Research on the Dynamic Responses of Simply Supported Horizontal Pipes Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
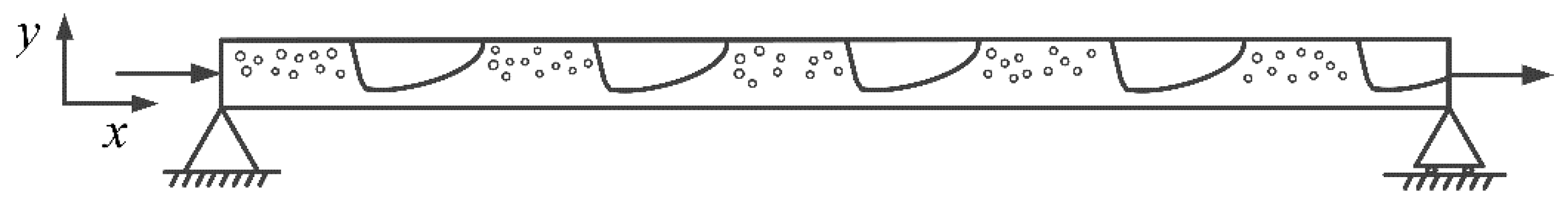
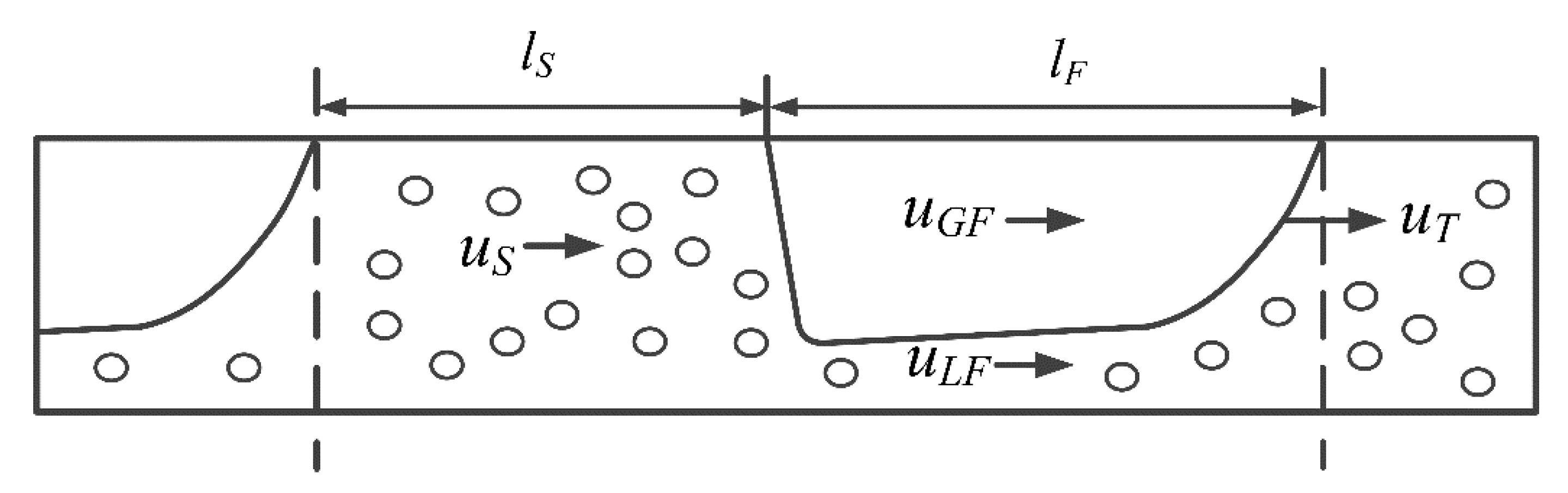
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
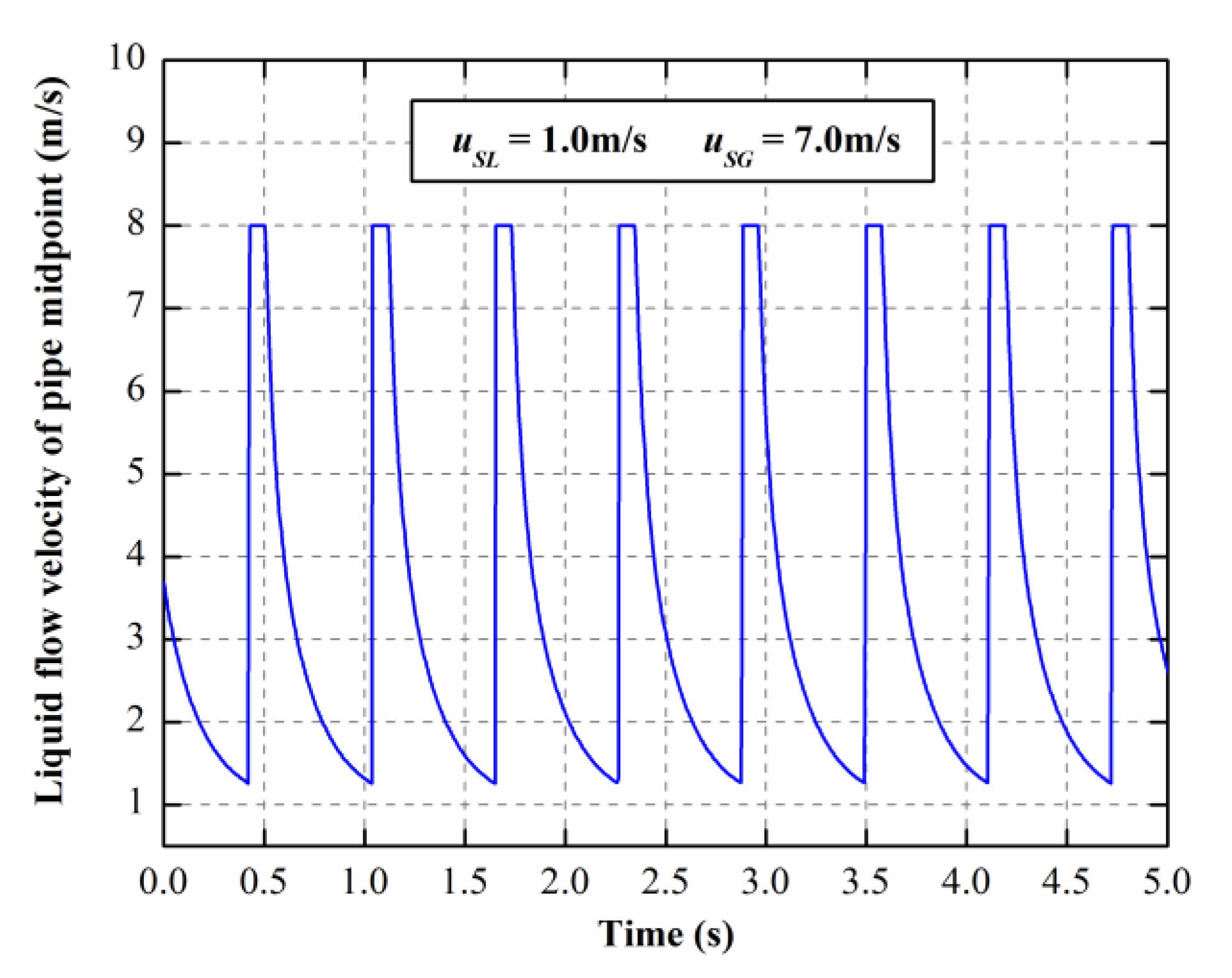
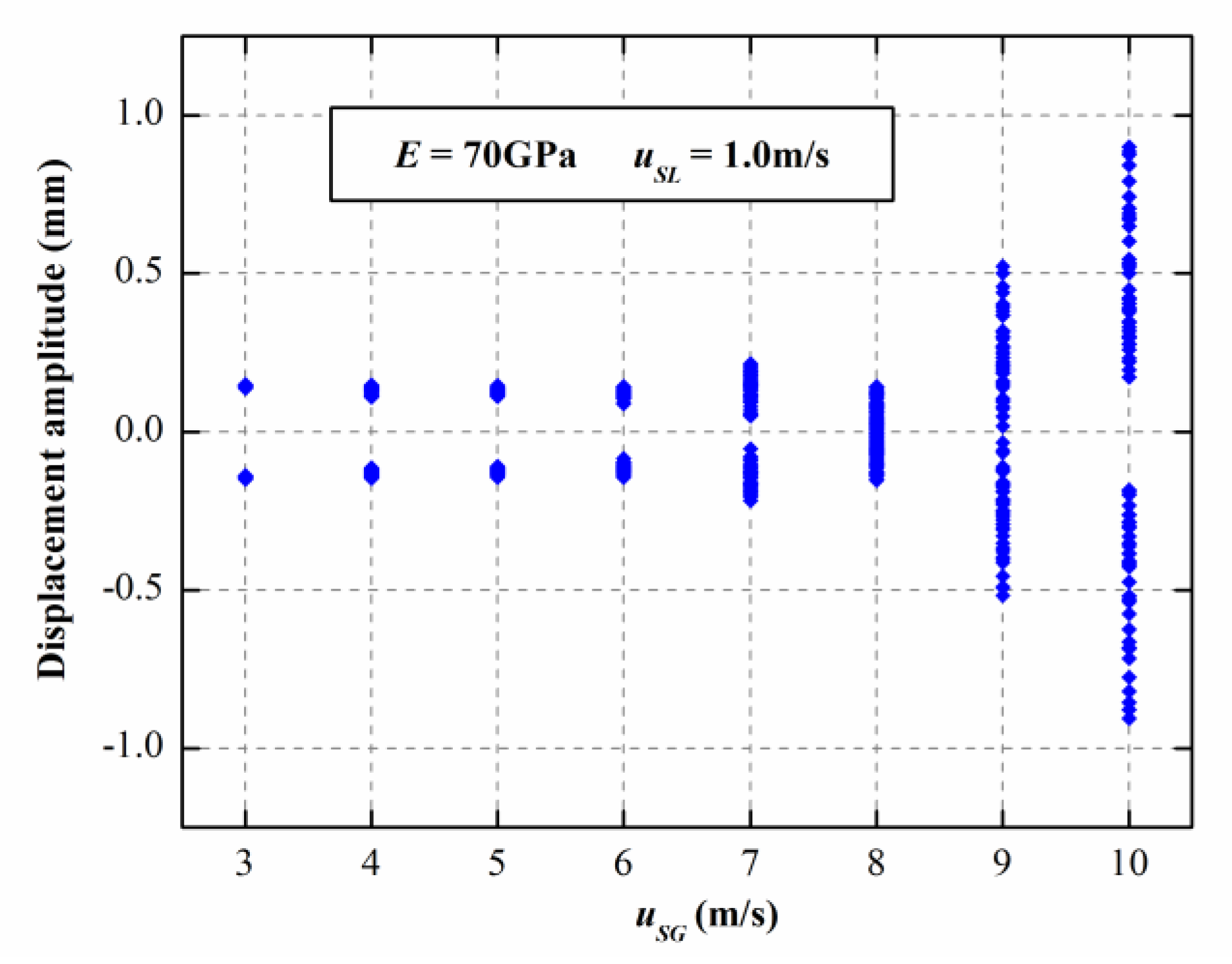
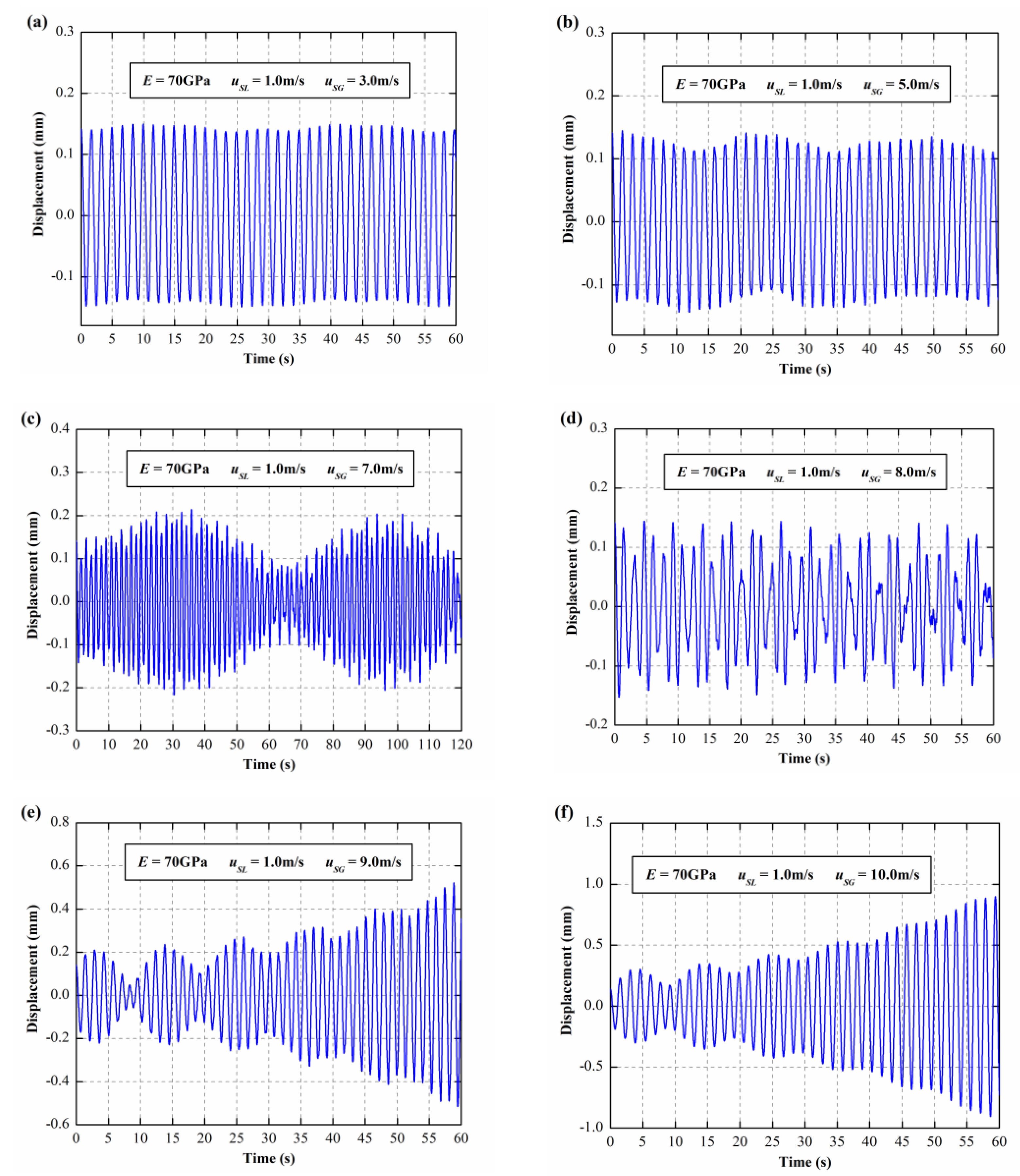
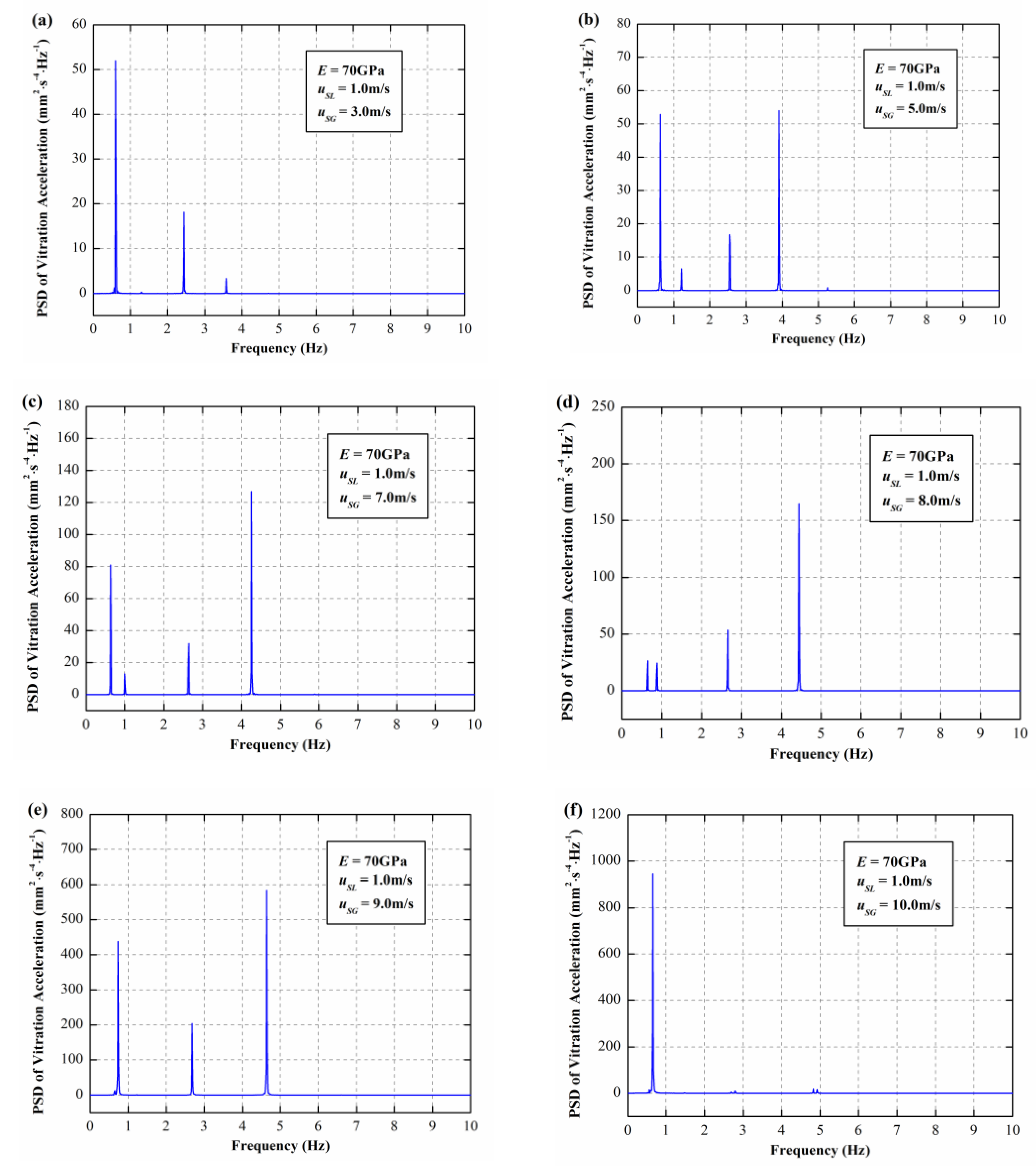
3.1. The Dynamic Responses of E = 70 GPa
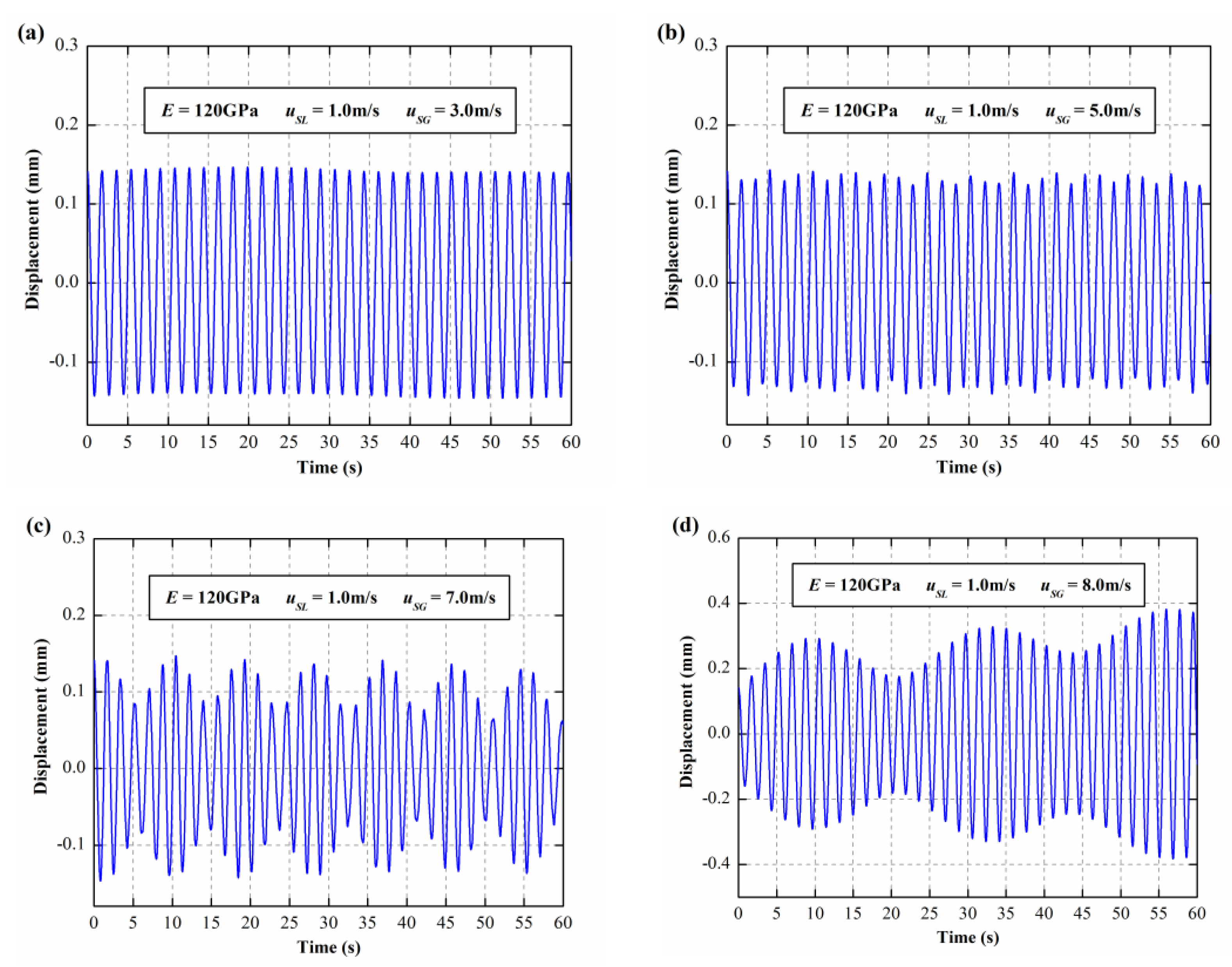
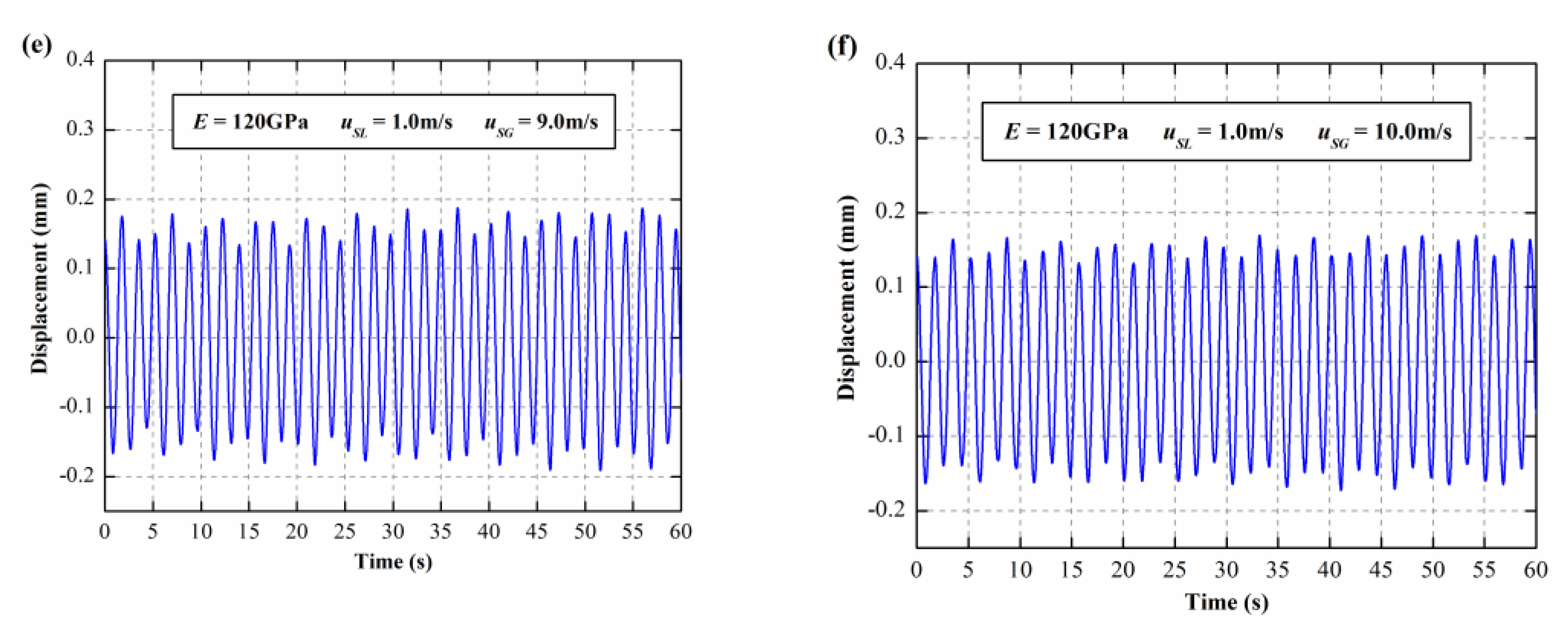
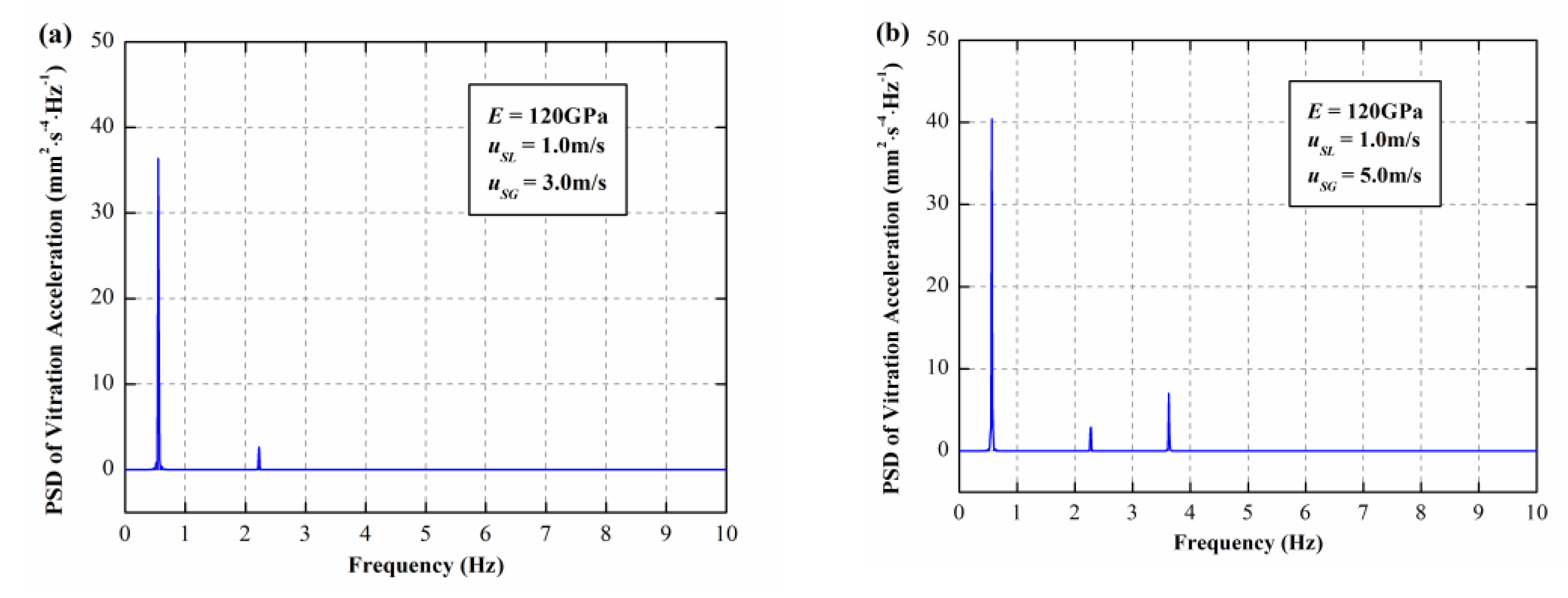
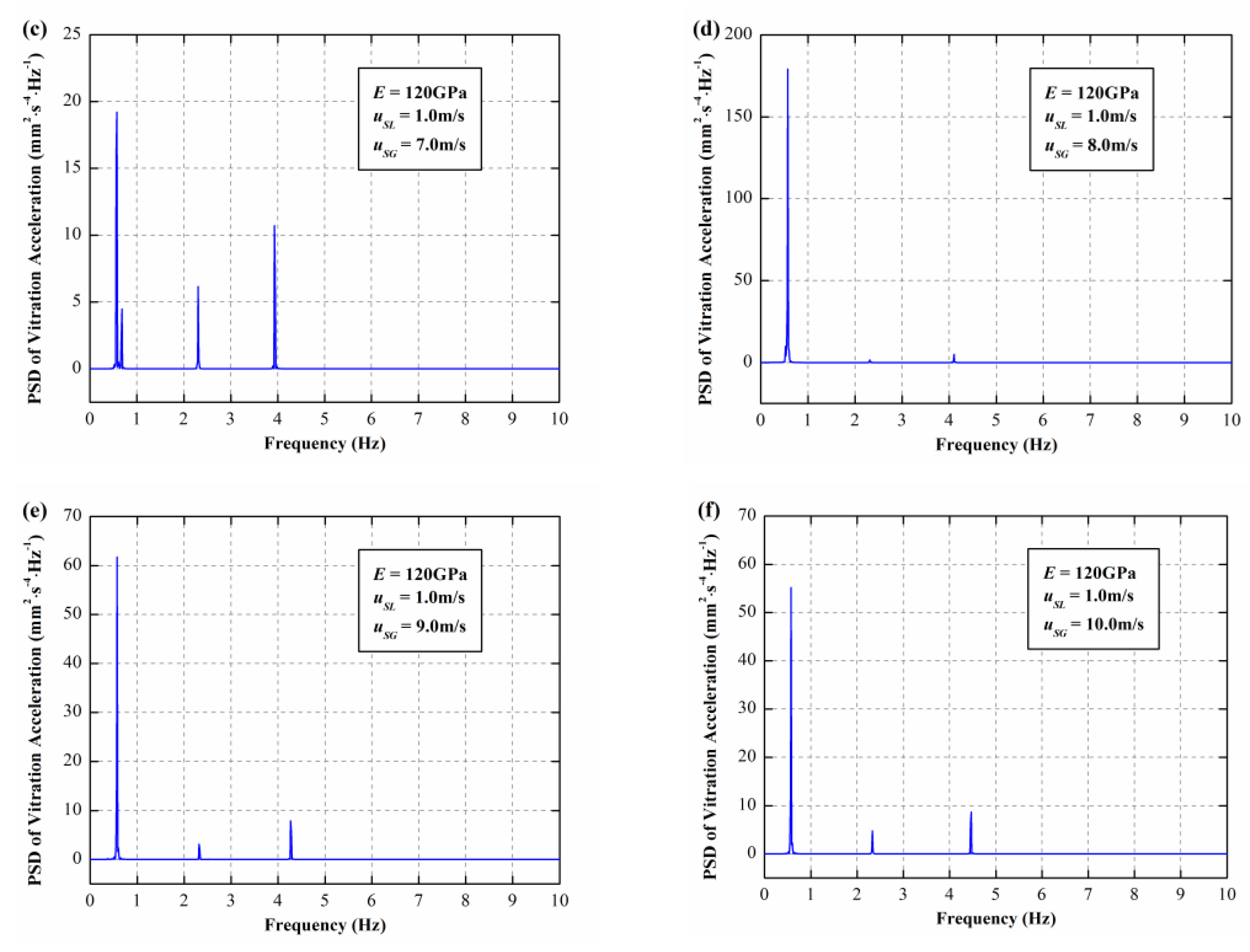
3.2. The Dynamic Responses of E = 120 GPa
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ai | sectional area of the inner pipe, m2 |
| E | Young’s modulus of the pipe, GPa |
| I | inertial moment of cross-section area, m4 |
| L | length of the pipe, m |
| mL(x,t) | mass of liquid phase per unit length at the coordinate x and moment t, kg/m |
| mG(x,t) | mass of gas phase per unit length at the coordinate x and moment t, kg/m |
| mP | mass of fluid per unit length, kg/m |
| QG | volume flow rates of the gas, m3/s |
| QL, | volume flow rates of the liquid, m3/s |
| uL(x,t) | local velocity of liquid phase at the coordinate x and moment t, m/s |
| uG(x,t) | local velocity of gas phase at the coordinate x and moment t, m/s |
| uSG | superficial gas velocity, m/s |
| uSL | superficial liquid velocity, m/s |
| y | transverse displacement of the pipe, m |
| Greek symbols | |
| ρ | density, kg/m3 |
| Subscripts | |
| L | liquid phase |
| G | gas phase |
References
- Païdoussis, M.; Issid, N. Dynamic stability of pipes conveying fluid. J. Sound Vib. 1974, 33, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaratnam, S.; Namachchivaya, N.S. Dynamic stability of pipes conveying pulsating fluid. J. Sound Vib. 1986, 107, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Song, Z. Parametric resonances of supported pipes conveying pulsating fluid. J. Fluids Struct. 2005, 20, 763–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, S.; Mori, M.; Hibiki, T. Two-phase flow induced vibration in piping systems. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2015, 78, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamian, R.; Behbahani-Nejad, M.; Ghanbarzadeh, A. A state space model for transient flow simulation in natural gas pipelines. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Safaei, M.R.; Vafai, K.; Ahmadi, G.; Dahari, M.; Kazi, S.; Jomhari, N. Investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in a shallow cavity using a two-phase mixture model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 75, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.R.; Mahian, O.; Garoosi, F.; Hooman, K.; Karimipour, A.; Kazi, S.N.; Gharehkhani, S. Investigation of Micro- and Nanosized Particle Erosion in a 90° Pipe Bend Using a Two-Phase Discrete Phase Model. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourfattah, F.; Arani, A.A.A.; Babaie, M.R.; Nguyen, H.M.; Asadi, A. On the thermal characteristics of a manifold microchannel heat sink subjected to nanofluid using two-phase flow simulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 143, 118518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, F.; Shadloo, M.; Hadjadj, A.; Ozbulut, M.; Tofighi, N.; Yildiz, M. Numerical simulations of multi-phase electro-hydrodynamics flows using a simple incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 81, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadloo, M.; Rahmat, A.; Karimipour, A.; Wongwises, S. Estimation of Pressure Drop of Two-Phase Flow in Horizontal Long Pipes Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2020, 142, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Ribatski, G.; Thome, J.R. Two-Phase Flow Patterns and Flow-Pattern Maps: Fundamentals and Applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2008, 61, 050802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Safran, E. Investigation and prediction of slug frequency in gas/liquid horizontal pipe flow. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2009, 69, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukler, A.E.; Hubbard, M.G. A Model for Gas-Liquid Slug Flow in Horizontal and Near Horizontal Tubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1975, 14, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Sarica, C.; Brill, J.P. Unified model for gas-liquid pipe flow via slug dynamics-part 1: Model development. Trans. ASME J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2003, 125, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riverin, J.; De Langre, E.; Pettigrew, M.J. Fluctuating forces caused by internal two-phase flow on bends and tees. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 298, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnelutti, M.F.; Belfroid, S.P.C.; Schiferli, W. Two-Phase Flow-Induced Forces on Bends in Small Scale Tubes. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2010, 132, 041305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miwa, S.; Hibiki, T.; Ishii, M.; Morita, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Tanimoto, K. Experimental study of internal two-phase flow induced fluctuating force on a 90° elbow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 76, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudeau, M.; Mureithi, N.W.; Pettigrew, M.J. Two-Phase Flow-Induced Forces on Piping in Vertical Upward Flow: Excitation Mechanisms and Correlation Models. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2013, 135, 030907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Su, J. Vibration Behavior of Marine Risers Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow. In Proceedings of the Volume 9: Ocean Renewable Energy; ASME International: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi-Mamaghani, A.; Sotudeh-Gharebagh, R.; Zarghami, R.; Mostoufi, N. Dynamics of two-phase flow in vertical pipes. J. Fluids Struct. 2019, 87, 150–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazesh, S.; Shams, S. Vibration analysis of cantilever pipe conveying fluid under distributed random excitation. J. Fluids Struct. 2019, 87, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudayarov, B.; Komilova, K.; Turaev, F. Numerical Modeling of pipes conveying gas-liquid two-phase flow. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2019; Volume 97, p. 05022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.-L.; Gao, Y. Experimental Investigation of Vibration Response of a Free-Hanging Flexible Riser Induced by Internal Gas-Liquid Slug Flow. China Ocean Eng. 2018, 32, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Miranda, J.M.; Paik, J.K. Two-phase flow induced vibrations in a marine riser conveying a fluid with rectangular pulse train mass. Ocean Eng. 2019, 174, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. A further study on the non-linear dynamics of simply supported pipes conveying pulsating fluid. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2009, 44, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Natural frequency analysis of a cantilevered piping system conveying gas–liquid two-phase slug flow. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 564–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Wang, Q.; Sarica, C.; Brill, J.P. Unified model for gas-liquid pipe flow via slug dynamics-part 2: Model validation. Trans. ASME J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2003, 125, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, W. Research on the Dynamic Responses of Simply Supported Horizontal Pipes Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow. Processes 2021, 9, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010083
Liu G, Hao Z, Wang Y, Ren W. Research on the Dynamic Responses of Simply Supported Horizontal Pipes Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow. Processes. 2021; 9(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Gang, Zongrui Hao, Yueshe Wang, and Wanlong Ren. 2021. "Research on the Dynamic Responses of Simply Supported Horizontal Pipes Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow" Processes 9, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010083
APA StyleLiu, G., Hao, Z., Wang, Y., & Ren, W. (2021). Research on the Dynamic Responses of Simply Supported Horizontal Pipes Conveying Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Slug Flow. Processes, 9(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010083




