Examining the Influence of Exploration and Parental Education Attainment on Students’ Acceptance of Collectivist Values
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To examine whether Chinese college students’ collectivist value acceptance is associated with their prior exploration experience.
- To examine whether the associations between students’ collectivist value acceptance and prior exploration experience are moderated by parental education attainment.
2. Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Foundation
2.1.1. Overview of the Mindsponge Theory
- (1)
- It expresses the natural patterns of the biosphere.
- (2)
- It functions through dynamically balanced processes.
- (3)
- It utilizes cost–benefit analysis, which targets the maximization of the perceived benefit of the system and the minimization of its perceived cost.
- (4)
- It uses energy for functioning; thus, energy conservation is a natural prioritization.
- (5)
- It establishes objectives and priorities based on its system’s requirements.
- (6)
- Its essential goal is to extend the existence of the system via survival, growth, and reproduction.
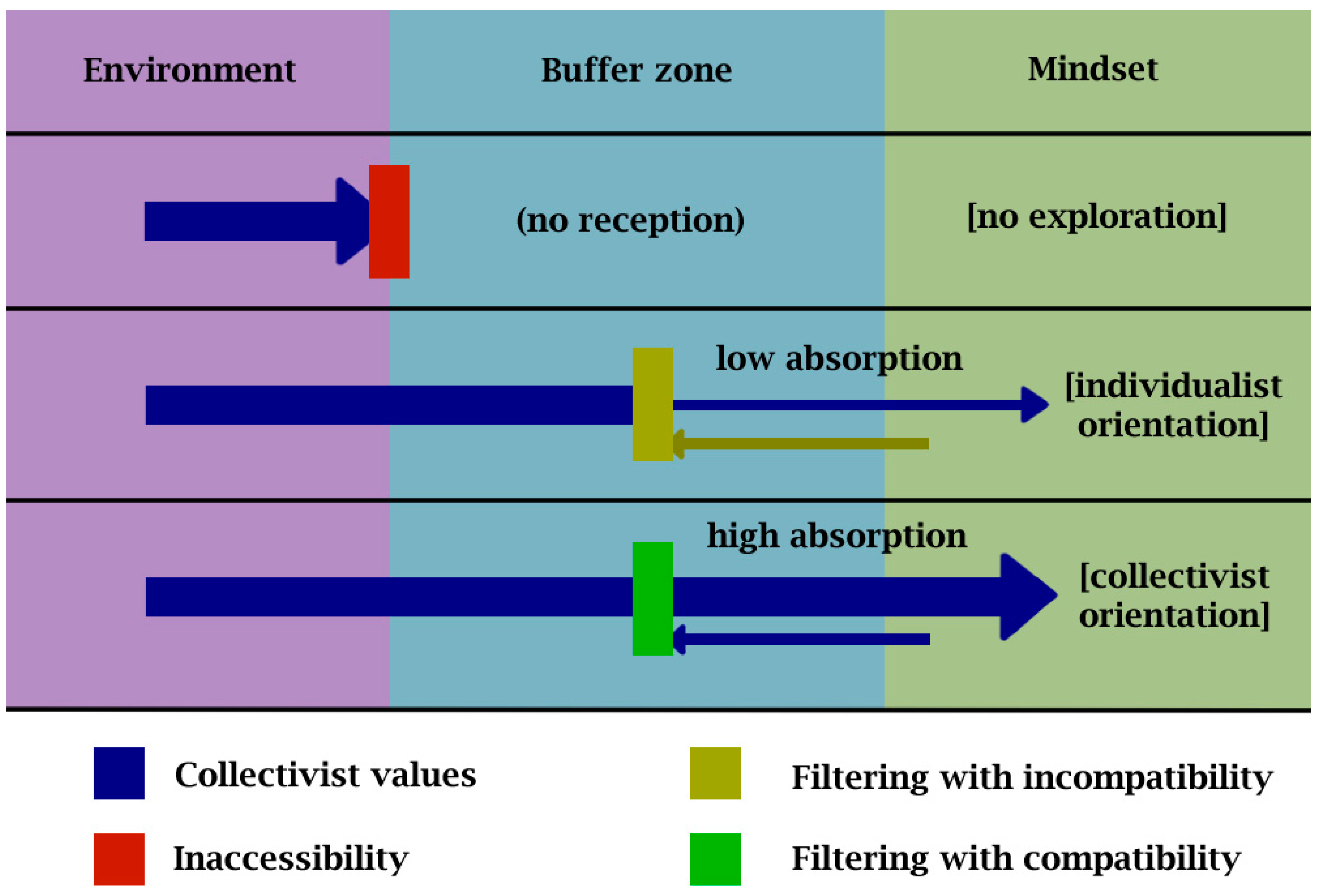
2.1.2. Mindset and Information Filtering
- (1)
- The buffer zone is a conceptual space where the mind temporarily stores information obtained from the surrounding environment or memory. The filtering system works to assess the information here.
- (2)
- During the filtering process, the mind uses subjective judgments to determine whether to accept or discard this information based on its perceived costs and benefits. If the perceived benefits outweigh the perceived costs, then the information will be allowed to enter the mindset, and vice versa. Previous trusted values stored in memory are used as references for comparison and connection to the currently evaluated information.
- (3)
- Once accepted, the information will be allowed to enter the mindset and become a new trusted value. Therefore, it can be used as a reference for future assessments of related information and thus will influence the formation of related thoughts, emotions, and behaviors [54].
2.1.3. Model Conceptualization
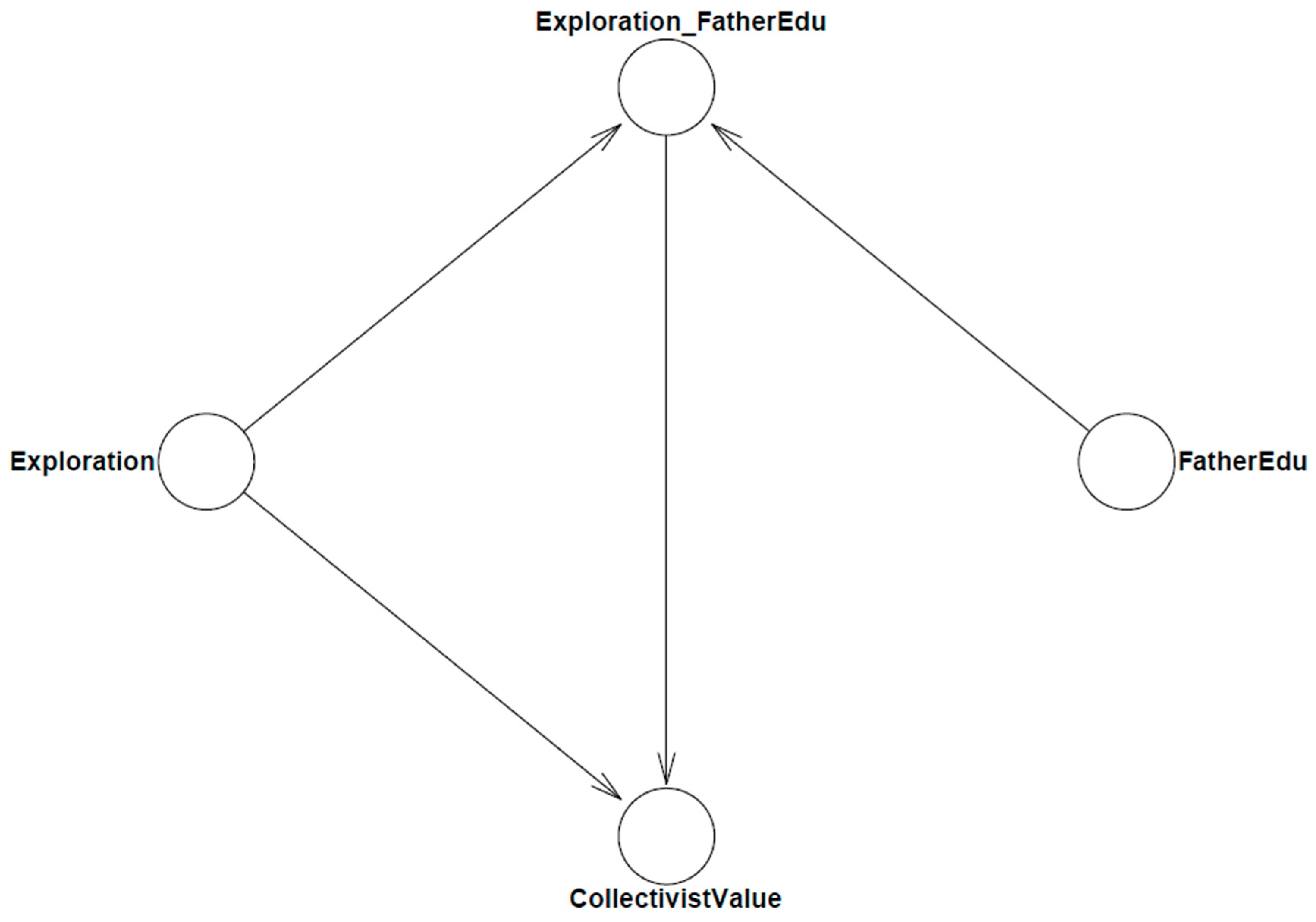
2.2. Model Construction
2.2.1. Variable Description
2.2.2. Models for Statistical Analysis
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model 1
3.2. Model 2 and Model 3
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


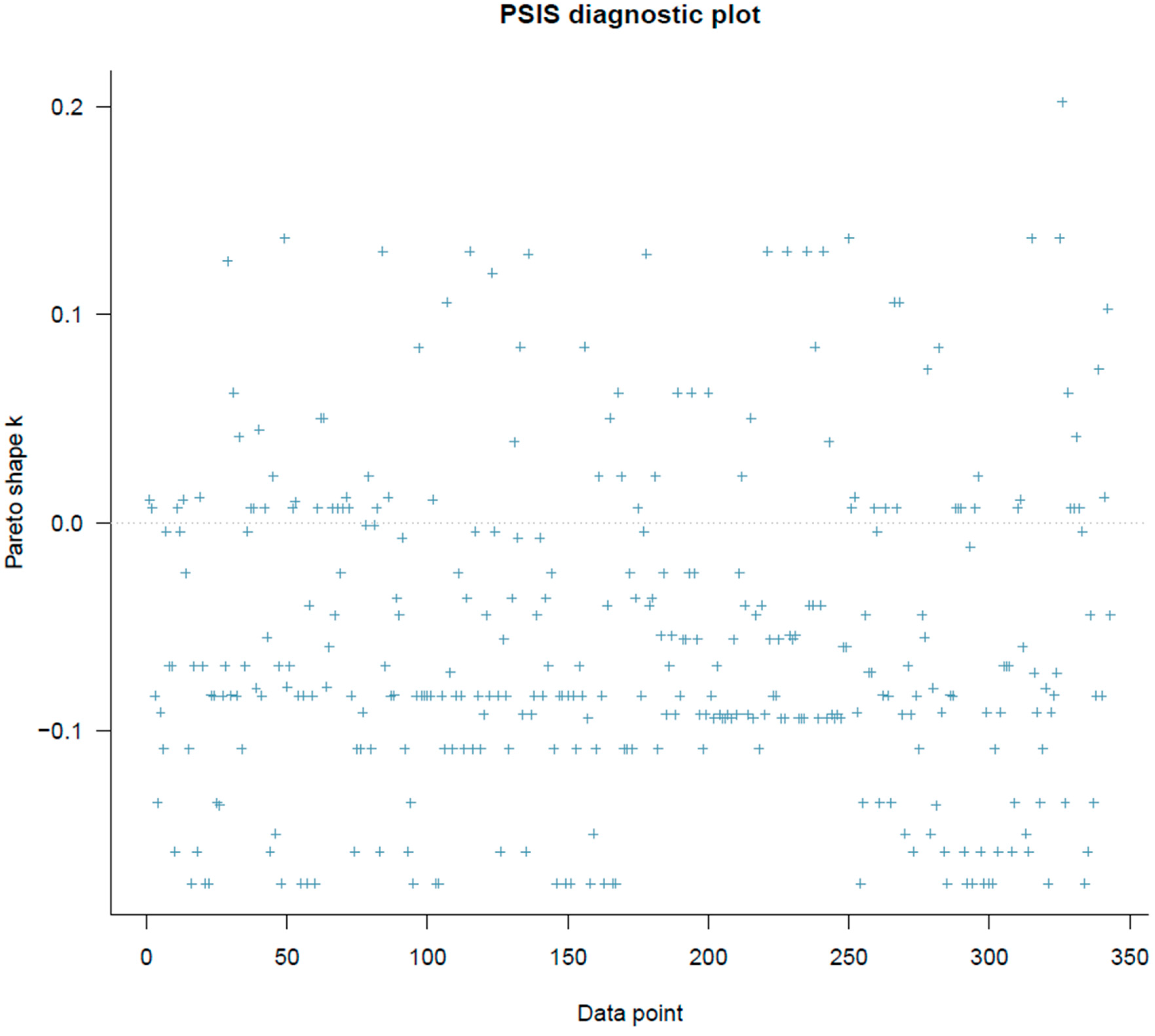


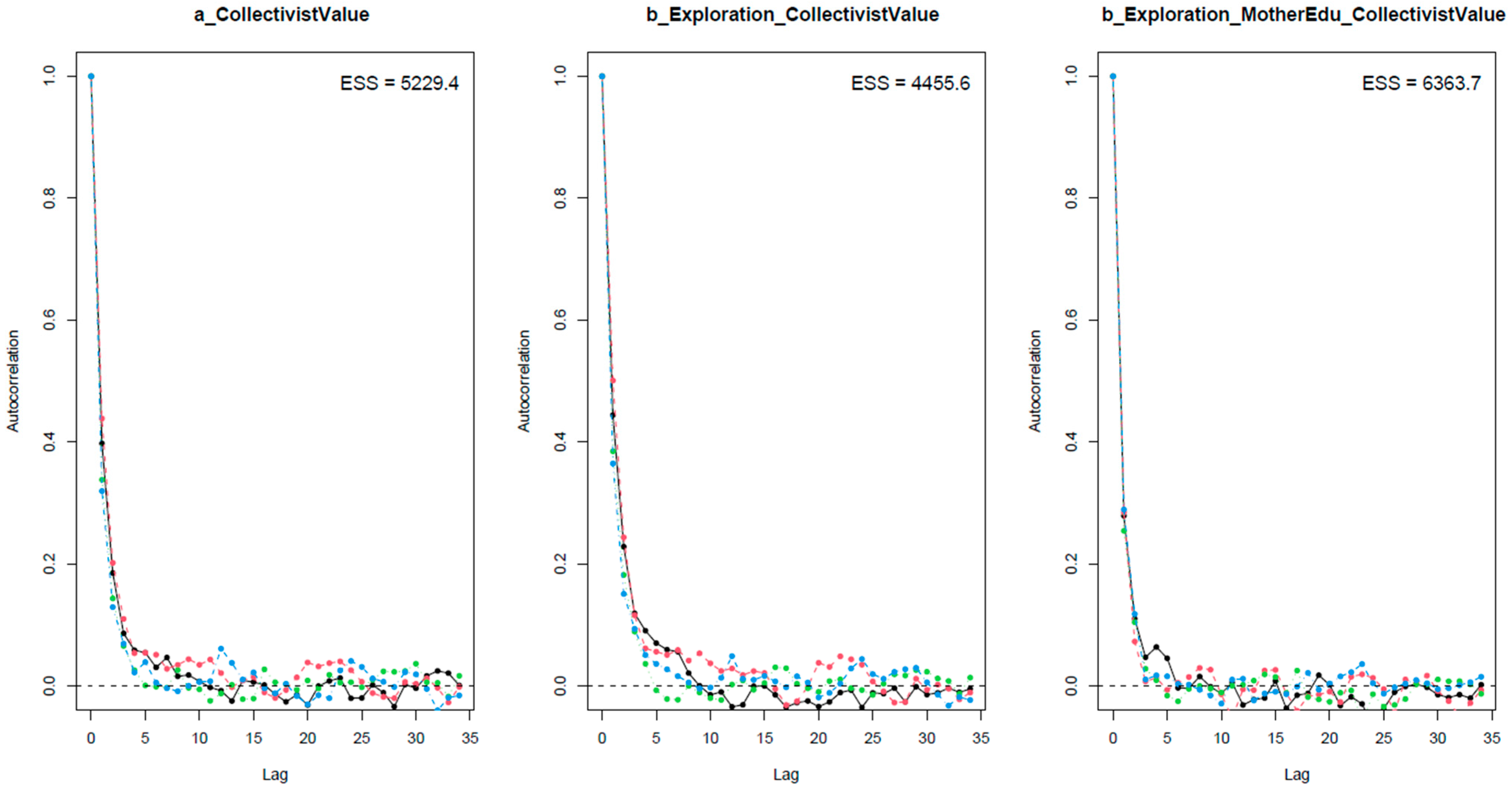
References
- Triandis, H.C.; Gelfand, M.J. A Theory of Individualism and Collectivism. In Handbook of Theories of Social Psychology; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Newcastle, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, H.R.; Kitayama, S. Culture and the Self: Implications for Cognition, Emotion, and Motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1991, 98, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodnichenko, Y.; Roland, G. Which Dimensions of Culture Matter for Long-Run Growth? Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyserman, D.; Coon, H.M.; Kemmelmeier, M. Rethinking Individualism and Collectivism: Evaluation of Theoretical Assumptions and Meta-Analyses. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, H.; Delhey, J.; Welzel, C.; Yuan, H. The China Puzzle: Falling Happiness in a Rising Economy. J. Happiness Stud. 2009, 10, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. Cultural Dimensions in Management and Planning. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 1984, 1, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. The Individualization of Chinese Society; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- STATISTA China: Gini Coefficient 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/250400/inequality-of-income-distribution-in-china-based-on-the-gini-index/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Hu, D. Trade, Rural–Urban Migration, and Regional Income Disparity in Developing Countries: A Spatial General Equilibrium Model Inspired by the Case of China. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2002, 32, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shum, W.Y.; Cheong, T.S.; Wang, L. COVID-19 and Regional Income Inequality in China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 687152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPI Environmental Performance Index|Environmental Performance Index. Available online: https://epi.yale.edu/epi-results/2022/component/epi (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- AirVisual, Iqa. World Air Quality Report. Reg. City PM2 2020, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, G.H.; Hofstede, G. Culture’s Consequences: Comparing Values, Behaviors, Institutions and Organizations across Nations; Sage: Newcastle UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew, T.F.; Tropp, L.R. A Meta-Analytic Test of Intergroup Contact Theory. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2006, 90, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, E.K.; Zelenski, J.M.; Murphy, S.A. The Nature Relatedness Scale: Linking Individuals’ Connection with Nature to Environmental Concern and Behavior. Environ. Behav. 2009, 41, 715–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Ho, C.-I. Tourism Information Technology Research Trends: 1990–2016. Tour. Rev. 2019, 74, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Fraile, F.J.; Ríos-Martín, M.Á.; Ceballos-Hernandez, C. Tourism and Mobile Devices: Provenance of Academic Research through a Bibliometric Study. J. Tour. Anal. 2018, 25, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, I. Tourism Development and Promotion in Central Kalimantan Post Pandemi COVID-19: A Sustainable Economic Approach. Int. J. Bus. Technol. Organ. 2023, 3, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarense, B.E.S.; Hidayah, T.; Abdillah, F. Digital Technology and Pentahelix Role Model for Sport Tourism Event of IVCA 2018 in Bali. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Applied Science and Technology (iCAST), Manado, Indonesia, 26–27 October 2018; IEEE: Manado, Indonesia, 2018; pp. 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Abramson, A. Cultivating Empathy. Available online: https://www.apa.org/monitor/2021/11/feature-cultivating-empathy (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Fu, W.; Wang, C.; Chai, H.; Xue, R. Examining the Relationship of Empathy, Social Support, and Prosocial Behavior of Adolescents in China: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Humanit Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.X.; Guy, B. Social Connectedness and Its Implication on Student–Teacher Relationships and Suspension. Prev. Sch. Fail. Altern. Educ. Child. Youth 2017, 61, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, E.M.; Davis, C.; Mandy, L.; Wong, C. The Role of School Connectedness in Supporting the Health and Well-Being of Youth: Recommendations for School Nurses. NASN Sch. Nurse 2022, 37, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeri, A.K.; Cruwys, T.; Barlow, F.K.; Stronge, S.; Sibley, C.G. Social Connectedness Improves Public Mental Health: Investigating Bidirectional Relationships in the New Zealand Attitudes and Values Survey. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Nguyen, M.-H.T.; Jin, R.; Nguyen, Q.-L.; La, V.-P.; Le, T.-T.; Vuong, Q.-H. Preventing the Separation of Urban Humans from Nature: The Impact of Pet and Plant Diversity on Biodiversity Loss Belief. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Jones, T.E. Predictors of Support for Biodiversity Loss Countermeasures and Bushmeat Consumption among Vietnamese Urban Residents. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 4, e12822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Jones, T.E. Building Eco-Surplus Culture among Urban Residents as a Novel Strategy to Improve Finance for Conservation in Protected Areas. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Education Expenditure and Parenting Styles: Evidence from Cognitive Development in China. J. Fam. Econ. Issues 2021, 42, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, X.; Ji, L.; Chen, L.; Deater-Deckard, K. Reconsidering Parenting in Chinese Culture: Subtypes, Stability, and Change of Maternal Parenting Style During Early Adolescence. J. Youth Adolesc. 2017, 46, 1117–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Chang, L. Education and Parenting in China. In School Systems, Parent Behavior, and Academic Achievement: An International Perspective; Sorbring, E., Lansford, J.E., Eds.; Young People and Learning Processes in School and Everyday Life; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 15–28. ISBN 978-3-030-28277-6. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Walker, L.M.; Nelson, L.J. Black Hawk down? Establishing Helicopter Parenting as a Distinct Construct from Other Forms of Parental Control during Emerging Adulthood. J. Adolesc. 2012, 35, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamborn, S.D.; Mounts, N.S.; Steinberg, L.; Dornbusch, S.M. Patterns of Competence and Adjustment among Adolescents from Authoritative, Authoritarian, Indulgent, and Neglectful Families. Child Dev. 1991, 62, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornbusch, S.M.; Ritter, P.L.; Leiderman, P.H.; Roberts, D.F.; Fraleigh, M.J. The Relation of Parenting Style to Adolescent School Performance. Child Dev. 1987, 58, 1244–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, L.; Lamborn, S.D.; Darling, N.; Mounts, N.S.; Dornbusch, S.M. Over-Time Changes in Adjustment and Competence among Adolescents from Authoritative, Authoritarian, Indulgent, and Neglectful Families. Child Dev. 1994, 65, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, X. Parenting Styles and Children’s Academic Performance: Evidence from Middle Schools in China. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 113, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, E.; Laursen, B.; Tardif, T. Socioeconomic Status and Parenting. In Handbook of Parenting: Vol. 2. Biology and Ecology of Parenting; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lansford, J.E.; Zietz, S.; Al-Hassan, S.M.; Bacchini, D.; Bornstein, M.H.; Chang, L.; Deater-Deckard, K.; Di Giunta, L.; Dodge, K.A.; Gurdal, S. Culture and Social Change in Mothers’ and Fathers’ Individualism, Collectivism and Parenting Attitudes. Soc. Sci. 2021, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwairy, M.; Achoui, M.; Abouserie, R.; Farah, A. Parenting Styles, Individuation, and Mental Health of Arab Adolescents: A Third Cross-Regional Research Study. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 2006, 37, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H. (Eds.) The Mindsponge and BMF Analytics for Innovative Thinking in Social Sciences and Humanities; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-83-67405-11-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q.H.; Napier, N.K. Acculturation and Global Mindsponge: An Emerging Market Perspective. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2015, 49, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslow, A.H. Motivation and Personality; Longman: Prabhat, Prakashan, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, G.; Hofstede, G.J.; Minkov, M. Cultures and Organizations: Software of the Mind; Mcgraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I.; Konno, N. The Concept of “Ba”: Building a Foundation for Knowledge Creation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1998, 40, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzberg, H. Nature of Managerial Work; Harpercollins College Div: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The Theory of Planned Behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Advantage of Nations: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q.-H. Mindsponge Theory; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maliske, L.; Kanske, P. The Social Connectome—Moving Toward Complexity in the Study of Brain Networks and Their Interactions in Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 845492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagleman, D. The Brain: The Story of You; Canongate Books: Edinburgh, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-78211-659-2. [Google Scholar]
- Costandi, M. Neuroplasticity; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-262-33707-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, H.; Damasio, A.R. Emotion, Decision Making and the Orbitofrontal Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger, E. What Is Life? With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical Sketches; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-0-521-42708-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hofman, M. Evolution of the Human Brain: When Bigger Is Better. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; Le, T.-T.; Jin, R.; Khuc, Q.V.; Nguyen, H.-S.; Vuong, T.-T.; Nguyen, M.-H. Near-Suicide Phenomenon: An Investigation into the Psychology of Patients with Serious Illnesses Withdrawing from Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Le, T.-T. Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2021, 11, 468–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Hoang, G.; Nguyen, T.-P.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Le, T.-T.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Vuong, Q.-H. An Analytical Framework-Based Pedagogical Method for Scholarly Community Coaching: A Proof of Concept. MethodsX 2023, 10, 102082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Jin, R.; Hoang, G.; Nguyen, M.-H.T.; Nguyen, P.-L.; Le, T.-T.; La, V.-P.; Vuong, Q.-H. Examining Contributors to Vietnamese High School Students’ Digital Creativity under the Serendipity-Mindsponge-3D Knowledge Management Framework. Think. Ski. Creat. 2023, 49, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Le, T.-T.; Vuong, T.-T.; Nguyen, T.-P.; Hoang, G.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Vuong, Q.-H. A Gender Study of Food Stress and Implications for International Students Acculturation. World 2023, 4, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; Le, T.-T.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Ho, M.-T.; Van Khuc, Q.; Nguyen, M.-H. Covid-19 Vaccines Production and Societal Immunization under the Serendipity-Mindsponge-3D Knowledge Management Theory and Conceptual Framework. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Le, T.-T.; Vuong, Q.-H. Ecomindsponge: A Novel Perspective on Human Psychology and Behavior in the Ecosystem. Urban Sci. 2023, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; Le, T.-T.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H. The Psychological Mechanism of Internet Information Processing for Post-Treatment Evaluation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Wang, X. “Somewhere I Belong?” A Study on Transnational Identity Shifts Caused by “Double Stigmatization” among Chinese International Student Returnees during COVID-19 through the Lens of Mindsponge Mechanism. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1018843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevre, R.; Guimarães, I.; Zhao, W. Parents, Individualism and Education: Three Paradigms and Four Countries. Rev. Educ. 2020, 8, 693–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Gu, T.; Wang, Y.; Jia, F. Improving Career Adaptability through Motivational Interview among Peers: An Intervention of at-Risk Chinese College Students Majoring in Foreign Language. J. Vocat. Behav. 2022, 138, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.-J.; Leung, S.A.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Xu, H. Career Adapt-Abilities Scale—China Form: Construction and Initial Validation. J. Vocat. Behav. 2012, 80, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; La, V.-P.; Le, T.-T.; Vuong, Q.-H. Introduction to Bayesian Mindsponge Framework Analytics: An Innovative Method for Social and Psychological Research. MethodsX 2022, 9, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Vuong, Q.H.; Tran, M.N. Central Limit Theorem for Functional of Jump Markov Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Huu, N.; Hoang, V.Q. On the Martingale Representation Theorem and on Approximate Hedging a Contingent Claim in the Minimum Deviation Square Criterion. In Some Topics in Industrial and Applied Mathematics; World Scientific: London, UK, 2007; pp. 134–151. [Google Scholar]
- Csilléry, K.; Blum, M.G.; Gaggiotti, O.E.; François, O. Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) in Practice. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunson, D.B. Commentary: Practical Advantages of Bayesian Analysis of Epidemiologic Data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J. Bayesian Methods: A Social and Behavioral Sciences Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Vehtari, A.; Gelman, A.; Gabry, J. Practical Bayesian Model Evaluation Using Leave-One-out Cross-Validation and WAIC. Stat. Comput. 2017, 27, 1413–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehtari, A.; Gabry, J. Bayesian Stacking and Pseduo-BMA Weights Using the Loo Package. Version Loo 2019, 2. [Google Scholar]
- McElreath, R. Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan, 2nd ed.; CRC Texts in Statistical Science; Taylor and Francis, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-367-13991-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S.P.; Gelman, A. General Methods for Monitoring Convergence of Iterative Simulations. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1998, 7, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.M. Introduction to Applied Bayesian Statistics and Estimation for Social Scientists; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- La, V.-P.; Vuong, Q.-H. Bayesvl: Visually Learning the Graphical Structure of Bayesian Networks and Performing MCMC with ‘Stan.’; The Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN), 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/bayesvl/index.html (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Vuong, Q.-H. The (Ir)Rational Consideration of the Cost of Science in Transition Economies. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, Q.-H. Reform Retractions to Make Them More Transparent. Nature 2020, 582, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


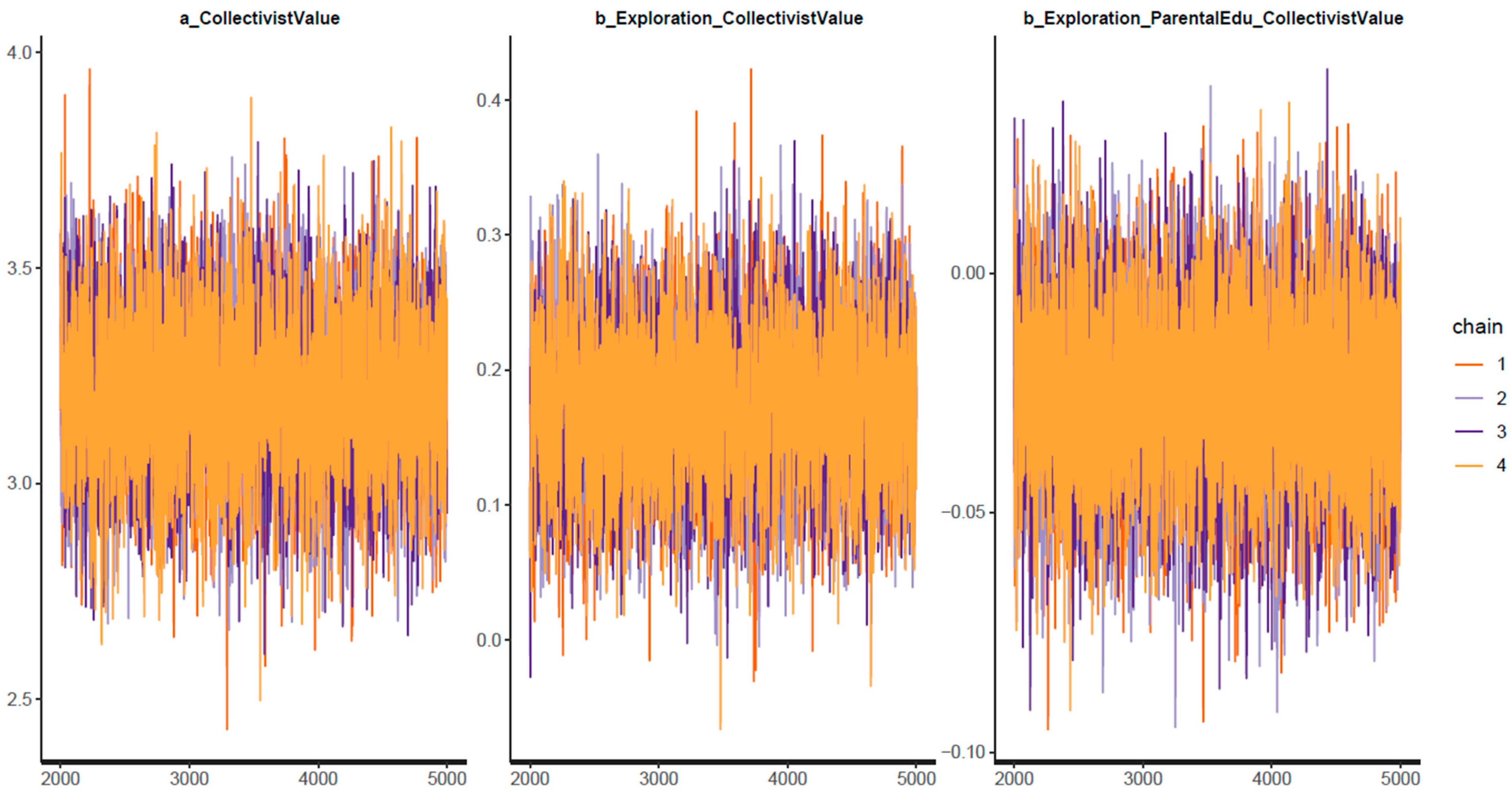
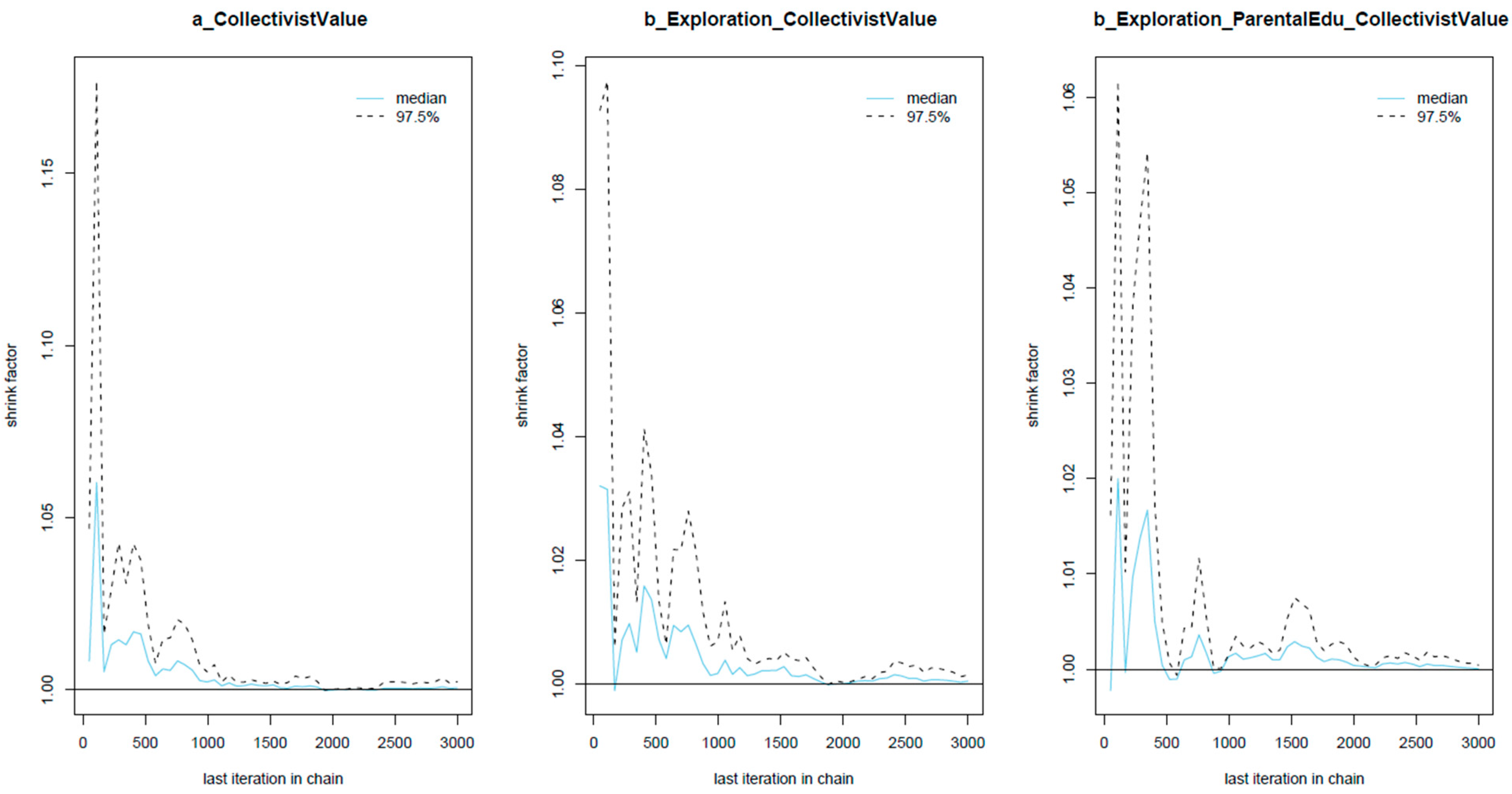


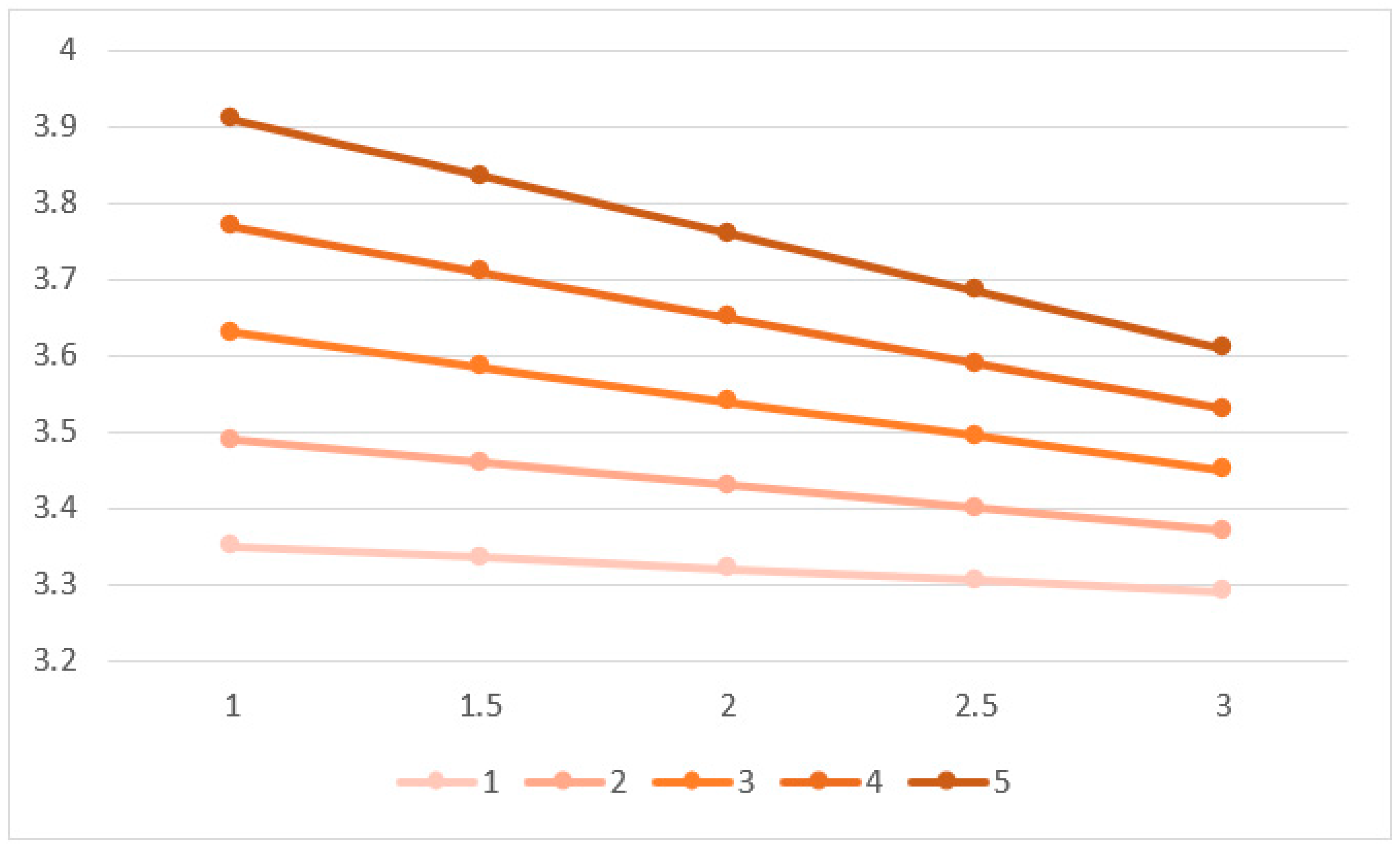


| Variable | Description | Type of Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exploration | The students’ level of exploration of the surroundings | Ordinal | Ranging from 1 (not strong) to 5 (very strong) |
| ParentalEdu | The average education attainment level of both parents | Numeric | Ranging from 1 (lowest) to 3 (highest) |
| MotherEdu | Mother’s education attainment | Ordinal | 1. Junior middle school or below 2. High school diploma or technical secondary education 3. College degree or above |
| FatherEdu | Father’s education attainment | Ordinal | 1. Junior middle school or below 2. High school diploma or technical secondary education 3. College degree or above |
| CollectivistValue | Level of caring about collective gains and losses as much as one’s own | Ordinal | 1. Completely disagree 2. Somewhat disagree 3. Difficult to determine 4. Somewhat agree 5. Completely agree |
| Parameters | Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 3.21 | 0.18 | 5237 | 1 |
| Exploration | 0.17 | 0.06 | 5249 | 1 |
| Exploration ∗ ParentalEdu | −0.03 | 0.02 | 7044 | 1 |
| Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 3.21 | 0.18 | 6123 | 1 |
| Exploration | 0.17 | 0.06 | 5545 | 1 |
| Exploration ∗ FatherEdu | −0.02 | 0.02 | 6843 | 1 |
| Parameters | Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 3.20 | 0.18 | 5663 | 1 |
| Exploration | 0.17 | 0.06 | 4772 | 1 |
| MotherEdu | −0.02 | 0.02 | 6216 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, R.; Le, T.-T.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Vuong, Q.-H. Examining the Influence of Exploration and Parental Education Attainment on Students’ Acceptance of Collectivist Values. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 1269-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13070094
Jin R, Le T-T, Nguyen M-H, Vuong Q-H. Examining the Influence of Exploration and Parental Education Attainment on Students’ Acceptance of Collectivist Values. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education. 2023; 13(7):1269-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13070094
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Ruining, Tam-Tri Le, Minh-Hoang Nguyen, and Quan-Hoang Vuong. 2023. "Examining the Influence of Exploration and Parental Education Attainment on Students’ Acceptance of Collectivist Values" European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 13, no. 7: 1269-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13070094
APA StyleJin, R., Le, T.-T., Nguyen, M.-H., & Vuong, Q.-H. (2023). Examining the Influence of Exploration and Parental Education Attainment on Students’ Acceptance of Collectivist Values. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 13(7), 1269-1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13070094













