Abstract
A wide range of analytical techniques have been reported to determine cordycepin (CDN) in various sample matrices. Nevertheless, greener analytical approaches for CDN estimation are scarce in the literature. As a result, this study was designed to develop and validate a stability-indicating greener “high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC)” technique for CDN determination in a laboratory-developed formulation. The greener eluent system for CDN detection was ethanol–water (75:25 v/v). At a wavelength of 262 nm, CDN was measured. The greenness scale of the proposed analytical technology was derived using the “Analytical GREENness (AGREE)” approach. The proposed stability-indicating HPTLC assay was linear for CDN analysis in the 50–1000 ng/band range with a determination coefficient of 0.9978. The proposed analytical technique for CDN analysis was simple, rapid, accurate, precise, robust, selective, stability-indicating, and greener. The AGREE score for the proposed stability-indicating HPTLC technique was calculated to be 0.79 using the AGREE calculator. The current protocol was able to detect CDN degradation products under various stress conditions, indicating its stability-indication characteristics and selectivity. The AGREE quantitative score indicated that the stability-indicating current protocol had outstanding greener characteristics. The amount of CDN in the laboratory-developed formulation was determined to be 98.84%, indicating the suitability of the current protocol in the assay of CDN in the formulations. These results suggested that CDN in a laboratory-developed formulation may be regularly determined using the stability-indicating greener HPTLC strategy.
1. Introduction
Cordycepin (CDN) is a derivative of nucleoside adenosine, which is chemically known as 3′-deoxyadenosine (Figure 1) [1]. It was isolated from Cordyceps militaris for the very first time, but it is also isolated from some other species of Cordyceps, such as Cordyceps sinensis [2,3]. Adenosine and CDN have been reported as the main phytoconstituents of C. militaris [4]. In the literature, CDN has been reported to have several therapeutic activities, which include antioxidant [5], antimicrobial [6], antibacterial [7], antifungal [6], anti-inflammatory [8], neuroprotective [9], lung-protective [10], hepatoprotective [11], immunomodulatory [12], prosexual [13], and anticancer activities [14,15]. CDN is found in various pharmaceutical formulations, food supplements, and mushroom products. As a consequence, both qualitative and quantitative methods must be used to identify CDN in a wide range of items, including food and pharmaceuticals.
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of cordycepin (CDN).
A detailed literature survey revealed a wide range of analytical procedures for CDN determination in foods, pharmaceuticals, and dietary supplements. For the determination of CDN in various species of Cordyceps and dietary supplements, various “high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)” techniques have been developed and validated [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. A few liquid-chromatography mass-spectrometry (LC-MS) methods have also been developed to determine CDN in C. militaris and C. sinensis, either alone or in combination with other nucleosides [24,25]. An eco-friendly/greener LC-MS method has also been used to simultaneously determine CDN and iso-CDN in ten different kinds of Cordyceps [26]. An online solid-phase extraction (SPE)-HPLC technique was also developed for the simultaneous detection of CDN and 2′-deoxyadenosine in C. militaris, C. sinensis, Hirsutella sinensis, and C. sobolifera [27]. Some column chromatography approaches have also been used to determine CDN in C. militaris and some other species of Cordyceps [28,29]. The separation and quantification of CDN and adenosine in C. sinensis have also been accomplished using a gradient ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) technique [30]. An UPLC approach coupled with mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) was also used for the simultaneous determination of CDN and its metabolite 3′-deoxyinosine in a rat whole-blood sample and for their pharmacokinetic assessment [31]. Additionally, some “high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC)” techniques have been created to identify CDN in different types of Cordyceps, either alone or in combination with other adenosines [32,33,34]. Other techniques such as capillary electrophoresis [35], near-infrared spectroscopy [36], and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy [37] have also been developed for the rapid determination of CDN in C. militaris.
The literature contains a wide variety of analytical techniques for CDN determination. However, neither a qualitative nor a quantitative assessment of the greenness profile of the reported analytical processes has been made. In addition, most of the assays of CDN analysis are based on liquid chromatography techniques, which are sensitive and accurate for CDN analysis, but these techniques are time-consuming, labor-intensive, complicated, expensive, and result in large amounts of solvent waste being added to the environment. So far, there are no reported greener HPTLC assays for CDN. Several qualitative and quantitative approaches are reported to forecast the greenness of analytical tests [38,39,40,41,42]. To forecast greenness characteristics, on the other hand, the “Analytical GREENness (AGREE)” technology takes into account all twelve green analytical chemistry (GAC) principles [40]. In order to determine the greenness profile of the current analytical protocol, the AGREE approach was used [40].
Based on all of these presumptions, this study’s goal was to design and validate a stability-indicating (a method able to detect an analyte in the presence of degradation products), greener, reverse-phase HPTLC technique for CDN analysis using a formulation that the laboratory produced. The term greener HPTLC is a more suitable term for the current method due to the use of green solvents (ethanol and water) compared to methods in the literature. Therefore, we used the term greener HPTLC in this work. The current protocol for CDN detection was proven efficient using “The International Council for Harmonization (ICH)”-Q2-R1 guidelines [43].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The reference standard of CDN was provided by “Beijing Mesochem Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China)”. The chromatography grade ethanol and methanol were obtained from “E-Merck (Darmstadt, Germany)”. The high pure water was collected from a “Milli-Q® (Milli-Q, Lyon, France)” unit. The nanoemulsion formulation of CDN was prepared via the aqueous-phase titration method using Triacetin (oil phase), Tween-80 (surfactant), Carbitol (cosurfactant), and water (aqueous phase). All additional reagents were of the analytical grade and procured from E-Merck (Darmstadt, Germany).
2.2. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Procedures
A “CAMAG HPTLC (CAMAG, Muttenz, Switzerland)” system was used for the determination of nanoemulsions of CDN. In order to apply the samples as 6 mm bands, a “CAMAG Automatic TLC Sampler 4 (ATS4) Sample Applicator (CAMAG, Geneva, Switzerland)” was used. The TLC plates used for the detection of CDN were “RP-60F254S plates (E-Merck, Darmstadt, Germany)”. The “Hamilton microliter syringe (Hamilton, Bonaduz, Switzerland)” was loaded on to the sample applicator. Throughout the course of the experiment, the application rate for CDN detection remained constant at 150 nL/s. The TLC plates were set up at an 80 mm distance in a “CAMAG automated developing chamber 2 (ADC2) (CAMAG, Muttenz, Switzerland)”. The greener eluent system was composed of the binary combination of ethanol and water (75:25 v/v). The greener eluent system’s vapors were used to saturate the chamber for 30 min at 22 °C. At a wavelength of 262 nm, CDN was quantified. The slit size was adjusted to 4 × 0.45 mm2, and the scan speed “(CAMAG TLC Scanner, Muttenz, Switzerland)” was set to 20 mm/s. For each procedure, three or six copies were applied. The “WinCAT’s (version 1.4.3.6336, CAMAG, Muttenz, Switzerland)” program was used for the processing and interpretation of data.
2.3. Calibration Curve and Quality Control (QC) Sample for CDN
The required amount of CDN was dissolved into the greener eluent system’s prescribed volume to obtain the CDN stock solution with the final concentration of 100 µg/mL in triplicate (n = 3). From the stock solution, serial dilutions were made to obtain ten different CDN concentrations, which were 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, and 1000 ng/band (range = 50–1000 ng/band), in triplicate (n = 3). Approximately 200 µL of each concentration was spotted onto reverse-phase TLC plates, and the respective chromatographic response was recorded. The CDN calibration plot was produced by graphing the CDN concentrations vs. the observed peak area (n = 6). Three distinct QC concentrations were freshly created for the evaluation of several parameters for validation studies.
2.4. Sample Processing for the Assay of CDN in Laboratory-Developed Nanoemulsion
Commercial formulations of CDN are not available in the Saudi Arabian market. As a result, a nanoemulsion formulation of CDN was developed and evaluated in the laboratory. The nanoemulsion formulation of CDN was prepared via the aqueous-phase titration method [44]. The components of the nanoemulsion were optimized by constructing a pseudo-ternary phase diagram [44,45]. The accurately weighed 10 mg of CDN was dissolved in 150 µL of Triacetin (oil phase). Then, 250 µL of Tween-80 (surfactant) and 250 µL of Carbitol (cosurfactant) were added to the aqueous phase via vortexing. To this mixture, 350 µL of water (aqueous phase) was added drop by drop until the clear and transparent nanoemulsion was obtained. One mL of a laboratory-developed nanoemulsion with 10 mg/mL of CDN was appropriately diluted with methanol to produce 100 mL of stock solution in order to determine the CDN content. Following a suitable dilution with the greener eluent system and a 15-min sonication of this solution, the CDN content was determined using the current protocol.
2.5. Analytical Method Validation
The current protocol for CDN measurement was validated for distinct parameters according to ICH-Q2-R1 procedures [43]. By plotting the CDN concentrations vs. the measured peak area, CDN linearity was derived. The linearity of the current protocol for CDN was assessed in the 50–1000 ng/band range in six copies (n = 6).
For the current protocol of CDN analysis, the computation of the retardation factor (Rf), asymmetry factor (As), and theoretical plates number/meter (N/m) was employed to find the system appropriateness characteristics. The reported equations were used to obtain the “Rf, As, and N/m” values [42].
The intra-day and inter-day accuracy of the current protocol for CDN analysis was assessed using the % recovery approach. Six replicates (n = 6) of solutions were performed on the same day to examine the intra-day accuracy at three different QC concentrations, namely low QC (LQC = 100 ng/band), middle QC (MQC = 500 ng/band), and high QC (HQC = 1000 ng/band). On three distinct days, six replicates (n = 6) of CDN’s LQC, MQC, and HQC solutions were used to determine inter-day accuracy. The percentage recovery for intra-day and inter-day accuracy was computed for the interpretation of the results.
The precision of the current protocol for CDN was determined as intra-day and inter-day variation. The intra-day variation for CDN was examined using the analysis of freshly produced CDN solutions at LQC, MQC, and HQC on the same day in six replicates (n = 6). The CDN inter-day precision was found by evaluating freshly generated CDN solutions at the same QC levels on three distinct days in six repetitions (n = 6). Both precisions were expressed in terms of the percentage of the relative standard deviation (%RSD).
By purposefully altering the composition of the greener eluent system, the CDN robustness was evaluated for the current protocol. The greener eluent system of ethanol–water (75:25, v/v) for CDN was altered to ethanol–water (77:23, v/v) and ethanol–water (73:27, v/v) for the current protocol, and the differences in the CDN chromatographic peaks and Rf were noted.
The sensitivity of the current protocol for CDN was calculated as the “limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ)” by applying a standard deviation methodology. For the current protocol, the blank sample was analyzed in six replicates (n = 6), and the standard deviation was calculated. The LOD and LOQ for CDN were derived using the standard deviation method in six replicates (n = 6) using the following equations [46]:
where is the standard deviation of the blank sample and S is the slope of the CDN calibration curve.
In order to assess the specificity of the current protocol for CDN analysis, the Rf values and UV-absorption spectra of CDN in a laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation were compared to those of standard CDN.
2.6. Forced Degradation/Selectivity Studies
To investigate the selectivity and stability-indicating capabilities of the current protocol, forced degradation studies under a variety of stress conditions, including acidic (HCl), basic (NaOH), oxidative (H2O2), thermal, and photolytic stress conditions, were carried out [42,47]. The MQC concentration (500 ng/band) of CDN was freshly prepared into the greener eluent system for acid and base-induced degradation. By mixing 4 mL of 1M HCl and 4 mL of 1M NaOH into an aliquot (1 mL) of this solution, acid and base hydrolyses were applied. For the determination of CDN in the presence of its acid and base degradation products, these mixtures were refluxed for 48 h at 60 °C before being examined using the current protocol [42].
The MQC concentration (500 ng/band) of CDN was freshly prepared and introduced into the greener eluent system for oxidative degradation examination. This solution was oxidatively degraded by adding 2 mL of 30% H2O2 to an aliquot (1 mL) of it. For the detection of CDN in the presence of its oxidative degradation products, this mixture was refluxed for 48 h at 60 °C before being examined using the current protocol [42].
For the purpose of conducting thermal degradation tests, an aliquot of the MQC concentration (500 ng/band) was placed in a hot air oven for 48 h at 60 °C. The determination of CDN in the presence of its thermal degradation products was then performed utilizing the current protocol [42].
For photolytic degradation examinations, an aliquot of the MQC concentration (500 ng/band) was subjected to a UV chamber at 254 nm for 48 h. Then, CDN was determined using the current protocol while the photolytic degradation products were present [42].
2.7. Application of Current Protocol in the Determination of CDN in Laboratory-Developed Nanoemulsion
The processed samples of the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation were spotted to reverse-phase TLC plates for the current protocol, and the peak areas of CDN in three copies (n = 3) were recorded. For the current protocol, the percent assay of CDN in the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation was calculated using a CDN calibration plot.
2.8. Assessment of Eco-Friendliness of Protocol
The AGREE technique was used to derive the greenness/eco-friendliness of the current protocol for CDN determination [40]. Using “AGREE: The Analytical Greenness Calculator (version 0.5, Gdansk University of Technology, Gdansk, Poland, 2020)”, the AGREE index (0.0–1.0) for the current protocol was obtained. The detailed AGREE protocol is included in the Supplementary Materials.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analytical Method Development
The goal of the present study was to develop a stability-indicating greener HPTLC method to determine CDN. As a result, only greener solvents such as ethanol and water were examined as the eluent system. Toxic solvents such as methanol and acetonitrile were not examined due to their toxicity. Different concentrations of ethanol and water, including ethanol–water (35:65, v/v), ethanol–water (45:55), ethanol–water (55:45), ethanol–water (65:35), ethanol–water (75:25), ethanol–water (85:15), and ethanol–water (95:5, v/v), were examined as the greener eluent systems in order to establish a suitable band for CDN determination. All greener eluent systems were developed using the chamber saturation conditions. A representative TLC chromo-plate for the standard CDN, laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation, and degradation samples is shown in Figure 2.
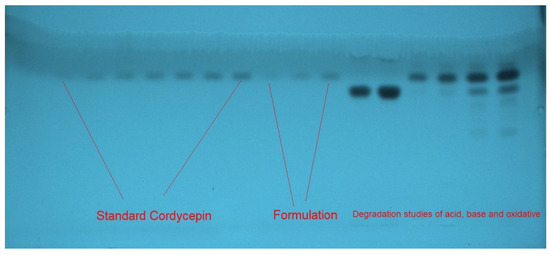
Figure 2.
A representative thin-layer chromatographic (TLC) chromo-plate of standard CDN, formulation, and forced degradation study samples recorded using greener ethanol–water (75:25 v/v) eluent system for current protocol.
It was discovered that the greener eluent systems, including ethanol–water (35:65, v/v), ethanol–water (45:55, v/v), ethanol–water (55:45, v/v), ethanol–water (65:35, v/v), ethanol–water (85:15, v/v), and ethanol–water (95:5, v/v), produced undesirable CDN chromatograms with undesirable As values (As > 1.15) when investigated. It was observed that the greener ethanol–water eluent system (75:5, v/v) produced a well-resolved and unbroken CDN chromatogram at Rf = 0.77 ± 0.02 (Figure 3A) when investigated. Additionally, CDN was discovered to have an acceptable As value of 1.02 for CDN analysis. As a result, the final greener eluent system for the current protocol of CDN detection was chosen to be ethanol–water (75:25, v/v). The greatest chromatographic response for CDN was discovered at 262 nm when the spectral bands for CDN were calculated in densitometry mode. Thus, 262 nm was used as the detection wavelength for all of the CDN investigations.
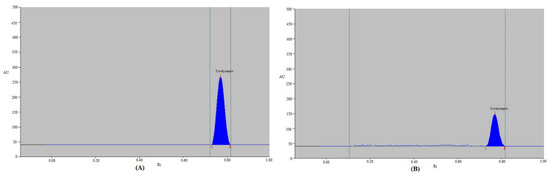
Figure 3.
Representative chromatograms of (A) standard CDN and (B) CDN nanoemulsion for current protocol.
3.2. Analytical Method Validation
To obtain numerous validation parameters for CDN measurement, the ICH-Q2-R1 procedures were followed [43]. Table 1 summarizes the data from the linear regression analysis of the CDN calibration curve for the current protocol. The CDN calibration curve for the current protocol was linear in the 50–1000 ng/band range. In densitometry techniques, such as TLC and HPTLC, samples are spotted as bands. Hence, the most convenient unit for densitometry analysis is ng/band or µg/band. Due to this reason, we used ng/band concentrations in this work. For the current protocol, CDN’s determination coefficient (R2) and regression coefficient (R) were found to be 0.9978 and 0.9988, respectively. The results pointed to a strong correlation between the measured peak area and the CDN concentrations. The linearity of the current protocol for CDN analysis over a wider range of concentrations was demonstrated by these results.

Table 1.
Resulting data for the linearity of cordycepin (CDN) for current protocol (mean ± SD; n = 6).
The system appropriateness parameters for the current protocol are listed in Table 2. The current protocol’s Rf, As, and N/m for CDN determination were found to be 0.77, 1.02, and 5321, respectively, which were reliable for CDN analysis.

Table 2.
System appropriateness parameters of CDN for current protocol (mean ± SD; n = 3).
The current protocol of the CDN measurement’s intra-day and inter-day accuracy was calculated in terms of % recovery. The accuracy information regarding the current protocol is illustrated in Table 3. The intra-day % recoveries of CDN at three distinct QC levels were determined to be 98.24–101.14% using the current protocol. The inter-day % recoveries of CDN at three distinct QC levels were found to be 98.45–101.68% for the current protocol. These data suggested that the current protocol was accurate in the determination of CDN.

Table 3.
Intra-day and inter-day accuracy data of CDN for current protocol (mean ± SD; n = 6).
The data for CDN analysis are expressed in terms of % RSD, and the intra-day and inter-day variation in the current protocol was investigated. The findings regarding the intra-day and inter-day variations for the current protocol of CDN analysis are shown in Table 4. The current protocol was shown to have a 0.77–1.01% RSD of CDN for intra-day precision. The current protocol was shown to have an RSD of CDN for the inter-day precision of 0.80–1.12%. The findings revealed the precision of the current protocol for CDN analysis.

Table 4.
Determination of CDN intra-day and inter-day fluctuation for current protocol (mean ± SD; n = 6).
The robustness of the current protocol for CDN analysis was evaluated by intentionally altering the composition of the greener eluent system. The findings regarding the data of robustness measurement for the current protocol are illustrated in Table 5. CDN % RSD for the current protocol was estimated to be 0.80–0.86%. CDN Rf values were found to be 0.76–0.78 for the current protocol. The findings revealed that the current protocol for CDN measurement was robust.

Table 5.
Measurement of CDN robustness for current protocol (mean ± SD; n = 6).
To evaluate the sensitivity of the current protocol for CDN analysis, the “LOD and LOQ” were computed. Table 1 summarizes the resulting values of “LOD and LOQ” of CDN for the current protocol. According to the results, the LOD and LOQ of CDN were computed to be 16.92 ± 0.14 and 50.76 ± 0.42 ng/band, respectively. The results demonstrated that the current protocol was sensitive for CDN measurement. The comparative evaluation of the Rf values and UV-absorption spectra of CDN in the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion with that of standard CDN allowed to assess the specificity of the current protocol for CDN assessment. The combined UV-absorption spectra of standard CDN and CDN in a laboratory-generated nanoemulsion are illustrated in Figure 4 for comparison. The peak response of standard CDN and the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion was measured at 262 nm. The initial peaks of the UV absorption spectra of the standard and nanoemulsion sample were not overlapped. However, the main peaks of CDN in both the samples were overlapped. The sample nanoemulsion contained some excipients. Due to the presence of some excipients, the initial peaks were not overlapped. The specificity of the current protocol for CDN assessment was demonstrated by finding the identical UV-absorption spectra, Rf values, and detection wavelengths of CDN in the standard and laboratory-developed nanoemulsion.
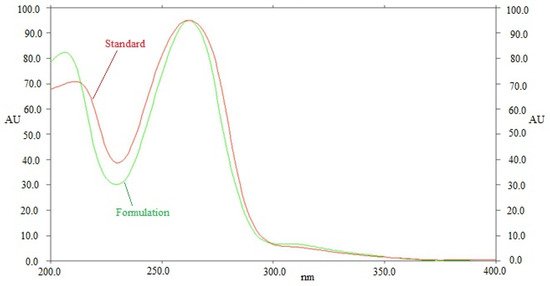
Figure 4.
UV-absorption spectra of standard CDN and formulation, superimposed.
3.3. Selectivity and Forced Degradation Studies
The selectivity and degradation of the current protocol were investigated under various stress conditions. The outcomes of the current protocol are shown in Figure 5 and Table 6. The CDN peaks in the chromatographic peaks from degradation circumstances were clearly distinguished from other peaks of degradation products (Figure 5). Because there was zero percent of CDN left after acid degradation, the entire amount of CDN (100% of it) was degraded (Table 6 and Figure 5A). As a result, under acid degradation conditions, CDN was totally decomposed. Peaks 1 and 2 in Figure 5A, which represent the acid-induced degradation peaks, were separated by Rf values of 0.69 and 0.86, respectively. Under the base degradation scenario, CDN remained at 81.14 percent, while 18.86 percent was degraded (Table 6 and Figure 5B). As a result, CDN was stable enough to withstand base deterioration. Peaks 1, 2, and 4 in Figure 5B, which represent the base-induced degradation peaks, were separated by Rf values of 0.21, 0.69, and 0.82, respectively. Under base degradation conditions, CDN’s Rf value was unchanged (Rf = 0.77). In total, 43.20 percent of CDN was decomposed, while 56.80 percent was still undergoing oxidative destruction (Table 6 and Figure 5C). Peaks 1, 2, 3, and 5 in Figure 5C, which were caused by H2O2, were separated by Rf values of 0.48, 0.62, 0.69, and 0.82, respectively. Under oxidative degradation conditions, the Rf value of CDN was slightly shifted (Rf = 0.76). During thermal and photolytic degradation conditions, CDN was kept at 100.00 percent, and no deterioration was seen (Figure not shown). Because of this, CDN had a high level of resistance to thermal and photolytic deterioration. The resolution of CDN in Figure 5 is fine. However, the resolution of the degradation components is low. The current protocol was developed for CDN instead of its degradation products. Forced degradation studies were performed to evaluate the ability of current protocol to determine CDN in the presence of its degradation products. In this study, the CDN was successfully separated in the presence of its degradation products. Hence, the methodology was selective and stability-indicating. Using the current protocol, the maximum CDN degradation under acid degradation conditions was found. All of these results demonstrated that CDN can be detected by utilizing the current protocol in the presence of its degradation products. These findings and observations suggested that the current protocol had selectivity and stability-indicating properties.
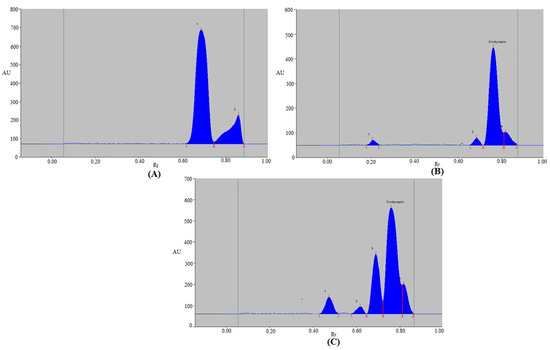
Figure 5.
Representative densitometry chromatograms of CDN derived under (A) acid-, (B) alkali-, and (C) oxidative-induced degradation of CDN.

Table 6.
Results of forced degradation evaluation of CDN at various stress conditions for current protocols (mean ± SD; n = 3).
3.4. Application of Current Protocol in the Determination of CDN in Laboratory-Developed Nanoemulsion
For the pharmaceutical assay of CDN in the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion, the current protocol was used as the alternative strategy to conventional analytical technologies. By contrasting the TLC band at Rf = 0.77 ± 0.02 for CDN with standard CDN utilizing the current protocol, the chromatogram of CDN from the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation was confirmed. The CDN peak in the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion had the same chromatographic profile as standard CDN when employing the current protocol. Furthermore, no additional peaks of nanoemulsion components were detected in the laboratory-developed formulation (Figure 3B), suggesting no interaction between CDN and formulation components. A CDN calibration plot was utilized to derive its content for the current protocol. Utilizing the current protocol, the % content of CDN in the laboratory-developed nanoemulsion was determined to be 98.84%. These results indicated the suitability of the current protocol for a CDN pharmaceutical assay.
3.5. Assessment of Eco-Friendliness of Protocol
Different qualitative and quantitative technologies are used to assess the greenness/eco-friendliness of analytical methods [38,39,40,41,42]. However, only AGREE uses all twelve GAC criteria to determine the eco-friendliness profile [40]. As a result, this approach was applied to gauge the analytical strategy’s greenness profile. A typical diagram for the AGREE index of the current protocol is illustrated in Figure 6. The AGREE sheet for each component of GAC is presented in Figure S1. For the current protocol, the AGREE score was determined to be 0.79, indicating that the current protocol for CDN measurement had an outstanding greenness profile.
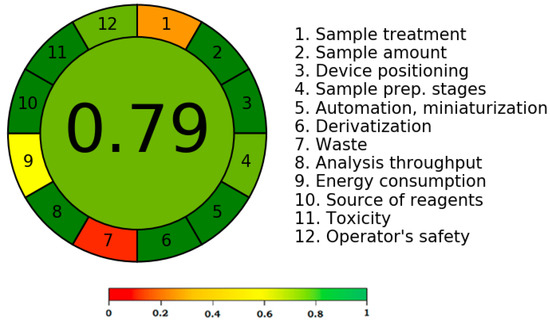
Figure 6.
The representative pictogram for AGREE scale for the current protocol derived using AGREE calculator.
4. Conclusions
Greener analytical protocols for CDN measurement are scarce in the literature. Therefore, in order to design and validate a stability-indicating greener HPTLC protocol for CDN detection in a laboratory-developed nanoemulsion formulation, this study was carried out. The current protocol of CDN measurement is simple, accurate, precise, rapid, robust, selective, greener, and stability-indicating. The AGREE results suggested an outstanding greenness profile of the current protocol. The current protocol was able to detect CDN in the presence of its degradation products, indicating the selectivity and stability-indicating nature of the current protocol. These results indicated that the current protocol can be used to determine CDN in formulations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations10010038/s1. Figure S1: AGREE score sheet presenting AGREE score for twelve different components of green analytical chemistry for the current protocol of CDN analysis derived using AGREE calculator. The detailed AGREE protocol is also included in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A. and F.S.; methodology, M.H.A., P.A., A.I.F. and T.M.A.; software, M.I. and M.M.G.; validation, S.A. and S.M.B.A.; formal analysis, M.M.G. and S.M.B.A.; investigation, A.A. and M.I.; resources, S.A.; data curation, A.I.F. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S.; writing—review and editing, M.I., S.M.B.A., P.A. and S.A.; visualization, S.A.; supervision, P.A. and F.S.; project administration, F.S. and P.A.; funding acquisition, M.M.G. and S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported via funding from Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2023/R/1444). The APC was funded by PSAU.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University for supporting this work via project number (PSAU/2023/R/1444). The authors are also grateful to AlMaarefa University for their generous support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bhandari, A.K.; Negi, J.S.; Bisht, V.K.; Rana, C.S.; Bharti, M.K.; Singh, N. Chemical constituent, inorganic elements and properties of Cordyceps sinensis—A review. Nat. Sci. 2010, 8, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, K.G.; Hutchinson, S.A.; Manson, W.; Spring, F.S. Cordycepin, a metabolic product from cultures of Cordyceps militaris (Linn.) link. Part I. Isolation and characterisation. J. Chem. Soc. 1951, 2299–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhar, M.G.; Giridhar, P.; Udaya Sankar, K.; Manohar, B. Bioactive principles from Cordyceps sinensis: A potent food supplement—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1013–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Li, S.P.; Xiang, J.J.; Lai, C.M.; Yang, F.Q.; Gao, J.L.; Wang, Y.T. Qualitative and quantitative determination of nucleosides, bases and their analogues in natural and cultured Cordyceps by pressurized liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESIMS/MS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 567, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.M.; Wang, B.-S.; Huang, S.C.; Duh, P.-D. Comparison of protective effects between cultured Cordyceps militaris and natural Cordyceps sinensis against oxidative damage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3132–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.; Ayyanar, M.; Amalraj, S.; Khanal, P.; Subramaniyan, V.; Das, S.; Gandhale, P.; Biswa, V.; Ali, R.; Gurav, N.; et al. Biogenic synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using mushroom fungus Cordyceps militaris: Characterization and mechanistic insights of therapeutic investigation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 73, E103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamthawon, K.; Kaewkod, T.; Bovonsombut, S.; Tragoolpua, Y. Efficacy of Cordyceps militaris extracts against some skin pathogenic bacterial and antioxidant activity. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; Guo, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Deng, Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin: A review. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Li, Z.; Schubert, B.; Huang, B.; Stoyanova, S.; Hamburger, M. Screening of entomopathogenic Deuteromycetes for activities on targets involved in degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Konoha, K.; Yoshikawa, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kagota, S.; Shinozuka, K.; Kunitomo, M. Effect of cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine) on hematogenic lung metastatic model mice. In Vivo 2005, 19, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.; Bao, T.; Xu, C.; Cooper, R.; Zhu, J.-S. CordyMax Cs-4 improves steady-state bioenergy status in mouse liver. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2001, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, E.K. Immunostimulating activity of the polysaccharides isolated from Cordyceps militaris. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.; Lee, C.; Chang, E. Optimization of solid state culture conditions for the production of adenosine, cordycepin, and D-mannitol in fruiting bodies of medicinal caterpillar fungus Cordyceps militaris (L.:Fr.) link (Ascomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2012, 14, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, M.K.; Chen, A.P. PARP inhibitor treatment in ovarian and breast cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2011, 35, 7–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Burger, P.; Vogel, M.; Friese, K.; Bruüning, A. The nucleoside antagonist cordycepin causes DNA double strand breaks in breast cancer cells. Invest. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Lue, M.-Y.; Pan, T.-M. Determination of adenosine, cordycepin and ergosterol contents in cultivated Antrodia camphorata by HPLC method. J. Food Drug Anal. 2005, 13, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. Determination and analysis of cordycepin and adenosine in the products of Cordyceps spp. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 3, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H.; Spandana, M. Simultaneous extraction, determination and analysis of adenosine, cordycepin and other derivatives of Cordyceps sinensis of Nepal by new validated HPLC method. J. Pharmacog. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, F.; Cai, H.; Sun, W.; Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Shen, W. Determination of cordycepin content of Cordyceps militaris recombinant rice by high performance liquid chromatography. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 2235–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cai, G.; He, Y.; Tong, G. Separation of cordycepin from Cordyceps militaris fermentation supernatant using preparative HPLC and evaluation of its antibacterial activity as an NAD+-dependent DNA ligase inhibitor. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Paje, L.A.; Kwon, B.; Noh, J.; Lee, S. Quantitative analysis of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris under different extraction methods. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangboonskul, J.; Amnuoypol, S.; Sangvatanakul, P. Analytical method development for quantitation of adenosine and cordycepin in cordyceps and related products. Pharm. Sci. Asia 2020, 47, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernthong, N.; Noisakul, S.; Saraphanchotiwitthaya, A.; Sripalakit, P. Validation and application of HPLC method for determination of cordycepin and adenosine in dietary supplements. Asia-Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.F.; Guo, F.Q.; Liang, Y.Z.; Chen, B.M. Determination of adenosine and cordycepin in Cordyceps sinensis and C. militarris with HPLC-ESI-MS. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2004, 29, 762–764. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.-W.; Huang, L.-F.; Hu, W.; He, Y.-B.; Wong, K.P. Analysis of the main nucleosides in Cordyceps sinensis by LC/ESI-MS. Molecules 2010, 15, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, Z.; Zou, Y.; Tan, G.; Li, W.; Lei, Q.; Li, R.; Lan, D. A simple, rapid, sensitive and eco-friendly LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of free cordycepin and isocordycepin in 10 different kinds of Cordyceps. Acta Chromatogr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; Qian, Z.-M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, M.-X.; Sun, W.-Y.; Yao, X.-S.; Li, W.-J.; Gao, H. Simultaneous determination of cordycepin and 2'-deoxyadenosine in Cordyceps genus by online SPE-HPLC. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017, 24, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Li, S. Analysis of Cordyceps by multi-column liquid chromatography. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, N.V.; Iuchi, Y.; Anh, L.H.; Hasan, M.; Xuan, T.D. Simple isolation of cordycepin from Cordyceps militaris by dual-normal phase column chromatography and its potential for making kombucha functional products. Separations 2022, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Chen, L.; Cao, Q. Separation and determination of cordycepin and adenosine in artificial Cordyceps sinensis Mycelium by gradient UPLC. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, E022019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Guan, H.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Liu, P.; Wei, H.; Liu, W. Simultaneous determination of cordycepin and its metabolite 3′-deoxyinosine in rat whole blood by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q exactive hybrid quadrupole orbitrap high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry and its application to accurate pharmacokinetic studies. J. Sep. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-W.; Chau, F.-T.; Wu, J.-Y. Analysis of the nucleoside content of Cordyceps sinensis using the stepwise gradient elution technique of thin-layer chromatography. Chin. J. Chem. 2004, 22, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-T.; Cheong, K.-L.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lv, G.-P.; Ju, Y.-J.; Feng, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.P. Characterization and discrimination of polysaccharides from different species of Cordyceps using saccharide mapping based on PACE and HPTLC. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, J.; Khan, W.; Ahmad, S.; Misra, K. Supercritical carbon dioxide extracts of Cordyceps sinensis: Chromatography-based metabolite profiling and protective efficacy against hypobaric hypoxia. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, E628924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.K.; Chou, C.-H.; Tzeng, Y.-M. A simple and rapid method for identification and determination of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 566, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singpoonga, N.; Rittiron, R.; Seang-on, B.; Chaiprasart, P. Determination of adenosine and cordycepin concentrations in Cordyceps militaris fruiting bodies using near-infrared spectroscopy. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27235–27244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.G.; Hyun, S.-H.; Sung, G.-H.; Choi, H.K. Simple and rapid determination of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris fruiting bodies by quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Abdelwahab, N.S.; Hegazy, M.A.; Fares, M.Y.; El-Sayed, G.M. Determination of the abused intravenously administered madness drops (tropicamide) by liquid chromatography in rat plasma; an application to pharmacokinetic study and greenness profile assessment. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, E105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. A green HPLC method for determination of nine sulfonamides in milk and beef, and its greenness assessment with analytical eco-scale and greenness profile. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE-Analytical GREEnness metric approach and software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Al-Joufi, F.A.; Alqarni, M.H.; Shakeel, F. Quantitative analysis of cabozantinib in pharmaceutical dosage forms using green RP-HPTLC and green NP-HPTLC methods: A comparative evaluation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, E100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudah, A.I.; Shakeel, F.; Alqarni, M.H.; Alam, P. A rapid and sensitive stability-indicating green RP-HPTLC method for the quantitation of flibanserin compared to green NP-HPTLC method: Validation studies and greenness assessment. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, E105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH), Q2 (R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures–Text and Methodology, Geneva, Switzerland. 2005. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Abushal, A.S.; Aleanizy, F.S.; Alqahtani, F.Y.; Shakeel, F.; Iqbal, M.; Haq, N.; Alsarra, I.A. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) of apremilast: In vitro evaluation and pharmacokinetics studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, W.A.; Alam, P.; Alshetaili, A.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Shakeel, F. Product development studies of cranberry seed oil nanoemulsion. Processes 2022, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Shakeel, F.; Ali, A.; Alqarni, M.H.; Foudah, A.I.; Aljarba, T.M.; Alkholifi, F.K.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Ali, A. Simultaneous determination of caffeine and paracetamol in commercial formulations using greener normal-phase and reversed-phase HPTLC methods: A contrast of validation parameters. Molecules 2022, 27, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, N.; Iqbal, M.; Alanazi, F.K.; Alsarra, I.A.; Shakeel, F. Applying green analytical chemistry for rapid analysis of drugs: Adding health to pharmaceutical industry. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, S777–S785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).