Hydroxyapatite Precipitation and Accumulation in Granules and Its Effects on Activity and Stability of Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactors Operation and Inoculum
2.2. Medium
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
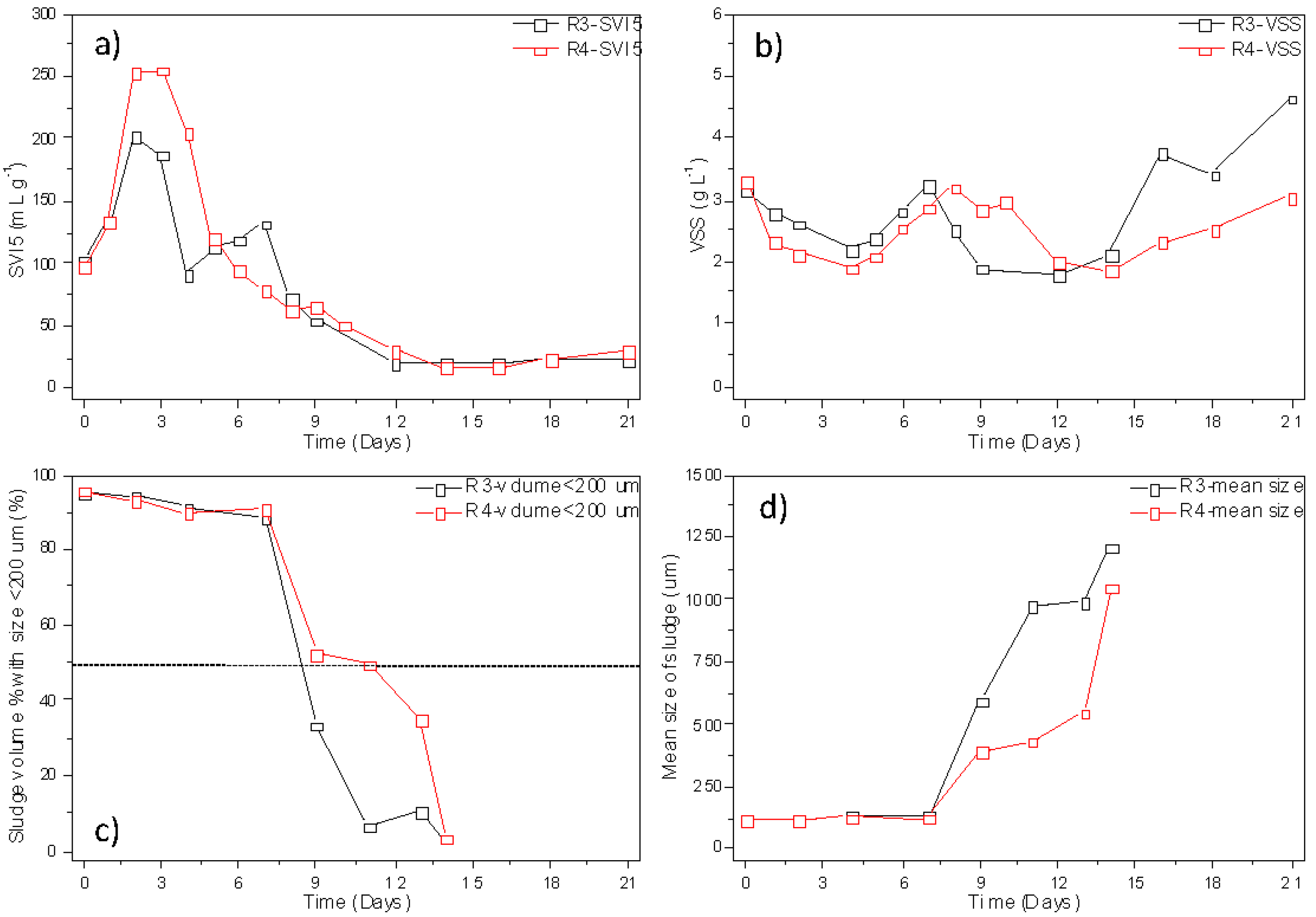
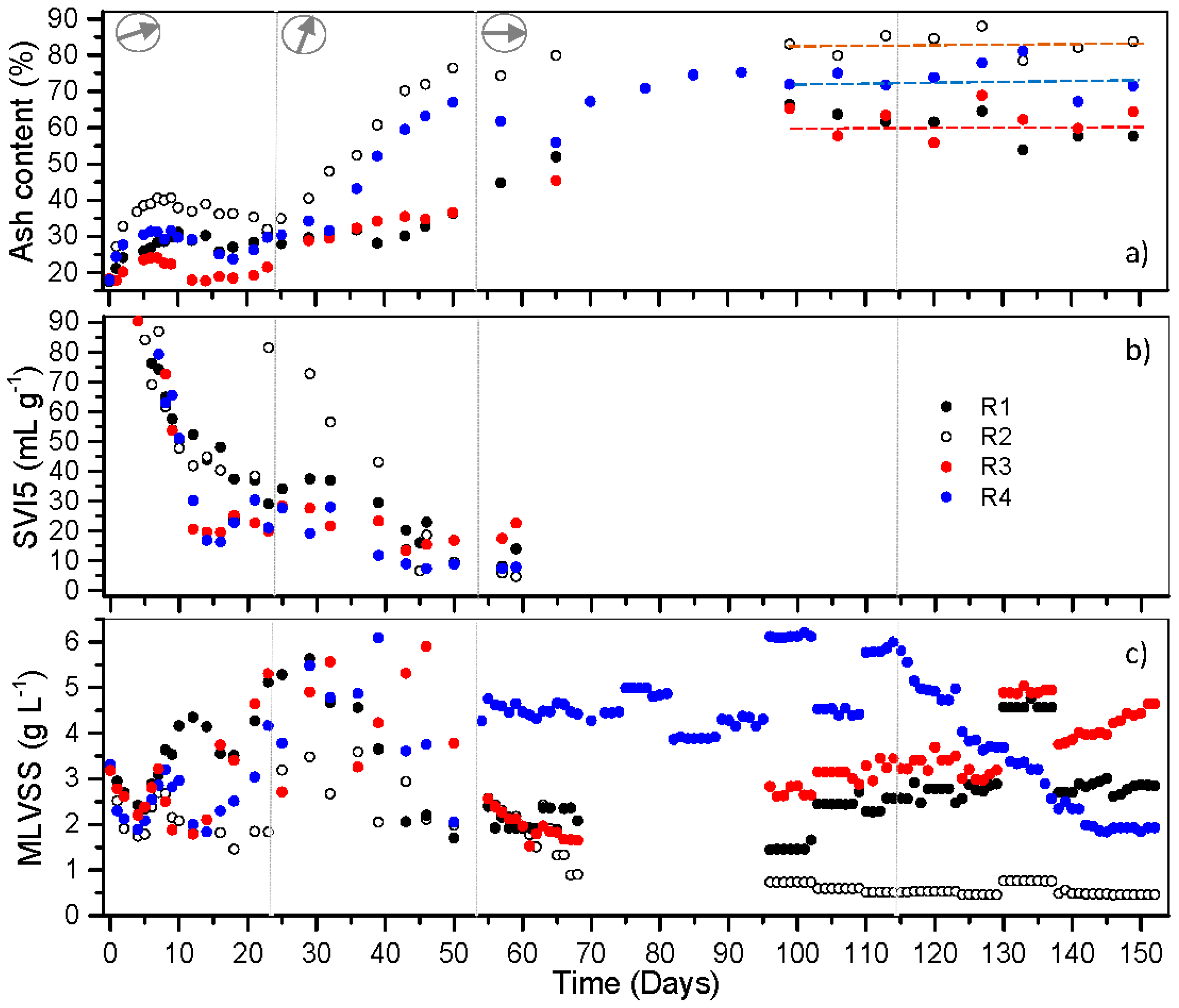
3.1. Formation of Heterotrophic Granules with Different COD/N Ratios at Different Temperatures
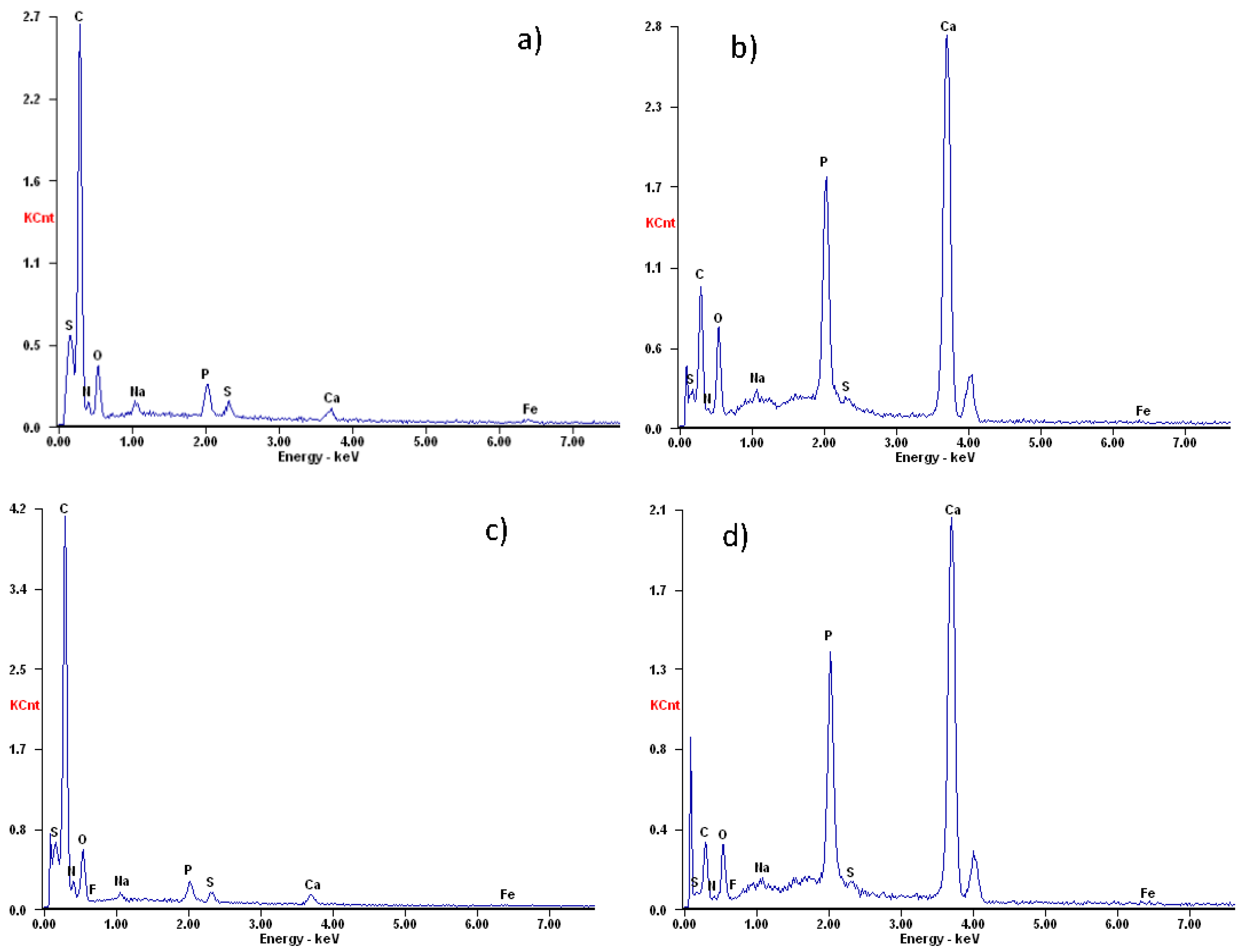
3.2. Mineral Accumulation in Nitrifying Granules Converted from Heterotrophic Granules at Different Temperatures and Minerals Effects on Granules’ Long-Term Stability
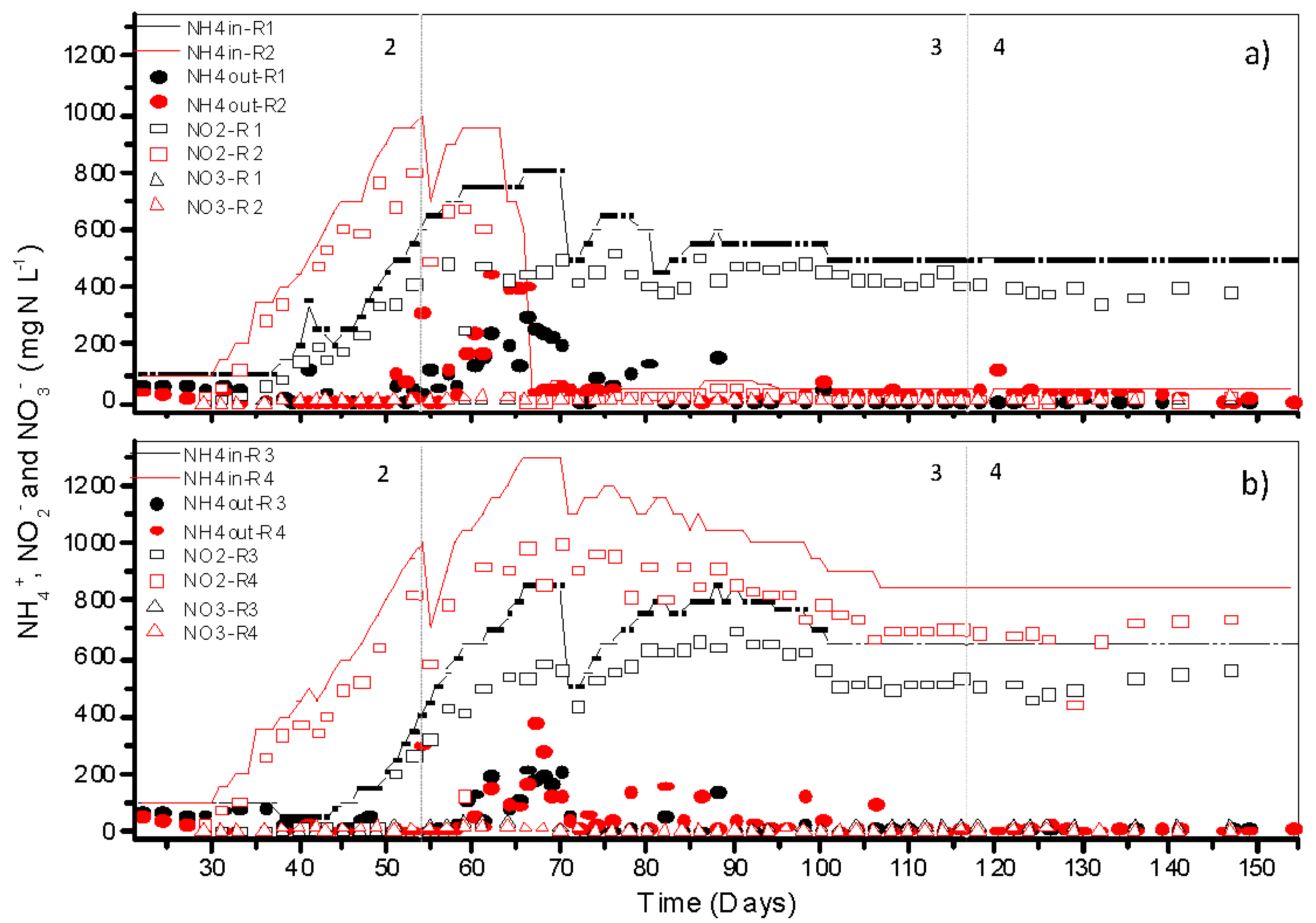
3.3. Performance of Nitrifying Granules at Different Temperatures and Their Specific Ammonium Oxidization Activities
3.4. Calcium Precipitation and Accumulation in Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures
4. Conclusions
- Initial ammonium concentration and temperature from moderate 21 °C to 32 °C had negligible effects on the speed of heterotrophic granules.
- Mature granules had much higher calcium precipitates accumulated inside compared with newly formed granules, and suspended sludge, indicating the importance of long sludge retention time for the accumulation of calcium precipitates.
- Higher temperature promoted more mineral precipitates in granules, in general. Specifically, high temperature promoted co-precipitation and accumulation of hydroxyapatite and calcite, while moderate temperature was more beneficial for the dominance of hydroxyapatite in granules.
- Increased calcium precipitates in nitrifying granules resulted in reduced microbial activities.
- High mineral content in granules led to the instability of nitrifying granules at a higher temperature in the short or long run.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fukuzaki, S.; Nishio, N.; Sakurai, H.; Nagai, S. Characteristics of methanogenic granules grown on propionate in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1991, 71, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.; Ruscalleda, M.; Colprim, J. Phosphorus recovery through biologically induced precipitation by partial nitritation-anammox granular biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.; Heijnen, J.; van Loosdrecht, M. Simultaneous COD, nitrogen, and phosphate removal by aerobic granular sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Lan, G.-H.; Zeng, P. Size-dependent calcium carbonate precipitation induced microbiologically in aerobic granules. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Lotti, T.; Sharma, P.; van Loosdrecht, M. Apatite accumulation enhances the mechanical property of anammox granules. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4556–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.-C.; Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H. Stable aerobic granules for continuous-flow reactors: Precipitating calci-um and iron salts in granular interiors. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8051–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Lan, G.-H.; Zeng, P. Excessive precipitation of CaCO3 as aragonite in a continuous aerobic granular sludge reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8225–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Tay, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Tay, S.T.-L. Ca2+ augmentation for enhancement of aerobically grown microbial gran-ules in sludge blanket reactors. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shi, W.; Yu, S.; Yi, X.; Yang, X. Formation of aerobic granules by Mg2+ and Al3+ augmentation in sequenc-ing batch airlift reactor at low temperature. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, G.; Bozkurt, U.; Magden, K.A. Effect of iron ions (Fe2+, Fe3+) on the formation and structure of aerobic gran-ular sludge. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kubota, K.; Li, Y.-Y. Simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recov-ery using an anammox expanded reactor operated at 25° C. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.-T.; Liu, L.; Sheng, G.-P.; Liu, X.-W.; Yu, H.-Q.; Zhang, M.-C.; Zhu, J.-R. Calcium spatial distribution in aerobic granules and its effects on granule structure, strength and bioactivity. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3343–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mañas, A.; Biscans, B.; Sperandio, M. Biologically induced phosphorus precipitation in aerobic granular sludge process. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Tian, L.; You, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Kang, D.; Xu, D.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, P. Deactivation mechanism of calcified anaerobic granule: Space occupation and pore blockage. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, H.; Alsina, X.F.; Ramin, P.; Kjellberg, K.; Jeppsson, U.; Batstone, D.J.; Gernaey, K.V. Assessing the effects of intra-granule precipitation in a full-scale industrial anaerobic digester. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Langerak, E.; Ramaekers, H.; Wiechers, J.; Veeken, A.; Hamelers, H.; Lettinga, G. Impact of location of CaCO3 precipitation on the development of intact anaerobic sludge. Water Res. 2000, 34, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.; Pronk, M.; van Loosdrecht, M. Formation of aerobic granules and conversion processes in an aerobic granular sludge reactor at moderate and low temperatures. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4476–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Halim, M.H.; Anuar, A.N.; Jamal, N.S.A.; Azmi, S.I.; Ujang, Z.; Bob, M.M. Influence of high temperature on the performance of aerobic granular sludge in biological treatment of wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Kong, Y.H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wong, F.S.; Tay, J.H.; Zhu, J.R.; Jiang, W.J.; Liu, W.-T. Microbial population dynamics of granular aerobic sequencing batch reactors during start-up and steady state periods. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beun, J.; Hendriks, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Morgenroth, E.; Wilderer, P.; Heijnen, J. Aerobic granulation in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2283–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BSI. BS 6068-2.11:1984, ISO 7150-1:1984 Water Quality. Physical, Chemical and Biochemical Methods. Determination of Ammonium: Manual Spectrometric Method; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Moy, B.; Kong, Y.-H.; Tay, J.-H. Formation, physical characteristics and microbial community structure of aerobic granules in a pilot-scale sequencing batch reactor for real wastewater treatment. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 46, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Kong, Y.; Tay, J.-H.; Zhu, J. Enhancement of start-up of pilot-scale granular SBR fed with real wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 82, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Characteristics and stability of aerobic granules cultivated with different starvation time. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-F.; Tay, J.-H.; Liu, Y. Inhibition of free ammonia to the formation of aerobic granules. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 17, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Fast formation of aerobic granules by combining strong hydraulic selection pressure with over-stressed organic loading rate. Water Res. 2015, 80, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H.; Ning, P. Rapid formation of nitrifying granules treating high-strength ammonium wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4445–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, H.; Kong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Bulking and floatation of the anammox-HAP granule caused by low phos-phate concentration in the anammox reactor of expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of Nitrification by Ammonia and Nitrous Acid. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, S. The impact of temperature on nitrification rate in fixed film biofilters. Aquac. Eng. 2002, 26, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.-S.; Guo, Q.; Yang, G.-F.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Li, P.; Guo, L.-X.; Jin, R.-C. The properties of anaerobic ammonium oxi-dation (anammox) granules: Roles of ambient temperature, salinity and calcium concentration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poot, V.; Hoekstra, M.; Geleijnse, M.A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Pérez, J. Effects of the residual ammonium concentra-tion on NOB repression during partial nitritation with granular sludge. Water Res. 2016, 106, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-J.; Seo, D. Selective enrichment and granulation of ammonia oxidizers in a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ishii, S.; Rathnayak, L.; Ito, T.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Development and characterization of the partial nitrifica-tion aerobic granules in a sequencing batch airlift reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xue, X.; Yan, L.-G.; Sun, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, L.; Du, B. Effect of influent ammonium concentration on the shift of full nitritation to partial nitrification in a sequencing batch reactor at ambient temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, E. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment, Disposal and Reuse; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, M. Phosphate fertilizer from sewage sludge ash (SSA). Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Vahala, R.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. 16S rRNA gene-based characterization of bacteria potentially associated with phosphate and carbonate precipitation from a granular autotrophic nitrogen removal bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 101, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Units | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 21 ± 3 | 32 ± 2 | 21 ± 3 | 32 ± 2 | |
| Phase 1 (0–21) | COD | mg L−1 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| NH4+ | mg N L−1 | 50 | 50 | 200 | 200 | |
| COD/N | 20 | 20 | 5 | 5 | ||
| Phase 2 (22–37/49 a) | COD | mg L−1 | 1000 to 0 | 1000 to 0 | 1000 to 0 | 1000 to 0 |
| NH4+ | mg N L−1 | 50 to 400 | 50 to 850 | 200 to 150 | 200 to 750 | |
| Phase 3 (38/50 a–107) | NH4+ | mg N L−1 | Varied influent ammonium concentration b | |||
| Phase 4 (108–171) | NH4+ | mg N L−1 | 500 | 65 | 650 | 850 |
| Unit | Na | Mg | P | K | Ca | Fe | Ca/P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R3 | mg g−1 TSS | 12.79 | 0.59 | 76.80 | 0.94 | 172.30 | 2.94 | 1.74 |
| R4 | mg g−1 TSS | 11.42 | 0.91 | 40.86 | 0.36 | 254.40 | 3.05 | 4.82 |
| Tap water | mg L−1 | 13.95 | 2.18 | 0.10 | 1.70 | 102.70 | 0.027 | |
| Feedstock elements | mg L−1 | 7210.00–3285.71 | 4.15 | 15.20 | 19.28 | 110.46 | 2.00 | 5.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-Q.; Cinquepalmi, S. Hydroxyapatite Precipitation and Accumulation in Granules and Its Effects on Activity and Stability of Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures. Processes 2021, 9, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101710
Liu Y-Q, Cinquepalmi S. Hydroxyapatite Precipitation and Accumulation in Granules and Its Effects on Activity and Stability of Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures. Processes. 2021; 9(10):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101710
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yong-Qiang, and Simone Cinquepalmi. 2021. "Hydroxyapatite Precipitation and Accumulation in Granules and Its Effects on Activity and Stability of Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures" Processes 9, no. 10: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101710
APA StyleLiu, Y.-Q., & Cinquepalmi, S. (2021). Hydroxyapatite Precipitation and Accumulation in Granules and Its Effects on Activity and Stability of Partial Nitrifying Granules at Moderate and High Temperatures. Processes, 9(10), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101710







