Bioenergy Potential of Albumin, Acetic Acid, Sucrose, and Blood in Microbial Fuel Cells Treating Synthetic Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
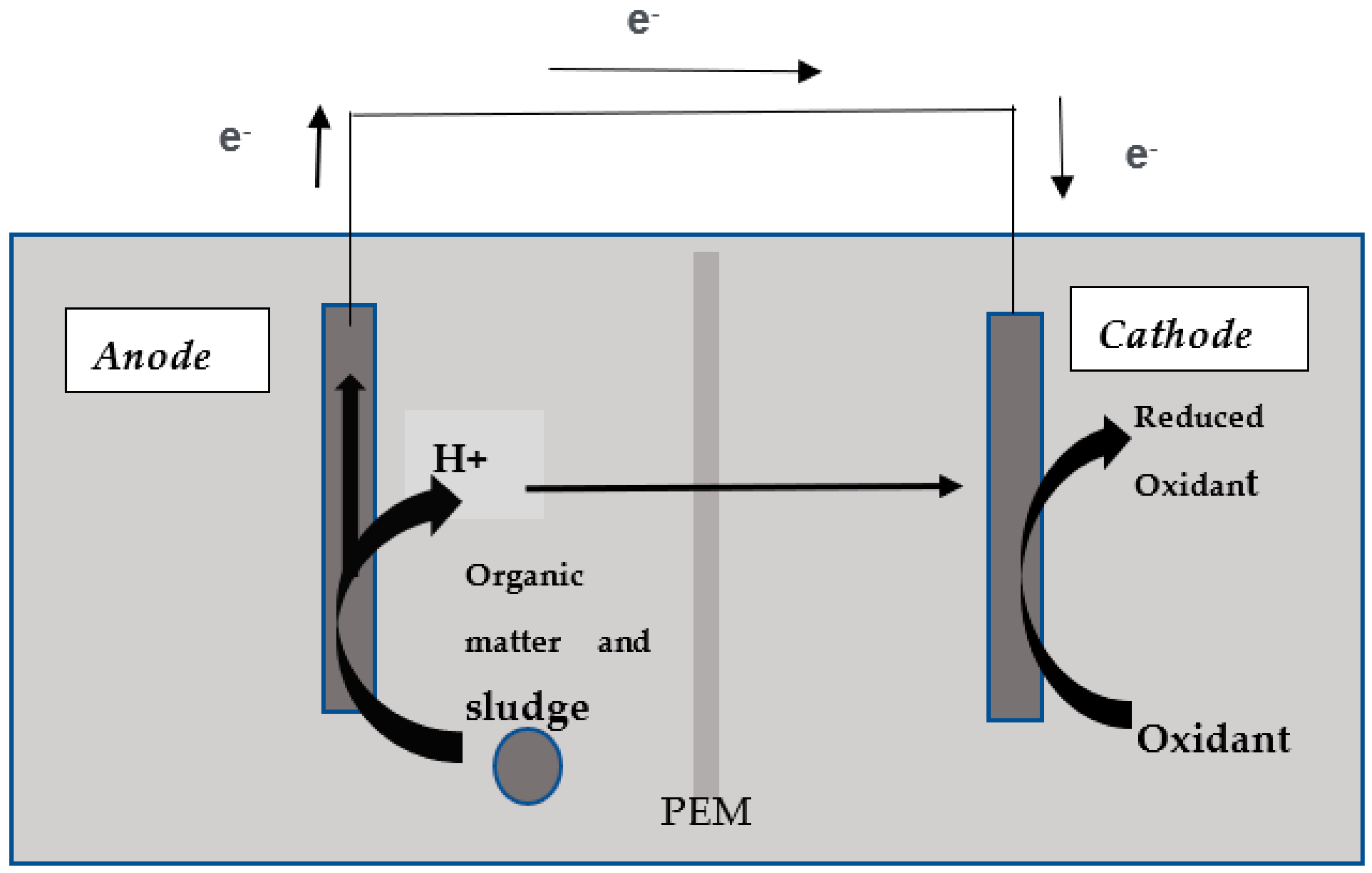
2.1. MFC Construction
2.2. MFC Operation
2.3. Analytical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
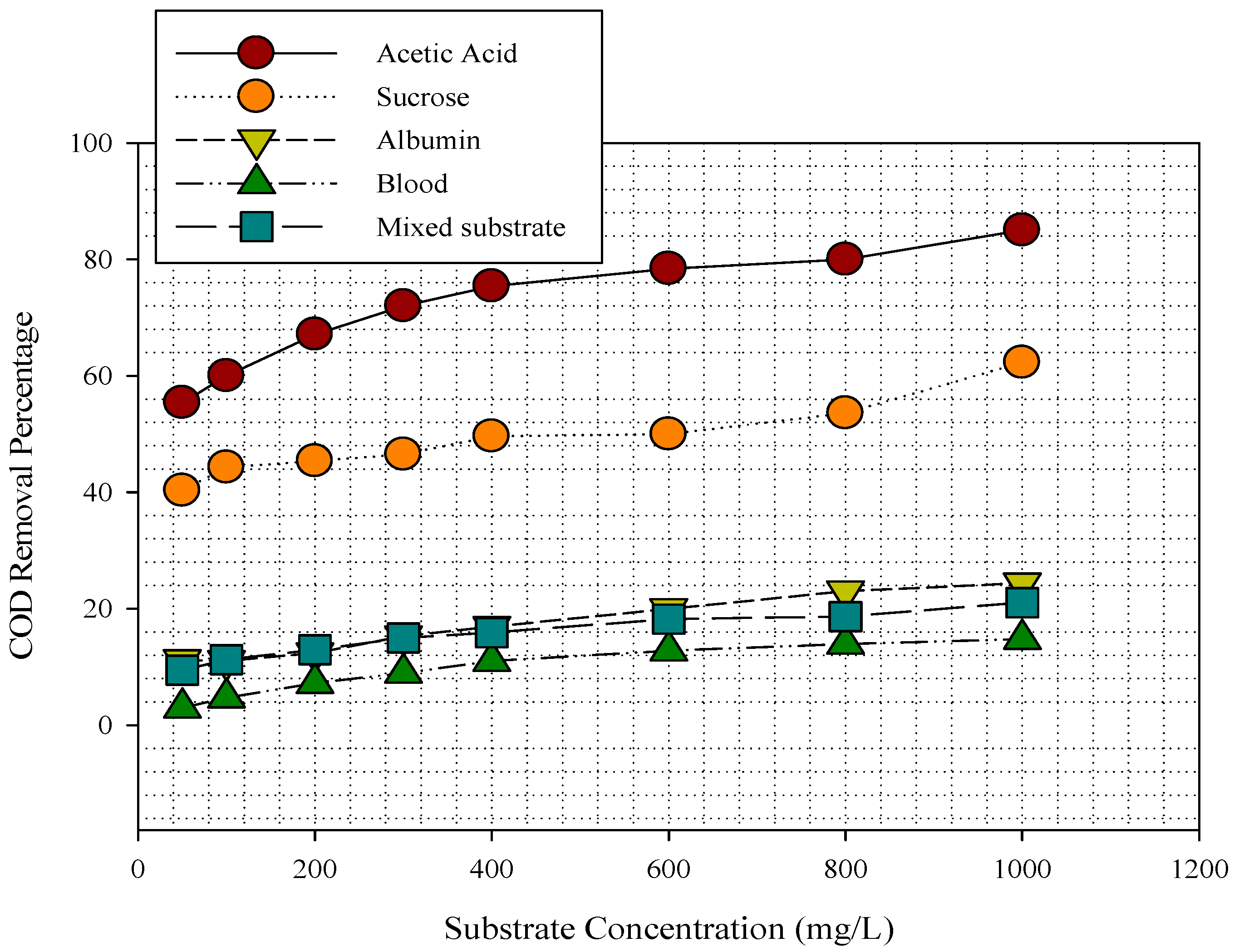
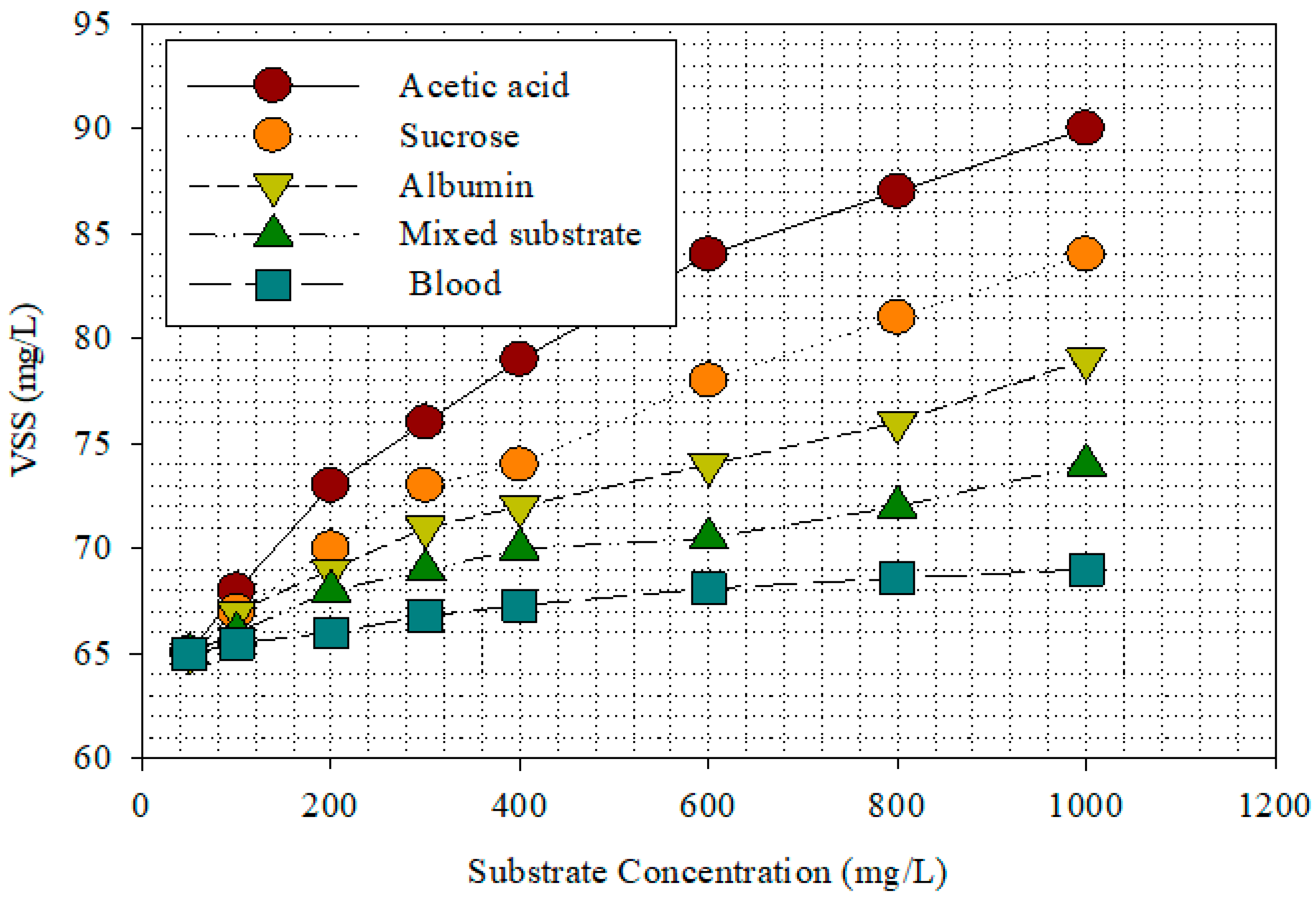
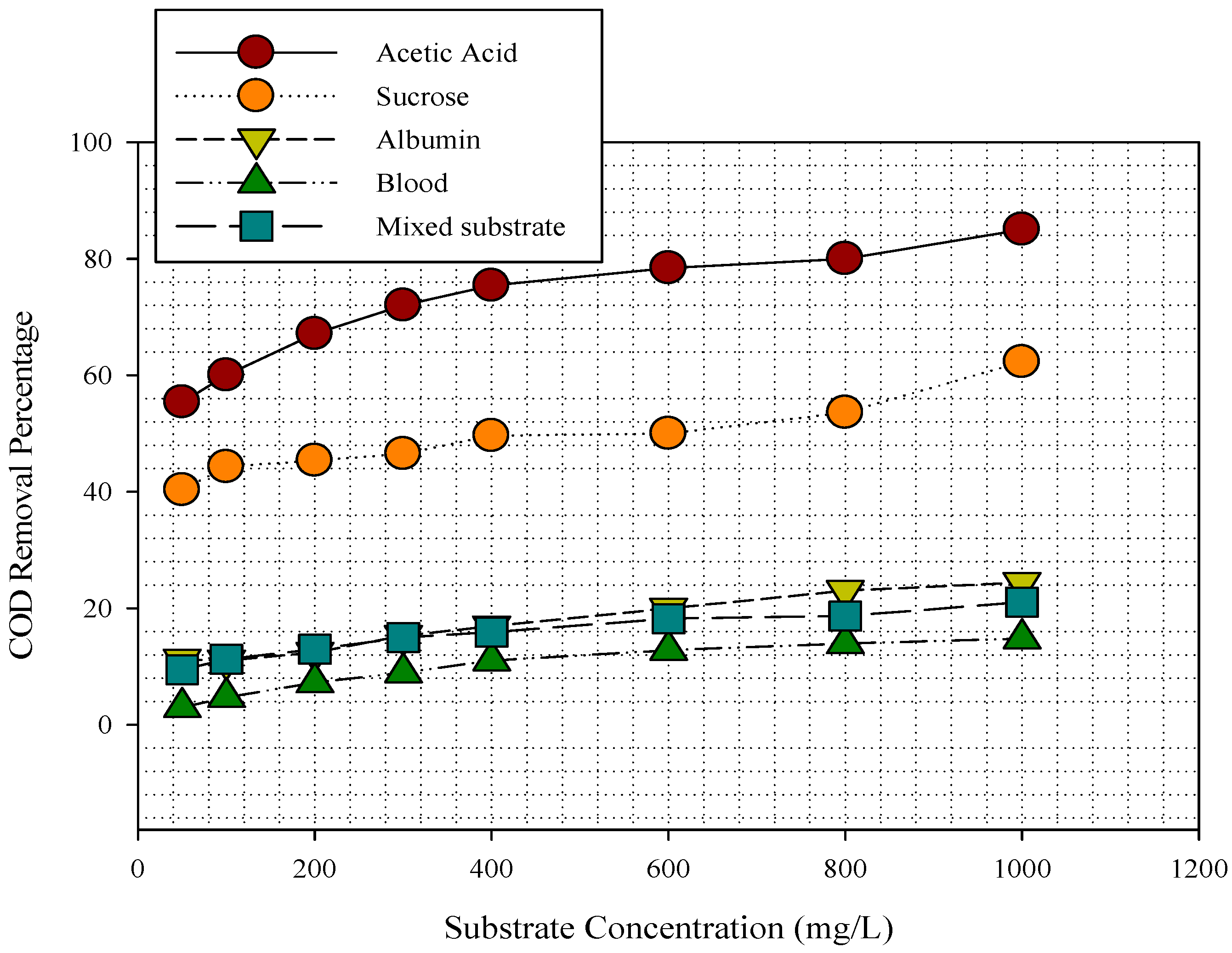
3.1. Substrates Removal in MFC
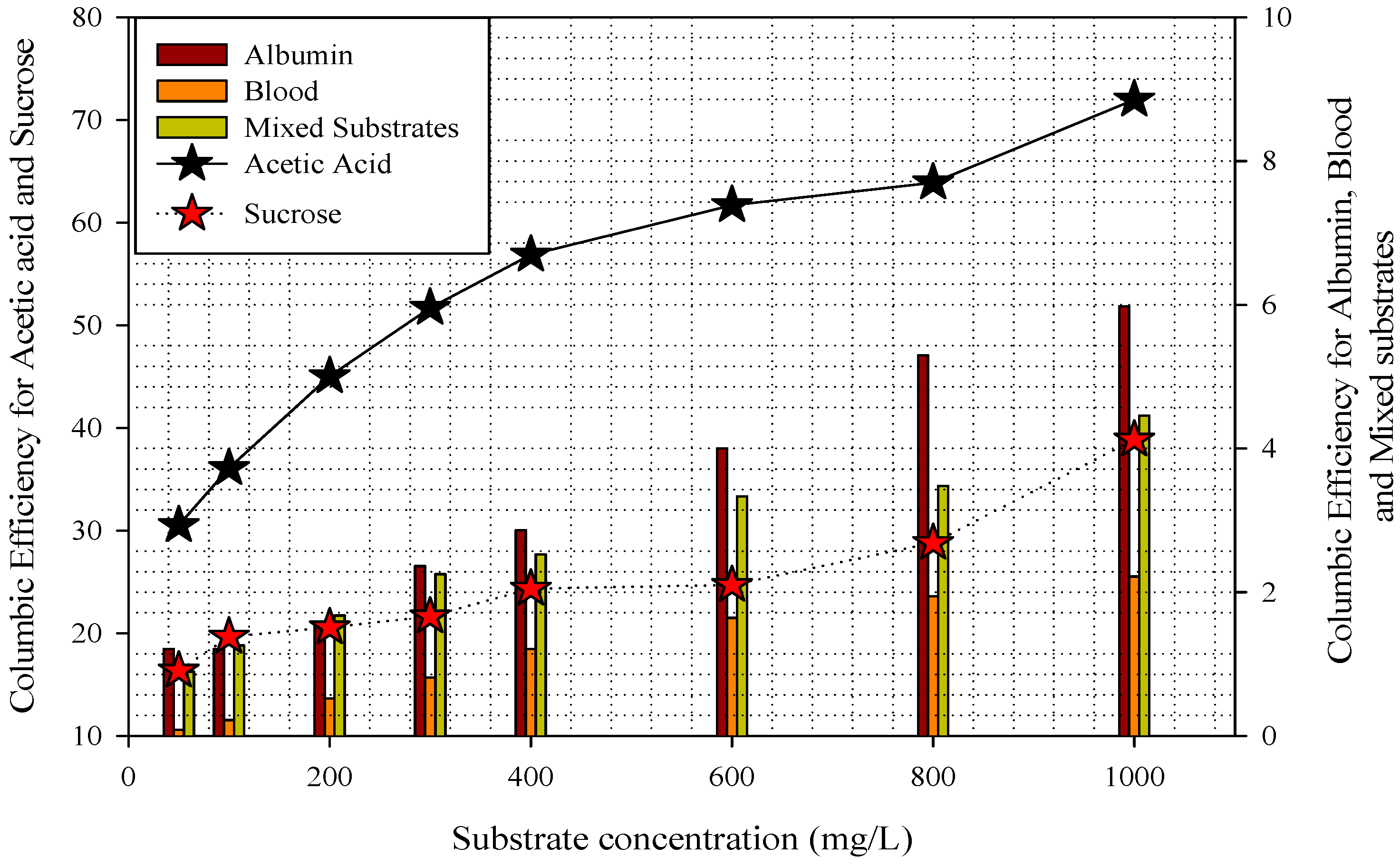
3.2. Substrate Removal, Current, Power Density, and Coulombic Efficiency
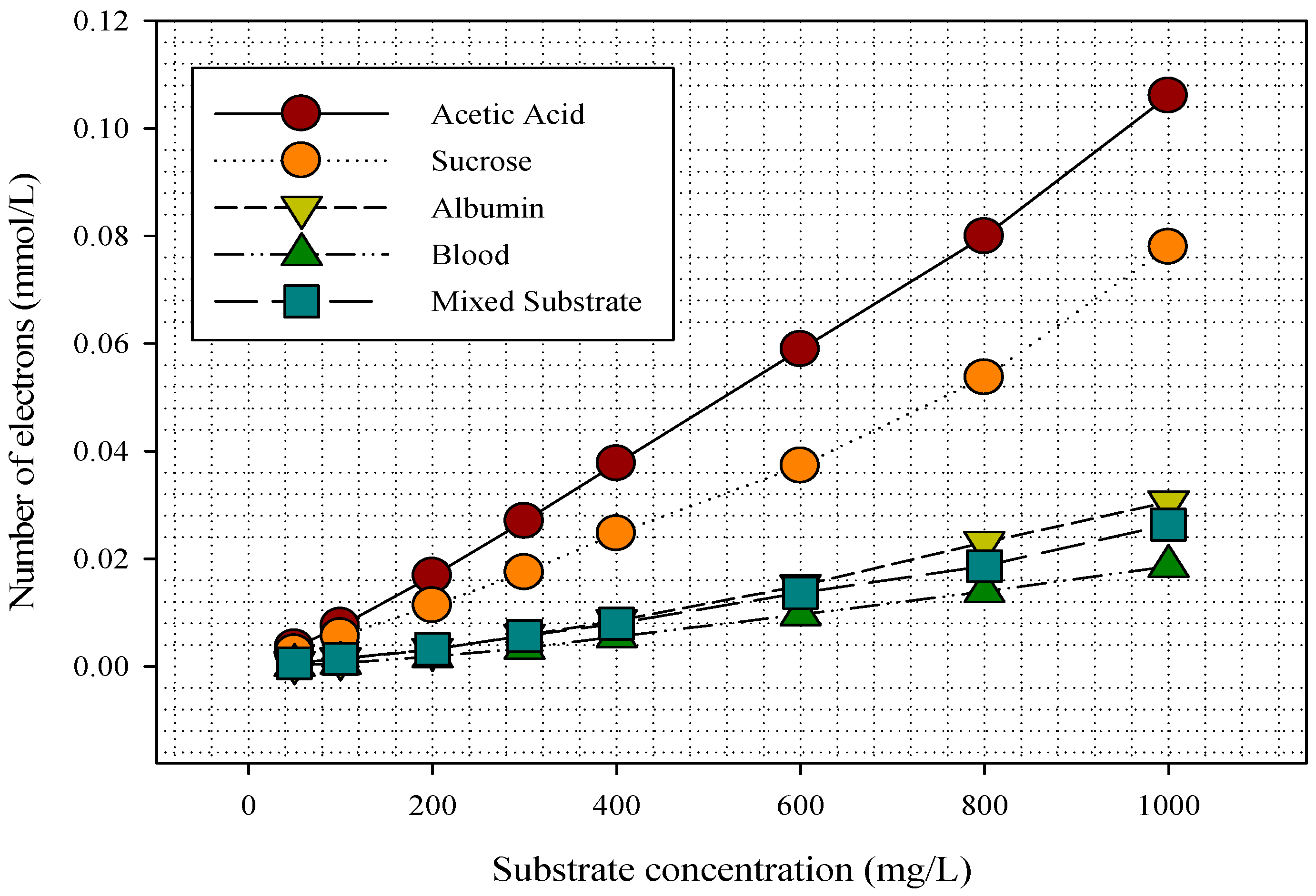
3.3. Electron and Voltage Generation in the MFC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. Domestic wastewater treatment as a net energy producer—Can this be achieved? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7100–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K. Recent developments in microbial fuel cell technologies for sustainable bioenergy. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 106, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathour, R.; Kalola, V.; Johnson, J.; Jain, K.; Madamwar, D.; Desai, C. Treatment of various types of wastewaters using microbial fuel cell systems. In Microbial Electrochemical Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 665–692. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, A.E.; Nevin, K.P. Microbial fuel cells, a current review. Energies 2010, 3, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duet, Z.; Li, H.; Gu, T. A state-of-the-art review on microbial fuel cells: A promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 464–482. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, V.B.; Simões, M.; Melo, L.F.; Pinto, A.M.F.R. Overview on the developments of microbial fuel cells. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 73, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Liu, X.; Weng, H.L. Sulfate and organic carbon removal by microbial fuel cell with sulfate-reducing bacteria and sulfide-oxidising bacteria anodic biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 156, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Su, Z. Study of operational performance and electrical response on mediator-less microbial fuel cells fed with carbon-and protein-rich substrates. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 45, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moga, I.C.; Ardelean, I.; Petrescu, G.; Crăciun, N.; Popa, R. The potential of biofilms from moving bed bioreactors to increase the efficiency of textile industry wastewater treatment. Ind. Text. 2018, 69, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, P. Treatment and disposal of pharmaceutical wastewater: Toward the sustainable strategy. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2018, 47, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. (Ed.) Sustainable Food Systems from Agriculture to Industry: Improving Production and Processing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadinezhad, B.; Ebrahimi, S.; Shokrkar, H. Evaluation of microbial fuel cell performance utilizing sequential batch feeding of different substrates. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 836, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Zeshan, S. Effect of substrate type and concentration on the performance of a double chamber microbial fuel cell. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova-Bautista, Y.; Ramirez-Morales, E.; Perez-Hernandez, B.; Ojeda-Morales, M.E.; Lopez-Lazaro, J.S.; Martinez-Pereyra, G. Electricity Production and Bioremediation from Synthetic Sugar Industry Wastewater by Using Microbial Isolate in Microbial Fuel Cell. Sugar Technol. 2020, 22, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, G.D.; Neethu, B.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Banerjee, R. Improved Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell by In Situ Methanogenesis Suppression While Treating Fish Market Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 192, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugazhendi, A.; Eid Al-Mutairi, A.; Jamal, M.T.; Jeyaku, R.B.; Palanisamy, K. Treatment of seafood industrial wastewater coupled with electricity production using air cathode microbial fuel cell under saline condition. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 12535–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, U.; Jin, W.; Pervez, A.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Tariq, M.; Shaheen, S.; Iqbal, A.; Mahmood, Q. Anaerobic microbial fuel cell treating combined industrial wastewater: Correlation of electricity generation with pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, Q.; Zheng, P.; Cai, J.; Hayat, Y.; Hassan, M.J.; Wu, D.L.; Hu, B.L. Sources of sulfide in waste streams and current biotechnologies for its removal. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2007, 8, 1126–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Mahmood, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Lou, J.; Wang, R. Coupled substrate removal and electricity generation in microbial fuel cells simultaneously treating sulfide and nitrate at various influent sulfide to nitrate ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of organic loading rate on the recovery of nutrients and energy in a dual-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Xie, Z.; Abbas, G. Kinetics of substrate degradation and electricity generation in anodic denitrification microbial fuel cell (AD-MFC). Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moestedt, J.; Westerholm, M.; Isaksson, S.; Schnürer, A. Inoculum source determines acetate and lactate production during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and food waste. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pant, D.; Van Bogaert, G.; Diels, L.; Vanbroekhoven, K. A review of the substrates used in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for sustainable energy production. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, G.S.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Performance of microbial fuel cell subjected to variation in pH, temperature, external load and substrate concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, R.A. Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lovley, D.R. The microbe electric: Conversion of organic matter to electricity. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catal, T.; Liu, H.; Fan, Y.; Bermek, H. A clean technology to convert sucrose and lignocellulose in microbial electrochemical cells into electricity and hydrogen. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 5, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Shigematsu, T.; Morimura, S.; Kida, K. Microbial community analysis of mesophilic anaerobic protein degradation process using bovine serum albumin (BSA)-fed continuous cultivation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiao, M. A microfabricated PDMS microbial fuel cell. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Christwardana, M.; Joelianingsih, J.; Yoshi, L.A. Performance of yeast microbial fuel cell integrated with sugarcane bagasse fermentation for cod reduction and electricity generation. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2021, 16, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Bakonyi, P. Treatment of dark fermentative H2 production effluents by microbial fuel cells: A tutorial review on promising operational strategies and practices. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 46, 5556–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Substrates Acetic Acid | Sucrose | Albumin | Blood | Mixed Substrates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mg/L) | Current (mA) | Power Density (mW/m2) | Current (mA) | Power Density (mW/m2) | Current (mA) | Power Density (mW/m2) | Current (mA) | Power Density (mW/m2) | Current (mA) | Power Density (mW/m2) |
| 50 | 2.01 | 23.76 | 1.03 | 6.24 | 0.51 | 1.56 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.28 |
| 100 | 3.09 | 56.16 | 1.15 | 7.82 | 0.69 | 2.80 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.43 |
| 200 | 4.17 | 102.28 | 1.21 | 8.61 | 0.70 | 2.93 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.73 |
| 300 | 4.61 | 125.01 | 1.55 | 14.24 | 0.78 | 3.60 | 0.3 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 1.08 |
| 400 | 5.93 | 206.85 | 2.01 | 23.76 | 0.83 | 4.08 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 0.52 | 1.59 |
| 600 | 6.86 | 276.82 | 2.49 | 36.55 | 0.99 | 5.83 | 0.45 | 1.22 | 0.71 | 3.01 |
| 800 | 6.96 | 284.95 | 3.05 | 54.93 | 1.13 | 7.59 | 0.53 | 1.67 | 0.84 | 4.18 |
| 1000 | 7.69 | 347.85 | 3.56 | 74.802 | 1.21 | 8.61 | 0.61 | 2.18 | 1.01 | 6.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tariq, M.; Wang, J.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Bilal, M.; Malik, A.J.; Akhter, M.S.; Mahmood, Q.; Hussain, S.; Ghfar, A.; Al-Anazy, M.M.; et al. Bioenergy Potential of Albumin, Acetic Acid, Sucrose, and Blood in Microbial Fuel Cells Treating Synthetic Wastewater. Processes 2021, 9, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081289
Tariq M, Wang J, Bhatti ZA, Bilal M, Malik AJ, Akhter MS, Mahmood Q, Hussain S, Ghfar A, Al-Anazy MM, et al. Bioenergy Potential of Albumin, Acetic Acid, Sucrose, and Blood in Microbial Fuel Cells Treating Synthetic Wastewater. Processes. 2021; 9(8):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081289
Chicago/Turabian StyleTariq, Madiha, Jin Wang, Zulfiqar Ahmad Bhatti, Muhammad Bilal, Adeel Jalal Malik, Mohammad Salim Akhter, Qaisar Mahmood, Shahid Hussain, Ayman Ghfar, Murefah Mana Al-Anazy, and et al. 2021. "Bioenergy Potential of Albumin, Acetic Acid, Sucrose, and Blood in Microbial Fuel Cells Treating Synthetic Wastewater" Processes 9, no. 8: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081289
APA StyleTariq, M., Wang, J., Bhatti, Z. A., Bilal, M., Malik, A. J., Akhter, M. S., Mahmood, Q., Hussain, S., Ghfar, A., Al-Anazy, M. M., & Ouladsmane, M. (2021). Bioenergy Potential of Albumin, Acetic Acid, Sucrose, and Blood in Microbial Fuel Cells Treating Synthetic Wastewater. Processes, 9(8), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9081289








