P.; Paxinos, E.; Marins, E. Correct use of percent coefficient of variation (% CV) formula for log-transformed data. MOJ Proteom. Bioinform 2017, 6, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, F.N.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Hajati, S.; Pezeshkpour, V. Ultrasonically assisted hydrothermal synthesis of activated carbon–HKUST-1-MOF hybrid for efficient simultaneous ultrasound-assisted removal of ternary organic dyes and antibacterial investigation: Taguchi optimization. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 31, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, F.N.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Jamshidi, A.; Hassani, G.; Montazerozohori, M.; Hajati, S.; Rajabi, M.; Bazrafshan, A. Preparation and characterization of an AC–Fe3O4–Au hybrid for the simultaneous removal of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cr3+ and Ni2+ ions from aqueous solution via complexation with 2-((2, 4-dichloro-benzylidene)-amino)-benzenethiol: Taguchi optimization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 19780–19791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption of residue oil from palm oil mill effluent using powder and flake chitosan: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszkarewicz, A.; Kaleta, J. The Efficiency of the Removal of Naphthalene from Aqueous Solutions by Different Adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

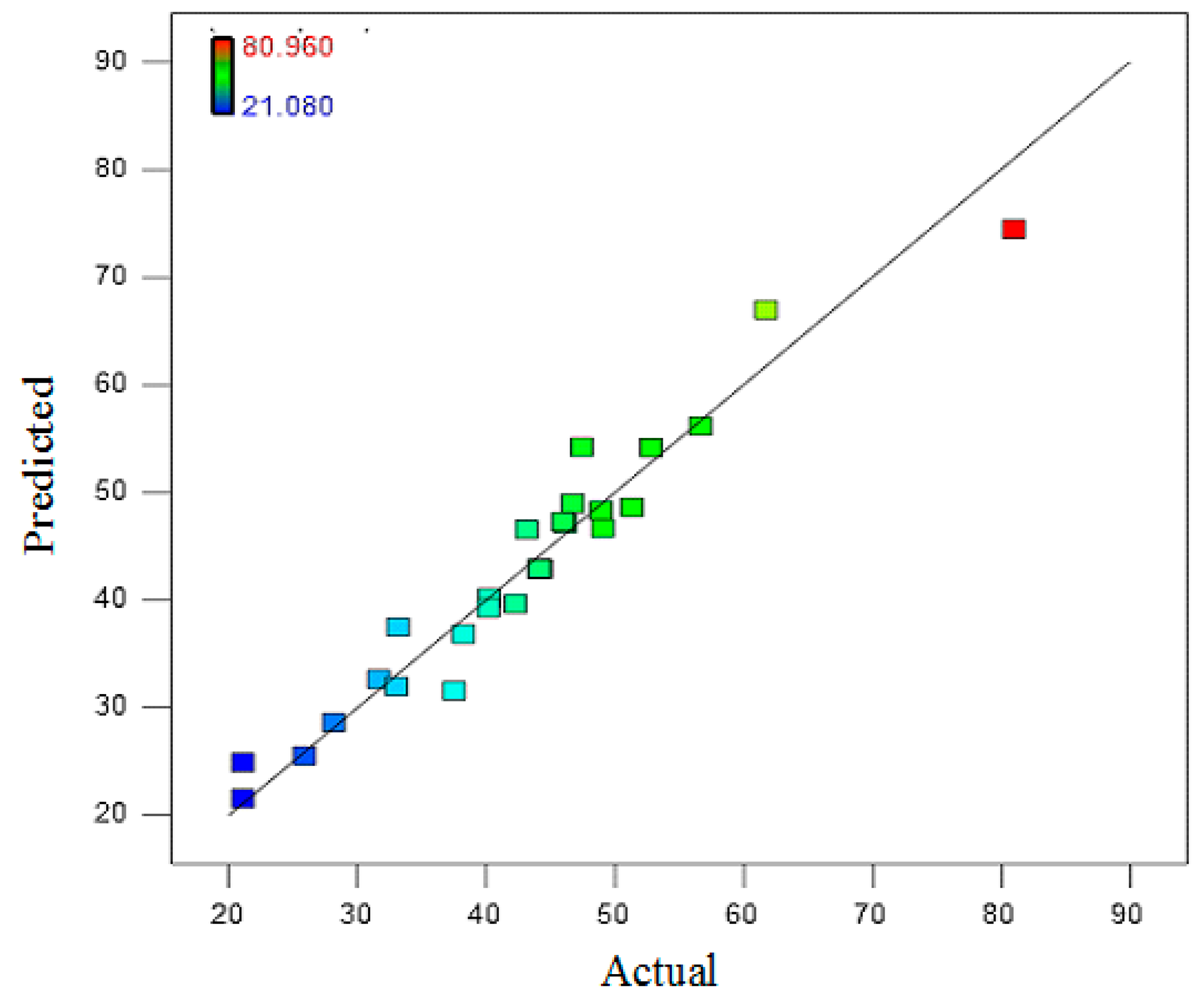
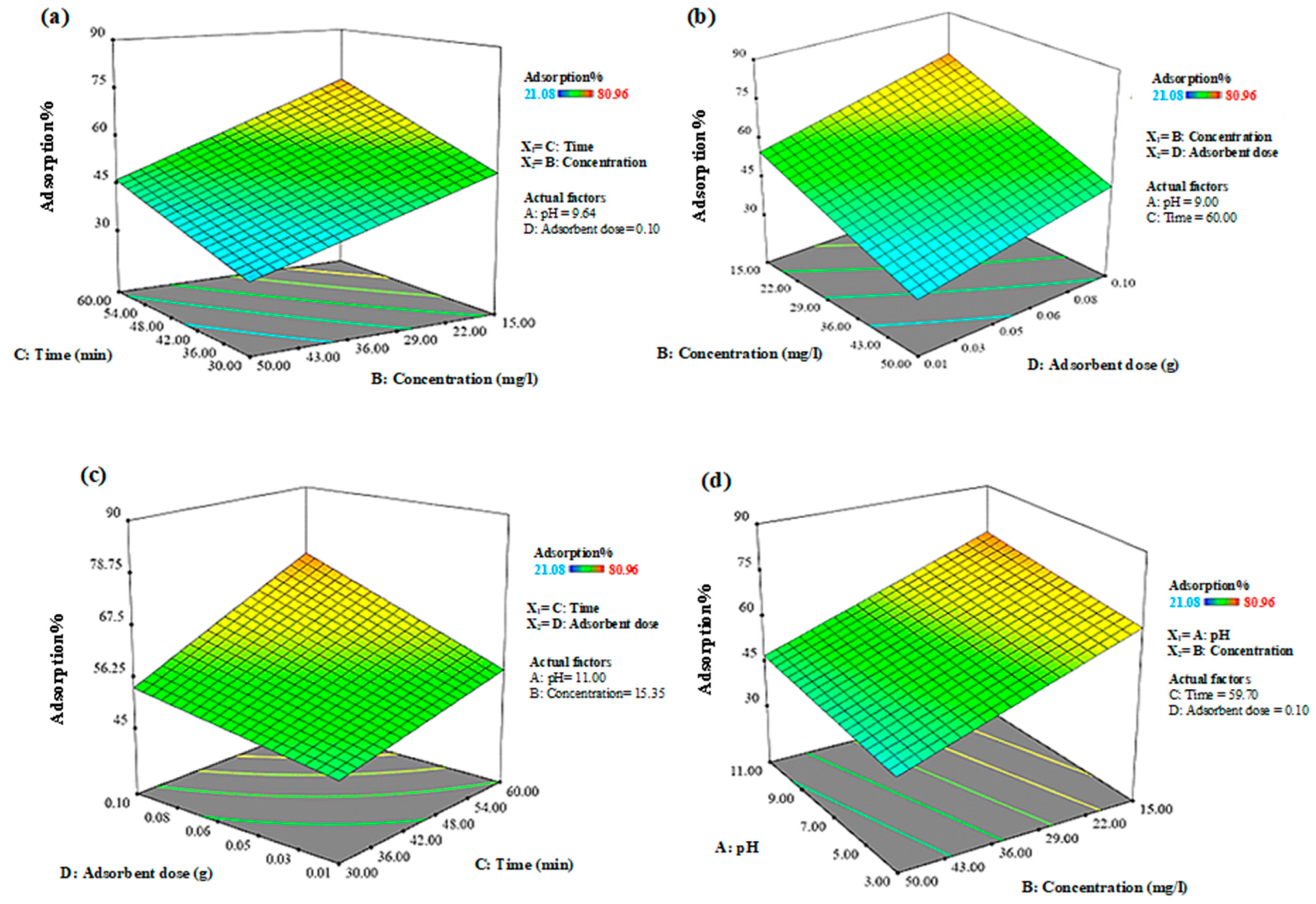
| Independent Variables | Range and Levels (Coded) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Coded | Units | −α | −1 | 0 | +1 | +α |
| pH | A | 3 | 3 | 7 | 11 | 11 | |
| Concentration | B | mg·L−1 | 15 | 15 | 32.5 | 50 | 50 |
| Time | C | min | 30 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 60 |
| Adsorbent dose | D | g·L−1 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.055 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| RUN | A: pH | B: Concentration (mg/L) | C: Time (min) | D: Adsorbent dose (g·L−1) | Adsorption % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 2 | 3 | 15 | 30 | 0.1 | 49.01 |
| 3 | 11 | 15 | 30 | 0.1 | 52.81 |
| 4 | 3 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 40.15 |
| 5 | 3 | 50 | 30 | 0.01 | 21.08 |
| 6 | 3 | 15 | 30 | 0.01 | 42.27 |
| 7 | 3 | 50 | 60 | 0.1 | 40.21 |
| 8 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 9 | 11 | 50 | 60 | 0.1 | 45.96 |
| 10 | 11 | 50 | 30 | 0.1 | 33.01 |
| 11 | 11 | 15 | 30 | 0.01 | 46.1 |
| 12 | 11 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 43.11 |
| 13 | 11 | 50 | 60 | 0.01 | 31.63 |
| 14 | 3 | 50 | 30 | 0.1 | 21.08 |
| 15 | 7 | 32.5 | 30 | 0.06 | 38.23 |
| 16 | 7 | 50 | 45 | 0.06 | 37.5 |
| 17 | 11 | 50 | 30 | 0.01 | 28.13 |
| 18 | 11 | 15 | 60 | 0.01 | 56.6 |
| 19 | 7 | 15 | 45 | 0.06 | 47.4 |
| 20 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.01 | 33.12 |
| 21 | 3 | 50 | 60 | 0.01 | 25.87 |
| 22 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 23 | 3 | 15 | 60 | 0.01 | 51.31 |
| 24 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 25 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.1 | 48.91 |
| 26 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 27 | 3 | 15 | 60 | 0.1 | 61.73 |
| 28 | 11 | 15 | 60 | 0.1 | 80.96 |
| 29 | 7 | 32.5 | 45 | 0.06 | 44.15 |
| 30 | 7 | 32.5 | 60 | 0.06 | 46.71 |
| Sample | Specific Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRMOF-3 | 718.11 | 0.378 | 2.105 |
| Adsorbent | Specific Area (m2·g−1) | PAHs | Adsorption Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 1299 | Acenaphthene | 60.7% | [71] |
| NH2-UiO-66(Zr) | 985 | Naphthalene | 97.7% | [72] |
| green mCS/GO | 22.8358 | Naphthalene | 70% | [73] |
| Fe@N-L-GM | 10.16 | Naphthalene | 97.81% | [74] |
| CuZnFeAlO | 125 | Naphthalene | 90.1% | [75] |
| IRMOF-3 | 718.11 | Naphthalene | 80.96 | This study |
| Response | 1 | Absorption | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA for Response Surface Reduced Quadratic Model | ||||||
| Analysis of variance table [Partial sum of squares—Type III] | ||||||
| Sum of | Mean | F | p-value | |||
| Source | Squares | df | Square | Value | Prob > F | |
| Model | 3902.805 | 10 | 390.2805 | 30.74218738 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-pH | 239.0756 | 1 | 239.0756 | 18.83185395 | 0.0004 | |
| B-Concentration | 2305.658 | 1 | 2305.658 | 181.6154259 | <0.0001 | |
| C-time | 663.2082 | 1 | 663.2082 | 52.24055604 | <0.0001 | |
| D-Absorbent dose | 528.8836 | 1 | 528.8836 | 41.65987941 | <0.0001 | |
| AB | 0.172225 | 1 | 0.172225 | 0.013566071 | 0.9085 | |
| BC | 25.1001 | 1 | 25.1001 | 1.977121484 | 0.1758 | |
| BD | 13.4689 | 1 | 13.4689 | 1.060938066 | 0.3159 | |
| CD | 127.2384 | 1 | 127.2384 | 10.02250088 | 0.0051 | |
| B2 | 0.000312 | 1 | 0.000312 | 2.46 × 10−5 | 0.9961 | |
| C2 | 0.000379 | 1 | 0.000379 | 2.98 × 10−5 | 0.9957 | |
| Residual | 241.2102 | 19 | 12.69527 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 241.2102 | 14 | 17.2293 | |||
| Pure Error | 0 | 5 | 0 | |||
| Cor Total | 4144.015 | 29 | ||||
| Std. Dev. | 3.563043 | R2 | 0.941793 | |||
| Mean | 42.92633 | Adj R2 | 0.911158 | |||
| C.V. % | 8.300366 | Pred R2 | 0.815208 | |||
| PRESS | 765.781 | Adeq Precision | 24.52136 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Babapoor, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Feizpoor, S.; Hashemi, S.A.; Binazadeh, M.; Chiang, W.-H.; Lai, C.W. Synthesis of Isoreticular Metal Organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) Porous Nanostructure and Its Effect on Naphthalene Adsorption: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Separations 2023, 10, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040261
Kalashgrani MY, Babapoor A, Mousavi SM, Feizpoor S, Hashemi SA, Binazadeh M, Chiang W-H, Lai CW. Synthesis of Isoreticular Metal Organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) Porous Nanostructure and Its Effect on Naphthalene Adsorption: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Separations. 2023; 10(4):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040261
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalashgrani, Masoomeh Yari, Aziz Babapoor, Seyyed Mojtaba Mousavi, Solmaz Feizpoor, Seyyed Alireza Hashemi, Mojtaba Binazadeh, Wei-Hung Chiang, and Chin Wei Lai. 2023. "Synthesis of Isoreticular Metal Organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) Porous Nanostructure and Its Effect on Naphthalene Adsorption: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology" Separations 10, no. 4: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040261
APA StyleKalashgrani, M. Y., Babapoor, A., Mousavi, S. M., Feizpoor, S., Hashemi, S. A., Binazadeh, M., Chiang, W.-H., & Lai, C. W. (2023). Synthesis of Isoreticular Metal Organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) Porous Nanostructure and Its Effect on Naphthalene Adsorption: Optimized by Response Surface Methodology. Separations, 10(4), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040261









