Abstract
The present study deals with the adsorptive removal of Escherichia coli (E. coli) by making use of chitosan-silica/calcium carbonate (CS-SiO2/CaCO3) nanocomposites (NCs) where it was synthesized using the waste eggshells and rice husks occurred by natural sources. The bioadsorbent CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs were synthesized by incorporating eggshell-CaCO3 nanoparticles (NPs) and rice husk-SiO2 NPs in chitosan NPs solution. The adsorbents were characterized using HRTEM, BET, DLS, and TGA. The characterization of NCs revealed the formation of adsorbents in the range of 10–50 nm and some structural changes to the spectra of adsorbents before and after the adsorption of E. coli was revealed by the FTIR analysis. Moreover, the adsorption efficiency of E. coli over the adsorbents after 35 min of incubation was about 80% for CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs. Further, the kinetics of adsorption studies were observed to be well-fitted to the Langmuir isotherm model with an adsorption capacity of 3.18 × 101 (CFU E. coil per gram of CS-SiO2/CaCO3). From the analysis, the synthesized bioadsorbent demonstrated the potential for ameliorating the inherent risk of pathogens in water.
1. Introduction
Bacterial interactions onto the surfaces of nanomaterials were reported to be governed by several mechanisms ranging from the bridging of surface macromolecules by steric effects to direct bond formation between the macromolecules at the cell surface or with the functional groups of the nanomaterials [1]. According to Oh et al. [2], the adhesive forces between the substrate and bacterium could also arise through van der Waals and electrostatic double-layer interaction. These key features/mechanisms are utilized to engineer nanomaterials with tailored properties that can be very much efficient for the adsorption of bacteria in water [3,4,5]. Despite the indispensability of water, the intermittent water supply system and operating systems, especially in developing economies, have created a window through which pathogens and other pollutants sipped through broken pipelines to the end user point of collection. Study shows that water quality for drinking purposes easily get compromised due to the induction of pollutants across the distribution pipelines, thus increasing the bacterial counts in the water samples at the consumer points [6]. The irregular or intermittent piped water supply according to the study serves as a causative medium for the presence of Escherichia coli (E. coli) in the water channels, thereby increasing the risk to public health. Several efforts were made to mitigate the induction of pollutants in public water sources through the implementation of various filtration/purification processes as the commonly used disinfectants such as chlorine, chloramines, and ozone by themselves are health-risk promoters [7]. Other methods such as reverse osmosis, chemical oxidation, membrane filtration, coagulation and flocculation, activated sludge, ozonation, precipitation, electro-dialysis, ion exchange, and electrochemical techniques besides being expensive methods, generate excess sludge [8].
The adsorption methods in a more practical sense were considered efficient compared to the aforementioned, reported to demonstrate effective adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solutions using chitosan-bentonite composite beads [9]. The interaction of microorganisms with carbon-based adsorbents [10], gold (Au) nanoparticles (NPs) [11], metal oxides [12], magnetic particles [1,13], and silicon carbides [14] were also reported. Although carbon-based materials are widely considered excellent adsorbents, drawbacks include the cost of regeneration, the intra-particulate resistance in the adsorption process, their low thermal stability, and their sensibility to the presence of moisture and impurities suffice [15]. The methods involving AuNPs, metal oxides, and magnetic particles are however observed to consist of issues related to the high cost of processing, often involving mechanical and chemical reduction processes [1]. Further studies involving zeolites [16], clay minerals [17], quartz, hematite, and other minerals [18] were also reported. These materials are low-cost, widely available, and possess cation exchange capacity. However, their adsorption properties were reported to depend strictly on the crystal-chemical, reactivity, adsorption capacity, and surface area. According to Zhang et al. [19], they are still endowed with great possibilities for modification through various methods. The adsorption methods were also used by Borkowski et al. [14] to adsorb E. coli onto silica-carbides synthesis using the combustion route. These routes were however observed to involve a series of steps and feeds consisting of synthetic chemicals.
In addition to several agricultural wastes, the adsorption behavior of eggshells (ES) were also reported by some researchers [12,20]. Chicken eggs with a global waste generation of 2.8 million tonnes in 2018 as reviewed by Ahmed et al. [21] are utilized as feeds for many important applications such as used as a tool to remove Direct Blue from wastewater [8]; when doped with TiO2, is for the photodegradation of methylene blue from synthetic wastewater [22]; deployed in the synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle (HAP) by chemical precipitation methods as an adsorbent for cephalexin (Ceph) antibiotic removal from aqueous solutions [23]. Similarly, RH as a cheap agricultural waste were also used as an excipient to prepare Rose Bengal-impregnated rice husk nanoparticles (RB-RH NPs) as photosensitizers to obtain efficient 1O2 generation [24]. Magnetic mesoporous silica (MMS) from RH ash were also reported by Li et al. [25], to remove aflatoxin B1 in an oil system. A recent study used eggshell powder as a carrier to enhance the antimicrobial activities of low-dose AgNPs against foodborne pathogens, and reported to enable 5-log reductions of Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua within 25 min and 60 min of treatments [26]. However, the study was narrowed to investigating the inhibitory effect of the low-dose AgNPs against foodborne pathogens. Eggshells blended with sheep bone were used to establish the minimum bacterial concentration and minimum inhibitory concentrations of nano-hydroxyapatite (NHA/Es) prepared by a sol–gel approach against four Gram-negative bacteria [27]. Sulfate-calcined eggshells were also reported to be effective in the adsorption of pathogenic bacteria and antibiotic-resistance genes in bacteria-contaminated landfill leachates [12].
In related efforts, Bashir and co-workers [28] prepared copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) incorporated into bagasse and rice husk for the removal of E. coli from synthetic water. Though the material as reported by the authors leads to 100% removal efficiency at a contact time of 100–120 min, the study was however limited to the efficacy on the quality of treated water in line with the existing environmental standard. Similarly, SiO2 NPs with a particle size of 60–80 nm were produced by sol–gel method and examined for their photocatalysts and antimicrobial activities. The number of coliform bacteria estimated in the untreated and treated SiO2 NPs was reported at 170 CFU/100 mL and 10 CFU/100 mL, respectively, with bacterial growth inhibition of 94.12% [29]. Furthermore, carbon/silica composites derived from rice husk waste (C/SiO2) composite doped with varying amounts of silver were reported by Unglaube et al. [30] as effective antimicrobial agents. These studies as reported by the various authors [29,30] were narrowed to the discussion of the antimicrobial efficacy of the materials, the adsorption processes, and the NPs-bacteria interaction mechanism were not fully elaborated. A novel core−shell nanomaterial, ZnO@SiO2, based on rice husk was reported to remove about 91% of E. coli [31]. In the same vain, as observed in the study, the adsorption isotherms were only discussed relative to the drug amoxicillin.
As discussed above, the RH and ES as feeds material for the synthesis of silica and calcium carbonate allow for an inexpensive production cost and support the circular efforts to improve the economy through efficient waste management strategies [32]. A previous study involving the use of silica calcium carbonate (SiO2/CaCO3) nanocomposite derived from semi-burned rice straw ash was carried out to improve the oil absorption capacity of a modified papermaking filler [33]. Similarly, a biopolymer matrix derived from crustaceans and rice husk-based silica was reported to efficiently increase the adsorption practical aspect of the materials for the removal of impurities from crude biodiesel [32]. Similar composites consisting of biopolymer-based SiO2/CaCO3 were also reported to remove phenol from water [34]. Thus, this present study utilized these aforementioned characteristics to prepare chitosan (CS)-based SiO2/CaCO3 derived from waste eggshells (ESCaCO3), and rice husk (RHSiO2) to investigate their adsorption processes and mechanism of interaction against E. coli using various models, and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The ability of E. coli to induce infection even at a very low dose, relative to its antibacterial resistance, in addition to its relative simplicity, inexpensiveness, and fast high-density cultivation [35], informed the choice of using E. coli against other bacteria strains for this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
The waste eggshells (ES) and rice husks (RH) used for the study were obtained from local fast-food restaurants in Mubi, Adamawa state Nigeria. The E. coli culture (ATCC-25922) was obtained from the Department of Microbiology, Adamawa State University Mubi. Low-molecular-weight chitosan (CS; 75%–85% degree of deacetylation) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). All other reagents, chemicals, and solvents were purchased from BDH Chemical Ltd. (Poole, UK).
2.2. Preparation of Adsorbents
For the preparation of adsorbents, we followed the sequential steps as described in Bwatanglang et al. [34]. The rice husk (RH) collected was first subjected to acid pretreatment using HCl: H2SO4 (10:30 wt%) followed by subsequent washing with H2O2 (30% v/v) at 70 °C for 60 min and the formed slurry was rinsed with distilled water and oven-dried. The RH-derived sodium silicate (RH-Na2SiO3) was prepared by dispersing in an aqueous 0.5 M NaOH solution the sieved RH under vigorous stirring for an hour. To prepare the RH-silicate (RHSiO2), the obtained RH-Na2SiO3 is subjected to 12 wt% H2SO4 under vigorous stirring for 15 min, washed in water, and aged in ethanol at 60 °C for 60 min. Further rinsed in water and dried under ambient temperature. The proteins denatured chicken ES powdered samples dispersed in distilled water were subjected to sonication, oven-dried at 600 °C for 3 h, and sieved using a 40–75 µm to form the ES-calcium carbonate (ESCaCO3) particles. An aqueous solution of the ESCaCO3 particles (5 wt%) was subjected to vigorous stirring at 3000 rpm for 30 min to form the ESCaCO3 NPS. The composite mixture of SiO2/CaCO3 particles was prepared in an aqueous solution of ESCaCO3 (with 5 wt%) in 20 mL of 1 g of RHSiO2 (20 mL/g) added gradually under heating at 80 °C and under stirring for 60 min. Dropwise addition of the aqueous RHSiO2/ESCaCO3 (1 g/20 mL) solution into chitosan (CS) suspensions (0.1 g in 10 mL of 1% acetic acid) under stirring for 30 min. The precursor was incubated at 60 °C for 3 h, centrifugation, and further allowed to age in 2.0 M NaOH solution for 2 h, washed using distilled water, and filtered to obtain the Bio-based CS-SiO2/CaCO3 nanocomposites.
2.3. Bacterial Adsorption Studies
The adsorption study of RHSiO2, ESCaCO3, and the bio-based NC of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 was investigated against E. coli where the bacterial cell line was cultured in nutrient broth (NB) media and incubated at 35 °C under continuous shaking conditions at 100 rpm for 24 h [1]. For the kinetic studies, a suspension of E. coli solution with an initial concentration of 2 × 105 CFU/mL (CFU: colony forming unit) was prepared. The UV absorbance with λmax = 260 nm was noted for E. coli. For the analysis, 5 mL of E. coli solution was added to 15 mL of adsorbent-water suspension (0.2 g/mL), and allowed to stir at 120 rpm under incubation at room temperature. At a predetermined time of 5–35 min, 1 mL of the bacterial/NPs suspension was withdrawn and the number of adsorbed E. coli was calculated [20]. The percentage removal efficiency of E. coli and the amount adsorbed over the adsorbent were determined from the equation where Ci and Ce are the initial and the equilibrium concentrations of E. coli (CFU mL−1). The uptake capacity (CFU g−1) of the sorbents for each concentration of E.coli at equilibrium was determined from the equation where V is the volume of the solution in L, while M is the mass of the biosorbent (g). The adsorption kinetics were determined using the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The pseudo-first-order kinetic model was determined using where K1 (CFU/g min) is the rate constant, qe (CFU/g) is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium, and qt (CFU/g) is the adsorption capacity at time t. The slope of the Log (qe − qt) vs. t was used for the determination of the equilibrium rate constant K1. The pseudo-second order kinetic was determined using The rate constant (K2) and qe are calculated from the intercept and slope of the plot of t/qt vs. t [34].
The adsorption behavior was analyzed using the Langmuir isotherms models, the Freundlich isotherm model, and the Dubinin–Radushkevich model [36,37,38]. The Langmuir isotherms models were determined from the equation where qe is the amount adsorbed at equilibrium (mg/g), Ce is the equilibrium concentration of the adsorbate, and qm and Ke are the Langmuir constants related to the maximum adsorption capacity and the energy of adsorption, respectively. These constants are evaluated from the intercept and slope of the linear plot experimental data of Ce/qe versus Ce. The following relation gives the linear form of the Freundlich isotherm model , where Kf and 1/n are the Freundlich constants related to adsorption capacity and adsorption intensity of the adsorbent. The values of Kf and 1/n were derived from the intercept and slope of the linear plot of Logqe versus LogCe. The dimensionless constant (separation factor, RL) taken from the Langmuir isotherm was estimated from the equation RL = 1/[KL Ci + 1], where Ci is the initial concentration and KL the concentration of Langmuir. If RL = 0, the adsorption is irreversible, is favorable when 0 < RL <1, linear when RL = 1, and unfavorable when RL >1. The Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model is generally applied to express the adsorption process that occurred onto both homogeneous and heterogeneous surfaces represented by the equations where 𝜖 is Polanyi potential, qm is the saturation capacity of the isotherm (mg g−1). The isotherm constants qm and Dubinin–Radushkevich constant are obtained from the intercept and the slope, respectively, from plotting on the ordinate lnqe and the ε2 on the abscissa. The constant gives the mean of the free energy, EDR is the adsorption per molecule of the sorbate when it is transferred to the surface from infinity in the solution and can be calculated using the following relationship [38].
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
In this study, different instruments were used at various stages of analysis to characterize the prepared samples. The surface analysis of the prepared RHSiO2, ESCaCO3, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs were established using the BET (Brunauer–Emmett-Teller) instrument, and the analyses were conducted on Micro-meritics Tristar II Plus (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) by using N2 adsorption at 77 K. The identification of functional groups was determined from the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy using PerkinElmer (Waltham, MA, USA. N3895). The morphology and particle were studied using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) on a Tecnai G2 F20 instrument (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA). Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were performed on the Malvern Nano series, Zetasizer instrument (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) to determine the particle diameter in the solution phase. The thermographic analysis (TGA) was conducted on a TG 7 PerkinElmer instrument at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 in a nitrogen atmosphere and the weight losses up to 600 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Studies
The objective of this study was to investigate the adsorption potentials toward E. coli of as-synthesized biopolymer composites consisting of SiO2/CaCO3 NPs derived from waste eggshell (ES) and rice husk (RH). The formed SiO2/CaCO3 was further functionalized using low molecular weight chitosan (CS) to form the CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs. The blend with CS was to enhance the biocompatibility and adsorption sites of the constructs for multiple functionalities.
3.1.1. HRTEM and Particle Size Analysis
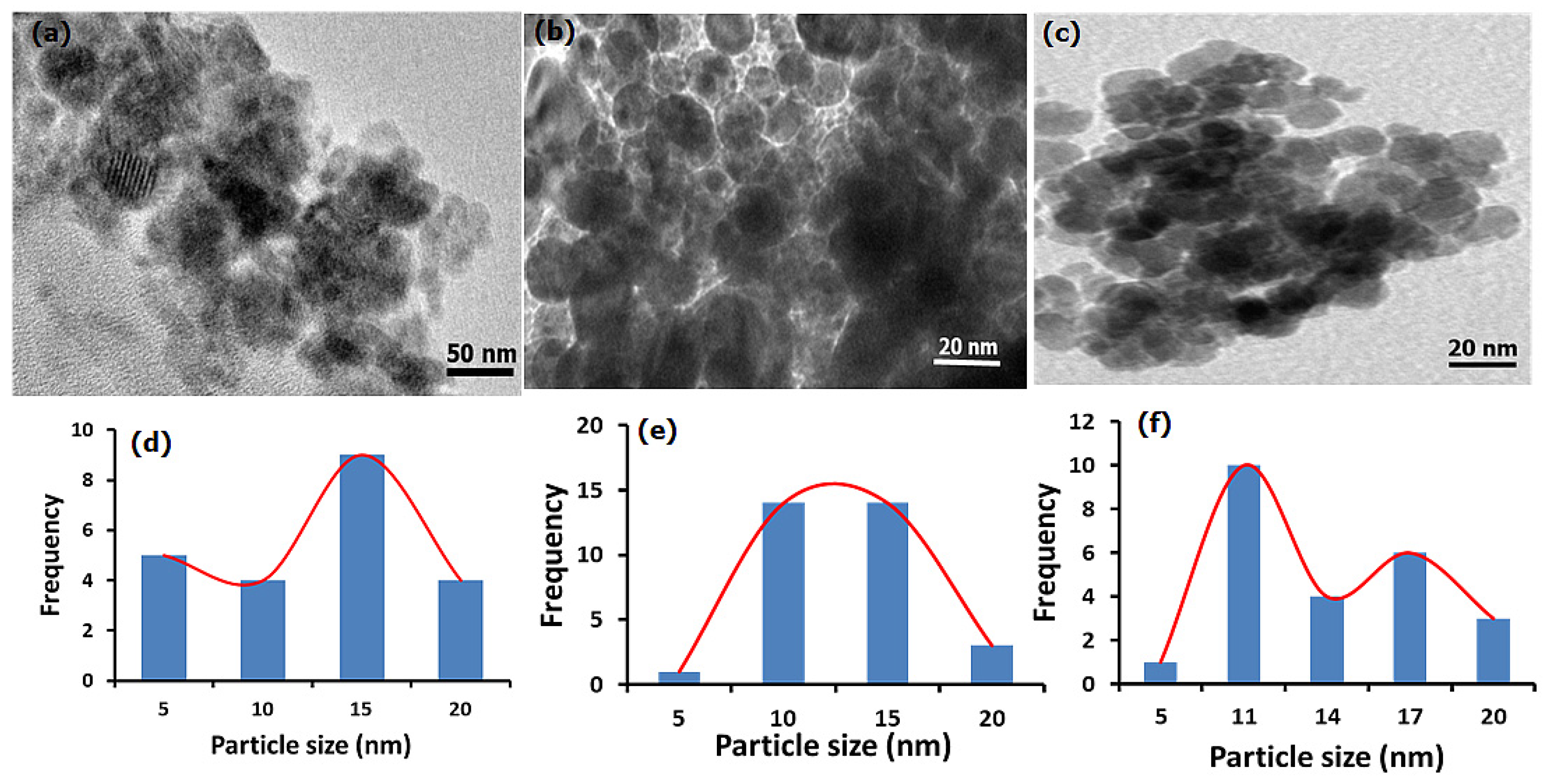
The morphology of as-synthesized samples is displayed in Figure 1. The ESCaCO3 sample produced in the first step shows an agglomerated and irregular morphology (Figure 1a) with particle sizes ranging from 5–17 nm and a mean of 11.93 ± 4.05 nm (Figure 1d). The morphology of the same sample as revealed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis shows an irregular surface structure with a random assembly of aggregated grains that form a densely packed structure but with size distribution up to 100 nm [34]. The study by Morsy et al. [33] reported the formation of rhombohedral nano-CaCO3 core particles with a particle size of 30–70 nm. ESCaCO3 NPs with an irregular surface structure and a size distribution of ~200 nm and 89 nm were also reported by Minakshi et al. [39] and Ahmad et al. [40] respectively. The micrograph in Figure 1b revealed a relatively spherical nanostructure of RHSiO2 of varying sizes ranges from 5–18 nm with a size of 11.18 ± 3.19 nm on average (Figure 1e). In the previous study, the SEM micrograph shows nearly spherical densely packed grains with an average particle size of 19.07 ± 4.63 nm [34]. Morsy et al. [33] prepared and reported narrow-size silica NPS from RH that are spherical with particle sizes ranging from 20–30 nm. In another study, Le et al. [41] reported uniformly dispersed spherical silica NPs derived from Vietnamese RH with an average particle size of 3 nm. A similar study was also reported by Phoohinkong and Kitthawee, [42].
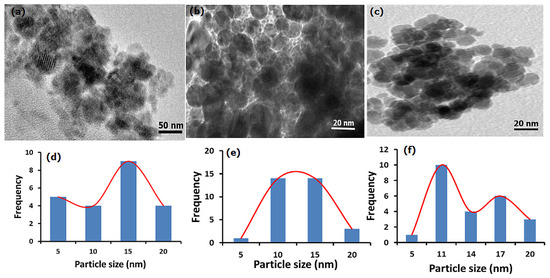
Figure 1.
Comparison of HRTEM morphology (a–c) and the corresponding size distributions (d–f) for the samples of ESCaCO3 NPs, RHSiO2 NPs, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs respectively.
The result as displayed in Figure 1c shows some irregular and near-spherical agglomerated morphology than those of the single ESCaCO3 particles. The SiO2/CaCO3 NPs-incorporated CS shows a mean particle size of 12.69 ± 4.05 nm (Figure 1f). The dispersion of SiO2/CaCO3 into CS suspension slows down the agglomeration to give relatively agglomerated spherical morphology. Besides its influence in preventing self-aggregation, the polymeric matrices were incorporated to promote cell adhesion, biocompatibility, and cellular uptake of NPs and their conjugates [43,44].
3.1.2. DLS and TGA Studies
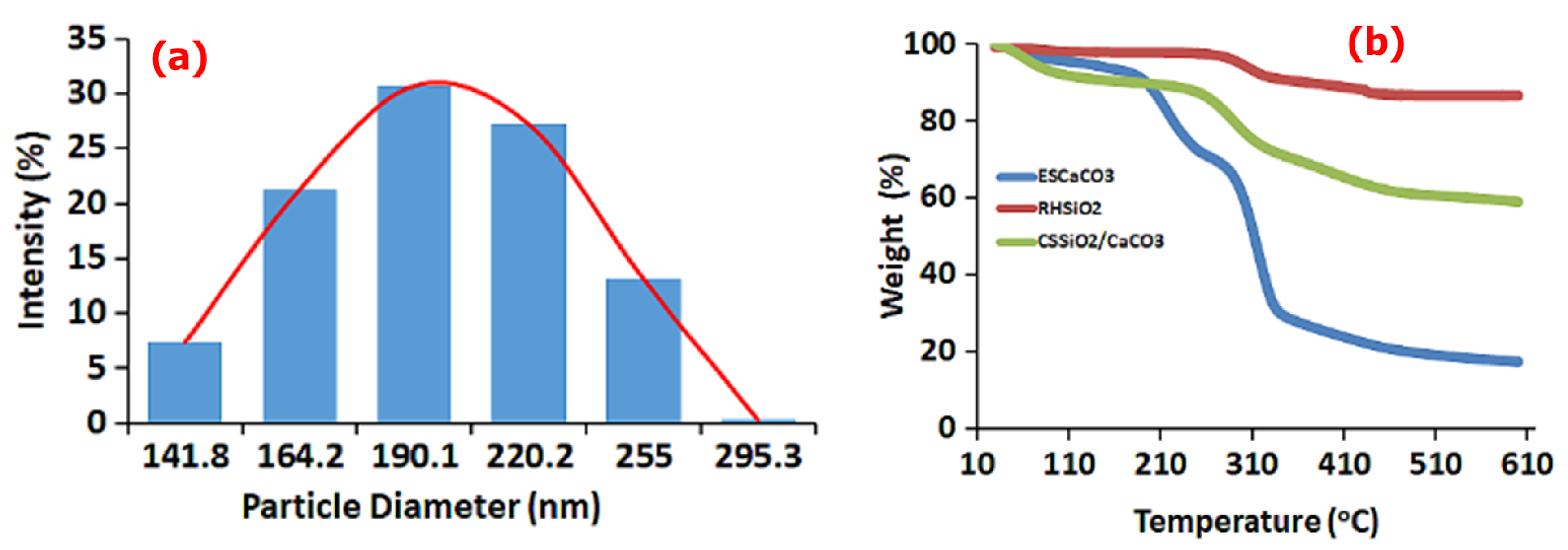
In caparison to the particle size from the HRTEM, the DLS analysis of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs (as presented in Figure 2a), due to the formation of a hydration layer show a hydrodynamic size of about 211 nm, suggesting appreciable colloidal stability of the particles in liquid suspension [45]. Further, the thermal behavior of as-formed CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs along with RHSiO2 and ESCaCO3 NPs are presented in Figure 2b. From the TGA spectra, the ESCaCO3 shows slight endothermic events from occluded water molecules in the temperature range of 50–190 °C, and other events around 140–261 °C which could be from the endothermic events associated with the decomposition of CaCO3 up to 485 °C. The RHSiO2 shows an endothermic event from 262–458 °C without any obvious events of the physiosorbed molecules [46,47]. The CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs however show a slight endothermic event due to the occluded water from 30–149 °C or associated events from CS [48], followed by an event around 258–480 °C probably from the loss of weight due to the decomposition of ESCaCO3 and the carboxylate molecules of CS [49]. The flat line observed up to 600 °C could be from the stability induced by the presence of RHSiO2.
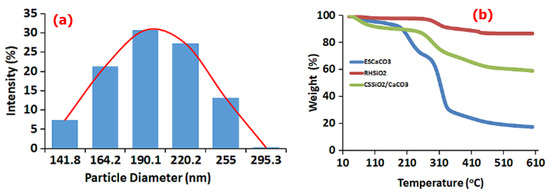
Figure 2.
(a) DLS of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs and (b) TGA analysis of ESCaCO3 NPs, RHSiO2 NPs, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs.
3.1.3. BET Adsorption/Desorption Isotherms
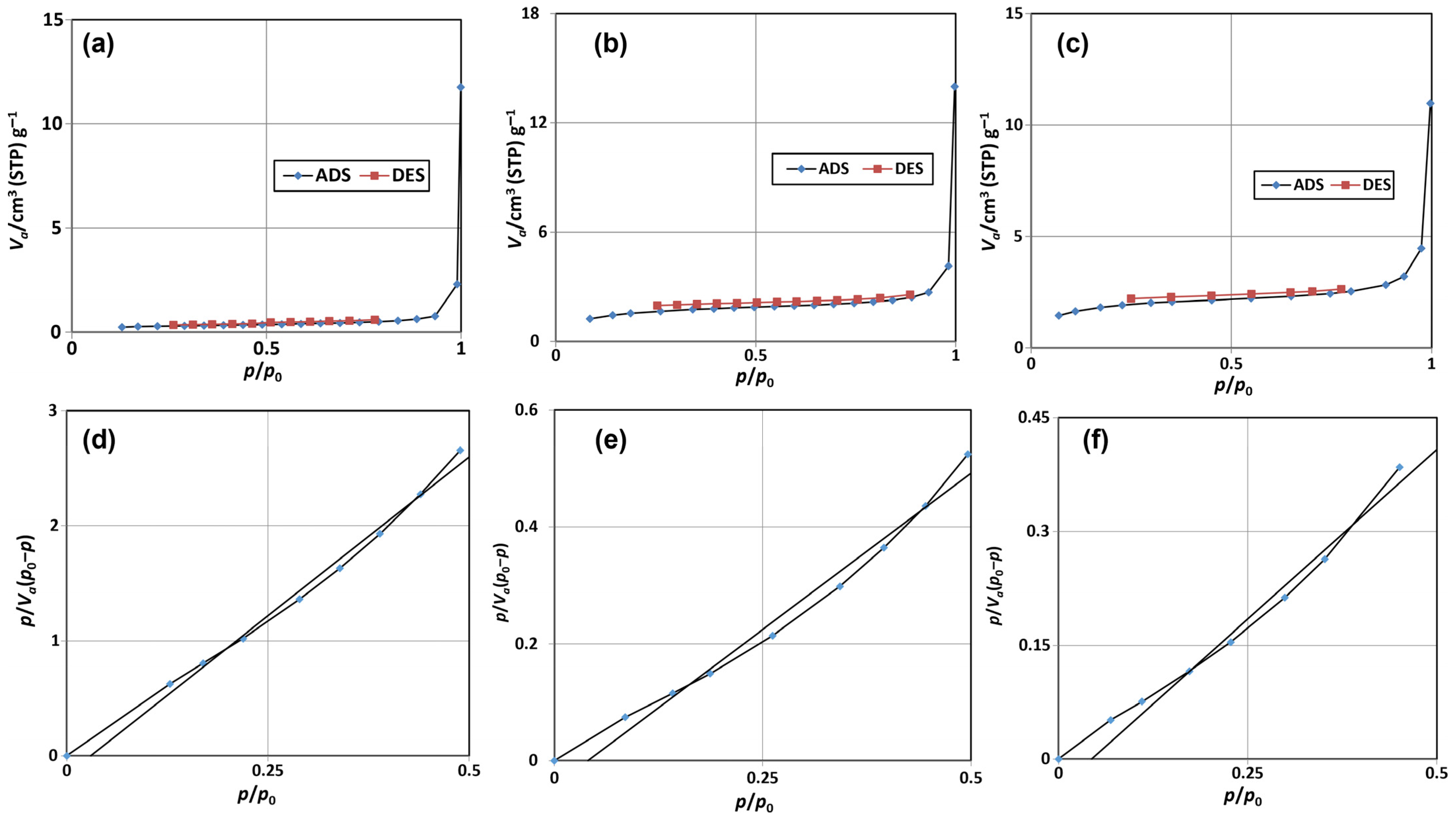
The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms for the ESCaCO3 NPs, RHSiO2 NPs, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 nanocomposites at 77 K are shown in Figure 3a–c. The adsorption/desorption plots show the isotherms are nearly superposed to each other, suggesting the existence of different related adsorption. The study by Ge et al. [50] reported a slightly bent isotherm arising from the superimposition between monolayer coverage and the initial amount of multi-layer adsorption. The almost flat line of the isotherm in this study suggests a nearly complete monolayer coverage and the small onset of successive multilayer formation processes. The lack of clear hysteresis of the adsorption/desorption isotherms represented an unrestricted monolayer-multilayer adsorption, with a small presence of varying pore sizes on the surfaces [51,52], thus putting the materials under Type II isotherm in the Brunauer classification [39]. Similarly restricted accessibility of adsorption to the internal volume and the surface of nonporous materials were also reported by Rahmani et al. [53]. This phenomenon is most obvious for the ESCaCO3 NPs, possibly due to the formation of single-layer or multilayer adsorption on the pore surface, which greatly increases the roughness of the inner surface of the pore and hence a decrease in pore diameter and surface areas is observed. Another possible reason could be the drying temperature used for this study (600 °C). Additionally, the study shows an increase in the BET surface area of ES-based materials (RES) increasing with calcination temperature. In the study, the BET surface area of eggshell NPs reported as 0.56 m2 g−1 increases as eggshell NPs were calcined up to 1000 °C [40].
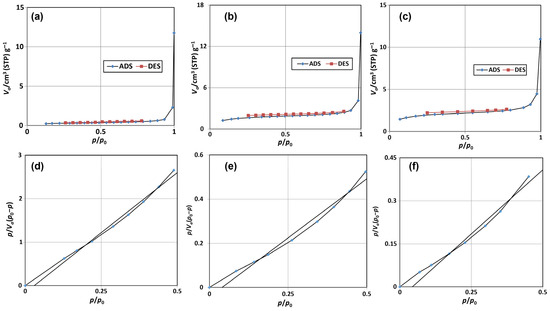
Figure 3.
Comparison of N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms (a–c), and BET isotherm (d–f) of ESCaCO3 NPs, RHSiO2 NPs, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs respectively.
The BET surface area of as-prepared ESCaCO3 NPs (Figure 3d) in this study was 0.81 m2 g−1 and the cumulative pore size diameter and volume are 22.93 nm and 0.0047 cm3 g−1 respectively. For the RHSiO2 NPs (Figure 3e), the BET surface area was 4.94 m2 g−1 with cumulative pore size diameter and volume of 13.69 nm and 0.0145 cm3 g−1 respectively. The SiO2/CaCO3 on surface modification with CS (CS-SiO2/CaCO3) shows an increase in the BET surface area (5.09 m2 g−1) and a reduction in the pore diameter (10.88 nm) (Figure 3f), alluding to the small BET surface area and the reduction in the pore diameter to the occlusion of internal pores by the incorporated CS NPs [54]. Aldahash et al. [54] reported a microporous solid structure of PA-12/PC nanocomposite with a relatively small external surface. The study by Gedam and Dongre [55] suggested a decrease in the porosity and specific surface area of iodate-doped composite to the blockage of internal pores by iodate upon doping with chitosan. The BET values generated in this study show very low BET surface areas (SBET) relative to the pore diameter. This phenomenon could not be far from the acid pretreatment and the temperature employed during the material preparations. The SBET of np-Au samples were reported to steadily decrease as the annealing temperature increased. Moreover, SBET were responsible for the observed increase in the pore diameters, and reduction in the surface area and surface energy. Decreasing the SBET from ~6.4 m2 g−1 to ~1.8 m2 g−1, with corresponding steady contraction of the total pore volume from 0.04 cm3 g−1 to 0.008 cm3 g−1, resulted in annealing temperature increases [56]. In another study, the average pore diameter of SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieve was reported by Bai et al. [57] to increase exponentially with a corresponding decrease in the specific surface area when the hydrothermal temperature increased above 140 °C during the synthesis. An increase in calcination temperature was also reported by Zhang et al. [58] to lead to enlarging pore size, shrinking pore volume, and decrease SBET of 0.5%Al-3%In-TiO2.
3.1.4. Kinetic and Adsorption Study
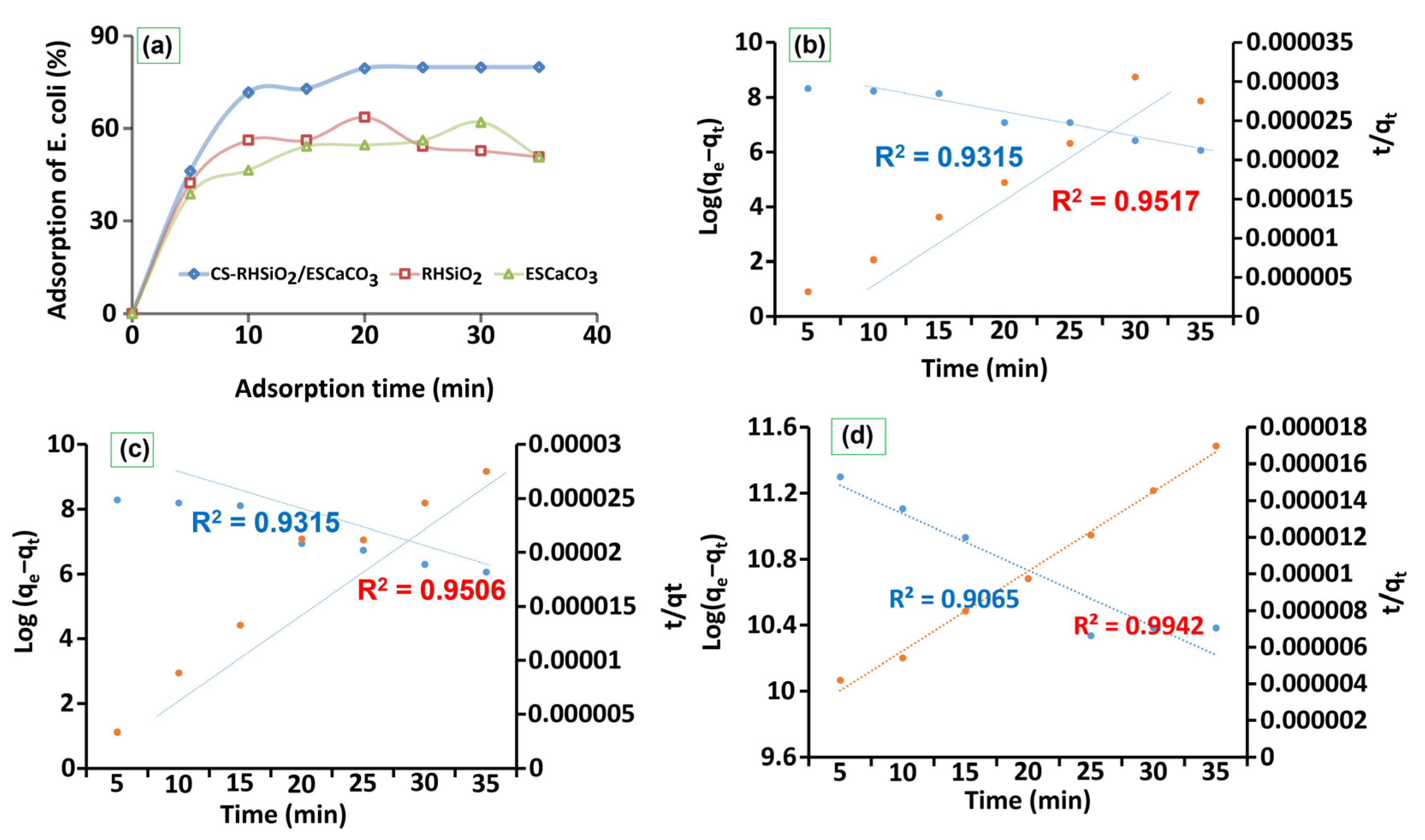
The adsorption study results (provided in Figure 4a) show approximately 50–70% loading of E.coli onto CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs, RHSiO2, and ESCaCO3 NPs and this range was achieved during the first 20 min under room temperature incubation. At the initial 10 min, the availability of more sorption sites resulted in fast adsorption, followed by a slight decrease and fluctuation for RHSiO2 and ESCaCO3 NPs as more and more surface was occupied by the adsorbed E.coli. The results further show more efficient adsorption onto CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs, demonstrating ~80% adsorption compared to the ~51% for the RHSiO2 and ESCaCO3 respectively. The addition of multiple binding sites from the formation of polymer composites increases the charge prevailing potentials and hence the interaction of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs with that of E. coli. As displayed in the adsorption process, the percentage of adsorbed E. coli onto the NPs fluctuated at some points over time. Similarly to this, one of the studies indicates the adsorption of microbes that get gradually fluctuated due to the influence of the hydration layer and steric hindrance [59]. This behavior was not so obvious for the polymer-based composites (CS-SiO2/CaCO3) used in this work. Another study reported high antimicrobial efficacy of E. coli (>90%) in NPs modified by quaternary ammonium compounds [60]. Although the adsorption processes show some semblance of pseudo-first-order for the adsorption of E. coli, the possible interaction mechanisms between the adsorbent and the adsorbate were found to be well-fitted to the pseudo-second-order kinetic models (Figure 4b–d), showing a higher correlation coefficient (R2) compared to the pseudo-first-order. These however suggest that E. coli adsorption may be governed by the homogeneity or the heterogeneity of the adsorption sites [34]. The K2 values, and adsorption capacity (qm) as summarized in Table 1 further suggest the applicability of pseudo-second-order reactions follows the order CS-SiO2/CaCO3 > RHSiO2 > ESCaCO3 NPs. Similar results were also reported by Darabdhara et al. [1] showing pseudo-second order describing the equilibrium of E. coli adsorption onto the Fe3O4B surface.
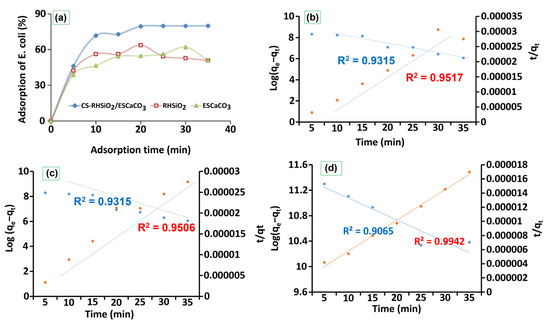
Figure 4.
Comparison of adsorption of E. coli (a), the pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetics of ESCaCO3 NPs (b), RHSiO2 NPs (c), and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs (d) respectively.

Table 1.
Parameters of pseudo–first order, pseudo–second order, Langmuir adsorption isotherm, Freundlich adsorption isotherm, and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs, RHSiO2 NPs, and ESCaCO3 NPs respectively.
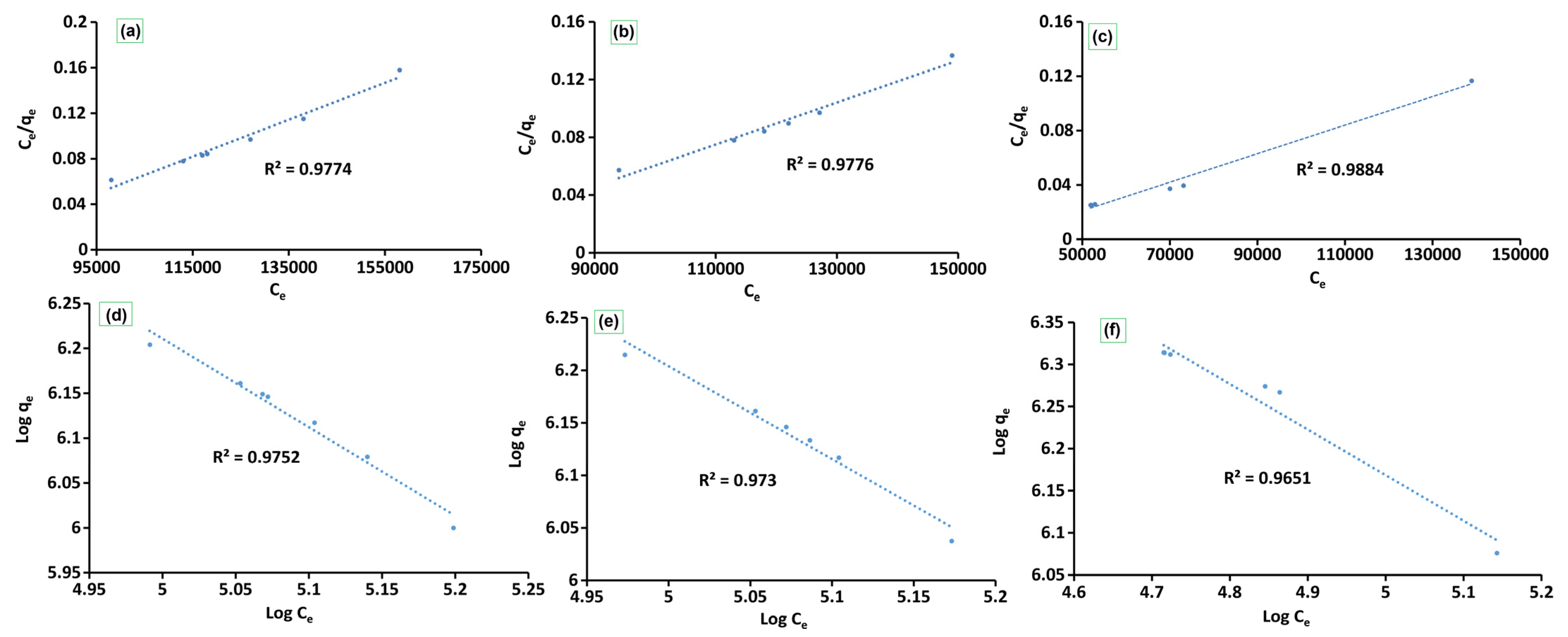
Similarly, the surface adsorption potentials of CS-SiO2/CaCO3, RHSiO2, and ESCaCO3 toward E. coli capturing from aqueous solution are presented in Figure 5a–f and the values are summarized in Table 1. The data show the number of bacteria in the suspension and the number adsorbed onto the sample surface, which fitted well with the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The Langmuir model (Figure 5a–c) showed the correlation coefficients R2 of 0.9884, 0.9776, and 0.980 for the CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs, RHSiO2, and ESCaCO3, respectively, as compared to 0.9651, 0.9730, and 0.9752 for the same adsorbent samples from the Freundlich adsorption (Figure 5d–f) isotherm, respectively. The CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs exhibit higher adsorption capacity (qmax) than the respective capacities of RHSiO2 and ESCaCO3 NPs. The KL of the Langmuir model indicates the affinity of the material toward the bacteria [14] and is observed in the order CS-SiO2/CaCO3 > RHSiO2 > ESCaCO3. The equilibrium parameter (RL) value established for the studied materials further suggests the monolayer coverage processes dominate the adsorption mechanism. Though the KF values from the Freundlich isotherm indicate multilayer adsorption of E.coli by the nanomaterials [34], the negative values of 1/n suggest the possibility of E.coli adhesion and de-adhesion processes in the adsorption mechanism. Creating a situation where the secondary repulsive force between E. coli and the adsorbents overcomes the bridges that connect the bacteria to the adsorbents leads to the deactivation of E.coli that are weakly attached by the electrostatic and van der Waals forces [61]. A situation was observed in the fluctuated adsorption percentage reported earlier in Figure 4a. Furthermore, these results demonstrated that the capability of various materials to adsorb is limited and influenced by their respective BET surface area and the availability of functional groups [62]. The doping of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 by CS enhances the adsorption properties of CS-SiO2/CaCO3, thus improving the surface-binding sites compared to the lower adsorption capacity of RHSiO2 and ESCaCO3 influenced by weak physical forces and low BET surface area.
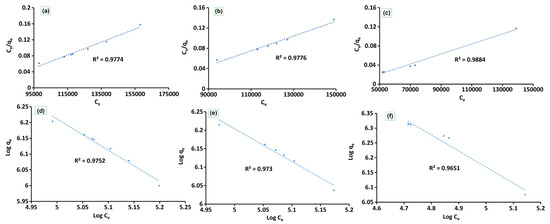
Figure 5.
Comparison of the adsorption isotherm showing, the Langmuir isotherms models of (a–c), and the Freundlich isotherm models (d–f) of ESCaCO3 NPs, RHSiO2 NPs, and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs respectively.
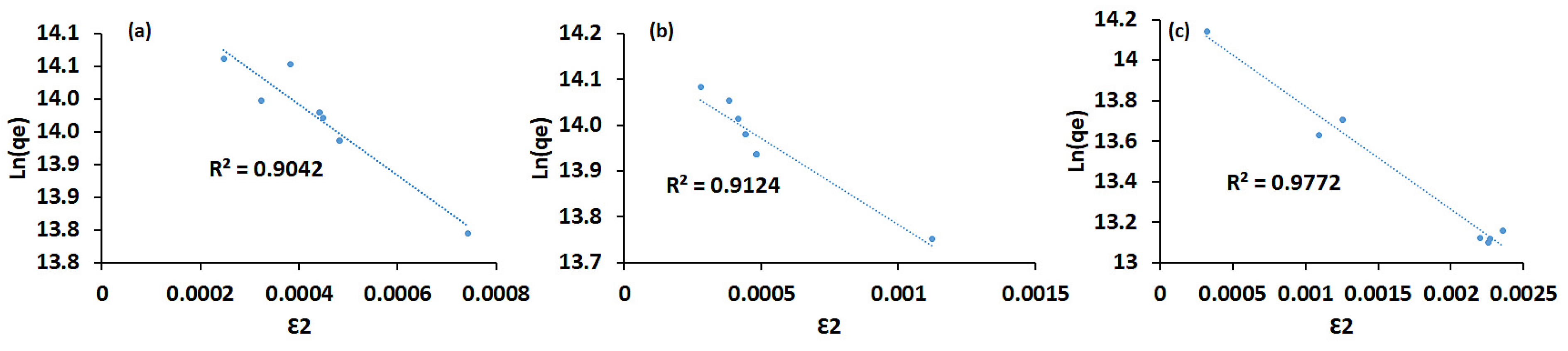
From the D-R model shown in Figure 6, the bio-sorption energy ED-R was calculated to be 3.14 × 10−2, 3.65 × 10−2, and 3.04 × 10−2 kJ mol–1 for the CS-SiO2/CaCO3, RHSiO2, ESCaCO3, respectively. It was suggested that physisorption (nonspecific adsorption) dominates the adsorption of E. coli onto the materials. An ED-R between 8 and 16 kJ mol−1 suggested chemical processes dominating the adsorption, while an ED-R < 8 kJ mol−1 suggests physisorption (nonspecific adsorption) dominates the adsorption processes [9]. Overall, the adsorption processes for the materials investigated in this study suggested Langmuir favored the adsorption of E. coli. Borkowski et al. [14] reported that Langmuir favored adsorption of E. coli onto different silica-based NPs. In another study, ES modified by sulphate/calcined at various temperatures were reported to fit to the Langmuir model. Similarly, silver NPs-loaded silica with the maximum adsorption capacity and R2 values of above 0.9 against E. coli were found to be fitted well with the Langmuir model [63]. The selective biosorption behavior of E. coli toward Pt(IV) and Pd(II) binary solution were also reported by Kim et al. [64] to favor the Langmuir model. In the study by Darabdhara et al. [1], a correlation coefficient of 0.9987 shows Fe3O4B adsorption toward E. coli fitting well into the Langmuir model. A study by Jiang et al. [4] reported changes in IR spectra after clay minerals and iron oxides NP were exposed to bacterial cells. According to Borkowski et al. [14], the adsorption of bacteria onto NPs strongly depended on their structure and functional group’s access to the biological organisms. Similarly, Ca2+ and CO32#x2212; in ESs were found to facilitate the adsorption between the surface pores [65]. The bacteria-silica surface interaction was also reported to be facilitated by the covalent and deformation vibrations of Si–O–Si siloxane bonds [20].
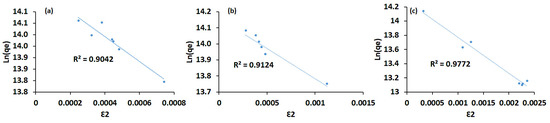
Figure 6.
Comparison of the Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model of ESCaCO3 NPs (a), RHSiO2 NPs, (b) and CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs (c), respectively.
Adsorption Mechanism of E. coli—NPs Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
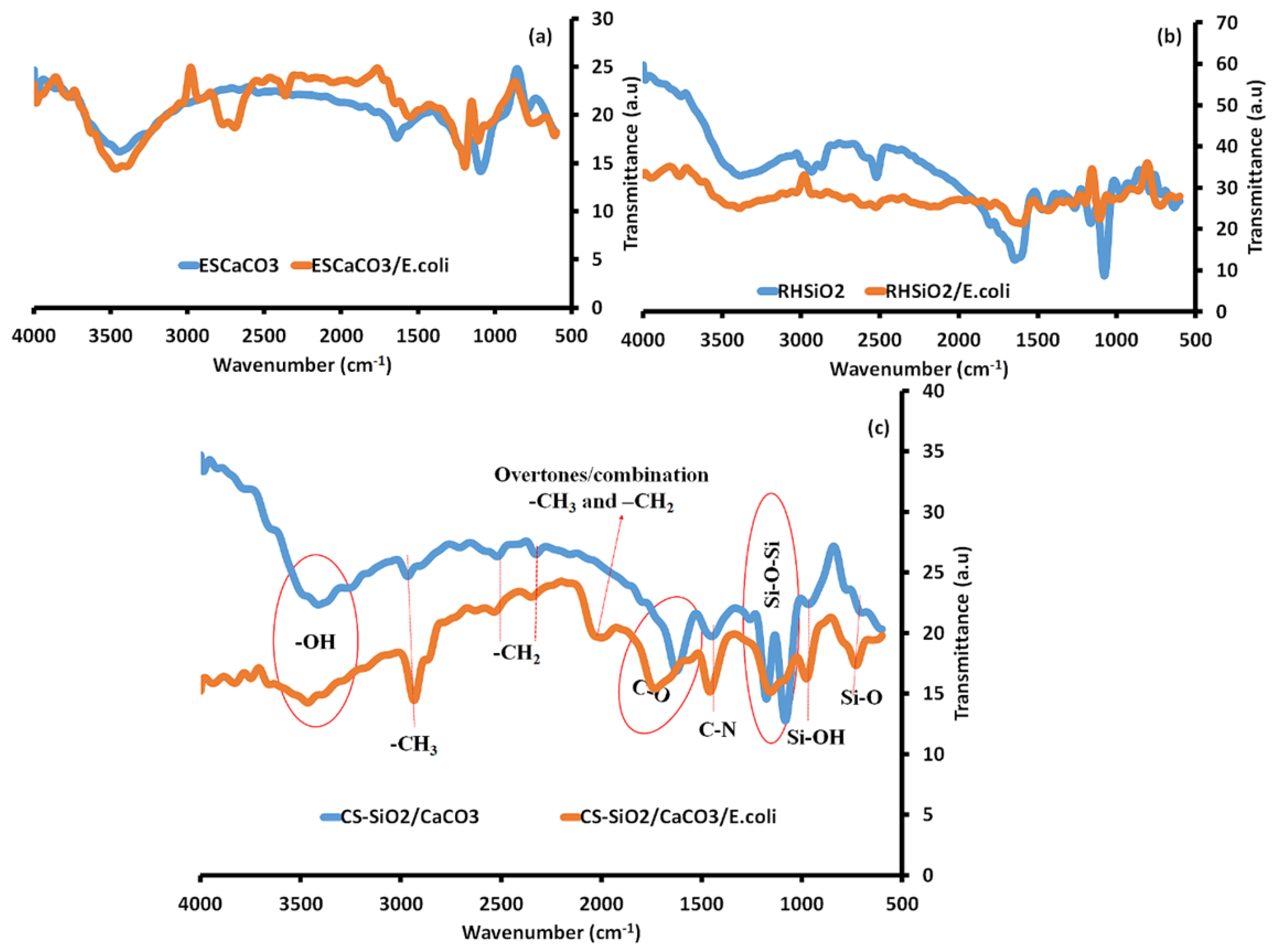
The possible mechanisms leading to bacteria–NP interactions detected using FTIR (Figure 7) as reported by Faghihzadeh et al. [66] and Darabdhara et al. [1] to consist of the amide A region placed at 3277 cm−1, the CH2/CH3 asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibration of fatty acids at 3100 cm−1 and 2800 cm−1. Others include the proteins and peptides (1800 and 1500 cm−1) which consist of amide I (C–O stretching vibrations) and amide II (N–H bending and C–N stretching vibrations) and amide III. The carbohydrates at 1300 and 900 cm−1 and the fingerprint region which consists of weak bands of nucleic acids and various nucleotides are also reported.
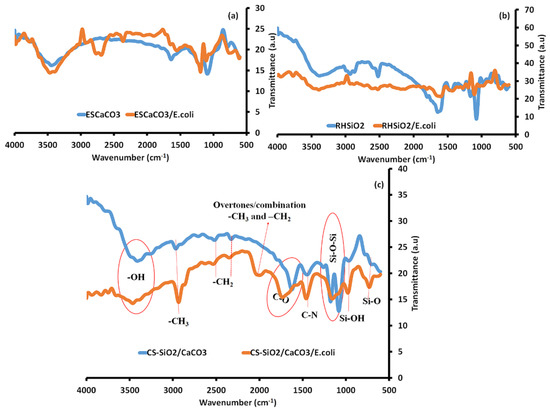
Figure 7.
FTIR of (a) ESCaCO3 NPs, (b) RHSiO2 NPs, and (c) CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs before and after treatment with E. coli.
The spectral profiles of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs (Figure 7c) consist majorly of the representative peaks of RHSiO2 (Figure 7a) and ESCaCO3 (Figure 7b). On interaction with E. coli, the spectral profile experiences some conformational changes in the –OH peak at 3412 cm−1 to 3464 cm−1 in CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E.coli spectra and is possible due to the N–H stretching of amide A of E. coli at 3277 cm−1. Similarly, the CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs also show minor peaks corresponding to asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of –CH3 and –CH2 of alkenes from CS at 2966, 2519, and 2327 cm−1 [48]. The CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs on interaction with E. coli induce some sharp changes to the –CH3 peak at 2966 cm−1, to 2934 cm−1 in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E.coli. The FTIR spectra from 2861 and 3026 cm−1, considered fatty acids region are uniquely used for E. coli discrimination. Changes in this fatty acids region, often involved the deformation of the lipid peroxidation of the –CH, leading to alter bacterial membrane permeability induced by the interaction of cells to NPs [67]. Study shows that the N–H stretching, the C–H stretching of CH2 in fatty acid, and the C–O–C and C–O ring vibration in various polysaccharides in E. coli spectra foster structural changes and molecular binding with the NPs [66,67]. As cited by Faghihzadeh et al. [66], amide A and amide B bands were reported to induce a shift in the bacteria-treated Ag NPs and further reported to introduce protein conformational changes in E. coli exposed quantum dot NPs at 3288 cm−1 [68]. Similar conformational changes were observed in the –CH bands at 2852–2963 cm−1 in bacteria-exposed to AgI/TiO2 NPs [69] and in bacteria-exposed ZnO nanowire at 2852, 2924, and 2959 cm−1 [70]. According to the studies, the change in the band is an indication of –CH modification of the fatty-tail structure by the interacting NPs [66].
A new feature appeared in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E.coli revealing an additional band at 1998 cm−1. Though no clear explanations to support the mechanism, it is however, likely for this new band to represent overtone and combination [71] of the asymmetric and symmetric stretching modes of various fatty-tail structures of E. coli with the corresponding –CH3 and –CH2 groups of the NCs. The incorporation of CS in CS-SiO2/CaCO3 were further detected in the spectra at 1625 cm−1, reported to signify the C-O stretching mode of the amine groups [48]. This band was observed to experience a shift in the spectral wavelength of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E. coli at 1733 cm−1. The observed shift in peak is likely from the C=O stretching vibrations at α-helical and β-pleated sheet structures of proteins [66]. An increase in the band at 1738 cm−1 NPs-treated bacteria was observed due to the vibration of the –C=O carbonyl group, which arises according to the study from the peroxidation of nucleic acid chains [72]. Further observation at 1690 and 1734 cm−1 correspond to an increase in the concentration of –C=O bonds in NP-exposed bacteria were also reported by Hu et al. [69].
The CO32- stretching vibrations in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 at 1449 cm−1 were observed to show a shift in wavelength for the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E.coli at 1459 cm−1. Responsible bands from 1440–1460 cm−1 in E. coli were observed to undergo some conformational changes on interaction with the NPs from the vibrational changes of –CH deformation in lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates [66,73,74]. The asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of siloxane (Si-O-Si) at 1176–1082 cm−1 in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs were observed to overlap to a broad peak at 1156 cm−1 in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E. coli. In E. coli, these regions are dominated by C–O–C and C–O ring vibrations of polysaccharides. Such polysaccharide band profiles were reported to produce a profound shift in the vibrational peaks of bacteria treated with metal/metal oxide NPs [4,66,69,75,76]. The small peaks at 967 cm−1 and 700 cm−1 are assigned to the vibrations of silanol (Si-OH) and Si-O. These bands on interaction with E. coli increased the wavelength to 977 cm−1 and 729 cm−1 in the spectra of CS-SiO2/CaCO3/E. coli. This region in the FTIR of E. coli consists of nucleic acids fingerprint and reported to induce these changes in the spectral bands [4,66,77]. The study by Faghihzadeh et al. [66] revealed changes in Ag NPs-exposed E. coli spectra at the fingerprint region, opined according to the study to alteration of secondary and tertiary helix structure of DNA, the generation of new gene fragments, or an increase in the transcriptions to the DNA molecule.
Comparison of the Maximum Sorption Capacity (qm) of E. coli onto CS-SiO2/CaCO3, RHSiO2, ESCaCO3 with Those of Other Adsorbents
The comparison between the performances of the CS-SiO2/CaCO3, RHSiO2, ESCaCO3, and other adsorbents is summarized in Table 2. The comparison were made based on the maximum adsorption capacity obtained from the Langmuir model. Though the adsorption capacity of some of the materials reported in the table were higher than that of the presents study except for the binary solutions, the utilization of agricultural-based waste materials without modification and without going through a series of processes activation in the preparation of the adsorbents allows for an inexpensive production of adsorbents that supports the local communities and creating value addition through waste management against the excessive disposal of waste. Thus, efficient process optimization and surface functionalization of adsorbents from these agricultural wastes will in turn increase their efficacy as biosorbents against other bacterial strains. Thus, future work is recommended to appraise their efficacy against other bacterial strains.

Table 2.
Comparison of the maximum sorption capacity (qm) of E. coli onto CS-SiO2/CaCO3, RHSiO2, ESCaCO3 with those of other adsorbents.
4. Conclusions
This study deals with the removal of E. coli bacteria from the aqueous solutions by making use of naturally derived NPs and NCs. In the study, the carbonyl groups, CO32-, Si–O–Si, Si-OH, and the Si-O bonds as revealed by FTIR were found to facilitate the interaction of the E. coli adsorption onto the CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs, ESCaCO3 NPs, and RHSiO2 NPs respectively. The results showed that the adsorption capacity is comparatively better for CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs when compared to the other biomaterials of ESCaCO3 NPs and RHSiO2 NPs. The morphology, hydrodiameter, and thermal behavior investigated on the materials in their natural unmodified forms conferred a promising adsorption potential for the removal of bacteria in water. Furthermore, the adsorption was observed to be well fitted to Langmuir isotherm model and the adsorption kinetics primarily govern by pseudo-second-order. Therefore, in a view toward the development of cheap and biodegradable bio-adsorbents for the purification of bacteria-contaminated drinking water, the CS-SiO2/CaCO3 NCs sorbent can serve as a potential sorbent material considering its non-toxic nature associated with its biodegradability and biocompatibility. Furthermore, future studies will aim to provide an easily accessible functional eco-friendly material as a local and cheap adsorbent on other bacterial strains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.B.B.; methodology, S.T.M. and I.B.B.; investigation, I.B.B. and F.M.; validation, formal analysis, and data curation, I.B.B., F.M. and S.T.M.; resources, I.B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, I.B.B. and F.M.; writing—review and editing, F.M. and I.B.B.; supervision, H.A.A.-L. and A.A.S.; project administration, H.A.A.-L. and A.A.S.; funding acquisition, I.B.B. and H.A.A.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Tertiary Education Trust Fund, Nigeria (TETFUND) and King Saud University’s Researchers Supporting Project (RSP2023R54).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the Department of Pure & Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Adamawa State University Mubi. Tertiary Education Trust Fund, Nigeria (TETFUND). Also, the KSU authors acknowledge the funding from Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R54), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Darabdhara, G.; Boruah, P.K.; Hussain, N.; Borthakur, P.; Sharma, B.; Sengupta, P.; Das, M.R. Magnetic nanoparticles towards efficient adsorption of gram positive and gram negative bacteria: An investigation of adsorption parameters and interaction mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 516, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Yegin, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Huang, S.; Verkhoturov, S.V.; Schweikert, E.A.; Perez-Lewis, K.; Scholar, E.A.; et al. The influence of surface chemistry on the kinetics and thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da’ana, D.A.; Zouari, N.; Ashfaq, M.Y.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Khraisheh, M.; Hijji, Y.M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of toxic elements and microbial contaminants from groundwater using low-cost treatment options. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 300–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, K.; Vachet, R.W.; Xing, B. Interaction between oxide nanoparticles and biomolecules of the bacterial cell envelope as examined by infrared spectroscopy. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18071–18077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obijole, O.; Mugera, G.W.; Mudzielwana, R.; Ndungu, P.; Samie, A.; Babatunde, A. Hydrothermally treated aluminosilicate clay (HTAC) for remediation of fluoride and pathogens from water: Adsorbent characterization and adsorption modelling. Water Resour. Ind. 2021, 25, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwatanglang, I.B.; Yonnana, E.; Ibrahim, L.D.; Kubo, A.I.; Elijah, B.K.; Ayagwa, C.A.; Abdulkarim, J.; Yerima, Y. Appraisal of public pipe-borne water quality in Jimeta/Yola Adamawa State (Nigeria): From the treatment-plants to end-user points. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2022, 21, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, A. Nanomaterials for removal of waterborne pathogens: Opportunities and challenges. Waterborne Pathog. 2020, 1, 385–432. [Google Scholar]
- Murcia-Salvador, A.; Pellicer, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Egg by-products as a tool to remove direct Blue 78 dye from wastewater: Kinetic, equilibrium modeling, thermodynamics and desorption properties. Materials 2020, 13, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Messaoudi, N.E.; Fernine, Y.; Keskin, Z.S. Bioremoval of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution by using agricultural solid waste (almond shell): Experimental and DFT modeling studies. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajerski, W.; Ochonska, D.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Indyka, P.; Jarosz, M.; Golda-Cepa, M.; Sojka, Z.; Kotarba, A. Attachment efficiency of gold nanoparticles by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains governed by surface charges. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Sun, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Wan, J.; Liu, K.; Tian, D.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Schwab, A.P.; et al. Feasibility of sulfate-calcined eggshells for removing pathogenic bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes from landfill leachates. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandiari, N.; Kashefi, M.; Mirjalili, M.; Afsharnezhad, S. On the adsorption kinetics and mechanism of enhanced photocatalytic activity of Fe3O4-SiO2-TiO2 core-multishell nanoparticles against E. coli. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, A.; Szala, M.; Cłapa, T. Adsorption studies of the Gram-negative bacteria onto nanostructured silicon carbide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; Santamaría, L.; Korili, S.A.; Vicente, M.A.; Barbosa, L.V.; De Souza, S.D.; Marçal, L.; De Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J. A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay based adsorbents for contaminants removal: Synthesis, perspectives and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, M.; Nakabayashi, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shiomi, T.; Yamada, Y.; Ino, K.; Yamanokuchi, H.; Matsui, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Mizukami, F.; et al. Selective adsorption of bacterial cells onto zeolites. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 64, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Cai, P.; Liang, W. Pseudomonas putida adhesion to goethite: Studied by equilibrium adsorption, SEM, FTIR and ITC. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.L.; Herman, J.S.; Hornberger, G.M.; DeJesús, T.H. Effect of solution ionic strength and iron coatings on mineral grains on the sorption of bacterial cells to quartz sand. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3300–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemnukhova, L.; Kharchenko, U.; Beleneva, I. Biomass derived silica containing products for removal of microorganisms from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Wu, L.; Younes, M.; Hincke, M. Biotechnological applications of eggshell: Recent advances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 675364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullo, T.A.; Bayisa, Y.M.; Bultum, M.S. Optimization and biosynthesis of calcined chicken eggshell doped titanium dioxide photocatalyst based nanoparticles for wastewater treatment. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, H.S.; Alahmadi, N.; Yasin, S.A.; Khalaf, M.Y.; Ali, G.A.M. Low-Cost and Eco-Friendly Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles Derived from Eggshell Waste for Cephalexin Removal. Separations 2022, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Kawasaki, H.; Nishida, E.; Kanemoto, Y.; Miyaji, H.; Umeda, J.; Kondoh, K. Rose bengal-decorated rice husk-derived silica nanoparticles enhanced singlet oxygen generation for antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 25, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Preparation of magnetic mesoporous silica from rice husk for aflatoxin B1 removal: Optimum process and adsorption mechanism. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Huang, K. Biobased Chicken Eggshell Powder for Efficient Delivery of Low-Dose Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) to Enhance Their Antimicrobial Activities against Foodborne Pathogens and Biofilms. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4390–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Rao, N.V.; Omidifar, N.; Gholami, A.; Ghahramani, Y.; Chiang, W.H.; Kalashgrani, M.Y. Antibacterial and cytotoxic efficacy of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Synthesized from Eggshell and Sheep bones bio Waste. Res. Sq. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, F.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Iqbal, J.; Butt, M.T.; Sadef, Y.; Umbreen, M.; Shaikh, I.A.; Moniruzzaman, M. Efficient utilization of low cost agro materials for incorporation of copper nanoparticles to scrutinize their antibacterial properties in drinking water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadhrami, A.; Mohamed, G.G.; Sadek, A.H.; Ismail, S.H.; Ebnalwaled, A.A.; Almalki, A.S. Behavior of silica nanoparticles synthesized from rice husk ash by the sol–gel method as a photocatalytic and antibacterial agent. Materials 2022, 15, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unglaube, F.; Lammers, A.; Kreyenschulte, C.R.; Lalk, M.; Mejía, E. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Properties of Nanosized Silver-Containing Carbon/Silica Composites from Rice Husk Waste. Chem. Open 2021, 10, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.D.; Truong, T.T.; Nguyen, H.L.; Hoang, L.B.; Bui, V.P.; Tran, T.T.; Dinh, T.D.; Le, T.D. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Core–Shell ZnO@ SiO2 Nanoparticles and Application in Antibiotic and Bacteria Removal. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42073–42082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riana, U.; Ramli, M.; Iqrammullah, M.; Raharjo, Y.; Wibisono, Y. Development of chitosan/rice husk-based silica composite membranes for biodiesel purification. Membranes 2022, 12, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, F.A.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Barhoum, A. Nano-silica and SiO2/CaCO3 nanocomposite prepared from semi-burned rice straw ash as modified papermaking fillers. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwatanglang, I.B.; Magili, S.T.; Kaigamma, I. Adsorption of phenol over bio-based silica/calcium carbonate (CS-SiO2/CaCO3) nanocomposite synthesized from waste eggshells and rice husks. PeerJ Phys. Chem. 2021, 2, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Uber die adsorption in losungen, zeitschrift fur phtsikalische chemie. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Abin-Bazaine, A.; Trujillo, A.C.; Olmos-Marquez, M. Adsorption Isotherms: Enlightenment of the Phenomenon of Adsorption. In Wastewater Treatment; Intech Open: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Higley, S.; Baur, C.; Mitchell, D.R.; Jones, R.T.; Fichtner, M. Calcined chicken eggshell electrode for battery and supercapacitor applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26981–26995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Sethupathi, S.; Munusamy, Y.; Kanthasamy, R. Valorization of raw and calcined chicken eggshell for sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide removal at low temperature. Catalysts 2021, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.H.; Thuc, C.N.; Thuc, H.H. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles from Vietnamese rice husk by sol–gel method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoohinkong, W.; Kitthawee, U. Low-cost and fast production of nano-silica from rice husk ash. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 979, pp. 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, F.; Arfin, T.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Enhanced biological activity and biosorption performance of trimethyl chitosan-loaded cerium oxide particles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandoli, C.; Pagliari, F.; Pagliari, S.; Forte, G.; Di Nardo, P.; Licoccia, S.; Traversa, E. Stem cell aligned growth induced by CeO2 nanoparticles in PLGA scaffolds with improved bioactivity for regenerative medicine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.; Haque, M.; Kumar, A.; Hoq, A.; Hyder, F.; Hoque, S.M. Manganese ferrite nanoparticles (MnFe2O4): Size dependence for hyperthermia and negative/positive contrast enhancement in MRI. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Amstad, E. Water: How does it influence the CaCO3 formation? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1798–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.H.; Reis, T.V.; Rovani, S.; Fungaro, D.A. Green synthesis and characterization of biosilica produced from sugarcane waste ash. J. Chem. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwatanglang, I.B.; Mohammad, F.; Yusof, N.A.; Abdullah, J.; Hussein, M.Z.; Alitheen, N.B.; Abu, N. Folic acid targeted Mn: ZnS quantum dots for theranostic applications of cancer cell imaging and therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 413. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, M.; Santhiya, D.; Dey, N. Zein coated calcium carbonate nanoparticles for the targeted controlled release of model antibiotic and nutrient across the intestine. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Wang, X.; Du, M.; Liang, G.; Hu, G.; SM, J.A. Adsorption analyses of phenol from aqueous solutions using magadiite modified with organo-functional groups: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Materials 2018, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Meikap, A.K. Dielectric relaxation and magnetodielectric response of mesoporous terbium manganate nanopaticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.C.; Burhan, M.; Shahzad, M.W.; Ismail, A.B. A universal isotherm model to capture adsorption uptake and energy distribution of porous heterogeneous surface. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Bouchmella, K.; Budimir, J.; Raehm, L.; Cardoso, M.B.; Trens, P.; Durand, J.O.; Charnay, C. Degradable hollow organosilica nanoparticles for antibacterial activity. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahash, S.A.; Higgins, P.; Siddiqui, S.; Uddin, M.K. Fabrication of polyamide-12/cement nanocomposite and its testing for different dyes removal from aqueous solution: Characterization, adsorption, and regeneration studies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedam, A.H.; Dongre, R.S. Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) ions onto iodate doped chitosan composite: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 54188–54201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Davis, J.A.; Fujikawa, K.; Ganesh, N.V.; Demchenko, A.V.; Stine, K.J. Surface area and pore size characteristics of nanoporous gold subjected to thermal, mechanical, or surface modification studied using gas adsorption isotherms, cyclic voltammetry, thermogravimetric analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6733–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Hao, J.; Yang, Y.; Qian, A. The effect of hydrothermal temperature on the properties of SBA-15 materials. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; He, H. Effects of calcination temperature on properties of 0.5% Al-3% In-TiO2 photocatalyst prepared using sol-gel method. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 2016, 19, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Zhou, T.; Xie, B.; He, L. Synthesis and characterization of colistin-functionalized silica materials for rapid capture of bacteria in water. Molecules 2022, 27, 8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, C.Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, M.; Ping, M.; Chen, M.; Wu, Z. Modification of microfiltration membranes by alkoxysilane polycondensation induced quaternary ammonium compounds grafting for biofouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.; Aziz, N.; Amr, S.; Palaniandy, P. Removal of lindane and Escherichia coli (E. coli) from rainwater using photocatalytic and adsorption treatment processes. Glob. Nest J. 2017, 19, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R.B.; Rahali, S.; Ben Aissa, M.A.; Albadri, A.; Modwi, A. Uptake of BF Dye from the aqueous phase by CaO-g-C3N4 Nananosorbent: Construction, descriptions, and recyclability. Inorganics 2023, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamilselvi, V.; Radha, K.V. Silver nanoparticle loaded silica adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, M.H.; Wei, W.; Yun, Y.S. Selective biosorption behavior of Escherichia coli biomass toward Pd(II) in Pt(IV)–Pd(II) binary solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovski, J.S.; Marković, D.D.; Đokić, V.R.; Mitrić, M.; Ristić, M.Đ.; Onjia, A.E.; Marinković, A.D. Arsenate adsorption on waste eggshell modified by goethite, α-MnO2 and goethite/α-MnO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihzadeh, F.; Anaya, N.M.; Schifman, L.A.; Oyanedel-Craver, V. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess molecular-level changes in microorganisms exposed to nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2016, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukprasert, J.; Thumanu, K.; Phung-On, I.; Jirarungsatean, C.; Erickson, L.E.; Tuitemwong, P.; Tuitemwong, K. Synchrotron FTIR light reveals signal changes of biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticle attachment on Salmonella sp. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.T.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.C. Toxicity evaluation of CdTe quantum dots with different size on Escherichia coli. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Qu, J.; Hu, X. Photocatalytic degradation of pathogenic bacteria with AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4982–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L. Photocatalytic degradation of E. coli membrane cell in the presence of ZnO nanowires. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, R.; Nara, A.; Matsuda, T. Near-infrared combination and overtone bands of the CH2 sequence in CH2X2, CH2XCHX2, and CH3(CH2)5CH3 and their characteristic frequency zones. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeroual, W.; Choisy, C.; Doglia, S.M.; Bobichon, H.; Angiboust, J.F.; Manfait, M. Monitoring of bacterial growth and structural analysis as probed by FT-IR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 1994, 1222, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Mauer, L.J. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy: A rapid tool for detection and analysis of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Res. Technol. Educ. Top. Appl. Microbiol. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Riding, M.J.; Martin, F.L.; Trevisan, J.; Llabjani, V.; Patel, I.I.; Jones, K.C.; Semple, K.T. Concentration-dependent effects of carbon nanoparticles in gram-negative bacteria determined by infrared spectroscopy with multivariate analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadtochenko, V.A.; Rincon, A.G.; Stanca, S.E.; Kiwi, J. Dynamics of E. coli membrane cell peroxidation during TiO2 photocatalysis studied by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and AFM microscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2005, 169, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yoon, S.H.; Choi, E.; Gil, B. Comparison of the adsorbent performance between rice hull ash and rice hull silica gel according to their structural differences. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Rockhold, M.; Strevett, K.A. Equilibrium and kinetic adsorption of bacteria on alluvial sand and surface thermodynamic interpretation. Res. Microbiol. 2003, 154, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Upadhyayula, V.K.; Smith, G.B.; Mitchell, M.C. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of microorganisms on single-wall carbon nanotubes. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 8, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).