Green Bio-Analytical Study of Gabapentin in Human Plasma Coupled with Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Assessment Using UPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Instruments
2.3. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
2.4. Stock Solutions
2.5. Establishment of Calibration Curves
2.6. Method Validation
2.6.1. Specificity Study
2.6.2. Carryover Study
2.6.3. Estimation of Linearity and Range Study
2.6.4. Precision and Accuracy Study
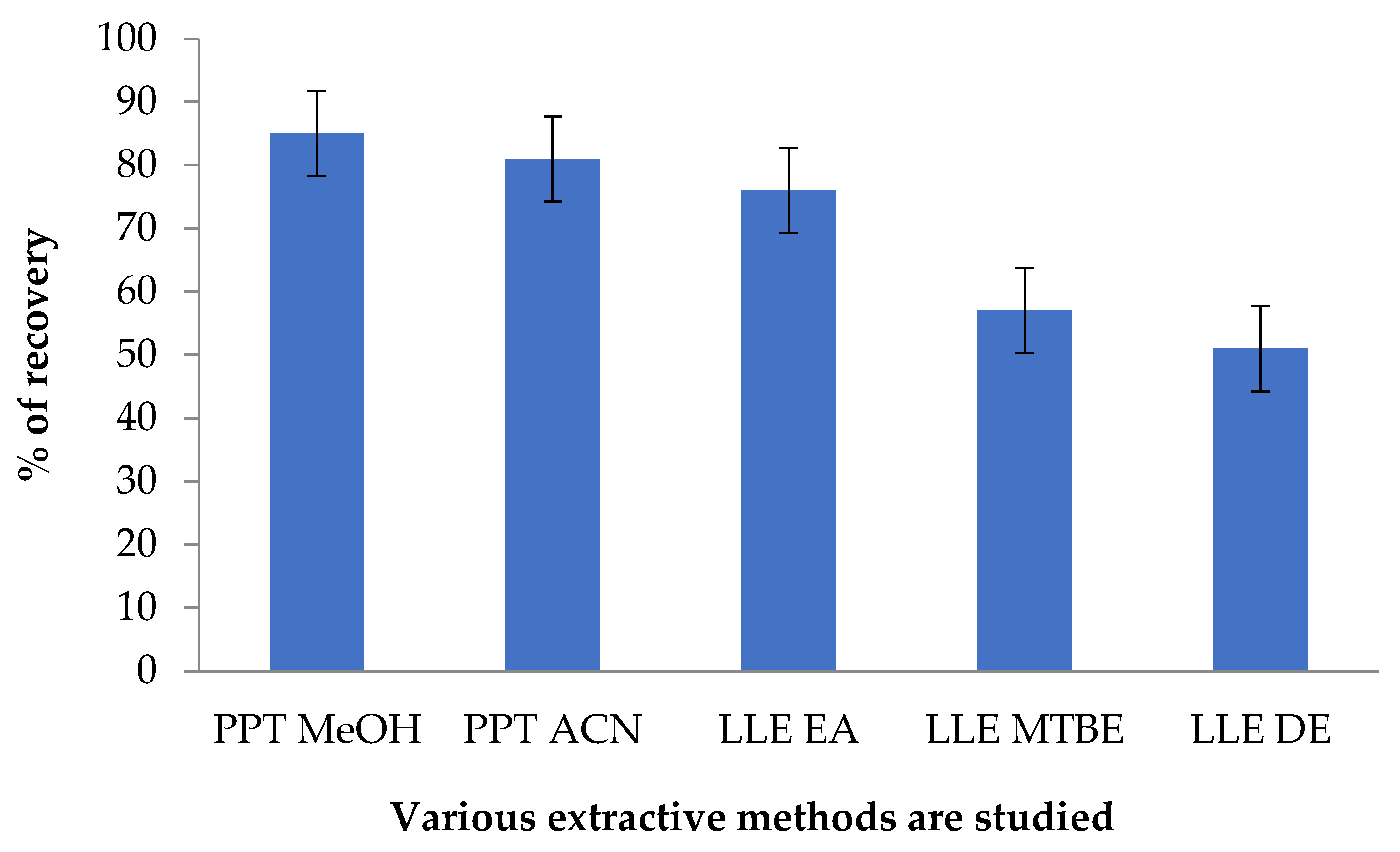
2.6.5. Assessment of Recoveries in the Extraction Process
2.6.6. Investigation of Matrix Effects
2.6.7. Stability Study
Stability in the Autosampler Study
Bench-Top Stability Study
Parent Solutions’ Stability Study
Freeze-Thaw Stability Study
Long-Term Stability Study
2.6.8. Investigation of Dilution Integrity
2.7. Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Treatment of Biological Samples
3.2. Mass Spectrophotometric and Chromatographic Settings
3.3. Chromatographic Method Validity
3.3.1. Method Specificity Study
3.3.2. Carryover Study
3.3.3. Linearity and Range Study
3.3.4. Accuracy and Precision Study
3.3.5. Results of Extraction Recovery Study
3.3.6. Matrix Influence Study
3.3.7. Stability Study
3.3.8. Investigation of Dilution Integrity
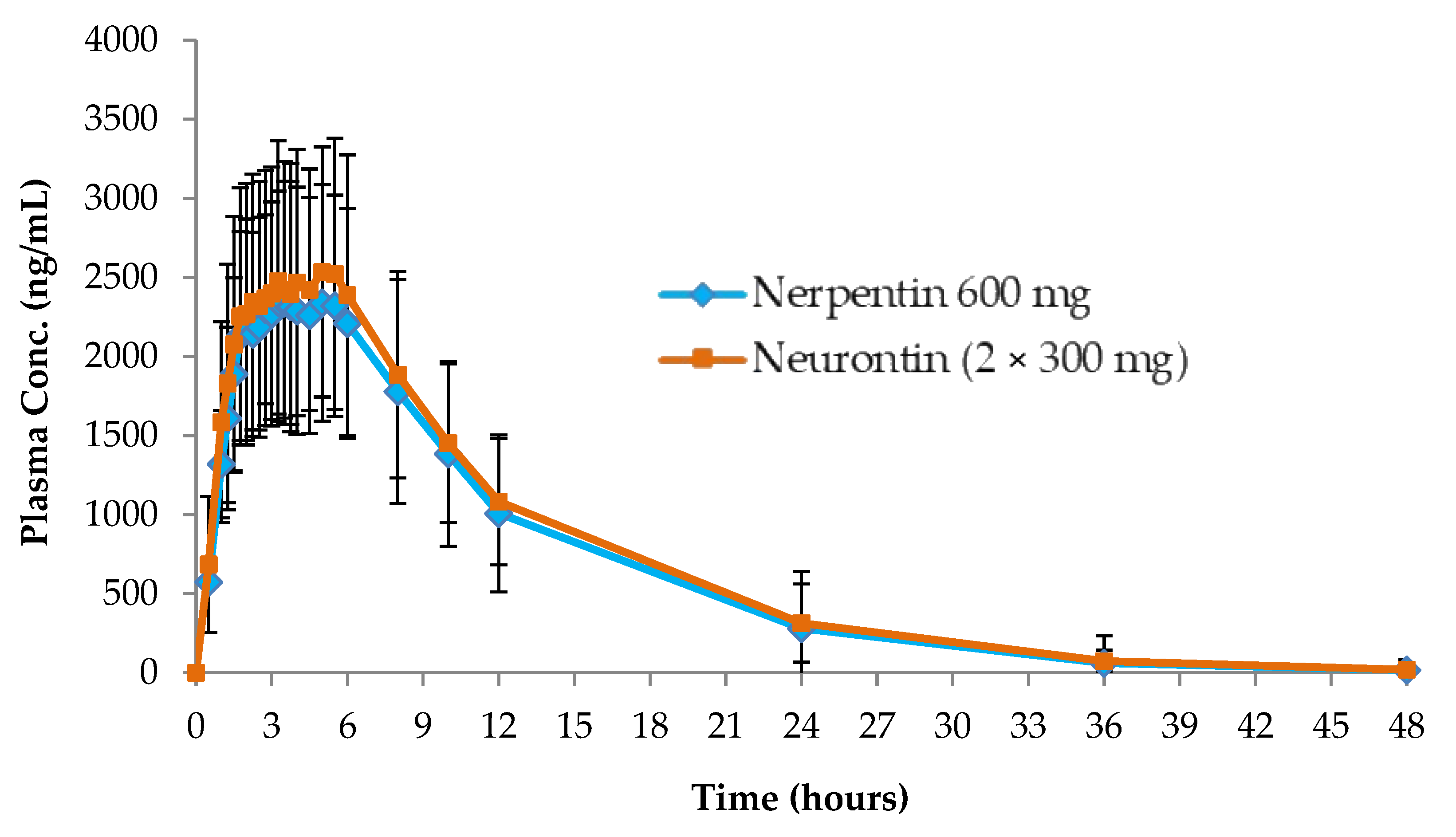
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
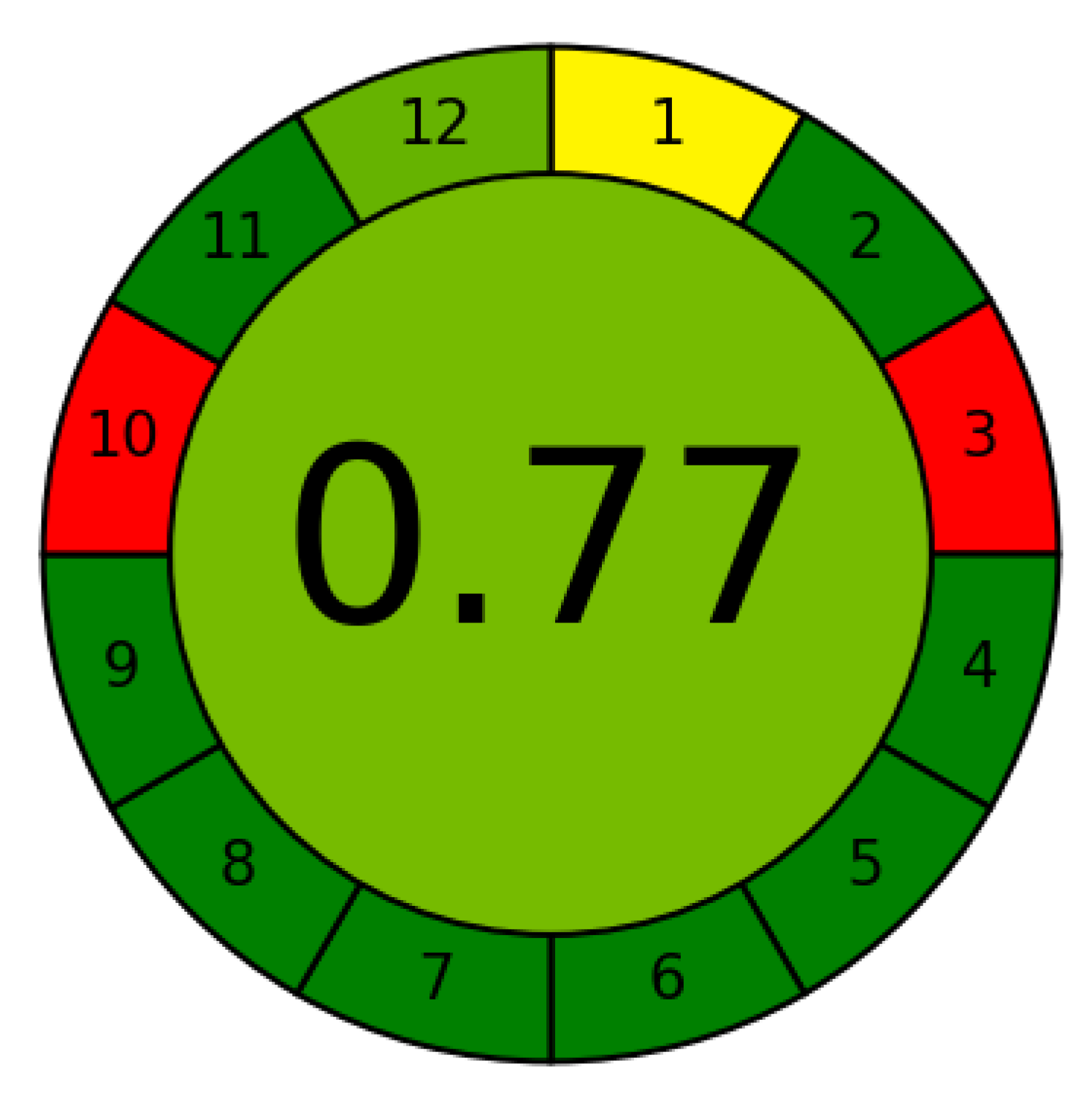
3.5. Greenness Study
3.6. Comparing the Suggested Strategy to Other Published Methods That Have a Similar Analytical Purpose
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Physicians’ Desk Reference and Thomson Reuters. Physicians’ Desk Reference, 59th ed.; Thomson PDR: Montvale, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zehouri, J.; Al-Madi, S.; Belal, F. Determination of the antiepileptics vigabatrin and gabapentin in dosage forms and biological fluids using Hantzsch reaction. Arzneimittel-Forschung 2001, 51, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belal, F.; Abdine, H.; Al-Majed, A.; Khalil, N.Y. Spectrofluorimetric determination of vigabatrin and gabapentin in urine and dosage forms through derivatization with fluorescamine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 27, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, G.; Sills, G.J.; Leach, J.P.; Brodie, M.J. Determination of gabapentin in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 681, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.H.; Miles, M.V.; Glauser, T.A.; DeGrauw, T. Automated microanalysis of gabapentin in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 727, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, D.; Gupta, R. Determination of Gabapentin in Plasma by Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection after Solid-Phase Extraction with a C18 Column. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Neirinck, L. High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of gabapentin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 779, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.-C.; Tai, C.-T.; Wu, H.-L. Simple and sensitive liquid chromatographic method with fluorimetric detection for the analysis of gabapentin in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1119, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagirli, O.; Çetin, S.M.; Önal, A. Determination of gabapentin in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV–vis detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, G.; Kiani, A. Sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic quantitation of gabapentin in human serum using liquid–liquid extraction and pre-column derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 835, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalizadeh, H.; Souri, E.; Tehrani, M.B.; Jahangiri, A. Validated HPLC method for the determination of gabapentin in human plasma using pre-column derivatization with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 854, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Rouini, M.-R.; Asad-Paskeh, A.; Shafiee, A. A New Pre-column Derivatization Method for Determination of Gabapentin in Human Serum by HPLC Using UV Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2010, 48, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinc, B.; Roškar, R.; Grabnar, I.; Vovk, T. Simultaneous determination of gabapentin, pregabalin, vigabatrin, and topiramate in plasma by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatography. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 962, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, N.V.S.; Vishwottam, K.N.; Koteshwara, M.; Manoj, S.; Santosh, M.; Chidambara, J.; Sumatha, B.; Varma, D.P. Rapid quantification of gabapentin in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattananat, T.; Akarawut, W. Validated LC-MS-MS Method for the Determination of Gabapentin in Human Plasma: Application to a Bioequivalence Study. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2009, 47, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, S.; McKeown, D.A.; Torrance, H.J.; Wylie, F.M.; Logan, B.K.; Scott, K.S. Simultaneous analysis of 22 antiepileptic drugs in postmortem blood, serum and plasma using LC-MS/MS with a focus on their role in forensic cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, L.; Smith, A.; Patel, R.; Andrews, R.; Paterson, S. Validated Method for the Screening and Quantification of Baclofen, Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Human Post-Mortem Whole Blood Using Protein Precipitation and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, M.M.; Crossett, J.; Brown, P.I.; Urry, F.M. Analysis of Gabapentin in Serum and Plasma by Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1999, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, C.E., II; Saady, J.I.; Poklis, A. Determination of Gabapentin in Serum Using Solid-Phase Extraction and Gas-Liquid Chromatography. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1996, 20, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrey, D.C.R.; Godderis, K.O.; Engelrelst, V.I.L.; Bernard, D.R.; Langlois, M.R. Quantitative determination of vigabatrin and gabapentin in human serum by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 354, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliana Garcia, L.; Shihabi, Z.K.; Oles, K. Determination of gabapentin in serum by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1995, 669, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-M.; Kou, H.-S.; Wu, S.-M.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, H.-L. Capillary electrophoresis analysis of gabapentin and vigabatrin in pharmaceutical preparations as ofloxacin derivatives. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 523, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Bai, K.; Li, H. Determination of gabapentin using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Se Pu = Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2010, 28, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Liang, S.; Tan, X.; Meng, J. Determination of gabapentin in human plasma by capillary electrophoresis-laser induced fluorescence detection with and without solid-phase extraction. Microchim. Acta 2012, 178, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Cai, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Li, H. Determination of Gabapentin in Human Plasma and Urine by Capillary Electrophoresis with Laser-Induced Fluorescence Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 53, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration, FDA, Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation, US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine (CV). 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Elizabeth, W.; Bruce, J.C.; Thomas, H.; Gary, S. The application of mass spectrometry in pharmacokinetics studies. Spectroscopy 2003, 17, 681–691. [Google Scholar]
- El Hamd, M.A.; Wada, M.; Ikeda, R.; Kawakami, S.; Nakashima, K. Validation of an LC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of Propofol, Midazolam, and Carbamazepine in Rat Plasma: Application to Monitor Their Concentrations Following Co-administration. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hamd, M.A.; Wada, M.; Ikeda, R.; Kawakami, S.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Simultaneous determination of propofol and remifentanil in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: Application to preclinical pharmacokinetic drug–drug interaction analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landersdorfer, C. Modern Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Techniques to Study Physiological Mechanisms of Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions and Disposition of Antibiotics and to Assess Clinical Relevance; The Bavarian Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg: Würzburg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ryvlin, P.; Perucca, E.; Rheims, S. Pregabalin for the management of partial epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Menachem, E. Pregabalin Pharmacology and Its Relevance to Clinical Practice. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blommel, M.L.; Blommel, A.L. Pregabalin: An antiepileptic agent useful for neuropathic pain. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2007, 64, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Naguib, I.A.; Panda, D.S.; Abdallah, F.F. Comparative study of four greenness assessment tools for selection of greenest analytical method for assay of hyoscine N-butyl bromide. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Fabjanowicz, M.; Kalinowska, K.; Namieśnik, J. History and Milestones of Green Analytical Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.L.; Yu, J.; He, J.F.; Qin, F.; Li, F.M. LC-MS/MS method for quantification and pharmacokinetic study of gabapentin in human plasma. Yao Xue Xue Bao Acta Pharm. Sin. 2011, 46, 1246–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B. Estimation of Gabapentin in human plasma using LC-MS/MS method. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Jhee, O.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.H.; Shaw, L.M.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, J.S. Validated LC-MS/MS method for quantification of gabapentin in human plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic and bioequivalence studies in Korean volunteers. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.Y.; Jeong, D.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.H.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, H.S. Determination of gabapentin in human plasma using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2006, 20, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahbouni, A.; Sinjewel, A.; den Burger, J.C.; Vos, R.M.; Wilhelm, A.J.; Veldkamp, A.I.; Swart, E.L. Rapid quantification of gabapentin, pregabalin, and vigabatrin in human serum by ultraperformance liquid chromatography with mass-spectrometric detection. Ther. Drug Monit. 2013, 35, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, P.; Kodali, B.; Datla, P.V.; Kovvasu, S.P. LC-MS/MS quantification of tramadol and gabapentin utilizing solid phase extraction. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1605950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
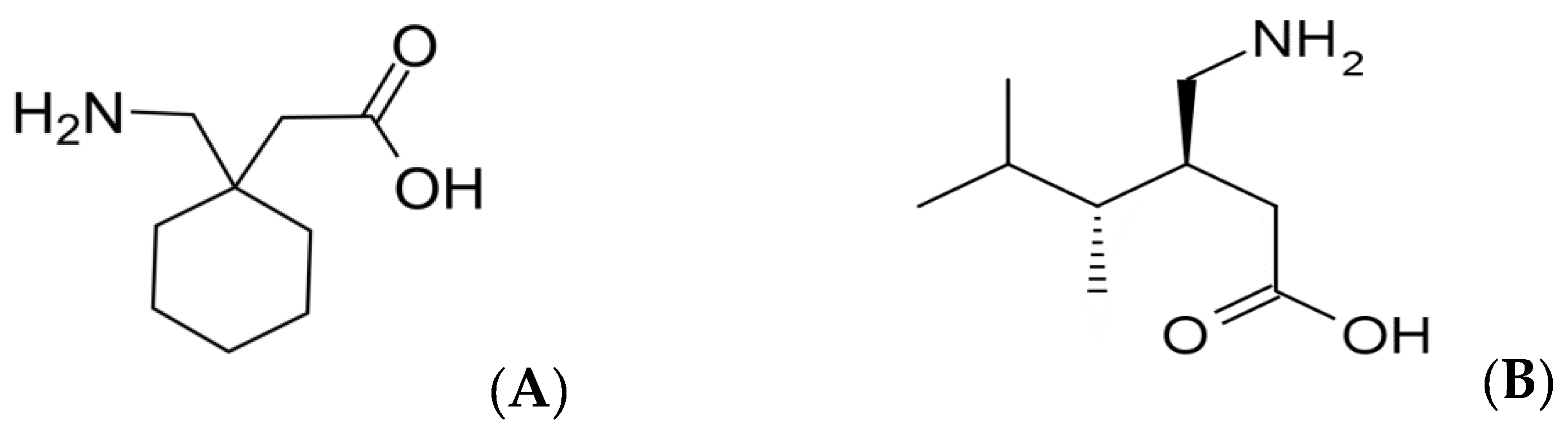
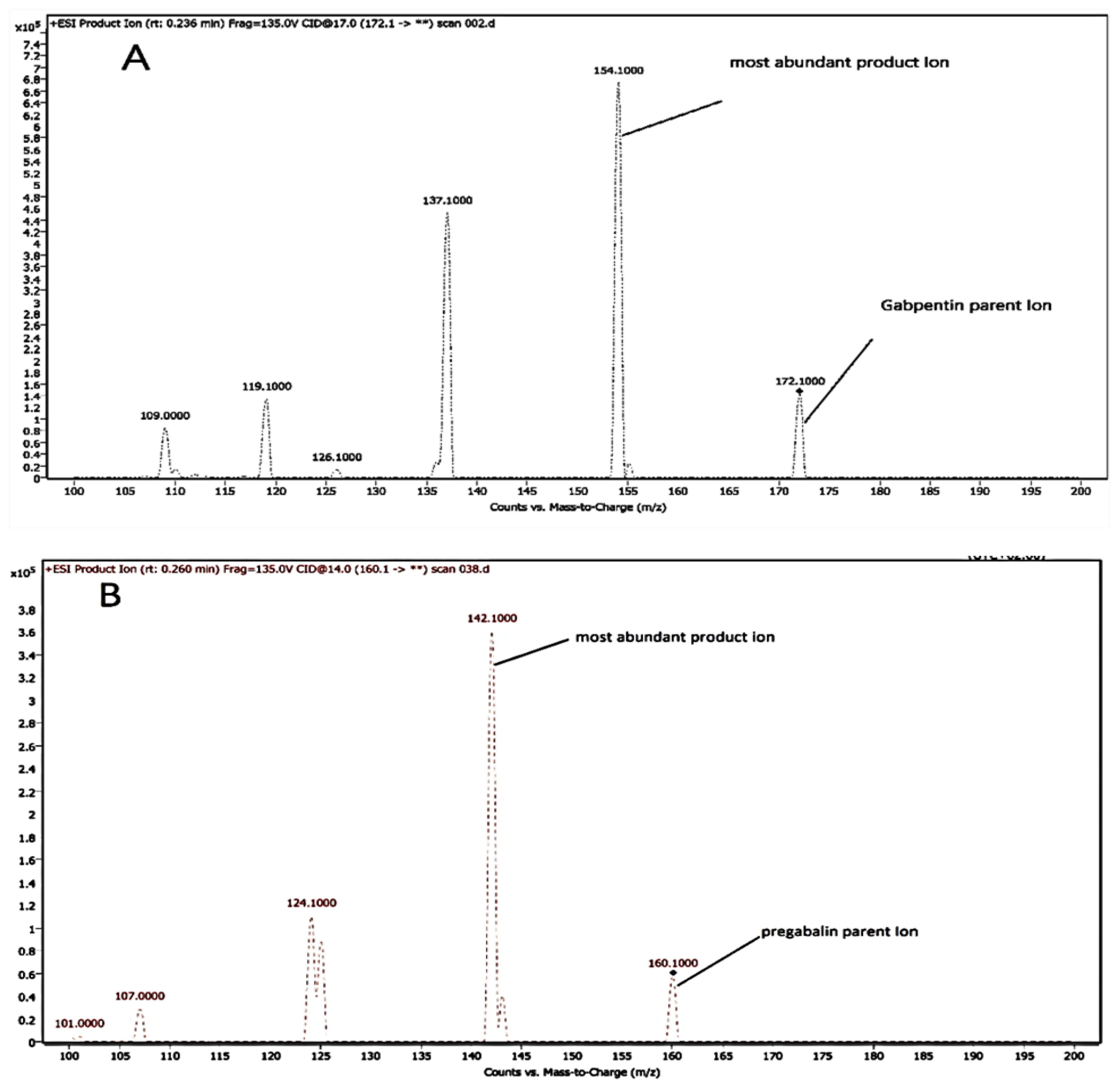

| Analyte | Q1 * (m/z) | Q2 * (m/z) | Fragmentor Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAB | 172.10 | 154.10 | 100.00 | 12.00 |
| PRE (IS) | 160.10 | 142.10 | 100.00 | 12.00 |
| The Injected Volume of Pretreated Human Plasma, μL | Extraction Solvent/Volume | Internal Standard | Liquid System | Speed of Flow, mL/min | Total Analysis Time, min | Stationary Chromatographic Material | Range of Linearity for GAB, μg/mL | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not reported | Reversed-mode solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridge | Baclofen | Sodium acetate buffer–methyl alcohol–acetonitrile (0.04 M) (48:40:12, by volumes) | 1.1 | 8 | Hypersil HyPurity Elite C (100 × 4.6 mm, 5 mm) | 0.03–10.0 | [7] |
| 20 | Trichloroacetic acid (20 uL), (30%, v/v) | GAB-D4 | Gradient mode: water, acetonitrile (containing 0.1% formic acid and 2 mM ammonium acetate) | 0.5 | 2 | Kinetex RP-C18 (50 × 2.6 mm, 2.1 μm) | 0.030–25.0 | [14] |
| 200 | Acetonitrile, (PPT), 0.5 mL | Metformin hydrochloride | Ammonium formate buffer (10 mM, pH 3.0, adjusted with formic acid) and acetonitrile (40:60, by volumes) | 0.2 | 2 | Acclaim 120 C8 (100 × 2.1 mm × 3 µm) | 0.050–5.0 | [15] |
| 250 | Methylene chloride, 2 mL | Gabapentin-D4 | Methyl alcohol: water (50:50, by volume, pH 3.0) | 0.8 | 2 | Zorbax Eclipse XDB -C18 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | 0.051–8.0 | [34] |
| 100 | Acetonitrile, (PPT) 0.3 mL | α-Amino cyclohexane propionic acid hydrate | Acetonitrile -ammonium acetate, 10 mM (20:80, by volume, pH 3.2) | 0.2 | 4 | Gemini C18 (150 × 2.0 mm, 5 µm) | 0.020–5.0 | [35] |
| 10 | Acetonitrile, (PPT), 0.1 mL | Metformin hydrochloride | Acetonitrile-ammonium formate (100 mM, pH 3.0) (85:15, by volume) | 0.5 | 3.5 | Atlantis HILIC silica column (50 × 3 mm × 5 µm) | 0.050–10.0 | [36] |
| 100 | Acetonitrile, (PPT), 0.5 mL | 1,1-Cyclohexane diacetic acid monoamide | Ammonium formate buffer-acetonitrile (20:80, by volume, 10 mM, pH 3.0) | 1.0 | 2 | Waters symmetry C18 (150 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) | 0.040–10.0 | [37] |
| 200 | SPE | Pregabalin | Ammonium formate buffer (5 mM, pH 3.0 ± 0.3), acetonitrile, and methyl alcohol in the percent of 25:50:25 by volume | 0.8 | 3.8 | Phenomenex, Kinetex PFP (50 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | 0.01–6.0 | [38] |
| 500 | Methanol, (PPT), the volume is not reported | Metformin hydrochloride | Methyl alcohol, 0.2% formic acid aqueous solution (80:20, by volume) | 0.3 | 2.2 | Inertsil ODS-3 (50 mm × 2.1 mm ID, 3 μm), Kromasil C18 (50 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | 0.04–8.0 | [39] |
| 450 | Methanol, (PPT), 1.5 mL | Pregabalin | Methyl alcohol: formic acid 0.1%, (65:35, by volume) | 0.2 | 1.6 | Agilent eclipse (50 × 2.1 mm × 1.8 μm) | 0.050–10.0 | The proposed method |
| QC Level | Inter-Day (n = 6) | Intra-Day (n = 6 × 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAB | ||||
| Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | |
| LOQ | 103.23 | 1.16 | 104.40 | 5.52 |
| LQC | 90.96 | 2.46 | 93.24 | 1.29 |
| MQC (A) | 92.50 | 1.14 | 95.05 | 3.43 |
| MQC (B) | 95.79 | 3.62 | 98.76 | 1.95 |
| HQC | 94.73 | 5.16 | 96.11 | 2.94 |
| QC Levels | Extraction Recovery *, (%) (n = 3) | Matrix Effect * (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAB | IS | GAB | IS | |
| LQC | 86.27 ± 4.78 | 75.88 ± 1.24 | 84.27 ± 3.71 | 76.08 ± 1.83 |
| MQC (A) | 85.52 ± 1.88 | 72.84 ± 1.62 | 83.28 ± 1.08 | 74.86 ± 1.76 |
| MQC (B) | 86.53 ± 0.56 | 74.24 ± 1.32 | 85.34 ± 0.96 | 73.48 ± 1.55 |
| HQC | 82.39 ± 0.86 | 84.08 ± 0.89 | 83.94 ± 1.06 | 81.04 ± 0.93 |
| Conditions | GAB | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LQC (n = 3) Recovery (%) ± RSD | MQC (n = 3) Recovery (%) ± RSD | HQC (n = 3) Recovery (%) ± RSD | |
| Autosampler stability | 101.72 ± 1.68 | 103.29 ± 1.38 | 106.58 ± 1.10 |
| Freeze–thaw stability (6 cycles) | 103.69 ± 2.53 | 105.53 ± 2.09 | 107.19 ± 1.36 |
| Short-term stability | 99.47 ± 2.19 | 102.21 ± 2.87 | 107.36 ± 2.91 |
| Long-term stability (after 63 days) | 97.17 ± 2.74 | 99.08 ± 2.48 | 101.15 ± 1.90 |
| Stock solution stability | 99.28 ± 1.90 | 101.03 ± 1.89 | 98.29 ± 1.37 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC0-t (ng.h/mL) | AUC0-∞ (ng.h/mL) | AUCextra (%) | AUC0-t/ AUC0-∞ (%) | Kel (1/h) | t ½ (h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurontin (2 × 300 mg hard gelatin capsules) | 2966.89 | 4.75 | 32737.58 | 34501.56 | 4.14 | 95.86 | 0.11 | 7.07 |
| The test product (600 mg of GAB film-coated tablet) | 2745.93 | 3.75 | 29966.73 | 31505.67 | 5.70 | 94.29 | 0.11 | 6.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tony, R.M.; El Hamd, M.A.; Gamal, M.; Saleh, S.F.; Maslamani, N.; Alsaggaf, W.T.; El-Zeiny, M.B. Green Bio-Analytical Study of Gabapentin in Human Plasma Coupled with Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Assessment Using UPLC-MS/MS. Separations 2023, 10, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040234
Tony RM, El Hamd MA, Gamal M, Saleh SF, Maslamani N, Alsaggaf WT, El-Zeiny MB. Green Bio-Analytical Study of Gabapentin in Human Plasma Coupled with Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Assessment Using UPLC-MS/MS. Separations. 2023; 10(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleTony, Rehab Moussa, Mohamed A. El Hamd, Mohammed Gamal, Safaa F. Saleh, Nujud Maslamani, Wejdan T. Alsaggaf, and Mohamed B. El-Zeiny. 2023. "Green Bio-Analytical Study of Gabapentin in Human Plasma Coupled with Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Assessment Using UPLC-MS/MS" Separations 10, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040234
APA StyleTony, R. M., El Hamd, M. A., Gamal, M., Saleh, S. F., Maslamani, N., Alsaggaf, W. T., & El-Zeiny, M. B. (2023). Green Bio-Analytical Study of Gabapentin in Human Plasma Coupled with Pharmacokinetic and Bioequivalence Assessment Using UPLC-MS/MS. Separations, 10(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10040234







