Improving the Efficiency of Cement Mortar to Immobilize Sulfate in Industrial Wastewater Using Different Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials and Mix Proportions
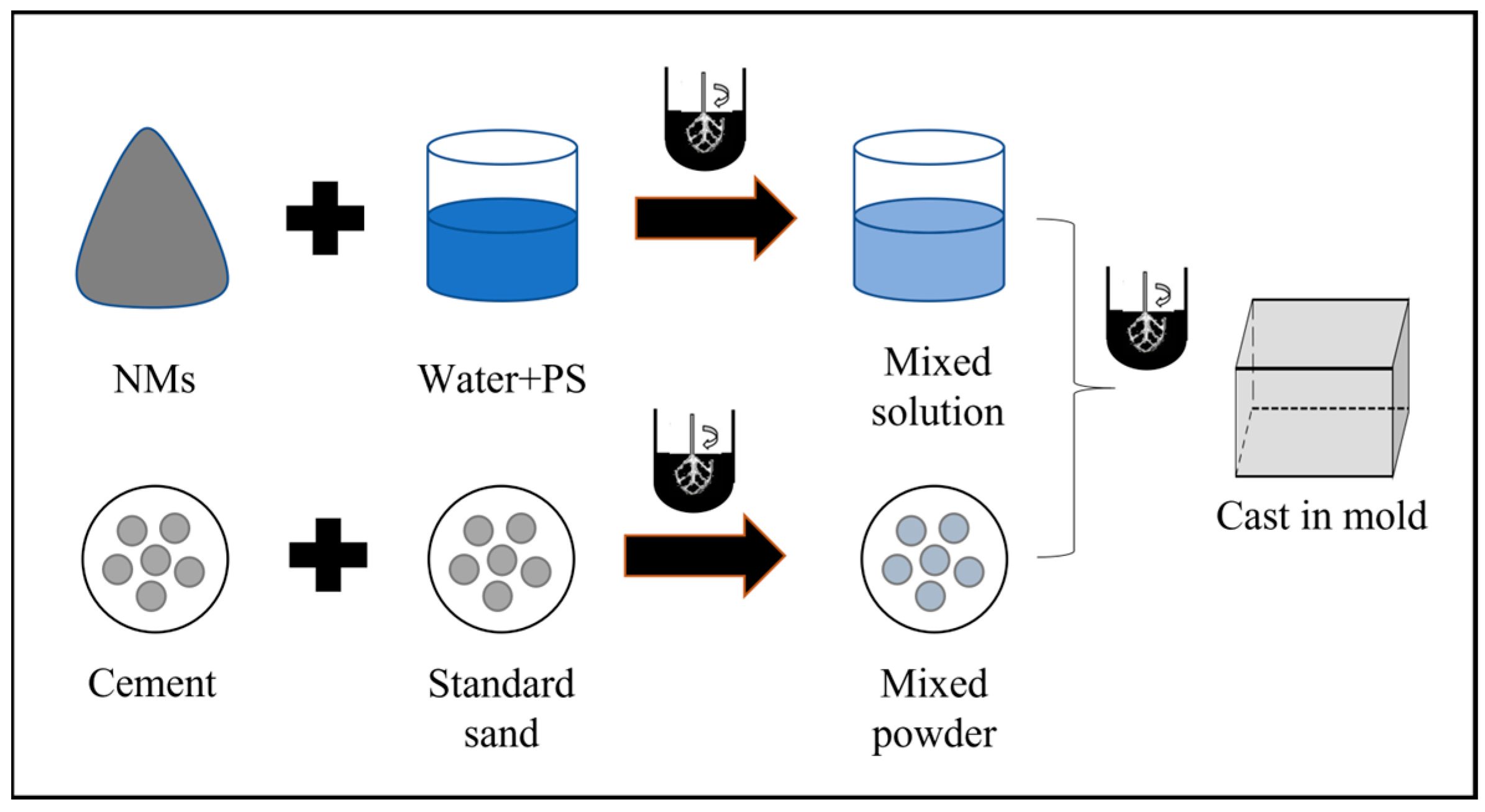
2.2. Preparation of IWWCM Specimens
2.3. Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
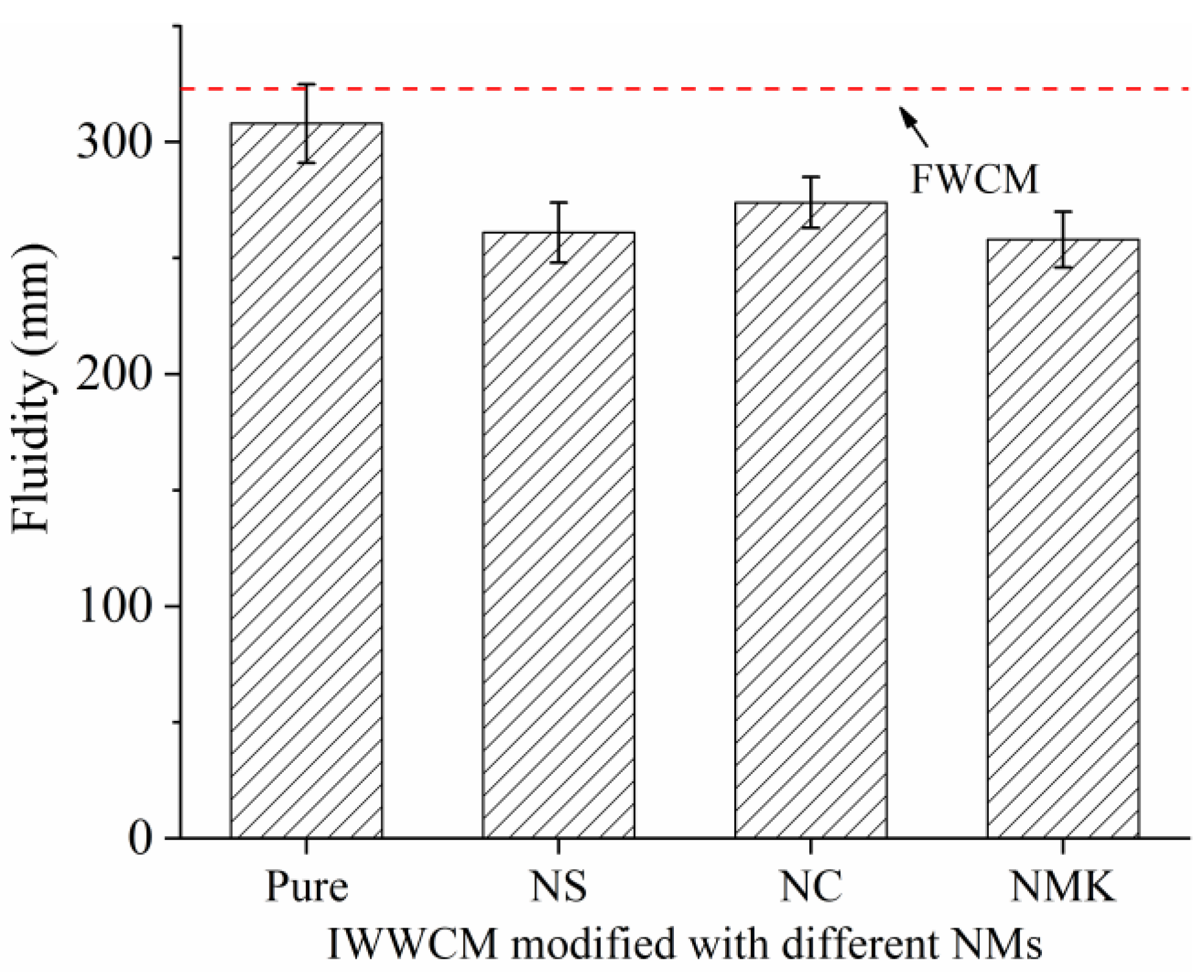
3.1. Fluidity
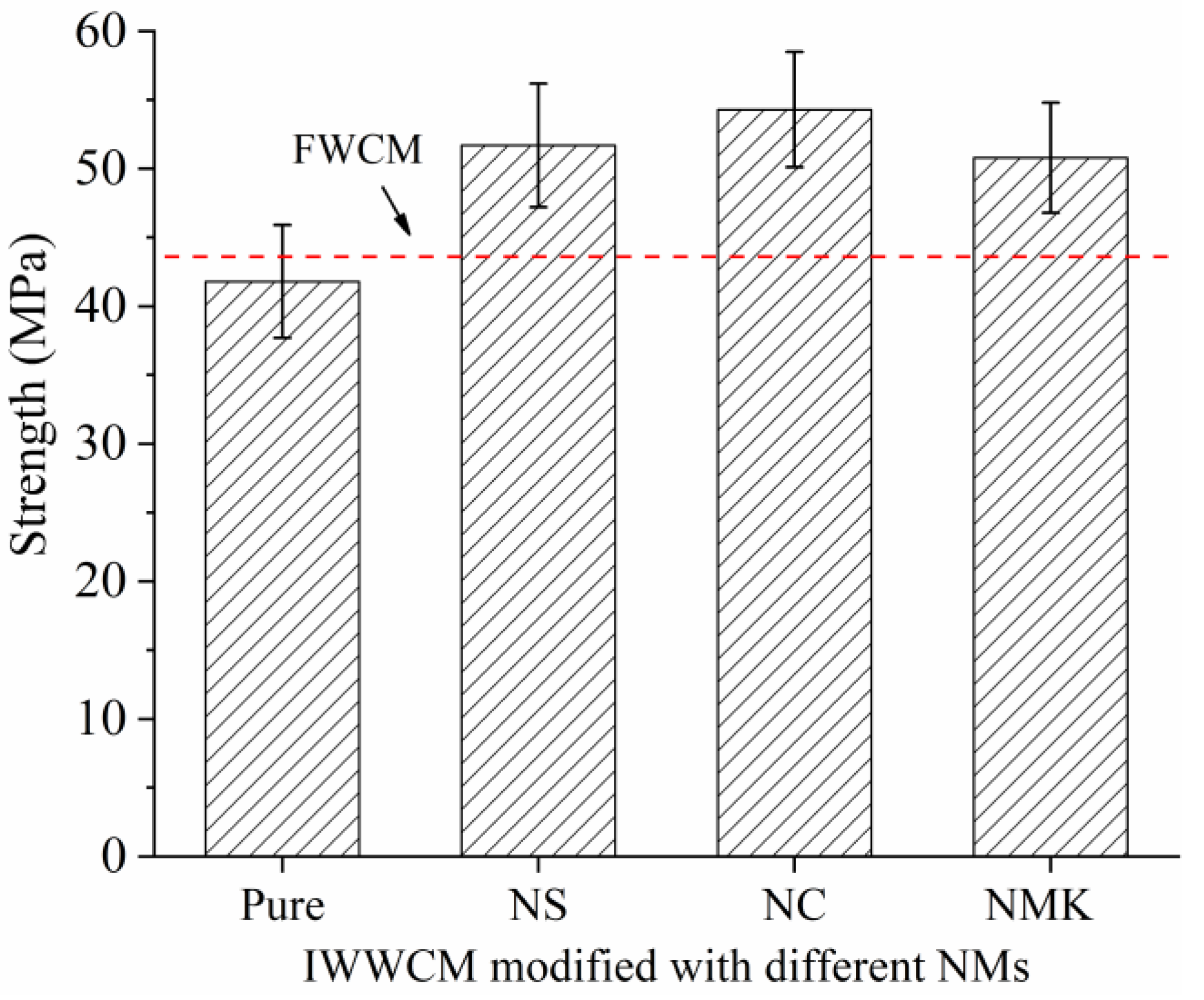
3.2. Mechanical Properties
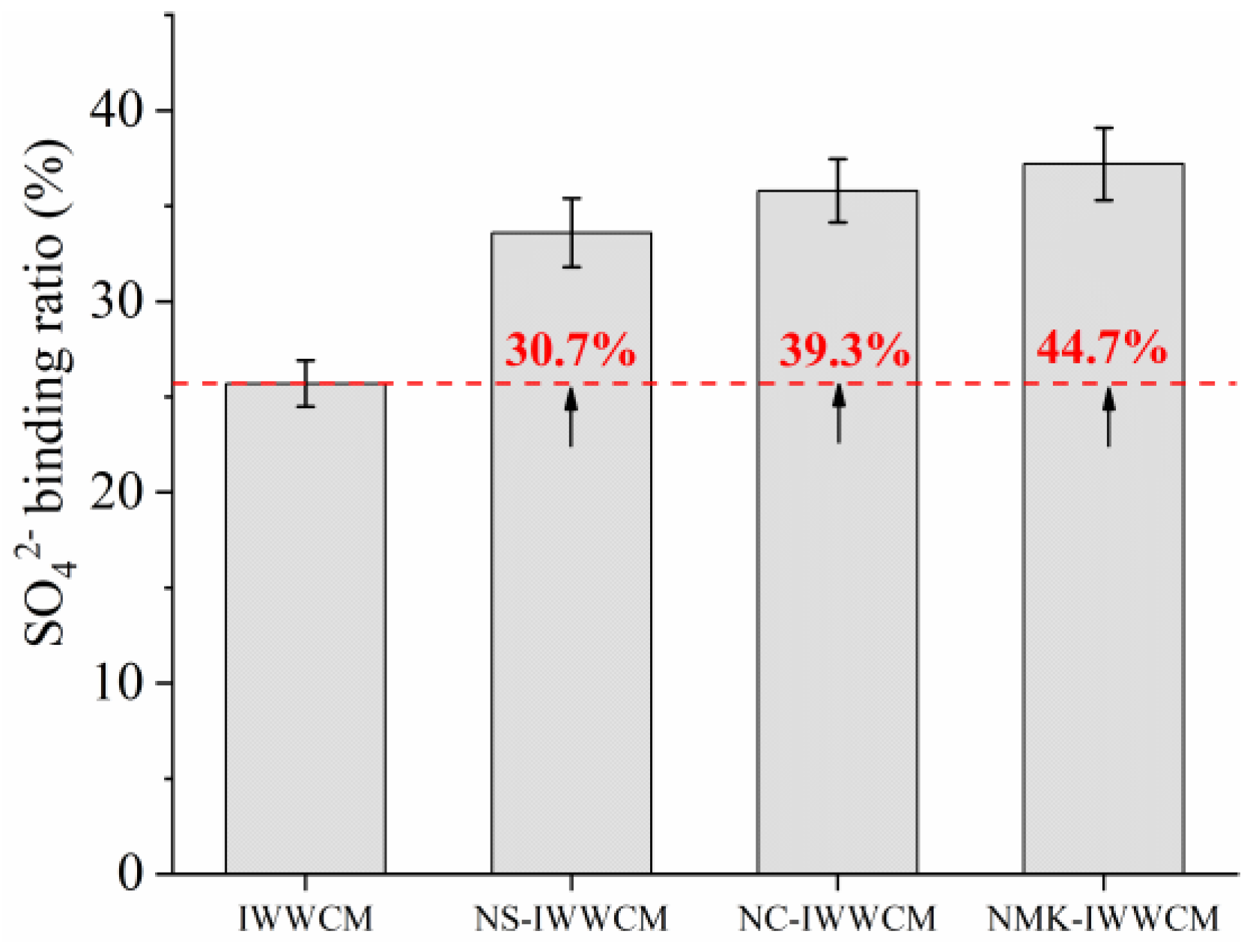
3.3. SO42− Content Measurement
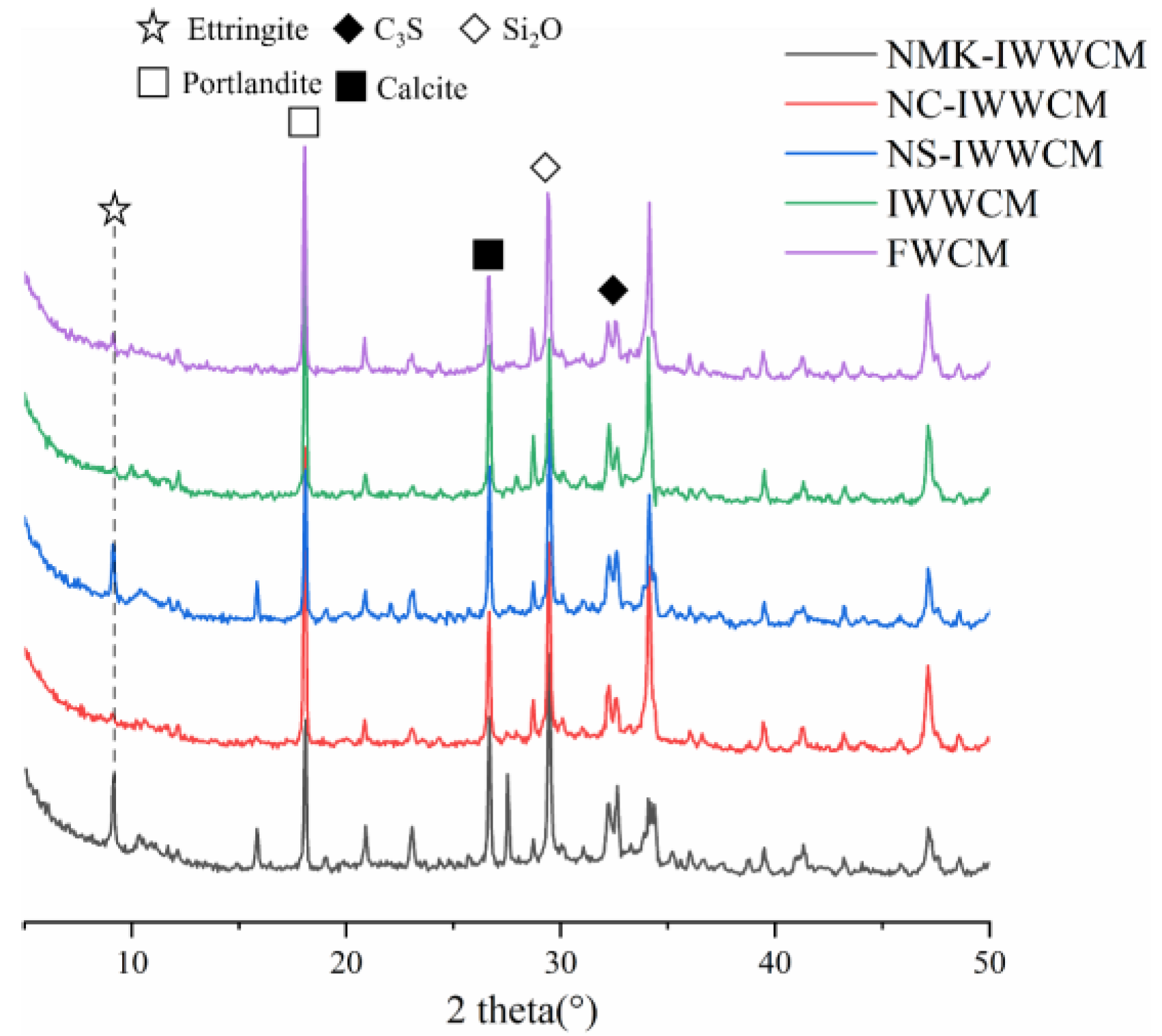
3.4. XRD Analysis
3.5. TG Analysis
3.6. Micropore Structure Analysis
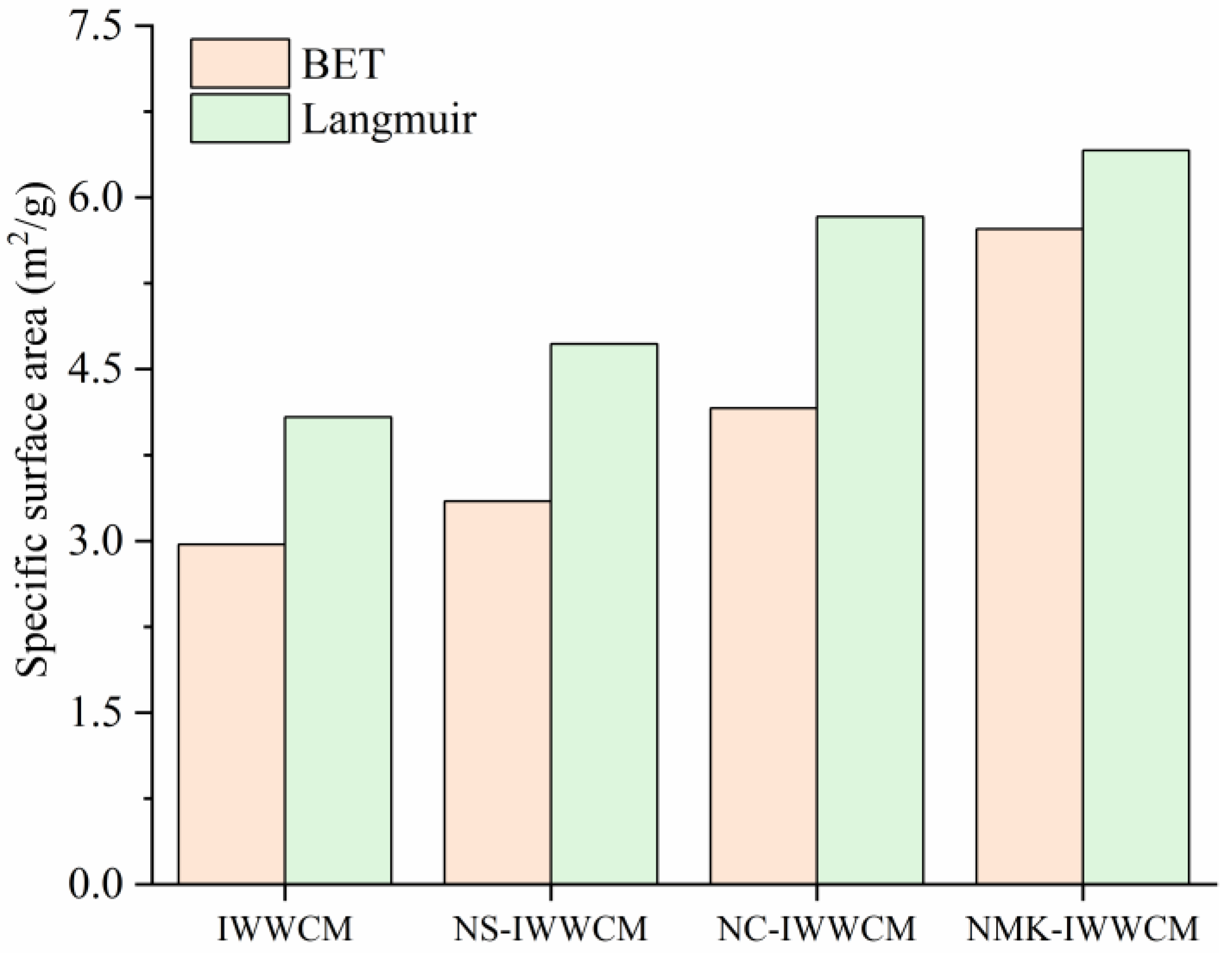
3.7. Specific Surface Area Measurement
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations and Future Aspects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opekunov, A.; Opekunova, M.; Kukushkin, S.; Lisenkov, S. Impact of drilling waste pollution on land cover in a high subarctic forest-tundra zone. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Z. Water-land resource carrying capacity in China: Changing trends, main driving forces, and implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 130003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.; Jamshidi Far, A.; Dionisi, D. Land and water requirements for the supply of renewable heating and transport energy using anaerobic digestion and water electrolysis. A case study for the UK. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 48, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Paul, N.A.; Cole, A.J.; de Nys, R. From waste water treatment to land management: Conversion of aquatic biomass to biochar for soil amelioration and the fortification of crops with essential trace elements. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaverková, M.D.; Maxianová, A.; Winkler, J.; Adamcová, D.; Podlasek, A. Environmental consequences and the role of illegal waste dumps and their impact on land degradation. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Yan, D. Emergy evaluation of ecological and economic value of water and soil resources in residential and industrial land based on energy analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiv, T.; Sobol, K.; Franus, M.; Franus, W. Mechanical and durability properties of concretes incorporating natural zeolite. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmee, N.M.; Shafiq, N. Ultra-high performance concrete: From fundamental to applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2018, 9, e00197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Chang, J.; Yang, W.; Yan, X.; Yu, H.; Shen, Y. Utilization of waste from alumina industry to produce sustainable cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Multi-structural evolution of conductive reactive powder concrete manufactured by enhanced ohmic heating curing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, M.; Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, W. Internal structural evolution of conductive cementitious composites subjected to multi-step ohmic heating curing strategy under severely cold temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.; Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, A. Synthesis of hybrid magnetic carbon nanotubes—C18-modified nano SiO2 under supercritical carbon dioxide media and their analytical potential for solid-phase extraction of pesticides. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 137, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, Á. Analytical nanometrological approach for screening and confirmation of titanium dioxide nano/micro-particles in sugary samples based on Raman spectroscopy—Capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Fan, Y. Effect of nano-metakaolin on the thixotropy of fresh cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 353, 129062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, R.; Lu, C.; Hong, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, J. Influence of Nano-SiO2 Content on Cement Paste and the Interfacial Transition Zone. Materials 2023, 16, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragwiha, M.B.; Fikeni, K.G.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, G.; Ge, H.; Pang, X. Influence of Various Nanomaterials on the Rheology and Hydration Kinetics of Oil Well Cement. Materials 2023, 16, 6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, L.J.; Peng, G.F.; Ma, Q.; Hu, H.M.; Gao, R.; Yao, Q.F.; Liu, Y.F.Y.; Bamforth, P.B.; Zhang, G.; Yu, H.; et al. Experimental study of deformation of early age concrete suffering from frost damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 17, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Cao, F.; Sun, Z.; Shah, S.P. Effects of nano-silica and nano-limestone on flowability and mechanical properties of ultra-high-performance concrete matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 95, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Enhanced ohmic heating and chloride adsorption efficiency of conductive seawater cementitious composite: Effect of non-conductive nano-silica. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 236, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; Khayat, K.H.; Wan, S. Effects of different nanomaterials on hardening and performance of ultra-high strength concrete (UHSC). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 70, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, J.; Kaur, M. Microstructure and strength development of fly ash-based geopolymer mortar: Role of nano-metakaolin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.M.; He, Z.H.; Ma, Z.M.; Liang, C.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Abreham, A.A.; Shi, J. Utilization of nano-metakaolin in concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fan, Y. Rheological evaluation of nano-metakaolin cement pastes based on the water film thickness. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, J.O.; Oliveira, L.V.S.; Ueki, M.M.; Barreto, L.S. Characterization and stabilization of nano-metakaolin colloidal suspensions. Powder Technol. 2021, 383, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Du, S.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y. Effects of nano-SiO2, nano-CaCO3 and nano-TiO2 on properties and microstructure of the high content calcium silicate phase cement (HCSC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaedi, H.; Alomayri, T.; Kaze, C.R.; Jindal, B.B.; Subaer, S.; Shaikh, F.; Alraddadi, S. Characterization and properties of geopolymer nanocomposites with different contents of nano-CaCO3. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, F.; Gong, G.; Hu, B.; Guo, M. An industrial applicable method to improve the properties of recycled aggregate concrete by incorporating nano-silica and micro-CaCO3. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, P. Chloride ions transport and adsorption in the nano-pores of silicate calcium hydrate: Experimental and molecular dynamics studies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, D.; Ma, H. Multi-scale study water and ions transport in the cement-based materials: From molecular dynamics to random walk. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 325, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, T. Removal of sulfate from aqueous solution using Mg-Al nano-layered double hydroxides synthesized under different dual solvent systems. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhou, L.Q.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.P. Degradation of Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide Concrete under Sulfate Attack and Freeze–Thaw Cycle Environment. Materials 2023, 16, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.Q.; Jiang, Y.J.; Sun, M.M.; Chen, E.J.; Lee, F.H. Effect of in situ water content variation on the spatial variation of strength of deep cement-mixed clay. Geotechnique 2019, 69, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, F.H.; Quek, S.T.; Chen, E.J.; Yi, J.T. Effect of spatial variation of strength and modulus on the lateral compression response of cement-admixed clay slab. Geotechnique 2015, 65, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, L.; Mo, L. Effects of ground coal bottom ash on the properties of cement-based materials under various curing temperatures. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zhang, R.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Shah, S.P. In situ Ca(OH)2 consumption of TEOS on the surface of hardened cement-based materials and its improving effects on the Ca-leaching and sulfate-attack resistivity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huo, B.; Cao, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Sulfate resistance of steam cured ferronickel slag blended cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 96, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Guo, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Cheng, X.; Kumar, R.; Srinivasaraonaik, B.; Singh, L.P. Comparison study on the sulfate attack resistivity of cement-based materials modified with nanoSiO2 and normal SCMs: Pore structure and phase composition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hou, P.; Shao, Y.; Zuo, X.; Li, Q.; Xie, N.; Cheng, X. Comparison study on the sulfate attack resistivity of cement-based materials modified with nanoSiO2 and conventional SCMs: Mechanical strength and volume stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Wang, K. Numerical investigation on interface crack initiation and propagation behaviour of self-healing cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Ohmic heating curing of high content fly ash blended cement-based composites towards sustainable green construction materials used in severe cold region. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, W. Performance and economic analyses of low-energy ohmic heating cured sustainable reactive powder concrete with dolomite powder as fine aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Ph, D.; Liu, Y.; Ph, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Ph, D. Performance Evolution and Chloride Adsorption Efficiency of Seawater Mixed Cement-Based Materials Subjected to Ohmic Heating Curing under a Severely Cold Environment. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Gradient power modified ohmic heating curing to prepare hybrid carbon fibers/high performance concrete under deep-freeze low temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Xu, N.; Jiang, S. Pore structure and permeability of concrete with high volume of limestone powder addition. Powder Technol. 2018, 338, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, W.; Qi, B.; Lei, Z.; Wang, W. Ohmic heating curing of carbon fiber/carbon nanofiber synergistically strengthening cement-based composites as repair/reinforcement materials used in ultra-low temperature environment. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cai, R.; Chen, E.; Tang, S. The investigation of early hydration and pore structure for limestone powder wastes blended cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Oxides | SiO2 | SO3 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | CuO | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | 96.64% | 0.88% | 0.32% | 0.05% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 0% |
| NC | 3.02% | 1.46% | 95.17% | 0.01% | 0.21% | 0% | 0% |
| NMK | 51.93% | 0.11% | 0.01% | 0.42% | 0.33% | 0% | 40.85% |
| Specimen | W/b | Binder/Sand | NM Content (%) | PS Addition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWCM | 0.36 | 1:1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| IWWCM | 0.36 | 1:1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| NS-IWWCM | 0.36 | 1:1 | 1.75 | 1 |
| NC-IWWCM | 0.36 | 1:1 | 1.75 | 1 |
| NMK-IWWCM | 0.36 | 1:1 | 1.75 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, J.; Shi, S. Improving the Efficiency of Cement Mortar to Immobilize Sulfate in Industrial Wastewater Using Different Nanoparticles. Separations 2023, 10, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10120586
Zheng Y, Guo M, Zhang X, Xia Z, Zhao J, Shi S. Improving the Efficiency of Cement Mortar to Immobilize Sulfate in Industrial Wastewater Using Different Nanoparticles. Separations. 2023; 10(12):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10120586
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yuxia, Mingke Guo, Xin Zhang, Zehua Xia, Juan Zhao, and Siyu Shi. 2023. "Improving the Efficiency of Cement Mortar to Immobilize Sulfate in Industrial Wastewater Using Different Nanoparticles" Separations 10, no. 12: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10120586
APA StyleZheng, Y., Guo, M., Zhang, X., Xia, Z., Zhao, J., & Shi, S. (2023). Improving the Efficiency of Cement Mortar to Immobilize Sulfate in Industrial Wastewater Using Different Nanoparticles. Separations, 10(12), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10120586





