Abstract
Large volumes of oil sands process-affected waters (OSPW) result from heavy oil extraction in Alberta, Canada. Currently, a toxic legacy of ca. 500 Mm3 is stored in tailings ponds under a zero-discharge policy. OSPW is a complex mixture of suspended and dissolved materials including a wide range of inorganic and organic contaminants. Classically defined naphthenic acids (NAs; CnH2n+ZO2) are one of the primary toxic fractions in OSPW and have therefore been the subject of considerable research interest. Most studies employ considerable sample cleanup followed by liquid chromatography and/or high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) for the characterization of these complex mixtures. However, these strategies can be time- and cost-intensive, limiting the scope of research and adoption for regulatory purposes. Condensed phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry (CP-MIMS) is emerging as a “fit-for-purpose” approach for the analysis of NAs. This technique directly interfaces the mass spectrometer with an aqueous sample using a hydrophobic semi-permeable membrane, requiring only pH adjustment to convert NAs to a membrane-permeable form. Here, we examine the perm-selectivity of classical NAs (O2) relative to their more oxidized counterparts (O3–O7) and heteroatomic (N, S) species collectively termed naphthenic acid fraction compounds (NAFCs). The investigation of 14 model compounds revealed that classically defined NAs are greater than 50-fold more membrane permeable than their oxidized/heteroatomic analogs. HRMS analysis of real OSPW extracts with and without membrane clean-up further supported selectivity towards the toxic O2 class of NAs, with >85% of the overall signal intensity attributable to O2 NAs in the membrane permeate despite as little as 34.7 ± 0.6% O2 NAs observed in the directly infused mixture. The information collected with HRMS is leveraged to refine our method for analysis of NAs at unit mass resolution. This new method is applied to 28 archived real-world samples containing NAs/NAFCs from constructed wetlands, OSPW, and environmental monitoring campaigns. Concentrations ranged from 0–25 mg/L O2 NAs and the results measured by CP-MIMS (unit mass) and SPE-HRMS (Orbitrap) showed good agreement (slope = 0.80; R2 = 0.76).
1. Introduction
The oil sands in Northern Alberta, Canada represent the fourth largest oil deposit in the world, with over 165 billion projected barrels of oil recoverable [1]. As a result of oil extraction methods, large volumes of oil sands process-affected waters (OSPW) are produced, with ca. 500 Mm3 currently stored [2]. OSPW is complex, containing high concentrations of inorganic salts and organic contaminants including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and both classical naphthenic acids (NAs) and their oxidized and heteroatomic analogs (naphthenic acid fraction compounds (NAFCs)) [3,4]. Remediation efforts have largely focused on attenuating classical NAs due to their acute toxicity at mg/L concentrations. However, both optimization of remediation technologies, as well as large-scale environmental monitoring efforts, are challenged by the complexity of analyzing NAs, particularly in the complicated samples and contexts in which they occur.
Classically, NAs are described as alicyclic and aromatic carboxylic acids adhering to the general formula CnH2n+ZO2, where n can range from 8 to 25 and Z from −2 to −20 [4]. Consequently, there are potentially 103–104 individual NAs in a single OSPW sample. Quantifying these in the presence of NAFCs, naturally occurring dissolved organic matter (DOM), and other matrix components is clearly a difficult analytical challenge, particularly when a high throughput analysis of many samples is desired. Infrared spectroscopy approaches have been employed based on the integration of the C=O stretch at 1740 (monomer) and 1703 cm−1 (dimer). While this approach is easy and robust it is not expected to distinguish between NAs and NAFCs and is prone to DOM interference [5,6]. In contrast, approaches employing liquid chromatography and/or high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) provide unparalleled molecular level information, imparting a high degree of molecular selectivity. However, these techniques generally require significant sample clean-up prior to analysis (filtration, solid phase, or liquid–liquid extraction) and separation time (for chromatographic approaches) which can limit sample throughput. An emerging technique that aims to bridge the gap between easy-to-use simple methods (with compromised information) and more exacting methods (with limited accessibility) is condensed phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry (CP-MIMS).
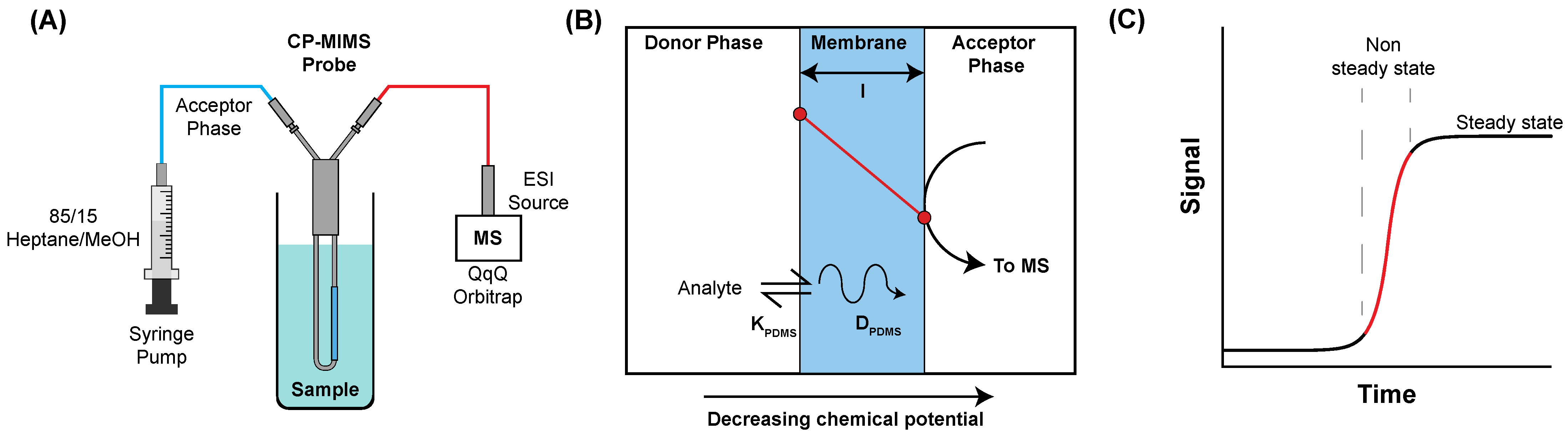
CP-MIMS employs a semi-permeable membrane to directly interface aqueous samples with a mass spectrometer. Several recent reviews cover the underlying theory and operation of CP-MIMS [7,8]. Briefly, permeability through the membrane is governed by Fick’s laws of diffusion [9,10]. The perm-selectivity of a particular analyte–membrane pair is related to the partition coefficient (K) and diffusion coefficient (D). In the case of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), membrane permeability is favored for hydrophobic analytes with high Kpdms and smaller analytes with high Dpdms (Figure 1). The PDMS membrane is impermeable to suspended solids and dissolved salts. Mounting a capillary hollow fiber membrane on an immersion probe provides a convenient online sample clean-up strategy. Permeating analytes are carried to an ionization source by a continuously flowing organic acceptor phase. This approach has been employed for fast, sensitive analysis of a range of organic contaminants including PAHs in water and soils [11,12], phthalates in house dust [13], and tire oxidation products in stormwater [14].
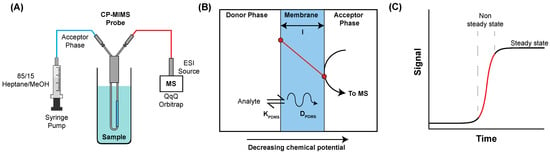
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of CP-MIMS operation and theory; (A) online monitoring with a hollow capillary membrane immersion probe with a flowing solvent (acceptor phase) directly infused into MS, (B) cross-section of sample (donor)/membrane/solvent (acceptor) depicting the analyte partitioning into (Kpdms) and diffusing across (Dpdms) the membrane under a concentration gradient, (C) time-resolved MS signal as analyte permeation reaches steady state.
Ongoing work in our group has been developing CP-MIMS for the analysis of classical NAs [15,16,17]. Duncan et al. compared quantitation from CP-MIMS and SPE-HRMS for NAs as they attenuate through time and space in a constructed wetland treatment system. Good relative agreement between the two techniques was observed, however, this wetland employed a commercial NA mixture (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) which has been noted to exhibit different properties from NAs derived from OSPW [18,19]. Recently, we employed a structurally related series of O2 carboxylic acids ranging in hydrophobicity (log Kow of 1–7) were used to characterize membrane perm-selectivity [20]. We have also elaborated CP-MIMS to include the use of a heptane co-solvent in the acceptor phase that enhances analyte permeation and reduces the analytical duty cycle [17,21] as well as online pairing with Orbitrap MS to enable molecular assignment [22]. The present work uses model compounds with varying oxygen content to verify that CP-MIMS is selective for the toxic, O2 class of naphthenic acids [23] even under heptane-enhanced permeability conditions. Selectivity is then further evaluated using Orbitrap-MS in a series of OSPW-derived mixtures of NAs and NAFCs (Table 1) measured with and without membrane clean-up. This information is leveraged to improve O2 class selectivity with unit mass resolution instrumentation to enhance the quantitation of classical NAs using online membrane introduction MS techniques. We demonstrate this by analysis of 28 environmental, engineered, or OSPW-affected wetland samples previously characterized by SPE-HRMS.

Table 1.
Summary of information for the OSPW extracts employed for evaluation of CP-MIMS membrane permeability.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Standards
Model compounds were purchased as analytical standards (>97% purity) from AKScientific (4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butanoic acid, 6-phenylhexanoic acid; San Francisco, CA, USA) and Sigma-Aldrich (all remaining model compounds (Full list available in Table 2); Oakville, ON, USA) and used as received. To prepare working solutions, 10–30 mg of model compound was dissolved in HPLC grade methanol (MeOH; Fisher Scientific, Hampton, NH, USA) to make a ca. 100 mg/kg stock which was subsequently diluted to a ca. 10 mg/kg working solution in methanol by volumetric dilution. Aqueous standards were prepared by volumetric dilution of the low (10 mg/kg) or high (100 mg/kg) methanolic stock into deionized water (Facility Scale Reverse Osmosis/Ion Exchange Water Purification System, Applied Membranes Inc., Vista, CA, USA), as needed. This working solution was added to the 15/85 heptane/MeOH (v/v) acceptor phase at 50–120 µg/kg for direct infusion to the MS.

Table 2.
Relative permeation efficiency (PE 1) across PDMS membrane using CP-MIMS with 15/85 heptane/MeOH.
The OSPW-NA extracts were supplied by Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) and prepared as described previously [24,25]. Briefly, organic contaminants were extracted twice with dichloromethane from OSPW acidified to pH = 2.5. The dichloromethane fractions were pooled and evaporated to dryness using rotary evaporation. The resulting residue was then dissolved in 0.1 N aqueous NaOH and the concentration of total NAFCs was determined by FTIR comparison with a commercial mixture of NAs. Table 1 provides information on the NAFC isolated from OSPW used for the evaluation of membrane permeability and as calibration standards. For CP-MIMS experiments, fresh dilutions in MeOH were prepared with 1-2 drops of 3M HCl, resulting in ca. 50 mg/kg sub-stocks. These methanol sub-stocks were spiked directly into aqueous solution to prepare calibration standards.
Archived samples were stored at 4 °C in glass vials between sampling (2017–2021) and analysis by SPE-HRMS (2017–2021) and CP-MIMS (July 2022). Samples were chosen to reflect a range of NAFC concentrations and compositions (i.e., varying O2 NA contribution). Samples collected also encompass a range of sources, including directly from the environment, at different stages in treatment processes, and from OSPW itself. Aside from refrigeration, samples were not filtered or preserved.
2.2. Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry
CP-MIMS experiments were performed using a standard “J-probe” geometry described previously [7,15,26]. Briefly, a capillary hollow fiber polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membrane (ID: 0.30 mm, OD: 0.64 mm, length: 2.5 cm; Silastic Tubing, Dow Corning, Midland, MI, USA) was mounted onto 22-gauge stainless steel tubing (McMaster-Carr, Douglasville, GA, USA). The tubing was joined to 1/16′′ PEEK tubing using zero-dead volume stainless steel unions. A syringe pump (Chemyx Fusion, Stafford, TX, USA) and gas-tight syringe (Hamilton 1000 series, Reno, NV, USA) was used to flow 50 µL/min of 15/85 heptane:methanol (v/v) acceptor phase through the membrane lumen. Between all analyses (quantitative and qualitative), the membrane probe was rinsed in a stirred solution of HPLC-grade methanol until signals returned to baseline levels (ca. 2 min). For every 3–5 samples, a deionized water blank and calibration standard were analyzed to ensure stable instrument performance.
CP-MIMS experiments employing high resolution, accurate mass (HRAM) mass spectrometry were performed on an Orbitrap Exploris 120 (Thermo Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) outfitted with a HESI electrospray ion source. Membrane extraction was performed offline and collected in 2 mL amber glass GC vials. These extracts were subsequently loop-injected into the Orbitrap (ca. 10 µL) either directly, or after addition of 0.1% NH4OH (v/v). A syringe pump was used to continuously deliver acceptor phase solvent to the ionization source at 25 µL/min. Source conditions were: spray voltage = −2.5 kV, RF lens = 70%, source fragmentation = 30 V, sheath gas = 25 (arbitrary units (AU)), auxiliary gas = 5 AU, ion transfer tube temperature = 320 °C, vaporizer temperature = 75 °C. Data were collected in full scan mode between m/z 100–1000 with resolution set to 120,000 at m/z 200. Mass calibration was performed using Pierce Flexmix calibration solution (Thermo Scientific, Lot# VJ313910) immediately before CP-MIMS analysis. Formulae assignments were performed using custom Matlab code (Version 2021b, Mathworks, Natick, MA) employed previously [22,27].
Quantitative CP-MIMS experiments were performed at unit mass resolution on an electrospray ionization triple quadrupole MS (QSight 220, Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The source parameters were: capillary voltage = −3 kV, cone voltage = −20V, hot-surface induced desolvation (HSAID) source temperature = 320 °C, nebulization gas = 120 psi, drying gas = 60 psi. Two full-scan experiments were collected throughout quantitative runs, one rapid “survey” scan and another slower, more selective quantitative scan for reporting of total naphthenic acid concentration ([NA]T). For the survey scan, m/z 100–500 was surveyed with step size of 1 m/z and 3 ms dwell time per step. For the quantitative scan, m/z 101–355 was measured with step size of 2 and 15 ms dwell time per step (i.e., every other m/z measured, covering the entire NA m/z range). Lauric acid-d2 internal standard (Sigma-Aldrich, Oakville, ON, Canada) was added to the acceptor phase at ca. 5 µg/kg and was monitored with a selected ion monitoring (SIM) experiment at m/z 201.1 (cone voltage = −22V; 500 ms dwell time). For quantitative work, all signal intensities were normalized to the lauric acid-d2 signal to correct for ion suppression at high analyte concentrations and signal drift during long runtimes [28]. For quantitative reporting, the instrument was calibrated against the 2018 OSPW extract.
For model compound permeation studies, a 6-port valve with ca. 10 µL injection loop (constructed from 15 cm of blue PEEK tubing; ID = 0.254 mm; OD = 1.59 mm) was included between the membrane probe and the ion source of the mass spectrometer. Details of the data processing for model compound permeation studies are provided in Text S1. Briefly, the target model compound was monitored at the corresponding [M-H]- ion. A multi-point calibration in water and a single-point calibration in acceptor phase were collected from aqueous and acceptor phase standards, respectively. The permeation efficiency across the membrane was then taken as the ratio of the slopes in donor aqueous phase vs. acceptor phase solvent, averaged across a triplicate set. The natural rise time (τ) was calculated by fitting non-steady state signal (between 20–90%) to a first-order process. A conditional partition constant (K′pdms) between sample and membrane for each analyte is then calculated as the product of permeation efficiency across the membrane and the natural rise time [20].
2.3. Peak Picking for Unit Mass Resolution Quantitation Method
To select peaks for the “exclusion list” method the spectra obtained from the high-resolution, Orbitrap-MS were employed. Every other m/z between 101 and 355 was considered for inclusion. After initial formulae assignment using the Matlab code described above, average spectra from triplicate injection of membrane permeate into the Orbitrap-MS were computed for each of the four OSPW extracts. For each m/z, the contribution of O2 signal intensity was calculated over a ± 0.5 m/z window. If the minimum O2 contribution across the OSPW extracts was <85%, that m/z was not included in the quantitative method. Additionally, signals at m/z 149 and 255 were excluded due to previously observed background interference from phthalates and palmitic acid, respectively. To select peaks for the “inclusion list” method, a multistep calibration was performed for the 2018 OSPW extract with CP-MIMS. The m/z peaks which exhibited a linear concentration response were included in the method, resulting in 39 selected ion monitoring experiments that were summed for the quantitative comparison. The selected m/z and their R2 are provided in Table S1.
2.4. SPE-Orbitrap
ENV+ solid-phase extraction cartridges (Biotage, Uppsala, Sweden) were rinsed with 6 mL of Milli-Q water, 6 mL of LCMS-grade methanol (Fisher Scientific, USA), and conditioned with a further 6 mL of Milli-Q water. Sample aliquots (100 mL each) were acidified to pH < 2 with formic acid, then passed through the pre-washed and conditioned SPE cartridges at 2–3 mL/min (3–4 drops/second). Once sample aliquots had been loaded onto the SPE cartridges, cartridges were rinsed with 6 mL of Milli-Q water to desalt inorganic ions, dried under gentle vacuum, and eluted with 6 mL of methanol. After drying under gentle N2 flow at approximately 40 °C the eluent was reconstituted in 1.00 mL of 50:50 acetonitrile:water with 0.1% v/v NH4OH and transferred to clean 2 mL LC-MS vials.
Sample extracts were analyzed by high resolution, accurate mass (HRAM) mass spectrometry under negative electrospray ionization conditions using a Thermo Fisher Scientific Orbitrap Velos EliteTM mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) via 5 µL loop injections, with spectra acquired in full-scan mode ranging from m/z 100–600, at a resolution of 240,000 at m/z 400. Source parameters were as follows: sheath gas flow rate of 25 (arbitrary units); spray voltage of 2.90 kV; auxiliary gas flow rate of 5 (arbitrary units); S lens radio frequency level at 67%; heater temperature at 50 °C; and capillary temperature at 275 °C. The infusion solvent was 50:50 acetonitrile:water with 0.1% NH4OH (v/v) at a flow rate of 200 µL/min.
NAFCs were quantified via loop injection against a NAFC standard prepared from OSPW, as was reported by [24]. The OSPW extract employed as calibrant was unavailable for CP-MIMS experiments at the time of this study. The O2 contribution in this OSPW extract was measured to be 74.5 ± 2.0% based on a series (n = 5) directly infused calibration solutions. Sets of up to 12 unknown samples were bracketed with calibration standards ranging from 10–100 mg/L total NAFCs. Calibration was linear, with an R2 = 0.99. Sample recovery from the SPE procedure was evaluated to be 103% ± 5%, and method limits of detection were approximately 0.1 mg/L, as has been previously described [29].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of PDMS Permselectivity
The hydrophobic character of polydimethylsiloxane [30,31] is expected to favor the permeation of hydrophobic analytes, consistent with our recent report of the membrane-based separation of naturally DOM from more hydrophobic analytes with log Kow > 3, including the O2 class of NAs [17,20]. This is largely due to the increased size and polarity imparted by additional oxygens and/or heteroatoms present in the broader class of NAFCs. For example, 3-phenylpropanoic acid (C9H10O2) and 2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoic acid (C9H10O3) differ only by the addition of a hydroxyl group yet exhibit an order of magnitude difference in hydrophobicity with log Kow of 2.29 and 1.06, respectively. To evaluate these effects more systematically and characterize the relative permeation efficiency of classical NAs versus O3, O4, and S-containing NAFCs, we assembled a suite of 14 structurally related model compounds with similar carbon skeletons bearing additional functionalization (Figure S1). A schematic overview of the experimental workflow and data processing to determine the relative membrane permeability is available in Figure S2. Table 2 summarizes the permeation efficiency across 170 µm thick PDMS membrane determined by the calibration slope in the donor aqueous phase relative to that in the 15/85 heptane/MeOH (v/v) acceptor phase for each model compound. The normalized ionization efficiency (IE; measured as the calibration slopes from the direct infusion of prepared standards in the acceptor phase) varied by less than an order of magnitude across the model compound series, indicating that the large differences in sensitivity by CP-MIMS for NAs/NAFCs are largely driven by membrane perm-selectivity. The impact of additional carbons (e.g., C9–C20) on permeation efficiency is apparent as this increases hydrophobicity as reported by the corresponding Kow values. For example, examining the O2 class compounds we observe a 6- and 22-fold increase in the permeation efficiency of C10 and C12 (respectively) over the C9 class. This increases further to 100–200-fold for the aliphatic C12, and C14–C20 model O2 compounds. On the other hand, the addition of a hydroxyl or carbonyl oxygen (i.e., O3 compounds) reduced the permeation efficiency markedly to less than 2% of the that of the corresponding O2 compound. The impact of ether moieties was less dramatic with 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butanoic (C11H14O3) acid exhibiting ca. 20% the permeation efficiency of the O2 analog (4-phenylbutanoic acid; C10H12O2). Interestingly, the thioether (3-(4-methylthiophenyl)propanoic acid; C11H14SO2) exhibited an enrichment over the corresponding O2 compound. Overall, the conditional partition constants for the model compounds examined here (log K’pdms) trended linearly with log Kow consistent with previous work [20] using a pure methanol acceptor phase (Figure S3).
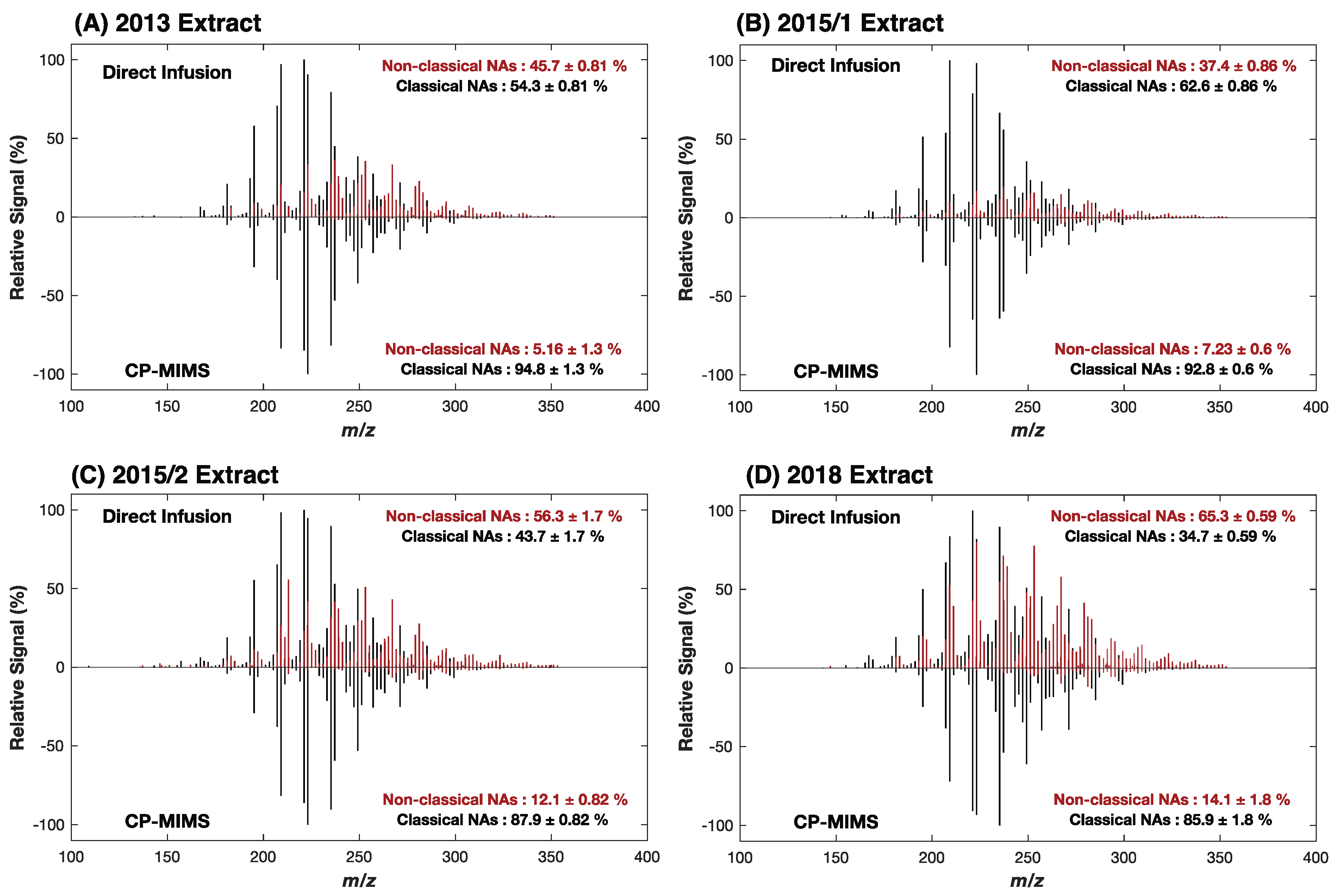
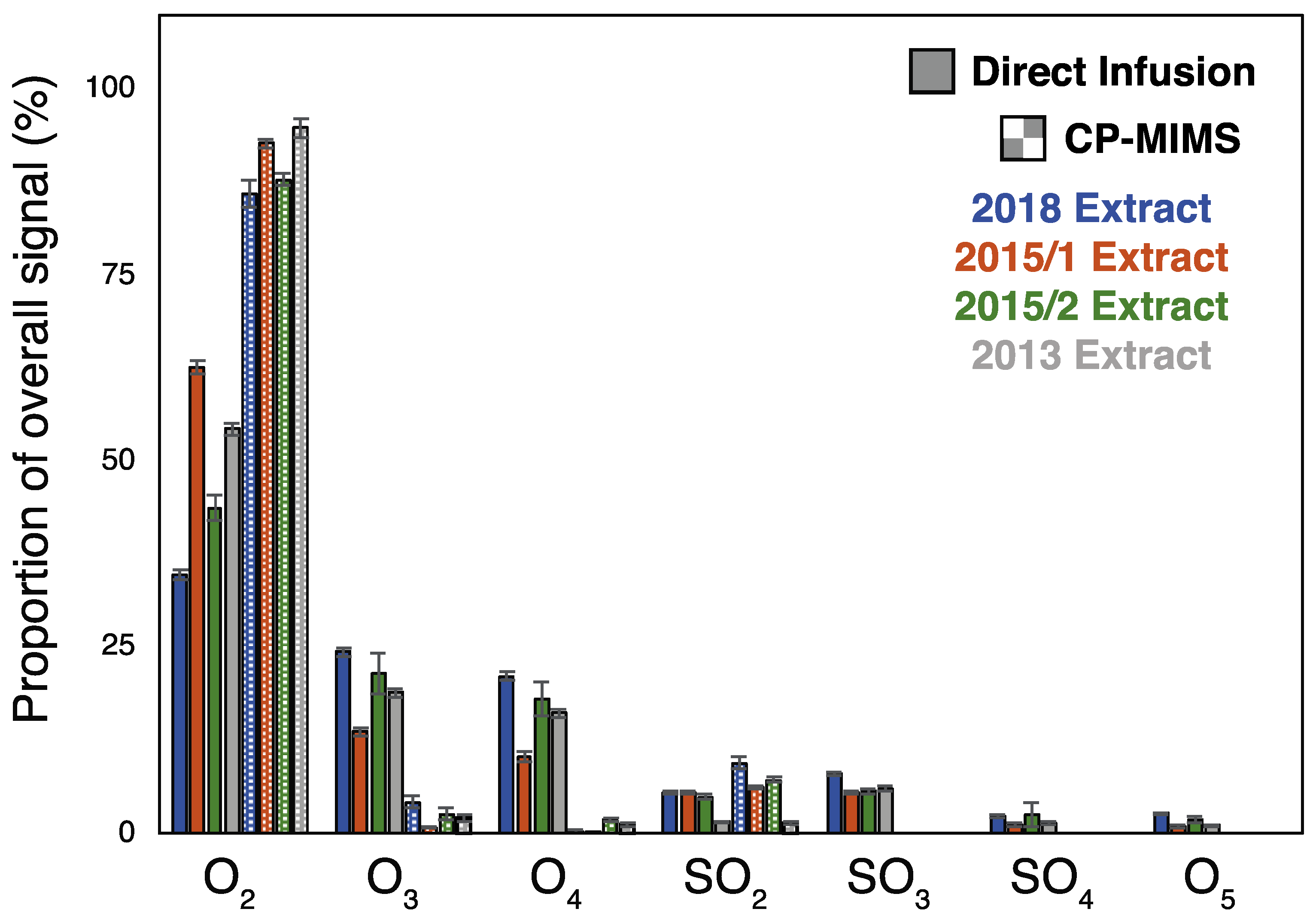
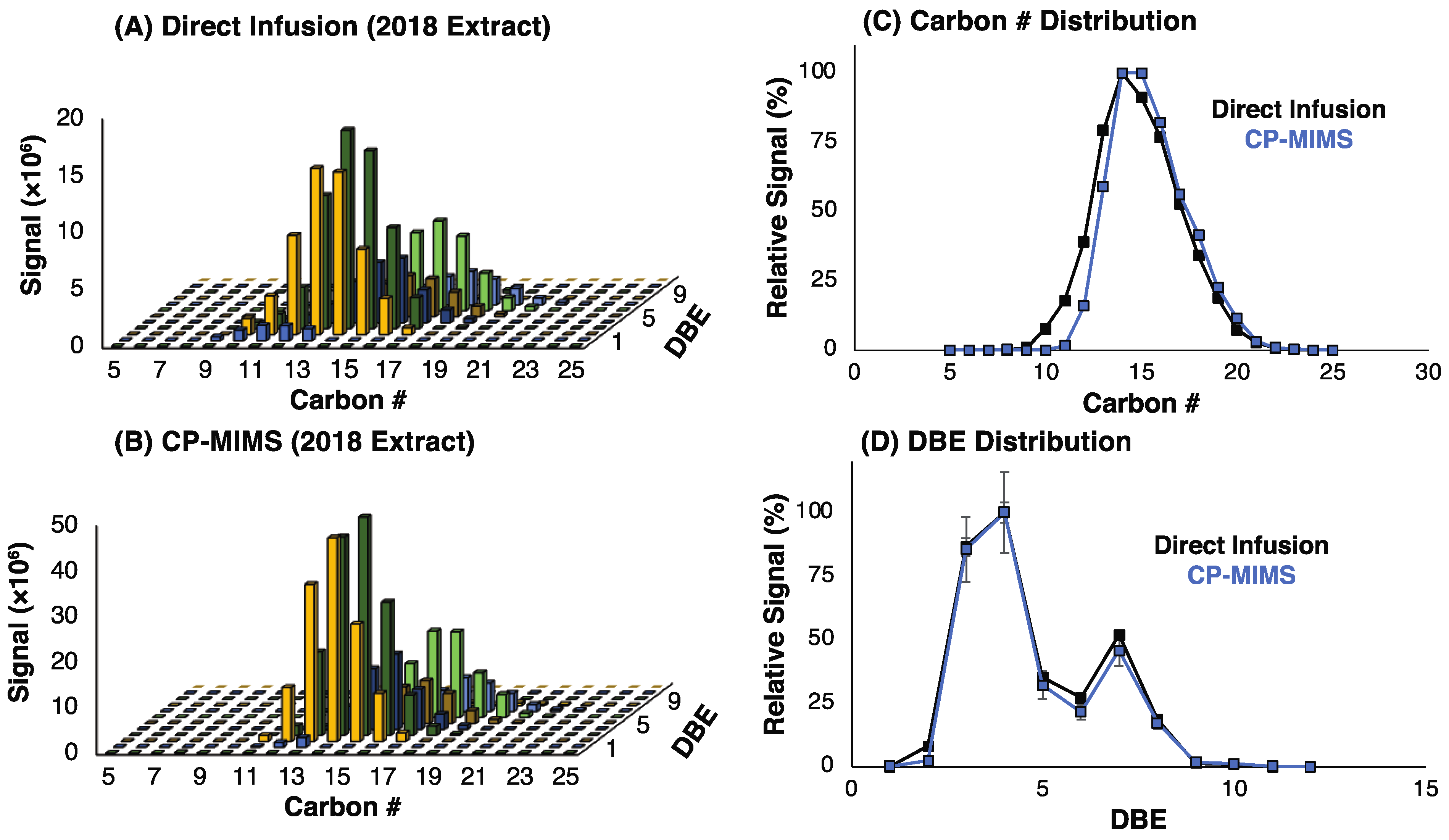
These results suggest that while non-classical NAs may permeate PDMS, they would need to be present in vast excess to their classical NA counterparts to have a significant impact on the mass spectral signal intensity. Given that the model compounds examined here do not capture the diversity of possible structures in actual NAFC mixtures, we evaluated the molecular composition for four real-world OSPW extracts using high-resolution, accurate mass (HRAM) Orbitrap-MS. An overview of the experimental workflow and data processing for this work is provided in Figure S4. Figure 2 shows the negative-ESI mass spectra of the whole OSPW mixtures by direct infusion (top) and of the PDMS membrane permeate (bottom). The mass spectra of the membrane permeate show a clear enrichment of classical O2 NAs over direct infusion for the NAFC mixtures at a similar concentration (ca. 2 mg/L). In all cases, the CP-MIMS mass spectra were dominated by O2 class NAs making up 85–95% of the signal intensity despite contributing as little as 35–65% O2 in the directly infused extracts. Table S2 and Figure 3 provide the class composition of the four NAFC extracts (isolated from OSPWs) with and without membrane clean-up. This increase in the relative contribution is accompanied by a concomitant decrease in O3-5 and SO3-4 species. Within the O2 class, the composition (by carbon #, DBE, and relative intensity) does not appear to differ substantially between direct infusion experiments and CP-MIMS for the 2018 OSPW extract (Figure 4) or several real-world samples (Figure S5). The membrane permeate may underrepresent low carbon # O2 class NAs due to their lower Kpdms, as observed for the model series 3-phenylpropanoic acid, 4-phenylbutanoic acid, and 6-phenylhexanoic acid which exhibited relative permeation efficiencies of 1.0, 6.2, and 22, respectively.
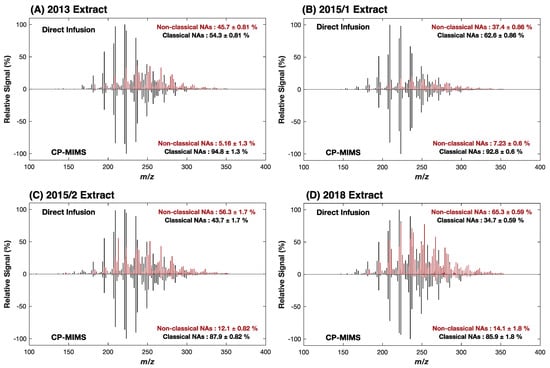
Figure 2.
Enrichment of O2 class NAs using CP-MIMS for 4 OSPW extracts. Full scan HRMS spectra of the [M-H]− of OSPW-NA extract showing O2 class (black) and all other NAFCs (O3–7, N, S; red) for direct infusion (upper panels) and CP-MIMS (lower panels). The directly infused spectra are comprised of only ca. 30–65% O2 class NAs by overall signal intensity, while this rises to >85% in the membrane permeate. Spectra are averaged over a triplicate series and overall assignments are presented with the standard deviation across the triplicate set.
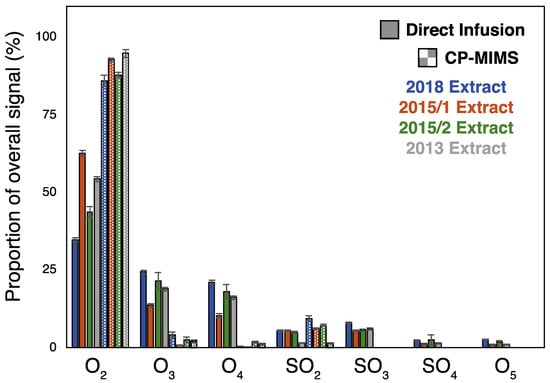
Figure 3.
Class composition for direct infusion and membrane permeate across 4 OSPW extracts. Bars represent the mean signal contribution across a triplicate set of injections, and error bars represent the standard deviation across that triplicate set.
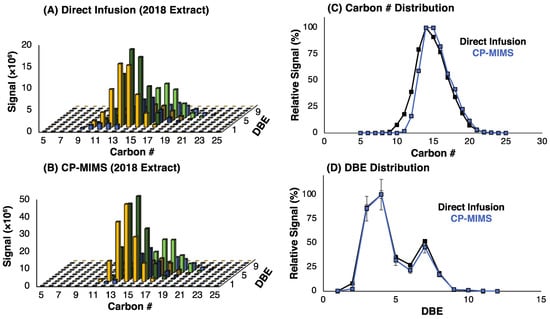
Figure 4.
Relative distribution of O2 class NAs by (A) direct infusion and (B) CP-MIMS with an Orbitrap HRMS. Panels (C,D) show the relative intensity by carbon # and double-bond equivalent, respectively. Points are the average of a triplicate injection, while error bars are the standard deviation across the triplicate set. The distribution of O2 class NAs appears to be largely unperturbed by membrane transport.
While previous work has not investigated PDMS membrane selectivity towards O2-NAs in any quantitative manner, these results qualitatively agree with our previous observations. Early work in our group [15] found that for a commercial mixture of NAs (Merichem, Houston, TX, USA), direct infusion resulted in a complex spectrum composed of O2–4, SO2, and SO3 compound. However, when this same mixture was analyzed with CP-MIMS, a much simpler mass spectrum was observed comprised of mostly O2 species. This was further supported in [17] and [20], where the presence of a variety of dissolved organic matter mixtures did not affect qualitative or quantitative results derived from CP-MIMS experiments.
Previous work examined the effect of transfer solvent pH on apparent OSPW class composition in electrospray ionization [32]. Basic transfer solvent appeared to favor classical O2-NAs, so to further improve CP-MIMS selectivity to O2-NAs we added 0.1% NH4OH (v/v) post-membrane and collected HRAM spectra for the 2018 and 2015/2 extracts. These solvent systems yielded slightly higher O2 assignments at 85.9 ± 1.8% (no base) vs. 87.6 ± 3.1% (base-enhanced) and 87.9 ± 0.8 vs. 89.4 ± 0.6%, respectively. Given the marginal improvements over the regular acceptor phase, we elected not to incorporate base enhancement into the quantitative method (described below) due to the challenges this presents to online membrane transport experiments described previously [33]. Future work will evaluate the use of a second membrane probe for the introduction of ionization-enhancing agents [34].
3.2. Adaptation to Unit Mass Resolution Instrumentation
A long-standing challenge in the quantitative analysis of NAs is the lack of an authentic, “universal” standard [35] and thus an appropriate scale for expressing the total naphthenic acid concentration. Various commercial mixtures of NAs have been employed (Sigma-Aldrich, Merichem), however, these have been noted to have a different isomer class distribution and behave differently (e.g., higher toxicity) from NAs derived from OSPW [18,19]. Another approach has been to quantify environmental samples against an NAFC mixture extracted from a real-world OSPW, however, this too presents challenges because the isomer class distributions can vary depending on when and where the OSPW is collected as is apparent in Figure 2 above. This makes a comparison between analytical methods employing different calibrants inherently problematic and has prompted some researchers to consider all NA concentrations to be semi-quantitative. To characterize the impact of different calibrants on [NA]T by CP-MIMS, we measured the calibration slopes using the full suite of possible NAs between m/z 101–355 for three OSPW extracts (2018, 2015/1, and 2015/2) and two commercial NA mixtures (Sigma-Aldrich, Merichem). The calibration slope for the CP-MIMS signal intensity increased with the proportion of O2 compounds in the mixture (Figures S6 and S7), with Merichem exhibiting the highest relative slope. Because this approach employs the same m/z for all calibrants, in principle, the ratio of calibration slopes (Table S3) could be used to scale the [NA]T between different calibrants. Alternatively, two methods using different calibrants could be compared by weighting the results by the O2–contribution in the calibrant, as employed below.
A long-term goal of developing CP-MIMS in our group is to apply the technique in the field. To this end, we set out to leverage the information provided at a high mass resolution to improve our unit mass resolution MS method for aqueous NA analysis. Previously, our quantitation methods were constructed based on an “inclusion list”, where peaks that calibrate linearly with aqueous concentration for a particular NA mixture are summed for quantitative experiments such as standard addition or direct calibration [16,17]. However, this approach makes a comparison between calibrants with different NA compositions difficult and will not include peaks that are present in samples but absent in the calibrant. Using data from the high-resolution experiments, we constructed an “exclusion list” wherein classical NAs are considered (i.e., every other m/z between 101–355 at nominal mass), and only peaks which either (a) are shown to be significantly influenced by non-classical NAs at high mass resolution (operationally defined as <85% intensity at that nominal m/z due to O2-NAs) or (b) are affected by known background laboratory contaminants (e.g., m/z 149 for phthalates or m/z 255 for palmitic acid) are rejected. Table S4 reports the relative O2 contribution to each (nominal) m/z. Of the possible 128 ion channels at the unit mass resolution, 49% (63 m/z) meet the criteria for exclusion, leaving 65 at unit mass resolution for quantitation. While imperfect, this is a significant improvement over our previous work.
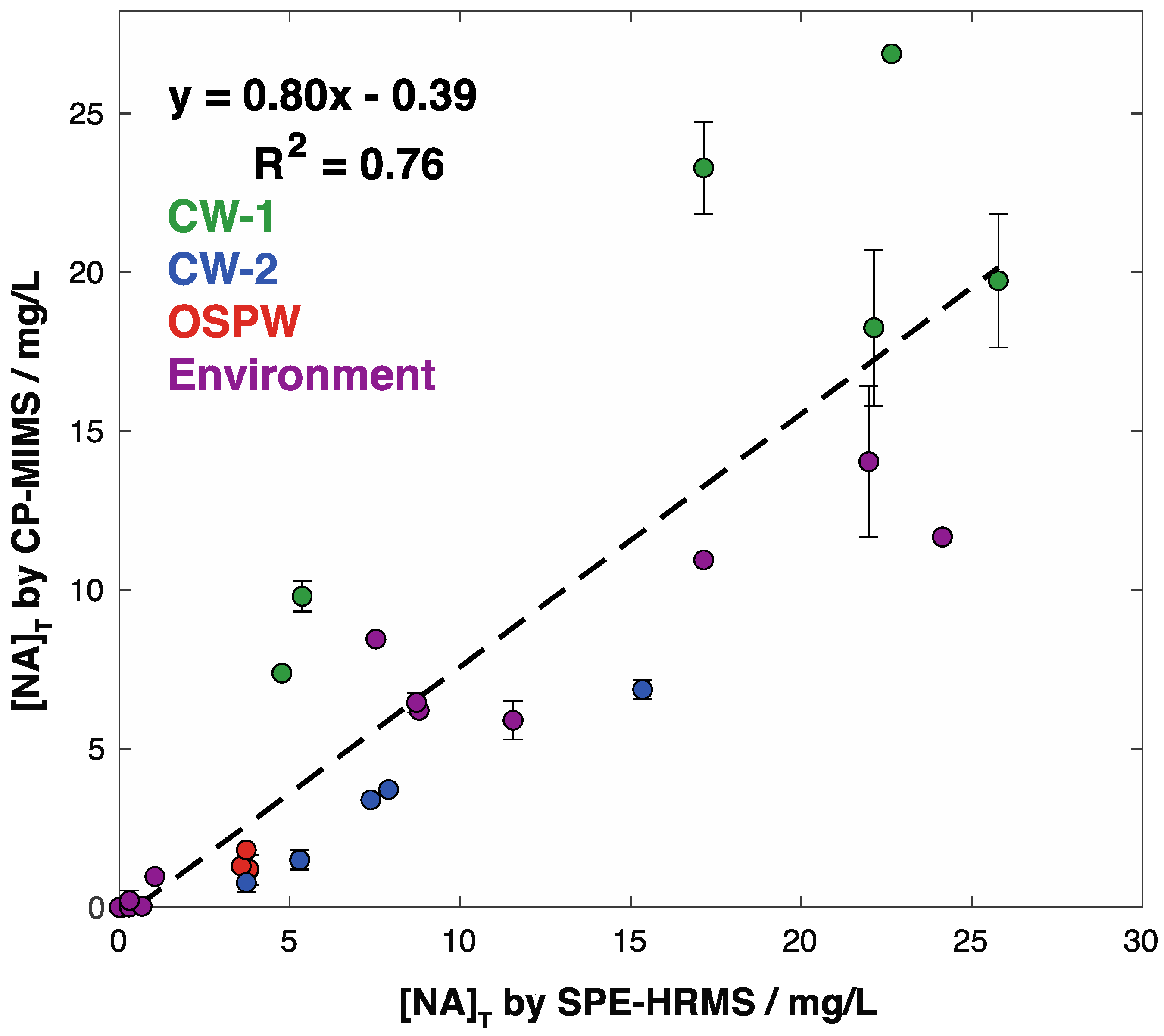
To evaluate this approach, we applied the new, unit mass resolution quantitation method to measure 28 samples previously analyzed by solid-phase extraction coupled to HRMS, comparing the relative quantitation results. We re-measured these samples by CP-MIMS on a unit mass resolution triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Figure S8). Analysis was simple and rapid (10 min/sample), requiring only dilution into the linear dynamic range (1–2000 µg/L NAs) and adjustment to pH < 3. Triplicate analysis of ca. 1000 µg/L calibration standards yielded a relative standard deviation in signal intensity of 6–10%. Similar precision was observed in the archived sample series, with relative standard deviations (RSDs) ranging from 5–20% for most samples, with low-concentration samples exhibiting somewhat higher imprecision (up to 40%). Samples covered a range of sources including constructed treatment wetlands in greenhouse conditions (CW-1 and CW-2), tailings ponds (OSPW), and environmental monitoring campaigns. The concentration of total naphthenic acids ([NA]T), after correcting for dilution steps, ranged from 0–30 mg/L [NA]T by CP-MIMS (Table S5). Comparing this new “exclusion list” approach to results obtained by CP-MIMS using our previous “inclusion list” strategy showed excellent agreement (Figure S9; Slope: 1.025, R2 = 0.994). While this agreement is reassuring, we believe the “exclusion list” approach is much more adaptable, particularly when comparing different calibrants discussed above. Since the extract used for SPE-HRMS results was unavailable for the subsequent CP-MIMS analysis at the time of this study, the most recent 2018 extract (Figure 2D) was employed here. Given the challenges outlined above comparing methods using two different calibrants, we weighted the calibrant concentration for both methods using the fraction of O2 contribution (i.e., weighted standard [NA]T = actual standard [NA]T × fO2) to promote meaningful quantitative comparison. This weighting resulted in a shift by a factor of 0.347 and 0.745 for extracts employed CP-MIMS and SPE-HRMS, respectively. This approach shows good agreement between the two methods (Figure 5; slope = 0.80, R2 = 0.76). The error bars on the CP-MIMS concentrations represent the standard deviation across several replicate measurements (n indicated in Table S5). Quantitative precision on the SPE-HRMS data is estimated at 10%. Given the age of these archived samples, we are encouraged by the level of agreement observed between the two methods after this O2 calibrant weighting. When comparing the unweighted results, the relative agreement is preserved but the slope increases to 1.7 due to the lower O2 contribution in the calibrant used for CP-MIMS analysis (Figure S10). Additional scatter in the data displayed in Figure 5 may be attributable to sample aging effects (up to 5 years between CP-MIMS and HRMS analysis) and/or the sample matrix. For instance, the samples from CW-1 (shown in green; Figure 5) all originate from the same constructed wetland treatment system and increase the slope on the correlation plot. The R2 improves to 0.893 and the slope decreases to 0.573 if these points are omitted. The presence of high background DOM in such samples may affect SPE-HRMS results by saturating the SPE cartridge or causing ion suppression. These are testable hypotheses that will be assessed in future work with a designed sampling campaign and inter-laboratory comparison using fresh samples.
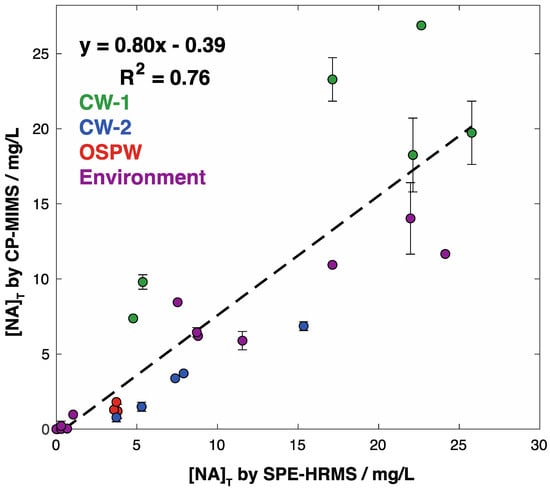
Figure 5.
Comparison of quantitative results derived from solid-phase extraction high-resolution mass spectrometry method and CP-MIMS paired with a unit mass resolution QqQ mass spectrometer after scaling results by the fraction of O2 signal contribution in the calibrant for each method. Quantitative precision on the SPE-HRMS data is estimated at ±10% from the propagated error of replicate injections and formulae assignment. Vertical error bars indicate the standard deviation across n replicates (Table S5) for CP-MIMS measurements.
4. Conclusions
Analysis of naphthenic acids is an inherently challenging analytical task due to the complexity of the analyte class and the matrices in which they occur, as well as the lack of a universal quantitative standard. Conventional analytical workflows can be time- and cost-prohibitive, thus limiting wide-scale surveillance campaigns and real-time feedback to inform operators. Condensed phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry is emerging as a “fit-for-purpose” analytical tool for direct analysis of NAs, requiring minimal sample preparation and an analytical duty cycle of just 10 min/sample. Using a series of structurally related model compounds, we show that the permeation efficiency increases with hydrophobic character and decreases markedly (>50-fold) for the more oxidized NAFC analogs. The selectivity of the method towards classically defined NAs (O2) was further observed in a series of real-world samples derived from oil sands process-affected waters measured with and without PDMS membrane cleanup at high mass resolution. Whereas 35–65% of the overall signal intensity for the directly infused mixture was attributable to the toxic O2 NAs, the contribution of this compound class in the membrane permeate was greater than 85%. This work represents the first quantitative evaluation of classical (O2 class) selectivity towards NAs by CP-MIMS. Leveraging the information collected at high mass resolution, a refined quantitative method was adapted to unit mass resolution triple quadrupole mass spectrometry for selective, high throughput analysis of NAs in water. This was applied to 28 real-world samples containing NAs/NAFCs previously analyzed using SPE-HRMS with good agreement (slope = 0.80; R2 = 0.76) between the two methods. In future work, efforts will be made to “detune” the sensitivity of CP-MIMS (e.g., less membrane surface area; acceptor phase dilution) to allow for direct analysis of OSPW samples without dilution. Alternative, lower cost detectors (e.g., IR) will also be explored for measurement of [NA]T without DOM or NAFC interference in the membrane permeate.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations10040228/s1, Text S1: Data processing for membrane partitioning of model NAs, Figure S1. Structures of model compounds shown employed to evaluate membrane permeability, Figure S2. Schematic overview of experimental workflow and data processing to evaluate permeability of model NAs/NAFCs, Figure S3. Measured membrane partition coefficient (K′pdms) vs. calculated KOW by EPISuite [36], Figure S4. Schematic Overview of experiments evaluating composition OSPW both with (green) and without (red) membrane clean-up, Figure S5. O2 class distribution for two environmental samples analyzed by SPE-Orbitrap (A,C) and CP-MIMS (B,D), Figure S6. Calibration curve for 2018 OSPW extract of NAs by CP-MIMS with a unit mass resolution quadrupole mass spectrometer, Figure S7. Relative calibration slope (%) using the developed QqQ method versus proportion of O2-NAs by direct infusion Orbitrap HRMS, Figure S8. Schematic overview of experimental workflow and data workup for quantitative analysis of real-world samples by CP-MIMS, Figure S9. Comparison of quantitation using the “exclusion list” and “inclusion list” CP-MIMS methods, Figure S10. Comparison of unweighted quantitative results derived from solid-phase extraction high-resolution mass spectrometry and CP-MIMS paired to a nominal mass instrument, Table S1: Summary of m/z included in the “inclusion list” strategy for OSPW-NAs calibration by CP-MIMS, Table S2: Class composition for direct infusion and membrane permeate across 4 OSPW extracts, Table S3. Relative calibration slope for various NA mixtures using CP-MIMS with a unit mass resolution quadrupole-MS, Table S4, Evaluation of O2 contribution to signal intensity at nominal mass resolution for an average of the 4 OSPW extracts, Table S5. Summary of quantitative data for archived samples measured by SPE-HRMS and CP-MIMS with a unit mass resolution quadrupole MS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M., I.J.V.M., J.V.H. and E.T.K.; formal analysis, J.M.; funding acquisition, J.V.H., C.G.G. and E.T.K.; investigation, J.M., D.S., I.J.V.M. and K.M.P.; methodology, J.M., D.S., C.G.G. and E.T.K.; project administration, J.V.H. and E.T.K.; resources, I.J.V.M., K.M.P., J.V.H., C.G.G. and E.T.K.; software, J.M.; supervision, J.V.H., C.G.G. and E.T.K.; writing—original draft, J.M.; writing—review and editing, J.M., D.S., I.J.V.M., K.M.P., J.V.H., C.G.G. and E.T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by an infrastructure grant from the Canada Foundation for Innovation/British Columbia Knowledge Development Fund (32238 and 40274), an NSERC RGPIN-2022-05349 (E.T.K.), and graduate CGS-D scholarship (J.M.). Project funding was provided by the Office of Energy Research and Development.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Vancouver Island University and the University of Victoria for the ongoing support of graduate/undergraduate students as well as infrastructure support for the AERL. The authors thank J. Hawkes for providing the MatLab script for the formulae assignment. We kindly thank Ashley Mahaffey, Dani Degenhardt, Jason Ahad, and Danna Schock for sample collection under the Oil Sands Monitoring Program.
Conflicts of Interest
Chris G. Gill and Erik T. Krogh hold patent #US 9583,325 issued to none. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goverment of Alberta. Oil Sands Facts and Statistics; Goverment of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alberta Energy Regulator. State of Fluid Tailings Management for Mineable Oil Sands; Alberta Energy Regulator: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, E.W. Process water treatment in Canada’s oil sands industry: I. Target pollutants and treatment objectives. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 7, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, J.V.; Peru, K.M.; Barrow, M.P. Advances in mass spectrometric characterization of naphthenic acids fraction compounds in oil sands environmental samples and crude oil--A review. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripmeester, M.J.; Duford, D.A. Method for routine “naphthenic acids fraction compounds” determination in oil sands process-affected water by liquid-liquid extraction in dichloromethane and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, M.N.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Huang, R.; Yang, L.; How, Z.T.; Klamerth, N.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Hughes, S.A.; Brown, C.; Mahaffey, A.; et al. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy as a surrogate tool for the quantification of naphthenic acids in oil sands process water and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry–Continuous, Direct and Online Measurements in Complex Samples. In Advances in the Use of Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)-Instrumentation Developments and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 173–203. [Google Scholar]
- Termopoli, V.; Piergiovanni, M.; Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V.; Cruz Muñoz, E.; Gosetti, F. Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry: A Direct Alternative to Fully Exploit the Mass Spectrometry Potential in Environmental Sample Analysis. Separations 2023, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- LaPack, M.A.; Tou, J.C.; Enke, C.G. Membrane mass spectrometry for the direct trace analysis of volatile organic compounds in air and water. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandergrift, G.W.; Monaghan, J.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Direct Analysis of Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil and Aqueous Samples Using Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Low-Energy Liquid Electron Ionization. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandergrift, G.W.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Direct, Isomer-Specific Quantitation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils Using Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry and Chemical Ionization. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15480–15488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandergrift, G.W.; Lattanzio-Battle, W.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry with In Situ Liquid Reagent Chemical Ionization in a Liquid Electron Ionization Source (CP-MIMS-LEI/CI). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.; Jaeger, A.; Agua, A.R.; Stanton, R.S.; Pirrung, M.; Gill, C.G.; Krogh, E.T. A Direct Mass Spectrometry Method for the Rapid Analysis of Ubiquitous Tire-Derived Toxin N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine Quinone (6-PPDQ). ES T Lett. 2021, 8, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, K.D.; Letourneau, D.R.; Vandergrift, G.W.; Jobst, K.; Reiner, E.; Gill, C.G.; Krogh, E.T. A semi-quantitative approach for the rapid screening and mass profiling of naphthenic acids directly in contaminated aqueous samples. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, K.D.; Richards, L.C.; Monaghan, J.; Simair, M.C.; Ajaero, C.; Peru, K.M.; Friesen, V.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V.; Gill, C.G.; et al. Direct analysis of naphthenic acids in constructed wetland samples by condensed phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, J.; Richards, L.C.; Vandergrift, G.W.; Hounjet, L.J.; Stoyanov, S.R.; Gill, C.G.; Krogh, E.T. Direct mass spectrometric analysis of naphthenic acids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters impacted by diluted bitumen and conventional crude oil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.J.; West, C.E.; Jones, D.; Scarlett, A.G.; Frank, R.A.; Hewitt, L.M. Steroidal aromatic ‘naphthenic acids’ in oil sands process-affected water: Structural comparisons with environmental estrogens. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9806–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marentette, J.R.; Frank, R.A.; Bartlett, A.J.; Gillis, P.L.; Hewitt, L.M.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Brunswick, P.; Shang, D.; Parrott, J.L. Toxicity of naphthenic acid fraction components extracted from fresh and aged oil sands process-affected waters, and commercial naphthenic acid mixtures, to fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, K.D.; Hawkes, J.A.; Berg, M.; Clarijs, B.; Gill, C.G.; Bergquist, J.; Lanekoff, I.; Krogh, E.T. Membrane Sampling Separates Naphthenic Acids from Biogenic Dissolved Organic Matter for Direct Analysis by Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandergrift, G.W.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Polymer Inclusion Membranes with Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry (CP-MIMS): Improved Analytical Response Time and Sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5629–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.; Xin, Q.; Aplin, R.; Jaeger, A.; Heshka, N.E.; Hounjet, L.J.; Gill, C.G.; Krogh, E.T. Aqueous Naphthenic Acids and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Meso-Scale Spill Tank Affected by Diluted Bitumen Analyzed Directly by Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.A.; Mahaffey, A.; Shore, B.; Baker, J.; Kilgour, B.; Brown, C.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Bailey, H.C. Using ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry and toxicity identification techniques to characterize the toxicity of oil sands process-affected water: The case for classical naphthenic acids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3148–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, V.V.; Liber, K.; MacKinnon, M.D. Isolation and characterization of naphthenic acids from Athabasca oil sands tailings pond water. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaero, C.; Peru, K.M.; Simair, M.; Friesen, V.; O’Sullivan, G.; Hughes, S.A.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Fate and behavior of oil sands naphthenic acids in a pilot-scale treatment wetland as characterized by negative-ion electrospray ionization Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, K.D.; McCauley, E.P.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Characterization of a condensed-phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry (CP-MIMS) interface using a methanol acceptor phase coupled with electrospray ionization for the continuous on-line quantitation of polar, low-volatility analytes at trace levels in complex aqueous samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, J.A.; D’Andrilli, J.; Agar, J.N.; Barrow, M.P.; Berg, S.M.; Catalán, N.; Chen, H.; Chu, R.K.; Cole, R.B.; Dittmar, T.; et al. An international laboratory comparison of dissolved organic matter composition by high resolution mass spectrometry: Are we getting the same answer? Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 2020, 18, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, K.D.; Vandergrift, G.W.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Ionization suppression effects with condensed phase membrane introduction mass spectrometry: Methods to increase the linear dynamic range and sensitivity. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Meulen, I.J.; Schock, D.M.; Parrott, J.L.; Simair, M.C.; Mundy, L.J.; Ajaero, C.; Pauli, B.D.; Peru, K.M.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V. Transformation of bitumen-derived naphthenic acid fraction compounds across surface waters of wetlands in the Athabasca Oil Sands region. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.W.; Pawliszyn, J. Detection of substituted benzenes in water at the pg/ml level using solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 1992, 625, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscaini, E.; Alexander, M.L.; Prazeller, P.; Märk, T.D. Investigation of fundamental physical properties of a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membrane using a proton transfer reaction mass spectrometer (PTRMS). Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 239, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peru, K.M.; Thomas, M.J.; Palacio Lozano, D.C.; McMartin, D.W.; Headley, J.V.; Barrow, M.P. Characterization of oil sands naphthenic acids by negative-ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: Influence of acidic versus basic transfer solvent. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, D.R. Rapid Quantitative and Qualitative Screening of Naphthenic Acids in Contaminated Waters Using Condensed Phase Membrane Introduction Mass Spectrometry. Chemistry. Master’s Thesis, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2016; pp. 1–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zarkovic, T.M.; Borden, S.A.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. A passive membrane system for on-line mass spectrometry reagent addition. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchik, K.A.; MacLennan, M.S.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Chen, D.D.Y. Standard method design considerations for semi-quantification of total naphthenic acids in oil sands process affected water by mass spectrometry: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemspider. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2022. Available online: https://www.chemspider.com/DatasourceDetails.aspx?id=186 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).