1. LC MS Methods for Analysis of Therapeutic Oligonucleotides and mRNA
Martin Gilar
Waters Corporation, Separations R&D and Martin
Abstract: We describe the development of liquid chromatography methods suitable for the analysis and purification of nucleic acid therapeutic compounds. Ion-pair reversed-phase chromatography (IP RP LC) or hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) are compatible with mass spectrometry (MS) analysis and can provide both separation and identification of oligonucleotides. mRNA vaccines can be analyzed as intact molecules or after their enzymatic digestion into a short and more manageable oligonucleotides. In addition to separation challenges, we show that negatively charged nucleic acids often interact with metal surfaces. The undesirable adsorption on LC system and column surfaces can lead to sample loss, peak tailing, and poor quantitative results. We demonstrate that high performance organic/inorganic surface technology used for LC column and system construction improves the robustness and sensitivity of LC MS methods.
Acknowledgement: The author acknowledges contribution of Waters researchers including Jennifer Nguyen, Michael Donegan, Matthew Lauber, Catalin Doneanu, and Maissa Gaye.
2. Ethics and Emergency Time
Bettina Couderc
Institut Claudius Regaud—IUCT-Oncopole, INSERM CERPOP UMR1295, 1 avenue Irène Joliot Curie, 31059 Toulouse cedex 9,
Abstract: In early 2020, the SARS-Cov2 epidemic spread throughout the world, causing hundreds of thousands of cases of COVID-19. In the absence of effective treatments and vaccinations, populations were confined. The media widely informed citizens of the impact of the epidemic (daily count of deaths due to COVID-19, medical emergency). Under economic and especially social pressure, governments in all countries immediately promoted and funded research programs aimed not only at learning more about the virus and the pathophysiology of the disease, but also at developing strategies to mitigate, cure or prevent COVID-19 and its consequences. Any new research program, whether basic or clinical, must be evaluated and approved before it can begin. Therefore, all proposals for new therapies (drugs or use of medical devices, repositioning of a drug, vaccine strategies, validation of new analytical methods or evaluation of practices) must be evaluated and approved at the scientific and ethical level before any initiation of a clinical trial by the regulatory authorities of the different countries. For their evaluations (scientific or ethical) (with respect for the benevolence, non-maleficence, autonomy, and equity of future patients or healthy volunteers), the experts rely on the publications of the researchers. Expert assessments are known to be long. Indeed, they are faced with the difficulty of detecting possible scientific fraud. During the pandemic, a number of scandals have broken out, highlighting the lack of scientific integrity. These scandals are the showcase of a perennial problem. However, in times of pandemic, regulatory authorities were required to give rapid favorable opinions. We will discuss two questions: Is it legitimate and desirable in times of a pandemic or for all “medical emergencies”, such as the identification of a so-called revolutionary treatment for a serious pathology such as cancer, to reduce the regulatory requirements (acceleration of deadlines for scientific publications, exemption from the evaluation of scientific results or clinical protocols by several authorities, exemption from a strict methodology, etc.) before the marketing of a new analytical method of assaying biological samples or administering a treatment to humans? How can we promote scientific research respecting scientific integrity?
3. The Complex Challenges of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances as Environmental Contaminants: A Soil Perspective
Christopher P. Higgins
Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA
Abstract: The challenges posed by the widespread contamination of soils and groundwater by poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are immense. Despite growing concerns about human exposure to perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), other PFASs, particularly those derived from aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs) have garnered little attention. Recent work using high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) has revealed that there are dozens, if not hundreds, of additional PFASs that may be associated with AFFF-impacted sites. Importantly, many of these newly discovered PFASs have diverse chemical structures, including anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic structures. Some of these PFASs clearly remain bound strongly to soil, while other AFFF-derived PFASs, including transformation products, likely migrate into AFFF-impacted drinking water. In this presentation, the complex challenges posed by PFASs for human and environmental risk will be presented and discussed. Particular attention will be given to the role of the anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic polyfluorinated substances at AFFF-impacted sites that can serve as precursors to the more persistent and mobile perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs). Collectively, these data suggest a need for more thorough assessments of soils as potential long-term sources of PFAAs to groundwaters and surface waters.
4. Electrochemiluminescence to Shed Light on Analytical Science
Joohoon Kim
Department of Chemistry, Kyung Hee
University, 26 Kyungheedae-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Korea
Abstract: Electrochemiluminescence (ECL) is a unique luminescent phenomenon in which electrochemically generated species are involved to form excited states emitting light. Since ECL provides beneficial characteristics over photoluminescence, including low background emission, good temporal and spatial controllability, robustness, and instrumental simplicity, the ECL technique has been utilized as a versatile tool in analytical science. Especially, since Bard and his co-workers presented for the first time a new approach for generating ECL (i.e., co-reactant pathways) in the 1980s, the ECL technique has been achievable in aqueous environment, and thus been popular to the clinical and bioanalytical applications. To further expand the usefulness of ECL in analytical science, many promising approaches have been suggested for amplification of ECL signals. We believe such studies are important for the use of ECL as a sensitive tool to detect analytes. Of the approaches, we recently reported the use of nanoscale functional materials such as dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles and Au nanoclusters for the enhancement of ECL. In the present talk, we discuss mainly about two research topics. The first topic is the synthesis of functional nanomaterials as catalytic materials and ECL luminophores. Specifically, we discuss the synthesis of ultra-small Pt nanoparticles having different but uniform sizes using dendrimers as a molecular template, which is usually denominated as dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles (DENs). We also discuss the synthesis and subsequent modification of Au nanoclusters as a bright ECL luminophore. The second topic concerns the catalytic features of the nanoscale functional materials and the use of such catalytic features for electrochemical applications, including ECL-based analysis.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning; NRF-2020R1A2C2013790 and NRF-2021R1A4A5032876).
5. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in a Population of Filipino Women: An ASEAN Perspective on PFAS
Michael C. Velarde
Institute of Biology, College of Science, University of the Philippines Diliman, Quezon City, PH,
Abstract: Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) represent a class of thermostable, waterproof, and grease-resistant synthetic chemical used in several consumer products. They have many useful industrial applications but tend to persist in the environment and bioaccumulate in humans and animals when exposed. Many developed countries have already been monitoring the level of PFAS in their population and environment and have already imposed several regulatory measures on these chemicals. However, there is limited information regarding PFAS contamination and exposure across Southeast Asia. This talk will describe PFAS studies performed in Southeast Asia, with an emphasis on PFAS measurements observed in a population of women living within the Greater Manila Area, one of the largest cities in the region. The association of PFAS concentration with factors, such as region of residence and occupation, will also be presented. Overall, this talk will present baseline information on the level of PFAS in women living in a megalopolis city within Southeast Asia and will provide evidence regarding the relevance of PFAS in this part of the world.
Acknowledgement This study is funded by the Philippine Commission on Higher Education—Philippine California Advanced Research Institute (CHED-PCARI, IHITM 2016-13).
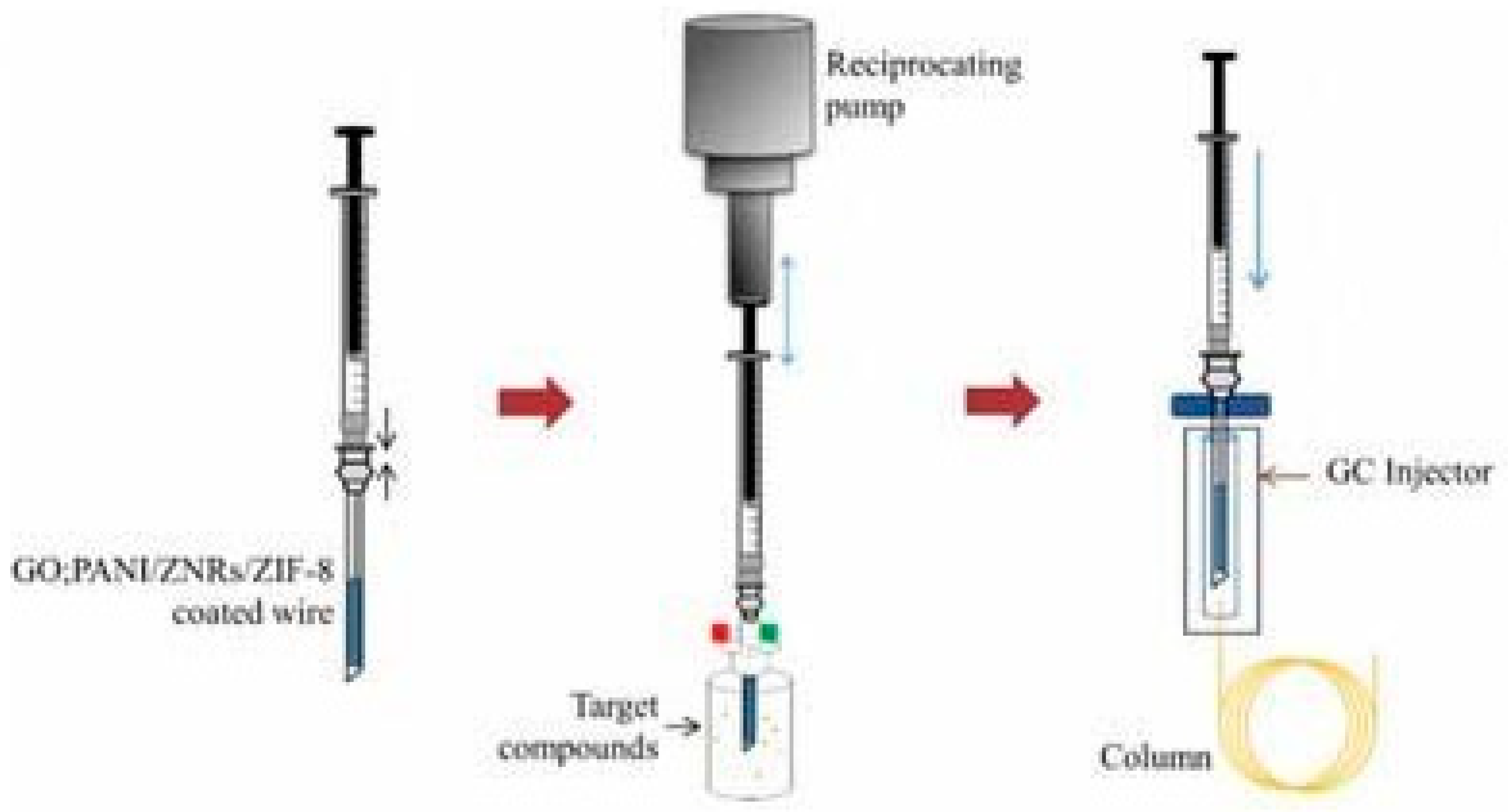
6. Development and Application of In-Needle Microextraction
Sunyoung Bae
Seoul Women’s University, Seoul, Korea,
Abstract: Needle-based microextraction has been widely used in trace analysis because it can be easily modified, automated, performed, and integrated with analytical instruments. Sample preparation using microextraction techniques is a particularly important process to improve performance of the extraction. In our laboratory, an in-needle microextraction (INME) technique shown in
Figure 1 has been developed to overcome the problems related to other microextraction methods and to enhance the sensitivity and the recovery. To increase adsorption capacity, numerous polymer adsorbents have been synthesized to fabricate the needle for INME. The adsorbents are synthesized via sol-gel polymerization and/or electrochemical deposition to be coated inside wall of the needle or on the wire. Different compositions of the polymer as adsorbents would change the distribution constant between adsorbent phase and sample and the thickness of the adsorbent modifies the thickness of the phase where target compounds are extracted at equilibrium to improve the microextraction efficiency. The INME needle is reusable and can be applied to the liquid or gaseous phase. INME can be suggested as a facile means for collecting and introducing the target compounds from the complex matrix.
References
Kim, S. Bae, S. Molecules 2022, 27, 4795.
Kim, S. Bae, S, Lee, D-S. Talanta, 2022, 245, 123463.
7. Microplastic Pollution in the Marine Environment
Fani Sakellariadou
Lab. of Geochemical Oceanography, Dept of Maritime Studies, University of Piraeus, Greece. Email:
Abstract: Plastics are synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymers included among the most commonly used type of materials today. They comprise a heterogeneous group of compounds characterized by versatility, resistance, high thermal and electrical insulation properties, and durability to degradation. Plastics are inexpensive and lightweight materials. Because of the ubiquitous environmental occurrence and abundance of plastics, they could serve as stratigraphic indicators of the Anthropocene era [1]. The presence of plastic waste in the natural environment is a growing concern. Macro- and microscopic fragments of plastics are present in all natural environments [2–4]. After their release, plastics are degraded into micro- and nano-plastics. The environmental degradation of plastics starts with an abiotic physical or chemical mechanism [5,6]. Microplastics are plastic pieces with a diameter of 0.1 μm–5 mm. The presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment is not only attributed to the degradation of larger plastic products as they are commonly produced in this particular size (i.e., fibers, microbeads, paint fragments, road markings, etc.). Microplastics are of particular interest for the quality status of the marine ecosystem [7]. They are present from the sea surface and water column to the beach and seabed sediment, in densely populated areas, but also in remote regions [8]. Particularly in the deep sea, the lack of UV light and the cold temperatures favor plastic preservation that is intensified in areas with free oxygen deficiency. Microplastic/nanoplastic pollution of the marine environment threatens marine biota entering the food web and causing a variety of negative impacts directly or indirectly. In the next step, microplastics and nanoplastics enter human bodies through the consumption of seafood. A recent study [9] supports that human exposure to plastic contamination causes the absorption of plastics into the bloodstream. Moreover, plastics manufacturing asks for various chemical additives, including some toxic ones. In addition, plastics act as physical traps for various contaminants, e.g., metals, POPs, etc., present in the seawater that could re-enter the water column and/or be up-taken by biota [10,11].
Acknowledgement: This study was carried out under “The Environment, Health and Food Safety Impact of Microplastics” project (2019-026-2-600) sponsored by IUPAC Chemistry and the Environment Division.
References
Zalasiewicz, J., Waters, C.N., Ivar do Sul J.A., Corcoran P.L., Barnosky A.D., et al., Anthropocene, 2016, 13, 4–17.
Barnes, D. K. A., Galgani F., R. C. Thompson, M. Barlaz, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, 2009, 364, 1985–1998.
Wagner, M., Scherer, C., Alvarez-Muñoz, D., Brennholt, N., Bourrain, X., et al., Environ. Sci. Eur., 2014, 26, 12.
Rillig, M. C., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 6453–6454.
Andrady, A. L. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2011, 62 (8), 1596– 1605.
Lucas, N., Bienaime, C., Belloy, C., Queneudec, M., Silvestre, F., Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Chemosphere, 2008, 73 (4), 429– 442.
Cole, M., Lindeque, P., Halsband, C., Galloway, T.S., Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2011, 62 (12), 2588-2597.
Lots, F.A.E., Behrens, P., Vijver, M.G., Horton, A.A., Bosker T. Mar. Pol. Bull., 2017, 123, 219-226.
Leslie, H.A., van Velzen, M.J.M., Brandsma, S.H., Vethaak, A.D., Garcia-Vallejo, J.J., Lamoree, M.H. Environ. Int., 2022, 163, 107199.
Zalasiewicz, J., Waters, C.N., PL., Barnosky A.D., et al., Anthropocene, 2016, 13, 4–17. Barnes, D. K. A., Galgani F., R. C. Thompson, M. Barlaz, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, 2009, 364, 1985–1998.
Wagner, M., Scherer, C., Alvarez-Muñoz, D., Brennholt, N., Bourrain, X., et al., Environ. Sci. Eur., 20Rillig, M. C., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 6453–6454.
8. The Effects of Herbal Primary Processing on the Change in Composition of Alkaloids from Magnoliae Cortex Evaluated by LC-MS/MS
Young Sik Park 1,
Chong Woon Cho 2,
Hyug Min Kim 2
and
Jong Seong Kang 2
1
Graduate School of New Drug Discovery and Development, Chungnam National University, Korea
2
College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, Korea,
Abstract: Herbal processing refers to the overall treatment in the course of production of herbal medicinal materials, herbal preparations, and herbal dosage forms. However, herbal primary processing serves several purposes, such as concentrating the ingredients, removing undesirable substances, modifying the therapeutic properties, and reducing toxicity, facilitating dispensing, compounding, and storage. Magnoliae Cortex is mainly used as herbal medicinal materials for the treatment of toothache, indigestion, and obesity diseases and so on. It is not consumed without its primary processing because of side effects such as the irritation of the throat and tongue. Hence, it is only used after primary processing treated with various methods, such as roasting, boiling, soaking in ginger juice or honey, etc. The purpose of this study is to compare the chromatogram patterns of main components for each primary processing method by the identification of components in samples using LC-MS/MS analysis. Nine compounds of the samples were specifically observed and identified as (1) 3-deoxyglucosulose, (2) magnoloside T, (3) magnoflolin, (4) magnoloside B, (5) magnoloside A, (6) isoacteoside, (7) randaiol, (8) honokiol, and (9) magnolol. The identified compounds were used for the evaluation of the effects of primary processing methods of Magnoliae Cortex.
9. Deep Eutectic Solvents in Greener Analytical Chemistry and Material Science
Ke Li 1,
Yuli Liu 1,
Seulgi Kang 1,
Jingyan Chen 1,
Boyeon Bae 1,
Inseon Hwang 1,
Eun-Young Ahn 2,
Youmie Park 2
and
Jeongmi Lee 1
1
School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Gyeonggi 16419, Republic of Korea
2
College of Pharmacy and Inje Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, Inje University, Gimhae, 50834, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Greenness is pursued in every field of chemistry, where solvents occupy a major portion in general. Green solvents are required to meet several criteria, including low toxicity, biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low cost to name a few. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as a new type of solvents to substitute for conventional toxic organic solvents. Exponential increase in DES studies has been observed in various chemistry fields including green analytical chemistry. In this context, sample preparation methods involving DESs have been increasingly reported. One of the main streams is found in liquid-phase microextraction (LPME)-based techniques. In this approach, several types of DESs could successfully replace water-immiscible, toxic solvents to extract diverse kinds of analytes in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, ultrasound-/air-/vortex/effervescence-assisted liquid-phase microextraction, and more. Our study on the application of in situ-formed DESs in LPME-based sample preparation method will be presented as an example for the first part of the talk. Another main stream of DES application in green analytical chemistry is found in sorbent-based techniques. DESs have been explored to prepare various kinds of solid sorbents including polymers and nanoparticles. For the second part of the talk, our recent study to apply DESs in the plant extract-based biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles will be presented. In this latter study, DES-based extracts of green tea leaves were used to biosynthesize silver nanoparticles, and the roles of DESs in the nanoparticle biosynthesis were investigated.
Acknowledgement: The authors would like to acknowledge the generous research grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (No. 2020R1A2C1014006 and 2022R1A6A1A03054419).
10. Capillary Electrophoresis Migration Time Alinement with the Help of Tandem Mass Spectrometry Data
Zi-Ao Huang,
Jiahua Tan,
Yueyang Li,
Siyu Miao
and
David D. Y. Chen
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Abstract:
Migration time fluctuation strongly affects the peak alignment and identification of unknown compounds, making migration time correction an essential step in capillary electrophoresis (CE)-based metabolomics. To obtain more reliable information, metabolites with different apparent mobilities are analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry. Applying a small pressure is a common practice for reducing the analysis time of anions in a positive mode CE, known as the pressure-assisted CE. However, applying pressure may reduce the separation efficiency and can be undesirable for cation analysis. A simple way to address this issue is to increase the pressure after a certain time, during the separation. We term this practice as dual pressure CE. However, changing the pressure during the CE separation complicates migration time correction. Previous migration time correction methods were established based on a consistent electroosmotic flow and a constant pressure-driven bulk-flow velocity. We proposed a new correction method to support the peak alignment when dual pressure CE is used. A Python-based script was developed to implement dual pressure CE migration time correction for semi-targeted metabolomics study performed by a multiple reaction monitoring–based method. This script can help select suitable endogenous metabolites as correction markers, perform migration time correction, and conduct peak alignment. A case study showed that the migration time precision of 156 metabolites in 32 samples can be improved from 4.8–11.4%RSD (relative standard deviation) to less than 1.8%RSD.
11. Separation Science to Ensure the Quality of mRNA Vaccines and Biopharmaceuticals
Finja Krebs 1,
Udo Burger 2,
Susanne Dörks 2,
Markus Kramer 3
and
Hermann Wätzig 1
1
Institute of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Beethovenstraße 55, 38106 Braunschweig, Germany
2
ProteinSimple, a Bio-Techne brand, Borsigstraße 7a, 65205 Wiesbaden-Nordenstadt, Germany
3
CureVac AG, Friedrich-Miescher-Straße 15, 72076 Tübingen, Germany
Abstract: In order to contribute to the world-wide SARS-CoV-2-related research, we have developed two quality-indicating methods to characterize mRNA-containing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to be used as vaccines. One method, using 9 M urea as an additive, shows two broad and jagged peaks in which the peak shape offers detailed information. The summed peak area of both peaks showed RSDs from 2 to 8% when one batch was measured in triplicate and apparently depends on the size of the LNPs. In the second method, a combination of 5.5 M urea and 2 M Nethylurea was used. This method is less selective but offers RSDs of approximately 1%. These methods together can easily distinguish between various batches, show instabilities due to, e.g., storage and freeze-thaw cycles, and can precisely quantify the mRNA content for a stability-indicating method [1].
Reference
Krebs, F., Burger, U., Dörks, S., Kramer, M., Wätzig, H. Electrophoresis 2022,
https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/elps.202200123.
12. Effective Separation of Glycoproteins Due to the Difference of Sugar Chains in Liquid Chromatography
Takuya Kubo
and
Koji Otsuka
Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan
Abstract: Most proteins include sugar chains after posttranslational modifications, which are called glycoproteins. Glycoproteins contribute to signal transduction, the immune system, and receptor reactions based on the differences in the sugar chains. Furthermore, sugar chains are related to a broad range of diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, Alzheimer, cancers, and hereditary diseases. Consequently, glycoproteins are targeted as biomarkers, and detailed analyses of sugar chains in glycoproteins is attracting attention. To fully evaluate bioactivities, glycoproteins must be separated based on the differences of the sugar chains. Boronic acid (BA) reversibly complexes with the diol structure. BA derivatives separate glycoproteins based on the differences in the sugar chains. Separation typically occurs under basic conditions, which does not guarantee the structural stability of glycoproteins. Here, 5-boronopicolinic acid (BPA), which is one of BA derivatives containing a pyridine moiety showing a lower pKa, is used to prepare silica-gel based columns with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) conjugated BPA. To increase the density of the BPA moiety, PEI was introduced after the PEG units. Both batch adsorption and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analyses suggested that the increased BPA density contributed to a higher binding affinity for glycoproteins. The optimized column, BPA-PEI1800-PEG600-SiO2 packed column, was suitable for the online LC concentration of the glycoprotein (HRP), even at low concentrations, which are below the detection limit in the typical LC analysis. Finally, the BPA-PEI1800-PEG600-SiO2 packed column showed a strong affinity to high mannose-type glycoproteins and a lower affinity to the non-reduced Neu5Ac. We also demonstrated the separation of glycoproteins due to the presence of the non-reduced Neu5Ac. Briefly, fetuin and asialofetuin were effectively separated based on the presence of the nonreduced Neu5Ac in the terminal of the sugar chains [1]. These results showed that effective separation of glycoproteins is possible using the differences in the sugar chains.
Reference
Kobayashi, H.; Masuda, Y.; Takaya, H.; Kubo, T.; Otsuka, K., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94, 6882–6892.
13. The Foundation of Molecular Medicine: A Chemical Biology Approach
Weihong Tan 1,2,3
1
Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences,
2
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), Hunan University
3
Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM), Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Abstract: Progress in the development and production of new, innovative protein therapeutics requires rapid and adjustable high-resolution bioseparation techniques. Sodium dodecyl sulfate capillary gel electrophoresis (SDSCGE) is widely employed today for fast consistency analysis of therapeutic proteins in manufacturing and release testing. Transiently cross-linked polymer chains provide a high-resolution separation gel for SDS-protein complexes. To understand the basis of migration and separation, various monomer cross-linker compositions were evaluated. Ferguson plots were analyzed for a mixture of protein standards with molecular weights ranging from 20 to 225 kDa, and the resulting nonlinear concave curves pointed to non-classical sieving behavior. The interplay between the electroosmotic flow and the viscosity of the matrices played a key role in the resulting migration time and resolution. A retention model was derived for better understanding of the separation selectivity between the non-glycosylated and glycosylated heavy chain fragments of monoclonal antibodies and Fc fusion proteins, exploiting the interaction between the gel matrix and the glycan moiety of the therapeutic antibody. Introduction of three-dimensional selectivity plots offered an easy separation optimization option for the separation problem in hand. High efficiency separations, in general, require good peak shape symmetry as defined by the Gaussian equation. To address this issue in SDS-CGE, a theoretical treatment will also be presented regarding how to minimize electromigration dispersion mediated fronting and tailing in the special case when the co-ion of the background electrolyte also acts as cross-linker for the sieving matrix.
14. Capillary Electrophoresis as a Tool for Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Biomolecular and Metal Complex Systems
Nobuhiko Iki
Tohoku University, Sendai 980-8579, Japan,
Abstract: A complex is defined as an entity composed of two or more components, such as metal–ligand, enzyme–substrate, and host–guest systems. At the intersection of analytical chemistry and biomedicinal chemistry, we are interested in two complex systems. First, metal-–igand complexes having probe functions such as near-infrared (NIR) light absorption [1], luminescence [2], and
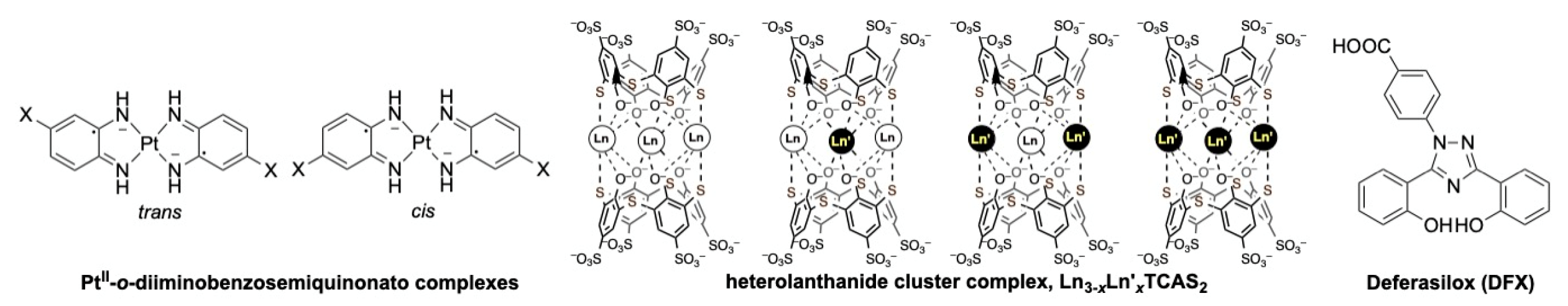
1H-relaxation [3] as well as iron(III) homeostasis. Second, biomolecular complexes, such as DNA-protein [4], enzyme-inhibitor [5], and so on. In the former, characterization in terms of kinetic stability and distribution of isomers and heterometal complexes is of particular importance to be applied in biomedical systems. In the latter, kinetics and thermodynamics of the biomolecular complex should help to understand processes in biology and physiology. To investigate and analyze such complex systems in aqueous solutions, we have used capillary electrophoresis (CE) as a tool by virtue of the separation ability in homogeneous solutions. Moreover, during the electrophoretic migration, components of the complex are steadily removed from the vicinity of the complex, that forces the complex to dissociate. From this, we have established a CE reactor to determine the dissociation rate of complexes [6]. In this talk, we will present our recent results on the application of CE as a versatile tool to investigate complex systems in aqueous solutions. Examples are as follows (
Figure 1): (1) Separation of
cis-trans isomers of Pt(II)-diradical complexes absorbing NIR light for a probe in photoacoustic imaging. (2) Separation of heterolanthanide cluster complexes with thiacalix [4]arene-
p-tetrasulfonate (TCAS) as a candidate of luminescence probe. (3) Kinetic stability of trypsin-aprotinin complex. (4) Kinetic stability of Fe(III)deferasilox complex.
Figure 1.
Structures of metal complexes.
Figure 1.
Structures of metal complexes.
References
N. Iki, et al., Chem Commun 2013, 49, 4812.
N. Iki, et al., Inorg Chem 2012, 51, 1648.
N. Iki, et al., Inorg Chem 2016, 55, 4000.
N. Iki, et al., Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3079.
N. Iki, et al., J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 150, 133.
T. Takahashi, N. Iki, in Capillary Electrophoresis and Microchip Capillary Electrophoresis: Principles, Applications, and Limitations (Eds.: C. D. García, K. Y. Chumbimuni-Torres, E. Carrilho), Wiley, 2013, pp. 127143.
15. Plasmonic Biosensors for Biomedicine
Tomas Springer,
Marketa Bockova,
Jiri Slaby,
Erika Hemmerova
and
Jiri Homola
Institute of Photonics and Electronics of the CAS, Prague, Czech Republic,
Abstract: Optical biosensors hold potential for applications in many important areas, such as molecular biology, medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, food safety, and security. Optical biosensors based on surface plasmons (sometimes referred to as surface plasmon resonance (SPR) or plasmonic biosensors) represent the most advanced and mature label-free optical biosensor technology [1,2]. While plasmonic biosensors have been widely used to investigate biomolecular interactions, their bioanalytical applications remain rather limited. Herein, we discuss the main challenges in developing plasmonic biosensors for applications in biomedicine and present selected advances in plasmonic biosensor research that aim to address these challenges. In particular, we cover advances in plasmonic nanostructures, sensor instrumentation, transport of target molecules in microfluidic systems, functional coatings, and assays for the detection of analytes in complex biological media. We also highlight three applications of plasmonic biosensors related to the investigation of biomolecular interactions related to Alzheimer’s disease and the diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) [3–5]. We present an extremely sensitive assay for detecting MDS-related microribonucleic acids and demonstrate that in conjunction with a plasmonic biosensor the assay enables the detection of miRNAs in blood plasma with a limit of detection < 350 aM. Moreover, we use a plasmonic biosensor to quantify interactions between selected MDS-related proteins immobilized on the surface of the plasmonic imaging sensor and blood plasma and show that this interatomic approach can help discriminate among different MDS subgroups and healthy donors.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by the Czech Science Foundation under contract #20–23787X.
Reference
M. Bocková, J. Slabý, T. Špringer, J. Homola, Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 12, 151–176.
H. Altug, SH. Oh, S.A. Maier, J. Homola: Advances and applications of nanophotonic biosensors. Nature Nanotechnology, 2022,17, 5–16.
T. Špringer, Z. Krejčík, J. Homola, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2021, 194, 113613.
L. Chrastinová, O. Pastva, M. Bocková, N. S. Lynn, P. Šácha, M. Hubálek, J. Suttnar, R. Kotlín, J. Štikarová, A. Hlaváčková, K. Pimková, J. Čermák, J. Homola, J. E. Dyr, Scientific Reports, 2019, 9, Article # 12647.
E. Hemmerová, T. Špringer, Z. Krištofiková, J. Homola 2020, Biomolecules, 10, Article # 1214.
16. Recent Advances in Rapid and Accurate Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Nanoplasmonic Biosensors
Jaebum Choo
Chung-Ang University, Seoul, South Korea,
Abstract: The COVID-19 pandemic is causing severe social and economic problems worldwide. RT-PCR has been considered a gold standard for detecting SARS-CoV-2 target genes. In RT-PCR, however, the total diagnostic time, including sample preparation, gene amplification, and detection, takes approximately 3–4 h. Thus, it is necessary to shorten the diagnostic time for rapid on-site diagnosis. Various rapid kits for immunodiagnosis using antigen-antibody reactions were also developed to shorten the diagnosis time. However, they have not been adopted as the standard diagnostic method due to their poor sensitivity and accuracy. In particular, the “false negative” problem of commercialized immunodiagnostic kits is recognized as a severe problem that can aggravate the spread of the SARS-CoV-2. To resolve these issues, we have developed innovative SERS-based assay platforms with a portable Raman reader for rapid and sensitive immunodiagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 in the field. This technique enables detecting SARS-CoV-2 with a limit of detection (LoD) of less than 5.0 PFU/mL within 15 min. The results of this study show the possibility of clinical application that can dramatically improve the detection limit and accuracy of the currently commercialized SARS-CoV-2 immunodiagnostic kit.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant Numbers 2019R1A2C3004375 and 2020R1A5A1018052).
References
Dang, H., Park, S. G., Wu, Y., Choi, N., Yang, J. Y., Lee, S., Joo, S. W., Chen, L., Choo, J., Adv. Func. Mat. 2021, 31, 2105703.
Chen, H., Park, S. G., Choi, N., Kwon, H. J., Kang, T., Lee, M. K., Choo, J., ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2378-2385.
17. Continuous Autonomous Environmental Monitoring by Capillary Electrophoresis
Michael Breadmore 1,
Maria Paniagua Cabarrus 1,
Min Zhang 2,
Marni Amuno 1,
Richard Alexander 3,
Fernando Maya 1,
Rosanne Guijt 3
and
Bernadette Proemse 4
1
Chemistry, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia,
2
Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin, China
3
Centre for Regional and Rural Futures, Deakin University, Waurn Ponds, Victoria, Australia
4
Derwent Estuary Program, Hobart Tasmania Australia
Abstract: The importance of our environment and the water within it is, and will continue to be, of great importance in the decades to come, and this will increase the analytical burden to provide technology that can determine water quality in near-real-time. We have developed a low-cost, portable capillary electrophoresis system that is suitable for long-term deployment in the field for the temporal resolution of water chemistry. Chemistry and hardware for nutrient monitoring (NPK) have been developed, with a unique continuous flow microfluidic filtration system for particulate removal allowing the direct analysis of sewage and turbid natural waters. These systems have been deployed for autonomous river monitoring for six weeks, with commercial prototypes developed and deployed around Tasmania and New Zealand.
18. Challenges in Chromatographic Analyses of Phytonutrients in Plant Extracts and Food
Irena Vovk 1,
Vesna Glavnik 1,
Maja Bensa 1,2,
Urška Jug 1
and
Katerina Naumoska 1
1
Laboratory for Food Chemistry, National Institute of Chemistry, Hajdrihova 19, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia,
2
Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences, University of Maribor, Pivola 10, SI-2311 Hoče, Slovenia
Abstract: Phytonutrients represent a big group of compounds with different bioactivities (antioxidant activity, enhancement of immune response or cell-to-cell communication, lowering blood pressure and/or cholesterol level, etc.). Many phytonutrients daily consumed in unprocessed food (e.g., fruits or vegetables) have not yet been identified. More research is needed to connect the mode of action with specific phytonutrient in medicinal plants and foods and to study their possible toxicity and interaction with medicines. Several phytonutrients are nowadays marketed as active ingredients of food supplements (globally considered as food) or functional foods, although many of them have not yet been properly scientifically investigated. Therefore, new analytical methods are needed to control food quality and safety and to provide more information about food composition, as well as to gain knowledge about new possible phytonutrient ingredients for functional food and food supplement products. Chromatographic techniques, especially their combined use and hyphenation to mass spectrometry, are indispensable in the research of phytonutrients. We will present several methods (HPTLC- UV/Vis, HPTLC-FLD, HPTLC-MS/(MS), HPLC-UV/Vis, (U)HPLCMS/(MS)) for the analysis and characterization of compounds from different groups of phytonutrients (e.g., flavonoids, triterpenoids, phytosterols) present in different plant and food matrices. The examples will include targeted and non-targeted analyses and challenges related to stability of the analytes, lack of chromophores, variety of isomeric structures, lack of commercial standards and issues related to ion suppression. Some examples of peculiar phenomena concerning the unexpected rising of densitometrically determined peak areas of some compounds will also be given.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding No. P1-0005).
19. Accurate Determination of Mycotoxins and Organic Nutrient by Isotope Dilution-Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Mohamed A. Gab-Allah 1,2,
Yared Getachew Lijalema 1,2,
Hyeonwoo Yu 1,2,
Byungjoo Kim 1,2
and
Kihwan Choi 1
1
Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, Daejeon, Republic of Korea,
2
University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Matrix certified reference materials (CRMs) are key tools for the method validation. To develop CRMs, a higher order reference method is required. Isotope dilution methodology combined with liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC/MS/MS) has proven to provide the highest possible analytical specificity and accurate quantitative results. In this presentation, we will introduce the ID-LC/MS/MS method to be used for the determination of mycotoxins and organic nutrients in food matrix. Mycotoxins, toxic compounds produced by various fungi are known to have carcinogenic, mutagenic, estrogenic effects. Because mycotoxins are widely found in agricultural products, government authorities have established regulations. Among mycotoxins, the analytical method for commonly found type B trichothecenes, zearalenone, has been developed. Separation conditions of structurally similar mycotoxins and cleanup procedure were optimized. The occurrence of these mycotoxins from grains samples was also investigated. In addition, an accurate analytical method for essential nutrient vitamin B12 in food has been developed. These developed methods were fully validated and applied for the value-assignment of food matrix CRMs.
20. Evolution of Scanning Probe Microscopy to Nanoscale Molecular Analysis
Sang-Joon Cho
Application Technology Center, Park Systems Corp., Suwon, Korea
Abstract: The most widely known scanning probe technology, atomic force microscope (AFM), has evolved from a scientific discovery tool in materials and applied physics to become an essential tool for industrial development, e.g., in semiconductors, displays, materials, pharmaceuticals, and bio industries. AFM belongs to a bigger scanning probe microscope (SPM) family. It has been 40 years since the introduction of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM), the first SPM, in a paper. It became the subject of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. The SPM, which has played a crucial role in developing nanotechnology over the past 30 years, still has many scientific, technical, and industrial possibilities for the future technological leaps. Recently, as semiconductor devices continue to shrink in size, SPM is drawing more attention and is expanding from basic and high-tech research to application and industrial fields. One of the most significant advantages of SPM is that it is possible to observe various physical phenomena in the nanoworld. It can measure nano-physical, electricity, magnetic, electrochemical, temperature, near field optical, and ionic properties using various probe sensors in the atomic force microscopic platform. However, AFM has been unable to identify the sample’s chemical composition. Newly introduced photoinduced force microscope (PiFM) technology offers chemical mapping images with spectroscopic contrast at a nanometer spatial resolution. A probe was used as a detector, making it possible to obtain spectral data below 10-nm resolution instead of an optical detector. This paper will introduce how photo-induced force spectra correlate beautifully with the conventional Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and their potential in nanoscale molecular analysis.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Project Number: (2022)ERIC_03) and the Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA).
Reference
Sifat, A. A., Jahng, J., & Potma, E. O. Chemical Society Reviews. 2022.
21. Integrative Analysis of Metabolomics and Glycomics Data for Identifying Markers of Asthma in Serum and Sputum Samples
Bao Hui Ng
and
Sam F. Y. Li
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543
Abstract: In this study, a classification model was optimized to differentiate healthy controls and asthma patients, as well as patients with different severity of asthma. The predictive accuracy of the model was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUCROC). The AUCROC obtained from using the omics data in the model were more than 0.8 in both the serum and sputum samples. This shows that asthmatic patients and healthy controls can be distinguished accurately from their metabolome and glycome profile. During the classification of patients with different severity of asthma, the AUCROC obtained when the metabolomics datasets were used were less than 0.5. This indicates that the model using the metabolomics datasets was unable to distinguish patients with different severity of asthma. However, the AUCROC obtained when the glycomics data were used was slightly better with a value greater than 0.6, suggesting that glycans may potentially be superior in classifying asthma severity. The performance of the model in classifying asthma severity using metabolomics data from gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and glycomics data from CE-LIF was poor with low AUCROC of 0.229, 0.486, and 0.629, respectively. An attempt to integrate all the omics data in the classification model did not improve the AUCROC, indicating that the model or omics changes may not be suitable in distinguishing asthma severity, although the method allows asthmatic patients and healthy controls to be distinguished accurately.
22. Off-Line Clean-Up and On-Line Preconcentration New Approaches Prior to Capillary Electrophoresis Separations of Drugs and Endogenous Substances
Tomasz Bączek
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Medical University of Gdańsk, Hallera 107, 80-416 Gdańsk, Poland
Abstract: Very often, the efficient use of liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS) capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), e.g., micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) or microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography (MEEKC)-based separation methods, cannot be sufficient without carrying out a proper off-line sample preparation procedure and selection of the most efficient on-line preconcentration technique for investigated compounds. To improve concentration detection limits, off-line sample preparation techniques, e.g., liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), liquid-liquid microextraction (LLME), dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME), solid-phase extraction (SPE) or solid-phase microextraction (SPME) are some of commonly applied techniques. Among on-line preconcentration methods, there are relevant approaches allowing the quantification of trace amounts of compounds in pharmaceutical and biomedical samples. Here, the field-amplified sample stacking (FASS) and field-amplified sample injection (FASI) are the best recognized ones. Sweeping, micelle to solvent stacking (MSS), p-ITP (pseudo-isotachophoresis), or FESI in conjunction with sweeping (sequential stacking featuring sweeping, SSFS) represent other analyte enrichment techniques. In parallel, one should also remember the possibilities to optimize CE methods playing with hydrodynamic injection (HDI), electrokinetic injection (EKI), simultaneous EKI and HDI (SEHI), or repetitive injection (RI). Several examples of novel approaches based on variable combinations of mentioned techniques and methods to be applied for the analysis of mixtures of selected drug and endogenous substances are going to be thoroughly presented and discussed. Special emphasis on the novel applications in pharmaceutical and biomedical practice of two of them is going to be shown. Namely, ionic liquid-assisted solid-phase microextraction prior to micellar electrokinetic chromatography (IL-SPME-MEKC) during the analysis of biogenic amines in urine samples from pediatric hematology patients, as well as solid-phase microextraction combined with sequential stacking featuring sweeping prior to micellar electrokinetic chromatography (SPME-SSFS-MEKC) during the analysis of sirolimus in plasma sample after its liberation from coronary stents, will be comprehensively presented.
References
N. Miękus, I. Olędzka, N. Kossakowska, A. Plenis, P. Kowalski, A. Prahl, T. Bączek, Ionic liquids as signal amplifiers for the simultaneous extraction of several neurotransmitters determined by micellar electrokinetic chromatography, Talanta, 186 (2018) 119-123.
N. Kossakowska, I. Olędzka, A. Kowalik, N. Miękus, P. Kowalski, A. Plenis, E. Bień, A. Kaczorowska, M.A. Krawczyk, E. Adamkiewicz-Drożyńska, T. Bączek, Application of SPME supported by ionic liquids for the determination of biogenic amines by MEKC in clinical practice, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 173 (2019) 24-30.
Olędzka, P. Kowalski, A. Plenis, N. Miękus, N. Grabow, T. Eickner, T. Bączek, Simultaneous electrokinetic and hydrodynamic injection (SEHI) and sequential stacking featuring sweeping for signal amplification following MEKC during the analysis of rapamycin (sirolimus) in serum samples, Electrophoresis, 39 (2018) 2590-2597.
M. Pieckowski, P. Kowalski, T. Bączek, Combination of large volume sample stacking with polarity switching and cyclodextrin electrokinetic chromatography (LVSS-PS-CDEKC) for the determination of selected preservatives in pharmaceuticals, Talanta, 211 (2020) 120673.
M. Pieckowski, P. Kowalski, I. Olędzka, N. Miękus-Purwin, A. Plenis, A. Roszkowska, T. Bączek, Simultaneous determination of mitotane, its metabolite, and five steroid hormones in urine samples by capillary electrophoresis using beta-CD2SDS1 complexes as hydrophobic compounds solubilizers, Electrophoresis, 43 (2022) 990-997.
N. Kaczmarczyk, J. Ciżewska, N. Treder, N. Miękus, A. Plenis, P. Kowalski, A. Roszkowska, T. Bączek, I. Olędzka, The critical evaluation of the effects of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on the separation efficiency of selected biogenic amines and their metabolites during MEKC analysis, Talanta, 238 (2022) 122997.
23. Transient Incomplete Separation of Species with Close Diffusivity to Study Stability of Affinity Complexes
Tong Ye Wang 1,
Jean-Luc Rukundo 1,
An T.H. Le 1,
Nikita A. Ivanov 1,
C. Yves Le Blanc 2,
Boris I. Gorin 3
and
Sergey N. Krylov 1
1
Department of Chemistry and Centre for Research on Biomolecular Interactions, York University, Toronto, Canada
3
Eurofins CDMO Alphora, Mississauga, Canada
Abstract: Large molecules can be generically separated from small ones, though partially and temporarily, in a pressure-driven flow inside a capillary. This transient incomplete separation has been only applied to species with diffusion coefficients different by at least an order of magnitude [1–5]. Here, we demonstrate, for the first time the analytical utility of transient incomplete separation for species with close diffusion coefficients. First, we prove in silico that even a small difference in diffusivity can lead to detectable transient incomplete separation of species. Second, we use computer simulation to prove that such separation can be used for the reliable determination of equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of complexes composed of similar-size molecules. Finally, we demonstrate experimentally the use of this separation for the accurate determination of Kd value for a protein-aptamer complex. We conclude that “Accurate Constant via Transient Incomplete Separation” (ACTIS) can serve as a reference method for affinity characterization of protein–aptamer binding in solution.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Egnineering Research Council of Canada.
References
M. Harada, T. Kido, T. Masudo, T. Okada. Anal. Sci. 2005, 21, 491–496.
R. Umehara, M. Harada, T. Okada. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 472–478.
N. Sisavath, J.-L. Rukundo. J. C. Y. Le Blanc, V. A. Galievsky, J. Bao, S. Kochmann, A. S. Stasheuski, S. N. Krylov. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6635−6639.
J.-L. Rukundo, J. C. Y. Le Blanc, S. Kochmann, S. N. Krylov. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11973−11980.
J.-L. Rukundo, S. Kochmann, T. Y. Wang, N. A. Ivanov, J. C. Y. Le Blanc, B. I. Gorin, S. N. Krylov. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11654–11659.
24. Quantitative Analysis of Oligo: mRNA Vaccine, Gene Therapy and mRNA End Capping
Seo Bong Chang
SCIEX Korea, Seoul, R.O.Korea
Abstract: Although possibly not be the first, the COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dramatically presents the need for quantitative purity analysis of oligos. Previously, the main focus of oligo analysis was on sequence information and qualitative analysis. However, recently, oligos have been adapted to therapeutic areas, such as mRNA analysis, gene therapy etc. Quantitative analysis is necessary for therapeutics, and capillary electrophoresis has been widely used for purity quantitative analysis. In this presentation, recent mRNA (mRNA vaccine) and/or transgene (viral vectors) purity analyses are presented. Moreover, 5’ methylguanosine cap and 3’ poly-A capping of mRNA can be analyzed by capillary electrophoresis. These are recently getting attention from the biopharma market for the quality estimation of products.
25. Porous Polymer Monoliths: A Universal Tool in Chromatography
Frantisek Svec
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Charles University, 500 05 Hradec Kralové, Czech Republic
Abstract: Modern monolithic columns emerged about 30 years ago. Their well-known advantages include ease of the preparation, robustness, high permeability to flow, mass transport via convection, and a vast variety of chemistries. The early polymer-based monoliths were used almost entirely for the rapid liquid chromatography separations of proteins and other large molecules. A number of new chemistries and functionalization methods were meanwhile developed to produce monolithic columns for the separations in various chromatographic modes including gas chromatography, electrochromatography, and microfluidics. In addition to typical chromatographic applications, new uses were recently described, thus confirming the versatility of the monoliths. For example, reversible functionalization via the attachment of gold nanoparticles to thiols provides materials for highly sensitive surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Thin monolithic layers are gaining more attention as well since they enable the efficient separation of proteins using very simple means followed by easy detection using mass spectrometry or SERS.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the project EFSA-CDN (No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000841) co-funded by the ERDF.
26. One-Flow Synthesis of Functional Chemicals via Diverse Phase Separation Steps
Dong-pyo Kim
Department of Chemical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang, 37673, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In semiconductor industry, electronic packaging materials require electrical insulation as well as good processability, low thermal expansion, and high thermal conductivity for a lower temperature packaging process and quick cooling from high power chip. At present, the epoxy-based precursor suffers from a time- and labor-intensive multi-step protocol. Here, we report one-flow multi-step synthesis of new type of epoxy monomer (Np-C4-Np) as a precursor of packaging resin with a low glass transition temperature via a three step reaction (esterification, deprotection, epoxidation) and multiple separation steps (extraction-ternary phasic separation-solvent switching). With integrating flow reactors and in-line separators, the Np-C4-Np could be synthesized rapidly with higher space-time-yield compared to the batch system, confirming the benefits in terms of productivity. In addition, several types of continuous-flow micro-separators as a membrane process or a membrane-free process with built-in superamphiphobic functional structure are developed on the basis of different principles, such as liquid-liquid extraction, liquid-gas distillation, and membrane separation in purifying the generated reagents.
27. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances: Personal Observations on Challenges for Risk Assessment and Management of Environmental Contamination
Karl Bowles 1,2
1
RPS AAP Consulting Pty Ltd., Sydney Australia
2
Adjunct University of Queensland QAEHS, Woolloongabba Australia
Abstract: Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are receiving considerable attention globally from environmental regulators, environmental consultants, researchers, politicians, and news media. Much interest stemmed initially from legacy use of firefighting foams especially for repeated training exercises over decades, acting as an effective pathway for PFAS exposure to the environment. More recently, the extent of PFAS use in an enormous range of products has become more widely known outside relevant industry, with resulting attention to waste sectors (landfills and sewage treatment). In some countries, household and workplace exposures have also been critically examined. Managing issues relating to PFAS in the environment requires effective risk assessment, and ultimately, sensible approaches for remediating impacted water, soil, and sediment. Risk assessment has been hampered by both toxicological uncertainty and key differences in environmental fate and transport between PFAS and other groups of chemicals. Similarly, the unique properties of PFAS have resulted in challenges for developing and validating effective and affordable treatment technologies. While considerable work has been devoted to these areas, many knowledge gaps remain, and understanding these uncertainties is important to decision makers. A discussion of risk assessment will include observation of changing human and ecological guidance values over time and between different countries. A discussion of remediation approaches will include high level coverage of currently available and emerging technologies. The talk will include personal observations drawn from experience working as a technical advisor to multiple stakeholders involved in managing PFAS, including at different levels of government and private industry, and from the perspective of both regulators and problem owners.
28. Potential Release of PFAS from Spent Engineered Sorbents
Melanie Kah 1,
Danielle Olive r 2
and
Rai Kookana 2,3
1
School of Environment, University of Auckland, 23 Symonds Street, Auckland 1010, New Zealand
2
CSIRO, Land & Water, Locked bag 2, Glen Osmond, SA, Australia
3
University of Adelaide, School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, Locked bag 1, Glen Osmond 5064, Australia
Abstract: The most common approach for treating PFAS contaminated water currently relies on sorption to engineered sorbents. The spent sorbents loaded with PFAS can potentially be disposed of at landfills, provided the sorbed contaminants remain sequestered and certain risk criteria are met. Hence, it is essential that remediation sorbents (i) rapidly adsorb a large variety of PFAS under varying water chemistry conditions and (ii) do not release the adsorbed PFAS in due course. The release of PFAS from spent sorbent materials, stored or deposited under conditions that vary over time, is highly undesirable as they can potentially become a secondary source of PFAS in the environment. This presentation will provide an overview of the current state of knowledge about the potential release of PFAS that may occur during and after treatment. The literature review was published [1] and highlights that data are only available for a very restricted range of long-chain PFAS, and that data on desorption processes remain very limited. The sorption of PFAS can be strongly affected by changes in the solution pH, ionic strength, and dissolved organic matter content, and the process is also subject to complex competition mechanisms in the presence of other PFAS as well as organic contaminants and inorganic salts. Desorption is more likely to occur for PFAS with shorter carbon chain lengths.
29. Electrostatic Interactions of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) with Soil Minerals
Balwant Singh 1
and
Rai Kookana 2
1
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, The University of Sydney, Australia
2
CSIRO Land and Water, Australia; University of Adelaide, Australia
Abstract: Concerns about the adverse impacts of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on human and ecosystem health are growing worldwide. Soils serve as an important sink as well as a source of PFAS in the environment. It is, therefore, important to develop a sound understanding of the fate and behavior (such as sorption, bioavailability, and mobility) of PFAS in the soil environment. PFAS have complex chemical properties (amphiphilic and surfactant properties as well as surface activity) that influence their sorption-desorption behavior in soils. Indeed, the mechanisms of sorption of PFAS in soils are more complex than many conventional organic chemicals. Studies have shown that, unlike most other organic compounds, the hydrophobic interactions of PFAS with soil organic matter alone cannot explain the sorption behavior of PFAS in soils. The charge characteristics of PFAS can be anionic, cationic, or zwitterionic depending on the chemistry of compounds, and the electrostatic interactions of PFAS with soil minerals play a major role in their adsorption in soils [1]. Many aluminosilicate clay minerals carry permanent negative charges and thus offer significant adsorption sites for positively charged PFAS (e.g., cationic or zwitterionic compounds) in soils. In addition to this, organic matter, Fe and Al oxides, and edges of layer silicate minerals (such as kaolin) have significant amounts of variable surface charge that could be positive under natural soil conditions. Therefore, soils rich in these minerals, particularly Fe and Al oxides, such as tropical soils, can electrostatically adsorb negatively charged PFAS from soil solution. The negatively charged PFAS (e.g., PFAS with a carboxylic acid or a sulfonic acid head group) are repelled by permanent negatively charged surfaces on clay minerals and thus generally adsorbed in smaller amounts than cationic or zwitterionic PFAS in soils. Electrostatic interactions of PFAS on soil minerals can include cation exchange, cation bridging, and anion exchange processes. For example, it has been reported that the sulfonate headgroup of some PFAS (e.g., PFOS) forms outer-sphere complexes with hematite surfaces [2]. In another study, metallic ions (Cu2+ and Pb2+) were found to influence the charge characteristics of inorganic oxides (Al2O3, Fe2O3, SiO2 and TiO2), and thus significantly enhanced the adsorption of PFOS through a cation bridging effect [3]. Overall, this presentation will highlight the importance of surface charge characteristic of soil minerals on the sorption behavior of PFAS in soils.
References
Li, Y., Oliver, D.P., Kookana, R.S. A critical analysis of published data to discern the role of soil and sediment properties in determining sorption of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628629, 110-120.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.167.
Gao, X., Chorover, J. Adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid to iron oxide surfaces as studied by flow-through ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Environ. Chem.2012, 9. 148-157.
https://doi.org/10.1071/en11119.
Lu, X., Deng, S., Wang, B., Huang, J., Wang, Y., Yu, G. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorooctane sulfonate on nanosized inorganic oxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2016, 474,199-205.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.04.032.
30. Electrochemiluminescence as a Versatile Tool for the Selective Detection of Diagnostic Biomarkers and Environmental Pollutants
Kyoung-Rok Kim,
Taemin Kim,
Yon Namgoong,
Hyun Seung No
and
Jong-In Hong
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
Abstract: Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) is a luminescent process which generates light through sequential electron transfer reactions on the electrode surface. ECL-based molecular sensors have several advantages over the conventional analytical techniques such as high sensitivity and low background signal. Additionally, the ECL provides the possibility of potential point-of-care-testing and field-monitoring with the simple equipment and method. However, ECL detection of small molecules is still a great challenge because most of ECL detection methods have been developed via specific biomacromolecular recognition, such as antibody–antigen and aptamer–protein interactions. Herein, we report ECL molecular sensors for selective detection of diagnostic biomarkers and environmental pollutants. In the first part, turn-on ECL chemodosimeters for H2O2 were designed and synthesized by connecting pyridineextended BODIPY (Py) and a [(pinacolato)boryl]benzyl moiety as an ECL reporter and a traceless reaction site to H2O2, respectively. The extraordinary electrochemical stability of Py enabled sensitive and reliable detection of H2O2 through the ECL channel. Fluorination at the reaction site accelerated the detection of H2O2 when compared with a non-fluorinated one. Moreover, a fluorine-substituted probe in combination with GOx was successfully applied for the quantitative analysis of glucose in human serum, providing feasibility as a versatile tool for point-of-care testing (POCT) devices. In the second part, we report ECL probes for selective detection of for biologically important analytes (hydrogen sulfide, homocysteine, cysteine, glutathione) and environmentally toxic molecules (thiophenol, glyphosate, Hg(II)) based on rationally designed cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes having both a reaction site and a signaling unit. Probe design principles, detection mechanisms, and practical applications will be presented.
References
Kim, K.-R., Kim, H. J., Hong, J.-I., Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1353-1359.
Park, J., Kim, T., Kim, H. J., Hong, J.-I., Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 4565-4573.
Kim, T., Hong, J.-I., ACS Omega. 2019, 4, 12616-12625.
Namgoong, Y., Oh, J., Hong, J.-I., Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7577-7580.
Kim, H. J., Kim, T., Hong, J.-I., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2020, 307, 127656.
No, H. S., Kim, T., Hong, J.-I., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2021, 342, 12986.
Kim, K.-R., Oh, J., Hong, J.-I., Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5091-5098.
31. Neural Mechanism Mimetic 2nd Generation Electronic Nose
Jin-Woo Oh
Department of Nanoenergy Engineering, Pusan National University
Abstract: From a practical point of view, the eventual dream is that the electronic nose will replace the K9-like tasks of detecting explosives, drugs, missing persons, diseases, etc. With this vision, electronic noses employing various materials and different detection methods are continuously being developed. Despite the strong potential of electronic noses, practical implementation remains a hurdle to overcome. The K9 olfactory receptors incorporate up to ~220 million units. To realize a biomimetic electronic nose with a detection performance comparable to that of the K9, the number of the sensor units should be equal. To overcome this, understanding how K9’s brain analyzes signals generated by its olfactory system is crucial. Signals generated by 220 million olfactory receptors are selectively and partially activated through the brain’s learning process, called the neural pattern separation (NPS). The brain solves the pattern-learning and pattern-recognition problems of the signals it generates for complex and noisy stimuli in large and complex olfactory systems. To understand this incredible success, neuroscientists go beyond the hardware-based perspective and provide a convincing explanation based on the information processing system of the neural network. The patterns that are generated in the olfactory organs are very large and complex, and the internal method by which the brain computes patterns is not yet clear. Therefore, it is difficult to find the direct correlation between them. However, mechanism studies in olfactory organs provide clues to the selective actions that drive specific combinations of input signals. Here, by mimicking olfactory network dynamics, we developed the NPS and used it to develop a second-generation electronic nose. To demonstrate the characteristics of the second generation electronic nose with the NPS, we conducted studies that applied it to a variety of applications, including polycyclic aromatic compound (PAH) detection, respiratory-based lung cancer diagnosis, and fruit freshness monitoring.
32. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Land and Water Environments of Asia
Rai S Kookana 1,2
1
CSIRO Land and Water, Waite Campus, Glen Osmond, Australia
2
University of Adelaide, Waite Campus, Glen Osmond, Australia
Abstract: Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have been in use worldwide for decades now. Concerns about their adverse impacts on human and ecosystem health are growing globally and some of the PFAS have already been included in the list of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) under the Stockholm Convention. As a result of their extreme persistence and high mobility, PFAS are now ubiquitous in land and water environments. Since the decision of 3M company in 2000 (under the guidance of US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA)) about the phasing out of perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), and related compounds, the production of PFAS shifted to Asia, most notably to China and India. This has gradually led to a greater exposure of the Asian environment to PFAS. Consequently, in recent years, a lot of work on the monitoring of PFAS has been conducted in Asia, especially in China, Japan, and South Korea. While the research and monitoring effort is patchy in Asian countries, a lot of data has become available in published in recent years. For example, a recent review of the published data on 24 different PFAS in surface and groundwater waters (Sims et al. 2022—DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151535) revealed that a number of data points on surface waters from Asia are indeed larger than those from other continents. This study has revealed that the concentration of PFOA in surface waters in Asia exceeded the USEPA guideline of 70 ng/L in 22% of cases as compared to 15% cases globally. In contrast, surveys on contaminated soils in Asia are currently lacking. Studies have shown that the receiving environments, such as surface water bodies and groundwaters, in the vicinity of production facilities, such as a mega fluoropolymer production industrial park in China, have been heavily contaminated and may be at higher ecological and human health risks. These data suggest that greater attention is warranted towards PFAS in other regions, such as South Asia and South East Asia.
Acknowledgement: This study is part of the project on Per and polyfluroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the Environments of Emerging Economies (2019-029-2-600), funded by International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
33. Electro-Driven Extraction Based on a Polymer Inclusion Membrane (PIM) Sampling Probe
Hui Yin Tey 1,2,
Michael C Breadmore 2,3
and
Hong Heng See 1,2
1
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia
2
Centre for Sustainable Nanomaterials, Ibnu Sina Institute for Scientific and Industrial Research, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Johor Bahru, Johor, Malaysia
3
Australia Australian Centre for Research on Separation Science (ACROSS), School of Natural Sciences-Chemistry, University of Tasmania, Private Bag 75, Hobart, TAS 7001, Australia
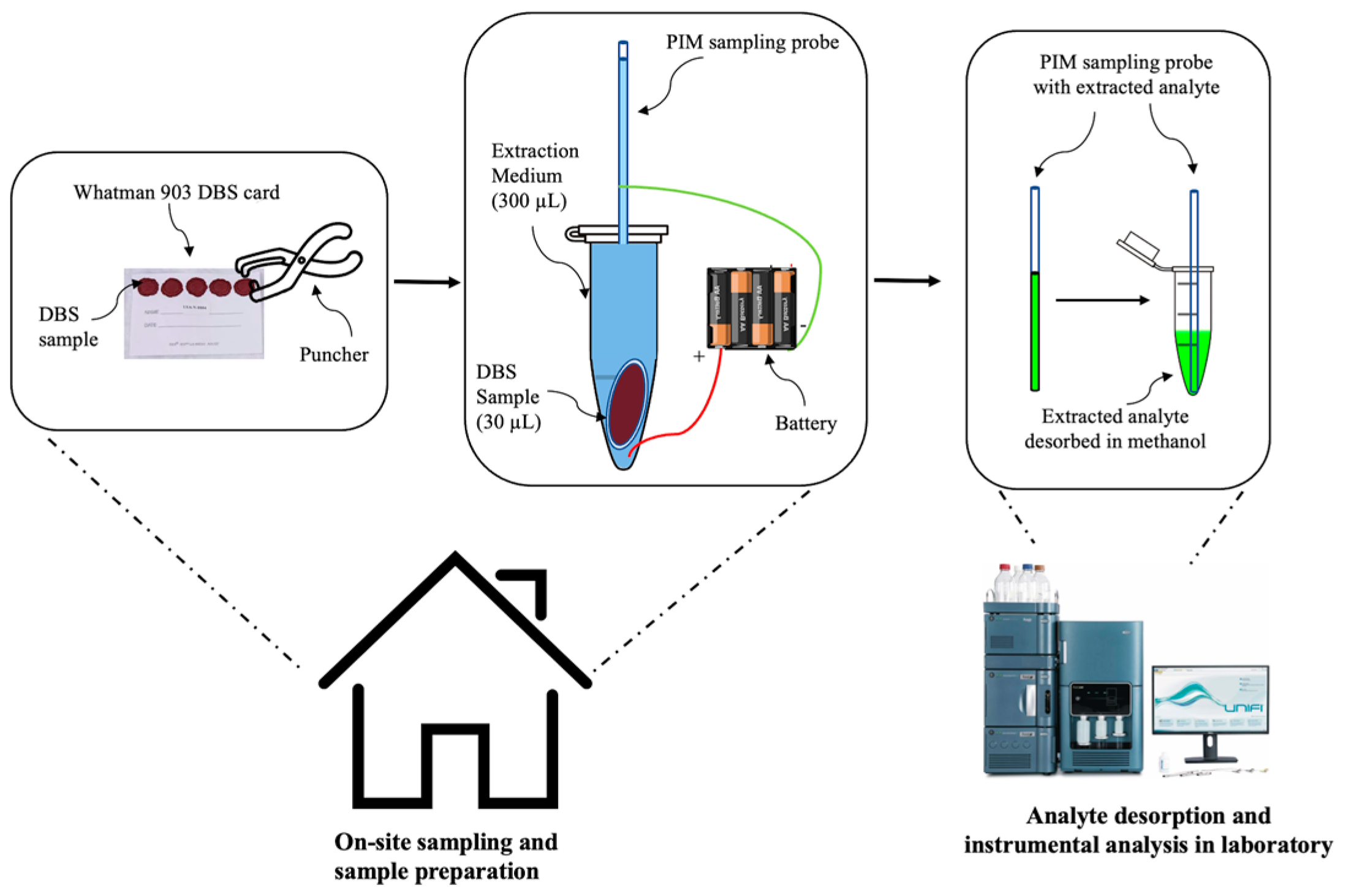
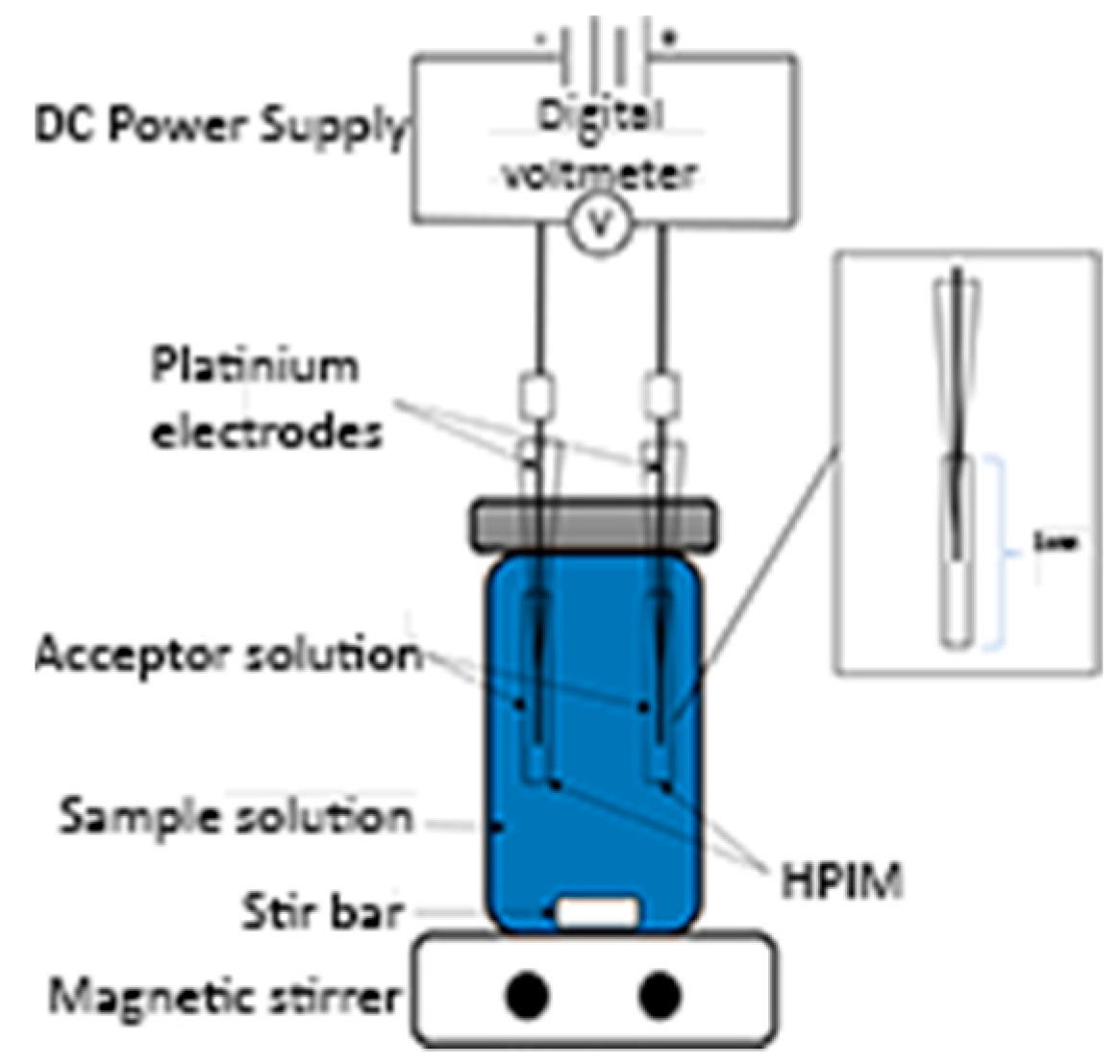
Abstract: A polymer inclusion membrane (PIM)-based sampling probe was developed for the electrokinetic extraction of drugs from biological fluids. The probe was fabricated by dip-coating a nonconductive glass capillary tube in a homogeneous PIM solution for three cycles. The PIM solution comprised cellulose triacetate (CTA), 2nitrophenyl octyl ether (NPOE) and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide [EMIM][NTf2] in a ratio of 5:4:2. The developed probe electrokinetically extracted doxorubicin from human plasma, human serum, and dried blood spot (DBS) samples. The practicability and reliability of the electrokinetic extraction process were evaluated using LC-MS/MS to quantify the desorption of extracted doxorubicin. Under the optimized conditions, a quantification limit of 0.4 to 2 ng/mL was achieved for the three biological samples. The probe was further integrated into a portable battery-powered device for safe, low-voltage (36 V) electrokinetic extraction. The developed technique is envisioned to provide a more efficient analytical workflow in the laboratory.
Figure 1.
Analytical concept of PIM sampling probe with LC- MS/MS analysis.
Figure 1.
Analytical concept of PIM sampling probe with LC- MS/MS analysis.
34. Photodegradation of HDPE and Assessing Its Contribution to Microplastic Pollution in Coastal Waters
Lokesh P. Padhye 1
and
Mahyar Ghanadi Shakerd Abdollahi 2
1
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand
2
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand
Abstract: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is one of the most widely used plastics in the industry (Lundbäck, 2005). HDPE has also found applications in coastal environments as in pile sleeves (Gong et al., 2021), pallets and crates (Emblem, 2012), pontoons, and supporting platforms for floating solar panels over water bodies (Sahu & Sudhakar, 2019). Knowing HDPE’s durability is important when selecting it for applications in the coastal environment. Since environmental factors, such as UV radiation, weathering, and/or mechanical stress (i.e., waves and vessel impact), can degrade the HDPE-containing materials, they may become a source of plastic pollution (at micro/macro scales) in the coastal environment. So far, very limited research has been conducted regarding the long-term degradation and weathering potential of HDPE in coastal waters. The present study focused on understanding the role of HDPE sleeves as a source of microplastics in coastal waters through understanding the impact of UV radiation. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used to investigate the chemical/structural changes of the HDPE. Carbon-oxygen, carbonyl, and hydroxyl surface groups were monitored for HDPE samples obtained from aged pile sleeves. Accelerated weathering of the HDPE under UVB irradiation made carbonyl groups disappear without regeneration. The role of anti-oxidant additives in HDPE weathering was confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Acknowledgement: The Authors thank Auckland Transport for providing the HDPE samples and funding support. We also wish to thank Catherine Hobbis for her assistance in SEM and XPS analyses.
References
Gong, Y., Wang, S. H., Zhang, Z. Y., Yang, X. L., Yang, Z. G., & Yang, H. G. (2021). Degradation of sunlight exposure on the high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipes for transportation of natural gases. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 194, 109752.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109752.
Lundbäck, M. (2005). Long-term performance of polyolefins in different environments including chlorinated water, Antioxidant consumption and migration, and polymer degradation. KTH Fibre Ans Polymer Technology, 11–51.
Sahu, A. K., & Sudhakar, K. (2019). Effect of UV exposure on bimodal HDPE floats for floating solar application. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 8(1), 147–156.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2017.10.002.
35. Microplastics Contamination and Their Impacts in Soil Ecosystems
Yuxin Huo,
Feike A. Dijkstra,
Malcolm Possell
and
Balwant Singh
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, The University of Sydney, Australia
Abstract: The production and consumption of plastics have increased to over 8300 million metric tons (Mt) since the 1950s when their large-scale commercial production commenced [1]. Because of the limited environmental degradation and widespread use, including in agricultural systems, an estimated 6500 million tons of plastics waste have accumulated in the terrestrial and aquatic environments. Over two thirds of the plastic waste has been deposited in landfills and natural environments including soils. Traditional plastics are generally highly resistant to degradation in soil and other terrestrial environments, but they can be progressively broken down into small fragments and particles called microplastics (MPs) with size < 5 mm. With the increasing use of plastics in agriculture and other industries, MPs accumulation has increased in soils. Recently, Huo et al. [2] reviewed the global state of plastics contamination in soils, including their distribution, concentration, shape, composition, and size. The concentration of MPs in soil was found to be highly variable globally, with a mean and a median value of 6.15×103 particles kg–1 and 1.08×103 particles kg–1, respectively. The composition of MPs in soils was also found to be extremely variable. However, polyethene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyamide (PA) were identified as the most dominant plastics. Wastewater, sewage sludge, composts, and agricultural films have been identified as the main contributors of MPs in soils. The introduction of MPs in soils has adverse impacts on soil flora, fauna, and soil properties. A meta-analysis study found a linear decrease in plant effect sizes of chlorophyll, belowground length, aboveground length, aboveground biomass, and germination, as well as a continuous increase in oxidative stress, with increasing plastic concentration in soils [3]. Vegetable crops were found to be more sensitive to plastics exposure than cereal plants. Similar to plants, MPs contamination in soils has negative effects on the faunal reproduction, locomotion, and growth of soil fauna. However, the effects were less clear in soils as compared to liquid growth medium. The effects of MPs contamination in soils on soil aggregation, soil structure, and water holding capacity have been studied. However, the results are inconclusive and further research is needed on these aspects.
References
Geyer, R., Jambeck, J.R., Law, K.L. Sci. Adv. 2017., 3, e1700782-e1700782.
Huo, Y., Dijkstra, F.A., Possell, M., Singh, B. Adv. Agron., 2022, 175, 1-132.
Huo, Y., Dijkstra, F.A., Possell, M., Singh, B. Environ. Pollut., 2022, 310, 119892.
36. We Need Easy and Feasible Methods to Quantify Microplastics in Drinking Water or Wastewater
Hyunook Kim 1,
Ingyu Lee 1,
Jung-Jae Kim 2
and
Juhyun Park 3
1
University of Seoul, Dept. of Environmental Engineering, Seoul, Korea
2
Hanbat University, Deajeon, Korea
3
National Institute of Environmental Research, Incheon, Korea
Abstract: Although many studies have been conducted to quantify microplastics (MPs) in drinking water and wastewater, no easy and standardized analytical method or apparatus has been proposed. Recently, a number of attempts have been made to standardize MP-measuring methods based on micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (μ-FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, or pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). These methods have been applied for evaluating MPs in both drinking water and wastewater. However, the spectroscopic approach is more suitable for MPs in drinking water while the mass-spectroscopic one is for MPs in wastewater. Nonetheless, they still require time-consuming and labor-intensive sample pretreatment, instrument configuration, and complex data processing. These methods may not be feasible in evaluating the removal performance of treatment processes for MP-containing water or wastewater. Therefore, in this presentation, we propose innovative methods which easily and feasibly quantify plastic particles in water or wastewater. For quantifying MPs in drinking water, an optics-based approach (OBA) has been evaluated. On the other hand, a TOC-analyzer-based approach (TAA) was applied for the MPs in wastewater. Microplastics of > 20 μm in drinking water could be easily detected and estimated by the OBA. A high-resolution camera was installed in flowing water to catch MP images. For TAA, wastewater samples were collected and filtered using stainless-steel filters to harvest particles between 45 μm and 500 μm. Then, the retentates of the filter were digested by Fenton’s reagent to remove organic matters other than plastic particles before TOC determination. The method detection limit of the proposed method was 0.003 mg (0.15 μg L−1 for a 20 L sample), and the recovery efficiency estimated with six different types of plastic particles ranged from 76% to 98%. We believe that the proposed OBA and TAA can be used to evaluate the performance of treatment plants for drinking water and wastewater, respectively.
Acknowledgement: National Research Foundation (No. 2020R1A2C2101347) funded by the Korean Government (MSIT). PostPlastics Graduate Program funded by Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute.
37. Moving Reaction Boundary Electrophoresis
Q. Zhang,
W. W. Liu
and
C. X. Cao
Department of Instrument Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
Abstract: In the last 30 years, moving reaction boundary (MRB) electrophoresis was greatly developed. First, a novel fluorescent stacking boundary (FSB) was proposed using monosaccharide or glycoprotein in the microcolumn and the complex probe of BBV-HPTS in chip electrophoresis. The relevant experiments showed that (i) the probe could interact with free glucose or bound one; (ii) the detection signal was as function of concentration of glucose or glycoprotein; and (iii) the band motion has relation with glucose content. The developed microscale technique had the following merits: (i) low cost; (ii) fair LOD (e.g., 2.0 pg HbA1c); and (iii) high throughput (12 runs). Second, a microarray isoelectric focusing (IEF) was designed based on the concept of MRB. A series of high-resolution separations were observed: (i) the separation of oxidized and reduced species of cyto C; (ii) the complete separations not only between HbA1c and HbA (ΔpI < 0.03, in 500 μm space), but also between HbA1c and its precursor (ΔpI < 0.015, in 200 μm); (ii) the clear separation between Hb species of glycated α- or β-chains and HbA1c. The high resolution was attributed to the “inner” and “outer” stabilities of array IEF. The array IEF has been designed as a special diagnosis instrument to be used for the Hb analysis of diabetes. Third, we developed the MRB titration models, concepts, relevant theory, and chip electrophoresis for the assays of protein, enzyme, and uric acid as well as melamine. The experiments showed that (i) the content of protein in milk sample could be detected MRB titration without interference of non-protein nitrogen; (ii) adulteration ratio of poor protein adulated into good protein sample could be assayed by double protein model titration; and (iii) protein content of milk could be determined via a portable MRB titration chip within 10 min. Furthermore, the portable and visual model of MRB titration could be developed for the assays of enzyme activity, uric acid in urine or blood samples, and melamine adulteration in milk.
References
C. X. Cao, J. Chromatogr. A, 1998, 813, 153-172.
C. X. Cao, L. Y. Fan, W. Zhang., Analyst, 2008, 133, 1139-1158.
J. Y. Dong, S. Li, H. Y. Wang, et al., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 5884-5891.
H. Y. Wang, C. Y. Gou, C. G. Gou, et al., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2013, 774, 92-99.
H. Y. Wang, Y. T. Shi, et al., Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 2888-2896.
L. X. Zhang, Y. R. Cao, et al., Biosens. Bioelectrons., 2016, 77, 284-291.
R. Zhong, H. Y. Zhang, Q. Zhang, et al., Lab Chip, 2016, 16, 3538-3547.
W. L. Li, Q. Zhang, F. Z. Kong, et al., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90, 6710-6717.
X. Y. Cao, F. Z. Kong, Q. Zhang, et al., Lab Chip, 2018, 18, 1758-1766.
C. H. Wang, Q. Zhang, et al., Y. X. Wang, et al., Lab Chip, 2019, 19, 484-492.
M. I. Khan, Q. Zhang, S. Saud, et al., Sensors & Actuators, B., 2019, 286, 9-15.
Q. Zhang, W. W. Liu, M. Idrees Khan, et al., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91, 7500-7504.
H. Kong, W. W. Liu, W. Zhang, et a., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11, 29549-29556.
X. T. Jiang, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, et al., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92, 12017–12025.
X. J. Wu, Q. H. Meng, Q. Zhang, et al., Sensors & Actuators: B, 2020, 309, 127773.
L. Chen, Q. Zhang, W. W. Liu, et al., Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2021, 170, 112676.
38. Improved Method for the Determination of Aqueous Nitrate and Nitrite Concentration Using Capillary Electrophoresis
Gabor Jarvas 1,
Marton Szigeti 1,
Robert Farsang 1
and
Andras Guttman 1,2,3
1
Translational Glycomics Group, MUKKI, University of Pannonia, Veszprem, Hungary
2
Horváth Csaba Memorial Institute of Bioanalytical Research, University of Debrecen, Hungary
3
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract: The role of nitrite (NO2-) and nitrate (NO3-) is essential in the global nitrogen cycle. Monitoring their concentration in environmental and industrial aqueous samples, surface water, soil, food, and agricultural products is of high importance. Especially, the effect of anthropogenic emission, i.e., intensified agriculture, is essential due to the overuse of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers [1,2]. The most widely utilized methods for nitrate determination are colorimetry, potentiometry, UV absorption, and liquid chromatography. UV spectroscopy is the most frequently used technique due to its versatility and simplicity. However, there is an industrial and academic need to develop new methods to overcome the known drawbacks, i.e., inadequate limit of detection and potential interferences with other organic compounds in the sample. In this presentation, we report on the development of a new analytical method based on capillary electrophoresis separation, capable to measure the concentration of nitrite and nitrate well below the limits of UV spectroscopy methods. During the development process, special attention was paid on practical aspects, so the method was tested to quantify nitrite and nitrate in various surface water samples.
Reference
Vitousek, P.M., et al., Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecological Applications, 1997. 7(3): p. 737-750.
Camargo, J.A., A. Alonso, and A. Salamanca, Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: a review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere, 2005. 58(9): p. 1255-67.
39. Some News for CE and Fatty Acid Separations
Hai Yen Ta,
Lucie Perquis,
Stéphane Balayssac,
Christophe Déjugnat,
Alexandre Wodrinski,
Fabrice Collin,
Véronique Gilard
and
François Couderc
Laboratoire IMRCP, UMR 5623, Université Paul Sabatier, Université de Toulouse, TOULOUSE, France
Abstract: For 30 years, less than 60 studies have reported the separation of free fatty acids by capillary electrophoresis (CE). It is true that the main technique for the analysis of these compounds is the GC of methyl esters. For example, for the analysis of oils and to identify the main fatty acids that make up the triglycerides, the FAME method using GC-FID is the standard method. However, this has the major drawback of requiring saponification in methanol/water medium, then acidification followed by extraction in organic medium, then neutralization and evaporation preceding methylation, extraction, dilution in organic solvent, and injection in GC-FID or GC -MS. In CE, the method can be much shorter: saponification in a methanol medium, injection in CE. Leal de Oliveira et al. [1] recalled that by using a buffer containing, e.g., sodium dodecylbenzensulfonate and SDS or Brij, saturated or unsaturated fatty acids could be detected, whereas in the presence of only SDS, unsaturated fatty acids are selectively detected. We used a very simple buffer with 60mM SDS to check the concentration of w-3 fatty acids in dietary supplements. In view of studying fatty acids by CE/MS, it seemed interesting to us to use a volatile surfactant, such as ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFOA), already used for various separations, e.g., amino acids, peptides, small aromatic molecules, carbamates [2] etc. However, perfluorinated compounds are known to have “hydrocarbon repellant” properties, i.e., it is difficult to have interactions between perhydrocarbonated and perhydrofluorinated chains. Thus, using CE, NMR, and light scattering techniques, we studied the structure of APFOA micelles in the presence of methanol to solubilize the C18 unsaturated fatty acids. Then, we carried out the separation of such fatty acids using CE in order to optimize their separations. We sought to understand the nature of the interactions between fatty acids and perfluorinated micelles in order to explain the separation mechanism.
Reference
Leal De Oliveira, M.A., Simas Porto B.L., Leite Faria I.D., Lopes De Oliveira P, Mendonça De Castro Barra P, De Jesus Coelho Castro R., Takabayashi Sato R, Molecules 2014, 19, 14094-14113.
Van Biesen, G. and Bottaro, C.S., ELECTROPHORESIS 2006, 27, 4456-4468.
40. Fluorescent Imaging and Analysis by Using De Novo Formation of Fluorophores in Biosamples
Yan Lee
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Most chemical fluorophores are synthesized prior to their introduction into biological molecules, which can be thereby quantified or tracked for sensitive and selective analysis and imaging of biological samples. In this presentation, we introduce some examples of the de novo generation of fluorophores from non-fluorogenic biological molecules under very mild conditions. Some amine-based molecules, such as amino acids and carbon metabolites, e.g., 2-oxoglutrate or citrate, could form bright fluorophores in biological specimens. We applied the fluorophore formation reaction to analyze the biological metabolites quantitatively. More importantly, we applied the reaction to visualize pathological tissue samples for 3D histology. The de novo fluorophore generation not only shed some light on the evolution of biopigments and the origin of autofluorescence, but also inspired synthetic chemists to design next-generation fluorophores. Moreover, the 3D-histological application may open the door to volumetric analyses of pathological features for more accurate diagnosis and prognosis.
References
Kim, Y., Kang, S., Lee, B. H., Song, Y., Kang, S., Park, H. Y., Lee, Y., Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 365-372.
Jung, D., Choi, D., Sim, C., Kim, Y., Kang, S., Nam, S. H., Jang, J., Kim, D., Chang, M. S., Park, J., Lee, Y., Chem. Commun., 2020, 56-74-77.
41. Nonlinear Electrokinetics Effects Enable High-Resolution Separations
Blanca H. Lapizco-Encinas
Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY 14623-5604, USA
Abstract: Microscale electrokinetics (EK), a major pillar in the field of microfluidics, has been used extensively for the sorting and separation of a wide array of target particles, across multiple size scales, ranging from micromoles to parasites. Electrokinetic methods are label-free and robust, as they rely solely upon physical mechanisms, i.e., no chemical reactions are needed. Electrokinetic phenomena are classified as linear and nonlinear, in accordance with their dependance with the electric field magnitude. Combining linear and nonlinear phenomena can result in effective separation methods with high selectivity. Insulator-based EK (iEK) microdevices are systems that feature insulating structures that distort the electric field distribution within a microchannel, creating zones of higher field intensity. These zones of higher field intensity are where nonlinear EK effects arise and can be then used to finetune a desired particle separation. This present work is focused on the combination of linear and nonlinear EK effects for carrying out particle separations. We employ microchannels made from PDMS, that contain an array of insulating structures that alter the electric field distribution within the channel when an electrical potential is applied. We studied these systems with both, extensive mathematical modeling with COMSOL Multiphysics and careful experimentation. This presentation includes an abstract of the latest developments from our laboratory, including the definition of the newly identified parameter of electrokinetic equilibrium condition (EEEC) and a discussion of the importance of the nonlinear mechanism of electrophoresis of the second kind [1,2]. Finally, we will highlight the distinct strategies employed to achieve efficient particle sorting and separation in just a few minutes.
Acknowledgement: This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Awards No. 1705895 and No. 2127592.
References
Cardenas-Benitez, B.; Jind, B.; Gallo-Villanueva, R. C.; Martinez-Chapa, S. O.; Lapizco-Encinas, B. H.; Perez-Gonzalez, V. H. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92 (19), 12871–12879.
Vaghef-Koodehi, A.; Dillis, C.; Lapizco-Encinas, B. H. Anal. Chem. 2022. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94 (17), 6451–6456.
42. Electrolytes in Nanoscale
Bohuslav Gas
and
Tomas Novotny
Faculty of Science, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Abstract: Strong Coulombic forces keep positive and negative ions in liquid solutions of electrolytes in intimate contact so the electroneutrality condition is strictly obeyed in the bulk solution. However, the situation is different on the boundary between solid and liquid phases. Such a structure is called the electrical double layer. The solid phase of the electrical double layer is charged and the charge is fixed and not moving. Consequently, the opposite electric charge is distributed in the adjacent layer in the liquid phase, which is called the diffuse layer. This leads to a violation of the electroneutrality condition in the diffuse layer in the nanometer vicinity of the solid phase. Many attempts have been made to calculate the exact concentration distribution of all ions in the diffuse layer, when the bulk concentrations of ions are known, but they were limited mostly to univalent strong ions. We have proposed a new mathematical model of the electrical double layer which considers the high deviation from electroneutrality in the diffuse layer when the liquid phase is composed of solution of weak multivalent electrolytes of any valence and of any complexity [1]. The mathematical model joins together the Poisson equation, the continuity equation for electric charge, the mass continuity equations, and the modified G-function. We solve the model numerically using simulation software COMSOL. The model is able to calculate profiles of all ionic forms of all electrolytes in the diffuse part of the double layer, which consequently enables to calculate pH and deviation from electroneutrality. The model even enables to simulate the electromigration of multivalent weak electrolytes in the outer electric field, which shows the distribution of pH in a nanochannel. The validity of the model is not limited just to the double layer but is valid for solutions of electrolytes in general.
Figure 1.
Electromigration in nanochannel.
Figure 1.
Electromigration in nanochannel.
Acknowledgement: The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Czech Science Foundation, GAČR Grant No. 1811776S and Agilent Foundation Research Gift No. 4135.
Reference
Novotny, T., Gas. B., Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 881–889.
43. From Cellulose (and Other Biopolymers) to Functional Sensors
Lucas Ayres 1,
Ezequiel Vidal 2,
Federico Gomez 3
and
Carlos D. Garcia 1
1
Clemson University, Clemson, USA,
2
INQUISUR, Departamento de Química, Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS)-CONICET, Av. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, Argentina
3
Instituto de Biología Agrícola de Mendoza (IBAM-CONICET) Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, Chacras de Coria, Mendoza, Argentina
Abstract: The wide availability and biocompatibility of natural polysaccharides, such as cellulose and alginate, have enabled their inclusion in diverse applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, or environmental remediation. In addition to those, the rich chemical functionality of these polymers has also enabled the development of traditional and wearable sensors that can not only play an essential role as a non-invasive tool to monitor multiple analytes in real time, but also provide information complementary to that potentially obtained by more complex (and invasive) systems. In addition, and while materials have the potential to diversify the substrates available for the development of biosensors, their application is still limited by several fundamental challenges that affect not only the fabrication procedures, but also the performance of the devices. Aiming to address these shortcomings, our group has explored several routes to use and modify these biopolymers and apply them towards biosensing applications. Specifically, this presentation will describe the possibility to perform the thermal treatment of cellulose at either low (leading to the formation of redox-active fluorescent molecules) or high temperatures (carbonization). In addition, the presentation will also describe approaches towards the fabrication of complementary electrochemical, optical, and chemiluminescent biosensors based on these biopolymers.
44. Evidence of Hexavalent Chromium Formation and Plant Uptake in Agricultural Soils after Simulated Fires
Ida Rascio 1,
Ignazio Allegretta 1,
Concetta Eliana Gattullo 1,
Carlo Porfido 1,
Matteo Spagnuolo 1,
Gerald Falkenberg 2,
Tanja Mimmo 3,
Stefano Cesco 3
and
Roberto Terzano 1
1
Department if Soil, Plant and Food Sciences, University of Bari “A. Moro”, Bari, Italy
2
Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, Hamburg, Germany
3
Faculty of Science and Technology, Free University of Bozen, Bolzano, Italy
Abstract: Controlled fires are widely used in many common agricultural practices to remove the vegetation residues and manage weeds and pests. High temperatures occurring during fire events can cause significant changes in soil physico-chemical properties and element biogeochemistry. Therefore, also potentially toxic elements (PTEs) can change their speciation and hence their bioavailability. In particular, chromium (Cr), depending on the soil redox conditions and the content and type of organic matter (OM), can modify its oxidation state thus forming highly mobile and toxic hexavalent species (Cr(VI)). In the present study, the effect of laboratory-simulated fires on the distribution, speciation, and plant uptake of Cr in highly polluted agricultural soils was investigated. Three thermal treatments (up to 300 °C, 400 °C, and 500 °C) were performed by means of a muffle furnace to simulate a fire event of medium severity. The soil chemical and mineralogical characteristics were assessed before and after each thermal treatment, as well as the Cr fractionation and speciation. The latter were assessed through an integrated approach based on conventional analyses (determination of total Cr, total Cr(VI), and exchangeable Cr(VI), DTPA extraction, BCR sequential extractions), and X-ray based techniques, including synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). Heating treatments strongly altered the soil chemical characteristics, especially the OM content and Cr fractionation and availability. After heating, a partial oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) was observed, and from 21% to 88% of the total Cr(VI) was in the exchangeable form. A combination of bulk and micro X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy (XANES) analyses allowed the identification of different Cr species in the polluted soil samples before and after the thermal treatments, showing an increase of chromite (FeCr2O4), Cr(III)goethite, and CaCrO4 with increasing temperature, and a decrease of Cr-OM complexes. The formation of Crgoethite and chromite caused a relative immobilization of Cr, while CaCrO4, being slightly soluble, could represent a potential risk for the environment with negative consequences for plants and human health. Indeed, rhizotest experiments with durum wheat plants confirmed an increased Cr accumulation in plant tissues. Cr concentration in roots increase from 34 mg kg−1 DW, in the unheated soil, to 467 and 825 mg kg−1 DW in 300 °C and 500 °C-heated soil, respectively. Cr was also detected in shoots of plants grown on 300 °C and 500 °C-heated soils, at concentrations of 26 and 51 mg kg−1 DW, respectively. The Cr accumulation in plants appeared to be related to the exchangeable Cr(VI) amount in soil. The overall results suggest that Cr was preferentially taken up by the plants as Cr(VI), as also supported by micro X-ray fluorescence analyses. Further experiments are needed to investigate Cr speciation inside the plant and Cr-uptake mechanisms underlying its plant acquisition.
45. Morphology Control of PEDOT: PSS Polyelectrolyte by Hard-Cation-Soft-Anion Ionic Liquids: Microscopic Observation by Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Changwon Choi 1,
Yves Lansac 1,2,3
and
Yun Hee Jang 1
1
Department of Energy Science and Engineering, DGIST, Daegu 42988, Korea
2
GREMAN, CNRS UMR 7347, Université de Tours, 37200 Tours, France
3
LPS, CNRS UMR 8502, Université Paris-Saclay, 91405 Orsay, France
Abstract: Water-processable mixtures of positively charged poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT) and negatively charged polystyrenesulfonate (PSS) have received great attention as a flexible, stretchable, conformable, lightweight, transparent, and low-cost organic (semi)conductor and electrochemical transistor, which can be used for applications, such as organic LED, solar cell, thermoelectric genera-tor, self-powered implantable sensor and actuator, and artificial skin. They form 10–30-nm granular domains, where conducting but hydrophobic PEDOT-rich regions are surrounded by hydrophilic but insulating PSS-rich regions, hindering the formation of large conducting PEDOT domains. This makes PEDOT:PSS water-soluble, thermally stable, and environmentally benign, but poor in terms of conductivity. Adding polar organic solvents, acids, or organic/inorganic salts to the PEDOT:PSS solution enhanced the conductivity by 2–3 orders of magnitude. Recently, a remarkable 5000-fold improvement of conductivity was achieved by mixing proper ionic liquids (ILs) in a PEDOT:PSS solution of deionized water and polar organic solvents. In a series of free energy calculations [1–5] using density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulations based on the classic “hard soft acid (cation) base (anion)” principle, we have demonstrated the following: (1) ion exchange between PEDOT+:PSS– and A+:X– ILs would help PEDOT+ to decouple from PSS– and to grow into large-scale conducting domains of π-stacked PEDOT+ decorated by IL anions X–; (2) the most spontaneous decoupling between hydrophobic/soft PEDOT+ and hydrophilic/hard PSS– would be induced by strong interaction with hydrophobic/soft anions X– and hydrophilic/hard cations A+, respectively; and (3) the most efficient IL anions X– remaining in the PEDOT domain after the ion exchange would sustain the highest number of charge carriers uniformly distributed along the PEDOT backbone to further enhance the conductivity.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by NRF, Korea (2019R1A2C2003118 and 2021H1D3A2A01099453).
References
Kee, S., et al., Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8625–8631.
de Izarra, A., Park, S., Lee, J., Lansac, Y., Jang, Y. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 5375–5384.
De Izarra, A., Choi, C., Jang, Y. H., Lansac, Y., J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 7, 1916–1923.
de Izarra, A., Choi, C., Jang, Y. H., Lansac, Y., J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 8601–8611.
Choi, C., de Izarra, A., Han, I., Jeon, W., Lansac, Y., Jang, Y. H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2022, 126, 1615–1624.
46. Protamine-Controlled Reversible DNA Packaging: A Molecular Glue
Yves Lansac 1,2,3,
Yun Hee Jang 1,
Arnab Mukherjee 1
and
Jeril Degrouard 3
1
GREMAN, CNRS UMR 7347, Université de Tours, 37200 Tours, France
2
Department of Energy Science and Engineering, DGIST, Daegu 42988, Korea
3
LPS, CNRS UMR 8502, Université Paris-Saclay, 91405 Orsay, France
Abstract: While DNA are among the longest and the stiffest molecules in nature and negatively charged, they are strongly condensed in a tiny space of cell nuclei. DNA undergo precise cycles of even stronger condensation and decondensation during cell division or in sperm cells. Packaging the paternal genome into tiny sperm nuclei during spermatogenesis requires 106-fold compaction of DNA, corresponding to a 10–20 times higher compaction than in somatic cells. Understanding and simulating the molecular-level principles underlying such fascinating and dynamic processes would not only bring us one step closer to the origin of life, but also have applications in various other fields, such as medicine, materials, and energy. However, while protamine, a small arginine-rich basic protein, is known to participate in such a high level of compaction, the precise mechanism at play is still unclear. In a series of our work [1,2], effective pair potential calculation and large-scale molecular dynamics simulation using a simple idealized model incorporating solely electrostatic and steric interactions clearly demonstrate a reversible control on DNA condensates formation by varying the protamine-to-DNA ratio (
Figure 1). Microscopic states and condensate structures occurring in semi-dilute solutions of short DNA fragments are in good agreement with experimental phase diagram and cryoTEM observations. The reversible microscopic mechanisms induced by protamination modulation should present valuable information to improve a mechanistic understanding of early and intermediate stages of spermatogenesis where an interplay between condensation and liquid-liquid phase separation triggered by protamine expression and post-translational regulation might occur. Moreover, recent vaccines to prevent virus infections and cancers using protamine as a packaging and de-packaging agent might be fine-tuned for improved in terms of efficiency using a protamination control.
Figure 1.
Reversible condensation and decondensation of DNA by varying the protamine-to-DNA ratio.
Figure 1.
Reversible condensation and decondensation of DNA by varying the protamine-to-DNA ratio.
Acknowledgement: YHJ and YL thank the National Research Foundation of Korea (2019R1A2C2003118 and 2021H1D3A2A01099453) for financial support.
References
Mukherjee, A.; de Izarra, A.; Degrouard, J.; Olive, E.; Maiti, P. K.; Jang, Y. H.; Lansac, Y. ProtamineControlled Reversible DNA Packaging: A Molecular Glue. ACS Nano 15, 13094–13104 (2021).
Lansac, Y.; Degrouard, J.; Renouard, M.; Toma, A. C.; Livolant, F.; Raspaud, E. A Route to Self-Assemble Suspended DNA Nano-Complexes. Sci. Rep. 6, 21995 (2016).
47. An artificial Neuronal Device, Cu2-xSe Ultrathin Film Memristor via Atomic Layer Deposition
Kyungsub Lee
and
Seonghoon Lee
School of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826, Korea
Abstract: The memristor is considered as one of the promising candidates for a next generation gas sensor and a neuromorphic computing device. Metal-chalcogenide memristors with a nanoscale thickness and high ionic mobility were fabricated with atomic layer deposition (ALD), shadow mask patterning technique, and metal electrode deposition. An ultrathin, 50-nm thick film of metal-chalcogenide, copper selenide was deposited using a home-made ALD apparatus. Synthesized copper pivalate and bis(triethylsilyl) selenide precursors were used. The deposition rate at 160 °C was 0.48 Å per atomic layer deposition cycle. The thickness was monitored by an in situ ellipsometer and further analyzed by an atomic force microscope. The composition and structure of the film were confirmed by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and x-ray diffraction, to be Cu1.16Se. The Fdoped tin oxide/Cu1.16Se/W-wire memristor was fabricated and its memristive effect was investigated. The nonlinear I–V curve and spike-timing-dependent plasticity of our Cu1.16Se memristor demonstrate that the short- and long-term potentiation that occurs in a human brain can be mimicked by adjusting voltage-pulse intervals. A memristor is the electrical equivalent of a synapse. Our memristor has a 1 ms switching time, a 400 s retention time, Roff/on= 2, and reproducibility over 1000 cycles.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through BK21.
Reference
Lee, K. and Lee, S., Nanotechnology. 2021, 32, 245202.
48. Integrative Multi-Omic Analysis to Study Autism Spectrum Disorders
Min-Sik Kim
Department of New Biology, DGIST, Daegu, Korea
Abstract: Mass spectrometry has become a central technology in the field of biomedical research, especially for the discovery of disease biomarkers and fundamental pathophysiological mechanisms. For example, proteins and metabolites altered in tissue and blood samples from patients with diseases can be screened, identified, and validated by mass spectrometry. In this lecture, I will show how mass spectrometry-based proteomics and metabolomics can be applied to discover underlying mechanisms and biomarkers for autism spectrum disorders (ASD). ASD is a major neurodevelopmental disorder in which patients present with core symptoms of social communication impairment, restricted interest and repetitive behaviors. Patients with ASD often present with medical, psychiatric, and neurological comorbidities resulting in personal, family, and social challenges. The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States has estimated that one in 54 children in the United States is affected by ASD. In this study, mouse models of ASD induced by a drug or a genetic mutation and blood samples from patients and their family were used to study mechanisms of ASD and to discover integrative proteometabolomics-based biomarkers or ASD.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by the NRF Brain Research Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Republic of Korea (2017M3C7A1027472) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korea government (2022R1A2C2013377 and DGIST R&D program [22-CoE-BT-04]).
49. Activity of Natural Compounds against Alzheimer Investigated by Foodomics
Alberto Valdés,
Gerardo Alvarez,
Jose A. Mendiola,
Miguel Herrero,
Elena Ibáñez
and
Alejandro Cifuentes
Foodomics Lab, Institute of Food Science Research, CIAL, CSIC, Madrid, Spain
Abstract: Worldwide, around 50 million people have dementia, with nearly 10 million new cases every year. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and it may contribute to 60–70% of these cases. This multifactorial pathophysiology has been widely characterized by neuroinflammation, extensive oxidative damage, synaptic loss, and neuronal cell death. However, only a few drugs have been approved for the treatment of some AD symptoms, although it is well-known that no cure has been found so far. As a result, new strategies are urgently required, and among them, several studies have suggested that diet and/or food components can prevent or delay the onset and progression of AD. In this work, many natural sources of potential bioactive compounds have been investigated. Based on several green extraction processes and in-vitro approaches, we found an olive leaves extract enriched in triterpenoids, a carotenoids-enriched extract from Dunaliella salina microalgae, and an extract from orange juice industry byproducts enriched in monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and triterpenes have a high neuroprotective potential. In addition, the neuroprotective activity of these extracts is confirmed in a neuronal cell culture model. Moreover, these extracts show very good neuroprotective activity in-vivo using a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans as AD model. Lipidomics (using CSH-QTOF MS/MS), combined with transcriptomics (using NGS methods) and metabolomics (using HILIC-QTOF MS/MS and GC-QTOF-MS/MS) are applied following a foodomics approach to investigate the effect of the best neuroprotective candidates on the transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. This work is a first step in the study of the role that food compounds can play in AD onset and progression.
Acknowledgement: This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Innovation (MCI), Spain, project PID2020-113050RBI00.
50. Microscopic DNA Sequence Visualization
Kyubong Jo
Department of Chemistry, Sogang University, Seoul, Korea
Abstract: DNA is the most essential molecule because it stores biological information to shape our bodies and determine our existence. This information is mainly in the DNA sequence. Therefore, knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied areas, such as medical diagnostics, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology, and biological systematics. In 1977, Sanger and Gilbert developed the first DNA sequencing methods, respectively. Following the development of automated fluorescence-based sequencing machines, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster. In the last two decades, there has been a remarkable development in sequencing technology, referred to as next-generation sequencing. Rapid DNA sequencing methods have greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Moreover, scientists recently discovered that above the DNA sequence is another layer of information on the DNA sequence called the epigenome. The epigenome is involved in the regulation of gene expression, development, tissue differentiation, and suppression of transposable elements. Unlike the underlying DNA sequence, which is mostly static in an individual, the epigenome can be dynamically altered by environmental conditions. Therefore, numerous approaches have been developed to analyze epigenomes. Among them is an approach using large DNA molecules obtained from the cell as a promising platform to investigate epigenomic information. The rapid development of the microscopic system, as well as the camera, allows us to capture their images with ease. A major challenge, however, is determining the sequence of DNA molecules that are imaged. Given these concerns, we have developed several approaches to identify the DNA sequence from the image. In this presentation, I would like to demonstrate how one can identify single DNA molecules based on their staining pattern in a microscopic image.
References
Lee S, Jo K, Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46, e108.
Park J, Jo K, Analyst, 2019, 144, 921.
Shin E, Jo K, Scientific Reports, 2019, 17197.
Jin X, Jo K, Analyst, 2020, 145, 4079.
51. Bending Short dsDNA: Structure and Mechanical Properties
Nam Ki Lee
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, South Korea
Abstract: Z-DNA, a noncanonical helical structure of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), plays pivotal roles in various biological processes, including transcription regulation. Mechanical stresses, such as twisting and stretching, on dsDNA help to form Z-DNA. However, the effect of DNA bending, one of the most common dsDNA deformations, on Z-DNA formation is utterly unknown. Here, we show that DNA bending induces the formation of Z-DNA, i.e., more Z-DNA is formed as the bending force becomes stronger. We regulated the bending force on dsDNA by using D-shaped DNA nanostructures. The B-Z transition was observed by single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. We found that as the bending force becomes stronger, Z-DNA is formed at lower Mg2+ concentrations. When dsDNA had cytosine methylations, the B-Z transition occurred at 78 mM Mg2+ (midpoint) in the absence of the bending force. However, the B-Z transition occurred at a 28-fold lower Mg2+ concentration (2.8 mM) in the presence of the bending force. Monte Carlo simulation suggested that the BZ transition stabilizes the bent form via the formation of the B-Z junction with the extrusion of bases, which effectively releases the bending stress on DNA. Our results clearly show that the bending force facilitates the BZ transition under physiological salt conditions.
References
Yi, J., Yeou, S., Lee, N. K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 13137–13145.
Yeou, S., Hwang, J., Yi, J., Kim, C., Kim, S. K., Lee, N. K., Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 7516-7525.
Kim, C., Lee, O., Kim, J.-Y., Sung, W., Lee, N. K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8943–8947.
52. UV Sterilization of Bacillus atrophaeus Spores on Various Conditions
Jeongkwon Kim
Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea
Abstract:Bacillus spores are highly resistant to toxic chemicals and extreme environments. Because some Bacillus species threaten public health, spore inactivation techniques have been intensively investigated. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the most common methods for sterilizing materials with suspected biological warfare agent contamination [1]. In this study, UV sterilization of Bacillus atrophaeus spores was investigated under various conditions, such as different UV intensities, different UV scan numbers, and different supporting materials, Although the outer coat of spores remained intact after UV irradiation, damage inside the spores was observed. Spore proteins were identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry during the course of UV irradiation. Photochemical and photothermal processes are believed to be involved in the UV sterilization of Bacillus spores. UV irradiation was performed on Bacillus spores on the surface of various tiles [2] and face masks [3] to investigate the UV sterilization effect on various surface conditions.
References
My-Chi Thi Nguyen, Huu-Quang Nguyen, Hanbyeol Jang, Sojung Noh, Seong-Yeon Lee, Kyoung-Soon Jang, Jaebeom Lee, Youngku Sohn, K. J. Yee, Heesoo Jung, Jeongkwon Kim, Analyst, 2021, 146(24), 7682-7692,
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AN01717A.
Hanbyeol Jang, My-Chi Nguyen, Sojung Noh, Woo Kyung Cho, Youngku Sohn, Kiju Yee, Heesoo Jung, Jeongkwon Kim, Ceramics International, 2022, 48(1), 1466-1450
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.09.221.
My-Chi Thi Nguyen, Huu-Quang Nguyen, Hanbyeol Jang, Sojung Noh, Youngku Sohn, Kiju Yee, Heesoo Jung, Jeongkwon Kim, Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 2022, 13, 23,
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-022-00332-7.
53. Proximity Labeling, an Enzymatic Tool for Spatial Biology
Hyun-Woo Rhee
Dept. of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Korea
Abstract: Proximity labeling can be defined as an enzymatic “in-cell” chemical reaction that catalyzes the proximity-dependent modification of biomolecules in live cells. Since the modified proteins can be isolated and identified via mass spectrometry, this method has been successfully utilized for the characterization of local proteomes such as the sub-mitochondrial proteome and the proteome at membrane contact sites, or spatiotemporal interactome information in live cells, which are not “accessible” via conventional methods. Currently, proximity labeling techniques can be applied not only for local proteome mapping, but also for that of local RNA and DNA, in addition to showing great potential for the elucidation of spatial cell-cell networks in live models. We expect that proximity labeling can be as an essential tool in “spatiomics”, i.e., for the extraction of spatially- distributed biological information in a cell or organism. In this seminar, I will introduce the basic concept of proximity labeling and present our development of advanced proximity labeling tools and its application for studying muscle-specific mitochondrial proteome mapping, liver-specific secretome profiling, and cell–cell interaction in live animal models.
54. Affinity Capillary Electrophoretic Study of Noncovalent Molecular Interactions Using Uncorrected and Ionic Strength Corrected Actual Mobilities of the Species Involved
Václav Kašička 1,
Petra Sázelová 1,
Dušan Koval 1,
Lukáš Severa 1,
Filip Teplý 1
and
Gyula Vigh 2
1
Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czechia
2
Texas A&M University, Department Chemistry, College Station, TX, USA
Abstract: In this study, the apparent binding constants and limiting ionic mobilities of the multiply charged complexes of the delta- and lambda-enantiomers of Ru(II)- and Fe(II)-polypyridyl associates ([Ru(2,2′-bipyridine)3]2+, [Ru(1,10-phenanthroline)3]2+, and [Fe(1,10-phenanthroline)3]2+) with single-isomer 2,3-diacetylated-6-sulfatedcyclodextrins (CDs) (12Ac-6S-α-CD, 14Ac-7S-β-CD, and 16Ac-8S-γ-CD) were determined by affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) using uncorrected and ionic strength corrected actual ionic mobilities of the species involved. Two limiting models were tested for the ionic strength correction of the actual mobilities based on an empirical relation for the ionic strength correction of multivalent ionic species. In the standard model 1, the nominal values of the charge numbers and analytical concentrations of the above CD selectors in the background electrolytes (BGEs) were applied for calculation of the BGE ionic strength. In model 2, the CD selectors were considered as singly charged species with X-times higher concentrations in the BGE than their analytical concentrations, where X is equal to the charge number of the applied CDs, i.e., X= 6, 7, or 8 for α-, β-, or γ-CDs, respectively. These X-times multiplied nominal CD concentrations were used in the calculation of the BGE ionic strength in this second model. In all three cases, with uncorrected actual mobilities as well as with actual mobilities corrected according to the two limiting models, the measured effective mobilities of the above enantiomers fit rather well the theoretical curves of their mobility dependences on the CD concentrations in the BGE, with high average coefficients of determination (R2 = 0.9890–0.9995). Nevertheless, the best physicochemically meaningful values of the apparent binding constants and the limiting ionic mobilities of the enantiomer-CD complexes with low RSDs were obtained using the actual ionic mobilities of the species involved corrected according to model 2.
Acknowledgement: The work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation, grant no. 20-03899S, and by the Czech Academy of Sciences, Research Project RVO 61388963.
55. Using Capillary Electrophoresis to Make Aptamer Selection a Quantitative Process
An T. H. Le,
Eden Teclemichael,
Sergey N. Krylov
and
Svetlana M. Krylova
Department of Chemistry and Centre for Research on Biomolecular Interactions, York University, Toronto, Canada
Abstract: Oligonucleotide aptamers serve as affinity probes and therapeutic agents. The selection of aptamers involves consecutive rounds of affinity isolation of target-binding oligonucleotides from a random-sequence oligonucleotide library using one of the available partitioning methods. Aptamer selection is typically performed with a pulldown approach using target molecules immobilized on magnetic beads. The selection process is still more an art than a science, and the results of aptamer selection are not characterized quantitatively. Consequently, results of selection campaigns performed by different groups can hardly be compared. We utilize CE as a partitioning tool to make aptamer selection not only highly efficient, but also quantitative [1–3]. Here, we present the development a CE-based bulk affinity assay for the reliable assessment of a round-to-round process of selection. We also present the results of the first ever experimental study of the influence of target concentration on the progress of aptamer selection.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
References
Le, A.T.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Krylova, S.M.; Beloborodov, S.S.; Krylov, S.N. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2578–2588.
Le, A.T.H.; Krylova, S.M.; Beloborodov, S.S.; Wang, T.Y.; Hili, R.; Johnson, P.E.; Li, F.; Veedu, R.N.; Belyanskaya, S.; Krylov, S.N. Anal. Chem. 2021, 9, 5343–5354.
Le, A.T.H.; Krylova, S.M.; Kanoatov, M.; Desai, S.; Krylov, S.N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2739– 2743.
56. Selective Detection of Protein Acetylation by NMR Spectroscopy
Jung Ho Lee
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
Abstract: Selective detection of biomolecules and their modifications in cells is essential for understanding cell functions and diseases. We have developed an NMR pulse sequence, Ac-FIND (acetylation-filtered and edited), which uses isotope editing/filtering techniques for selective detection of protein acetylation. Acetylation of the N terminus and lysine side chains by N-succinimidyl acetate was selectively observed for intrinsically disordered αsynuclein and well-ordered ubiquitin. Furthermore, when nonacetylated 13C/15N-enriched α-synuclein was introduced into live HEK293 cells, intracellular N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein was detected by the appearance of a single peak using Ac-FIND. This work demonstrates the utility of NMR to detect a specific protein modification both in vitro and in live cells.
Acknowledgement: The authors appreciate the helpful comments from Jonghyuk Im and kind technical support from Eunhee Kim.
Reference
Lee, K., Park, S.H., Lee, J.H., J. Magn. Reson. 2022, 337, 107169.
57. New Analytical Approach for Distinguishing Biomolecular Topologies Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Jiyeon Lee,
Dahye Im
and
Jongcheol Seo
Department of Chemistry, Pohang University of Science and Technolgy (POSTECH)
Abstract: The efficient topological identification of biomolecules has drawn significant attention in biological, bioanalytical science and biomolecular engineering because it is critical for studying topology-related biological activities and self-assemblies. Especially, structural/conformational characterizations of biomolecules, such as proteins and oligonucleotides (DNAs and RNAs), remain challenging due to the lack of efficient methods to discover and identify their topologies. Often, the complexity of high-order folded biomolecular structures, e.g., secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures in proteins, induce large difficulties in finding the original topological features. In the present work, we developed a new method based on supercharging electrospray ionization (ESI) and ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) for the quick topological identification of proteins and oligonucleotides. Electrospraying with supercharging reagents in protein and oligonucleotide samples results in the observation of those biomolecules incorporating as many charges as possible, which induces excessive charge-induced unfolding. IMS-MS enables us to determine the collision cross section (CCS) values of specific biomolecular ions, providing their size, conformation, and shape (including topology) information. Therefore, the biomolecules’ higher-order structures become untangled with the help of the extensive charge–charge repulsions, providing wonderful conditions for identifying topologies without the interference of higher-order folded structures. Furthermore, the details in the folded structures and topological construction can be also estimated by analyzing the CCS evolutions at increasing charge states. Here, we successfully distinguished and indexed the protein topologies into three categories: the linear, the ring-containing, and the mechanically interlocked using the present approach. Furthermore, progressive changes in CCS values observed as the increasing charge states of model DNAs and RNAs provide insights into the topological elements of oligonucleotides, such as rings, hairpins, G-quadruplex, and several more. Moreover, the present method has been successfully applied to monitor the topological transformation and identify any topological side product of topologically engineered synthetic biomolecules. Therefore, we expect that the present approach will provide a new analytical tool for investigating biomolecular topologies.
Acknowledgement: We acknowledge the financial support from the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Grant No. 2019R1C1C1008414 and 2020R1A5A1019141).
58. Acrylate Monolith Precursor Having Carboxy Surface and Its Functionalization with Polar, Non-Polar, and Chiral Ligands for Capillary Electrochromatographic Separation
Ziad El Rassi
and
Theophilus Neequaye
Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK, USA
Abstract: A carboxy precursor monolithic column, namely poly(carboxy ethyl acrylate-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) was first produced in a 100 µm i.d. fused-silica capillary and subsequently surface bonded with four different polar, nonpolar, and chiral ligands by a post-polymerization functionalization process at room temperature in the presence of carbodiimide which link the carboxy surface function to the amino group of the individual ligand yielding a stable amide bond. The four ligands were (i) TRIS, (ii) n-octadecyl (C18), (iii) 2-amino anthracene and (iv) (S)-(-)-1-(2-naphthyl) ethylamine. The resulting monoliths exhibited a very low electroosmotic flow (EOF), a fact that required the incorporation of small amounts of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS) in the polymerization solution to produce a precursor monolith with fixed negative charges of sulfonate groups. This may indicate that the conjugation of the carboxy functions with amino ligands occurred to a large extent so that the amount of residual carboxy functions was sparsely dispersed and not enough to produce a desirable EOF. The polar TRIS monolithic column proved very useful for hydrophilic interaction CEC (HI-CEC) of various relatively polar species, such as sugars, nucleotides, nucleosides, and nucleic acid bases, as well as dansyl amino acids and phenoxy acid herbicides. The two nonpolar monoliths, namely octadecyl and anthracenyl columns, exhibited reversed-phase behaviors towards nonpolar species with widely differing resolving power in the sense that while the octadecyl column separated based on hydrophobic interactions, the anthracenyl column offered both hydrophobic and π-interactions. In fact, the resolving power by RP-CEC on the anthracenyl column was superior to that observed on the octadecyl column toward nonpolar solutes bearing aryl functional groups in their structures, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), toluene derivatives, and aniline derivatives as well as solutes carrying in their structures electron withdrawing substituents, such as dinitrophenyl-amino acids (DNPAAs) and di-DNP-AAs. Finally, the carboxy monolith with surface bound (S)-(-)-1-(2-naphthyl) ethylamine exhibited RP-CEC separations for both chiral and achiral solutes. Typical chiral separations were demonstrated for dansyl-DL-amino acids and phenoxy acid enantiomers while representative achiral separations were achieved for alkyl benzenes, nitroalkanes, PAHs, and toluene derivatives.
59. APCI, APPI, APLI, and LTP: Uncommon Ionisation Methods for GC-MS
Juan F. Ayala Cabrera
and
Oliver J. Schmitz
Applied Analytical Chemistry and Teaching and Research Center for Separation, University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany
Abstract: Although the coupling of GC/MS with atmospheric pressure ionisation (API) was reported as early as the 1970s, interest in coupling GC with atmospheric pressure ion sources has increased in the last decade. The requirement for a “soft” ion source to obtain highly diagnostic molecular ions is desirable, in contrast to “hard” ionisation techniques, such as electron ionisation (EI) in conventional GC/MS, which fragments the molecule to a high degree. Here, the ion sources we have developed for atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation (APCI), atmospheric pressure photoionisation (APPI), atmospheric pressure laser ionisation (APLI) and low-temperature plasma (LTP) for coupling with GC-MS are presented, compared with each other and the advantages and disadvantages of these analytical platforms are carefully discussed. A closed APCI ion source leads to a better repeatability in comparison with an open APCI ion source. APLI is the most sensitive ion source for the analysis of aromatic compounds such as PAHs, and GC-APLI-MS shows 1000-fold better sensitivity as compared to GC-EI-MS. The derivatization of non-aromatic compounds with an aromatic ionization marker increases the field of applications. LTP allows the ionization of a wide range of compounds and highly electronegative compounds are preferably ionized by charge exchange reactions while the presence of –NO2, –OH, and –CO groups enhance the formation of the protonated molecule. GC-LTP allows the ionization of a wider range of compounds than other API sources and GC-APLI shows an outstanding sensitivity and selectivity for PAHs.
60. Machine Learning in Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Microplastic Analysis
Han Bin Oh
Sognag University, Seoul, Korea
Abstract: In recent years, we have witnessed the expansion of the machine learning (ML) approaches in many scientific areas, including mass spectrometry analysis. In liquid chromatography-(tandem) mass spectrometry (LC-MS or LC-MS/MS) analysis, identifying small molecules is often formidable, due to the lack of a database. Since the chemical space is very extensive, it is often necessary to narrow down the chemicals into a few subgroups. Along this direction, an approach to label chemicals can be used, e.g., dansylation that is selectively conjugated at phenolic -OH or amine group. Using this approach, only the subgroups of chemicals, which have a phenol or amine functional group can be selected and identified in LC-MS. However, this dansylation approach has a weakness in that MS/MS of the dansylated chemicals cannot produce characteristic fragments upon collisional activation, thus with MS/MS not being used for molecular identification. In this situation, the retention time of LC can be a piece of valuable information. Thus, we have attempted to construct an artificial neural network (ANN) model for the dansylated compounds. Furthermore, a standalone software, equipped with a graphic user interface, is constructed to aid the identification of compounds under examination. Moreover, a number of ML approaches in LC-MS/MS spectra classification into specific subgroups of illicit drugs or controlled substances/psychoactive substances will be introduced. Last, a new ML approach for microplastic analysis of FTIR images will be delineated in the symposium.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Enducation (2018R1A6A1A03024940).
References
Jang, I. A., Lee, J. M., Lee, J.-U., Kim, B. H., Moon, B. J., Hong, J. K., Oh, H. B. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91(14), 9119-9128.
Lee, S.Y., Lee, S.T., Suh, S.I., Ko, B.J., Oh, H.B. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46(7), 732-742.
61. Development of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy for Chimney Telemetry System
Jin Hong Kim,
Kyung Sik Seo,
Eu Sung Chu,
Hyung Gun Na
and
Jong Hae Lee
S-Fac. Inc., Daejeon, Korea
Abstract: The Ministry of Environment in Korea has established and implemented various policies to improve air quality. In particular, in order to induce a reduction in the emission of pollutants from fixed sources, to prevent various pollution accidents, to induce the proper operation of emission facilities and preventive facilities, and to systematically manage them, the government control center is operating a chimney remote monitoring system (TMS) that connects the installed pollutant meter online and manages the emission status 24 h a day. However, from 2022 onwards, HCl and HF will be added to the existing total emission gas system, and the number of mandatory installation sites will be expanded to 4500 sites. There is no Korean company that has the core technology to simultaneously measure SO2, NOx, HCl, HF, NH3, and CO, which are the measurement targets of the chimney TMS. After seven years of research and development, our company succeeded in localizing a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer for chimney TMS. In this presentation, the first section concerns the element technology development process of this equipment, the second, technology development process for stability, durability, and reliability verification of each element technology, the third, mechanical engineering, control engineering, electronic engineering, software engineering, optics, and chemical technology integration process, the fourth, final product performance verification technology development process, and finally, the gas analysis performance verification result of the developed product.
62. Better Analysis with Nanobio-Conjugated Sensing Platforms for Biomedical Applications
Sang Hyuk Lee
and
Hye Jin Lee
Department of Chemistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41566, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this talk, I will highlight our latest efforts made in the development of highly sensitive and selective bioaffinity sensing platforms in conjunction with bioconjugated metallic and non-metallic nanoparticles, surface sandwich complexes, and surface enzyme reactions for biomedical applications, such as disease diagnosis [1–4]. Our efforts involve an integrated approach focusing on the preparation of a wide range of nano-biomolecule conjugates and the introduction of new bioaffinity sandwich assays alongside the integration of surface enzyme reactions. Various surface-based antibody-aptamer sandwich assays with optical and electrochemical techniques targeting different disease protein biomarkers and metabolites will be introduced. Finally, some of the challenging issues and potential suggestions when analyzing human biofluids with the proposed biosensing platforms in conjunction with bionanoconjugates will be discussed.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT, MSIT) (grant number: NRF-2020R1A4A1018393).
References
Goh, E., Kim, G. W., Ha, J. W., Lee, Y. H., Lee, M. H., Lee, H. J.* Dyes Pigm., 2022, 197, 109896.
Supianto, M., Lee, S. H., Jhung, S. H., Mohammad, H. B., Vu, H. M., Kim, M., Song, W., Kim, T., Lee, H. J.* Micorchmica Acta 2021, 188, 386-396.
J. Li, J., Si. Y., Park, Y. E., Choi, J.-S., Jung, S. M., Lee, J. E., Lee, H. J.*, Micorchm. Acta 2021, 188, 146153.
Lee, S., Park, Y. E., Lee, J. E., Lee, H. J.*, Biosens. Bioeletron., 2020, 154,112065-112070.
63. Coupling Organoids and Organ-On-A-Chip with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Steven Ray Wilson 1,2,
Hanne Røberg-Larsen 1,2,
Frøydis Sved Skottvoll 3,
Chistine Olsen 1,2,
Stian Kogler 1,2,
Kristina Sæterdal Kømurcu 1,2,
Aleksandra Aizenshtadt 1,2,
Frederik André Hansen 1,
Inger Lise Bogen 4,
Jörg P Kutter 5,
Stig Pedersen-Bjergaard 1
and
Stefan Krauss 1,2
1
University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
2
Hybrid Technology Hub, Faculty of Medicine, Oslo, Norway
3
SINTEF Digital, Oslo, Norway
4
Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
5
University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
Abstract: Organoids are laboratory-grown organs, that are developed from, e.g., human induced pluripotent stem cells. These miniature organ models are being developed and applied for drug discovery and disease models, and serve as an alternative approach to, e.g., animal models. Although organoids have great potential for representing human patients, as they may be grown from a single patient/patient group, their development and applications are still in their early stages. Therefore, analytical tools are required to study the capabilities of organoids toward improved models, which will likely accelerate drug discovery and our understanding of developmental biology. Our approach is to study organoids with liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS) [1–3], and to couple organoids and LC-MS in online systems, for high throughput and automated analysis [4]. Examples are organ-on-a-chip-LC-MS, and “organ-in-a-column”-LC-MS. Our findings demonstrate that organoids share many traits with the organs they are meant to represent, e.g., their proteome, metabolome, and drug metabolism capabilities. Results of our work with liver organoids and islet organoids will be presented.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Research Council of Norway through its Centre of Excellence scheme, project number 262613, and project number: 295910 (National Network of Advanced Proteomics Infrastructure). Support was also provided by UiO:Life Science and the Olav Thon Foundation.
Reference
Ann Lin et al. 3D cell culture models and organ-on-a-chip: meet separation science and mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 56–64.
Electromembrane extraction and mass spectrometry for liver organoid drug metabolism studies. Froydis Sved Skottvoll et al. 2021, Analytical Chemistry 93, 7, 3576–3585.
On-line reduction of insulin disulfide bonds with photoinduced radical reactions, upstream to nano liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Christine Olsen et al., 2022, Separation Science.
Direct Electromembrane Extraction-Based Mass Spectrometry: A Tool for Studying Drug Metabolism Properties of Liver Organoids. Frøydis Sved Skottvoll, et al. 2022, Analysis and Sensing 2 (2), e202100051.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anse.202100051.
64. Stabilisation Treatments for PFAS in Soils: Assessment of Durability and Longevity
Divina A. Navarro 1,2,
Shervin Kabiri 2,
Michael J. McLaughlin 2,
Greg Davis 3
and
Rai S. Kookana 1,2
1
CSIRO Land and Water, PMB 2, Glen Osmond, SA, 5064, Australia
2
School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, The University of Adelaide, Waite Campus, PMB1, Glen Osmond, South Australia 5064, Australia
3
CSIRO Land and Water, 147 Underwood Ave, Floreat, 6014, Australia
Abstract: Studies have demonstrated that amendments (usually sorbents) are suitable for the stabilization of poly- and perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS), as shown in the laboratory [1,2] and in field trials [3]. However, most studies only assess the immediate sorption/leaching aspect of the technology using single leaching conditions with limited consideration of the longevity of stabilization, i.e., PFAS leaching potential after aging, and/or effect of leaching conditions on the release of PFAS. In this study, we assessed the longevity and durability of soil stabilization approaches in reducing the leachability of PFAS. Herein, we present results from our trials with activated carbon (AC) and biochars as low-cost options to remediate contaminated sites in developing nations. Results revealed that both AC and biochars were able to reduce leaching of PFAS albeit to varying degrees. AC sorbents were able to reduce leaching of PFHxS, PFOS and PFOA by at least 95%, whilst biochars reduced leaching of the same PFAS by at least 80%. After four years of ageing, the efficacy of biochars significantly decreased, reducing the leaching of PFHxS, PFOS and PFOA below 80%. On the other hand, the AC sorbents (i.e., powdered and colloidal) assessed in this study were less affected by ageing during storage and were still able to reduce leaching of PFHxS, PFOS, and PFOA by at least 95%. These sorbents were also least affected by pH changes (pH 4 to 10.5), as well as repetitive leaching conditions. Overall, the performance of the sorbents appeared to be related to their surface area, i.e., sorbents with high surface area were also the most effective in reducing the concentration of leachable PFAS. These results highlight the importance of comprehensive longevity and durability studies in assessing suitability of soil stabilization treatments.
Acknowledgement: We are grateful to the Australian Government Department of Defence for providing the funding support for these studies.
References
Kabiri, S., Centner, M., and McLaughlin, M.J. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 766:144857.
Kah, M., Oliver, D., and Kookana, R. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 765:142770.
McDonough, J., Anderson, R., Lang, J., Liles, D., Matteson, K. and Olechiw, T. ACS Omega. 2022, 7: 419429.
65. Preparation and Characterization of Metallic Hybrid Nanostructures for Diclofenac Detection
Bui Duy Hai 1,
Pham Do Chung 2,
Vu Thi Thu 1
and
Nguyen Thi Thanh Ngan 1
1
University of Science and Technology of Hanoi (USTH), Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST), 18 Hoang Quoc Viet, Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
2
Hanoi National University of Education (HNUE), 134 Xuan Thuy, Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Abstract: The association between noble metal nanoparticles and magnetic metal oxide brings the advantages of both plasmonics and magnetic properties [1–3]. In this paper, the hybrid nanostructures Fe3O4/Ag have been prepared and characterized as a highly efficient surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate for the detection of diclofenac (DCF). The as-prepared nanostructures exhibited stable crystallize sizes of 15–20 nm and 45–50 nm for Fe3O4 and Ag, respectively. The XRD and XPS results indicated that Fe3O4/Ag hybrid was successfully synthesized. The saturation magnetization (Ms) is 64 emu/g for Fe3O4 and decrease to 28 emu/g with the presence of Ag and present the superparamagnetic behavior.
References
A. Taufid, R. E. Saputro, Heliyon 6, 2020, e05813.
M. T. Shah, Materials Science & Engineering C 118, 2021, 111390.
A. Saha, Talanta 231, 2021, 122372.
66. PFAS in the Pearl River System
Guang-Guo Ying
School of Environment, South China Normal University, Guangzhou University Town, Guangzhou 510006, China
Abstract: Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are widely used in various sectors and have been detected in environmental compartments, such as air, water, sediment, soil, and biota. Some of them are very persistent and regarded as “forever chemicals”. Here, we investigated the occurrence and spatial distribution of PFAS in the Pearl River System by target and nontarget analyses. The results showed wide presence of various PFAS in water and sediment of the Pearl River Systems, with high levels found in those sites near industrial and urban areas. PFAS were also detected in fish, with more accumulated in liver than in muscle, and with an increasing trend with increasing fish length and weight. PFAS were widespread in urban water cycle, from wastewater to tap water. The conventional activated sludge process used in WWTPs could not efficiently remove PFAS, while MBR and Unitank could effectively remove the long chain PFCAs with satisfactory removal rates. In DWTPs, activated carbon could partially remove PFASs, with PAC being more effective than GAC. Nontarget analysis showed the presence of many PFAS, including transformation products in wastewater, drinking water, and groundwater, suggesting slow transformation and degradation.
67. Metrology of PFAS
Zoltan Mester
National Research Council Canada
Abstract: An overview will be provided on the challenges associated with PFAS determination. Available measurement approaches and standards will be discussed. Limitations regarding the comparability of measurement data in time and space will be explored.
68. Alkaline Poly(ethylene) Glycol 8000-Based Solid-Phase Extraction (AP-SPE): A Novel Infield Compatible, Rapid Sample Preparation Method
Soomin Lee,
Ryan Nai,
Egan H. Doeven,
Hari Kalathil Balakrishnan,
Dan Yuan
and
Rosanne M. Guijt
Centre for Regional and Rural Futures (Deakin University, Geelong, Australia)
Abstract: Point-of-need testing (PONT) has been highly demanded for the early-stage detection of infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) is one of the advanced molecular technologies that identify target nucleic acids (NAs) with high detection sensitivity and specificity. However, the integration of NAAT into portable devices for PONT assays is still challenging. The conventional solid-phase NA extraction methods recover pure NAs suitable for sophisticated downstream applications (e.g., Next Generation Sequencing, DNA barcoding), but the extraction protocols contain complex chemistries and multiple steps, while the alkaline PEG (AP) method established in 2006 is operated in a single step using a simple chemical reagent. Nevertheless, the extensive sample dilution of AP makes it unattractive for early-stage diagnostic assays that require high detection sensitivity. Here, we introduce a novel DNA extraction method, AP-SPEI, combining the advantages of AP and solid-phase reversible immobilization (SPRI) that offers rapid (5 min) and high detection sensitivity (up to single DNA copy/reaction) in a simplified protocol (four steps). The effect of various parameters (15% PEG8000, 0.5 M NaCl, and 1500 ng/reaction magnetic bead) was studied to optimize DNA binding efficiency. Furthermore, the operational parameters (elution and washing) of AP-SPE were investigated to simplify workflow and achieve direct on-bead amplification without washing and elution steps. As a result, the optimal AP-SPE detected a single copy number of target Escherichia coli (E. coli) BL21 sample with 10–100 times improved detection sensitivity compared to AP and commercial DNA extraction kits. We also verified E. coli detection in body fluidic samples (saliva, sweat, and urine) as a proof of concept and detected as few as 15 cells in all types of fluidic using AP-SPE. This rapid and simplified protocol of AP-SPE promises the potential to be translated into portable devices for early-stage PONT application to identify the low abundant DNA detection.
69. Extraction of Intact Proteins from Biological Fluids by Non-Immunoaffinity Sample Preparation Method
Katarína Maráková 1,2,
Beatriz J. Renner 3,
Shannon L. Thomas 3
and
Kevin A. Schug 3
1
Faculty of Pharmacy, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia
2
Toxicological and Antidoping Center, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia
3
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, United States
Abstract: The direct quantitation of intact proteins from complex biological matrices by mass spectrometry is still a very challenging research area. One of the crucial steps in such an analytical workflow is also sample preparation to achieve sufficient specificity and sensitivity. While the primary advantage of commonly used immunoaffinity-based methods is high selectivity, this can also be a drawback if one desires to simultaneously analyze a large number of different proteins from a single sample. Therefore, the growing area of intact protein analysis also needs more effort concerning the development of more universal and affordable non-immunoaffinity sample pretreatment methods.
In our work, we developed non-immunoaffinity sample preparation based on a generally widely affordable solid phase extraction in a micro-plate format for eleven model intact proteins (5.5–29 kDa) with various isoelectric points (4.5–11.3). Extracted intact proteins were afterwards analyzed by reversed-phase liquid chromatography coupled with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer operated in a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. Reversed-phase separations were performed on the Restek wide-pore Viva C4 column, as mobile phases served water and acetonitrile acidified by 0.1% difluoroacetic acid and 0.2% formic acid. The best recoveries for most of the selected proteins were obtained by using the HLB stationary phase. Moreover, 1% trifluoroacetic acid and 0.2% Triton X-100 were used as efficient pretreatment reagents to release interactions between the proteins and biological matrix. Multiple sample loading was found to be essential to obtain recoveries >65% in urine for all targeted proteins (up to 30kDa) and >50% in serum/plasma for most of the proteins. Limits of quantitation in biological matrices were in the range of 2–1200 ng/mL, corresponding to 0.23–97.6 nM.
Acknowledgement: The research stay of Maráková at the University of Texas at Arlington was supported by the Fulbright Scholarship Program. This work was also partially supported by the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education, Science, Research and Sport of the Slovak Republic under the project VEGA 1/0483/20.
70. Recent Advances in the Analysis and Impact of Microplastics in Food
Clementina Vitali 1,
Anna Undas 1,
Hans-Gerd Janssen 2,3,
Francesco Simone Ruggeri 3,4
and
Michel W.F. Nielen 1,3
1
Wageningen Food Safety Research, Wageningen University & Research, Akkermaalsbos 2, 6708 WB Wageningen, NL
2
Unilever Foods Innovation Centre—Hive, Bronland 14, 6708 WH Wageningen, NL.
3
Wageningen University, Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, Stippeneng 4, 6708WE, Wageningen, NL
4
Wageningen University, Physical Chemistry and Soft Matter, Stippeneng 4, 6708WE, Wageningen, NL
Abstract: The mismanagement of plastic waste and its accumulation in the environment has resulted in the presence of microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) in the food chain and the exposure of consumers and wildlife. Various analytical techniques have been developed for detecting and characterizing synthetic polymer particles at the micro- and nano-scale. Yet, no unique method stands out for its ability to properly yield all the relevant information required to address MPs and NPs contamination. Consequently, there is still a severe lack of information about the occurrence of plastic particles in food which prevents the correct assessment of the food safety risks related to those contaminants. In this presentation, two European Horizon 2020 projects addressing the issue of MPs and NPs analysis will be presented: the MONPLAS project on enabling methodologies for robust, easy, and low-cost determination of MPs and NPs; and PlasticsFatE, on improved understanding of the impact of MPs and NPs and associated additives/adsorbed contaminants on human health. An overview of the most recent advances in the sample preparation and analysis of MPs in food will be given, emphasizing reliable quantification strategies in microscopy and the potential of direct mass spectrometry (MS) for single particle analysis of MPs. In particular, we propose the combined detection and quantification of MPs by Nile red staining and fluorescence microscopy in addition to the chemical characterization of individual particles by ambient ionization mass spectrometry using an Atmospheric Solids Analysis Probe (ASAP). The methodology developed includes an extensive assessment of quality parameters and, thanks to its multimodal characteristics, even enables the discrimination of MP polymers belonging to the same chemical class without interferences from MP surface contamination. Finally, emerging analytical techniques for the detection and characterization of NPs will be briefly discussed, with particular emphasis on infrared nanospectroscopy.
Acknowledgement: MONPLAS has received funds from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and Innovation Programme under the Marie Sklodowska Curie Grant Agreement No. 860775. PlasticsFatE has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme, under the Grant Agreement number 965367.
71. Status of Microplastics in India
Bipul Behari Saha
Dean, Sagar Group of Institutions, CHEVALLA, Hyderabad 501503, India
Abstract: The plastics industry is a fast-growing industry in India and large quantity of plastic waste is generated every year in this country. Microplastics are widely distributed in the Indian environment. The commonly found polymers are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, nylon, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene terephthalate, polyester, etc. These are found in various sizes and shapes. Several studies have indicated the presence of microplastics in aquatic animals, sediments, salts, and water bodies. Microplastics have been found in fishes like tuna, sardine, mackerel, and others. Beach sand and sediments have lots of microplastics. Tests carried out on salt derived from sea showed microplastics contamination. India is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south. Apart from marine water, microplastics were also found in the river bed, surface water, ground water, and bottled water. In order to tackle the problem of plastic waste, in 2011, the Indian government introduced the Plastic Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011. These rules helped to set up a plastic waste management system and a regulatory framework for restricting the manufacture and use of plastic carry bags. The rules were then replaced with the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 which emphasized for a complete ban on plastics below 50 microns. Since then, several amendments have taken place. In order to regulate identify and monitor the source of plastic litter along India’s coastline, the Union Ministry of Earth Sciences devised an initiative to clean up the oceans by adopting the National Marine Litter Policy along with UN Environment’s global ‘Clean Seas Campaign’ in 2018. This policy concerns how we can reuse and recycle plastic for cleaner sea. The National Marine Litter Policy aims to (i) identify the path of plastics from source to sink, promoting the reduce, reuse and recycle (3R’s) concept to create awareness; (ii) to enumerate the plastic litter in marine sediments, water, and biota along the Indian coast; and (iii) to build monitoring, management, and mitigation procedures to overcome the impact of microplastics to clean up oceans. Details will be discussed.
Acknowledgement: Director, Sagar Group of Institutions.
72. An Overview of the Technologies for Microplastic Remediation
Diane Purchase
Department of Natural Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology, Middlesex University, London, UK
Abstract: The reliance on plastics in our everyday lives has resulted in significant environmental pollution. When plastics are abraded to a size smaller than 5mm, they become microplastics. These are of particular concern as they persist in the ecosystem and are easily transported between different habitats. Unlike macro scale plastics that can be readily removed by physical and mechanical means, microplastics require special treatment for their removal. This presentation gives an overview of the state-of-the-art technologies for microplastic remediation. Microplastics can broadly be remediated using two main strategies: separation and degradation. Separation involves the detachment of the microplastics from the environmental matrix via a chemically induced process (e.g., flocculation, electrocoagulation, and agglomeration), or by using an adsorbent (e.g., biochar and microalgae), or the application of membrane technology (e.g., disk filter, dissolved air floatation, and membrane bioreactor). Microplastics can be degraded using a chemical, biological, or thermal process. Chemical degradation via advanced oxidation processes, such as photocatalytic or ozone degradation and electro-Fenton oxidation, are efficient methods of microplastic treatment. Enzymatic biodegradation of microplastic by microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi, and algae) has received much attention as a sustainable way of removing microplastics. Thermal treatments (e.g., pyrolysis, gasification, and liquefaction) have also gained popularity in microplastic remediation due to their potential to generate energy and value-added materials (e.g., nanotubes). Many of these strategies have been combined successfully in wastewater treatment plants to remove microplastics. Recent advancements in microplastic remediation include the use of nanotechnologies (e.g., as a filter membrane, magnetic adsorbent and flocculant catalyst) and bionanomaterials (either those fabricated biologically or nanomaterials coupled with an organic component) to enhance the efficiency of the treatment technologies. Whilst technologies exist to combat prevailing microplastic pollution, the overuse of plastics should be addressed to prevent the escalation of the crisis. For example, replacing petroleum-based plastic with biodegradable plastics can be one of many strategies to help control microplastic production. Reducing the input of plastics to the environment can only be achieved through a global multidisciplinary approach involving consumers, producers, scientists, waste professionals, and policymakers.
73. Metabolomics Study for the Evaluation of Toxicity by Environmental Pollutant
Hyung Min Kim
College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University
Abstract: There is a growing concern regarding the toxic effects of emerging environmental contaminants. However, an all-encompassing phenotyping- and omics-based strategy for the toxicity assessment of contaminants on soil living organisms remains to be established. Herein, we applied a comprehensive phenotyping and multi-omics profiling method to examine the molecular disturbance of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) exposed to various types of environmental toxicant. We evaluated the ability of reproduction and locomotion, as well as the oxidative stress of worms upon exposure to environmental toxicant. Additionally, we developed analytical method to evaluate the metabolome and lipidome of the C. elegans. This allowed to evaluate the dysregulation of metabolic pathways. Along with metabolomics and lipidomics, transcriptome profiles of C. elegans were monitored to find the association between metabolic pathways and transcriptome. Collectively, we demonstrated that comprehensive phenotyping and omics-based profiling establish a practical framework that allows us to gain deeper insights into the maladaptive consequences induced by environmental toxicants in C. elegans. Thus, it can be utilized for the evaluation of emerging environmental contaminants in the terrestrial ecosystem.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1I1A304724811).
74. Bioanalytic Approaches to Control Target Protein Functions by Modulating Proteinprotein Interactions Based on Structural Analysis
Youngjoo Kwon
College of Pharmacy, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, 03760, Korea
Abstract: Highly complex and interconnected networks make protein–protein interactions (PPIs) an essential event for maintaining homeostatic function under normal conditions in the body. However, if not properly regulated, PPIs are known to be responsible for a variety of diseases. Efforts to disrupt the dysregulated PPIs in disease states have been challenging because the PPI interfaces are mostly large and shallow and generally lack well-defined binding sites. Some protein or peptide PPI inhibitors have been developed. However, due to a series of disadvantages associated with protein or peptide PPI inhibitors, such as low cellular internalization, low bioavailability, and high immunogenicity [1,2], continuous attempts have been made to identify small-sized ligands capable of specifically binding to the PPI interface with high affinity. Nevertheless, only a few small molecule PPI modulators have reached clinical use as therapeutic agents. We have been working on developing small molecule modulators for a single specific PPI based on the identification of a ‘hotspot’ for each PPI, representing a small region within the PPI interface primarily responsible for the binding affinity between two proteins. Among numerous PPIs of which the hotspot residues are yet unclarified, in this study, we focused on the interaction between E74 Like ETS Transcription Factor 3 (ELF3) and mediator complex subunit 23 (MED23) [3–5]. Using diverse biochemical and analytical tools and in silico structural studies, we identified a small molecule ELF3-MED23 PPI inhibitor showing excellent in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity. Our findings serve as a representative case, showing (1) how a small molecule can be utilized to define exact hotspot residues of a specific PPI, (2) how efficiently the developed small molecule PPI inhibitor can be directly applied as an anticancer agent with superior druggability, and (3) how our approach can efficiently identify inhibitors for a single specific PPI in response to the needs to regulate specific biological pathways while reducing side effects and off-target effects.
References
Bojadzic D, Buchwald P. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018, 18, 674-699.
Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 21-39.
Shimogawa H, Kwon Y, Mao Q, Kawazoe Y, Choi Y, Asada S, Kigoshi H, Uesugi M. J Am Chem Soc. 2004, 126, 3461-347.
Seo SH, Hwang SY, Hwang S, Han S, Park H, Lee YS, Rho SB, Kwon Y. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e52977.
Hwang SY, Park S, Jo H, Hee Seo S, Jeon KH, Kim S, Jung AR, Song C, Ahn M, Yeon Kwak S, Lee HJ, Uesugi M, Na Y, Kwon Y. J Adv Res. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.003.
75. Chiral HPLC and Molecular Modeling Study for Enantiodiscrimination of Chiral Amines as Three Naphthaldimine Derivatives Using Amylose or Cellulose Derived Chiral Stationary Phases
Suraj Adhikari 1,
Man-Jeong Paik 2
and
Wonjae Lee 1
1
College of Pharmacy, Chosun University, Gwangju 61452, South Korea
2
College of Pharmacy, Sunchon National University, Suncheon 540-950, South Korea
Abstract: This study describes the enantioseparation of three chiral amines as naphthaldimine derivatives, using normal phase HPLC with amylose and cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) chiral stationary phases (CSPs). Three chiral amines were derivatized using three structurally similar naphthaldehyde derivatizing agents, and the enantioselectivity of the CSPs toward the derivatives was examined. Efficient enantiomer separation was observed for 2-hydroxynapthaldimine derivatives on cellulose derived CSPs. Moreover, among the three analytes as naphthaldimine derivatives, the resolution of amino alcohol analytes was superior to aliphatic chiral amine analyte under same analytical conditions. Molecular docking studies of three naphthaldimine derivatives of 2-amino-4methyl-1-pentanol (leucinol) on cellulose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) were performed to estimate the binding energies and conformations of the CSP–analyte complexes. The obtained binding energies were in good agreement with the experimentally determined enantioseparation and elution order.
76. Environmental and Human Exposure Associated Consequences of Micro- and Nano-Size Plastic Polymers
Roland Kallenborn 1,
Torstein J. Koppen 1,
Petter L. Grimstad 1
and
Stine Eriksen Hammer 2
1
Norwegian University of Lifee Sciences (NMBU), Faculty f Chemistry, Biotechnology and Food Sciences (KBM), NO-14333 Ås, Norway
2
The National Institute of Occupational Health in Norway (STAMI), NO-0304 Oslo, Norway
Abstract: For the past 60 years, polymer production has developed into an important, high-volume production branch of chemical industry worldwide. Plastic associated polymer production accounted for ca. 368 million metric tons in 2019 on a global basis. A large number of international research activities confirmed the ubiquitous presence of macro, micro (MP), and nano-meter (NP) size plastic particles in the environment. Currently, mainly advanced automated spectroscopic methods (mFTIR and mRaman) as well pyrolysis-gas chromatography and mass selective detection (Pyr-GC/MS) are applied for the quantitative determination of micro- and nano-meter size polymers in the environment and in human tissues. The uptake of MP and NP into organisms is currently an important priority research topic, especially for the exposure risk assessment. MP and NP particles are expected as products of a long-term weathering process. Hence< the polymeric materials represented by NP/MP are expected to be exposed to environmental processes for a long time (years). As a consequence, recent research confirm that MP/NP may scavenge and accumulate organic contaminants on the particles surface and, ultimately, carry potentially harmful chemical residues into organisms. Since atmospheric MP/NP burdens are assumed to be an important exposure pathway, environmental distribution and uptake processes will be presented and the role of MP/NP as carrier for harmful chemicals will be discussed. Furthermore, environmental MP/NP levels will be compared with MP/NP levels in standard indoor environments and workplaces plastic materials are actively used for production purposes. Based upon this general overview, the overall exposure risk for humans and environments will be discussed.
77. Pesticide Sorption by Microplastics and Other Constituents in Prairie Rivers
Annemieke Farenhorst
and
Marufa Fatema
Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agricultural and Food Sciences, University of Manitoba, Canada
Abstract: Microplastics are widely detected in surface waters, including in rivers of the Canadian Prairies. These Prairie rivers are also known to contain at low concentrations a wide range of pesticides, such as current-use herbicides 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), atrazine, and glyphosate, but also legacy insecticide DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane). Almost all previous studies on pesticides in Prairie rivers monitored the water-column only, but in our recent studies we analyzed for up to 172 pesticide compounds in both the water-column and bottom sediments. Although approximately the same number of active ingredients were detected in the water-column (i.e., 34 pesticide compounds) and bottom sediments (i.e., 32 pesticide compounds), only 15 active ingredients were detected in both compartments (67% herbicides and 33% fungicides). Understanding the affinity of current-use pesticides for a wide range of river constituents is important because the degradation rate and transport potential of a pesticide sorbed by a constituent is different than when the same pesticide is dissolved in the water-column. Microplastics are considered river contaminants. In addition to that, they have shown to be carriers of chemicals, such as persistent organic pollutants like DDT. For current-use pesticides, although there are substantial data available concern to what extent they are sorbed by river sediments, there is virtually no information available for the sorption of current-use pesticides by other river constituents, such as microplastics. This presentation provides examples of microplastics as well as pesticides detected in the water-column and bottom sediments of Prairie rivers. The presentation particularly highlights how current-use pesticides (2,4-D, atrazine, glyphosate) show a completely different affinity for microplastics than legacy pesticide DDT, and that the river water quality substantially influenced the affinity of glyphosate for polyvinyl chloride microplastics as well as sediments.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) through its Collaborative Research and Training Experience program (CREATE grant# 432009-2013) and Discovery Grant Program (Grant#RGPIN-2018-06030).
78. From Macroplastics to Nanoplastics: The Presence of Plastic Particles in Personal Hygiene Products and Their Possible Impact on the Environment and on Human Health
Leonardo Pantoja Munoz 1,
Alejandra Gonzalez Baez,
Deena McKinney 2,
Diane Purchase,
Huw Jones
and
Hemda Garelick 3
1
Department of Natural Sciences, Faculty of Science and Technology, Middlesex University, The Burroughs, NW4 4BT, London, UK
2
External Affairs and Sustainability Education Team, Maple Lodge STW, Thames Water, Denham Way, Rickmansworts, Herts WD3 9SQ, UK
Abstract: Plastic debris in the aquatic environment is of increasing global concern due to its impact on ecosystems and wildlife. The effects of plastic debris in the marine environment have been well documented, through the entanglement or ingestion of the synthetic materials. This includes the physical and biological damage to marine fauna, from zooplanktonic organisms to mammals [1,2]. The degradation of plastics in the environment leads to the production of microplastics (<5 mm in diameter) and nanoplastics (<100 nm in diameter) which are a growing source of contamination in aquatic environments and have the potential human health risk through direct contact and through entering the human food chain [3]. Many personal hygiene products (e.g., wet-wipe, tampon, cosmetic products etc.) are disposed into the domestic wastewater collection systems, transported to wastewater treatment plants, and eventually into the environment. We studied two different personal hygiene products and analyzed the plastic content in them using infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), confocal Raman microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) [4,5]. Both these products are nonwoven materials, some are which are labelled as flushable and some as non-flushable. However, both products end up in the sewers (intentionally or unintentionally) and they do not degrade while in the sewers or through much of the treatment process [6]. Any degradation of these fabrics may release materials, such as microplastics and nanoplastic, into the environment and in the case of tampons into the vaginal cavity. The potential toxicity of these released particles is currently investigated [8–10]. Both studies demonstrated the presence of synthetic polymers with potential health and environmental impact, such as polyester (polyethylene terephthalate (PET)) in wet-wipes, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polyethylene/vinyl acetate (PEVA/EVA) in some flushable wipes, and PET in all non-flushable wipes. Other polymers include polypropylene (PP), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), expanded polystyrene (EPS), and polyurethane (PU).
References
Wright SL, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (203) The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environ Pollut 483–492.
Wilcox C, Mallos N, Leonard G, Rodriguez A, Hardesty B (016) Using expert elicitation to estimate the impacts of plastic pollution on marine wildlife. Mar Policy 65:107–114.
Rochman CM, Hoh E, Kurobe T, Teh SJ (201) Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci Report.
Pantoja Munoz L, Gonzalez Baez A, McKinney D, Garelick H. Characterisation of flushable and non-flushable commercial wet wipes using microRaman, FTIR spectroscopy and fluorescence microscopy: to flush or not to flush. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2400-9.
Pantoja Munoz L, Gonzalez Baez A, Purchase D, Jones H and Garelick h. 2021. Release of microplastic fibres and fragmentation to billions of nanoplastics from period products: preliminary assessment of potential health implications. Environmental Science: Nano. RSC. DOI: 10.1039/d1en0075f.
Ziajahromi S, Neale P, Leusch FD (201) Wastewater treatment plant effluent as a source of microplastics: review of the fate, chemical interactions and potential risks to aquatic organisms. Water Sci Technol 74:2253– 2269.
Fournier S, D’Errico J, Adler D, Kollontzi S, Goedken M, Fabris L, et al. Nanopolystyrene translocation and fetal deposition after acute lung exposure during late-stage pregnancy. Particle and Fibre Toxicology. 2020.
Xie X, Deng T, Duan J, Xie J, Yuan J, Chen M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p3 MAPK signaling pathway. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2020.
Pan L, Yu D, Zhang Y, Zhu C, Yin Q, Hu Y, et al. Polystyrene microplastics-triggered mitophagy and oxidative burst via activation of PERK pathway. Science of The Total Environment. 2021.
Nie Jh, Shen Y, Roshdy M, Cheng X, Wang G, Yang X. Polystyrene nanoplastics exposure caused defective neural tube morphogenesis through caveolae-mediated endocytosis and faulty apoptosis. Nanotoxicology. 2021.
79. Exhaled Breath Condensate, Saliva and Sweat: Alternative, Non-Invasive Biological Samples Suitable for Medical Diagnostics by CE and HPLC
Petr Kubáň,
Petra Itterheimová,
Věra Dosedělová
and
František Foret
Department of Bioanalytical Instrumentation, Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic,
Abstract: Exhaled breath condensate (EBC), saliva, and sweat are unconventional samples of biological fluids that can be used for various diagnostic purposes. They can be obtained completely noninvasively, and their diagnostic potential is yet to be fully explored. We have devoted the last decade to the development of various approaches to acquire and analyze these non-invasive samples and developed many new diagnostic approaches based on novel sampling concepts and analysis by capillary electrophoresis and HPLC. We shall first discuss the developed instrumentation and approaches for sampling EBC, saliva, and sweat. This includes the construction of various EBC sample collection devices, either passively or actively cooled, testing the approaches for collection representative saliva samples and the development of miniature skin-wipe and skin-wash samplers for sweat collection. We will further discuss the analytical potential of small ions and organic acids in EBC for diagnosing pulmonary diseases and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Saliva is another non-invasive sample which can be used in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The analysis of various small molecules and bile acids in saliva will be presented and its clinical importance will be discussed. Eventually, we will also show how sweat analysis can be performed in a simple manner for diagnosing cystic fibrosis and present some recent novel approaches, namely skinwipe and skin-wash, that utilize simple cotton swabs or 3D printed devices. Finally, we will outline some sample preconcentration and pretreatment approaches to analyze trace amounts of different compounds in non-invasive samples that will conclude the variety of different approaches applied with microcolumn separation techniques for clinical diagnostics.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Grant No. 22-23815S), European Regional Development Fund-Project “SINGING PLANT” (No.CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_026/0008446) and the institutional support RVO: 68081715.
80. Biological Sample Analysis by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography
Makoto Tsunoda
University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Abstract: Hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC) is useful for separation of highly polar compounds. Aqueous organic solvents are used as mobile phase on polar stationary phases. In my talk, I will describe analytical methods for biological compounds based on HPLC-fluorescence detection under HILIC conditions. Low-molecular-weight biothiols, e.g., cysteine, homocysteine, and glutathione, and catechol compounds, e.g., norepinephrine and dopamine, are studied as biological compounds. Application to human plasma or urine samples is also described.
81. Hybrid Film Based on Gold Nanoparticles, Reduced Graphene Oxide and Polydopamine towards Electrochemical Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells
Nguyen Dieu Linh 1,
Vu Minh Thu 1,
Nguyen Thi Trang Huyen 1,
Pham Do Chung 2,
Le Hoang Long 1,
Nguyen Van Chuc 3
and
Vu Thi Thu 1
1
University of Science and Technology of Hanoi (USTH), Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST), 18 Hoang Quoc Viet, Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
2
Hanoi National University of Education (HNUE), 134 Xuan Thuy, Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
3
Institute of Materials Science (IMS), Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST), 18 Hoang Quoc Viet, Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Abstract: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) that detached from the tumor lesion and then traveled in the blood stream during tumor metastasis represent an important biomarker for monitoring cancer stages and validating cancer treatment processes [1]. In this work, we aim to develop an impedimetric cytosensor based on polydopamine in combination with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). An electrochemical platform based on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide and electro-deposited gold nanoparticle was first prepared to ensure a good electron transfer rate at the electrode surface [2]. Herein, the presence of carbonaceous matrix (rGO) might help to prevent aggregation, and thus provide more homogenously distributed AuNPs [3,4]. The gold particles not only support the improvement of electrochemical signals, but also partially increase cell adhesion on the electrode surface. Polydopamine (PDA) was introduced onto AuNPs/rGO hybrid film by self-polymerization of dopamine in alkaline conditions [5,6]. As usual, this PDA coating probably enhanced the adhesion of cells onto electrode surface, thus improving the sensing performance of the as-developed sensor. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), a versatile and non-destructive technique, will be further used to analyze CTCs in a label-free manner.
Acknowledgement: This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 103.02-2018.360.
References
Chao Jin, Sarah M FcFaul, Simon P Duffy, Xiaoyan Deng, Peyman Tavassoli, Peter C Black, Hongshen Ma, Lab on a chip 2014, 14, 32-44.
Vu Cam Nhung, Nguyen Ngoc Tien, Dau Thi Ngoc Nga, Pham Do Chung, Nguyen Thi Thanh Ngan, Vu Cam Tu, Vu Thi Thu, Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2022, 24, p. 34.
Nguyen Tien Hoang, Pham Truong Thuan Nguyen, Pham Do Chung, Vu Thi Thu Ha, Tran Quang Hung, Pham Thi Nam, Vu Thi Thu, RSC Advances 2022, 12, p. 8137.
R Ayranci, B Demirkan, B Sen, A Savk, M Ak, F Sen, Materials Science and Engineering C 2019, 99, 951956.
Gulcin Bolat, Oznur Akbal Vural, Yesim Tugce Yaman, Serdar Abaci, Materials Science and Engineering C 2021, 119, p. 111549.
H Lee, SM Dellatore, WM Miller, PB Messersmith, Science 2007, 318, 426-430.
82. Metabolomics in the Analysis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour Samples
Szymon Macioszek 1,
Danuta Dudzik 1,
Agnieszka Woźniak 2,
Tomasz Stokowy 3
and
Michał J. Markuszewski 1
1
Department of Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacodynamics, Medical University of Gdańsk, Hallera 107, 80-416 Gdańsk, Poland,
2
Laboratory of Experimental Oncology, Department of Oncology, KU Leuven, and Department of General Medical Oncology, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven Cancer Institute, Leuven, Belgium
3
IT Division, University of Bergen, 5021, Bergen, Norway
Abstract: Although imatinib is a well-established first-line drug for treating most gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), GISTs acquire secondary resistance during therapy. Multi-omics approaches provide an integrated perspective to empower the development of personalized treatments through a better understanding of functional biology underlying the disease and molecular-driven selection of the best-targeted, individualized therapy. This study uses integrative metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses to elucidate tumor biochemical processes affected by imatinib treatment. A GIST xenograft mouse model was used in the study, including ten mice treated with imatinib and ten non-treated controls. Metabolites in tumor extracts were analyzed using gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). RNA sequencing was also performed on the sample subset (n = 6). Metabolomic analysis revealed 21 differentiating metabolites, whereas next-generation RNA sequencing data analysis resulted in 531 differentially expressed genes. Imatinib significantly changed the profile of metabolites associated mainly with purine and pyrimidine metabolism, butanoate metabolism, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism. The related changes in transcriptomic profiles included genes involved in kinase activity and immune responses and supported its impact on the purine biosynthesis pathway. Our multi-omics study confirmed previously known pathways involved in imatinib anticancer activity and correlated the imatinib-relevant downregulation of expression of purine biosynthesis pathway genes with the reduction of respectful metabolites. Furthermore, considering the importance of the purine biosynthesis pathway for cancer proliferation, we identified a potentially novel mechanism for the anti-tumor activity of imatinib.
83. The Development of Nanoparticles for Improved SERS Detection
Vladimir Jonas 1,2,
Jiri Volanek 1,2,
Anna Tycova 1,
Jan Prikryl 1
and
Frantisek Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry CAS, Brno, Czechia
2
Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czechia
Abstract: The probability of Raman scattering is too low for sensitive measurement. However, on the surface of some nanostructured metals, Raman scattering can be enhanced, pushing the sensitivity down to a single molecule [1]. The analyte, being close to the metal surface, represent one of the important conditions for reaching such an excellent result. Therefore, we focused on the synthesis of metal particles with improved affinity between the analyte and the particle. We present the development of such particles and new challenges that such a procedure presents.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge financial support from Czech Science Foundation (Grant No. 20-14069Y) and the institutional support RVO: 68081715.
Reference
Nie, S., Emory, S. R., Science 1997, 275, 5303.
84. Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis of PM10 and PM2.5 Samples Collected at Daejoen in Korea
Jong-Hwa Moon
and
Ji-Soek Kim
Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Air quality in urban areas is one of the most important environmental issues and air particulates consisting of various elements from both artificial and natural origins represent an indicator of an air quality. Especially, fine air particulates can be accumulated in the lungs by inhalation and incur serious harmful effects to human health. PM10 and PM2.5 air particulate samples were collected by using high volume samplers (HiVol 3000, Ecotech, Austria) and a quartz filter (8 × 10 inches) at Daejeon in Korea during the winter and spring season, 2021. Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis (INAA) was applied for quantitative analysis of the trace elements in the PM10 and PM2.5 samples. Hence, 10 blank filters and 45 samples for PM10 and PM2.5 were analyzed, respectively. A total of 28 elements, i.e., Al, As, Ba, Br, Ca, Ce, Cl, Co, Cr, Cs, Eu, Fe, Hf, I, In, K, La, Mn, Na, Rb, Sb, Sc, Se, Sm, Th, V, W, Zn, in the PM samples were determined by INAA. Analytical quality control was performed using NIST SRMs. Finally, the air concentrations (ng/m3) of the 28 elements were calculated with air flow volume and their average concentrations were evaluated. In the case of PM10, the results can be divided into six groups: (1) >1000 ng/m3: Al, Fe, Ca; (2) 100∼1000 ng/m3: K, Na, Cl; (3) 10∼100 ng/m3: Zn, Mn, Ba, Br; (4) 1~10 ng/m3: I, Cr, Rb, V, As, Ce, W, Se, Sb, La; (5) 0.1∼1 ng/m3: Co, Th, Sc, Cs, Sm, Hf; (6) 0.01∼0.1 ng/m3: In, Eu. The average PM2.5/PM10 concentration ratios for each element ranged from 0.54 (Ca) to 0.88 (Se) in this work. The concentration ratio of the elements, such as Br, I, In, Sb, Se, W, and Zn, known to be of anthropogenic origin, was higher than 0.8.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF- 2018M2A2B3A06071695).
85. Milk Protein Assays by Capillary Electrophoresis for Nutrition Evaluation
Walter Feng
Abstract: Milk proteins (casein and whey proteins) are almost the most important protein sources for human nowadays. However, the complicated sample matrix makes the quality assessment difficult. Capillary electrophoresis has shown its advantages in dairy product assays. This talk summarized several successful methods established for milk quality assessment, including the separation of whey and casein proteins, A2 β-Casein determination, and the assay of Lactoferrin.
86. New Methodologies for Improving Safety and Bioactivity in Green Foodomics
J.D. Sánchez-Martínez,
J.A. Mendiola,
A. Cifuentes
and
E. Ibáñez
Laboratory of Foodomics, Institute of Food Science Research, CIAL, CSIC, Madrid, Spain
Abstract: At present, one of the great challenges facing humanity is the eradication of hunger, one of the top commitments on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [1]. New approaches on agricultural development for food security and nutrition are challenging our research since they will allow easier access to safe and nutritious food for sustaining life and promoting good health. In our laboratory, we are continuously trying to provide needed answers towards sustainability through the application of green chemistry and green analytical chemistry (GAC) principles in our everyday life [2]. This is the main focus of green foodomics [3], that integrates those principles in each of the -omics platforms during method development to determine food constituents and nutrients at the molecular level. Moreover, green foodomics also deal with food safety and quality assessment and with the bioprospecting of compounds with nutritional or functional value using, among others, green solvents and environmentally friendly extraction techniques, measured using different green metrics. In the present work, we evaluate the safety of agricultural by-products intended to be applied as potential sources of compounds with neuroprotective activity against Alzheimer’s disease. A new methodology, based on the use of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES), has been developed, tested, and validated for twelve pesticides commonly employed in the citrus industry. The greenness of the procedure has been evaluated using an AGREE calculator. Finally, the whole method has been applied for the safety assessment of seven citrus by-products produced in Spain, finding the presence of several of the evaluated compounds at concentrations higher than the established limits for similar products. Moreover, new methodologies, based on the use of compressed fluids were applied to improve the recovery of neuroprotective compounds (mainly terpenoids) from citrus by-products. A comparison among conventional extraction procedures and pressurized liquid extraction has been carried out in terms of yields, in-vitro bioactivities, and composition. Promising results were obtained with in-vivo models for citrus by-product extracts obtained with ethyl acetate under PLE conditions.
References
Bizikova L et al., Glob Food Sec 2020, 26:100450.
Gilbert-López B et al., TrAC Trends Anal Chem 2017, 96:31–41.
Ballesteros-Vivas D, et al., Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry 2021, 31:100522.
87. Analysis of Semi-Ionic C-F Bonds on Photoreduced Graphene Oxide
Xin Hong Tai 1,
Chin Wei Lai 1,
Thomas Chung Kuang Yang 2,
Kian Mun Lee 1,
Chia-Yun Chen 3,4
and
Joon Ching Juan 1,5
1
Nanotechnology & Catalysis Research Centre (NANOCAT), Institute for Advanced Studies (IAS), University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2
Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan
3
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan 70101, Taiwan
4
Hierarchical Green-Energy Materials (Hi-GEM) Research Center, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan 70101, Taiwan
5
Faculty of Engineering, Technology and Built Environment, UCSI University, Cheras, 56000, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Abstract: There is great interest to dope fluorine (F) on graphene-based material to improve the physicochemical properties. However, the F doped graphene oxide induces various types of C-F bonds. For instance, there are three type of bonding, such as (i) covalent C-F bond (sp3-hybridized C atom), (ii) ionic C-F bond (sp2-hybridized C atom), and (iii) semi-ionic C-F bond as an intermediate state between the covalent and ionic bond [1]. The first discovery of semi-ionic C-F bond was reported by Sato and coworkers 2004 [2]. Due to the high electronegativity of F, it tends to polarizes the C atoms of the graphene [3]. The formation of semi-ionic C-F bond possesses a greater polarity than the ionic and covalent C-F bond [3]. This changes the graphene-based material to a p-type semiconductor material [4]. In this work, fluorine (F) atom was doped on graphene oxide (GO) via an easy, economical, and environmental benign photoirradiation method. Various analyses, such as XPS, FTIR, RAMAN, photoluminescence, and Mott–Schottky techniques, were used to determine the type of C-F bonds. The formation of semi-ionic C-F bonds after doping with F doped GO (FPRGO) provided a large density of hole charge carrier and a high p-type conductivity.
Acknowledgement: The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Education, Malaysia (FRGS/1/2021/STG05/UM/02/3) and University of Malaya, Malaysia (PPSI-2020-CLUSTER-IDIG03 and ST080-2021) for the funding.
References
Feng, W., et al., Advanced Science, 2016. 3(7): p. 1500413.
Sato, Y., et al., Carbon, 2004. 42(15): p. 3243-3249.
Kim, J., et al., RSC advances, 2018. 8(26): p. 14152-14156.
Simon, J., et al., Science, 2010. 327(5961): p. 60-64.
88. N-Glycosylation Alteration of Serum and Salivary Immunoglobulin A as a Possible Biomarker in Oral Mucositis
Enikő Gebri 1,
Ferenc Tóth 2,
Attila Kiss 3,
Hajnalka Jankovics 4,
Ferenc Vonderviszt 4,
András Guttman 4,5
and
Tibor Hortobágyi 6,7,8
1
Department of Dentoalveolar Surgery and Dental Outpatient Care, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
2
Department of Biomaterials and Prosthetic Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
3
Department of Hematopoietic Transplantation Centre, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
4
Research Institute of Biomolecular and Chemical Engineering, University of Pannonia, Veszprém, Hungary
5
Horváth Csaba Laboratory of Bioseparation Sciences, Research Center for Molecular Medicine, Doctoral School of Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
6
Institute of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary
7
MTA-DE Cerebrovascular and Neurodegenerative Research Group, Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
8
Institute of Psychiatry Psychology and Neuroscience, King’s College London, London, UK
Abstract: Oral and enteral mucositis due to high-dose cytostatic treatment administered during autologous and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation increases mortality. Salivary secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) is a basic pillar of local immunity in the first line of defense. Altered salivary sialoglycoprotein glycosylation is important in the pathologies of the oral cavity, including inflammation, infection, and neoplasia. We used capillary electrophoresis to assess whether changes in the salivary and serum IgA glycosylation correlated with the development and severity of oral mucositis. A comparative analysis of serum and salivary IgA total N-glycans was conducted, including eight patients with autologous peripheral stem-cell transplantation (APSCT) at four different stages of transplantation (day −3/−7, 0, +7, +14) and 10 healthy controls. Fourteen out of 31 N-glycan structures were identified in serum and six out of 38 in saliva, which showed significant changes upon transplantation compared with the control group. The serum core fucosylated, sialylated, bisecting biantennary glycan (FA2BG2S2) showed significant differences between any two stages of transplantation (day −3/−7 and day +14; p = 0.0279). Our results suggested that changes in the serum IgA total N-glycan profile could serve as a disease-specific biomarker in patients undergoing APSCT, while the analysis of salivary IgA N-glycan reflected the effect of APSCT on local immunity.
89. Exploration of the Metabolic Alterations of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and TCA Cycle Intermediates in Human Plasma with Gastric Disorders
Wonwoong Lee
College of Pharmacy, Woosuk University, Wanju 55338, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are produced by bacterial fermentation from dietary fiber, permeate the intestinal cell membrane, and are distributed in the human body via the blood circulation. Since absorbed SCFAs could be introduced into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in host cells, the relationships between SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates might influence the energy metabolism, homeostasis, and disease conditions in the human body. For this reason, information on profile changes between SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates could help unveil pathological mechanisms of intractable diseases, including gastric cancer. In this study, a gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) method was developed to simultaneously determine SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates in human plasma from patients with gastric disorders. Due to differences in characteristics between mono-carboxylates of SCFAs and di-/tri-carboxylates of TCA cycle intermediates, sophisticated analytical methods are necessary to comprehensively profile SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates in biological samples. We applied a tetra-alkyl ammonium pairing method to prevent the loss of volatile SCFAs and base decarboxylation of TCA cycle intermediates during sample preparation. Based on the optimized tetra-alkyl ammonium pairing method, SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates were effectively extracted from human plasma without significant loss. To assess gastric disorders with dysbiosis, metabolic alterations of SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates in human plasma with gastric disorders were analyzed using GC-MS/MS combined with N-methylN-tert-butyldimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide (MTBSTFA) derivatization. Significantly different metabolic alterations based on the plasma levels of SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates were investigated in cancer metabolic pathways. This study provides valuable profiling results for SCFAs and TCA cycle intermediates in human plasma and elucidates etiological mechanisms underlying gastric diseases based on profiles of host-gut microbiome co-metabolic pathways.
Acknowledgement: This study was financially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF2017M3A9F3047858 and 2021R1C1C1005957).
Reference
Kim, Y.L., Lee W., Chung, S.H., et al. Life Sciences 2022, 309, 121010.
90. Nanoparticle Tag Counting for Tissue Imaging Using Infrared Laser Ablation
Jan Preisler 1,
Marek Stiborek 1,
Lenka Jindřichová 1,
Stanislava Meliorisová 1,
Antonín Bednařík 1,
Vadym Prysiazhnyi 1,
Jiří Kroupa 2,
Pavel Houška 2,
Barbora Pavlatovská 1,3,
Jarmila Navrátilová 1,3
and
Viktor Kanický 1
1
Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic,
2
Brno University of Technology, Brno, Czech Republic
3
St. Anne’s University Hospital, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: We report a new laser ablation technique employing a pulsed 2940 nm laser and a simple ablation cell for the digital mapping of biomarkers in tissues using metal nanoparticle tags. Unlike the conventional laser ablation systems, where nanoparticles are ablated, we are able to desorb intact nanoparticles and count them. The method is demonstrated on monitoring proliferating cells in 3D aggregates of human colorectal carcinoma cells. Precise counting of the tags in each pixel generates sharp distribution maps of a proliferation biomarker in the tissue. A mass spectrometer detects up to 83% nanoparticles of a selected element with a single particle detection limit. Advantageously, the desorption of nanoparticles from regions outside the tissue is strongly suppressed.
Acknowledgement: The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Czech Science Foundation (GA18-16583S), Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic (MUNI/A/1325/2021), European Regional Development Fund—Project ENOCH (CZ.02.1.01/0.0/16_019/0000868) and the project National Institute for Cancer Research (Programme EXCELES, ID Project No. LX22NPO5102)—Funded by the European Union—Next Generation EU.
91. (1. R,2S)-N-Dodecyl-N-methylephedrinium Bromide as a Chiral Selector in Enantioseparations Using Capillary Electrophoresis
Pavel Jáč,
Kateřina Műllerová
and
Miroslav Polášek
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy in Hradec Králové, Charles University, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic,
Abstract: Chiral ionic liquid (1R,2S)-N-dodecyl-N-methylephedrinium bromide (DMEB) was tested as a potential chiral selector for the enantioseparations of selected drugs, such as chiral quinolones and 2-arylpropionic acids using capillary electrophoresis (CE). The effect of several parameters on the separation was examined: (i) the type and pH of the separation buffer, (ii) the concentration of DMEB, and (iii) the type and amount of the organic modifier. Only the separation of ofloxacin enantiomers was achieved under the tested conditions, while the enantiorecognition of other model chiral analytes was not successful. The results were compared with those published previously that described the potential of DMEB as the chiral selector towards methaqualone [1] and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [2]. We developed a CE method for the assay of levofloxacin to demonstrate the applicability of DMEB as chiral selector in the pharmaceutical analysis of single-isomer drugs. The best separation was achieved with 20 mmol/L tris buffer pH 8.5 containing 100 mmol/L DMEB and 20% (v/v) acetonitrile as the background electrolyte. The separation was carried out in 50 µm id fused silica capillary (80.5 cm/72 cm) at −30 kV with UV detection at 291 nm. The resolution between the peaks of ofloxacin enantiomers was 4.22 ± 0.02 (n = 3). Linearity of the method for levofloxacin was proven in the range of 10–100 µg/mL (y = 0.0305x − 0.0107, r = 0.9987) with gatifloxacin (40 µg/mL) used as the internal standard. The method was then applied to the analysis of tablets containing levofloxacin.
Acknowledgement: The work was supported by SVV 260 548.
References
Bunke, A., Jira, Th., Beyrich, Th., Pharmazie 1997, 52, 762-764.
Dey, J., Mohanty, A., Roy, S., Khatua, D., J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1048, 127-132.
92. Oxysterols Are Secreted from Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Induced Organoids
Kristina Sæterdal Kømurcu 1,
Alexandra Aizensthadt 2,
James L Thorne 3,
Stefan Krauss 2,
Steven Ray Wilson 1,2
and
Hanne Røberg-Larsen 1
1
Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo, Norway
2
Hybrid Technology Hub—Centre of Excellence, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Oslo, Norway
3
School of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Leeds, United Kingdom
Abstract: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a collection of heterogeneous liver disorders with rapidly growing worldwide prevalence. The stages of the disease are differentiated by the severity of the conditions, from fatty liver and fibrosis (both reversible) to irreversible cirrhosis, where a liver transplant might be needed. Today, the most used and accurate diagnostic tool for disease progression is an invasive liver biopsy, which can cause more scarring of the liver and push the progression of the disease further. There is a need to find markers for disease progression that can be monitored in a non-invasive way compared to liver biopsies. Organoids are three-dimensional tissue models of human organs. The organoids can be generated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) or adult tissue-resident cells and better reflect the physiological conditions and complexity in humans compared to animal models and immortalized cell lines. Organoids have the potential to become an important tool in disease monitoring, drug development, and personalized medicine, and it is also possible to use organoids as a disease model, such as NAFLD. We have established an organoid model of liver steatosis, representing the early stages of NAFLD using human primary hepatocyte and iPSC-derived liver organoids. With a modified version of our established UHPLC-ESIMS/MS method for oxysterol analysis [1], utilizing robust and automatic on-line sample clean-up after derivatization to enhance the ionization of these non-polar isomers with ESI, we were able to separate the isomeric oxysterols (hydroxycholesterols and dihydroxycholesterols) in organoid growth media. We were able to detect Liver X receptor (LXR)-active oxysterols at picomolar levels in organoid growth media, showing the secretion of oxysterols from liver organoids. Steatotic organoids secrete more oxysterols than healthy organoids, including dihydroxycholesterols. The increased secretion of some oxysterols in steatotic liver organoids implies that the oxysterol profile is affected in fatty livers. The system will be used to evaluate if oxysterols are suitable as a diagnostic tool for NAFLD disease progression and the establishment of using organoids as disease models.
93. Recent Developments in the Synthesis of High-Performance Anion-Exchange Materials Based on Hyperbranched Polymers
Christopher Pohl
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA
Abstract: Since my original development of hyperbranched anion exchange materials 19 years ago, this class of anion exchange material has been widely used commercially in more than 25 stationary phases ranging from high-performance separation products to fouling-resistant guard columns. One of the advantages of this synthetic chemistry is the ability to tailor the stationary phase architecture by controlling geometric parameters, such as the distance between ion-exchange sites and the nature of these ion exchange sites. In this work, we report the evaluation of ion-exchange architectures, manipulation of reaction conditions, and investigate the impact of such parameters on ion-exchange selectivity and ion exchange capacity. We also examine the utility of such materials with real-world samples, comparing the effect of synthetic variables on separation performance.
References
Pohl, C. A.; Saini, C. Coated ion exchanged substrate and method of forming. U. S. Patent 7,291,395, November 6, 2007.
Pohl, C., Saini, C., New developments in the preparation of anion exchange media based on hyperbranched condensation polymers. Journal of Chromatography A. 2008; 1213(1): p. 37-44.
94. New Studies on Poly(ethylene glycol)-Based Hydrogels in Electrophoresis
Chenchen Liu 1,
Takuya Kubo 2,
Takayuki Kawai 1
and
Koji Otsuka 2
1
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishi-ku, Fukuoka 819-0395, Japan
2
Department of Material Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Katsura, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto, 615-8510, Japan
Abstract: Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based materials are promising in electrophoretic analysis for biomolecules owing to the merits of economic, biocompatible, and less unspecific interactions with analytes. Useful applications have been demonstrated in electrophoretic size sieving by using, e.g., thermal controllable PEG polymers [1] and ideally structural homogenous PEG polymer network [2]. Here, we report our original PEG-based hydrogels as a size sieving matrix and the affinity framework in biomolecule electrophoresis. A copoly(poly(ethylene glycol) acrylate/poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate) (copoly(PEGA/PEGDA)) hydrogel was fabricated in a capillary with 50 μm inner diameter. This copoly(PEGA/PEGDA) hydrogel is featured with a highly adjustable structure via simply optimizing the compositions of PEGA and PEGDA. A tunable size sieving was realized using a standard DNA ladder. In addition, we found that the copoly(PEGA/PEGDA) hydrogel could realize a high-resolution separation of small DNAs, which is compatible with the authentic poly(acrylamide) hydrogel. Meanwhile, the required analysis time was reduced to one quarter of that of PA hydrogel [3]. The copoly(PEGA/PEGDA) hydrogel was further modified for affinity electrophoresis as a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP). Our MIP was polymerized with sodium allylsulfonate (SA) as a functional monomer and cytochrome c as a template. The adsorption test showed that the MIP was highly specific to the target cytochrome c under the optimized conditions. Meanwhile, as a negative control, the nonimprinted polymer showed no adsorption. In electrophoretic tests, the MIP retarded cytochrome c more severely than other proteins including trypsin, lysozyme, and bovine serum albumin [4]. We are now further investigating other characteristics of the PEG-based MIP in electrophoresis.
Acknowledgement: This research was partly supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Research Activity Start-up [Grant Number 22K20560].
References
Wang, F., He, W., Zhang, J., Chu, B., Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 2448-2498.
Li, X., Khairulina, K., Chung, U.-i., Sakai, T., Macromolecules 2013, 46, 8657-8663.
Liu, C., Kubo, T., Naito, T., Otsuka, K., ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3886-3893.
Liu, C., Kubo, T., Otsuka, K., J. Mater. Chem. B, in press. [DOI: 10.1039/D2TB00501H].
95. Ionization by Au+: A New Tool for Mass Spectrometry of Volatile Organic Compounds
Antonin Bednarik,
Monika Koktava,
Vadym Prysiazhnyi
and
Jan Preisler
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: The investigation of gas-phase chemistry of metals can provide priceless information transferable into the study of condensed state chemistry and catalysis. Among the metals, gold, and specifically its Au+ ion, attracts considerable attention due to its rather high reactivity and ability to drive hydride abstraction of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons. In our work, we proposed Au+ ions as chemical ionization agents for the mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The ionization is carried out in a commercially available dual sub-atmospheric pressure MALDI/ESI interface. The Au+ ions are generated by the laser ablation of a gold nanolayer with the UV MALDI laser (355 nm) and VOCs are infused via the ESI capillary. The interaction of Au+ ions with VOCs typically results in the formation of ion molecule complexes with general formula [Au+2M]+. Some of the VOCs, e.g., aliphatic hydrocarbons and alcohols, interact in more intricate ways, e.g., hydride abstraction and C-C bond cleavages result in more complicated spectra. Formed complexes and other reaction products are straightforwardly identified thanks to the ultra-high resolving power and sub-ppm mass accuracy of the employed mass spectrometer based on their molecular formulas. The performance of the technique is demonstrated in the analysis of various classes of organic molecules (alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, aromatic compounds, carboxylic acids, ethers, and organosulfur compounds). The calculated LOD of acetone in air was 0.8 ppb. Our technique presents the novel utilization of commercial dual MALDI/ESI interface and expands the portfolio of currently available methods for the analysis of VOCs, e.g., SESI, PTR, and SIFT-MS.
Acknowledgement: We gratefully thank for financial support of Czech Grant Agency (Grants no. 19-20927Y and 21-12262S).
Reference
Bednarik, A., Prysiazhnyi, V., Preisler, J. Anal Chem. 2021, 93(27), 9445-9453.
96. Development of Certified Reference Materials for the Determination of Bisphenol A in Polycarbonate/Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (PC/ABS)
Dong Kyu Lim,
Sunyoung Lee,
Jeesoo Han,
Byungjoo Kim,
Ki Hwan Choi
and
Song-Yee Baek
Group for Organic Analysis, Division of Chemical and Biological Metrology, Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS), Daejeon 34113, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Certified reference material (CRM; KRISS CRM 113-02-002) was developed for the accurate determination of representative additive, bisphenol A, in plastic (PC/ABS). CRM containing an arbitrary concentration, related to potential restrictions, was produced. An isotope dilution-liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (ID-LC/MS) based optimized method was established for certification of the CRM. (i) 13C-labeled bisphenol A was spiked as internal standards. (ii) Due to the high concentration of content, the analysis was conducted through stepwise dilution. Through the method, the certified values of the CRMs, (188.6 ± 3.7) mg/kg for bisphenol A, were confirmed. The stabilities of the CRMs were evaluated for one year at room temperature. Developed CRM can be applied for the validation of measuring procedures for compounds in industry and certification bodies.
97. High Sensitivity Portable Gas Chromatography
Sun Jong Baek
Bioneer Corporation, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In BIONEER’s instrument R&D center, a ppb-grade portable gas chromatography ‘AccuGC™100’, built for the analysis of organic compounds in the air, is awaiting it is launch. AccuGC™100, characterized by its portability and design, showcases a compact size and portability of 7.5 kg while maintaining the performance of a normal GC (gas chromatography) with a photoionization detector (PID). Notably, the device has an exceptionally high sensitivity and is capable of detecting ppb-level concentrations within gas phase samples. Using this equipment, we aim to contribute to the reduction of air pollution by conduct detection and real-time quantification of components, such as VOCs (volatile organic compounds), at hazardous gas discharge locations and leak areas within industrial sites.
Acknowledgement: This work was financially supported by the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute (Project No. L122-00005-0024-0).
98. “In-Vivo” Study of the Kinetics of Changes in the Plant Saps Composition by Laboratorybuilt Capillary Electrophoresis Device
Natália Melicherová 1,2,
Jana Lavická 1
and
František Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Veveří 967/97, 602 00 Brno, Czech Republic
2
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 753/5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: This work combines a highly efficient capillary electrophoresis-based (CE) method with an “in-vivo” sampling of plants to study the kinetics of changes in the apoplast composition during the stress response without almost entirely distorting the plant environment. Besides short analysis time, one must also emphasize high separation efficiency, sensitivity, and very low volumes of analyzed samples regarding CE method [1]. The latter is a big advantage if the sample from analyzed living plants is reduced to sub microliter volume [2]. A laboratory-built CE device was developed to ensure both semi-invasive sampling and analysis of various ionogenic species in the plant sap. This device allows us to discontinuously collect data during an experiment on the plant’s stress response in short consecutive cycles. After the plant sap is directly injected into the separation capillary, a capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) method analysis is performed, data are collected, and the cycle is repeated. The advantage of a short CZE analysis time, usually several minutes, allows us to capture the time-dependent changes of the kinetics within a living plant during the stress response more closely. The CE device utilizes two types of detection, i.e., UV detector and a capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detector (C4D). On the base plate of the device, there are two vessels for background electrolyte and a swinging arm on the inlet side designed for the rapid, precise positioning of the sampling end of the capillary. On the outlet side, there is a unit used for flushing the capillary after each analysis by applying negative pressure. The study is focused on salt stress and analysis of inorganic ions in the plant sap. Methods for analyzing both inorganic cations and anions were successfully performed using this device. The study aims to comprehensively assess plant fitness under stress conditions.
Acknowledgement: The work has been supported by European Regional Development Fund-Project “SINGING PLANT” (No.CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_026/0008446).
References
Jarvas, G., Guttman, A., Miekus, N., Baczek, T., Jeong, S., Chung, D.S., Patoprstý, V., Masar, M., Hutta, M., Datinska, V., Foret, F., TRAC 2020, 122, 115702.
Melicherová, N., Řemínek, R., Foret, F., J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 271-284.
99. D Printing of Porous Materials Integrated Miniaturized Fluidic Devices for Electrokinetic DNA Extraction and Soil Analysis
Hari Kalathil Balakrishnan 1,
Ludovic F. Dumée 2,
Andrea Merenda 3,
Cyril Aubry 2,
Dan Yuan 1,
Egan H. Doeven 1
and
Rosanne M. Guijt 1
1
Deakin University, Australia
2
Khalifa University, United Arab Emirates 3RMIT University, Australia
Abstract: 3D printing for integrating porous materials into fluidic devices has evolved into a new fabrication technique to implement functionalities, such as selective membranes for specific adsorbents, stationary phases, catalysts, and cell scaffold-related materials. However, the lack of ability to control and alter the structural (pore morphology and porosity) and chemical properties of the 3D printed porous separation materials remains a challenge. Here, DLP 3D printing combined with polymerization-induced phase separation has been used to directly 3D print submicron and nanoporous (<1 µm) membranes. The effects of parameters, such as initiator concentration, exposure time, and porogen concentration, have been studied to fine control the morphology (pore features) and bulk (porosity, density) characteristics enabling the pore sizes from 100 nm to 1 µm. Finally, the millifluidic devices developed using a print-pause-print approach have been used for electrokinetic DNA extraction. Furthermore, a novel technique has been presented for simultaneously printing dense and porous structures with finely controlled porous features in all three dimensions using a single hybrid ink. Grayscale digital light projection (G-DLP) 3D printing of a hybrid polymerization induced phase separation (PIPS) ink is introduced to print hierarchical porous structures. The structural properties of the printed material can be controlled from effectively dense to porous material with interconnected pores up to 250 nm within an individual print layer using a single ink. Heterostructures with physically dense areas are formed contiguous to intrinsically porous domains (porosity 23%) within a single layer using greyscale masks. Materials with skeletal densities spanning from 1.01 to 1.21 g cm−3 were found to allow for highly controlled wicking rates from complete diffusion blockage up to 4.5 mm h−1, and the novel functionally integrated fluidic devices were applied for the elemental metal sensing of iron for soil. This approach demonstrates a single-step fabrication of functionally graded porous materials (FGM) within a single layer, which can act as tunable membranes or adsorbents for environmental and healthcare applications.
100. The Global Scenario and Challenges Presented by Radioactive Waste in the Marine Environment
Silvina A. Di Pietro 1,
Joon Ching Juan 2
and
Nicholas Priest 3
1
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Washington, USA
2
University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
3
Department of Chemistry, Laval University, Quebec, Canada
Abstract: The project will bring together a series of critical reviews that are concerned with aspects of the fate and transport of radionuclides and radioactive waste in the marine environment. In addition to naturally occurring radionuclides, anthropogenic radionuclides have entered the aquatic environment either directly (e.g., from direct global weapons fallout deposition, reactor accidents and discharges, fuel production facilities, fuel reprocessing plants, aircraft accidents, reactor disposals, etc.) or indirectly (e.g., terrigenous input of global fallout, as windborne dusts from contaminated areas, via contaminated river systems, etc.). Given the complexity of the marine environment, the measurement of radionuclides may present unique radiochemical, biochemical, and regulatory challenges. Some insoluble radionuclides are deposited close to the site of their release, where they could produce a local hazard. In contrast, others are redistributed globally by ocean currents. Subsequently, some contaminated biota may enter the human food chain where their incorporated radionuclides (e.g., long-lived nuclear fuel components and fission products) present a health hazard. Of particular concern is the risk to some coastal communities that may have much higher-than-average exposure to radionuclides present in coastal air, sediments, and biota. While there is general agreement that marine radionuclides levels are currently of low concern, they, and their sources, are subject to strict, national, and international regulatory control. It is expected that state-of-the-art critical reviews will cover the three main objectives of the present project. These are related to the problems of detection, identification, and behavior of radionuclides within different aquatic environmental compartments, including land-to-sea and sea-to-land transfer; the current classification and regulation of radioactive wastes entering the marine environment; the potential health risks associated with radioactive discharges; and future challenges presented by a resurgent nuclear industry.
Acknowledgement: Thank you, Dr. Nick Priest, (prof.nick.priest@gmail.com) for helping us draft the abstract; thank you Dr. Luis Leon (luis.leon@ucd.ie) for editing it, and thank you to the entire task group for the support on our IUPAC project #2021-027-2-600.
101. Analysis of Biogenic Amines and Benzo[α]pyrene in Black Pepper Prepared under Various Cooking Methods
Byungjoo Yoo,
Hyunwoo Ahn
and
Kwang-GeunLee
Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, 32, Dongguk-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10326, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this study, the levels of biogenic amines (BAs) and benzo[α]pyrene (Bαp) in roasted, pan-fried, and boiled black pepper were analyzed. The validation results of the two analytical methods, high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography−mass spectrometry showed good linearity (R2 = 0.999–0.9997), LOD (0.12–1.12 μg/g), LOQ (0.36–3.63 μg/g), recovery (97.53–113.63%), and precision (1.45–3.11%). In 43 cooked black pepper samples, the detection range of BAs was 5.32–548.05 μg/g. In 54 cooked black pepper samples, the Bαp content ranged from 0.78 to 11.2 ng/g. The levels of BAs in black pepper were significantly increased as the temperature and time of roasting and pan-frying increased (p < 0.05) but significantly decreased when the boiling temperature and time increased (p < 0.05). The Bαp content of black pepper increased significantly in all three cooking conditions as the temperature and time increased (p < 0.05). Through this study, it is possible to provide various parameters that can minimize the levels of BAs and BαP in household cooking and food manufacturing process, including black pepper.
102. Analysis of Furan in Red Pepper Powder Treated by Three Methods—Boiling, Roasting, and Frying
Sookyoung Kim,
Seung-Woo Ha
and
Kwang-Geun Lee
Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, 32, Dongguk-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10326, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this study, furan analysis was conducted on dried red pepper powder treated by three cooking methods (boiling, roasting, and frying). A total of 144 samples were prepared and their furan levels were analyzed using automated solid-phase micro-extraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The furan concentration in boiled soup ranged from 1.26 to 4.65 ng/g, and from 7.37 to 27.68 ng/g for boiled red pepper samples. For the roasting method, a furan concentration between 6.66 and 761.37 ng/g was detected. For the frying method, the furan level of edible oils ranged from 3.93 to 125.88 ng/g, and a concentration ranging from 4.88 to 234.52 ng/g was detected for the fried red pepper samples. The cooking method using edible oil obtained a higher furan concentration than the water-based method. Samples using corn germ oil (linoleic acid-rich oil) obtained the highest furan concentration among the four edible oils. In all cooking methods, the higher the heating temperature and time, the higher the furan concentration detected. A kinetic study was performed using the roasting model system and the apparent activation energy was 60.5 kJ/mol. The results of this study could be useful as a database for furan concentration in dried red pepper powder according to various cooking methods.
103. Arduino-Based Autosampler for an In-House Built Capillary Electrophoresis Instrument
Petra Itterheimová 1,2,
Martin Kubáň 3,
František Foret 1
and
Petr Kubáň 1
1
Department of Bioanalytical Instrumentation, The Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic
2
Central European Institute of Technology and Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
3
Gymnázium Brno, Vídeňská, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: With the extension of open-source hardware and acceptance of the open-source paradigm in science, in-house built instruments are very often being developed in analytical chemistry. Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a suitable candidate technique for open source, as it offers flexibility and a low-cost instrumentation development. Major parts of capillary electrophoretic systems have been already described in the literature, hence constructing an in-house built CE instrument is relatively easy. However, automated injection is often a neglected part, and the injection is carried out manually. An autosampler allows carrying out number of analyses in a row automatically and thus it is a very helpful and time-saving part of any instrument. In our work, we developed an inexpensive and simple autosampler that can be used as a modular component of any in-house built CE instrument. It consists of two parts, the injection carousel and the flushing box with a pump. The enclosures were 3D printed using a Prusa i3 MK3S+ 3D printer. The entire system is driven by an Arduino Mega microcontroller placed inside of the box on the sampling side of the capillary. The sample injection is ensured hydrodynamically by lifting the carousel with sample vials. Its movement is driven by two stepper motors, allowing it to move up and down and to turn in any direction. The autosampler can be programmed to operate autonomously through a keypad with LCD display accessible from the outer side of the cover box. Between measurements, the capillary can be washed with the background electrolyte by applying pressure in the flushing box. The functionality of our developed autosampler was tested by analyzing biothiols preconcentrated with gold nanoparticles and further compared to analysis, where hydrodynamic sample injection was carried out manually. In a related publication, a complete manual for construction of the device, together with the source code for the driver, will be provided. Any analytical chemist should be able to construct such an autosampler without any deeper programming knowledge. We believe that our autosampler may be a useful and time-saving addition for any open-source/in-house built CE instrument.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge financial support from Czech Science Foundation (grant 22-23815S) and the institutional support RVO: 68081715.
104. Biodegradation Degree Analysis and Examination of Biodegradable Resin PHA (Poly Hydroxy Alkanoate) in Composting and Natural Soil Condition
Han Chang Hoon,
Lee Se Jin
and
Won Cheol Hyun
Korea Conformity Laboratories, Incheon, Korea
Abstract: The rapid development of consumption culture is continuously increasing the number of new problems with environmental pollution accompanying the pursuit of convenience in life. One such problem is the waste disposal of plastics used throughout the industry, and plastic waste is recognized as one of the biggest sources of environmental pollution. The trend toward eco-packaging has also changed its paradigm towards bio-plastics that overcome the shortcomings of biodegradable plastics, and the scope of eco-packaging has become wider at home and abroad. One of the most notable packaging materials, PHA, is known as a polyester-structured carbon and energy storage material in which many types of bacteria are synthesized and condensed in the body when other nutrients are scarce under conditions of large carbon sources. Moreover, PHA, a biosynthetic substance, is an environmentally friendly substance that reduces environmental pollution because it is completely decomposed by microbial soil in nature. Major factors affecting the rate of biodegradable plastics in soil include the thickness of plastics, the characteristics of secondary structures, and the activity, moisture, temperature, and pH of decomposed microorganisms. In this study, the biodegradability of PHA under composting conditions and natural soil conditions was evaluated by referring to the ISO 14855-1 method and ISO 17556 method, and the biodegradability according to the conditions was investigated.
105. Biomaterial Actuator of M13 Bacteriophage in Tunable Gap Plasmonic Color Film for Diagnosing Lung Cancer
Thanh Mien Nguyen 1,
Gyeong-Ha Bak 2,
You Hwan Kim 2,
Tae-Young Jeong 1,
TaeYeon Kim 3,
YeongHwa Kim 4,
Jeong Seok Han 4,
YeNi Cho 5
and
Jin-Woo Oh 1,2,4
1
Bio-IT Fusion Technology Research Institute, Pusan National University, Busan, 46241, Republic of Korea
2
Department of Nano Fusion Technology, Pusan National University, Busan 46214, Republic of Korea
3
Department of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 46214, Republic of Korea
4
Department of Nano energy engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 46214, Republic of Korea
5
New Energy Industry Convergence and Open Sharing Center of Pusan National University, Busan 46214, Republic of Korea
Abstract: One of the most exciting plasmonic fields, the gap plasmonic coupling structures, is getting much attention in a wide variety of applications, such as photonic sensors, biomedical, and photonic applications, highly enhancing a large electric field near the surface of the nanoparticles and metal film. Meanwhile, a series of studies have attempted to control the gap distance structure based on various materials with unique characteristics. In these achievements, one of the popular applications is humidity sensors. Nevertheless, the inflexible properties of materials that lack wide sensitivity make it difficult to guarantee realistic application requirements. Therefore, the investigation into next-generation materials that can easily control the properties to reversibly tune the gap between nanoparticles with a metal film is still challenging. In this study, we present the biomaterial from the M13 phage as an actuator in the dielectric layer to control the gap size at the nanoscale to tune the plasmonic resonance. The Ag nanocubes were positioned on M13 phage self-assembled into nanostructures a few nanometers thick as a dielectric spacer to enhance the plasmonic resonance. The FDTD simulations of resonance peak and surface charge contribution revealed that the coupling strength strongly depends on the M13 phage thickness. By exploiting the hydrophilic possibility based on the protein surface of the M13 phage, we demonstrated the dynamic tunability of the M13 phage layer through atomic force microscopy (AFM) under different humidity levels. Based on the mechanism gap plasmonic coupling system and the genetically engineered M13 phage, we developed a colorimetric sensor array that detected VOCs gas and lung cancer breath with high classification success rate.
106. Characterization of Isomeric Lipid-A Species from Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Nonaqueous CE-MS/MS with Collision-Induced Dissociation
Viktor Sándor 1,
Anikó Kilár 1,
Bettina Ürmös 2,
Ibrahim Aissa 2
and
Ágnes Dörnyei 2
1
Institute of Bioanalysis, Medical School and Szentágothai Research Centre, University of Pécs, Hungary
2
Department of Analytical and Environmental Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Pécs, Hungary
Abstract:Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a ubiquitous nosocomial pathogen, one of the deadliest bacteria in hospitals. Moreover, this Gram-negative bacterium has numerous intrinsic resistance mechanisms against the majority of antibiotics, leading to most antibiotics becoming useless. For these reasons, P. aeruginosa is ranked by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a priority number one pathogen for the research and development of new antibiotic strategies. One of the new directions in antibiotic strategy development involves membrane active agents that induce bacterial cell membrane destabilization, leading to the loss of its integrity. For this purpose, it is necessary to know the detailed composition and structure of the bacterial cell wall constituents. The outer leaflet of the Gram-negative outer membrane is mainly a highly ordered lipopolysaccharide (LPS) monolayer. LPS molecules (or often called endotoxins) are built up of three distinct structural regions: a polysaccharide called the O-antigen, the core oligosaccharide and the hydrophobic and endotoxic lipid-A portion. Lipid-As, as the membrane-integrated part of LPSs, generally consist of a β-(1′ → 6)-linked 2-amino-2-deoxyD-glucose disaccharide backbone carrying phosphate groups at the C4′ and C1 positions, as well as amide and ester linked hydroxy fatty acids or O-acylated hydroxy fatty acids at the C2′/C2 and C3′/C3 positions, respectively. Naturally, lipid-A isolates are heterogeneous mixtures of various lipid-A molecules that differ in the number, the position, and the type of acyl chains and phosphate groups. Herein, a non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) method coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) in the positive and negative ionization modes with collision-induced dissociation (CID) activation technique was applied for the deep characterization of the lipid-A isolate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as one of the critical priority targets for antibiotic research. This new and unique strategy has revealed hitherto unreported isomeric monophosphorylated lipid-A constituents in the naturally heterogeneous sample. The electrophoretic separation, orthogonal to the former chromatographic techniques, of P. aeruginosa lipid-A ions allowed for the observation and structural evaluation of both acyl chain and phosphate positional isomers. CID of the separated monophosphorylated species using only the obvious negative ionization mode is insufficient to fully characterize lipid-A, as the phosphate positions remain unresolved. Our new strategy involved the parallel fragmentation of the ions in the complementary positive and negative ionization modes as well, facilitating the full structural assignment of this class of molecules.
Acknowledgement: The research was supported by the grants NKFIH FK-129038. The research was performed in collaboration with the Mass Spectrometry Core Facility at the Szentágothai Research Centre of the University of Pécs.
107. Characterization of Tau Proteome in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid
Andrej Kovac 1,
Juraj Piestansky 2,
Petra Majerova 1
and
Jozef Hanes 1
1
Institute of Neuroimmunology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dubravska cesta 9, 84510, Bratislava, Slovak Republic
2
Department of Pharmaceutical analysis and nuclear pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy of Comenius University, Odbojarov 10, 832 32, Bratislava, Slovak Republic
Abstract: Tauopathies involve around twenty neurodegenerative diseases, including the most frequent Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, Pick’s disease, frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism linked to chromosome-17, and dementia pugilistica/traumatic brain injury/chronic traumatic encephalopathy complex among others. Tauopathies are characterized by abnormal depositions of hyperphosphorylated microtubule-associated protein tau into intracellular neurofibrillary tangles. In the human brain, six tau isoforms are expressed (0N3R, 1N3R, 2N3R, 0N4R, 1N4R, 2N4R). Only scarce information exists concerning the amount of each of these isoforms in human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Here, we investigated different tau forms that are present in the human CSF. The CSF tau protein was separated using the reverse phase chromatography on 4000-angstrom pore size poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) particle column, and the fractions were analyzed using the ELISA and Western blot. Several different tau protein fragments were present in CSF. The pattern of tau showed a series of N-terminal and mid-domain fragments that were recognized by different monoclonal antibodies. Western blot analysis also revealed the subset of phosphorylated tau species. Taken together, our results showed that the tau proteome in human CSF represents a complex mixture of fragments.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by APVV-21-0321, APVV-21-0254 and VEGA 2/0129/21.
108. Chiral Resolution of Thyroxine Enantiomers Using Chiral Crown Ether Column by UPLCtandem Mass Spectrometry
Suraj Adhikari 1,
Jisun Lee 2,
Wonjae Lee 1
and
Hye-Ran Yoon 2
1
College of Pharmacy, Chosun University, Gwangju, 61452, South Korea
2
College of Pharmacy, Duksung Women’s University, Seoul, 01369, South Korea
Abstract: Chiral discrimination of thyroxine (T4) enantiomers was performed using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) on a chiral crown ether-derived ChiroSil SCA(-) column. The different composition of mobile phases and the effect of column oven temperatures were investigated and the optimum chromatographic separation with respect to resolution and analysis time was achieved using a mixture of 60% methanol/water (v/v) with 0.1% formic acid at 40 °C having a flow rate of 1.4 mL/min. The thermodynamic data from van’t Hoff plots of temperature experiments revealed that the enantioseparation was an enthalpically favored process. The method was validated in the concentration range of 0.5–100 μg/mL for both enantiomers and proved to be a rapid, precise, sensitive, and selective method for the enantiodiscrimination of T4 under the optimized conditions. The calibration curves of both D- and L-T4 showed an excellent linearity with coefficient of determination (R2) > 0.9997. The developed chiral method was successfully applied for a quantitative assay to check the enantiomeric purities of the six pharmaceutical formulations of levothyroxine sodium tablets and the enantiomeric impurities identified were in the range of 0.11–0.29%. This method could be applied for the determination of enantiomeric purity of pharmaceuticals and for the monitoring of thyroid hormone levels.
109. Chiral Separation and Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Bioactive Indolecontaining Pyrazino [2, 1-b] Quinazoline-3,6-Diones for Metabolism Study
Long Solida 1,2,
Song Sousdey 1,
Ven Sovannaroth 1
and
Emilia Sousa 3
1
Department of Bio-engineering, Royal University of Phnom Penh, Phnom Phen, Cambodia
2
Cambodian Chemical Society, Phnom Penh, Cambodia
3
Faculty of Pharmarcy, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal
Abstract: In recent decades, fungi-derived naturally occurring quinazolines have emerged as potential drug candidates. Nevertheless, most studies are conducted for bioactivity assays, and little is known about their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) properties. To perform metabolic studies, the synthesis of the naturally occurring quinazolinone, fiscalin B (1), and its chloro derivative, 4-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-8,10dichloro-1-isobutyl-1,2-dihydro-6H-pyrazino [2,1- b]quinazoline-3,6(4H)-dione (2), disclosed as an antibacterial agent, was performed in a gram scale using a microwave-assisted polycondensation reaction with 22% and 17% yields, respectively. The structure of the non-natural (+)-fiscalin B was established, for the first time, by X-ray crystallography as (1R,4S)-1, and the absolute configuration of the naturally occurring fiscalin B (−)-1 was confirmed by a comparison of its calculated and experimental electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra as (1S,4R)-1. The chiral separation technique using a amylose-1 column was successful at milligram scale. In vitro metabolic studies were monitored for this class of natural products for the first time by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). The metabolic characteristics of 1 and 2 in human liver microsomes indicated hydration and hydroxylation mass changes introduced to the parent drugs.
Acknowledgement: The authors thanks to Higher Education Improvement Project grand number HEIP-RUPP-SGA-11 for supporting partially on structure elucidation.
References
Resende, D.I.S.P.; Boonpothong, P.; Sousa, E.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.M.M. Chemistry of the fumiquinazolines and structurally related alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 7–34.
Long, S.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Kijjoa, A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Fernandes, R.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.M.M. Synthesis of New Proteomimetic Quinazolinone Alkaloids and Evaluation of Their Neuroprotective and Antitumor Effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 534.
Long, S.; Resende, D.; Kijjoa, A.; Silva, A.; Pina, A.; Fernández-Marcelo, T.; Vasconcelos, M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M. Antitumor Activity of Quinazolinone Alkaloids Inspired by Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 261.
Sousa, M.E.L.S.; Pinto, M.M.d.M.; Resende, D.I.S.P.; Kijjoa, A.; Martins da Costa, P.; Freitas da Silva, J.M.M.; Nogueira, F. Pyrazino [1,2-b]Quinazoline-3,6-diones Derivatives, Their Production and Uses. Thereof. Patent WO/2021/033159, 25 February 2021.
110. Correlation Analysis between Volatile Compounds and α-Dicarbonyl Compounds in Various Beans as Responses to Different Roasting Conditions
Gaeun Lee,
Haeun Lee
and
Kwang-Geun Lee
Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, 32, Dongguk-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10326, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this study, volatile compounds and α-dicarbonyl compound (α-DCs; glyoxal, methylglyoxal, and diacetyl) contents were analyzed with beans (soybeans, black soybeans, and mung beans) roasted at different times and temperatures. Among the volatile compounds detected in unroasted soybeans, 1-octen-3-ol was the most abundant. After roasting, 1-octen-3-ol decreased by up to 86%. In unroasted beans, 3-ethyl-2,5-dimethyl pyrazine and 2,3,5-methyl pyrazine were not detected. However, they became the main volatile compounds after roasting. Roasting at 180 °C for 25 min led to the highest amount of volatile compounds. Roasting at 200 °C for 25 min led to the highest amount of α-DCs content. As the roasting temperature and time increased, the level of α-DCs and volatile compounds showed a positive correlation (spearman correlation, r = 0.878, 0.890, 0.867 in soybeans, black soybeans, and mung beans, respectively). However, the production of volatile compounds and color value showed a negative correlation (spearman correlation, r = −0.917, −0.967, −0.850 in soybeans, black soybeans, and mung beans, respectively). The results of this study suggest 180 °C for 25 min roasting as optimal roasting conditions for beans, in which the generation of flavor compounds is maximized while the generation of α-DCs is relatively small.
111. Determination of Nutrient Concentration in Cyanobacterial Liquid Culture by CE and ICP-MS
Natália Melicherová 1,2,
Tomáš Vaculovič 3,
Radka Kočí 4,
Martin Trtílek 4,
Jana Lavická 1
and
František Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Veveří 967/97, 602 00 Brno, Czech Republic
2
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 753/5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic
3
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Kamenice 753/5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic
4
PSI (Photon Systems Instruments), spol. s r.o., Průmyslová 470, 664 24 Drásov, Czech Republic
Abstract: This work focused on developing a highly efficient CE-based method for monitoring changes in the liquid cultivation media during the growth of cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. under sterile and defined conditions. Developing this type of approach, we can monitor changes in the liquid media after the growth of cyanobacteria in the future, e.g., in the presence of plant growth regulators or stressors. The cyanobacterial culture was cultivated in a lab-scale cultivator, Multi-Cultivator MC 1000-OD MIX (Photon System Instruments. s.r.o.), with eight different cultivation slots. The cultivation experiment was set in multivariant screening mode, i.e., different wavelengths and/or combinations for growth in each independent vessel. LEDs with different peak wavelengths were used for culture illumination. The device also provided independent OD monitoring (680 and 720 nm) for each vessel and uniform temperature and aeration control for all vessels. The cultivation experiment was set as a batch and terminated after all eight different growth conditions reached the plateau in their growth curves. The optical density was periodically recorded via the provided OD View program to monitor continuous growth. Small aliquots of cultivation suspension were periodically harvested through the aeration tubing for consecutive analyses during the growth. The analysis targeted macro and micronutrients in the cultivation medium and profiled the produced metabolites. Macronutrients, present in a milli- and micromolar concentration, were analyzed with the CE-based methods coupled with a capacitively-coupled contactless conductivity detector (C4D). The CE method was optimized for a short analysis time to allow the analysis of many samples as the cultivation experiment lasted days and hundreds of samples were harvested. ICP-MS (inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry) was used for quantitation of the micronutrients which were out of the sensitivity range of the CE-C4D method (nanomolar concentrations).
Acknowledgement: The work has been supported by European Regional Development Fund-Project “SINGING PLANT” (No.CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_026/0008446).
References
Kubáň, P., J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 964, 227-241.
Da Silva, J. A. F., J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 265-268.
Dosedělová, V., Electrophoresis 2019, 41, 116-122.
112. Determination of Vancomycin in Livestock and Fishery Products Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Bohyun Shin,
Chohee Jeong
and
Sang Beom Han
College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, 84 Heukseok-ro, Dongjak-gu, Seoul, 06974, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Veterinary drugs are used for animal therapeutic and prophylactic purposes to control bacterial infections and prevent outbreaks of animal disease. When used properly, the levels of veterinary drug residues in foods are usually very low, such that acute food poisoning incidents would not occur. However, since veterinary drugs remaining in livestock products may be harmful to humans by consuming them, it is necessary to develop a method for analyzing veterinary drugs residues in foods. Antibiotics, especially those used in livestock, increase the risk of developing antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and people who ingest them may cause antibiotic-resistant infections. Vancomycin is an antibiotic to treat serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, and in Korea, it is regulated as a substance that should not be detected in food (prohibited drugs). In this study, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was developed to analyze vancomycin, one of the banned substances, in pork, beef, chicken, shrimp, flatfish, eel, milk, and egg. Vancomycin is easily decomposed in a strong base or acid within a short time. Considering these characteristics, after extracting livestock and fishery products with a 15% acetonitrile solution containing 50 mM ammonium acetate, MCX SPE purification method using water saturated hexane was optimized. In this way, the recovery rate was improved from less than 50% in the existing method to more than 80%, and the limit of quantitation (LOQ) of 0.5 ppb was satisfactorily obtained. The analytical method was validated according to the Codex guidelines (CAC/GL-71-2009), and vancomycin was satisfactorily detected with selectivity, linearity, recovery, accuracy, and precision in all matrices.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by a grant (20162MFDS622) from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2021.
113. Development of a New Biomarker Model for Predicting Preterm Birth in Cervicovaginal Fluid
Ji-Youn Lee,
Sun Koung Joung,
Dong-Kyu Lee
and
Sang Beom Han
College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, 84 Heukseok-ro, Dongjak-gu, Seoul, 06974, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Preterm birth (PTB) is a social problem that adversely affects not only the survival rate of the fetus, but also the premature babies and families, so there is an urgent need to find accurate biomarkers. We noted that, among the causes, the change from eubiosis to dysbiosis of the vaginal microbiome leads to changes in metabolite composition. Therefore, in this study, cervicovaginal fluids (CVF) from 30 preterm birth and 60 term birth mothers were collected, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), organic acids, amino acids, and other polar metabolite compounds were analyzed. Targeted analysis was performed by first extracting CVF with an organic solvent, derivatizing SCFAs with N-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-N-methy ltrifluoroacetamide, and then analyzing them by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). In residual aqueous CVF, the polar metabolites produced in the biochemical process were derivatized using methoxyamine and N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA), and analyzed by GC-MS to perform non-targeted analysis. As a result, nine SCFAs including hextanoate were quantified, and 58 polar metabolites were detected in 90 clinical samples. The criteria of statistical analysis and detection rate of clinical sample for development of PTB biomarkers were presented, on the basis of which 19 biomarkers were selected, consisting of one SCFA, two organic acids, four amine compounds, and 12 amino acids. In addition, the model was evaluated as a suitable indicator for predicting PTB without distinction between sample collection times. We hope that the developed biomarkers based on microbiota-derived metabolites could provide useful diagnostic biomarkers for actual patients and pre-pregnancy.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (grant number 2021R1A6A1A03044296).
114. Development of the Simultaneous Analytical Methods of Nine Compounds in Magnoliae Cortex Treated with the Herbal Primary Processing Using HPLC
Chong Woon Cho 1,
Young Sik Park 2,
Hyung Min Kim 1
and
Jong Seong Kang 1
1
College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2
Graduate School of New Drug Discovery and Development, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Generally, the herbal primary processing method can modify or improve the concentration of ingredients, therapeutic and physical properties, and the toxicity in herbal medicines. Magnoliae Cortex has been mainly used for herbal medicinal materials for the treatment of toothache, indigestion, and obesity diseases for a long time in Korea, Japan, and China. However, it is not consumed without its primary processing, because it has side effects, such as irritation of the throat and tongue. In addition, the medicinal effects of the processed herbal medicines are dependent on the skill of manufacturer, because manufacturer has manually made herbal medicines. Therefore, the standardization of the herbal processing methods is required to quality control. The purpose of this study is to develop the simultaneous analytical methods for quantifying the contents of nine compounds changed specifically in the processed samples using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Nine compounds are 3deoxyglucosulose, (2) magnoloside T, (3) magnoflolin, (4) magnoloside B, (5) magnoloside A, (6) isoacteoside, (7) randaiol, (8) honokiol and (9) magnolol. The HPLC condition was carried out on a Monotech C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm (ID), 3 μm) with mobile phase of 20 mM ammonium acetate in water–methanol (95:5) (A) and 20 mM ammonium acetate in water–methanol (10:90) (B) under the following gradient elution: 5 to 30 B% in 17 min, 30 B% to 65 B% in 11 min, 65 B% in 7 min, 65 to 100 B% in 15 min monitored at the wavelength of 283 nm. Other conditions were controlled at the flow rate of 0.4 mL/min, column temperature of 25 ℃, and injection volume of 10 μL. In terms of results, the contents of nine compounds presented a large difference depending on the compound type and the processing treatment method. Moreover, the developed analytical method was successfully validated very well in accordance with MFDS and ICH guideline. In conclusion, the developed methods will be used for the quality control of the processed Magnoliae Cortex and its products.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by the creative challenge research program (NRF-2021R1L1A1A01057992) of the National Research Foundation of Lorea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Education, Republic of Korea.
115. Development of UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Analysis of Topotecan in Plasma and Vitreous Humor Samples for Application in Retinoblastoma Therapy
Barbora Mudrova 1,2,
Katerina Hrabakova 1,
Petr Kozlik 1,
Jakub Sirc 2
and
Zuzana Bosakova 1
1
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
2
Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, Heyrovsky Sq. 2, Prague, Czech Republic
Abstract: Topotecan is a chemotherapy agent in the form of its hydrochloride salt, used for the treatment of various human cancers, including ovarian cancer, small cell lung cancer, or retinoblastoma, the most common malignant intraocular tumor in children. Topotecan is a camptothecin derivative that has been structurally modified to increase its solubility in water. The antitumor activity of topotecan lies in its ability to inhibit intranuclear enzyme, topoisomerase I. This enzyme plays an important role in replication, transcription, and DNA repair. Topotecan, like other camptothecin analogues, binds to DNA-topoisomerase complex I. Topotecan intervenes in the process of DNA breakage and resealing during DNA replication, blocking the progress of the replication. This process leads to DNA fragmentation and cell death [1]. Topotecan undergoes pH-dependent hydrolysis of the lactone ring to form the ring-opened carboxylate form. However, the lactone form shows significantly higher antitumor activity than the carboxylate form [2]. That is why it is important to understand the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of lactone ring opening to achieve the most effective treatment of the tumor. Therefore, there is a clinical requirement for a highly sensitive analytical method to monitor topotecan concentration during medical treatment. We have developed a rapid, selective, and highly sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of both forms of topotecan in porcine plasma and vitreous humor samples. Separation was performed at 15 °C on a Waters Acquity-UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm × 50 mm, particle size 1.7 µm) with linear gradient elution. The protocol was validated to demonstrate its reliability in the determination of both forms of topotecan in plasma and vitreous humor samples. The method showed an excellent linear range from 0.4 to 120 ng ml−1 for lactone (1.0–120 ng ml−1 for carboxylate) in plasma and vitreous humor. The novel method will undergo comprehensive medical research testing based on hydrogels in order to develop an innovative delivery implant system for topotecan via transscleral diffusion for the treatment of retinoblastoma.
References
Arun, B., Frenkel, E.P., Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy, 2001, no. 2:3, pp. 491-505.
Wall, M.E., Wani, M.C., Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 1977, no. 17, pp. 117-132.
116. Discovery of Potential Quality Marker of Duliang Herbal Formula for Migraine via Network Pharmacology and LC-PDA-MS/MS Analysis
Duc Thanh Chu,
Chong Woon Cho,
Hyung Min Kim
and
Jong Seong Kang
College of Pharmacy, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Quality control is great important to clinical application of drugs for ensuring safety and efficacy. Due to properties of herbal formula such as the chemical complexity, as well as holistic and synergistic bio-effects, quality control of herbal medicine still faces challenges and need to be upgraded. Duliang herbal formula used for migraine treatment was derived from the traditional Chinese prescription containing Angelica dahurica radix and Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome. With the integrated approach of network pharmacology and LC-PDA-MS/MS analysis, this study aims to discover potential quality markers of the Duliang formula for migraine treatment, which enhances its standard criteria. First, network pharmacology was applied to investigate relationship among bio-active compounds, targets and migraine. Based on the topological attributes of network analysis, the compound nodes with high degree value were considered as key active compounds in the herb-compound-target pathway-disease network. Second, chemical profiling of Duliang formula was performed by LC-PDA-MS/MS analysis. Last, potential quality markers were selected by integrating the analysis of chemical profile and network pharmacology. The results indicated that compounds, such as imperatorin, ligustilide, isoimperatorin, senkyunolide I, senkyunolide A, ferulic acid, etc., could be considered as quality markers of Duliang formula for migraine treatment. This study also indicates that the chemical analysis and network pharmacology can be applied as an effective integrated approach for discovering quality markers of herbal formula based on the holistic synergistic effectiveness and measurability of compounds in herbal formula.
Acknowledgement: Authos thank the BK21 FOUR Program by the Chungnam National University Research Grant, 2022 and by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2021R1I1A3047248) for their funding.
117. Dissipation Patterns and Dietary Risk Assessments of Acrinathrin and Cyenopyrafen in Sweet Pepper Using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS
Jung-Hoon Jung 1,2,
Seong-Hoon Jeong 1,
Jong-Wook Song 1,
Jong-Su Seo 1
and
Jong-Hwan Kim 1
1
Korea Institute of Toxicology, Jinju, Republic of Korea
2
Korea Institute of Toxicology, Jinju, Republic of Korea
Abstract: The dissipation patterns of two insecticides (acrinathrin and cyenopyrafen) were investigated in sweet pepper under greenhouse condition at three different field trials. A quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) method was applied for the extraction and clean-up of both target compounds. Analytical methods were developed using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). Limits of detection (LODs) and quantification (LOQs) observed for acrinathrin and cyenopyrafen were 0.01 and 0.002 mg/kg, respectively. The good calibration curves of r2 > 0.995 for acrinathrin and r2 > 0.999 for cyenopyrafen were obtained. Additionally, recovery tests were conducted at different LOQ levels, namely, LOQ level, 10 and 50 times of LOQ, and each concentration was treated with five replicates. As the result, mean recoveries ranged from 80.8–108.4% with the relative standard deviation (RSD) of ≤15.0% for acrinathrin and 79.9–114.8% with the RSD of ≤4.3% for cyenopyrafen, respectively. The insecticides were applied to three field trial sites (two times at seven-day intervals) in accordance with the Korean good agricultural practice (GAP). The samples were harvested at 0 (approximately 2 h after), one, three, five, seven, and 14 days after the last insecticide application. Based on the results obtained from the tests, the maximum residue limits (MRL) were calculated using the OECD MRL calculator and recommended as 0.15 mg/kg for acrinathrin and 0.5 mg/kg for cyenopyrafen. Moreover, the half-lives estimated were 45.7 days and 13.7 days for acrinathrin and cyenopyrafen, respectively. Finally, the estimated daily intake (EDI) for both insecticides were calculated and compared with the acceptable dietary intake (ADI). The results suggested that the two insecticides did not pose any human health risk when sprayed in compliance with GAP.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by Grant No. PJ0136412022 from the Rural Development Administration (RDA), Republic of Korea.
118. Dissipation Patterns and Risk Assessment of the Insecticides Propiconazole, Hexaconazole, Tetraniliprole, and Isopyrazam in Green Pepper Using LC-MS/MS
Seong-Hoon Jeong 1,2,
Jung-Hoon Jung 1,
Jong-Wook Song 1,
Jong-Su Seo 1
and
Jong-Hwan Kim 1
1
Korea Institute of Toxicology (KIT), Jinju, Republic of Korea
2
Korea Institute of Toxicology (KIT), Jinju, Republic of Korea
Abstract: The dissipation patterns of four different insecticides, propiconazole, hexaconazole, tetraniliprole, and isopyrazam, were investigated in green pepper under greenhouse conditions in three different field trials. A simultaneous analytical method was developed based on high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). A quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe method, QuEChERS, was applied for extraction and clean-up to analyze the target compounds in green pepper. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) recorded were 0.005 and 0.01 mg/kg, respectively. Additionally, a good linearity was observed (r2 > 0.998) and the mean recoveries at different LOQ levels, namely 10 and 50 times the LOQ level, each with five replicates, were 77.1–116.8%, respectively, with a relative standard deviation of ≤13.2%. The insecticides were applied to three field trial sites (two or three times at 7-d intervals) in accordance with the Korean good agricultural practice (GAP) and after the last application, the decline in the concentration of four insecticides in green pepper was investigated at 0, 1, 2 or 3, 5, 7, and 14 d at three different sites of field trial. After a removal of the cap of the green pepper, all samples were weighed using a weighing balance and homogenized, then stored at a temperature below −20 °C until used for analysis. The storage stability (below −20 °C) of the samples treated with insecticides was in the range of 90.0–105.9% for a maximum of 80d. The average half-lives of the insecticides were 7.5, 8.9, 17.5, and 10.1d, respectively. From the results regarding residual amounts of green pepper, we confirmed that the four insecticides did not pose any human health risk based on the values of the risk index calculated using the estimated daily intake (EDI) and acceptable dietary intake (ADI) when the insecticides were sprayed in compliance with GAP.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by Grant No. PJ0136412022 from the Rural Development Administration (RDA), Republic of Korea.
119. Effect of Roasting after Sugar-Soaking on the Level of Volatile Compounds, Total Polyphenols, Total Flavonoids, and Isoflavones in Black Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr)
Jaehee Choi,
Daehyeop Lee
and
Kwang-Geun Lee
Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, 32, Dongguk-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10326, Republic of Korea
Abstract: This study was conducted to identify the level of volatile compounds and isoflavones and the antioxidant activity of roasted black soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr) after soaking in various sugars. Different black soybean samples were prepared as following conditions; black soybeans were soaked in five types of monosaccharide (glucose, fructose, arabinose, xylose, ribose) solution at three concentrations (1, 3, 5%, w/v) for 2 h, followed by drying and roasting. The drying and roasting conditions were 50 ℃ for 20 min and 200 ℃ for 20 min, respectively. Volatile compounds and isoflavones were analyzed by a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography, respectively. Out of 22 volatile compounds identified in black soybean headspace, 2,5-dimethylpyrazine presented the highest abundance of 1790 μg/kg. The highest content of total volatile compounds was detected in the sample prepared by 5% glucose, 67.9% higher than control. The highest content of total isoflavones was detected in the sample prepared by 1% arabinose, 18.6% higher than control. As the concentration of glucose, fructose, and ribose solutions increased, the contents of total volatile compounds, total isoflavones, total polyphenols, and total flavonoids were significantly increased (p < 0.05). However, for xylose and ribose solutions, those were significantly decreased (p < 0.05), except for the total polyphenols. This study provides practical information on the changes of volatiles, isoflavones, and antioxidants in roasted black soybeans after soaking in five monosaccharide solutions.
120. Electrospray Ionization Charge-Detection Mass Spectrometry (ESI-CDMS) for Analysis of Microplastics
Elaura Gustafson,
George Gao,
Kate Hales
and
Daniel E. Austin
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, United States of America
Abstract: Charge-detection mass spectrometry (CDMS) is an emerging technique ideally suited to studying the mass distributions of sub-micron to micron-sized particulates in solution. In contrast to optical techniques, CDMS provides a histogram of the full-size range of individual particles in a sample rather than population averages and is especially helpful to characterize the tails of the size distribution. In ESI-CDMS, microparticles are first charged using electrospray (ESI), then introduced through a vacuum interface to the CDMS analyzer consisting of a series of electrodes. As a charged particle passes across the electrodes, the resulting image charge is amplified and recorded. The pattern of these peaks provides particle velocity and electrical charge, and by applying a DC offset on one or more electrodes, the change in particle velocity can be measured, giving the mass-to-charge ratio. These measurements combine to yield the mass of each particle in the sample. We have constructed a CDMS instrument for the analysis of sub-micron to micron-sized particles in which the electrodes are made by patterning conductive features onto the facing surfaces of two printed circuit boards (PCBs). Particles pass through the space between the two PCBs. The resulting image charge is amplified, filtered, and shaped using a combination of commercial charge amplifiers and custom amplifier/shaper circuits. Experiments using polystyrene and other materials in the size range of 100 nanometers to 10 μm demonstrate that these particles are sufficiently charged during electrospray (hundreds to thousands of elementary charges) to be observed in the CDMS setup. Data analysis is ongoing to determine the uncertainty of the mass measurement as a function of particle size. The chemical attachment of proton-accepting groups (amines) to the polymer surface prior to the analysis enhances the charging process, and hence the range of the technique with respect to the smallest particle sizes.
References
Gao, J.; Austin, D.E., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 2044-2052.
Gustafson, E.L.; Murray, H.V.; Caldwell, T.; Austin, D.E., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 2161-2170.
121. Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry with Reducing Agents
Yunseop Choi,
Sanghwang Park
and
Jongcheol Seo
Department of Chemistry, POSTECH, Pohang, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) is one of the most powerful molecular identification techniques which enables us to measure the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of analyte ions with less fragmentation. However, ESI-MS is difficult to use in hardly ionized materials. In many cases, ionization in ESI-MS can be achieved by the transfer of protons or metal cations. Therefore, molecules with no protonation/deprotonation site, or polar functional groups, such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), fullerenes, metal clusters, and several more, are difficult to detect in ESI-MS. In this study, we have tried to use several reducing agents to ionize molecules negatively and detect them in ESI-MS. We successfully obtained ESI mass spectra of molecules that are hardly ionized with proton transfer by applying reducing agents. Furthermore, several charge-reduced molecules exhibit aggregation behaviors distinct from those without reductions. Representatively, stacked hemin dimers with and without reductions show distinguishable collision cross section values in ion mobility spectrometry, indicating that the molecular charges and their distributions should have a significant impact on the aggregation, such as π-π stackings. Further calculations are ongoing to find out their structure. This work suggests a new method to ionize the molecules, which are known to be poorly ionized, by the transfer of electrons. Furthermore, this will benefit the diverse studies on the charge-dependent aggregation behavior since it can provide a rational way to control the molecular charges of the analyte in the solution.
122. Emission Behavior of VOC and Formaldehyde from Cut Edges in Building Products
Man-Goo Kim
and
Jun-Ho Park
Department of Environmental Science, Kangwon National University, Chunchon, Korea
Abstract: Many kinds of building materials, such as wood flooring, vinyl floor covering, partition etc., have a multilayer structure in which specific emission rate and the kinds of emitting contaminants are much different between the surface and cutting edge. Standards of each country are supposed to measure only the surface emission strength and some countries prepare testing specimens to contain not only surface, but also cut edges. Other countries prepare test specimens to consider the ratio of the surface and the cut edges. As the cut edges are exposed at the time of actual use of the building product, the exposure of the cut edges should be considered in the emission test of the building materials. The cutting edge of the test specimen is sealed in a variety of ways. Laminate flooring products consist of E0 grade MDF and coated with LPM which have two surfaces and four cut edges. The test specimen is sealed, its edges cut by the aluminum adhesive tape. The number of sealed cutting edges is 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 with hole; the corresponding sealing rate of cutting edge is 0%, 25%, 75%, and 95%, respectively. The emission chamber test was performed over 56 days and TVOC and Formaldehyde were analyzed following the ISO 16000-6 and ISO 16000-3, respectively. We examined the sealing rate of cut edges for its effect on the area specific emission rate of TVOC and Formaldehyde. Except for the test specimen with a hole (95% sealing rate), the area specific emission rates of TVOC are almost the same regardless of the sealing rate after 14 days. A comparison of formaldehyde emission rate changes between different sealing rates is shown. The changes in the formaldehyde emission rate showed a clear difference between the test specimens with different sealing rates from day 7 to day 56. Moreover, although the absolute value of the emission rate decreased somewhat, the change in the ratio of the emission rates of these test specimens did not show much. The test method of cut edges emission is being developed as an ISO standard.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT) standard technology improvement project (No. 2001528).
123. Evaluation of Different Ionic Liquids for Electromembrane Extraction across a Hollow Polymer Inclusion Membrane for Analysis of Herbicides
Ye Tim Pung,
Sabita Samy
and
Hong Heng See
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Johor Bahru, Johor Malaysia
Abstract: Herbicides with high mobility and retention in the hydrologic system currently represent approximately 60% of all pesticides used globally to control weed growth. Unfortunately, herbicides often present as complex matrices, which could potentially interfere with the separation and analysis stage. However, the miniaturized sample preconcentration methods available, such as SPME and SDME, present a number of disadvantages, including a limited lifetime and instability of extraction. Therefore, in the present work, the technique of electromembrane extraction across a hollow polymer inclusion membrane (EME-HPIM) was employed to extract and analyze herbicides in environmental samples. Several asymmetrical and symmetrical ionic liquids (IL) were used as carriers in the HPIM. Cationic herbicides, namely paraquat dichloride hydrate (PQ) and diquat dibromide monohydrate (DQ), and anionic herbicides, namely 4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid (4-CPA) and 2-(2,4dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid (2,4-D), were chosen as the target analytes in this work. The HPIMs were prepared using the dipping technique, whereby a solution containing considerable amounts of cellulose triacetate (CTA), tris(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate (TEHP), and ILs in dichloromethane is cast onto glass capillary tubing. The herbicides were extracted across the membrane into a 20-µL aqueous acceptor solution inside the hollow membrane lumen via EME conducted at a fixed voltage of 300V with a stirring rate of 800 rpm for 10 min. Individual extraction performances of all HPIMs with different ILs were investigated and compared. This technique displayed good linearity in the range of 850–5000 ng/mL with a correlation above 0.995. The limit of detection (LOD) was 280,300 ng/mL, while the reproducibility was very good, with a value of 6.5–7.6% (n = 3 for 1000 ng/mL) for all analytes. Based on the findings, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (BMIMHFP) proved to be the best carrier for the extraction of PQ and DQ, achieving high enrichment factors of 123 and 71, respectively. Aliquat 336 was shown to be the most effective carrier for the extraction of 4-CPA and 2,4-D, with an enrichment factor of 2 for both analytes. It is expected that this developed method will be employed not only for herbicides in the future, but also for a wide range of targeted environmental substances in order to ensure a safe environment for human beings.
Figure 1.
Simultaneous EME across HPIM set up.
Figure 1.
Simultaneous EME across HPIM set up.
124. Food Supplements—Fact or Fiction?
Maja Bensa 1,2,
Vesna Glavnik 2
and
Irena Vovk 2
1
Faculty of Agriculture and Life Sciences, University of Maribor, Pivola 10, SI-2311 Hoče, Slovenia
2
Laboratory for Food Chemistry, National Institute of Chemistry, Hajdrihova 19, SI-1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract: Food supplements are consumed in small amounts to supplement the normal diet with nutrients and other substances with nutritional or physiological properties. One of the popular ingredients in food supplements is also resveratrol, which is produced in plants as a secondary metabolite. Resveratrol is also present in our diet in grapes (wine), cranberries, strawberries, mulberries, currants, pistachio, peanuts, etc. The increased interest in resveratrol (both scientific and of the food industry) is due to various properties (antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, estrogenic, cardioprotective, antitumor and antiviral) contributing to positive effects on health. The food supplements with resveratrol are promoted for health benefits, such as cardiovascular support, cellular anti-aging properties, promoting a healthy response to biological stress, etc. In a growing market of food supplements, food safety and, in the European Union, also various regulatory requirements (regarding food labelling, health claims, etc.), are of great importance. Despite that, food supplements are still connected with many practices that are noncompliant with regulations, ranging from mislabeling or differences in declared and actual nutrient contents to the use of ingredients harmful to health and even food fraud. In our study, the market of food supplements containing resveratrol in Slovenia was examined from two points of view: resveratrol content and overall labelling regulatory compliance with EU requirements for food information, nutrition, and health claims on food, food supplements, and novel foods. An evaluation of declared content of resveratrol in 20 food supplements was carried out using a method based on high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) coupled with densitometry. The analyses were performed on HPTLC silica gel plates developed with developing solvent n-hexane–ethyl acetate–formic acid (20:19:1, v/v/v) [1] in a saturated twin through chamber. The development of plates was followed by derivatization with anisaldehyde detection reagent. The results offer an informative overview of compliance of resveratrol contents with declared contents for food supplement products available in the Slovenian market, which is quite concerning from a food safety point of view as 95% of products contained different contents of resveratrol than declared and 25% of products even exceeded the maximum level stated in conditions under which a food supplement with trans-resveratrol may be used (150 mg/day).
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding No. P1-0005), the generous support of Merck KGaA, Germany (providing HPTLC plates).
Reference
B. Simonovska, I. Vovk, S. Andrenšek, K. Valentová, J. Ulrichová, J. Chromatogr. A 1016 (2003) 89–98.
125. From Basic Research to Application: A High Performance Immune-Affinity Based Extracorporeal Virus Capture System
G. Jarvas 1,
D. Szerenyi 1,
H. Jankovics 2,
F. Vonderviszt 2,
J. Tovari 3,
L. Takacs 4,
F. Foldes 5,6,
B. Somogyi 5,6,
F. Jakab 5,6
and
A. Guttman 1,7
1
Research Institute of Biomolecular and Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Pannonia, Veszprem, Hungary
2
Bio-Nanosystems Laboratory, Research Institute of Biomolecular and Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Pannonia, Veszprem, Hungary
3
Department of Experimental Pharmacology, National Institute of Oncology, Budapest, Hungary
4
Laboratory of Monoclonal Antibody Proteomics, Department of Human Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary
5
National Laboratory of Virology, BSL-4 Laboratory, Szentagothai Research Centre, University of Pecs, Pecs, Hungary
6
Institute of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Pecs, Pecs, Hungary
7
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this poster presentation, we demonstrate how separation science tools can be directly utilized to fight virus infections. Inspired by various hemoperfusion and immune-affinity capture systems, a blood virus depletion device has been developed that offers highly efficient capture and removal of the targeted virus from the circulation, thus decreasing virus load. Single domain antibodies against the VHH-72 virus variant produced by recombinant DNA technology were immobilized on the surface of glass micro-beads, which were then utilized as immune-affinity stationary phase. For feasibility testing, the virus suspension was flown through the prototype device that captured the viruses and the filtered media left the column. The feasibility test of the proposed technology was performed in a BSL-4 classified laboratory using the actual SARS-CoV-2 strain. The laboratory scale device specifically captured ~120,000 virus particles from the culture media circulation, which corresponded to ~15 million virus particle capture ability of a therapeutic size column. This represents 3x over-engineering with the assumption of 5 million genomic virus copies in an average viremic patient. Our feasibility results suggested that this new therapeutic virus capture device could significantly lower virus load, and thus prevent the development of more severe COVID-19 cases, consequently reducing the mortality rate.
126. Gold Nanoparticles—From Synthesis to Extraction of Biological Thiols and CE-LIF Analysis
Věra Dosedělová
and
Petr Kubáň
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) exhibit several unique properties, including redox activity, surface plasmon resonance, a high surface-to-volume ratio, or spontaneous formation of a stable Au-S dative bond with biological thiols. Biothiols are endogenous compounds that play a significant role in biological systems and their altered levels have been associated with disease states. However, levels of biothiols are low in non-invasive biological samples, such as saliva or exhaled breath condensate (EBC). In this work, AuNP synthesis and AuNP-based extraction of biological thiols from samples followed by CE-LIF analysis are investigated. AuNPs were synthetized by a reduction of tetrachloroauric acid by trisodium citrate. The increasing gold-to-citrate ratio led to the synthesis of bigger particles (∼30-60 nm) but of worse particle size monodispersity. The particle size and distribution were determined by scanning electron microscopy and UV–Vis spectrophotometry. AuNPs with the size of ∼17 nm were further used for the investigation of the AuNP-biothiol interaction using different AuNP stabilizing agents (i.e., citrate, Tween 20) by UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Binding of cysteamine and homocysteine on the AuNP surface caused rapid AuNP aggregation and a color change of the suspension from red to blue. On the other hand, glutathione did not cause any visible aggregation. For biothiol extraction and enrichment, EBC samples were incubated with AuNPs and different reagents were tested (i.e., dithiothreitol, thioglycolic acid) to release biothiols from AuNPs. Prior to CE-LIF analysis, biothiols were derivatized with eosin-5-maleimide and separated in the 15 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid electrolyte (pH 7.5). A further optimization of biothiol release from AuNPs to achieve better enrichment will be conducted in future research.
Acknowledgement: This work was financed from the grant of the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Grant no. 22-23815S) and the institutional support RVO: 68081715.
127. Headspace In-Tube Microextraction Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry
Joon Yub Kwon
and
Doo Soo Chung
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
Abstract: When higher sensitivity or/and sample cleanup is needed for capillary electrophoresis/mass spectrometry (CE/MS), laborious off-line, instead of automatic and convenient in-line/on-line, coupled sample pretreatment techniques are commonly employed. This is because the run buffer for CE/MS should be volatile and of low ionic strength, and because the most popular interface of CE/electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS lacks an outlet vial exposing the ESI tip in the open air. We present in-tube microextraction (ITME) as the simplest possible but powerful headspace (HS) extraction technique in-line coupled with CE/MS. Using a basic liquid plug inside the separation capillary inlet as an acceptor phase, HS-ITME-CE/MS of acidic volatile analytes, namely trichlorophenols in an acidified water sample, was performed simply by placing the capillary inlet in the HS above the sample.
128. Highly Efficient Three-Phase Single Drop Microextraction Coupled with a Commercial Capillary Electrophoresis Instrument
Sunkyung Jeong 1,
Joseph E. Valdez 1,2,
Natalia Miękus 3,
Joon Yub Kwon 1,
Wooyong Kwon 1,
Tomasz Bączek 3
and
Doo Soo Chung 1
1
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
2
Department of Natural Sciences, College of Arts and Sciences, Nueva Vizcaya State University, Bayombong, Nueva Vizcaya, 3710, Philippines
3
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University of Gdańsk, Al. Gen. J. Hallera 107, 80-416 Gdańsk, Poland
Abstract: A high-performance version of in-line, three-phase direct immersion-single drop microextraction (DI-SDME) coupled with capillary electrophoresis (CE) was demonstrated using a commercial CE instrument, and all the major and minor details were described to provide an easy-to-follow and user-friendly protocol. The excellent sample cleanup and enrichment power of this method was demonstrated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in human urine. The only preparation of urine samples was the addition of HCl to acidify the urine sample to pH 2. The acidic NSAIDs in the acidified urine sample were extracted into a basic acceptor drop covered with a thin organic layer attached to the inlet tip of a capillary immersed in the sample. A simple but powerful DI-SDME-CE method could be carried out automatically without any modification of the existing CE instrument. For improved performance, sample agitation and heating were employed by installing a microstirrer and a thermostating jacket in the sample tray. With 10 min of DI-SDME at 35 °C with stirring, NSAIDs such as ketoprofen, ibuprofen, and naproxen in urine were enriched 340–970-fold with intraday and interday RSDs of 0.8–2.4% and 1.1–3.6%, respectively. The LODs obtained with in-line coupled CE/UV were 10–50 nM (2–10 µg/L). The performance of DI-SDME-CE/UV was also demonstrated by determining the naproxen level in human urine collected 24 h after taking a single oral dose of the drug. The spike recovery of naproxen from a single-point standard addition to the urine sample was 80%. Our high-performance three-phase DI-SDME-CE method is quite promising for the analysis of ionizable trace analytes in a complex sample matrix.
129. Highly Sensitive Analysis of Cationic Ink by Large Volume Sample Stacking with an Electroosmotic Flow-Nonaqueous Capillary Electrophoresis
Jiwoong Seol 1,
Sunkyung Jeong 2,
Eunjung Kwon 2,
Seung-Hoon Bahng 3
and
Doo Soo Chung 2
1
Faculty of Liberal Education, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
2
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
3
Scientific Investigation Lab, Ministry of National Defense, Seoul 04418, Korea
Abstract: Since capillary electrophoresis (CE) is usually conducted for the analysis of hydrophilic/water-soluble chemical species, only water-soluble inks have been widely investigated in CE-based forensic analyses. Most ballpoint pen inks are, however, oil-based and difficult to be analyzed with conventional CE. Nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) adopting the background electrolytes (BGE), capable of dissolving oil-based ballpoint pen inks, can be applied to the analysis of documents prepared using a ballpoint pen. In order to minimize the destruction of original documents, it is strongly required to minimize the sampling amount and to lower the detection limit of NACE of ballpoint pen inks. Large volume sample stacking with an electroosmotic flow pump (LVSEP) is an efficient and powerful concentrating method of CE in that it concentrates analytes from a whole-capillary filled sample without other maneuvers, e.g., polarity switching. For LVSEP, the electroosmotic mobility (EOM) should have a smaller magnitude than the analyte electrophoretic mobilities and its sign should be the opposite of those of the analyte mobilities. When a large volume of a sample of lower conductivity than that of the BGE is injected and a voltage for an electroosmotic flow (EOF) to move toward the inlet is applied, the analytes are stacked at the boundary between the sample and BGE. The average EOF decreases as the sample matrix of lower conductivity is removed into the inlet vial and the BGE of higher conductivity is introduced from the outlet. Once the EOF is reduced enough, the stacked analytes migrate against the EOF forward to the detector automatically. For LVSEP of cations, the surface charge of the capillary should be positive to generate a reversed EOF. In this experiment, the reversed EOF with an appropriate magnitude was achieved by dynamic coating of the negatively charged capillary inner wall with a double layer of a cationic surfactant or a polymer such as polybrene. LVSEP-NACE was applied for cationic dye standard samples and real ballpoint pen ink extracts and hundredfold sensitivity enhancements were obtained. Thus LVSEP-NACE is promising in resolving the difficulties regarding the forensic analysis of documents with minimal destructive sampling.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1I1A1A01068394 and 2021R1F1A1045947).
130. Host-Guest Chemistry of CB [7] and Imipramine: Impact on the Protonation Site
Jiyeon Lee,
Hyerim Kim
and
Jongcheol Seo
Department of Chemistry, POSTECH, Pohang, South Korea
Abstract: Observation of molecules existing either in the gas or solution phase by changing the surrounding environment has been actively studied, using ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS), especially for the molecules going through various physiological environments. In the case of benzocaine and benzoic acid, protonation sites of molecules highly depend on the solvent, showing a significant difference in collision cross section (CCS) value for the ions favored in the gas and solution phase. On the other hand, for the small molecules for which CCS values are not clearly discriminated, there is still a lack of analytical tools for the easy and rapid classification of protonation isomeric molecules. In the present work, we directly distinguished two imipramine protonation isomers, based on the different host–guest interaction between protomers and cucurbit [7] uril (CB [7]). Imipramine is a well-known anti-depression drug containing two nitrogen atoms, located in a cycloheptadiene ring and side chain. Imipramine itself exhibited no significant difference in drift time by protonation sites. However, imipramine-CB [7] complexes successfully distinguished two protonation isomers, showing distinctive CCS values. A few possible structures of complexes are predicted by density functional theory (DFT) calculation, which is in line with the measured CCS trend. Based on the complex structures and their energetics suggested by DFT calculation, we conclude that imipramine inclusion complex appeared as a result of kinetically trapped structure from solution phase, while exclusion complex is generated in the gas phase. The NMR spectra of imipramine and CB [7] sample further support that CB [7]-imipramine inclusion complex is derived from the solution phase.
131. Hybrid Similarity Search Algorithm Applications in Identifying Unknown Compounds in a Variety of Products Using Mass Spectrometry: Consumer Chemical Products and Drug Analogues
Jin Woo Kim,
So Yeon Lee,
Han Bin Oh
and
Bong June Sung
Sogang University, Seoul, Korea,
Abstract: In the area of mass spectrometry (MS), identifying unknown compounds is one of the most formidable challenges. In general, the identification of compounds using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is made by comparing the m/z values, tandem mass spectrometry fragment pattern, and LC retention times with those of the compounds in database. However, as the database is often lacking, the identification of unknown compounds becomes challenging. In this regard, a new search algorithm of hybrid similarity search (HSS) can become a good alternative. In HSS, the database can be extended through its own generic database expansion approach. That is, using the mass value difference between the compounds of interest and the ones in database, i.e., delta mass, each peak of tandem mass spectrum can be shifted by the delta mass. When the shifted peaks match well with some peaks in the tandem mass spectrum, this peak can be left shifted. Otherwise, the shifted peaks can be returned as before. In this way, all the peaks in the tandem mass spectrum can be either shifted or left untouched, thus generating a so-called hybrid spectrum. Using this approach, it was found that many unknown compounds that are not present in the database can be successfully identified. In particular, this HSS approach has been used for identifying unknown compounds in consumer chemical products and drug analogues. In the symposium, the details of these results will be discussed in detail.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEIT) through Technology Development Project for Safety Management of Household Chemical Products Program, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (Grant Number 2020002960002).
References
Cooper, B., Yan, X., Simon, Y., Tchekhovskoi, D., Mirokhin, Y., Stein, S. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91(21), 1392413932.
Jang, I. A., Lee, J. M., Lee, J.-U., Kim, B. H., Moon, B. J., Hong, J. K., Oh, H. B. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91(14), 9119-9128.
Lee, S.Y., Lee, S.T., Suh, S.I., Ko, B.J., Oh, H.B. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46(7), 732-742.
132. Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry of Phosphorylated Tau Peptides from Alzheimer’s Disease Brain
Petra Majerova
and
Andrej Kovac
Institute of Neuroimmunology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dubravska cesta 9, Bratislava, Slovakia
Abstract: Tauopathies are sporadic or familial neurodegenerative disorders characterized by intracellular inclusions of abnormal hyperphosphorylated and truncated tau protein. Under physiological conditions, tau protein is a soluble intracellular protein whose function is to control the stability of the axonal microtubules. However, it was shown that tau protein is abnormally hyperphosphorylated in neurofibrillary pathological lesions. The altered phosphorylation of tau protein results from the dysregulation of the kinases and phosphatases that modulate the phosphoproteome. The longest full-length tau isoform consists of 441 amino acids and has 85 potential phosphorylation sites. In this context, qualitative and quantitative characterization of tau protein phosphorylation is important to describe these changes during the aggregation of insoluble tau throughout disease progression. The analysis of phosphoproteome in tauopathies is, therefore, an important area of current research. Analytical techniques for the detection and quantification of the selectively phosphorylated residues on different isoforms of tau protein in biological fluids for diagnostic purposes is essential for the development of effective treatments. Ion mobility has been reported recently as a highly resolving gas phase ion separation technique linked to mass spectrometry. Besides the mass and charge of ions, mobility separation is determined by their shape, which enables to distinguish isomers and isobars. Ion mobility is an effective and innovative tool for the analysis of complex biomolecular structures. This work applies ion mobility to resolving complex conformations of hyperphosphorylated tau protein as the main component of neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Different, closely positioned phosphorylation sites, S214, T212, and T217, of a tryptic peptide, TPSLPTPPTREPK, were investigated. The method has been applied to an immunoaffinity purified extract of an Alzheimer patient’s brain and confirmed the presence of all three major suspected sites of unnatural phosphorylation.
Acknowledgement: APVV-21-0321, APVV-21-0254 and VEGA 2/0129/21.
133. Liquid Extraction Surface Analysis-Capillary Electrophoresis/2C4D for the Simultaneous Analysis of Cations and Anions on Lithium Battery Anode Surface
Sunkyung Jeong 1,
Byung-Hee Choi 2,
Jonggeol Kim 2,
Hee-Sun Yun 2
and
Doo Soo Chung 1
1
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea,
2
LG Chem Research Park, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34122, Korea
Abstract: Due to the strong electroosmotic flow (EOF) from the negatively charged inner wall of a fused silica capillary, analytes in CE migrate in the order of cations, neutrals, and anions under an electric field of normal polarity. However, for most inorganic ion analyses, either only cations or only anions are analyzed. This is because small inorganic ions have high electrophoretic mobilities, which are proportional to the charge/size ratios, and their detection times can be very long if their electromigration and the EOF are in the opposite directions. In the worst cases, highly mobile ions migrate backward against the EOF and cannot be detected. To analyze both cations and anions on a solid surface with a single run of a reasonable detection time, two contactless, capacitively coupled conductivity detectors (C4D) were placed on a single capillary of 130 cm length, one 20 cm from the inlet and the other 20 cm from the outlet. From the investigated range of 400–550 mM background electrolytes, 450 mM Tris/CHES was chosen as optimal. Liquid extraction surface analysis (LESA) was carried out by forming a liquid microjunction of 100 nL water between the surface of a sample and the inlet of a coated fused silica capillary. Then, the extracts were placed between the two C4Ds by applying a pressure of 1.3 psi. When a reverse voltage (–30 kV) was applied across the capillary having a weak but reversed EOF, the cations and anions migrated backward and forward, respectively, and were detected with the C4D located in each direction in 20 min. The ionic composition of a lithium battery anode surface was investigated by this LESA-CE/2C4D.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge support from the National Research Foundation of Korea (49678310).
References
I.H. Sung, Y.W. Lee, and D.S. Chung, Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 838, 45-50.
S. Jeong, F. Shakerian, and D.S. Chung, Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2463-2468.
H.A Duong, M. Duc Le, K.D.M Nguyen, P.C. Hauser, H.V. Pham and T.D Mai, Environ. Sci. 2015, 17, 19411951.
I-O. Neaga, B.C, lacob and E. Bodoki, J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 2072-2090.
A.J. Gaudry, R.M. Guijt, M. Macka, J.P. Hutchinson, C. Johns, E.F. Hilder, G.W. Dicinoski, P.N. Nesterenko P.R. Haddad, M.C. Breadmore, Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 781, 80-87.
134. MALDI-MS of Semiconductor Nanoparticles with Porphyrin Matrices and Focused Electrospray Deposition
Sanghwang Park,
Jiyeon Lee
and
Jongcheol Seo
POSTECH (Department of Chemistry, Pohang, Korea)
Abstract: Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical method to study nanoparticles, providing useful information about their mass and composition. Especially, matrix-assist laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) has been applied to studies of various nanoparticles, including quantum dots (QDs). However, since QDs usually struggle for the ionization, increasing ionization efficiency is one of the critical issues to be solved in the study of QDs using MS. When QDs are investigated by MALDI-MS, the ionization efficiency is highly dependent on the matrix, which can help support ionization process. In this study, we investigate the ionization efficiency of QDs with several matrices in MALDI-MS. In order to compare commonly used trans-2-[3-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-2methyl-2-propenylidene] malononitrile (DCTB) and porphyrin-based matrices, we introduced the focused electrospray (FES) deposition method. FES makes a spray of charged droplets, which is focused onto a sample well on a MALDI plate. Interestingly, compared to other conventional matrices, porphyrin-based matrices showed remarkable improvement in intensity on the mass spectrum regardless of types of QDs, indicating an increase in electron transfer. This improvement of intensity in mass spectrum can be explained with the ionization mechanism based on properties of QDs and electron acceptor matrix. Porphyrin-based matrices, as good electron acceptors, possibly well deprive electrons from exited electrons in QD. This study allows us to know the effect of matrix properties on ionization in MALDI-MS, and the porphyrin-based matrices will be helpful for QDs analysis.
135. Microplastic Pollution in Athens Riviera, Greece
Ioanna Maria Trifona
and
Fani Sakellariadou
Geochem. Ocean. Lab., Dept of Maritime Studies, Univ. of Piraeus, Greece
Abstract: Microplastic pollution in coastal environments is a topic of interest as the coastal zone is important from environmental, economical, and social considerations. In this research, we conduct a quantitative and qualitative study of microplastics present in beach sediment from the Athens Riviera, which is located in the southern suburbs of Athens, Greece. Samples were collected at the high tide line. After being dried, they were examined visually. The sediment grain size was defined following the Wentworth classification. Dried samples were sieved (using metallic sieves) and the microplastic class (1–5 mm) was weighted in a high precision balance. Each sieved and homogenized sample was examined with ZEISS Stemi 508 Stereo Microscope to observe the number of microplastics and their morphological characteristics. A microscope camera, ZEISS Axiocam ERc5s, attached to the stereoscopic microscope was used to take photos of the microplastics found. The very coarse sand sediment showed enrichment in microplastic. Microplastic particles were divided into four groups, which are fragments (dominant group, 50%), fibers, foams, and films. The dominance of fragments suggests that their source could be the breakdown of larger plastic debris. The dominant color of fragments was blue and of fibers green, probably resulting from the decomposition of water bottles, bags, drinking straws, synthetic fabrics, or fishing nets and ropes. The presence of colored microplastics is of high significance since they could easily be mistaken for food by the biota. In addition, colored microplastics are considered vectors of contamination. Samples were ground and further analyzed by ATR FT-IR. For this purpose, a PerkinElmer Spectrum Two FT-IR spectrometer with Universal ATR (attenuated total reflection) accessory was used. The accessory is supplied with a flat top-plate ZnSe crystal. Spectra indicated the presence of quartz and feldspars. Furthermore, ATR FT-IR was used for the study of microplastics detected stereoscopically. Interpretation of the spectra supports the presence of polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). Samples were also observed for the presence of macroplastics. Among them, various large fragments, a piece of styrofoam, and a piece of plastic wrap were found.
Acknowledgement: This work has been partly supported by the University of Piraeus Research Center.
136. Miniaturized Liquid Junction-Based ESI Interfaces
Roman Řemínek 1,
Elizaveta Vereshchagina 2,
Andreas Vogl 2,
Tomáš Václavek 1
and
František Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, v. v. i., Veveří 967/97, 636 00 Brno, Czechia
2
Department of Smart Sensors and Microsystems, SINTEF Digital, Gaustadalléen 23C, 0373 Oslo, Norway
Abstract: Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS) represents a well-established, hyphenated analytical technique. It has been successfully applied for many biological, pharmaceutical, environmental, and forensic applications [1]. Among a variety of methods suitable for CE-MS coupling, electrospray ionization (ESI) is the most used. This technique provides a soft ionization of analytes with multiple charges favorable for analyses of macromolecules, such as peptides, proteins, and oligosaccharides. Whereas the standard sheath liquid ESI interfaces are commercially available, the potential of nanoESI systems has not been fully explored. Due to ultralow flow rates, typically below 100 nL/min, the nanoESI technology holds a promise of superior ionization efficiency and reduction of the ion suppression [2]. For these reasons, one of the main goals of the uBIOSEP project is to develop a miniaturized ESI interface in a miniaturized format using Si technology. The microfabricated ESI are based on Si wafers (150 mm in diameter, 400 µm thick). The fabrication process relies on the combination of thin film deposition, deep reactive ion etching (DRIE), and lithographic techniques. ESI comprises a pointed emitter, a transport channel, and a self-aligning liquid junction structure. The mechanical adjustment of the separation capillary before the analysis is therefore not needed [3]. In the liquid junction, the separation capillary and transport channel are connected by a small gap filled with a spraying buffer. The ESI system thus enables the use of the separation buffer optimized for a desired resolution of analytes. and the spraying buffer selected for optimal ESI performance. The chip with ESI is positioned in a mechanical support with securing ports for connection of the CE and ESI current source, as well as for automated flushing of both the liquid junction and the separation capillary. The basic functionality and performance of the interface were tested, and high-impact applications shall follow to demonstrate the potential of the presented system as a versatile CE-nanoESI/MS platform for various relevant applications in the life and pharmaceutical sciences.
Acknowledgement: The uBIOSEP benefits from a € 1.2 mil grant from Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway through the EEA Grants and the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic.
References
Stolz, A., Jooß, K., Höcker, O., Römer, J., Schlecht, J., Neusüß, C., Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 79–112.
Schmidt, A., Karas, M., Dülcks, T., J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 14, 492–500.
Krenkova, J., Kleparnik, K., Luksch, J., Foret, F., Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2263–2270.
137. Monitoring of Biologically Relevant Molecules in Multicellular 3D Spheroids Cultivated Inside Microfluidic Systems
Karel Kleparnik 1,
Michael Killinger 1,2
and
Marketa Prochazkova 1,2
1
Department of Bioanalytical Instrumentation, Institute of Analytical Chemistry, Academy of Sciences, Brno, Czech Republic,
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: Bioengineering of three-dimensional (3D) cell cultures is a promising strategy for the development of alternatives aiming at the reduction, refinement, and replacement of animal usage for research or pre-clinical studies. Thus, the objectives of this research are (i) the construction of microfluidic systems for 3D spheroid or even organoid culturing and (ii) simultaneous single-cell monitoring of dynamics of activation and transport of signaling pathways molecules in the spatiotemporal context of cell development. In these microfluidic systems, the physical conditions, e.g., temperature, CO2 concentration, including the flow of nutrients, paracrine factors, chemical sensors, and withdrawal of waste metabolites, are precisely controlled. In addition, specially designed and synthesized stable fluorescence probes based on the Förster resonance energy transfer of quantum dots (QD) are prerequisites for long-term, sensitive, and selective imaging under the fluorescence microscope. The synthesis strategy is based on the ligand exchange of carboxylated QDs with custom peptide comprising cleavage site DEVD, specific for caspase 3/7, followed by conjugation reaction with commercial quencher BHQ-2 succinimidyl ester. Since 3D cell spheroids can replicate tissue functions, we have developed a polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic platform suitable for the in vitro cultivation of 3D bone cells (MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts) directly on the table of a fluorescence microscope. This developed system is used for the monitoring of crucial processes in the animal body, including cell morphogenesis and integration of tissue, and can also be useful for clinically relevant drug testing.
Acknowledgement: The research was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic, project no. 20-00726S. Michael Killinger is Brno Ph.D. Talent Scholarship Holder funded by the Brno City Municipality.
138. NACE-ESI-MS/MS Method for the Separation and Characterization of Phosphate and Acyl Chain Positional Isomers of Bacterial Lipid
Anikó Kilár 1,
Ágnes Dörnyei 2,
Aissa Ibrahim 2
and
Viktor Sándor 1
1
Institute of Bioanalysis, Medical School and Szentágothai Research Centre, University of Pécs, Honvéd utca 1., H-7624 Pécs, Hungary,
2
Department of Analytical and Environmental Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, University of Pécs, Ifjúság útja 6, H-7624 Pécs, Hungary
Abstract: Bacterial lipid A is a glycophospholipid moiety present in endotoxins (lipopolysaccharides) that build up the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Once lipid A enters into the blood circulatory system of the human body, it is capable of stimulating an immune response that (during a severe bacterial infection) may lead to endotoxic shock and sepsis. Not only the quantity, but also the fine structure of lipid A from different bacterial species determine the strength of the induced immune response. With the help of separation science, we directed our research to accurately understand the structure of lipid A and to explore the type of phosphorylation sites and fatty acyl chains attached to the basic sugar backbone. We succeeded in developing a pressure-assisted non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE)–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method for the baseline separation of both, phosphate and acyl chain positional isomers. We have studied both the effect of the solvent composition and the electrolyte composition to separate the different lipid A species present in a single bacterial strain (Shigella sonnei). As a result, we could achieve for the first-time separation and full structural identification of C1- and C4′-monophosphorylated isomers, which are known to differently activate the innate immune system. Structural information specific to phosphorylation was provided by MS/MS mass spectra recorded in the positive ion mode (it should be noted here that most studies use the negative ionization mode MS/MS for the structural analysis of lipid A). Based on our results, diagnostic B2-type ions (used in sugar chemistry) identify the phosphorylation position, while B1-type ions allow the characterization of acylation isomers. The application of constant external pressure (3 mbar) from the inlet was needed to overcome the cathodic mobility of the EOF so as to ensure detection at the anodic end. The present method can complement the LC-MS/MS methods previously developed to probe bacterial endotoxin samples. Moreover, it can be a good screening procedure of phosphate positional isomers in different lipid A-based therapeutics.
Acknowledgement: The research was supported by Technology from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund, NKFIH FK-129038. The research was performed in collaboration with the Mass Spectrometry Core Facility at the Szentágothai Research Centre of the University of Pécs.
139. Photon-Upconversion Sensing in Droplet Microfluidics
Jana Křivánková,
Antonín Hlaváček
and
František Foret
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, v. v. i., Brno, Veveří 97, Czech Republic,
Abstract: Droplet microfluidics allows the acquisition of large amounts of data with only minute consumption of reagents. Therefore, they present an example of a high-throughput tool for biological and biomedicine applications [1]. The detection of cancer biomarkers plays a significant role in clinical diagnostics [2]. However, the sensitivity of current methods is limited. We are overcoming the limitations of fluorescence labels by introducing photonupconversion nanoparticles for microfluidic assays [3,4]. These nanoparticles (diameter 1–100 nm) emit short wavelengths under near-infrared excitation (976 nm), which mitigates optical background interferences (autofluorescence, light scattering). This unique photoluminescent feature enables the detection of photonupconversion nanoparticles at the single nanoparticle level by conventional wide-field microscopy [2]. Here, we present novel instrumentation for recording photon-upconversion from water microdroplets in affordable polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chips on a glass substrate [3,4].
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge financial support from the Czech Science Foundation (21-03156S) and the institutional support RVO 68081715.
References
Shang, L. R., Cheng, Y., Zhao Y., J. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964−8040.
Hlaváček, A., Farka, Z., Mickert, M.J, Kostiv, U., Brandmeier, J.C., Horák, D., Skládal, P., Foret, F., Gorris, H.H., Nature Protocols 2022, 17, 1028−1072.
Hlaváček, A., Křivánková, J., Pizúrová, N., Václavek, T., Foret, F., Analyst, 2020, 145, 7718−7723. [4] Hlaváček, A., Křivánková, J., Přikryl, J., Foret, F., Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12630−12635.
140. Preliminary Stable Isotope Analyses for the Discrimination of Shotshell Propellants
Nam Yee Kim,
Byeong-Yeol Song
and
Dong-Hwan Kim
Forensic Chemistry Division, National Forensic Service, Wonju 26460, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this study, we aimed to develop methods to determine the identity and trace the origin of propellants used in shotshells. Specifically, organic component analysis, bulk stable isotope analysis (BSIA), and compound specific isotope analysis (CSIA) techniques were performed on nine samples of propellants with different end uses (birdshot and buckshot) from different brands of shotshells manufactured in different countries. Shotshell propellants were analyzed for their explosive components and additives by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) and thin layer chromatography (TLC). BSIA of the propellant was achieved using elemental analysis/isotope ratio mass spectrometry (EA/IRMS) without a pretreatment process. For the CSIA of nitroglycerin (NG), double-base powder propellants were extracted with ether, and the isotope ratios of carbon and nitrogen were measured by GC/IRMS. Nine samples drawn from seven brands from four countries were classified into five groups by the organic component analysis; however, eight classes were identified by the BSIA. Two samples belonged to the same group and could not be distinguished by either BSIA or organic components analysis. Subsequently, with the results obtained by CSIA for NG, all samples were classified into different groups. These findings suggest that the nine propellant samples were composed of different ingredients or raw materials from different sources. Stable isotope ratio analyses were performed for propellant discrimination. The combined BSIA, CSIA, and organic component analysis techniques successfully distinguished the nine shotshell propellants from seven brands sourced from four different countries, and the results suggest that the samples are composed of different ingredients or raw materials from different sources. Therefore, we conclude that reliable origin tracing and identity determination can be achieved using combined isotope analysis methods, such as CSIA, BSIA, and organic component analysis.
141. Preparation of Turmeric Powder with Various Extraction and Drying Methods
Junyoung Park,
Hyunwoo Ahn
and
Kwang-Geun Lee
Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, 32, Dongguk-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, 10326, Republic of Korea
Abstract: In this study, turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) powder was prepared with various extraction and drying methods. Extractions were performed using three solvents (water, 50% ethanol, and 70% ethanol) and three drying methods, namely spray drying (SD), freeze-drying (FD), and spray-freeze drying (SFD). Levels of the curcuminoids, curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, in turmeric powder preparations were analyzed using HPLC, and scanning electron microscopy and laser particle size analysis were used to observe and estimate the surface and size distribution of particles. The total amount of curcuminoids ranged from 0.59 to 14.35 mg/g turmeric powder, and as the concentration of ethanol increased, the level of curcuminoids, antioxidant activity, and average particle size significantly increased (all p < 0.05). In addition, the abundance of curcuminoids significantly increased in the order of SFD, FD, and SD (p < 0.05), whereas the average particle size significantly increased in the order of FD, SFD, and SD (p < 0.05). The highest TPC and TFC were detected in SFD turmeric powder preparations, whereas the average particle size significantly increased in the order of FD, SFD, and SD. Based on this study, we also showed that the level of curcuminoids, antioxidant activity, TPC, TFC, and average particle size were most affected by the extraction solvent.
142. Preparative 3D Printed Device for the Short DNA Fragment Separation
Helena Hrušková 1,2,
Roman Řemínek 1
and
František Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, v. v. i., Veveří 97, 60200, Brno, Czech Republic
2
Masaryk University, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry, Kotlářská 2, 602 00, Brno, Czech Republic
Abstract: The demand for non-invasive tools in cancer diagnosis is constantly growing. Liquid biopsies represent an expanding family of techniques enabling the detection and monitoring of the disease without or with minimal patient discomfort. Unlike some highly invasive tools used in modern medicine, they provide the possibility to use only venous blood sampling as a source of diagnostic information. Sampling is followed by common DNA sequencing techniques, such as PCR or NGS, providing evidence of the presence of tumor DNA fragments. Nevertheless, liquid biopsy techniques are still under development, and specific requirements are made on the composition of the blood sample. For this reason, we developed a new 3D-printed device for preparative precleaning blood plasma samples from larger DNA fragments. Such a sample adjustment should increase the quality of data obtained from subsequent PCR [1,2], where only particular short DNA fragments are considered to be biomarkers of the cancer disease. In our study, the device was designed, fabricated by 3D-printing from the polymeric material HD PLA, and tested. A method based on electromigration separation techniques for the preparative separation of short DNA fragments from larger fragments has been developed and partially validated.
Acknowledgement: This ALIQUID project is co-financed with the state support of the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic and the Ministry of Industry and Trade under the TREND2 Programme (FW02020209).
References
Mouliere, F., Robert, B., Arnau Peyrotte, E., Del Rio, M., Ychou, M., Molina, F., Gongora, C., Thierry, A. R., High Fragmentation Characterizes Tumour-Derived Circulating DNA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23418.
Mouliere, F., Chandrananda, D., Piskorz, A. M., Moore, E. K., Morris, J., Ahlborn, L. B., Mair, R., Goranova, T., Marass, F., Heider, K., Wan, J. C. M., Supernat, A., Hudecova, I., Gounaris, I., Ros, S., Jimenez-Linan, M., Garcia-Corbacho, J., Patel, K., Østrup, O., Murphy, S., Eldridge, M. D., Gale, D., Stewart, G. D., Burge, J., Cooper, W. N., van der Heijden, M. S., Massie, C. E., Watts, C., Corrie, P., Pacey, S., Brindle, K. M., Baird, R. D., Mau-Sørensen, M., Parkinson, C. A., Smith, C. G., Brenton, J. D., Rosenfeld, N., Enhanced detection of circulating tumor DNA by fragment size analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921.
143. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Major Constituents from Pomegranate Rind (Punica granatum L.): Establishment of an Herbal Pharmacopeial Standardization
Bunleu Sungthong,
Cathaleeya Mekjaruskul,
Wanida Caichompoo
and
Somsak Nualkaew
Faculty of Pharmacy, Mahasarakham University, Khamriang, Kantharawichai District, Maha Sarakham, 44150, Thailand,
Abstract: Pomegranate rind has been listed in the National List of Essential Medicines of Thailand; List of Herbal Medicinal Product as a vehicle for herbal remedies in treatment of diarrhea. Controlling raw plant material can provide a reproducible therapeutic effect of herbal products. The aim of this study was to establish a standardization of pomegranate rind for the qualitative and quantitative analyses of major constituents of authentic and commercial pomegranate rinds from all regions of Thailand. A reversed-phase HPLC-DAD was performed using gradient elution with various ratios of 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid and acetonitrile. The major compounds were detected at 254 nm with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The method was validated according to ICH guideline Q2(R1). Gallic acid, punicalin, punicalagin A and B, and ellagic acid in pomegranate rind were identified by their retention times and UV-spectra. Linearity of a bioactive marker, ellagic acid was in the range of 2–150 µg/mL with correlation coefficient at 0.999. Intraday and interday precision (%RSD) were 2.13–2.70 and 3.19–3.91, respectively. Percent recovery was higher than 96.47%. LOD and LOQ were 0.32 and 1.06 µg/mL, respectively. The validated method was also applied for quantitative analysis of ellagic acid in pomegranate rind. The contents of ellagic acid in were ranged between 0.0629–0.8945% w/w (0.2296 ± 0.1959, mean ± S.D). In conclusion, the current method was successful applied for qualitative and quantitative analyses of the major constituents of pomegranate rind. Further studies related to others specifications, such as botanical, pharmacognostic, and physicochemical properties of the plant, must be performed to authenticate and standardize pomegranate rind raw material.
144. Recovery of Clean Polymers from Waste Plastics
Pallab Das 1
and
Jong-Min Lee 1,2
1
SCARCE laboratory, Energy Research Institute, Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Drive, Singapore 639798, Singapore
2
School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 62 Nanyang Drive, Singapore 637459, Singapore
Abstract: The current study focuses on the decontamination and degradation of e-waste plastics. It was estimated that around 25–30% of the e-waste consists of plastics. Often the plastics components get destroyed during the metal extraction or disposed of as waste in the landfills and incineration. The e-waste plastics often contaminated with brominated flame retardants (BFRs) and heavy metals such as lead (Pb), chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd) and mercury (Hg) etc. The presence of toxins makes the e-waste plastics ill-suited for mechanical recycling. In this work, novel processes were developed to extract the toxins from e-waste plastics using thermochemical treatments such as extraction and pyrolysis etc. The quantitative analysis of metals and heavy metals present in some of the plastic components of e-waste were found to be alarmingly higher than the allowable limit. However, BFRs (hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBA), etc.) can be precursors to the emission of hazardous polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PBDD) and polybrominated dibenzofurans (PBDF) under the thermal stress during recycling. Extraction with microwave-assisted extraction (MEA) processes was found efficient in the removal of toxins from the e-waste plastics. Different solvent combination has been tried for optimal result. Different process parameters were optimized for the extraction process.
Acknowledgement: This research/project is supported by the National Research Foundation, Singapore, and National Environment Agency, Singapore under its Closing the Waste Loop Funding Initiative (Award No. USS-IF-2018-4).
145. Salicylic Acid Metabolism in Plants—LC-MS/MS Method Development
Jitka Široká 1,
Lucie Polášková 1,
Asta Žukauskaitė 2
and
Ondřej Novák 1
1
Laboratory of Growth Regulators, Institute of Experimental Botany of the Czech Academy of Sciences & Palacký University, Šlechtitelů 27, CZ-78371 Olomouc, Czech Republic
2
Department of Chemical Biology, Faculty of Science, Palacký University, Šlechtitelů 27, CZ-78371 Olomouc, Czech Republic
Abstract: Salicylic acid (SA) is a phytohormone playing a principal role in the control of immunity and defense mechanisms in plants. Defense-related SA accumulation stems from its biosynthesis, transport, and possible release from some of its metabolites. The aim of our research is to develop a comprehensive LC-MS/MS method for sensitive determination of known (e.g., salicylic acid glucosyl ester, salicylic acid glucoside, salicylic acid methyl ester glucoside, 2,3- and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid) and putative (e.g., salicyloyl-alanine) metabolites of SA in plants. In general, the method development comprised setting of MS instrumentation, optimization of chromatographic conditions, and pH stability study under acidic and alkaline conditions prior to optimization of plant sample preparation. The optimization of chromatographic conditions was carried out by testing different analytical columns and mobile phase compositions considering the peak shape of analytes, baseline separation of six positional isomers of dihydroxybenzoic acids, and formation of molecular ions suitable for quantification. The sample preparation included a choice of an extraction solvent and SPE purification sorbent. The final application of the method will provide essential information on the dynamics of SA metabolism in plant immunity-related biological research.
Acknowledgement: The work was supported by Czech Science Foundation project No. 22-17435S.
146. Sample Pretreatment by Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized with Ionic Liquids and a Double-Chained Surfactant
Natalia Treder 1,
Anna Roszkowska 1,
Ilona Olędzka 1,
Tomasz Bączek 1
and
Alina Plenis 2
1
Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Medical University of Gdańsk, Hallera 107, 80-416 Gdańsk, Poland,
2
Department of Analytical Chemistry, Medical University of Gdańsk, Hallera 107, 80-416 Gdańsk, Poland
Abstract: The application of magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) for sample pretreatment is a more environmentally friendly alternative compared to traditional SPE and LLE techniques. Their high specific surface area and the possibility of separation from the matrix using external magnetic field allow to avoid the high consumption of harmful organic solvents and miniaturize the sample preparation procedure. However, in order to obtain a high sorption capacity of NPs, and thus also a high extraction efficiency, a necessary step is their functionalization. In recent research related to the search for new coating materials, attention has been paid to surfactant and ionic liquids (ILs) [1–4]. Their structural diversity, wide commercial availability, as well as promising results confirmed in other IL or surfactant-based extraction methods suggest that the presence of these ionic structure in the NP shell may allow the design of magnetic sorbents adapted to the experimental conditions and increase the extraction efficiency as a result of increased affinity analyte to the sorbent. In this communication, the results of a study in which Fe3O4 NPs functionalized with long- and short-chain ILs and a double-chained surfactant were used to extract analyte from biological samples will be presented. The effect of length and amount of alkyl chain in the coating material, as well as the influence of the NPs synthesis and functionalization procedure on the extraction efficiency, will be discussed. For NPs that provided the highest extraction efficiency, their full characterization, including XRD, FR-IR, TEM and TG results, will be demonstrated. Additionally, the evaluation of the self preparation of magnetic sorbents will be also performed, based on a comparison of the results for synthesized and commercially available NPs cores.
References
N. Treder, T. Bączek, K. Wychodnik, J. Rogowska, L. Wolska, A. Plenis, Molecules, 25 (2020) 286.
N. Treder, I. Olędzka, A. Roszkowska, T. Bączek, A. Plenis, Journal of Chromatography A, 1651 (2021) 462257.
N. Kaczmarczyk, J. Ciżewska, N. Treder, N. Miękus, A. Plenis, P. Kowalski, A. Roszkowska, T. Bączek, I. Olędzka, Talanta, 238 (2022) 122997.
N. Trader, I. Olędzka, A. Roszkowska, P. Kowalski, T. Bączek, Microchemical Journal, 178 (2022) 107396.
147. Separation and Identification of Volatile Constituents in Herbal Medicine Prescription Dry Extract by Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS/MS)
Sumin Seo
and
Sang Beom Han
College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, 84 Heukseok-ro, Dongjak-gu, Seoul, 06974, Republic of Korea
Abstract: The efficacy of herbal medicines varies greatly depending on the conditions, such as the climate, production area, collection time, origin, and contents of ingredients where they are produced. Therefore, it is possible to achieve the modernization and globalization of herbal medicines through accurate quality control and maintaining the same production conditions so that these various variables can be minimized and the efficacy can be constant. As part of this quality standardization project, in this study, the separation and identification of volatile compounds in herbal medicine extracts were performed. Headspace gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HS-GC-MS/MS) with solid phase microextraction (SPME) is developed for the fast analysis of volatile constituents in the herbal medicines. The SPME of fiber, namely PDMS, PDMS-DVB, and DVB-CAR-PDMS, was investigated, and the best extraction was achieved with the mixed fiber DVB-CAR-PDMS. Several HSSPME parameters, including fiber coating, extraction temperature, and extraction time, are optimized. The volatile components (122 chemical compounds) of 20 types of herbal medicines were identified by HS-SPME-GCMS/MS using the GC NIST MS library (Version. 2.3). When compared to the results of HS-GC-MS/MS, the SPME method dramatically improves peak sensitivity and peak sharpness, providing good selectivity to identify volatile compounds in complicated matrices. In conclusion, HS-SPME is an effective analysis method for determining the volatile compounds present in herbal medicines. This research was supported by a grant (20173첨단약561) from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2021.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by a grant (20173첨단약561) from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2021.
148. Simultaneous Determination of 61 Fentanyl Analogues in Patch Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Sojung Park,
Jiyu Kim
and
Sang Beom Han
College of Pharmacy, Chung-Ang University, 84 Heukseok-ro, Dongjak-gu, Seoul, 06974, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Fentanyl is an opioid narcotic analgesic that is about 50–100 times stronger than morphine, and one of its analogues, carfentanil, is estimated to be 10,000 times more potent. Fentanyl and its analogues, like opioids, such as morphine and codeine, have the potential for abuse or misuse due to illegally manufactured fentanyl analogues. Therefore, numerous fatal overdoses have been reported worldwide, particularly in the North American continent. However, recently in Korea, social problems caused by misuse of fentanyl have become an issue, and countermeasures are needed. Considering this, it is necessary to establish an analytical method that can detect trace amounts of fentanyl analogues that have been illegally added to foods and drugs. In this study, an LCMS/MS method was developed to screen and quantify 61 types of fentanyl analogues among illegal fentanyl substances published by the United Nations/International Narcotics Control Board (UN-INCB) in pharmaceutical patch formulations. Sample preparation was optimized with salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction (SALLE), and a phenyl hexyl column was used as the HPLC analytical column. The analytical method validation parameters were selectivity, linearity, limit of quantitation, accuracy, precision, and carryover in accordance with the guidelines from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) in Korea. In addition, peak purity analysis was performed using HPLC-DAD on the fentanyl analog synthetic standards provided by the synthesis research team to confirm the presence of impurities, thereby improving the accuracy and reliability of the analysis. The developed analytical method will contribute to the regulation and monitoring of illegal fentanyl analogues in the future.
Acknowledgement: This research was supported by a grant (21202MFDS309) from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2022.
149. Single Bubble In-Tube Microextration
Sunkyung Jeong,
Xamyo Noulorsaytour,
Joseph E. Valdez
and
Doo Soo Chung
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Korea
Abstract: Headspace (HS) extraction is a sample pretreatment technique for volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in a complex matrix. Recently, in-tube microextraction (ITME) coupled with CE using an acceptor plug placed in the capillary inlet was developed as a simple but powerful HS extraction method. Here, we present single bubble (SB) ITME using a bubble hanging to the capillary inlet immersed in a sample donor solution as a HS of submicroliter volume (200 nL). The analytes evaporated to the bubble were extracted into the acceptor phase through the capillary opening, then electrophoresis of the enriched extract was carried out. Since the bubble volume was much smaller than conventional HS volume (1 mL), it was filled with the evaporated analytes rapidly and the analytes could be enriched much faster compared to conventional HS-ITME. Owing to the high surface to volume ratio of the single bubble, 5-min SB-ITME yielded the enrichment factor (EF) values similar to those of 10-min HS-ITME. When 5-min SB-ITME at room temperature was applied to a tap water sample, the EFs of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (TCP), 2,3,6-TCP and 2,6-dichlorophenol were 53, 41, and 60, respectively, and the LOQs obtained by monitoring the absorbance at 214 nm were about 7.8 ppb, much lower than 200 ppb, the World Health Organization guideline for the maximum permissible concentration of 2,4,6-TCP in drinking water.
150. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectrometry: Online Detection in Capillary Electrophoresis
Anna Tycova 1,
Jan Prikryl 1,
Jakub Novotny 1,
Detlev Belder 2
and
Frantisek Foret 1
1
Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the CAS, Brno, Czech Republic
2
University of Leipzig, Faculty of Chemistry and Mineralogy, Leipzig, Germany
Abstract: Surface-enhanced Raman spectrometry (SERS) is an optical technique for the ultimate identification of analytes, which has shown promise to overcome the traditionally low sensitivity of conventional Raman spectroscopy [1] The enhancement of Raman signal (i.e., inelastically scattered light) originates from the interaction of an analyte with the surface of silver/gold nanostructures. Unfortunately, the employment of metal nanosubstrate in a separation channel as well as nanosubstrate–analyte strong interaction challenges the online coupling of SERS to column separations [2]. Herein, we present the arrangement for online detection of SERS signal in capillary zone electrophoresis. The presented design operates with the supply of silver nanoparticles into electrophoretically separated zones and realizes the nanoparticlesanalytes contact via diffusion [3]. We also demonstrate that if the silver nanostructures are immobilized on polystyrene microbeads, the quality of the SERS spectra can be further improved via their acoustofluidic-driven manipulation.
Acknowledgement: Grant Agency of the Czech Republic (Grant No. 20–14069Y), the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant No.BE 1922/16-1), and institutional support RVO 68081715 of the Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the CAS.
References
Fleischmann, M., Hendra, P., Mcquillan, A. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166.
Tycova, A., Kleparnik, K. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 431–444.
Tycova, A., Gerhardt, R. F., Belder, D. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1541, 39–46.
151. The Effect of the Sample Glucose Content on PNGase F Mediated N-Glycan Release
R. Torok 1,
F. Auer 1,
R. Farsang 1,
E. Jona 1,
G. Jarvas 1
and
A. Guttman 1,2,3
1
Translational Glycomics Group, Research Institute of Biomolecular and Chemical Engineering, University of Pannonia, Veszprem, Hungary
2
Horváth Csaba Memorial Laboratory of Bioseparation Sciences, Research Center for Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Doctoral School of Molecular Medicine, University of Debrecen, Hungary
3
Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Republic of Korea
Abstract: Biologics and their biosimilar counterparts are recently gaining high importance in the biopharma industry along with applied clinical research. Therefore, it is important to understand the structure – function relationship of these new generation drugs. One of the important critical quality attributes of therapeutic proteins is their asparagine bound carbohydrates, reportedly impacting the efficacy, immunogenicity, clearance rate, stability, solubility, pharmacokinetics, and mode of action of the product. In most instances, the linked N-glycans are analyzed after endoglycosidase, e.g., PNGase F, mediated release. In this poster presentation the effect of sample glucose content is demonstrated as a potential endoglycosidase activity modification agent. First the N-glycan release efficiency was evaluated by using an in-house made 6His-PNGase F enzyme. The resulting deglycosylation profiles were analyzed by capillary gel electrophoresis and the optimal digestion time was also determined. Next, a comparative Michaelis-Menten kinetics study was accomplished using a frequently employed commercial PNGase F product with and without the presence of glucose in the digestion reaction mixture. It was found that, in the case of the use of the in-house made enzyme, the N-glycan release was enhanced with increasing glucose concentration in the sample in contrast to the commercial enzyme where it stayed unchanged. The charge heterogeneity of the in-house made and commercial PNGase F enzymes were analyzed by capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) that revealed subtle differences which might be somewhat responsible for the observed activity changes.
152. The Study of Fingerprint Degradation and Composition According to Aging
Nam Yee Kim 1,
Woo-Yong Park 2
and
Jong Shin Park 1
1
National Forensic Service, Wonju 26460, Republic of Korea,
2
National Forensic Service, Daejeon Institute, Daejeon, 34054, Republic of Korea
Abstract: The latent fingerprint is among the most important evidence for individualization at a crime scene. As crime becomes more intelligent, it is becoming increasingly important to determine when a latent fingerprint was deposited. Fingerprint aging was studied by keeping fingerprint samples deposited by volunteers on polystyrene boxes in a dark room. An emulsion black technique (iron oxide) was used for fingerprint development. Even latent fingerprints from fingerprint samples stored for more than six months and up to two years were possible to identify. After identification of latent fingerprints using the emulsion black technique, the sample was used to analyze the components by GC/MS with TMS derivatization for the fingerprint aging. The area ratio of cholesterol and squalene (Ch/Sq) as aging indicator was calculated. The ratio was about 0.01 from the initial time to one month of storage, but after that, it increased gradually to more than 0.1 over six months, and the absolute amount of cholesterol and squalene decreased much more after the initial time. Applying heat to the fingerprint sample or storing the developed fingerprint sample also affected the aging.
153. Untangling Pathways of RNA Hairpins in Gaseous Phase Investigated Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Dahye Im
and
Jongcheol Seo
Department of Chemistry, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang, Korea
Abstract: RNA hairpin is an essential secondary structure that serves as an RNA folding guide, mRNA protection, and recognition motif for RNA-binding proteins. Recently, studies of the features of RNA hairpin have become active. However, despite diligent efforts, the answer to fundamental questions such as the formation, folding, and untangling of RNA hairpin remains unknown. Here, we present the disorganization of the RNA hairpin by charge–charge repulsion as a clue to these fundamental questions. Four RNAs containing six different base pairs but expected to form the same hairpin structure in solution were compared for their untangling process by charge step. The charge added to RNAs during overcharge in the gas phase may break the hydrogen bonds of the base pairs, but may also simply unfold the bent structures. In this research, collision cross-section (CCS) obtained from electrospray ionization (ESI) and ion mobility spectrometry-mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) provide a subtle distinction between hydrogen bond cleavage and structural unfolding. Furthermore, this experimental results on the charge-dependent untangling of hairpin structures presents an insight into small RNA stability.
154. Use of a Minimally-Invasive Method for the Proteomic Sex Estimation from Human Tooth Enamel
Ivan Mikšík 1,2,
Jaroslav Brůžek 3,4,
Anežka Kotěrová 3,
Marine Morvan 1,2,
Jiřina Dašková 5,6,
Petr Velemínský 6,
Fréderic Santos 4,
Jana Velemínská 3,
Alžběta Danielisová 7,
Eliška Zazvonilová 3,7
and
Bruno Maureille 4
1
Institute of Physiology, CAS, Prague, Czech Republic,
2
Faculty of Chemical Technology, University of Pardubice, Pardubice, Czech Republic
3
Faculty of Science, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
4
De la Préhistoire à l’Actuel: Culture, Environnement et Anthropologie, Université de Bordeaux, France
5
Institute of Geology, CAS, Prague, Czech Republic
6
National Museum, Prague, Czech Republic
7
Institute of Archaeology, CAS, Prague, Czech Republic
Abstract: Proteomics has become an attractive method to study the human and animal material, biological profile, and origin as an alternative to DNA analysis which is limited by DNA amplification present in ancient samples and its contamination, high cost, and limited preservation of nuclear DNA. Currently, three approaches are available to estimate sex–osteology, genomics, or proteomics, but little is known about the relative reliability of these methods in applied settings. Proteomics provides a new, seemingly simple, and relatively non expensive means of sex estimation without the risk of contamination. It uses two sexually distinct forms of the protein amelogenin in tooth enamel detectable by LC-MS. The AMELY protein (amelogenin Y isoform) is present in enamel dental tissue only in males, while AMELX (isoform X) can be found in both sexes. From the archaeological, anthropological point of view, but also considering forensic research and applications, the minimal destructiveness of the methods used is important, as well as the minimum requirements for sample size.
Acknowledgement: This work was supported by a grant from the Czech Science Foundation 20-03899S.