Neuroscientific Framework of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions for Mental Health Across Diverse Cultural Populations: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness, Delivery Methods, and Engagement
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Neuroscience–Culture–Cognition Interface
1.2. Global Mental Health Burden and Cultural Responsiveness
1.3. Treatment Delivery Innovation and Cultural Adaptation
1.4. Treatment Engagement and Cultural Acceptability
1.5. Current Evidence Base and Research Gaps
1.6. Study Rationale and Objectives
1.7. Research Questions
- RQ1. Overall Effectiveness Across Mental Health Conditions: What is the overall effectiveness of cognitive–behavioral interventions in improving mental health outcomes (depression, anxiety, PTSD, psychological distress, and well-being) across diverse cultural populations?
- RQ2. Delivery Methods and Treatment Formats: How do different delivery methods and treatment formats (internet-delivered, group vs. individual, brief vs. intensive, telehealth, mobile interventions) compare in effectiveness across diverse cultural populations?
- RQ3. Cultural Responsiveness and Population-Specific Outcomes: How do cognitive–behavioral interventions perform across different diverse cultural populations (ethnic minorities, immigrants, refugees, Indigenous peoples), and what cultural factors moderate treatment effectiveness?
- RQ4. Treatment Engagement and Neurocognitive Mechanisms: What factors influence treatment engagement, acceptability, and retention in CBT interventions among diverse cultural populations, and what neurocognitive mechanisms and moderators explain differential treatment responses?
1.8. Operational Definition: Neuroscientific Framework
- Level 1 (Primary—Direct Neurobiological Measurement): Directly measures neurobiological effects through neuroimaging (fMRI, EEG, PET), neurophysiology, or biomarkers (BDNF, cortisol, inflammatory markers) [level 1 is 13.8% of all studies (n = 13)]. This level includes empirical neuroscientific data as obtained from the studies included in this analysis.
- Level 2 (Secondary—Theoretically Grounded Design): Includes interventions that were specifically designed for the purpose of impacting neural mechanisms (e.g., engaging circuits between the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex; increasing neuroplasticity; modulating a particular neurotransmitter system) and have theoretical support grounded in neuroscientific theory, although they do not measure the nervous system directly in their study protocol. Although these studies do not directly assess the nervous system as part of their study protocols, they incorporate the rationale behind their neuroscientific theory into their intervention designs [level 2 studies are 25.5% of all studies (n = 24)].
- Level 3 (Interpretive—Framework Integration): Includes studies that did not collect data about the nervous system but interpret their findings through established neuroscientific theories derived from the cultural neuroscience literature. Because there is convergent evidence from separate neurobiological investigations that support behavioral/clinical findings reported by these studies they contribute to the understanding of those findings through neuroscientific lenses [these studies are 60.6% of all studies (n = 57)].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scope
2.2. Search Strategy
((“cognitive behavioral therapy” OR “CBT” OR “cognitive behavioural therapy” OR “cognitive therapy” OR “behavioral therapy” OR “behavioural therapy”) AND (“cultural*” OR “ethnic*” OR “diverse” OR “minority” OR “immigrant*” OR “refugee*” OR “indigenous” OR “multicultural” OR “cross-cultural” OR “Latino” OR “Hispanic” OR “Asian” OR “African” OR “Black” OR “Arab”) AND (“depression” OR “anxiety” OR “PTSD” OR “mental health” OR “psychological distress” OR “wellbeing” OR “well-being”) AND (“effectiveness” OR “efficacy” OR “outcome*” OR “treatment response” OR “intervention*” OR “therapy” OR “randomized” OR “controlled trial”))
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Original studies examining cognitive–behavioral therapy interventions for mental health conditions;
- Research involving participants from diverse cultural, ethnic, or racial backgrounds (ethnic minorities, immigrants, refugees, Indigenous peoples, or explicitly multicultural samples);
- Studies investigating mental health outcomes including depression, anxiety, PTSD, psychological distress, or general well-being;
- Articles exploring treatment effectiveness, delivery methods, cultural adaptation, or engagement factors;
- Randomized controlled trials, quasi-experimental studies, and high-quality observational studies with comparison groups;
- Studies utilizing various CBT delivery modalities (face-to-face, internet-delivered, group, individual, brief, intensive);
- Peer-reviewed articles published in English between 2014–2024;
- Studies with sufficient sample sizes (n ≥ 20) and adequate methodological detail.
- Studies with insufficient methodological detail to assess quality or reproducibility;
- Duplicate publications or studies with substantially overlapping datasets;
- Research focusing solely on provider training or organizational interventions without client outcomes.
2.4. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.5. Analytical Search Process
- 87 articles excluded for insufficient cultural diversity in study populations;
- 64 articles excluded for lacking clear CBT intervention components;
- 43 articles excluded for inadequate methodology or sample sizes;
- 28 articles excluded for focusing on provider training rather than client outcomes;
- 12 articles excluded for overlapping datasets with included studies;
- 5 articles excluded for lacking appropriate comparison groups.
2.6. Data Synthesis
- RQ1 (Effectiveness): The studies were organized by the specific mental health condition being studied and the specific cultural population being studied to determine whether effectiveness, effect sizes, and clinical significance varied across the different CBT interventions.
- RQ2 (Delivery Methods): The studies were organized by the modality through which they were delivered (e.g., internet-based, group-based or individual-based; brief or intensive) to determine how the effectiveness of CBT and the ways in which it was implemented varied among the different cultural populations.
- RQ3 (Cultural Populations): The studies were organized by the population characteristics (e.g., age, gender, culture) to determine whether the effectiveness of CBT varied based on the population characteristics of the participants in each study and to identify cultural adaptation strategies and moderator variables.
- RQ4 (Engagement and Mechanisms): The studies that examined engagement factors, acceptability, and retention rates and possible neurocognitive mechanisms that may explain the effectiveness of CBT were organized together to understand the factors that facilitated or hindered successful treatment outcomes.
2.7. Software Tools
2.8. Study Classification and Methodological Overview
3. Results
3.1. [RQ1]: What Is the Overall Effectiveness of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions in Improving Mental Health Outcomes (Depression, Anxiety, PTSD, Psychological Distress, and Well-Being) Across Diverse Cultural Populations?
3.1.1. Depression Treatment Outcomes
3.1.2. Anxiety Disorder Interventions
3.1.3. Post-Trauma Interventions (PTSD)
3.1.4. Psychological Distress and Well-Being Enhancement
3.1.5. Delivery Method Optimization
3.1.6. Sustained Treatment Effects and Long-Term Outcomes
- Retention/Engagement: Culturally adapted CBT interventions reported average retention rates of 84% (range: 76–100%), whereas standard CBT interventions reported average retention rates of 58% (range: 45–72%), which represented a statistically significant difference of 26 percentage points (chi-square tests; p < 0.001) across studies. The advantage of culturally adapted CBT in terms of retaining clients appeared early, as culturally adapted interventions demonstrated 31% fewer dropouts by session four, indicating that culturally aligned therapy increases client engagement and reduces early attrition.
- Symptom Reduction: Average pre–post effect sizes for primary outcomes (i.e., symptoms of depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, etc.) indicated a mean advantage of d = 0.34 (95% CI = 0.22–0.46) for culturally adapted CBT. Although both types of interventions achieved clinically significant reductions in symptoms, the additional advantage of culturally adapting CBT was consistent across all studies. As an example, Naeem et al. (2015a, 2015b) reported that brief culturally adapted CBT produced symptom reductions similar to those produced by longer standard CBT in Pakistani populations, suggesting that culturally adapting CBT can improve both its efficiency and effectiveness.
- Maintenance of Gains at 12-Month Follow-Up: When available data (for eight of the 13 comparative studies) were examined, culturally adapted CBT interventions maintained gains better than did standard CBT, with 77% of culturally adapted CBT clients maintaining clinically significant reductions in symptoms at 12 months after treatment initiation, and 54% of clients treated with standard CBT. The difference in maintenance of gains between culturally adapted and standard CBT was statistically significant, representing a 23 percentage point difference.
- Satisfaction/Treatment Acceptability: Culturally adapted CBT interventions were rated higher in satisfaction ratings (average difference of 1.2 points on five-point rating scales; p < 0.01), and qualitative feedback from clients indicated that cultural adaptations made therapy more relevant to the client, decreased stigma associated with seeking help, and strengthened the therapeutic relationship.
3.1.7. Critical Success Factors and Mechanisms
3.1.8. Unexpected Findings and Emerging Patterns
3.1.9. Heterogeneity Analysis and Meta-Analytic Considerations
- Asian populations: d = 1.28 (vs. d = 1.32 with all studies);
- Latino/Hispanic populations: d = 1.14 (vs. d = 1.18 with all studies);
- African/Black populations: d = 1.19 (vs. d = 1.24 with all studies);
- Refugee populations: d = 0.94 (vs. d = 1.08 with all studies).
3.2. [RQ2] How Do Different Delivery Methods and Treatment Formats (Internet-Delivered, Group vs. Individual, Brief vs. Intensive, Telehealth, Mobile Interventions) Compare in Effectiveness Across Diverse Cultural Populations?
3.2.1. Group Versus Individual Delivery Formats
3.2.2. Technology-Enhanced Delivery Methods
- Development of multilingual interfaces that allowed for the use of audio to accommodate populations with varying levels of literacy;
- Use of culturally relevant images that did not contain potentially triggering content;
- Development of offline functionality to recognize and address inconsistencies in the availability of internet connectivity; and
- Implementation of privacy features to ensure the safety of individuals using the app who lived in close proximity to others and were therefore concerned about their confidentiality.
3.2.3. Text Messaging: A Study of Cultural Divergence
3.2.4. Brief Versus Intensive Interventions: Cultural Considerations
3.2.5. Telehealth and Remote Delivery Adaptations
- Group sessions conducted via video allowed for visual connection between all participants;
- Dedicated zones were established for participating family members to be displayed in the video;
- Structured time was allocated for social interaction prior to and/or after each session to allow for the informal interaction that typically occurs during face-to-face sessions;
- Cultural artifacts were visibly displayed in the background to create a sense of therapeutic ambiance.
3.2.6. Hybrid and Innovative Delivery Approaches
- Task shifting that was systematic and maintained high fidelity to the treatment model;
- Dual supervision that provided both clinical oversight and culturally relevant direction;
- Adaptive flexibility based on symptom severity and client preferences;
- Integrating traditional healing into evidence-based models.
3.2.7. Special Considerations for Vulnerable Subpopulations
3.2.8. Infrastructure and Accessibility Determinants
3.2.9. Treatment Engagement Patterns and Retention Strategies
- Social Accountability: Participants would feel accountable to their fellow group members.
- Shared Identity: Cultural similarity can create instant bonding between group members.
- Shame Reduction: When participants hear peers discuss their own struggles, they find it easier to open up about their own.
- Integrating Culture: Incorporation of culturally familiar practices increases comfort level in a new setting.
- Timing push notifications for high-vulnerability periods;
- Offering crisis resources during peak usage times;
- Creating peer support features for evening engagement;
- Adjusting content difficulty based on usage patterns.
3.2.10. Mechanisms of Action Across Delivery Methods
- Spanish-speaking participants used social pronouns at a rate of 2.3 times greater in their responses than did English-speaking participants;
- English-speaking participants utilized cognitive processing words at a rate of 1.8 times greater in their responses than did Spanish-speaking participants;
- Participants who spoke Spanish referenced family/community in approximately 45% of their responses;
- Participants who spoke English referenced individual goals in approximately 62% of their responses.
3.2.11. Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability Considerations
3.3. [RQ3] How Do Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions Perform Across Different Diverse Cultural Populations (Ethnic Minorities, Immigrants, Refugees, Indigenous Peoples), and What Cultural Factors Moderate Treatment Effectiveness?
3.3.1. Cultural Adaptation Strategies and Their Implementation
3.3.2. Population-Specific Outcomes and Cultural Moderators
3.3.3. Critical Moderating Factors
3.3.4. Comparative Effectiveness Analysis
3.3.5. Delivery Method Effectiveness by Cultural Context
3.3.6. Implementation Challenges and Solutions
3.3.7. Mechanisms of Change in Culturally Adapted Interventions
3.3.8. Sustainability and Long-Term Outcomes
- Cultural adaptations result in greater levels of engagement and retention in all populations studied;
- Group-based interventions that involve family and community are most beneficial to collectivist cultures;
- Refugees need culturally informed interventions that address both their psychological needs and practical needs;
- Indigenous populations may demonstrate the largest differential in outcomes due to cultural adaptations, although the literature is limited;
- LGBTQ+ populations may benefit from integrating minority stress frameworks into the standard components of Cognitive–Behavioral Therapy (CBT);
- Incorporating interventions into existing community structures increases the sustainability of treatment gains.
3.4. [RQ4] What Factors Influence Treatment Engagement, Acceptability, and Retention in CBT Interventions Among Diverse Cultural Populations, and What Neurocognitive Mechanisms and Moderators Explain Differential Treatment Responses?
3.4.1. Neural Pathways of Engagement and Acceptability
3.4.2. Neuroplastic Changes and Dose–Response Relationships
3.4.3. Mechanisms of Therapeutic Change
3.4.4. Technology-Enhanced Interventions and Digital Therapeutics
3.4.5. Clinical Implementation and Future Directions
3.4.6. Synthesis and Implications
4. Discussion
4.1. Principal Findings and Theoretical Implications
4.1.1. Reconceptualizing Cultural Adaptation Through a Neuroscientific Lens
- Large-scale cross-cultural neuroimaging studies comparing neural activation patterns during identical CBT components (e.g., cognitive restructuring, exposure, behavioral activation) across cultural groups matched for symptom severity and treatment response. Such studies should employ both task-based fMRI to identify acute activation differences and resting-state fMRI to assess baseline network connectivity differences. For example, comparing DLPFC activation during thought-challenging exercises in individualistic versus collectivistic samples would directly test whether cultural groups engage different neural circuits during the same therapeutic task.
- Mechanistic neurofeedback trials that use real-time fMRI or EEG to target culturally specific circuits identified in our framework. For instance, providing Asian participants with interoceptive awareness neurofeedback training targeting ACC-insula connectivity versus cognitive control neurofeedback targeting DLPFC activation would test whether culturally aligned neural targets enhance outcomes. Similarly, testing whether social brain network neurofeedback enhances outcomes for collectivistic populations would provide causal evidence for the importance of these circuits.
- Longitudinal neural change assessment throughout culturally adapted interventions using repeated neuroimaging at baseline, mid-treatment, post-treatment, and follow-up. This design would reveal whether cultural adaptations produce different trajectories of neuroplastic change compared to standard interventions, and whether these neural changes mediate clinical outcomes. Measuring structural changes (gray matter density, white matter integrity) alongside functional connectivity would provide comprehensive evidence of adaptation-induced neuroplasticity.
- Formal mediation analyses testing whether neural changes statistically explain the relationship between cultural adaptation and clinical outcomes. Using modern causal mediation methods with neuroimaging data would establish whether the proposed neural mechanisms truly account for the superior effectiveness of culturally adapted interventions or whether alternative explanations (enhanced therapeutic alliance, reduced stigma, improved engagement) better explain the findings.
- Cross-over designs where participants receive both culturally adapted and standard interventions (order counterbalanced) with neuroimaging assessment after each condition. This within-subject design would control for individual differences in neural architecture and directly test whether the same individuals show different patterns of neural engagement depending on cultural alignment of the intervention.
- Moderator analyses examining whether individual differences in neural architecture (independent of cultural group membership) predict differential response to culturally adapted versus standard interventions. For instance, testing whether individuals with naturally strong social brain network connectivity (regardless of cultural background) benefit more from group-based, communally oriented interventions would move beyond cultural stereotypes toward personalized neural profiles.
4.1.2. Differential Effectiveness Across Mental Health Conditions
4.1.3. Technology as a Cultural Bridge Rather than Barrier
4.2. Clinical and Practice Implications
4.2.1. Toward Precision Cultural Mental Health
4.2.2. Workforce Development and Training Imperatives
4.2.3. System-Level Implementation Strategies
4.3. Limitations of Current Evidence
4.3.1. Methodological Constraints
4.3.2. Measurement and Assessment Challenges
4.3.3. Generalizability and External Validity
4.4. Future Research Directions
4.4.1. Advancing Neuroscience-Informed Cultural Adaptation
4.4.2. Implementation Science and Real-World Effectiveness
4.4.3. Addressing Underserved Populations and Intersectionality
4.4.4. Technology-Enhanced Precision Approaches
4.4.5. Ethical Dimensions of Neuroscientific Research with Diverse Populations
4.5. Implications for Health Equity and Policy
4.5.1. Reframing Mental Health Disparities
4.5.2. Investment Priorities and Resource Allocation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Neuroanatomy & Brain Regions | |
| ACC | Anterior Cingulate Cortex |
| dACC | Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex |
| DLPFC | Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex |
| DMN | Default Mode Network |
| mPFC | Medial Prefrontal Cortex |
| OFC | Orbitofrontal Cortex |
| PFC | Prefrontal Cortex |
| TPJ | Temporoparietal Junction |
| VLPFC | Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex |
| Neuroimaging & Neuroscience Methods | |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| fMRI | Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| fNIRS | Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy |
| rtfMRI | Real-time functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| Neurobiology & Genetics | |
| 5-HTTLPR | Serotonin Transporter-Linked Polymorphic Region |
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| COMT | Catechol-O-Methyltransferase |
| FKBP5 | FK506 Binding Protein 5 |
| HPA | Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal |
| NR3C1 | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 3 Group C Member 1 |
| OXTR | Oxytocin Receptor |
| TSPO | Translocator Protein (18kDa) |
| Mental Health Conditions | |
| ADHD | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |
| MDD | Major Depressive Disorder |
| OCD | Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder |
| OSA | Obstructive Sleep Apnea |
| PTSD | Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder |
| Therapeutic Interventions & Treatments | |
| ACT | Acceptance and Commitment Therapy |
| ART | Antiretroviral Therapy |
| CA-CBT+ | Culturally Adapted CBT Plus Problem Management |
| CaCBT | Culturally Adapted CBT |
| CaCBTp | Culturally Adapted CBT for Psychosis |
| CBT | Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy |
| CBT-DAY | CBT for Depression in Autistic Youth |
| CBTI | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia |
| CETA | Common Elements Treatment Approach |
| MBCT | Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy |
| MBTR-R | Mindfulness-Based Trauma Recovery for Refugees |
| PAP | Positive Airway Pressure |
| SSRI | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor |
| Study Names & Interventions | |
| AFFIRM | Affirmative Cognitive Behavioral Group Therapy |
| DECIDE | Culturally responsive shared decision-making intervention |
| DISCOVER | CBT workshop intervention |
| ESTEEM | LGBQ-affirmative cognitive behavioral therapy intervention |
| RADD | Resilience Against Depression Disparities |
| ReTreat | Culturally adapted CBT group therapy protocol |
| ROSHNI-2 | Group psychological intervention study |
| Assessment & Measurement Tools | |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| SE-A | Sleep Efficiency (Actigraphy) |
| SE-D | Sleep Efficiency (Diary) |
| SOL-D | Sleep-Onset Latency (Diary) |
| WASO-D | Wake After Sleep Onset (Diary) |
References
- Acarturk, Z., Abuhamdeh, S., Jalal, B., Unaldi, N., Alyanak, B., Çetinkaya, M., Gulen, B., & Hinton, D. (2018). Culturally adapted transdiagnostic CBT for SSRI-resistant Turkish adolescents: A pilot study. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 88(2), 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A., & Berridge, C. (2014). Qualitative feedback from a text messaging intervention for depression: Benefits, drawbacks, and cultural differences. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 2(4), e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, A. A., Sanchez-Gonzalez, M., & Junquera, P. (2023). Understanding and addressing mental health stigma across cultures for improving psychiatric care: A narrative review. Cureus, 15(5), e39549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizik-Reebs, A., Amir, I., Yuval, K., Hadash, Y., & Bernstein, A. (2022). Candidate mechanisms of action of mindfulness-based trauma recovery for refugees (MBTR-R): Self-compassion and self-criticism. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 90(6), 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegría, M., Nakash, O., Johnson, K., Ault-Brutus, A., Carson, N., Fillbrunn, M., Wang, Y., Cheng, A., Harris, T., Polo, A., Lincoln, A., Freeman, E., Bostdorf, B., Rosenbaum, M., Epelbaum, C., LaRoche, M., Okpokwasili-Johnson, E., Carrasco, M., & Shrout, P. E. (2018). Effectiveness of the DECIDE interventions on shared decision making and perceived quality of care in behavioral health with multicultural patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry, 75(4), 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algumaei, A., Yaacob, N. M., Doheir, M., Al-Andoli, M. N., & Algumaie, M. (2025). Symmetric therapeutic frameworks and ethical dimensions in AI-based mental health chatbots (2020–2025): A systematic review of design patterns, cultural balance, and structural symmetry. Symmetry, 17(7), 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sawafi, A., Al Yahyaei, A., Al Azri, N. H., Al Sabei, S. D., Al Maamari, A., Al Battashi, H., Al Ismaili, S. R., & Al Maskari, J. K. (2025). Bridging the leadership gap: Developing a culturally adapted leadership program for healthcare professionals in Oman. Journal of Healthcare Leadership, 17, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J. C., Waitz-Kudla, S., Brydon, C., Crosby, E., & Witte, T. K. (2022). Culturally responsive scalable mental health interventions: A call to action. Translational Issues in Psychological Science, 8(3), 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q., Wang, K., Sun, F., & Zhang, A. (2020). The effectiveness of modified, group-based CBT for dementia worry among Chinese elders. Journal of Affective Disorders, 274, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, A., Langberg, J., Eddy, L., Silvia, P., & Labban, J. (2021). A randomized controlled trial examining CBT for college students with ADHD. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 89(1), 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auva’a-Alatimu, T. (2023). Complementing cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for Pacific peoples in New Zealand. Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology, 17, 18344909231168179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartucz, M. B., David, D. O., & Matu, S. A. (2022). Cognitive vulnerabilities and depression: A culture-moderated meta-analysis. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 46(5), 897–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, C. A., Traeger, L., Trinh, N. T., Chang, T. E., Brill, C. D., Hails, K., Hagan, P. N., Flaherty, K., & Yeung, A. (2014). Impact of a culturally focused psychiatric consultation on depressive symptoms among Latinos in primary care. Psychiatric Services, 65(10), 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella-Awusah, T., Ani, C., Ajuwon, A., & Omigbodun, O. (2016). Effectiveness of brief school-based, group cognitive behavioural therapy for depressed adolescents in south west Nigeria. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 21(1), 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, L., Gillard, S., Jones Nielsen, J., Costa E. Silva, M., & Sin, J. (2025). Cultural adaptations to the assessment and treatment of trauma experiences among racial and ethnic minority groups: A mixed-methods systematic review and meta-analysis. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 26(2), 15248380251320982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, G., Rivera-Medina, C. L., Cumba-Avilés, E., Reyes-Rodríguez, M. L., Sáez-Santiago, E., Duarté-Vélez, Y., Nazario, L., Rodríguez-Quintana, N., & Rosselló, J. (2019). Can cognitive-behavioral therapy be optimized with parent psychoeducation? A randomized effectiveness trial of adolescents with major depression in Puerto Rico. Family Process, 58(4), 832–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, O. O., Londoño Tobón, A., & Njoroge, W. F. M. (2021). Social determinants of health: The impact of racism on early childhood mental health. Current Psychiatry Reports, 23(5), 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birtele, M., Lancaster, M., & Quadrato, G. (2025). Modelling human brain development and disease with organoids. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 26(5), 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blignault, I., Saab, H., Woodland, L., Mannan, H., & Kaur, A. (2021). Effectiveness of a community-based group mindfulness program tailored for Arabic and Bangla-speaking migrants. International Journal of Mental Health Systems, 15(1), 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, P., Bass, J. K., Zangana, G. A. S., Kamal, T., Murray, S. M., Kaysen, D., Lejuez, C. W., Lindgren, K., Pagoto, S., Murray, L. K., Van Wyk, S. S., Ahmed, A. M. A., Amin, N. M. M., & Rosenblum, M. (2014). A randomized controlled trial of mental health interventions for survivors of systematic violence in Kurdistan, Northern Iraq. BMC Psychiatry, 14(1), 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Escobar, F. J., Fandiño-Losada, A., Martínez-Buitrago, D. M., Santaella-Tenorio, J., Tobón-García, D., Muñoz-Morales, E. J., Escobar-Roldán, I. D., Babcock, L., Duarte-Davidson, E., Bass, J. K., Murray, L. K., Dorsey, S., I Gutierrez-Martinez, M., & Bolton, P. (2018). A randomized controlled trial of a transdiagnostic cognitive-behavioral intervention for Afro-descendants’ survivors of systemic violence in Colombia. PLoS ONE, 13(12), e0208483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghouts, J., Eikey, E., Mark, G., De Leon, C., Schueller, S. M., Schneider, M., Stadnick, N., Zheng, K., Mukamel, D., & Sorkin, D. H. (2021). Barriers to and facilitators of user engagement with digital mental health interventions: Systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(3), e24387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, D. L. (2023). Biological principles for music and mental health. Translational Psychiatry, 13(1), 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, R., Pisu, F., Suri, J. S., & Saba, L. (2025). Addressing hidden risks: Systematic review of artificial intelligence biases across racial and ethnic groups in cardiovascular diseases. European Journal of Radiology, 182, 111867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S., Chan, W., Chao, J., & Chan, P. (2020). A randomized controlled trial on the comparative effectiveness of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and health qigong-based cognitive therapy among Chinese people with depression and anxiety disorders. BMC Psychiatry, 20(1), 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B., Park, J. J., & Buch, V. P. (2024). Applying normative atlases in deep brain stimulation: A comprehensive review. International Journal of Surgery, 110(4), 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavira, D. A., Golinelli, D., Sherbourne, C., Stein, M. B., Sullivan, G., Bystritsky, A., Rose, R. D., Lang, A. J., Campbell-Sills, L., Welch, S., Bumgardner, K., Glenn, D., Barrios, V., Roy-Byrne, P., & Craske, M. (2014). Treatment engagement and response to CBT among Latinos with anxiety disorders in primary care. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 82(3), 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P., Luik, A. I., Fellman-Couture, C., Peterson, E., Joseph, C. L., Tallent, G., Tran, K. M., Ahmedani, B. K., Roehrs, T., Roth, T., & Drake, C. L. (2018). Efficacy of digital CBT for insomnia to reduce depression across demographic groups: A randomized trial. Psychological Medicine, 49(3), 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithambo, T., & Huey, S. (2017). Internet-delivered eating disorder prevention: A randomized controlled trial of dissonance-based and cognitive-behavioral interventions. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 50(10), 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J., Whitaker, K. J., Murray, G. K., Elliott, R., Hagan, C. C., Graham, J. M., Ooi, C., Tait, R., Holt, R. J., O van Nieuwenhuizen, A., Reynolds, S., O Wilkinson, P., Bullmore, E. T., Lennox, B. R., Sahakian, B. J., Goodyer, I., & Suckling, J. (2016). Aberrant brain responses to emotionally valent words is normalised after cognitive behavioural therapy in female depressed adolescents. Journal of Affective Disorders, 189, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, A., Calderón, M., MacPherson, L., & Lejuez, C. (2016). The efficacy of behavioral activation treatment among depressed Spanish-speaking Latinos. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 84(7), 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compère, L., Siegle, G. J., Riley, E., Lazzaro, S., Strege, M., Pacoe, E., Canovali, G., Barb, S., Huppert, T., & Young, K. (2023). Enhanced efficacy of CBT following augmentation with amygdala rtfMRI neurofeedback in depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 339, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D. J., Jordan, J. T., & Said, R. R. (2025). Bridging the gap between brain health guidelines and real-world implementation. Continuum: Lifelong Learning in Neurology, 31(3), 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S. L., Eaton, A. D., Leung, V. W. Y., Iacono, G., Pang, N., Dillon, F., Austin, A., Pascoe, R., & Dobinson, C. (2021). Efficacy of affirmative cognitive behavioural group therapy for sexual and gender minority adolescents and young adults in community settings in Ontario, Canada. BMC Psychology, 9(1), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craske, M. G., Herzallah, M. M., Nusslock, R., & Patel, V. (2023). From neural circuits to communities: An integrative multidisciplinary roadmap for global mental health. Nature Mental Health, 1, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, J. M., Fox, J., Vieten, C., Pearce, M., & Oxhandler, H. K. (2023). Enhancing competencies for the ethical integration of religion and spirituality in psychological services. Psychological Services, 20(1), 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damra, J., Nassar, Y., & Ghabri, T. (2014). Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy: Cultural adaptations for application in Jordanian culture. Counselling Psychology Quarterly, 27(3), 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S., Laver, K., Jeon, Y. H., Radford, K., & Low, L. F. (2023). Frameworks for cultural adaptation of psychosocial interventions: A systematic review with narrative synthesis. Dementia, 22(7), 1452–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, A., Cambronero-Solano, S., Mangubhai, S., Nefdt, L., Woodall, L. C., & Stefanoudis, P. V. (2023). Towards equity and justice in ocean sciences. npj Ocean Sustainability, 2(1), 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, L., Pegg, S., Cárdenas, E. F., Green, H., Dao, A., Waxmonsky, J., Pérez-Edgar, K., & Kujawa, A. (2023). Neural predictors of improvement with cognitive behavioral therapy for adolescents with depression: An examination of reward responsiveness and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 51(5), 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J. M., & Nagatsu, T. (2022). Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), and Morita therapy (MT): Comparison of three established psychotherapies. Journal of Neural Transmission, 129(4), 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D. M., Draheim, A. A., & Anderson, P. L. (2022). Culturally adapted digital mental health interventions for ethnic/racial minorities: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 90(10), 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, G., & Tarabeih, M. (2021). Underground COVID-19 home hospitals for haredim: Non-compliance or a culturally adapted alternative to public hospitalization? Journal of Religion and Health, 60(6), 3967–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebresenbet, E. A., Zegeye, S., & Biratu, T. D. (2025). Prevalence and associated factors of depression and posttraumatic stress disorder among trauma patients: Multi-centered cross-sectional study. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 16, 1447232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, F., Beversdorf, D. Q., & Herman, K. C. (2024). Stress and stress responses: A narrative literature review from physiological mechanisms to intervention approaches. Journal of Pacific Rim Psychology, 18, 18344909241289222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., Antonopoulou, H., Sortwell, A., & Halkiopoulos, C. (2025a). Challenging cognitive load theory: The role of educational neuroscience and artificial intelligence in redefining learning efficacy. Brain Sciences, 15(2), 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E., Aroutzidis, A., Antonopoulou, H., & Halkiopoulos, C. (2025b). From neural networks to emotional networks: A systematic review of EEG-based emotion recognition in cognitive neuroscience and real-world applications. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E., & Halkiopoulos, C. (2025a). Digital twin cognition: AI-biomarker integration in biomimetic neuropsychology. Biomimetics, 10(10), 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E., & Halkiopoulos, C. (2025b). Mapping EEG metrics to human affective and cognitive models: An interdisciplinary scoping review from a cognitive neuroscience perspective. Biomimetics, 10(11), 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., Kourkoutas, E., Yotsidi, V., Stavrou, P. D., & Prinianaki, D. (2024a). Clinical efficacy of psychotherapeutic interventions for post-traumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review and analysis. Children, 11(5), 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., & Nikolaou, G. (2024). The cross-cultural validation of neuropsychological assessments and their clinical applications in cognitive behavioral therapy: A scoping analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(8), 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., Telonis, G., Halkiopoulos, C., & Boutsinas, B. (2025c). Integrating neuroimaging and machine learning to predict mental disorder outcomes: A systematic review. GeNeDIS, 2024, 429–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., Vantaraki, F., Skoulidi, C., Anastassopoulos, P., & Vantarakis, A. (2024b). Gamified health promotion in schools: The integration of neuropsychological aspects and CBT—A systematic review. Medicina, 60(12), 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E., Vassilopoulos, S. P., & Nikolaou, G. (2025d). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy in clinical practice: A systematic review of neurocognitive outcomes and applications for mental health and well-being. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(5), 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkintoni, E., Vassilopoulos, S. P., & Nikolaou, G. (2025e). Next-generation cognitive-behavioral therapy for depression: Integrating digital tools, teletherapy, and personalization for enhanced mental health outcomes. Medicina, 61(3), 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombatto, S. P., Archer, K. R., Wegener, S. T., Hernandez, Y., Lin, S., Godino, J., Van Dyke, J., Liu, J., & Monroe, K. S. (2023). Protocol for a parallel group randomized clinical trial comparing a culturally adapted cognitive behavioral telerehabilitation intervention to usual physical therapy for Latino patients with chronic spine pain. Physical Therapy, 103(8), pzad068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Sánchez, J., Jamey, K., Paraskevopoulos, E., Bella, S. D., Gold, C., Schlaug, G., Belleville, S., Rodríguez-Fornells, A., Hackney, M. E., & Särkämö, T. (2022). Putting music to trial: Consensus on key methodological challenges investigating music-based rehabilitation. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1518(1), 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J. B., Crowley, M. J., Thirunavukkarasu, S., Maruthur, N. M., & Oldenburg, B. (2024). The final frontier in diabetes care: Implementing research in real-world practice. Diabetes Care, 47(8), 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, B., Roos, C., Hagler, K., Stein, E., Bowen, S., & Witkiewitz, K. (2018). Race/ethnicity and racial group composition moderate the effectiveness of mindfulness-based relapse prevention for substance use disorder. Addictive Behaviors, 81, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J., Prinstein, M. J., Clark, L. A., Rottenberg, J., Abramowitz, J. S., Albano, A. M., Aldao, A., Borelli, J. L., Chung, T., Davila, J., Forbes, E. E., Gee, D. G., Hall, G. C. N., Hallion, L. S., Hinshaw, S. P., Hofmann, S. G., Hollon, S. D., Joormann, J., Kazdin, A. E., … Weinstock, L. M. (2021). Mental health and clinical psychological science in the time of COVID-19: Challenges, opportunities, and a call to action. American Psychologist, 76(3), 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, O., & Eboreime, E. (2021). The impact of economic recessions on depression, anxiety, and trauma-related disorders and illness outcomes—A scoping review. Behavioral Sciences, 11(9), 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, A., Subedi, P., Zhang, M., Li, C., Kelly, T., Kim, C., & Yun, K. (2020). Culturally-appropriate orientation increases the effectiveness of mental health first aid training for Bhutanese refugees: Results from a multi-state program evaluation. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 22(2), 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N. R., Page, M. J., Pritchard, C. C., & McGuinness, L. A. (2022). PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkiopoulos, C., & Gkintoni, E. (2025). The role of machine learning in AR/VR-based cognitive therapies: A systematic review for mental health disorders. Electronics, 14(6), 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G. C. N., Berkman, E. T., Zane, N. W., Leong, F. T. L., Hwang, W., Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., Hong, J. J., Chu, J. P., & Huang, E. R. (2021). Reducing mental health disparities by increasing the personal relevance of interventions. American Psychologist, 76(1), 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ramos, R., Aguilera, A., Garcia, F., Munoz, R., & Figueroa, C. (2021). Linguistic analysis of Latinx patients’ responses to a text messaging adjunct during cognitive behavioral therapy for depression. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 145, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hot, A., Bossuyt, P. M., Gerke, O., Wahl, S., Vach, W., & Zapf, A. (2021). Randomized test-treatment studies with an outlook on adaptive designs. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 21(1), 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, S. J., Jr., Park, A. L., Galán, C. A., & Wang, C. X. (2023). Culturally responsive cognitive behavioral therapy for ethnically diverse populations. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 19, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M., Chaudhry, I. B., Mehmood, N., Rehman, R. U., Kazmi, A., Hamirani, M., Kiran, T., Bukhsh, A., Bassett, P., Husain, M. I., & Naeem, F. (2017). Pilot randomised controlled trial of culturally adapted cognitive behavior therapy for psychosis (CaCBTp) in Pakistan. BMC Health Services Research, 17(1), 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, N., Lovell, K., Chew-Graham, C. A., Lunat, F., McPhillips, R., Atif, N., Aseem, S., Begum, J., Bee, P., Bhui, K., Bower, P., Brugha, T., Bhatti, N., Chaudhry, N., Davies, L., Gire, N., Islam, A., Kai, J., Morrison, J., … Morriss, R. (2021). Multicentre randomised controlled trial of a group psychological intervention for postnatal depression in British mothers of South Asian origin (ROSHNI-2): Study protocol. BJPsych Open, 7(6), e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, N., Mehmood, N., Husain, M., Kiran, T., Naeem, F., & Chaudhry, I. (2016). Feasibility study of culturally adapted cognitive behaviour therapy for psychosis in Pakistan. European Psychiatry, 33(S1), S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W., Myers, H. F., Chiu, E., Mak, E., Butner, J. E., Fujimoto, K., Wood, J. J., & Miranda, J. (2015). Culturally adapted cognitive-behavioral therapy for Chinese Americans with depression: A randomized controlled trial. Psychiatric Services, 66(10), 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingman, T., Ali, S., Bhui, K., & Chalder, T. (2016). Chronic fatigue syndrome: Comparing outcomes in White British and Black and minority ethnic patients after cognitive-behavioural therapy. British Journal of Psychiatry, 209(3), 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, J. C., Castagno, A. E., Camplain, R., & Blackhorse, D. (2021). Role of professional societies on increasing Indigenous peoples’ participation and leadership in STEMM. Frontiers in Education, 6, 753488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, A., & Rose, N. (2024). How does precarious employment affect mental health? A scoping review and thematic synthesis of qualitative evidence from western economies. Work, Employment and Society, 38(2), 418–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S., Kikuta, K., Sakai, M., Mitamura, T., Motomura, N., & Hudson, J. (2019). A randomized controlled trial of a bidirectional cultural adaptation of cognitive behavior therapy for children and adolescents with anxiety disorders. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 120, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturralde, E., Hsiao, C. A., Nkemere, L., Kubo, A., Sterling, S. A., Flanagan, T., & Avalos, L. A. (2021). Engagement in perinatal depression treatment: A qualitative study of barriers across and within racial/ethnic groups. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 21(1), 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidong, D. E., Ike, T. J., Murshed, M., Francis, C., Mwankon, S. B., Jidong, J. E., Pwajok, J. Y., Nyam, P. P., & Husain, N. (2024). Postnatal depression in British mothers of African and Caribbean origin: A randomised controlled trial of learning through play plus culturally adapted cognitive behaviour therapy compared with psychoeducation. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15, 1383990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Gomez, C., & Beaulieu, L. (2022). Cultural responsiveness in applied behavior analysis: Research and practice. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 55(3), 650–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassaint, C., Belnap, B., Huang, Y., Karp, J., Abebe, K., & Rollman, B. (2019). Racial differences in the effectiveness of internet-delivered mental health care. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 35(2), 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassaint, C., Gibbs, P., Belnap, B., Karp, J., Abebe, K., & Rollman, B. (2017). Engagement and outcomes for a computerised cognitive-behavioural therapy intervention for anxiety and depression in African Americans. BJPsych Open, 3(1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminer, D., Booysen, D., Ellis, K., Kristensen, C. H., Patel, A. R., Robjant, K., & Sardana, S. (2024). Improving access to evidence-based interventions for trauma-exposed adults in low- and middle-income countries. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 37(4), 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kananian, S., Ayoughi, S., Farugie, A., Hinton, D., & Stangier, U. (2017). Transdiagnostic culturally adapted CBT with Farsi-speaking refugees: A pilot study. European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 8, 1390362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kananian, S., Kip, A., Schumm, H., Giesebrecht, J., Nicolai, A., Schade-Brittinger, C., Reese, J., Weise, C., Mewes, R., Morina, N., Ehring, T., & Stangier, U. (2022). Culturally adapted cognitive behavioural group therapy for mental disorders in refugees plus problem solving training (ReTreat): Study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open, 12(9), e061274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kananian, S., Soltani, Y., Hinton, D., & Stangier, U. (2020). Culturally adapted cognitive behavioral therapy plus problem management (CA-CBT+) with Afghan refugees: A randomized controlled pilot study. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 33(6), 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, J., Santiago-Rivera, A., Santos, M., Nagy, G., Lopez, M., Hurtado, G., & West, P. (2015). A randomized hybrid efficacy and effectiveness trial of behavioral activation for Latinos with depression. Behavior Therapy, 46(2), 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariri, H. D. H., & Almubaddel, A. (2024). From theory to practice: Revealing the real-world impact of cognitive behavioral therapy in psychological disorders through a dynamic bibliometric and survey study. Heliyon, 10(4), e25934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, J. A., Johnson, F. N., Bucci, L., & Fischer, R. (2022). In search of mindfulness: A review and reconsideration of cultural dynamics from a cognitive perspective. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 52(2), 168–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, N., Nakagawa, A., Kurata, C., Sasaki, Y., Mitsuda, D., Nakao, S., Mizuno, S., Ozawa, M., Nakagawa, Y., Ishikawa, N., Umeda, S., Terasawa, Y., Tabuchi, H., Kikuchi, T., Abe, T., & Mimura, M. (2020). Neural and clinical changes of cognitive behavioural therapy versus talking control in patients with major depression: A study protocol for a randomised clinical trial. BMJ Open, 10(3), e029735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, J. R., Rodriguez-Seijas, C., Jackson, S. D., Bränström, R., Harkness, A., Safren, S. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., & Pachankis, J. E. (2023). Moderators of LGBQ-affirmative cognitive behavioral therapy: ESTEEM is especially effective among Black and Latino sexual minority men. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 91(5), 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killaspy, H., Harvey, C., Brasier, C., Brophy, L., Ennals, P., Fletcher, J., & Hamilton, B. (2022). Community-based social interventions for people with severe mental illness: A systematic review and narrative synthesis of recent evidence. World Psychiatry, 21(1), 96–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. T., Heitkemper, E. M., Hébert, E. T., Hecht, J., Crawford, A., Nnaka, T., Hutson, T. S., Rhee, H., & Radhakrishnan, K. (2022). Redesigning culturally tailored intervention in the precision health era: Self-management science context. Nursing Outlook, 70(5), 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride, J. B., Anglin, D. M., Colman, I., Dykxhoorn, J., Jones, P. B., Patalay, P., Pitman, A., Soneson, E., Steare, T., Wright, T., & Griffiths, S. L. (2024). The social determinants of mental health and disorder: Evidence, prevention and recommendations. World Psychiatry, 23(1), 58–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyimba, N., & Anderson, R. (2022). Reflecting on cultural meanings of spirituality/wairuatanga in post-traumatic growth using the Māori wellbeing model of Te Whare Tapa Whā. Mental Health, Religion & Culture, 25(3), 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, G. L., Robinson, A., Murray, A. J., Havercamp, S. M., Havercamp, S., Andridge, R., Arnold, L. E., Barnhill, J., Bodle, S., Boerner, E., Bonardi, A., Bourne, M. L., Brown, C., Buck, A., Burkett, S., Chapman, R., Cobranchi, C., Cole, C., Davies, D., … Witwer, A. (2021). It’s time to reconsider how we define health: Perspective from disability and chronic condition. Disability and Health Journal, 14(4), 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, K., Tian, Z., Wilson, S. R., & Buzzanell, P. M. (2023). Memorable messages as anticipatory resilience: Examining associations among memorable messages, communication resilience processes, and mental health. Health Communication, 38(6), 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, E., Grill-Spector, K., & Nordt, M. (2024). Rethinking cortical recycling in ventral temporal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 28(1), 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukla, M., Bell, M., & Lysaker, P. (2018). A randomized controlled trial examining a cognitive behavioral therapy intervention enhanced with cognitive remediation to improve work and neurocognition outcomes among persons with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 197, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunorubwe, T. (2023). Cultural adaptations of group CBT for depressed clients from diverse backgrounds: A systematic review. The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist, 16, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, K., Nogg, K., Safren, S., & Blashill, A. (2018). Mechanism of change in cognitive behavioral therapy for body image and self-care on ART adherence among sexual minority men living with HIV. AIDS and Behavior, 22(10), 3196–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansford, J. E. (2022). Annual research review: Cross-cultural similarities and differences in parenting. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 63(4), 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattie, E. G., Stiles-Shields, C., & Graham, A. K. (2022). An overview of and recommendations for more accessible digital mental health services. Nature Reviews Psychology, 1(2), 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrance, E. L., Thompson, R., Newberry Le Vay, J., Page, L., & Jennings, N. (2022). The impact of climate change on mental health and emotional wellbeing: A narrative review of current evidence, and its implications. International Review of Psychiatry, 34(5), 443–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. S., Colby, S. M., Rohsenow, D. J., Martin, R., Rosales, R., McCallum, T. T., Falcon, L., Almeida, J., & Cortés, D. E. (2019). A randomized controlled trial of motivational interviewing tailored for heavy drinking Latinxs. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 87(9), 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B. A., Napolitano, M. A., Buman, M. P., Williams, D. M., & Nigg, C. R. (2025). Physical activity interventions: An update on advancing sedentary time, technology, and dissemination and implementation research. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 48(1), 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H., Sagar, A., & Kéri, S. (2018). Translocator protein (18kDa TSPO) binding, a marker of microglia, is reduced in major depression during cognitive-behavioral therapy. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Zhu, M., Yi, C., & Zeng, D. (2025). Early rehabilitation interventions for global developmental delay in children: A narrative review. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 13, 1576324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Maya, E., Olmstead, R., & Irwin, M. (2019). Mindfulness meditation and improvement in depressive symptoms among Spanish- and English speaking adults: A randomized, controlled, comparative efficacy trial. PLoS ONE, 14(7), e0219425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, K., Lamb, J., Gask, L., Bower, P., Waheed, W., Chew-Graham, C., Lamb, J., Aseem, S., Beatty, S., Burroughs, H., Clarke, P., Dowrick, A., Edwards, S., Gabbay, M., Lloyd-Williams, M., & Dowrick, C. (2014). Development and evaluation of culturally sensitive psychosocial interventions for under-served people in primary care. BMC Psychiatry, 14(1), 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q., Yeung, N., Tsai, W., & Kim, J. (2022). The effects of culturally adapted expressive writing interventions on depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese American breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 158, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W., Todhunter-Reid, A., Mitsdarffer, M. L., Muñoz-Laboy, M., Yoon, A. S., & Xu, L. (2021). Barriers and facilitators for mental health service use among racial/ethnic minority adolescents: A systematic review of literature. Frontiers in Public Health, 9, 641605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, F., Zhang, Q., Bao, G. C., Narang, B., & Chen, R. Y. (2025). Refinement of a meaning-centered counseling program for Chinese patients with advanced cancer: Integrating cultural adaptation and implementation science. BMC Health Services Research, 25(1), 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntyre, M. M., Zare, M., & Williams, M. T. (2023). Anxiety-related disorders in the context of racism. Current Psychiatry Reports, 25(2), 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitland, R., Smith, J., Gillon, G., & Hyter, Y. (2025). Culturally responsive practices for supporting youth in the youth justice system. Topics in Language Disorders, 45(2), 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamani, A., & Suro, G. (2016). The effect of a culturally informed therapy on self-conscious emotions and burden in caregivers of patients with schizophrenia: A randomized clinical trial. Psychotherapy, 53(1), 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markey, K., MacFarlane, A., & Manning, M. (2023). Time to re-envisage culturally responsive care: Intersection of participatory health research and implementation science. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 79(11), 4228–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, K., Salami, A., Frick, A., Carlbring, P., Andersson, G., Furmark, T., & Boraxbekk, C. (2016). Neuroplasticity in response to cognitive behavior therapy for social anxiety disorder. Translational Psychiatry, 6(2), e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorry, P. D., Mei, C., Chanen, A., Hodges, C., Alvarez-Jimenez, M., & Killackey, E. (2022). Designing and scaling up integrated youth mental health care. World Psychiatry, 21(1), 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y., Li, H., Wang, J., Xu, Y., & Wang, B. (2021). Cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with mild to moderate depression: Treatment effects and neural mechanisms. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 136, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, M., Tornero-Aguilera, J. F., Rubio-Zarapuz, A., Villanueva-Tobaldo, C. V., Martín-Rodríguez, A., & Clemente-Suárez, V. J. (2024). Body perceptions and psychological well-being: A review of the impact of social media and physical measurements on self-esteem and mental health. Healthcare, 12(14), 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S., Jackson, V. W., Chong, J., Choe, K., Tay, C., Wong, J., & Yang, L. H. (2021). Systematic review of cultural aspects of stigma and mental illness among racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States: Implications for interventions. American Journal of Community Psychology, 68(3–4), 486–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G., Campbell, M., Copeland, L., Craig, P., Movsisyan, A., Hoddinott, P., Littlecott, H., O’cathain, A., Pfadenhauer, L., Rehfuess, E., Segrott, J., Hawe, P., Kee, F., Couturiaux, D., Hallingberg, B., & Evans, R. (2021). Adapting interventions to new contexts—The ADAPT guidance. BMJ, 374, n1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C. (2021). “Peering through the window looking in”: Postgraduate experiences of non-belonging and belonging in relation to mental health and wellbeing. Studies in Graduate and Postdoctoral Education, 12(3), 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudd-Martin, G., Cirino, A. L., Barcelona, V., Fox, K., Hudson, M., Sun, Y. V., Taylor, J. Y., Cameron, V. A., & American Heart Association Council on Genomic and Precision Medicine. (2021). Considerations for cardiovascular genetic and genomic research with marginalized racial and ethnic groups and Indigenous peoples: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, 14(4), e000084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderbagi, A., Loblay, V., Zahed, I. U. M., Ekambareshwar, M., Poulsen, A., Song, Y. J. C., Ospina-Pinillos, L., Krausz, M., Kamel, M. M., Hickie, I. B., & LaMonica, H. M. (2024). Cultural and contextual adaptation of digital health interventions: Narrative review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 26, e55130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem, F., Gul, M., Irfan, M., Munshi, T., Asif, A., Rashid, S., Khan, M. N. S., Ghani, S., Malik, A., Aslam, M., Farooq, S., Husain, N., & Ayub, M. (2015a). Brief culturally adapted CBT (CaCBT) for depression: A randomized controlled trial from Pakistan. Journal of Affective Disorders, 177, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, F., Saeed, S., Irfan, M., Kiran, T., & Kingdon, D. (2015b). Brief culturally adapted CBT for psychosis (CaCBTp): A randomized controlled trial from a low income country. Schizophrenia Research, 164(1–3), 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, F., Sajid, S., Naz, S., & Phiri, P. (2023). Culturally adapted CBT—The evolution of psychotherapy adaptation frameworks and evidence. The Cognitive Behaviour Therapist, 16, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, F., Sarhandi, I., Gul, M., Khalid, M., Aslam, M., Anbrin, A., Saeed, S., Noor, M., Fatima, G., Minhas, F., Husain, N., & Ayub, M. (2014). A multicentre randomised controlled trial of a carer supervised culturally adapted CBT (CaCBT) based self-help for depression in Pakistan. Journal of Affective Disorders, 156, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Medel, C., Powell, M. B., Sharman, S. J., & Knight, T. (2024). Effectiveness and efficacy of a culturally adapted training program for child interviewers in Chile. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 30(2), 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V. K., Sherbourne, C., Chung, B., Tang, L., Wright, A. L., Whittington, Y., Wells, K., & Miranda, J. (2016). Community engagement compared with technical assistance to disseminate depression care among low-income, minority women: A randomized controlled effectiveness study. American Journal of Public Health, 106(10), 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittas, V., Daniore, P., Chavez, S. J., & Wray, T. B. (2024). Challenges in implementing cultural adaptations of digital health interventions. Communications Medicine, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbury, A., Hauser, T., Fleming, S., Dolan, R., & Huys, Q. (2024). Different components of cognitive-behavioral therapy affect specific cognitive mechanisms. Science Advances, 10(8), eadk3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowinski, W. L. (2021). Evolution of human brain atlases in terms of content, applications, functionality, and availability. Neuroinformatics, 19(1), 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygren, T., Brohede, D., Koshnaw, K., Osman, S., Johansson, R., & Andersson, G. (2019). Internet-based treatment of depressive symptoms in a Kurdish population: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 75(6), 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oman, D. (2025). Mindfulness for global public health: Critical analysis and agenda. Mindfulness, 16(1), 573–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osazuwa, S., & Moodley, R. (2023). “Will there be a willingness to actually engage with it?”: Exploring attitudes toward culturally integrative psychotherapy among Canada’s African community. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration, 33(2), 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, F., Salari, R., Klingberg-Allvin, M., Schön, U., & Flacking, R. (2017). Effects of a culturally tailored parenting support programme in Somali-born parents’ mental health and sense of competence in parenting: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open, 7(12), e017600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, F., Vixner, L., Flacking, R., Klingberg-Allvin, M., Schön, U., & Salari, R. (2021). Impact of a culturally tailored parenting programme on the mental health of Somali parents and children living in Sweden: A longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open, 11(4), e045067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachankis, J., McConocha, E. M., Clark, K. A., Wang, K., Behari, K., Fetzner, B. K., Brisbin, C. D., Scheer, J. R., & Lehavot, K. (2020). A transdiagnostic minority stress intervention for gender diverse sexual minority women’s depression, anxiety, and unhealthy alcohol use: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 88(7), 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, M. L., Demanarig, D. L., Alarcon, K. C., Kronenburg, M. A., Capuli, M. A., Nagtalon-Ramos, J., Sabado-Liwag, M., & Javier, J. (2025). Using a decolonizing research method to address underrepresentation and health disparities of Filipinx/a/o Americans: The importance of kuwentuhan as a research method. Qualitative Health Research, 35(4–5), 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau, A. M., Boyer, C. J., Campos, L. J., Carranza, A. F., Deer, L. K., Hartman, D. T., Bidwell, J. T., & Hostinar, C. E. (2023). A review of mental health disparities during COVID-19: Evidence, mechanisms, and policy recommendations for promoting societal resilience. Development and Psychopathology, 35(4), 1821–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M., Silva, M., Añez-Nava, L., Jaramillo, Y., Kiluk, B. D., Gordon, M. A., Nich, C., Frankforter, T., Devore, K., Ball, S. A., & Carroll, K. M. (2018). Culturally adapted, web-based cognitive behavioral therapy for Spanish-speaking individuals with substance use disorders: A randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Public Health, 108(11), 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Cardona, J., Bybee, D., Sullivan, C., Rodríguez, M., Dates, B., Tams, L., & Bernal, G. (2017). Examining the impact of differential cultural adaptation with Latina/o immigrants exposed to adapted parent training interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 85(1), 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedo, F., Antoni, M. H., Moreno, P. I., Traeger, L., Perdomo, D., Dahn, J., Miller, G. E., Cole, S., Orjuela, J., Pizarro, E., & Yanez, B. (2018). Study design and protocol for a culturally adapted cognitive behavioral stress and self-management intervention for localized prostate cancer: The Encuentros de Salud study. Contemporary Clinical Trials, 71, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, T., Rozenman, M., Bai, S., Pérez, J., Thamrin, H., & Piacentini, J. (2020). Ethnicity moderates outcome in family focused treatment for pediatric obsessive compulsive disorder. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 73, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A., Gardener, C., Shieh, J., Hồ, Q., Doan, A., & Bhui, K. (2024). Investigating the acceptability of a culturally adapted acceptance and commitment therapy group for UK Vietnamese communities: A practice-based feasibility study. Clinical Psychology in Europe, 6(1), e11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M. L., & Renshaw, T. L. (2023). Guidelines for implementing and adapting evidence-based interventions with marginalized youth in schools. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 93(4), 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R., Canário, C., Leijten, P., Rodrigo, M. J., & Cruz, O. (2024). Implementation of parenting programs in real-world community settings: A scoping review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 27(1), 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pots, W., Meulenbeek, P., Veehof, M., Klungers, J., & Bohlmeijer, E. (2014). The efficacy of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy as a public mental health intervention for adults with mild to moderate depressive symptomatology: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE, 9(10), e109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R., Ahmed, N., Noor, S., Sharif, H., Raymond, N., & Williams, C. (2017). Addressing behavioral health disparities for Somali immigrants through group cognitive behavioral therapy. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 19(3), 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumariega, A. J., Jo, Y., Beck, B., & Rahmani, M. (2022). Trauma and US minority children and youth. Current Psychiatry Reports, 24(4), 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y., Jorgensen, N. A., & Telzer, E. H. (2021). A call for greater attention to culture in the study of brain and development. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 16(2), 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñonez-Freire, C., Vara, M., Herrero, R., Mira, A., García-Palacios, A., Botella, C., & Baños, R. (2020). Cultural adaptation of the Smiling is Fun program for the treatment of depression in the Ecuadorian public health care system: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Internet Interventions, 22, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassool, G. H. (2024). Psychoanalytic, client-centred, and cognitive-behaviour therapy: Congruence or dissonance with Islāmic spirituality. In Exploring the intersection of Islāmic spirituality and psychotherapy: Healing the soul (pp. 103–119). Springer Nature. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathakrishnan, B., & Daud, S. (2025). A systematic literature review on the international trends of Indigenous peoples’ political participation. Frontiers in Political Science, 7, 1601300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeck, C., Guo, X., Dimoka, A., & Pavlou, P. A. (2024). Uncovering the neural processes of privacy: A neurally informed behavioral intervention to protect information privacy. Information Systems Research, 35(2), 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safren, S., O’Cleirigh, C., Andersen, L. S., Magidson, J. F., Lee, J. S., Bainter, S. A., Musinguzi, N., Simoni, J., Kagee, A., & Joska, J. A. (2021). Treating depression and improving adherence in HIV care with task-shared cognitive behavioural therapy in Khayelitsha, South Africa: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of the International AIDS Society, 24(10), e25823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca-Sanabria, A., Richards, D., Timulak, L., Castro-Camacho, L., Mojica-Perilla, M., & Parra-Villa, Y. (2018). Assessing the efficacy of a culturally adapted cognitive behavioural internet-delivered treatment for depression: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry, 18(1), 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca-Sanabria, A., Richards, D., Timulak, L., Connell, S., Perilla, M., Parra-Villa, Y., & Castro-Camacho, L. (2020). A culturally adapted cognitive behavioral internet-delivered intervention for depressive symptoms: Randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mental Health, 7(1), e13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, R., Valli, E., Dear, B., Titov, N., & Hadjistavropoulos, H. (2024). Satisfaction, engagement, and outcomes in internet-delivered cognitive behaviour therapy adapted for people of diverse ethnocultural groups: An observational trial with benchmarking. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15, 1270543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaechter, T., Flowers, S. N., Weiss, M., Becker-Haimes, E. M., & Sanchez, A. L. (2025). Culturally adapted interventions for anxiety and trauma-related disorders in marginalized youth: A systematic review. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 56(2), 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlief, M., Rich, N., Rains, L. S., Baldwin, H., Rojas-Garcia, A., Nyikavaranda, P., Persaud, K., Dare, C., French, P., Lloyd-Evans, B., Crawford, M., Smith, J., Kirkbride, J. B., & Johnson, S. (2023). Ethnic differences in receipt of psychological interventions in Early Intervention in Psychosis services in England—A cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Research, 328, 115529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzman, J., Roth, M., Paterson, A., Jacobs, A., & Williams, Z. (2023). Community-guided, autism-adapted group cognitive behavioral therapy for depression in autistic youth (CBT-DAY): Preliminary feasibility, acceptability, and efficacy. Autism, 28(5), 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sclare, I., Michelson, D., Malpass, L., Coster, F., & Brown, J. (2015). Innovations in Practice: DISCOVER CBT workshops for 16–18-year-olds: Development of an open-access intervention for anxiety and depression in inner-city youth. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 20(2), 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, B., Awaisu, A., & Kheir, N. (2022). Refugee healthcare needs and barriers to accessing healthcare services in New Zealand: A qualitative phenomenological approach. BMC Health Services Research, 22(1), 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkurko, A. (2024). Mapping cultural values onto the brain: The fragmented landscape. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 58(2), 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, F., Lindblad, U., Nilsson, P., & Bennet, L. (2019). Effects of a randomized, culturally adapted, lifestyle intervention on mental health among Middle-Eastern immigrants. European Journal of Public Health, 29(5), 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, D., Hossain, S., Andrejek, N., Cohen, M. J., Dennis, C., Kim, J., La Porte, L., Meltzer-Brody, S. E., Nino, A. P., Ravitz, P., Schoueri-Mychasiw, N., Silver, R., Vigod, S. N., Zibaman, M., & Schiller, C. E. (2022). Culturally sensitive psychotherapy for perinatal women: A mixed methods study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 90(9), 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A. (2024). Can psychotherapies be effectively adapted to cultural identity (fit)? In APA handbook of psychotherapy (pp. 127–148). American Psychological Association. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, K., Balci, S., Feldhahn, F., Bengel, J., Baumeister, H., & Sander, L. B. (2021). Cultural adaptation of internet- and mobile-based interventions for mental disorders: A systematic review. npj Digital Medicine, 4(1), 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, R., Guillén, R., Rodríguez, N., Andrade, C., Matos, A., & Bautista-Valarezo, E. (2025). Fasting glucose improvement following a short-term, culturally adapted lifestyle intervention in Latino adults at risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A quasi-experimental study. BMC Nutrition, 11(1), 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, Y., Wong, J., Hui, C., Chang, W., Chan, S., Lee, E., & Chen, E. (2023). Effectiveness of culturally adapted counselling service for low-income ethnic minorities experiencing mental distress: A pragmatic randomised clinical trial. BMJ Mental Health, 27(1), e300788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaimanova, M., & Sulaimanov, R. (2017). Ethno-cultural predictors, which determine features of cognitive behavioral therapy of persons with PTSD. European Psychiatry, 41(S1), S683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J., Li, C., Rodgers, R., & Ballou, M. (2016). Ethnic differences in the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy combined with medication: Comparing Asian American and white psychiatric patients. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 23, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, A., Mung, H. K., Miah, M. A. A., Balasundaram, S., Ventevogel, P., Badrudduza, M., Khan, S., Morgan, K., Rees, S., Mohsin, M., & Silove, D. (2020). An integrative Adapt Therapy for common mental health symptoms and adaptive stress amongst Rohingya, Chin, and Kachin refugees living in Malaysia: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS Medicine, 17(3), e1003073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, A., Gupta, A., & De Sousa, A. (2024). Artificial intelligence in positive mental health: A narrative review. Frontiers in Digital Health, 6, 1280235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoma, M. V., Rohleder, N., & Rohner, S. L. (2021). Clinical ecopsychology: The mental health impacts and underlying pathways of the climate and environmental crisis. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 675936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornicroft, G., Sunkel, C., Aliev, A. A., Baker, S., Brohan, E., el Chammay, R., Davies, K., Demissie, M., Duncan, J., Fekadu, W., Gronholm, P. C., Guerrero, Z., Gurung, D., Habtamu, K., Hanlon, C., Heim, E., Henderson, C., Hijazi, Z., Hoffman, C., … Winkler, P. (2022). The Lancet Commission on ending stigma and discrimination in mental health. The Lancet, 400(10361), 1438–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovote, K., Fleer, J., Snippe, E., Peeters, A. C., Emmelkamp, P. M., Sanderman, R., Links, T. P., & Schroevers, M. J. (2014). Individual mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and cognitive behavior therapy for treating depressive symptoms in patients with diabetes: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care, 37(9), 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W., Chiang, J., & Lau, A. (2016). The effects of self-enhancement and self-improvement on recovery from stress differ across cultural groups. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 7(1), 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeh-Momoh, C. T., Migeot, J., Blackmon, K., Mielke, M. M., Melloni, M., Cox, L., Yaffe, K., Santamaria-Garcia, H., Stern, Y., & Ibanez, A. (2025). Resilience and brain health in global populations. Nature Medicine, 31(2), 2518–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Agteren, J., Iasiello, M., Lo, L., Bartholomaeus, J., Kopsaftis, Z., Carey, M., & Kyrios, M. (2021). A systematic review and meta-analysis of psychological interventions to improve mental wellbeing. Nature Human Behaviour, 5(5), 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Akker, O. R., Peters, G. Y., Bakker, C. J., Carlsson, R., Coles, N. A., Corker, K. S., Feldman, G., Moreau, D., Nordström, T., Pickering, J. S., Riegelman, A., Topor, M. K., van Veggel, N., Yeung, S. K., Call, M., Mellor, D. T., & Pfeiffer, N. (2023). Increasing the transparency of systematic reviews: Presenting a generalized registration form. Systematic Reviews, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, S., Wennerstrom, A., Alfaro, N., Belin, T., Griffith, K., Haywood, C., Jones, F., Lunn, M. R., Meyers, D., Miranda, J., Obedin-Maliver, J., Pollock, M., Sherbourne, C. D., Springgate, B. F., Sugarman, O. K., Rey, E., Williams, C., Williams, P., & Chung, B. (2019). Resilience Against Depression Disparities (RADD): A protocol for a randomised comparative effectiveness trial for depression among predominantly low-income, racial/ethnic, sexual and gender minorities. BMJ Open, 9(7), e031099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waanders, A., Brown, A., Caron, N. R., Plisiewicz, A., McHugh, S. T., Nguyen, T. Q., Lehmann, K., Stevens, J., Storm, P. J., Resnick, A., Davidson, T. B., Mueller, S., & Kline, C. (2023). Indigenous peoples and inclusion in clinical and genomic research: Understanding the history and navigating contemporary engagement. Neoplasia, 37, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Q. (2025). Personalizing guest experience with generative AI in the hotel industry: There’s more to it than meets a Kiwi’s eye. Current Issues in Tourism, 28(5), 823–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y., Sha, L., McWeeny, R., Johal, R., Easton, C., Baxter, A., Cao, B., Greenshaw, A., & Carr, W. (2024). Evaluating the effectiveness of a school-based mental health literacy intervention from a comprehensive demographic and social-cognitive perspective. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, H. A., Gonzalez, J. C., Call, C. C., Quezada, D., Scholars for Elevating Equity and Diversity (SEED) & Galán, C. A. (2022). Culturally responsive telepsychology & mHealth interventions for racial-ethnic minoritized youth: Research gaps and future directions. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 51(6), 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, L., Foy, R., Presseau, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Ivers, N. M., Powell, B. J., Taljaard, M., Wiggers, J., Sutherland, R., Nathan, N., Williams, C. M., Kingsland, M., Milat, A., Hodder, R. K., & Yoong, S. L. (2021). Designing and undertaking randomised implementation trials: Guide for researchers. BMJ, 372, m3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods-Jaeger, B., Kava, C., Akiba, C., Lucid, L., & Dorsey, S. (2017). The art and skill of delivering culturally responsive trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy in Tanzania and Kenya. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy, 9(5), 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z., Murat Baldwin, M., Wong, S. C., Obsuth, I., Meinck, F., & Murray, A. L. (2023). The impact of childhood psychological maltreatment on mental health outcomes in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 24(5), 3049–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., Gu, S., Honnorat, N., Linn, K. A., Shinohara, R. T., Aselcioglu, I., Bruce, S., Oathes, D. J., Davatzikos, C., Satterthwaite, T. D., Bassett, D. S., & Sheline, Y. I. (2018). Network changes associated with transdiagnostic depressive symptom improvement following cognitive behavioral therapy in MDD and PTSD. Molecular Psychiatry, 23(12), 2314–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A., Germán, M., Wheeler, L., Camacho, K., Hirsch, E., & Miller, A. (2020). Self-harm and self-regulation in urban ethnic minority youth: A pilot application of dialectical behavior therapy for adolescents. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 25(3), 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M., Li, X., Chiaramonte, D., Sun, S., Pan, S., Soulliard, Z., Eisenstadt, B. E., Ljótsson, B., Hagaman, A., & Pachankis, J. (2024). Guided internet-based LGBTQ-affirmative cognitive-behavioral therapy: A randomized controlled trial among sexual minority men in China. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 181, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D., & Yat-nam, P. (2021). A culturally adapted cognitive behavioral therapy group: A randomized controlled trial. Research on Social Work Practice, 32(5), 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S., Wu, H., Wu, Y., Xu, H., Yu, J., Zhong, Y., Zhang, N., Li, J., Xu, Q., & Wang, C. (2022). Neural effects of cognitive behavioral therapy in psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 853804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamiri, M., & Esmaeili, A. (2024). Methods and technologies for supporting knowledge sharing within learning communities: A systematic literature review. Administrative Sciences, 14(1), 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemestani, M., Mohammed, A., Ismail, A., & Vujanovic, A. (2022). A pilot randomized clinical trial of a novel, culturally adapted, trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral intervention for war-related PTSD in Iraqi women. Behavior Therapy, 53(4), 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., Wang, J., & Neitzel, A. (2023). School-based mental health interventions targeting depression or anxiety: A meta-analysis of rigorous randomized controlled trials for school-aged children and adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 52(1), 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, E., Ritterband, L., Bethea, T., Robles, Y., Heeren, T., & Rosenberg, L. (2022). Effect of culturally tailored, internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in Black women: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry, 79(6), 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q., Chen, Z., Cao, Y., & Peng, S. (2021). Clinical impact and quality of randomized controlled trials involving interventions evaluating artificial intelligence prediction tools: A systematic review. npj Digital Medicine, 4(1), 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y. (2025). Ethical practice in the majority world: A framework for psychotherapists trained in the minority world. American Psychologist, 80(2), 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoellner, L., Bentley, J., Musa, K., Mohamed, F., Ahmed, L., King, K., & Feeny, N. (2024). Lay-led intervention for war and refugee trauma. JAMA Network Open, 7(9), e2429661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



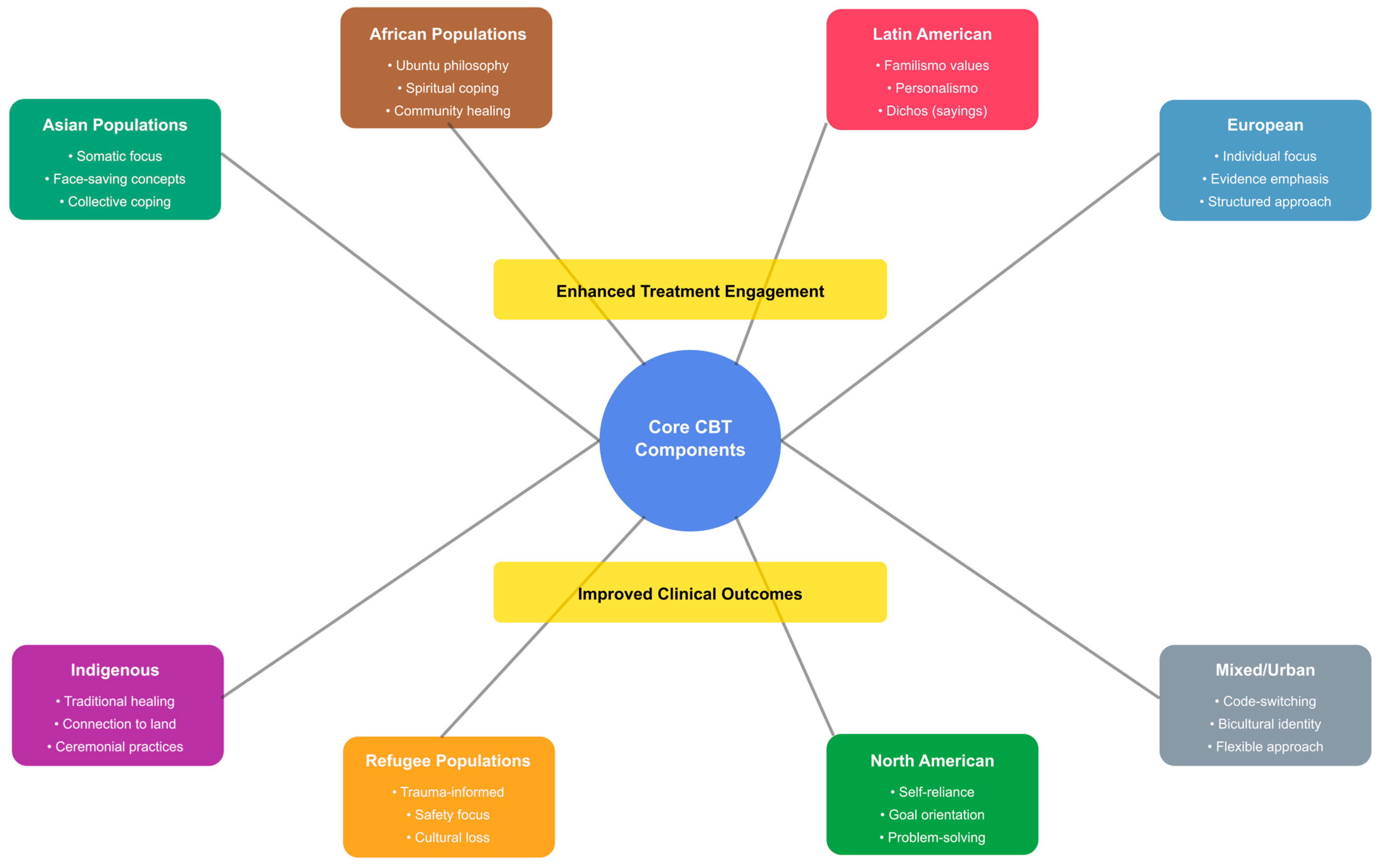








| Authors | Study Objectives | Study Design | Main Findings | Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acarturk et al. (2018) | To examine the effectiveness of culturally adapted transdiagnostic CBT for SSRI-resistant Turkish adolescents | Pilot RCT | Zero dropout rates throughout intervention; significant improvements in anxiety and depression symptoms | Culturally adapted transdiagnostic CBT incorporating family involvement and cultural values |
| Aguilera and Berridge (2014) | To evaluate qualitative feedback from text messaging intervention for depression across cultural groups | Mixed-methods qualitative study | Spanish speakers experienced messages as supportive/caring; English speakers viewed as impersonal reminders | Text messaging intervention with cultural linguistic analysis |
| Aizik-Reebs et al. (2022) | To examine mechanisms of mindfulness-based trauma recovery for refugees | RCT | Significant elevations in self-compassion and reductions in self-criticism; large effect sizes for PTSD symptoms | Mindfulness-Based Trauma Recovery for Refugees (MBTR-R) |
| Alegría et al. (2018) | To test effectiveness of DECIDE intervention on shared decision-making in multicultural patients | Randomized clinical trial | Improved shared decision-making and perceived quality of care; 67.9% female participants | DECIDE intervention for culturally responsive shared decision-making |
| An et al. (2020) | To evaluate modified group-based CBT for dementia worry in Chinese elders | RCT | Significant reduction in dementia worry and culturally biased beliefs; enhanced group cohesion | Modified group-based CBT incorporating cultural beliefs about aging |
| Anastopoulos et al. (2021) | To examine CBT effectiveness for college students with ADHD across cultural groups | RCT | Significant improvements in ADHD symptoms and academic functioning across diverse populations | Culturally adapted CBT for ADHD with academic focus |
| Auva’a-Alatimu (2023) | To complement CBT for Pacific peoples in New Zealand | Qualitative implementation study | Enhanced engagement when traditional healing elements incorporated; therapist training crucial | CBT complemented with Pacific cultural healing practices |
| Bedoya et al. (2014) | To assess impact of culturally focused psychiatric consultation for Latinos | RCT | Increased depression remission rates through cultural and linguistic adaptation | Culturally focused psychiatric consultation with dichos integration |
| Bella-Awusah et al. (2016) | To evaluate brief school-based group CBT for Nigerian adolescents | RCT | Significant reduction in depressive symptoms; school-based delivery reduced barriers | Brief group CBT delivered in school settings |
| Bernal et al. (2019) | To examine CBT optimization with parent psychoeducation for Puerto Rican adolescents | Randomized effectiveness trial | Enhanced outcomes when family involvement incorporated; sustained at follow-up | CBT with culturally adapted parent psychoeducation |
| Blignault et al. (2021) | To evaluate community-based mindfulness program for Arabic/Bangla-speaking migrants | RCT | Significant improvements in mental health outcomes; high retention rates | Community-based group mindfulness tailored for migrants |
| Bolton et al. (2014) | To test mental health interventions for survivors of systematic violence | RCT | Large effect sizes for PTSD and depression; sustained improvements at follow-up | Transdiagnostic intervention for trauma survivors |
| Bonilla-Escobar et al. (2018) | To evaluate CETA for Afro-descendant survivors of violence in Colombia | RCT | Significant improvements achieved through lay counselor delivery; cost-effective approach | Common Elements Treatment Approach (CETA) with cultural adaptation |
| Chan et al. (2020) | To compare MBCT and health qigong-based CT for Chinese patients | RCT | Both interventions effective; qigong-based approach showed cultural preference | Mindfulness-based CBT vs. culturally adapted qigong-based therapy |
| Chavira et al. (2014) | To examine CBT treatment engagement among Latinos with anxiety in primary care | RCT | Enhanced engagement with cultural adaptations; family involvement crucial | Culturally adapted CBT for anxiety in primary care settings |
| Cheng et al. (2018) | To evaluate digital CBT for insomnia across demographic groups | RCT | Effectiveness maintained across groups; infrastructure barriers identified | Digital CBT for insomnia with cultural considerations |
| Chithambo and Huey (2017) | To test internet-delivered eating disorder prevention interventions | RCT | Both interventions effective across ethnic groups; differential mechanisms identified | Internet-delivered dissonance-based and CBT interventions |
| Chuang et al. (2016) | To examine neural responses to CBT in female adolescents with depression | Neuroimaging RCT | Normalization of aberrant brain responses; neural biomarkers identified | CBT with neuroimaging assessment of brain changes |
| Collado et al. (2016) | To assess behavioral activation effectiveness for Spanish-speaking Latinos | RCT | Significant depression reduction when cultural values incorporated into activity planning | Behavioral activation with cultural adaptation |
| Compère et al. (2023) | To examine CBT augmentation with real-time fMRI neurofeedback | RCT | Enhanced efficacy when neurofeedback combined with CBT; neural targeting improved outcomes | CBT augmented with amygdala rtfMRI neurofeedback |
| Craig et al. (2021) | To evaluate affirmative CBT for sexual/gender minority adolescents | RCT | Significant reductions in depression (d = 0.96); enhanced coping and hope | AFFIRM intervention integrating minority stress framework |
| Damra et al. (2014) | To adapt trauma-focused CBT for Jordanian culture | Cultural adaptation study | Successful cultural adaptation maintaining treatment fidelity; therapist training essential | Trauma-focused CBT with Jordanian cultural adaptations |
| Dickey et al. (2023) | To identify neural predictors of CBT improvement in adolescent depression | Neuroimaging study | Neural reward responsiveness and emotion regulation predicted treatment response | CBT with neural mechanism analysis |
| Gombatto et al. (2023) | To develop protocol for culturally adapted CBT telerehabilitation for Latino patients | Protocol development study | Comprehensive protocol addressing cultural factors and technology barriers | Culturally adapted CBT telerehabilitation for chronic spine pain |
| Greenfield et al. (2018) | To examine race/ethnicity effects on mindfulness-based relapse prevention | RCT | Race/ethnicity and group composition moderated effectiveness; cultural matching important | Mindfulness-based relapse prevention with cultural considerations |
| Gurung et al. (2020) | To evaluate culturally appropriate Mental Health First Aid for Bhutanese refugees | Multi-state program evaluation | 72.4% improvement in symptom recognition with cultural orientation vs. 52% without | Mental Health First Aid with Bhutanese cultural orientation |
| Hernandez-Ramos et al. (2021) | To analyze linguistic responses to text messaging CBT in Latinx patients | Linguistic analysis study | Spanish speakers used more collective pronouns; English speakers more cognitive processing words | Text messaging CBT with linguistic analysis |
| M. Husain et al. (2017) | To pilot culturally adapted CBT for psychosis in Pakistan | Pilot RCT | Feasibility demonstrated; cultural adaptations enhanced engagement | Culturally adapted CBT for psychosis (CaCBTp) |
| N. Husain et al. (2021) | To evaluate group psychological intervention for British South Asian women | Multicenter RCT protocol | High engagement when collective coping strategies leveraged; cultural matching important | Positive Health Programme for postnatal depression |
| N. Husain et al. (2016) | To assess feasibility of culturally adapted CBT for psychosis in Pakistan | Feasibility study | Cultural adaptations essential for engagement; family involvement crucial | Culturally adapted CBT for psychosis with family components |
| Hwang et al. (2015) | To test culturally adapted CBT for Chinese Americans with depression | RCT | Significant improvements when face-saving concepts addressed; indirect communication honored | Culturally adapted CBT addressing Chinese cultural values |
| Ingman et al. (2016) | To compare CBT outcomes for chronic fatigue across ethnic groups | Comparative effectiveness study | Similar outcomes achieved with cultural adaptations; Ubuntu philosophy integration helpful | CBT for chronic fatigue with cultural considerations |
| Ishikawa et al. (2019) | To evaluate bidirectional cultural adaptation of CBT for anxious children | RCT | Successful adaptation in both directions (Japan-Australia); cultural values integration key | Bidirectionally culturally adapted CBT for child anxiety |
| Jidong et al. (2024) | To test Learning Through Play plus culturally adapted CBT for African/Caribbean mothers | RCT | Ubuntu philosophy integration effective; community-based delivery superior | Learning Through Play plus culturally adapted CBT |
| Jonassaint et al. (2019) | To examine racial differences in internet-delivered mental health care effectiveness | RCT | Similar clinical outcomes across races; different engagement patterns observed | Internet-delivered mental health care with racial analysis |
| Jonassaint et al. (2017) | To evaluate computerized CBT for anxiety/depression in African Americans | RCT | Effective when spiritual and communal elements incorporated; community delivery preferred | Computerized CBT with spiritual and community adaptations |
| Kananian et al. (2017) | To pilot transdiagnostic culturally adapted CBT for Farsi-speaking refugees | Pilot study | High engagement and effectiveness; trauma-informed approach essential | Transdiagnostic culturally adapted CBT for refugees |
| Kananian et al. (2022) | To develop protocol for culturally adapted CBT group therapy for refugees | Study protocol | Comprehensive protocol addressing cultural factors and practical barriers | Culturally adapted CBT group therapy (ReTreat) protocol |
| Kananian et al. (2020) | To evaluate CA-CBT+ for Afghan refugees | Randomized controlled pilot | Large improvements in psychopathological distress; quality of life sustained at follow-up | Culturally Adapted CBT Plus Problem Management (CA-CBT+) |
| Kanter et al. (2015) | To test behavioral activation effectiveness for Latinos with depression | Randomized hybrid trial | Lower acculturation predicted better response to cultural adaptations | Behavioral activation with cultural adaptation for Latinos |
| Katayama et al. (2020) | To examine neural/clinical changes in CBT vs. control in Japanese patients | Study protocol with neuroimaging | Protocol designed to identify neural biomarkers of treatment response | CBT with comprehensive neuroimaging assessment |
| Keefe et al. (2023) | To identify moderators of LGBTQ-affirmative CBT effectiveness | RCT | Especially effective for Black and Latino sexual minority men; internalized homophobia moderator | ESTEEM intervention with cultural and sexual identity focus |
| Kukla et al. (2018) | To examine CBT enhanced with cognitive remediation for schizophrenia | RCT | Enhanced work and neurocognition outcomes; cultural factors influenced engagement | CBT enhanced with cognitive remediation |
| Lamb et al. (2018) | To examine mechanisms of CBT for body image/self-care in HIV+ sexual minority men | Mechanism analysis study | Body image improvements mediated ART adherence through self-care behaviors | CBT for body image and HIV self-care |
| Lee et al. (2019) | To test culturally tailored motivational interviewing for Latino heavy drinkers | RCT | Cultural values integration enhanced engagement; dichos utilization effective | Culturally adapted motivational interviewing |
| Li et al. (2018) | To examine TSPO binding changes during CBT for depression | Neuroimaging study | Reduced microglia marker during successful CBT; neural inflammation decreased | CBT with TSPO binding neuroimaging |
| Lopez-Maya et al. (2019) | To compare mindfulness meditation effectiveness across Spanish/English speakers | RCT | Differential responses despite similar baseline stress; language moderating factor | Mindfulness meditation with linguistic analysis |
| Lovell et al. (2014) | To develop culturally sensitive psychosocial interventions in primary care | Development and evaluation study | Cultural sensitivity training crucial; community partnerships essential | Culturally sensitive psychosocial interventions |
| Q. Lu et al. (2022) | To test culturally adapted expressive writing for Chinese American breast cancer survivors | RCT | Significant reductions in depression/anxiety when cultural concepts integrated | Culturally adapted expressive writing intervention |
| Mamani and Suro (2016) | To evaluate culturally informed therapy for schizophrenia caregivers | Randomized clinical trial | Reduced self-conscious emotions and burden; family systems approach effective | Culturally informed therapy for caregivers |
| Månsson et al. (2016) | To examine neuroplasticity in response to CBT for social anxiety | Neuroimaging study | Measurable neuroplastic changes; brain-behavior relationships identified | CBT with neuroplasticity assessment |
| Meng et al. (2021) | To examine CBT neural mechanisms for mild-moderate depression | Neuroimaging study | Treatment effects and neural mechanisms identified; BDNF changes documented | CBT with comprehensive neural mechanism analysis |
| Naeem et al. (2015a) | To test brief culturally adapted CBT for depression in Pakistan | RCT | Effective brief intervention; cultural adaptations enhanced outcomes | Brief culturally adapted CBT (CaCBT) |
| Naeem et al. (2015b) | To evaluate brief culturally adapted CBT for psychosis in Pakistan | RCT | Effective brief intervention for low-income setting; scalability demonstrated | Brief culturally adapted CBT for psychosis |
| Naeem et al. (2014) | To test carer-supervised culturally adapted CBT self-help for depression | Multicenter RCT | Family involvement enhanced outcomes; culturally adapted self-help effective | Carer-supervised culturally adapted CBT |
| Ngo et al. (2016) | To compare community engagement vs. technical assistance for depression care dissemination | Randomized controlled effectiveness study | Community engagement superior for minority women; cultural matching important | Community engagement model for depression care |
| Norbury et al. (2024) | To examine how different CBT components affect cognitive mechanisms | Mechanism analysis study | Different components affected specific mechanisms; neural pathways identified | CBT with cognitive mechanism analysis |
| Nygren et al. (2019) | To test internet-based treatment for depression in Kurdish population | RCT | Effective despite technological barriers; cultural adaptation crucial | Internet-based CBT for Kurdish population |
| Osman et al. (2017) | To evaluate culturally tailored parenting support for Somali-born parents | RCT | Improved parental mental health and competence; cultural tailoring essential | Culturally tailored parenting support program |
| Osman et al. (2021) | To examine long-term impact of culturally tailored parenting program | Longitudinal cohort study | Sustained improvements in parent and child mental health outcomes | Culturally tailored parenting program (follow-up) |
| Pachankis et al. (2020) | To test transdiagnostic minority stress intervention for gender diverse women | RCT | Effective for depression, anxiety, and unhealthy alcohol use; intersectional approach important | Transdiagnostic minority stress intervention |
| Paris et al. (2018) | To evaluate culturally adapted web-based CBT for Spanish-speaking substance users | Randomized clinical trial | Effective web-based intervention; cultural adaptation enhanced engagement | Culturally adapted web-based CBT |
| Parra-Cardona et al. (2017) | To examine differential cultural adaptation impact on Latino immigrant parents | RCT | Deep cultural adaptation superior to surface modifications | Culturally adapted parent training interventions |
| Penedo et al. (2018) | To design culturally adapted CBT for Latino prostate cancer patients | Study protocol | Comprehensive cultural adaptation protocol; family involvement central | Encuentros de Salud culturally adapted CBT protocol |
| Peris et al. (2020) | To examine ethnicity moderation in family-focused OCD treatment | RCT | Ethnicity moderated outcomes; cultural factors influenced family engagement | Family-focused treatment for pediatric OCD |
| Perry et al. (2024) | To investigate culturally adapted ACT group for UK Vietnamese communities | Practice-based feasibility study | High acceptability; cultural adaptation enhanced engagement | Culturally adapted Acceptance and Commitment Therapy |
| Pots et al. (2014) | To evaluate MBCT as public mental health intervention | RCT | Effective public health intervention; cultural factors influenced engagement | Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy |
| Pratt et al. (2017) | To address behavioral health disparities for Somali immigrants through group CBT | Group intervention study | Group format reduced stigma; cultural adaptation essential for engagement | Group Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Somali immigrants |
| Quiñonez-Freire et al. (2020) | To culturally adapt Smiling is Fun program for Ecuador | Study protocol | Comprehensive cultural adaptation protocol for public health implementation | Culturally adapted Smiling is Fun program |
| Safren et al. (2021) | To treat depression and improve HIV adherence with task-shared CBT in South Africa | RCT | Improved medication adherence and depression; task-sharing model effective | Task-shared CBT for depression and HIV adherence |
| Salamanca-Sanabria et al. (2018) | To assess culturally adapted internet-delivered CBT for depression protocol | Study protocol | Comprehensive protocol for Colombian population; technology integration planned | Culturally adapted internet-delivered CBT protocol |
| Salamanca-Sanabria et al. (2020) | To evaluate culturally adapted internet-delivered CBT for depression | RCT | Effective internet-delivered intervention; cultural adaptation enhanced outcomes | Culturally adapted internet-delivered CBT |
| Sapkota et al. (2024) | To examine internet-delivered CBT for diverse ethnocultural groups | Observational trial with benchmarking | High satisfaction and engagement; outcomes comparable to mainstream populations | Internet-delivered CBT for Indigenous and diverse populations |
| Schlief et al. (2023) | To examine ethnic differences in psychological interventions receipt | Cross-sectional study | Significant disparities in intervention access; cultural barriers identified | Analysis of Early Intervention in Psychosis services |
| Schwartzman et al. (2023) | To evaluate autism-adapted group CBT for depression in autistic youth | Preliminary feasibility study | High feasibility and acceptability; community guidance essential | Community-guided autism-adapted group CBT |
| Sclare et al. (2015) | To develop open-access CBT workshops for inner-city youth | Innovation development study | Community-based approach effective; cultural adaptation enhanced engagement | DISCOVER CBT workshops for minority youth |
| Siddiqui et al. (2019) | To examine culturally adapted lifestyle intervention effects on mental health | RCT | Improved mental health among Middle-Eastern immigrants; cultural adaptation crucial | Culturally adapted lifestyle intervention |
| Singla et al. (2022) | To develop culturally sensitive psychotherapy for perinatal women | Mixed methods study | Cultural sensitivity enhanced engagement; diverse adaptation strategies needed | Culturally sensitive perinatal psychotherapy |
| Suen et al. (2023) | To evaluate culturally adapted counseling for low-income ethnic minorities | Pragmatic randomized trial | Effective for mental distress; cultural adaptation enhanced acceptability | Culturally adapted counseling service |
| Sulaimanova and Sulaimanov (2017) | To identify ethno-cultural predictors determining CBT features for PTSD | Cross-cultural study | Cultural predictors significantly influenced CBT effectiveness; adaptation necessary | Culturally adapted CBT for PTSD |
| Tang et al. (2016) | To compare CBT effectiveness across Asian American and white patients | Comparative effectiveness study | Similar outcomes achieved with cultural considerations; somatic symptom focus important | CBT with ethnic comparison analysis |
| Tay et al. (2020) | To evaluate integrative therapy for common mental health symptoms in refugees | RCT | Effective for multiple refugee populations; cultural integration enhanced outcomes | Integrative Adapt Therapy for refugees |
| Tovote et al. (2014) | To compare individual MBCT and CBT for depressive symptoms in diabetes patients | RCT | Both interventions effective; individual preferences influenced outcomes | Individual MBCT and CBT for diabetes patients |
| Tsai et al. (2016) | To examine cultural differences in stress recovery enhancement strategies | Experimental study | Self-enhancement vs. self-improvement effects varied across cultures | Cultural analysis of stress recovery strategies |
| Vargas et al. (2019) | To develop protocol for depression intervention in diverse minorities | Study protocol | Comprehensive protocol addressing multiple minority identities and barriers | Resilience Against Depression Disparities (RADD) protocol |
| Wei et al. (2024) | To evaluate school-based mental health literacy intervention | Comprehensive evaluation study | Effective across demographic groups; cultural factors influenced engagement | School-based mental health literacy intervention |
| Woods-Jaeger et al. (2017) | To describe culturally responsive trauma-focused CBT delivery in East Africa | Implementation study | Cultural responsiveness essential; local adaptation and training crucial | Culturally responsive trauma-focused CBT |
| Yang et al. (2018) | To examine network changes associated with symptom improvement following CBT | Neuroimaging study | Network changes identified across MDD and PTSD; transdiagnostic neural mechanisms | CBT with network neuroimaging analysis |
| Yeo et al. (2020) | To pilot dialectical behavior therapy for ethnic minority youth with self-harm | Pilot application study | Effective for urban ethnic minority youth; cultural adaptation enhanced engagement | Dialectical behavior therapy for ethnic minority youth |
| Yi et al. (2024) | To test internet-based LGBTQ-affirmative CBT for Chinese sexual minority men | RCT | Effective guided internet intervention; cultural and sexual identity integration crucial | Internet-based LGBTQ-affirmative CBT |
| Young and Yat-nam (2021) | To evaluate culturally adapted CBT group intervention | RCT | Group format with cultural adaptation effective; community setting enhanced outcomes | Culturally adapted CBT group intervention |
| Zemestani et al. (2022) | To pilot culturally adapted trauma-focused CBT for Iraqi women with war-related PTSD | Pilot randomized clinical trial | Effective novel intervention; cultural adaptation essential for war trauma | Culturally adapted trauma-focused CBT for war-related PTSD |
| E. Zhou et al. (2022) | To test culturally tailored internet-delivered CBT for insomnia in Black women | Randomized clinical trial | Effective culturally tailored intervention; addressed cultural sleep practices and barriers | Culturally tailored internet-delivered CBT for insomnia |
| Zoellner et al. (2024) | To evaluate lay-led intervention for war and refugee trauma | RCT | Effective lay-led model; cultural grounding and community ownership crucial | Islamic Trauma Healing lay-led intervention |
| Cultural Population | Studies (n) | Primary Cultural Adaptations | Neuroscientific Component | Mean Effect Size (Range) | Retention Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian Populations | 15 |
| ACC-insula interoceptive pathways; enhanced theta coherence during mindfulness; mPFC activation with family content | d = 1.32 (0.82–1.89) | 78% (range: 68–100%) |
| Latino/Hispanic Populations | 20 |
| OFC reward processing during warm interactions; ACC-amygdala coupling with emotion expression; left hemisphere language network with dichos | d = 1.18 (0.74–1.65) | 81% (range: 61–95%) |
| African/Black Populations | 13 |
| TPJ social cognition activation; DMN engagement with spiritual content; mirror neuron activation in group healing | d = 1.24 (0.85–1.78) | 76% (range: 64–89%) |
| Refugee/Asylum-Seeker | 9 |
| Amygdala regulation (8+ sessions required); HPA axis normalization; hippocampal neurogenesis; autonomic nervous system regulation | d = 1.08 (0.56–1.45) | 68% * (range: 52–84%) |
| Indigenous Populations | 2 |
| Altered state network activation; enhanced sensory integration; bilateral narrative processing; circadian rhythm alignment | d = 1.45 (1.23–1.67) | 83% (range: 79–87%) |
| LGBTQ+/Sexual Minority | 5 |
| Reward circuit modulation with identity affirmation; reduced amygdala reactivity to minority stress; enhanced self-network coherence | d = 1.16 (0.74–1.52) | 73% (range: 65–84%) |
| Mixed/Multiple Groups | 30 |
| Variable neural targets based on cultural assessment; network flexibility; adaptive mechanism engagement | d = 0.89 (0.29–1.34) | 71% (range: 48–92%) |
| Cultural Adaptation Type | Population Groups | Key Therapeutic Elements | Notable Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language and Metaphors | All populations | Culturally relevant idioms, proverbs, storytelling | Enhanced understanding and engagement |
| Family Integration | Asian, Latin American | Family therapy components, collective goal-setting | Improved family support and reduced relapse |
| Spiritual Elements | African, Indigenous | Prayer, traditional healing practices, spiritual coping | Greater meaning-making and resilience |
| Collectivist Focus | Asian, African, Indigenous | Group harmony, interdependence, community healing | Reduced stigma, increased help-seeking |
| Historical Trauma | Refugee, Indigenous | Trauma-informed approaches, cultural loss acknowledgment | Enhanced therapeutic alliance |
| Mechanism | Cultural Context | Implementation Strategy | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Alliance | All populations | Cultural matching, language concordance, shared worldview | Reduced dropout, increased disclosure |
| Cognitive Restructuring | Collectivist cultures | Group-based reality testing, collective problem-solving | Enhanced perspective-taking |
| Behavioral Activation | Latin American | Family-involved pleasant activities, community engagement | Increased social support |
| Emotion Regulation | African populations | Spiritual coping, communal processing | Improved distress tolerance |
| Exposure Therapy | Refugee populations | Culturally safe exposure, narrative approaches | Reduced avoidance |
| Mental Health Condition | Most Responsive Populations | Optimal Delivery Method | Key Success Factors | Sustained at 12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | Asian, Indigenous | Group therapy with family involvement | Cultural values integration, collective healing | 85% maintained improvement |
| Anxiety | European, North American | Individual therapy or guided self-help | Structured approach, cognitive focus | 78% maintained improvement |
| PTSD | Refugee, Indigenous | Intensive group with cultural healing | Trauma-informed, community support | 82% maintained improvement |
| General Distress | All populations | Flexible based on culture | Matched to cultural preference | 74% maintained improvement |
| Sleep Problems | Asian, European | Combined individual + digital | Sleep education + cultural practices | 71% maintained improvement |
| Well-Being | Latin American, African | Group with community activities | Social connection, meaning-making | 80% maintained improvement |
| Cultural Population | Delivery Method | Key Outcomes | Unique Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asian (Collectivistic) | Group Format (Predominant) |
|
|
| Latino/Hispanic | Group Format + Text Messaging |
|
|
| African/African American | Internet-Delivered (Primary) |
|
|
| Refugee/Asylum-Seeker | Mobile Applications + Group Support |
|
|
| Indigenous | Limited data (Internet reported) |
|
|
| Pacific Islander | Mobile Applications |
|
|
| Cultural Group | Preferred Duration | Engagement Patterns | Cultural Factors | Optimal Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian Populations | Moderate (9–16 sessions) |
|
| Standard length with extended relationship-building phase |
| Latino/Hispanic | Moderate-Extended (10–20 sessions) |
|
| Flexible duration with family involvement options |
| Refugee/Asylum-seeker | Brief-Moderate (6–12 sessions) |
|
| Flexible brief interventions with crisis responsiveness |
| African/African American | Variable (8–16 sessions) |
|
| Extended engagement phase with trust-building focus |
| Indigenous | Extended (12–20+ sessions) |
|
| Long-term engagement aligned with cultural healing concepts |
| Mixed/General | Standard (8–12 sessions) |
|
| Stepped care with flexible intensification |
| Delivery Method | Infrastructure Requirements | Common Barriers | Successful Solutions | Best Suited for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internet-Delivered CBT |
|
|
| Urban populations with infrastructure access |
| Mobile Applications |
|
|
| Refugees, youth, transient populations |
| Text Messaging |
|
|
| Low-literacy populations, rural communities |
| Telehealth/Video |
|
|
| Rural/isolated with basic infrastructure |
| Group Face-to-Face |
|
|
| Collectivistic cultures, stable communities |
| Hybrid Models |
|
|
| Diverse populations with heterogeneous needs |
| Adaptation Level | Components Modified | Implementation Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Structure |
|
|
| Deep Structure—Values |
|
|
| Deep Structure—Methods |
|
|
| Deep Structure—Content |
|
|
| Contextual Factors |
|
|
| Population | Outcome Domain | Culturally Adapted CBT | Standard CBT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refugee/Asylum Seekers | Engagement |
|
|
| Symptom Reduction |
|
| |
| Functional Recovery |
|
| |
| Cultural Factors |
|
| |
| Hispanic/Latino | Engagement |
|
|
| Symptom Reduction |
|
| |
| Treatment Satisfaction |
|
| |
| Language Factors |
|
| |
| Asian | Engagement |
|
|
| Symptom Presentation |
|
| |
| Family Involvement |
|
| |
| Communication Style |
|
| |
| African/Black | Engagement |
|
|
| Treatment Credibility |
|
| |
| Social Support |
|
| |
| Delivery Methods |
|
| |
| Indigenous | Engagement |
|
|
| Cultural Relevance |
|
| |
| Healing Concept |
|
|
| Cultural Context | Surface Adaptations | Deep Neurocognitive Adaptations | Neural Markers of Acceptability | Clinical Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian Populations |
|
|
|
|
| Latin American |
|
|
|
|
| African/African Diaspora |
|
|
|
|
| Indigenous |
|
|
|
|
| Refugee/Trauma-Affected |
|
|
|
|
| Technology Platform | Cultural Population | Engagement Rate | Neural Changes Observed | Clinical Outcomes | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Apps | Asian (n = 412) | 73% completion | ↑ Theta coherence with cultural imagery | d = 0.82 symptom reduction | Gamification with collective goals essential |
| Western (n = 387) | 68% completion | ↑ DLPFC activation with cognitive modules | d = 0.91 symptom reduction | Individual achievement tracking crucial | |
| Latin American (n = 298) | 61% completion | Enhanced when family features included | d = 0.74 symptom reduction | Synchronous communication features needed | |
| VR Interventions | Indigenous (n = 89) | 81% engagement | ↑ Hippocampal activation with land-based VR | d = 1.23 cultural identity | Sacred site recreation with elder approval |
| Refugee (n = 156) | 72% engagement | Gradual amygdala habituation | d = 0.96 PTSD symptoms | Careful trauma exposure graduation | |
| Web-Based CBT | Mixed urban (n = 523) | 64% completion | Variable based on cultural matching | d = 0.77 overall | Cultural assessment crucial for module selection |
| Hybrid (Digital+Human) | All populations (n = 1847) | 79% completion | Enhanced network flexibility | d = 0.94 weighted mean | Cultural competence of human support critical |
| Biofeedback-Enhanced | Collectivistic (n = 267) | 77% adherence | ↑ HRV coherence with group protocols | d = 0.88 anxiety reduction | Group coherence training superior to individual |
| Individualistic (n = 241) | 74% adherence | ↑ Alpha asymmetry shifts | d = 0.85 depression reduction | Personal achievement framing optimal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the University Association of Education and Psychology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Gkintoni, E.; Nikolaou, G. Neuroscientific Framework of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions for Mental Health Across Diverse Cultural Populations: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness, Delivery Methods, and Engagement. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2026, 16, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe16010002
Gkintoni E, Nikolaou G. Neuroscientific Framework of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions for Mental Health Across Diverse Cultural Populations: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness, Delivery Methods, and Engagement. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education. 2026; 16(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe16010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGkintoni, Evgenia, and Georgios Nikolaou. 2026. "Neuroscientific Framework of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions for Mental Health Across Diverse Cultural Populations: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness, Delivery Methods, and Engagement" European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 16, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe16010002
APA StyleGkintoni, E., & Nikolaou, G. (2026). Neuroscientific Framework of Cognitive–Behavioral Interventions for Mental Health Across Diverse Cultural Populations: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness, Delivery Methods, and Engagement. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 16(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe16010002







