Mass Mortality of Shallow-Water Temperate Corals in Marine Protected Areas of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean)
Abstract
1. Introduction
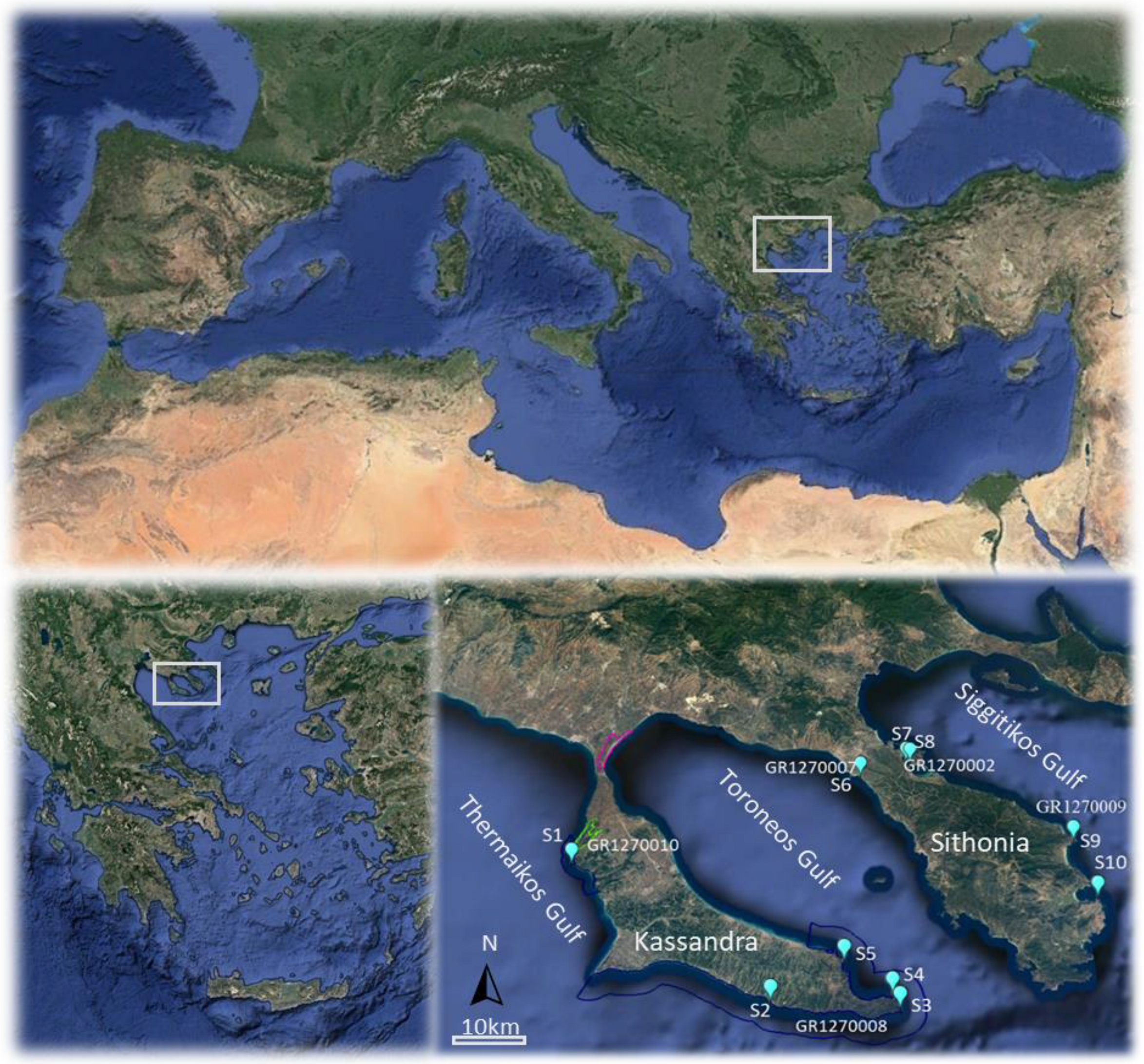
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
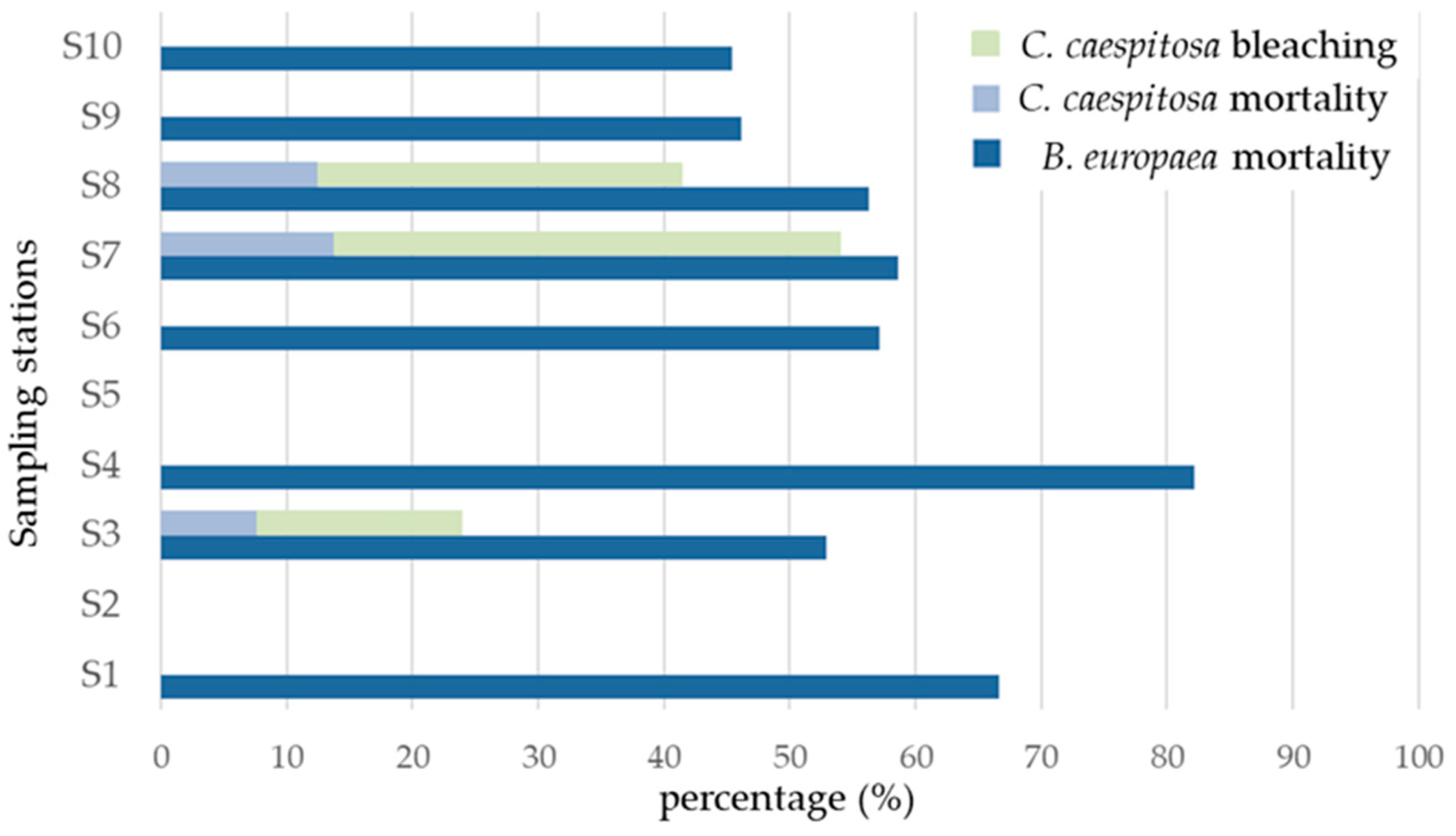
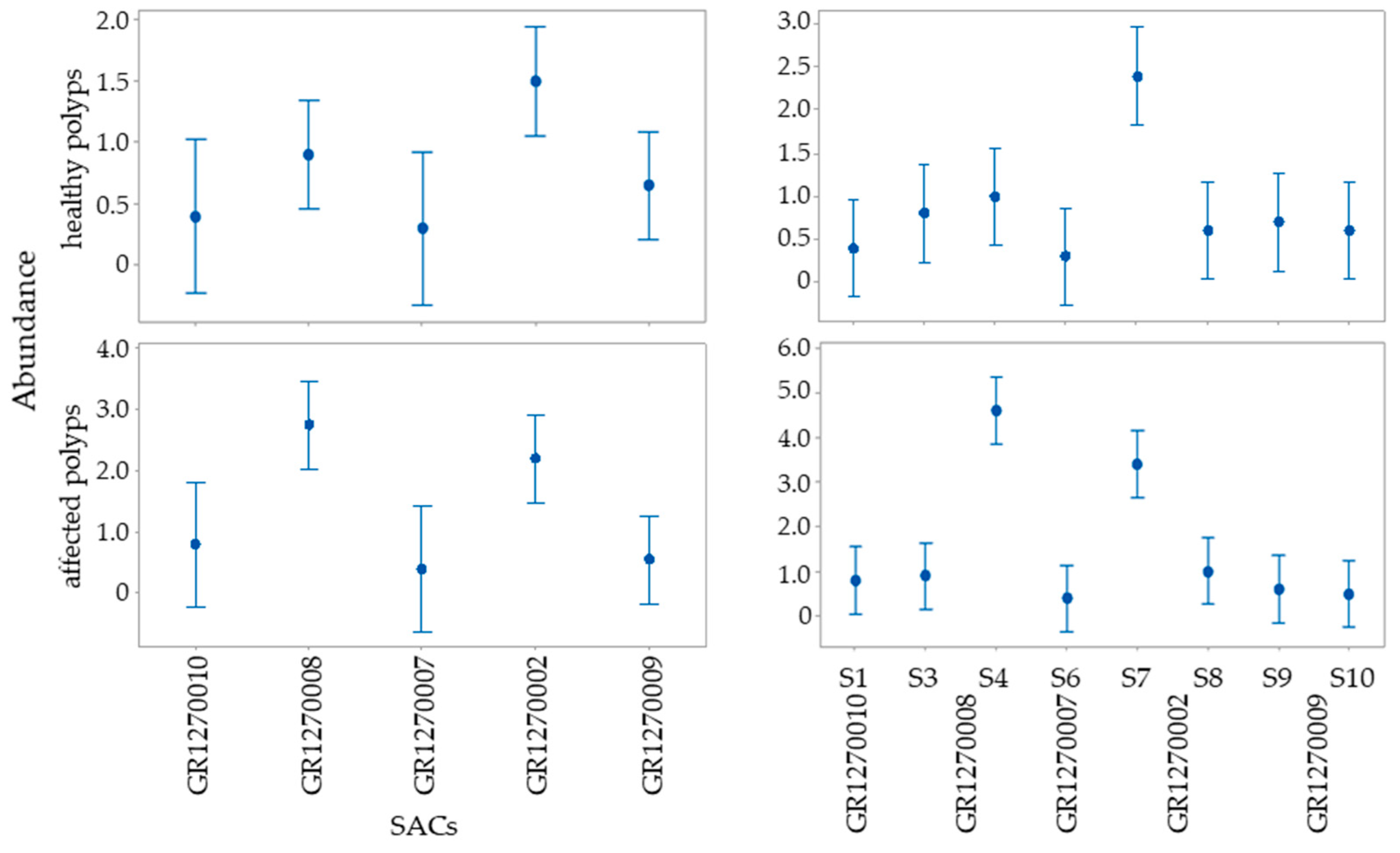
3.1. Balanophyllia europaea
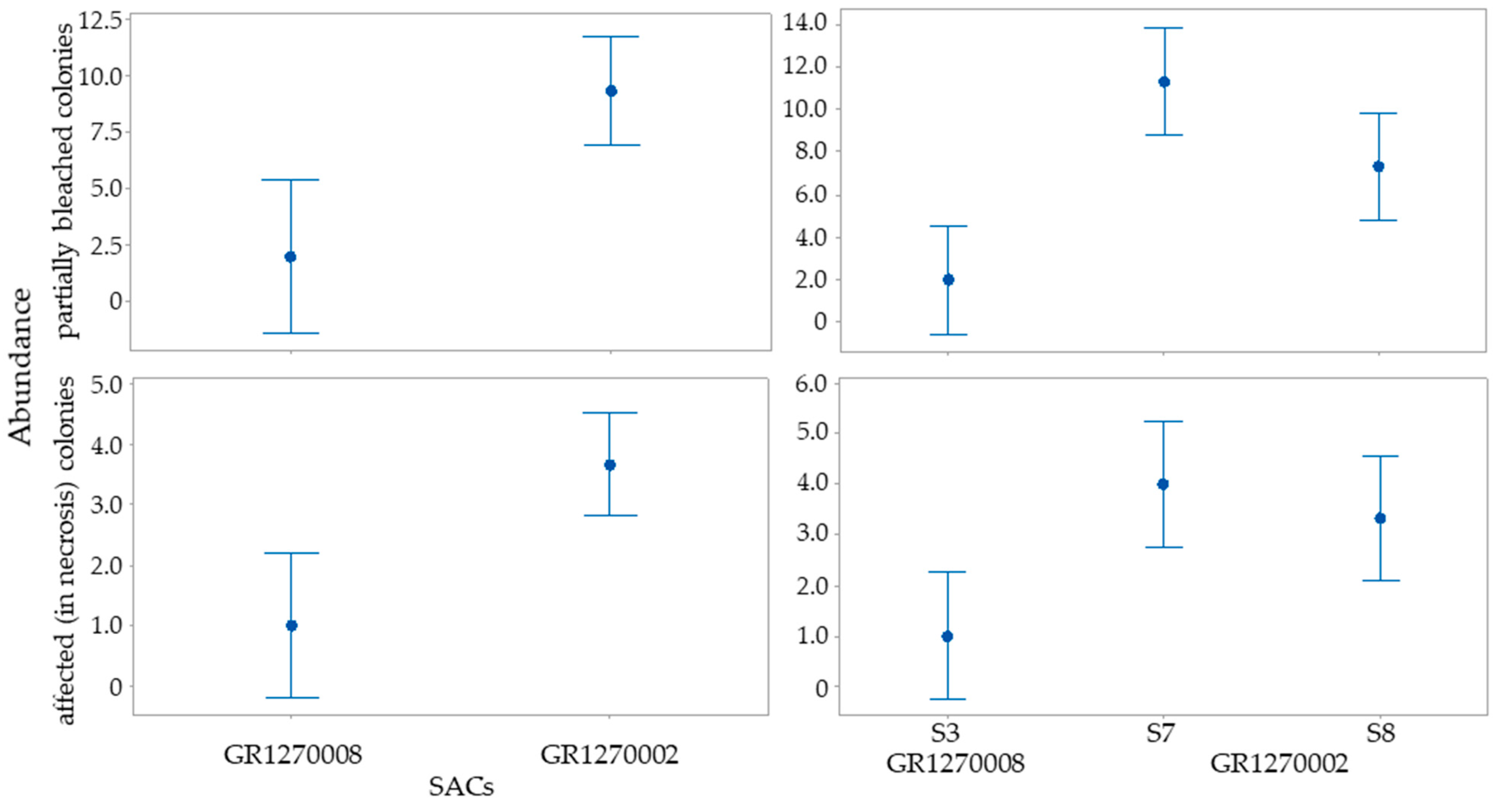
3.2. Cladocora caespitosa
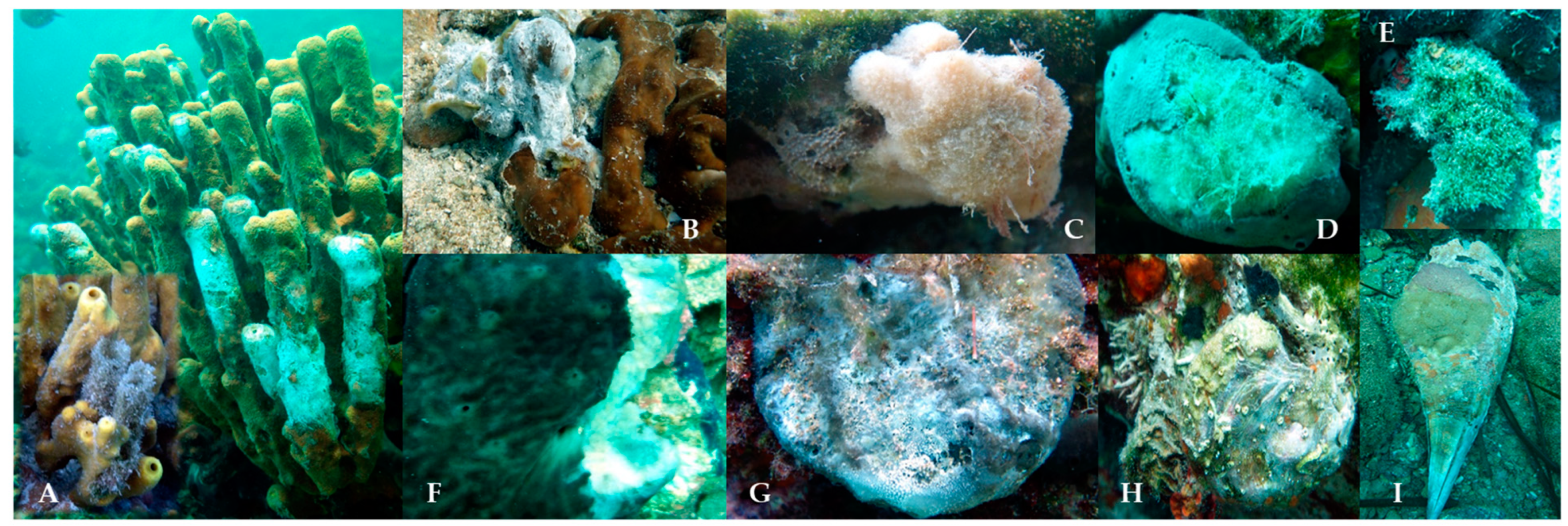
3.3. Various Other Affected Sessile Invertebrates
3.4. Seawater Temperature, pH, and Dissolved Oxygen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Lam, V.W.Y.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Kearney, K.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Projecting global marine biodiversity impacts under climate change scenarios. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, P.G.; Steger, J.; Bošnjak, M.; Dunne, B.; Guifarro, Z.; Turapova, E.; Hua, Q.; Kaufman, D.S.; Rilov, G.; Zuschin, M. Native biodiversity collapse in the eastern Mediterranean. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20202469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J.; Tsai, P.; Wong, P.S.; Cheung, A.K.L.; Basher, Z.; Chaudhary, C. Marine biogeographic realms and species endemicity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF. The Climate Change Effect in the Mediterranean. Six Stories from an Overheating Sea; WWF Mediterranean; Marine Initiative: Rome, Italy, 2021; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Global sea warming and “tropicalization” of the Mediterranean Sea: Biogeographic and ecological aspects. Biogeographia 2003, 24, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N. Biodiversity issues for the forthcoming tropical Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verges, A.; Steinberg, P.D.; Hay, M.E.; Poore, A.G.B.; Campbell, A.H.; Ballesteros, E.; Heck Jr, K.L.; Booth, D.J.; Coleman, M.A.; Feary, D.A.; et al. The tropicalization of temperate marine ecosystems: Climate-mediated changes in herbivory and community phase shifts. Proc. R. Soc. B 2014, 281, 20140846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, O.; Guy-Haim, T.; Yeruham, E.; Silverman, J.; Rilov, G. Tropicalization may invert trophic state and carbon budget of shallow temperate rocky reefs. J. Ecol. 2020, 108, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juza, M.; Fernández-Mora, A.; Tintoré, J. Sub-regional marine heat waves in the Mediterranean Sea from observations: Long-term surface changes, sub-surface and coastal responses. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 785771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androulidakis, Y.; Krestenitis, I. Sea Surface Temperature Variability and Marine Heat Waves over the Aegean, Ionian, and Cretan Seas from 2008–2021. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bava, S.; Morganti, C.; Morri, C.; Picco, P.; Sara, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; et al. A catastrophic mass mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (North-western Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol. Let. 2000, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, E.; Uriz, M.J.; Garrabou, J.; Ballesteros, E. Sponge mass mortalities in a warming Mediterranean Sea: Are cyanobacteria-harboring species worse off? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonne, P.; Ciglianos, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: Effects of the 2003 heat wave. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivetti, I.; Fraschetti, S.; Lionello, P.; Zambianchi, E.; Boero, F. Global warming and mass mortalities of benthic invertebrates in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Turicchia, E.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; et al. Marine heatwaves drive recurrent mass mortalities in the Mediterranean Se. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kružić, P.; Lipej, L.; Mavrič, B.; Rodić, P. Impact of bleaching on the coral Cladocora caespitosa in the eastern Adriatic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 509, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kružić, P.; Rodić, P.; Popijač, A.; Sertić, M. Impacts of temperature anomalies on mortality of benthic organisms in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 1190–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisanti, L.; de Sabata, E.; Visconti, G.; Chemello, R. Towards a local mass mortality of the Mediterranean orange coral Astroides calycularis (Pallas, 1766) in the Pelagie Islands marine protected area (Italy). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2022, 32, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, T.; Garrabou, J.; Sartoretto, S.; Harmelin, J.G.; Francour, P.; Vacelet, J. Massive mortality of marine invertebrates: An unprecedent event in northwestern Mediterranean. C. R. Acad. Sci. III 2000, 323, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodolpho-Metalpa, R.; Bianchi, C.N.; Peirano, A.; Morri, C. Tissue necrosis and mortality of the temperate coral Cladocora caespitosa. Ital. J. Zool. 2005, 72, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kružić, P.; Popijač, A. Mass mortality events of the coral Balanophyllia europaea (Scleractinia, Dendrophylliidae) in the Mljet National Park (eastern Adriatic Sea) caused by sea temperature anomalies. Coral Reefs 2015, 34, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gras, D.; Linares, C.; López-Sanz, A.; Amate, R.; Ledoux, J.B.; Bensoussan, N.; Drap, P.; Bianchimani, O.; Marschal, C.; Torrents, O.; et al. Population collapse of habitat-forming species in the Mediterranean: A long-term study of gorgonian populations affected by recurrent marine heatwaves. Proc. Royal Soc. B 2021, 288, 20212384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Nikolaidis, A.; Evriviadou, M.; Lange, M. Mortality of the scleractinian coral Cladocora caespitosa during a warming event in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus). Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Pantelidou, M.; Skoularikou, M.; Chintiroglou, C. Mass mortality event of the tooth coral Balanophyllia europaea in Natura 2000 sites of Chalkidiki peninsula (north Aegean Sea, eastern Mediterranean). In Proceedings of the Marine and Inland Waters Research Symposium, Porto Heli, Greece, 16–19 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zibrowius, H. Les Scléractiniaires de la Méditerranée et de l’Atlantique nord-oriental; Mémoires de l’Institute Océanographique: Monte Carlo, Monaco, 1980; 284p. [Google Scholar]
- Goffredo, S.; Caroselli, E.; Mattioli, G.; Pignotti, E.; Zaccanti, F. Variation in biometry and population density of solitary corals with solar radiation and sea surface temperature in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, S.; Caroselli, E.; Mattioli, G.; Pignotti, E.; Zaccanti, F. Relationships between growth, population structure and sea surface temperature in the temperate solitary coral Balanophyllia europaea (Scleractinia, Dendrophylliidae). Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Numa, C.; Bo, M.; Orejas, C.; Garrabou, J.; Cerrano, C.; Kružić, P.; Antoniadou, C.; Aguilar, R.; Linares, C.; et al. Overview of the Conservation Status of Mediterranean Anthozoans; IUCN: Malaga, Spain, 2017; x + 73p. [Google Scholar]
- Chefaoui, R.M.; Casado_Amezúa, P.; Templado, J. Environmental drivers of distribution and reef development of the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Linares, C. Living evidence of a fossil survival strategy raises hope for warming-affected corals. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Bensoussan, N.; Linares, C. Long-Term Responses of the Endemic Reef-Builder Cladocora caespitosa to Mediterranean warming. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.K.; Cebrian, E.; Verdura, J.; Ballesteros, E. A new Cladocora caespitosa population with unique ecological traits. Medit. Mar. Sci. 2017, 18, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, C.; Peirano, A.; Bianchi, C.N.; Sassarini, M. Present-day bioconstructions of the hard coral, Cladocora caespitosa (L.) (Anthozoa, Scleractinia), in the Eastern Ligurian Sea (NW Mediterranean). Biol. Mar. Medit. 1994, 1, 371–372. [Google Scholar]
- Peirano, A.; Morri, C.; Mastronuzzi, G.; Bianchi, C.N. The coral Cladocora caespitosa (Anthozoa, Scleractinia) as a bioherm builder in the Mediterranean Sea. Mem. Descr. Carta Geol. d’It 1994, 52, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Morri, C.; Peirano, A.; Bianchi, N.C. Is the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa an indicator of climatic change? Arch. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2001, 22, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadou, C.; Chintiroglou, C. Biodiversity of zoobenthic hard-substrate sublittoral communities in the Eastern Mediterranean (North Aegean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Voultsiadou, E.; Chintiroglou, C. Sublittoral megabenthos along cliffs of different profile (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). Belg. J. Zool. 2006, 136, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Chintiroglou, H.; Dounas, C. Benthic bionomy of the North Aegean Sea. III. A comparison of the macrobenthic animal assemblages associated with seven sponge species. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1985, 26, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Koukouras, A.; Russo, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Arvanitidis, C.; Stefanidou, D. Macrofauna associated with sponges of different morphology. PSZNI Mar. Biol. 1996, 17, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouras, A.; Kuhlmann, D.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E.; Vafidis, D.; Dounas, C.; Chintiroglou, C. The macrofaunal assemblage associated with the scleractinian coral Cladocora caespitosa (L.) in the Aegean Sea. Ann. Inst. Oceanogr. 1998, 72, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadou, C.; Chintiroglou, C. Biodiversity of zoobenthos associated with a Cladocora caespitosa bank in the North Aegean Sea. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Médit 2010, 39, 432. [Google Scholar]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Pyrounaki, M.M.; Chintiroglou, C. The habitat engineering tunicate Microcosmus sabatieri Roule, 1885 and its associated peracarid epifauna. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 74, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Kyrodimou, M.; Antoniadou, C.; Vafidis, D. Sponge epibionts on ecosystem-engineering ascidians: The case of Microcosmus sabatieri. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as ecosystem engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.F.; Bates, A.E.; Cacciapaglia, C.; Pike, E.P.; Amstrup, S.C.; van Hooidonk, R.; Henson, S.A.; Aronson, R.B. Climate change threatens the world’s marine protected areas. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, S.M.; Archer, S.K.; Friesen, S.K.; Hunter, K. A global assessment of climate change adaptation in marine protected area management plans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 711085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafidis, D.; Koukouras, A.; Voultsiadou-Koukoura, E. Actiniaria, Corallimorpharia, and Scleractinia (Hexacorallia, Anthozoa) of the Aegean Sea, with a checklist of the eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea species. Isr. J. Zool. 1997, 43, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P.; Schuttenberg, H. A Reef Manager’s Guide to Coral Bleaching; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, Australia, 2006; 163p.
- Underwood, A.J. Experiments in Ecology. Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; 504p. [Google Scholar]
- Kružić, P. Polyp expulsion of the coral Cladocora caespitosa (Anthozoa, Scleractinia) in extreme sea temperature conditions. Nat. Croat. 2007, 16, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gambi, M.C.; Sorvino, P.; Tiberti, L.; Gaglioti, M.; Teixido, N. Mortality events of benthic organisms along the coast of Ischia in summer 2017. Biol. Mar. Mediter. 2018, 25, 212–213. [Google Scholar]
- Mačić, V.; Dordević, N.; Petović, P. First monitoring of Cladocora caespitosa (Anthozoa, Scleractinia) in the Boka Kotorska Bay (Montenegro). Stud. Mar. 2019, 32, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kružić, P.; Sršen, P.; Benković, L. The impact of seawater temperature on coral growth parameters of the colonial coral Cladocora caespitosa (Anthozoa, Scleractinia) in the eastern Adriatic Sea. Facies 2012, 58, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurensen, S.O.; Topcu, N.E.; Oztürk, B. Distribution and mortality of the Mediterranean stony coral (Cladocora caespitosa Linnaeus, 1767) around Gokceada Island (Northern Aegean Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rodolfo-Metalpa, R.; Richard, C.; Allemand, D.; Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Ferrier-Pages, C. Response of zooxanthellae in symbiosis with the Mediterranean corals Cladocora caespitosa and Oculina patagonica to elevated temperatures. Mar. Biol. 2006, 150, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühlman, D. Preliminary report on Holocene submarine accumulations of Cladocora caespitosa (Linnaeus 1767) in the Mediterranean. Göttingen Arb. Geol. Paläontol. 1996, 2, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Voultsiadou, E.; Fryganiotis, C.; Porra, M.; Damianidis, P.; Chintiroglou, C. Diversity of Invertebrate Discards in Small and Medium Scale Aegean Sea Fisheries. Open Mar. Biol. J. 2011, 5, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganias, K.; Christidis, G.; Kompogianni, I.F.; Simeonidou, X.; Voultsiadou, E.; Antoniadou, C. Fishing for cuttlefish with traps and trammel nets: A comparative study in Thermaikos Gulf, Aegean Sea. Fish. Res. 2021, 234, 105783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalopoulou, K.; D’Alessandro, W.; Longo, M.; Pecoraino, G.; Calabrese, S. Shallow sea gas manifestations in the Aegean Sea (Greece) as narural analogs to study ocean acidification: First catalog and geochemical characterization. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 775247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.U.TH. Account and Assessment of the Marine Coastal Zone of Kassandra Peninsula (GR1270008 and GR1270010) within the Jurisdiction of Thermaikos Gulf Management Body; Technical Report, A.U.TH: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2022; pp. 1–115. [Google Scholar]
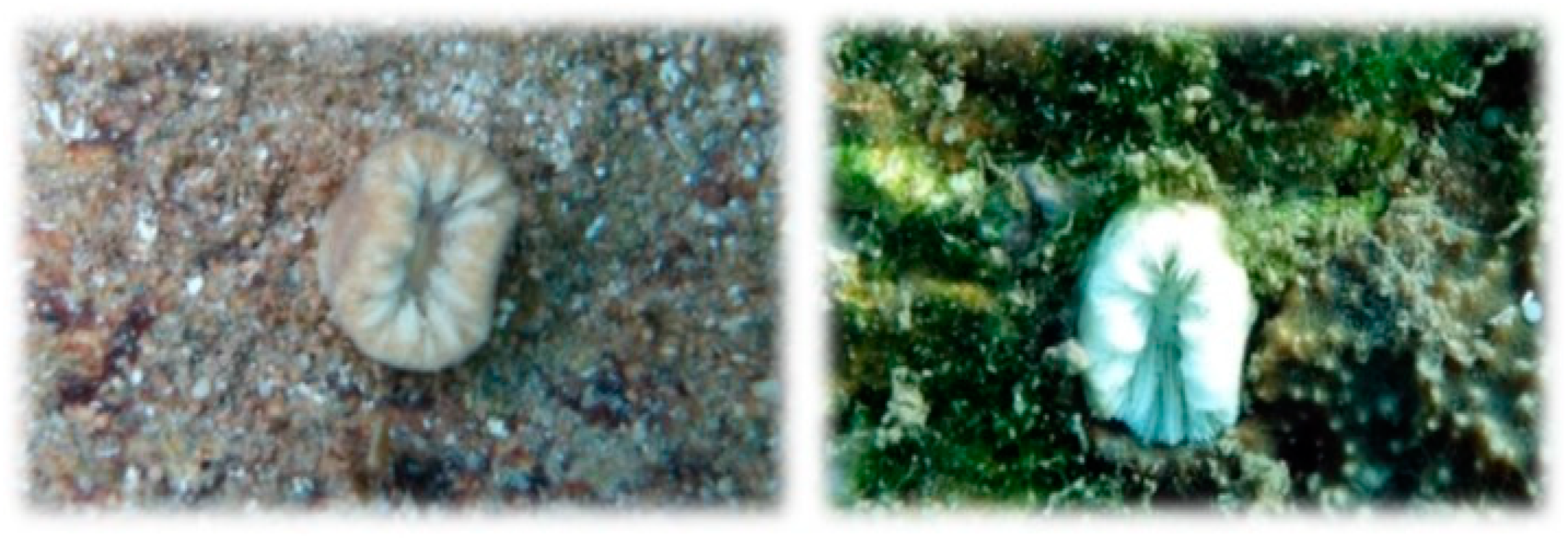
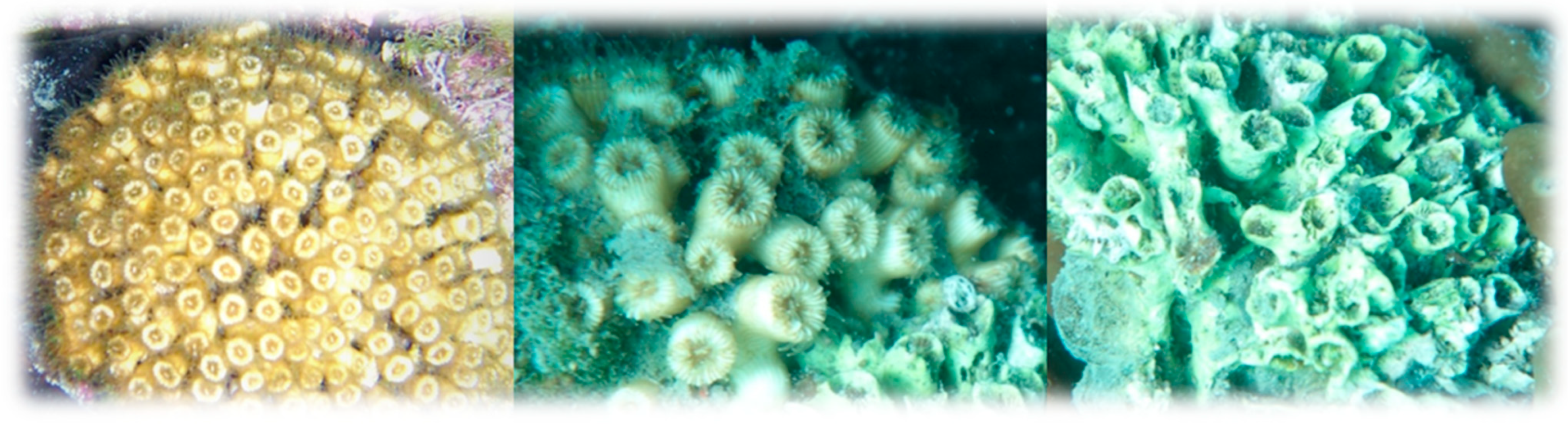


| Chalkidiki | Natura 2000 SAC | Station | Number of Polyps | Mortality (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Affected | ||||
| Kassandra | GR1270010 | S1 | 12 | 8 | 66.67 |
| GR1270008 | S2 | 0 | – | – | |
| S3 | 17 | 9 | 52.94 | ||
| S4 | 56 | 46 | 82.14 | ||
| S5 | 0 | – | – | ||
| S3–4 | 67.54 | ||||
| Sithonia | GR1270007 | S6 | 7 | 4 | 57.14 |
| GR1270002 | S7 | 58 | 34 | 58.62 | |
| S8 | 16 | 9 | 56.25 | ||
| S7–8 | 57.43 | ||||
| GR1270009 | S9 | 13 | 6 | 46.15 | |
| S10 | 11 | 5 | 45.45 | ||
| S9–10 | 45.80 | ||||
| Source of Variation | Abundance of B. europaea Polyps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Affected | ||||
| df | F | p | F | p | |
| SACs | 4 | 13.61 | <0.0001 | 7.21 | <0.0001 |
| Sampling stations (nested on SACs) | 7 | 23.21 | <0.0001 | 17.72 | <0.0001 |
| Chalkidiki | Natura 2000 SAC | Station | Number of Colonies | Partially Bleached | Mortality (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||||
| Kassandra | GR1270010 | S1 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| GR1270008 | S2 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| S3 | 13 | 10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15.38 | 7.69 | ||
| S4 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| S5 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Sithonia | GR1270007 | S6 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| GR1270002 | S7 | 29 | 13 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 37.93 | 13.79 | |
| S8 | 24 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 29.16 | 12.50 | ||
| S7–8 | 33.54 | 13.14 | ||||||||
| GR1270009 | S9 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| S10 | 0 | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Source of Variation | Abundance of C. caespitosa Colonies | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Partial Bleached | Affected | |||||
| df | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| SACs | 1 | 1.04 | 0.34 | 33.38 | <0.001 | 18.29 | <0.005 |
| Sampling stations (nested on SACs) | 2 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 7.45 | <0.034 | 0.86 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoniadou, C.; Pantelidou, M.; Skoularikou, M.; Chintiroglou, C.C. Mass Mortality of Shallow-Water Temperate Corals in Marine Protected Areas of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiology 2023, 2, 311-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology2020020
Antoniadou C, Pantelidou M, Skoularikou M, Chintiroglou CC. Mass Mortality of Shallow-Water Temperate Corals in Marine Protected Areas of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiology. 2023; 2(2):311-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoniadou, Chryssanthi, Martha Pantelidou, Maria Skoularikou, and Chariton Charles Chintiroglou. 2023. "Mass Mortality of Shallow-Water Temperate Corals in Marine Protected Areas of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean)" Hydrobiology 2, no. 2: 311-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology2020020
APA StyleAntoniadou, C., Pantelidou, M., Skoularikou, M., & Chintiroglou, C. C. (2023). Mass Mortality of Shallow-Water Temperate Corals in Marine Protected Areas of the North Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiology, 2(2), 311-325. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology2020020






