IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) with Unique Combined Generalized Skin Rashes and Biliary Tract Manifestation: A Comprehensive Immunological Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies and Reagents
2.2. Flow Cytometry
2.3. Surface Markers of Subsets of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
2.4. Surface Markers of Subsets of Follicular Helper T Cells
2.5. Surface Markers of B Cell Subsets
2.6. Markers of Members of Regulatory Lymphocyte Club
3. Results
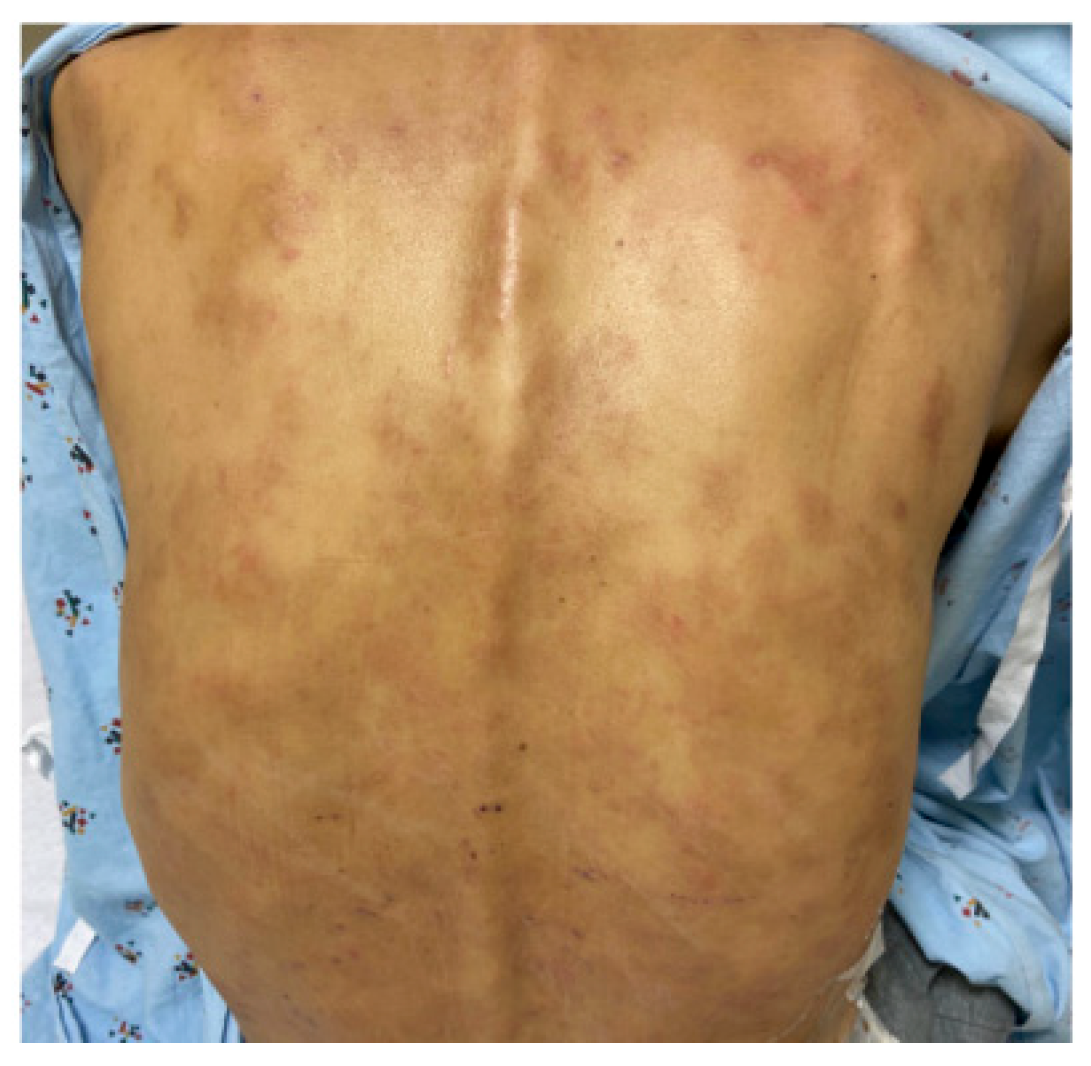
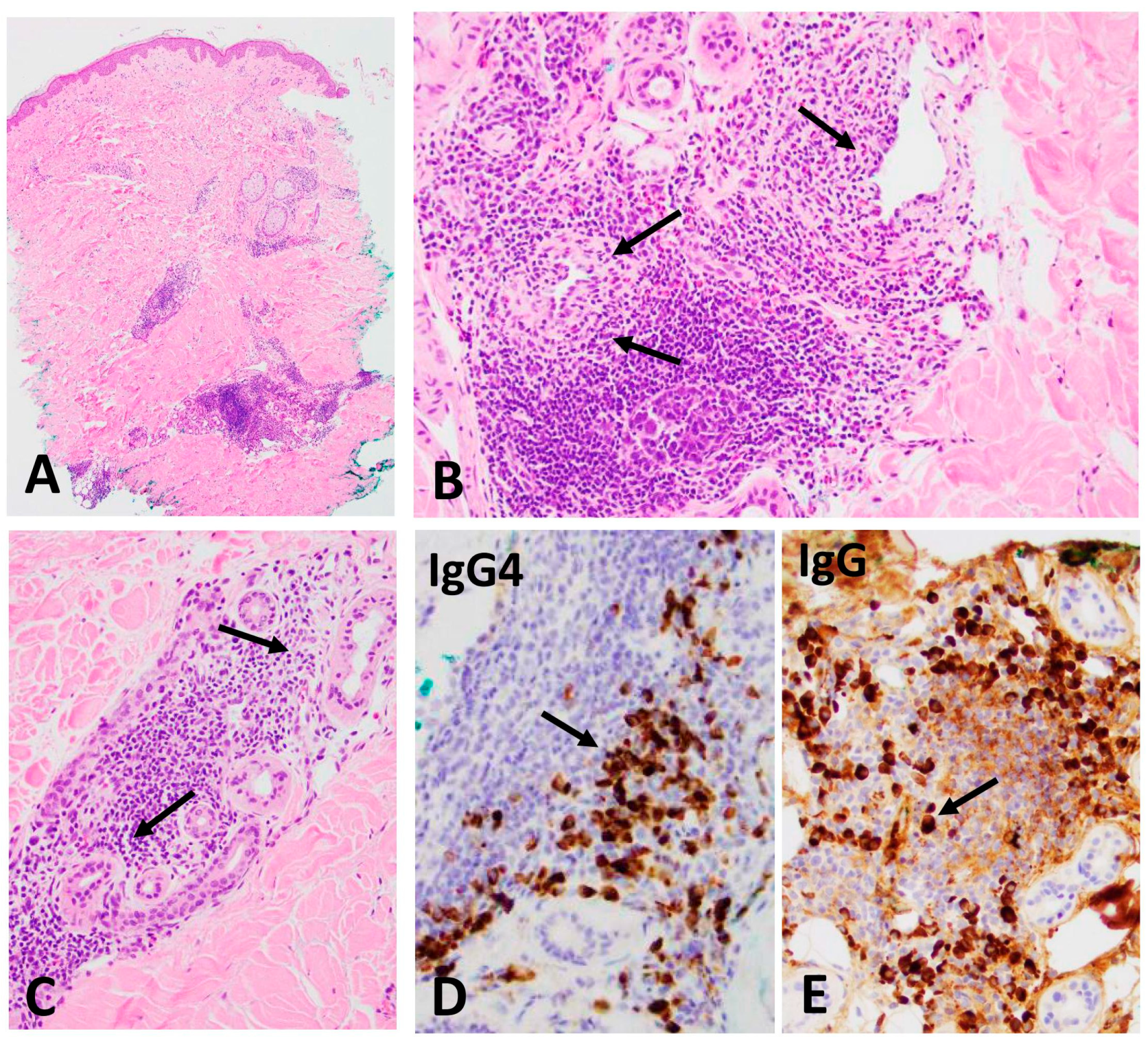
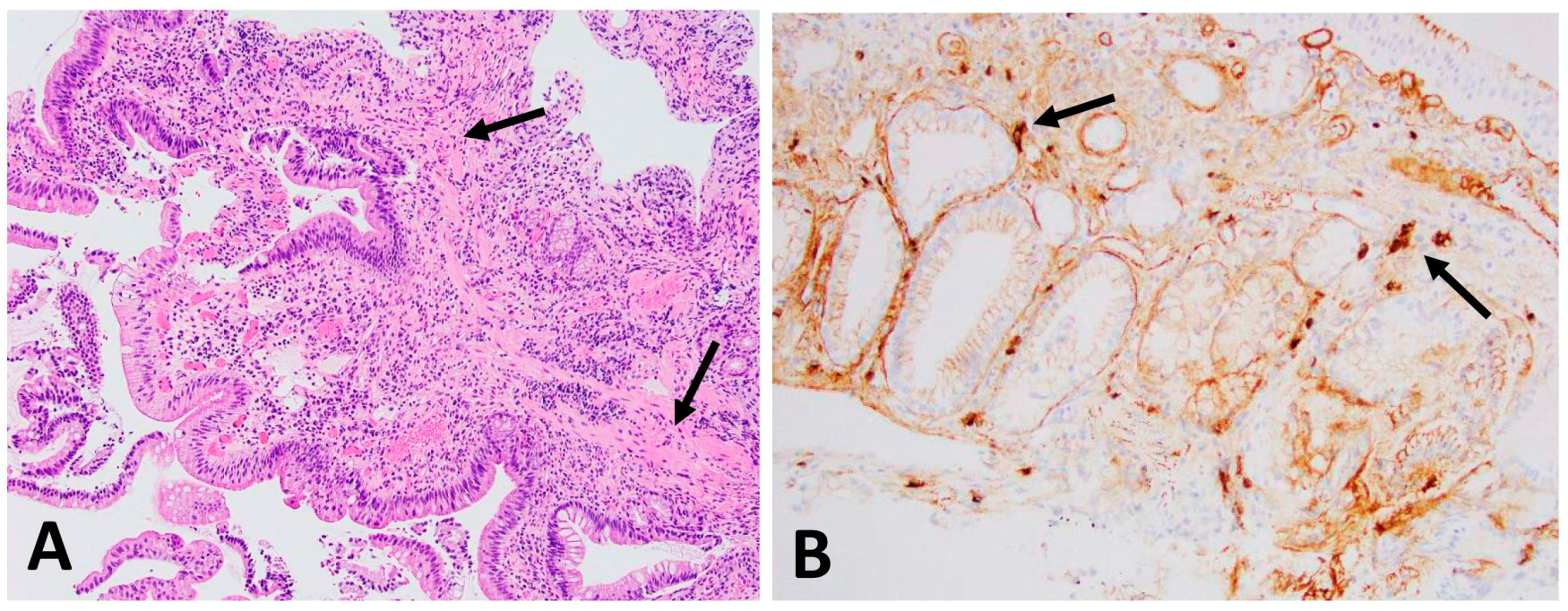
3.1. IgG4+ Plasma Cells in Skin and Ampulla Biopsy
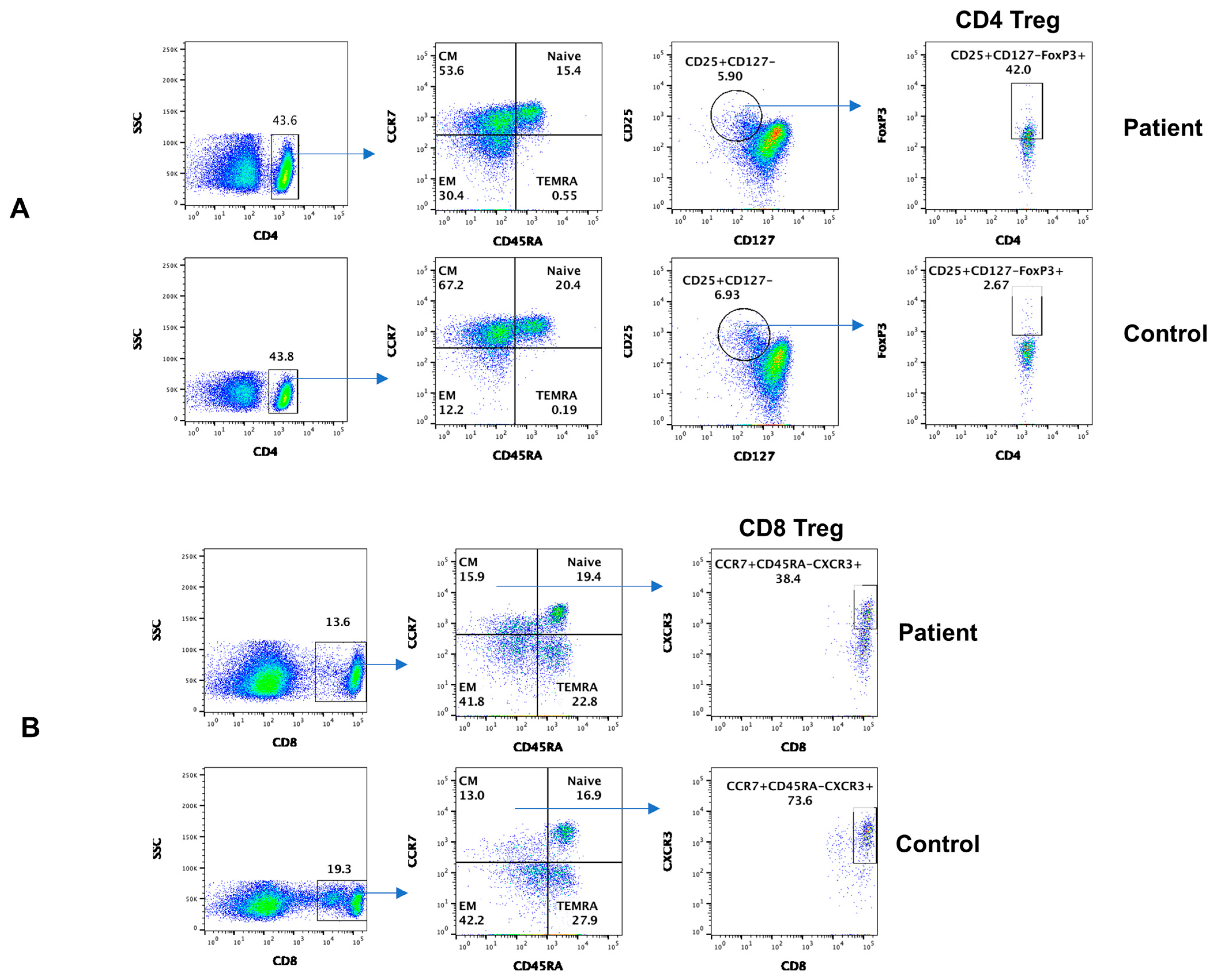
3.2. Subsets of CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
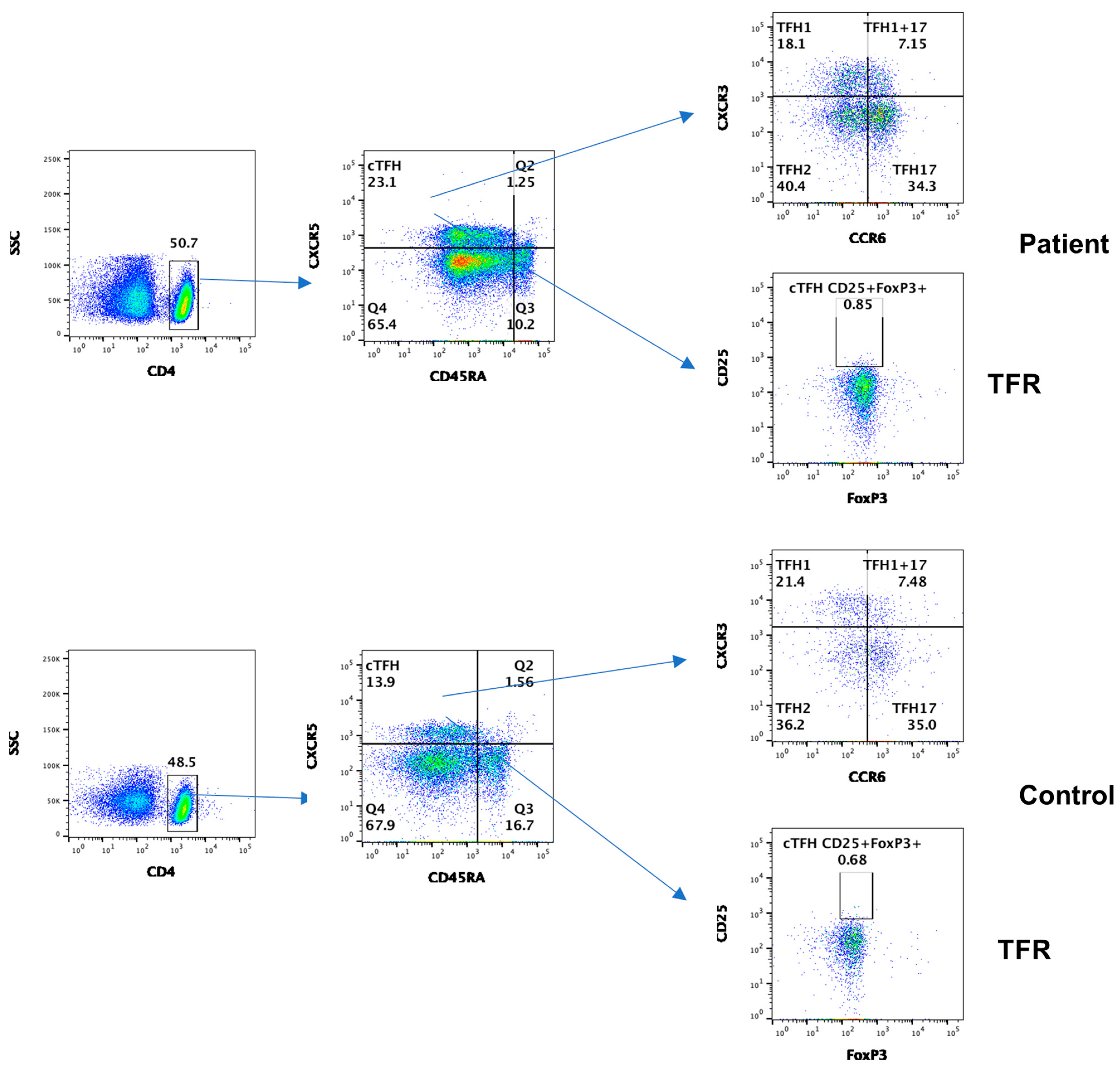
3.3. Subsets of Circulating T Follicular Helper Cells (cTFH)
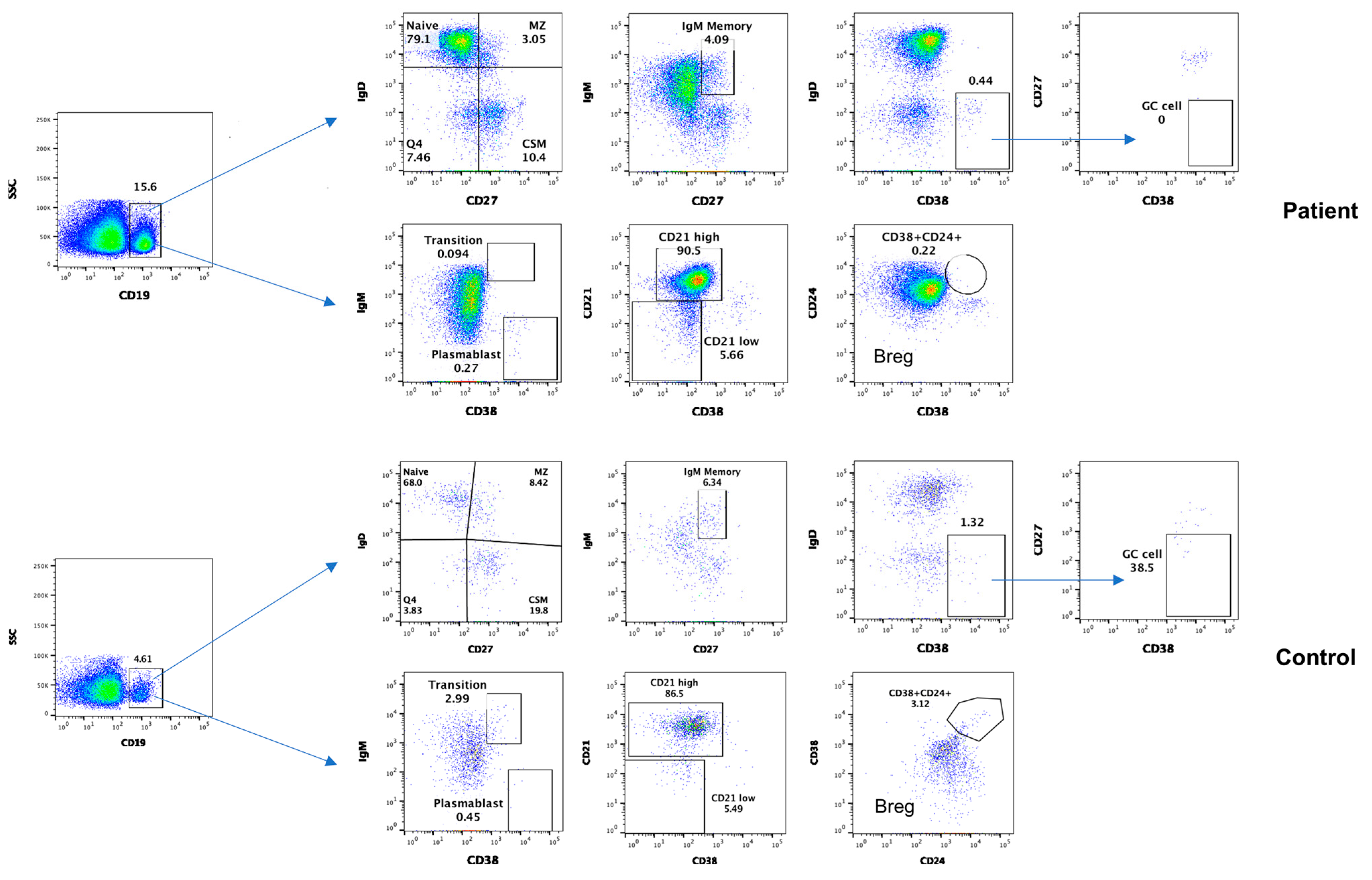
3.4. Subsets of B Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umehara, H.; Okazaki, K.; Kawa, S.; Takahashi, H.; Goto, H.; Matsui, S.; Ishizaka, N.; Akamizu, T.; Sato, Y.; Kawano, M.; et al. The 2020 revised comprehensive diagnostic (RCD) criteria for IgG4-RD. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawa, S.; Ota, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Horiuchi, A.; Hamano, H.; Ochi, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Tokutake, Y.; Katsuyama, Y.; Saito, S.; et al. DRB10405-DQB10404 haplotype is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in the Japanese population. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, T.; Ota, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Katsuyama, Y.; Ichijo, T.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K. Association of autoimmune pancreatitis with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients. Hepatol. Res. 2008, 38, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Yamashita, K.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Shiokawa, M.; Uza, N.; Kodama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Okazaki, K.; Chiba, T. Toll-like receptor activation in basophils contributes to the development of IgG4-related disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, E.L.; Chapman, R.W. IgG4-related hepatobiliary disease: An overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löhr, J.-M.; Vujasinovic, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Stone, J.H.; Beuers, U. IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H. IgG4-related digestive diseases: Diagnosis and treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1278332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Takata, K.; Ohno, K.; Iwaki, N.; Orita, Y.; Goto, N.; Hida, A.I.; Iwamoto, T.; Asano, N.; et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of IgG4-related skin disease. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamada, K.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Saeki, T.; Yagi, K.; Ito, N.; Kakuchi, Y.; Yamagishi, M.; Takehara, K.; Nakanuma, Y.; Kawano, M. Investigations of IgG4-related disease involving the skin. Mod. Rheumatol. 2013, 23, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerji, R.; Smoller, B.R. Immunoglobulin-G4—related skin disease. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Nakayamada, S.; Zhao, J. Correlation of T follicular helper cells and plasmablasts with the development of organ involvement in patients with IgG4-related disease. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, W.; Yang, H. Aberrant expansion and function of follicular helper T cell subsets in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 70, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M.; Suzuki, K.; Yamaoka, K.; Yasuoka, H.; Takeshita, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kondo, H.; Kassai, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Morita, R.; et al. Number of circulating follicular helper 2 T cells correlates with IgG4 and interleukin-4 levels and plasmablast numbers in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Lipsky, P.E. Circulating plasmablasts/plasma cells: A potential biomarker for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lighaam, L.C.; Vermeulen, E.; Bleker, T.D.; Meijlink, K.J.; Aalberse, R.C.; Barnes, E.; Culver, E.L.; Van Ham, S.M.; Rispens, T. Phenotypic differences between IgG4+ and IgG1+ B cells point to distinct regulation of the IgG4 response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 267–270.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Su, H.; Agrawal, S. Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in 2 Men. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 183, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallusto, F.; Lenig, D.; Förster, R.; Lipp, M.; Lanzavecchia, A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature 1999, 401, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uneo, H. Human circulating T follicular helper cell subsets in health and disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 36 (Suppl. S1), 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, R.; Schmitt, N.; Bentebibel, S.-E.; Ranganathan, R.; Bourdery, L.; Zurawski, G.; Foucat, E.; Dullaers, M.; Oh, S.; Sabzghabaei, N.; et al. Human blood CXCR5+CD4+ T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011, 34, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y.-C. T follicular helper cells, T follicular regulatory cells and autoimmunity. Int. Immunol. 2016, 28, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, H.; Kawa, S.; Horiuchi, A.; Unno, H.; Furuya, N.; Akamatsu, T.; Fukushima, M.; Nikaido, T.; Nakayama, K.; Usuda, N.; et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Tabeya, T.; Suzuki, C.; Naishiro, Y.; Shinomura, Y.; Imai, K. The immunobiology and clinical characteristics of IgG4 related diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.H.; Khosroshahi, A.; Deshpande, V.; Chan, J.K.C.; Heathcote, J.G.; Aalberse, R.; Azumi, A.; Bloch, D.B.; Brugge, W.R.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, H.; Arakura, N.; Muraki, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Kiyosawa, K.; Kawa, S. Prevalence and distribution of extrapancreatic lesions complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Tazuma, S.; Okazaki, K.; Tsubouchi, H.; Inui, K.; Takikawa, H. Nationwide survey for primary sclerosing cholangitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis in Japan. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sci. 2013, 21, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazale, A.; Chari, S.T.; Zhang, L.; Smyrk, T.C.; Takahashi, N.; Levy, M.J.; Topazian, M.D.; Clain, J.E.; Pearson, R.K.; Petersen, B.T.; et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: Clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuchi, Y.; Yamada, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Ito, N.; Yagi, K.; Matsumura, M.; Yamagishi, M.; Umehara, H.; Zen, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. IgG4-related skin lesions in a patient with IgG4-related chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Kojima, M.; Takata, K.; Morito, T.; Asaoku, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Mizobuchi, K.; Fujihara, M.; Kuraoka, K.; Nakai, T.; et al. Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: A clinical and pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman’s disease. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koneczny, I. A New Classification System for IgG4 Autoantibodies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoo, H.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S. Clonally expanded cytotoxic CD4+ T cells and the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmunity 2017, 50, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.S.; Maehara, T.; Deshpande, V.; Della-Torre, E.; Wallace, Z.S.; Kulikova, M.; Drijvers, J.M.; Daccache, J.; Carruthers, M.N.; et al. Clonal expansion of CD4(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Miyara, M.; Costantino, C.M.; Hafler, D.A. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, H.; Uchida, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Yazumi, S.; Matsushita, M.; Takaoka, M.; Okazaki, K. Circulating naïve and CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 36, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Su, H.; Agrawal, S. CD8 Treg cells inhibit B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin production. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Demirdag, Y.; Gupta, A.A. Members of the immunoregulatory lymphocyte club in common variable immunodeficien-cy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 864307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumie, I.; Ryuta, K.; Motohisa, Y.; Kenichi, T.; Hiromi, T. IL-10+ T follicular regulatory cells are associated with the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 207, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, C.; Blair, P.A. Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity: Developments and controversies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Patient | Reference Ranges |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute lymphocyte counts | 3774 | 900–3300 |
| HepBs IgG antibodies | Positive | Negative |
| HepC antibodies | Negative | Negative |
| Autoantibodies: | ||
| ANA | Negative | Negative < 1:40 |
| ANCA | Negative | Negative |
| SSA | Negative | Negative |
| SSB | Negative | Negative |
| Serum Immunoglobulins (mg/dL) | ||
| IgA | 106 | 68–378 |
| IgM | 45 | 37–318 |
| IgG | 728 | 610–1616 |
| IgG1 | 247 | 239–1083 |
| IgG2 | 34 | 148–548 |
| IgG3 | 16 | 27–134 |
| IgG4 | 448 (50 #) | 5–125 |
| Specific antibodies | ||
| Strep. Pneumoniae (Protected titers > 1.3 µg/mL) | ||
| 20/23 | 17–21/23 | |
| Isohemagglutinins | 1:8 * | 1:16–1:64 |
| Lymphocyte subsets% (numbers) | ||
| CD3+ T cells | 61 (1159) | 62–84 (619–1847) |
| CD4+ T cells | 47 (895) | 31–61 (338–1194) |
| CD8+ T cells | 14 (66) | 10–38 (85–729) |
| CD19+ B cells | 36 (684) ** | 5–26 (51–473) |
| CD3−CD56+CD16+ NK | 2 (38) | 1–17 (12–349) |
| Interleukin-6 | normal | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, Y.L.; Agrawal, S.; Wang, B.; Gupta, S. IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) with Unique Combined Generalized Skin Rashes and Biliary Tract Manifestation: A Comprehensive Immunological Analysis. Dermatopathology 2024, 11, 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030023
Jung YL, Agrawal S, Wang B, Gupta S. IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) with Unique Combined Generalized Skin Rashes and Biliary Tract Manifestation: A Comprehensive Immunological Analysis. Dermatopathology. 2024; 11(3):218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ye La, Sudhanshu Agrawal, Beverly Wang, and Sudhir Gupta. 2024. "IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) with Unique Combined Generalized Skin Rashes and Biliary Tract Manifestation: A Comprehensive Immunological Analysis" Dermatopathology 11, no. 3: 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030023
APA StyleJung, Y. L., Agrawal, S., Wang, B., & Gupta, S. (2024). IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) with Unique Combined Generalized Skin Rashes and Biliary Tract Manifestation: A Comprehensive Immunological Analysis. Dermatopathology, 11(3), 218-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030023







