Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Heavy Crude Oil Samples and Their SARA Fractions with 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SARA Fractionation
2.2. 13C NMR Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Speight, J. The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.K. Analytical Characterization Methods for Crude Oil and Related Products; JohnWiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J.G. Petroleum asphaltenes: Part 1: Asphaltenes, resins and the structure of petroleum. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. IFP 2004, 59, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamin, G.V.; Gafurov, M.R.; Yusupov, R.V.; Gracheva, I.N.; Ganeeva, Y.M.; Yusupova, T.N.; Orlinskii, S.B. Toward the asphaltene structure by electron paramagnetic resonance relaxation studies at high fields (3.4 T). Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6942–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, M.; Mamin, G.; Gracheva, I.; Murzakhanov, F.; Ganeeva, Y.; Yusupova, T.; Orlinskii, S. High-Field (3.4 T) ENDOR investigation of asphaltenes in native oil and vanadyl complexes by asphaltene adsorption on alumina surface. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizatullin, B.; Gafurov, M.; Rodionov, A.; Mamin, G.; Mattea, C.; Stapf, S.; Orlinskii, S. Proton–radical interaction in crude oil—A combined NMR and EPR Study. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 11261–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvalheim, O.M.; Aksnes, D.W.; Brekke, T.; Eide, M.O.; Sletten, E. Crude oil characterization and correlation by principal component analysis of 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Cao, J.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, K. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of crude oil as proxies for oil source and thermal maturity based on 1H and 13C spectra. Fuel 2020, 271, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzel, D.A.; Thompson, L.F. Aromatic tertiary carbons as a check of the validity of NMR fossil fuels. Fuel 1986, 65, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitmaier, E.; Hass, G.; Voelter, W. Atlas of Carbon-13 NMR Data; Heyden and Son: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, J.C. A review of applications of NMR spectroscopy in the petroleum industry. In Spectroscopic Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants; Nadkarni, R.A., Ed.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 423–473. [Google Scholar]
- Derome, A.E. Modern NMR Techniques for Chemistry Research; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, H. NMR Spectroscopy: Basic Principles, Concepts, and Applications in Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, R.; Bodenhausen, G.; Wokaun, A. Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions; International Series of Monographs on Chemistry, Book 14; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rule, G.S.; Hitchens, T.K. Fundamentals of Protein NMR Spectroscopy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Friedel, R.A. Absorption spectra and magnetic resonance spectra of asphaltene. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 31, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutter, D.R.; Petrakis, L.; Stenger, J.R.L.; Jensen, R.K. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry of petroleum fractions. Carbon-13 and proton nuclear magnetic resonance characterizations in terms of average molecule parameters. Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, C.E.; Ladner, W.R.; Bartle, K.D. Survey of carbon-13 chemical shifts in aromatic hydrocarbons and its application to coal-derived materials. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Minero, F.; Ancheyta, J.; Silva-Oliver, G.; Flores-Valle, S. Predicting SARA composition of crude oil by means of NMR. Fuel 2013, 110, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, M.V.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K. Determination of SARA fractions of crude oils by NMR technique. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, J.; Kung, J.; Kingston, D.; Kotlyar, L.; Sparks, B.; McCracken, T. Canadian crudes: A comparative study of SARA fractions from a modified HPLC separation technique. Oil Gas Sci. Tech. 2008, 63, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.; Uribe, U.N.; Murgich, J. Correlations between SARA fractions and physicochemical properties with 1H NMR spectra of vacuum residues from Colombian crude oils. Fuel 2010, 89, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.; AlHumaidan, F.; Al-Rabiah, H.; Halabi, M.A. Study on thermal cracking of Kuwaiti heavy oil (vacuum residue) and its SARA fractions by NMR spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4321–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh, S.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.; Yelithao, K.; Klochkov, V.; Rakhmatullin, I. An arabinogalactan isolated from Boswellia carterii: Purification, structural elucidation and macrophage stimulation via NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeder, G.; Weniger, P.; Blumenberg, M. Geochemical implications from direct Rock-Eval pyrolysis of petroleum. Org. Geochem. 2020, 146, 104051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, V.V.; Dudkin, V.I.; Vysoczky, M.G.; Myazin, N.S. Small-size NMR Spectrometer for Express Control of Liquid Media State. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2020, 51, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudyk, S. Relationships between SARA fractions of conventional oil, heavy oil, natural bitumen and residues. Fuel 2018, 216, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzgrabe, U. Quantitative NMR, methods and applications. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Tranter, G.E., Koppenaal, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 816–823. [Google Scholar]
- Poveda, J.-C.; Molina, D.-R.; Pantoja-Agreda, E.-F. 1H- and 13C-NMR structural characterization of asphaltenes from Vacuum residua modified by thermal cracking. CtF 2014, 5, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Da Silva, E.C.; Neto, A.C.; Valdemar, L.J.; De Castro, E.V.R.; De Menezes, S.M.C. Study of Brazilian asphaltene aggregation by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Fuel 2014, 117, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, A.V.; Smernik, R.J.; Schneider, M.P.W.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Plant, E.L. Determination of the aromaticity and the degree of aromatic condensation of a thermosequence of wood charcoal using NMR. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergoug, T.; Bouhadda, Y. Determination of Hassi Messaoud asphaltene aromatic structure from 1H & 13C NMR analysis. Fuel 2014, 115, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Glavincevski, B.B. NMR method for determination of aromatics in middle distillate oils. Fuel Process. Technol. 1999, 60, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizatullin, B.; Gafurov, M.; Vakhin, A.; Rodionov, A.; Mamin, G.; Orlinskii, S.; Mattea, C.; Stapf, S. Native Vanadyl Complexes in Crude Oil as Polarizing Agents for In Situ Proton Dynamic Nuclear Polarization. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 10923–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.S.; Archipov, R.V.; Ivanov, A.A.; Gnezdilov, O.I.; Gafurov, M.R.; Skirda, V.D. The low-field pulsed mode dynamic nuclear polarization in the pentavalent chromium complex and crude oils. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2014, 45, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poindexter, E. An Overhauser Effect in Natural Crude Oil. Nature 1958, 182, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peksoz, A.; Almaz, E.; Yalciner, A. The characterization of asphaltene behavior in some aromatic solvents by dynamic nuclear polarization technique. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 75, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C. Characterizing oils in oil-water mixtures inside porous media by Overhauser dynamic nuclear polarization. Fuel 2019, 257, 116107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzilius, B. High-Field Dynamic Nuclear Polarization. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2020, 71, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmatullin, I.Z.; Efimov, S.V.; Tyurin, V.A.; Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Klimovitskii, A.E.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Klochkov, V.V. Application of high resolution NMR (1H and 13C) and FTIR spectroscopy for characterization of light and heavy crude oils. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 168, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissada, K.K.A.; Tan, J.; Szymczyk, E.; Darnell, M.; Mei, M.; Zhou, J. Group-type characterization of crude oil and bitumen. Part I: Enhanced separation and quantification of saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes (SARA). Org. Geochem. 2016, 95, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmatullin, I.Z.; Efimov, S.V.; Margulis, B.Y.; Klochkov, V.V. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of oil samples extracted from some Bashkortostan and Tatarstan oilfields based on NMR spectroscopy data. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 156, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
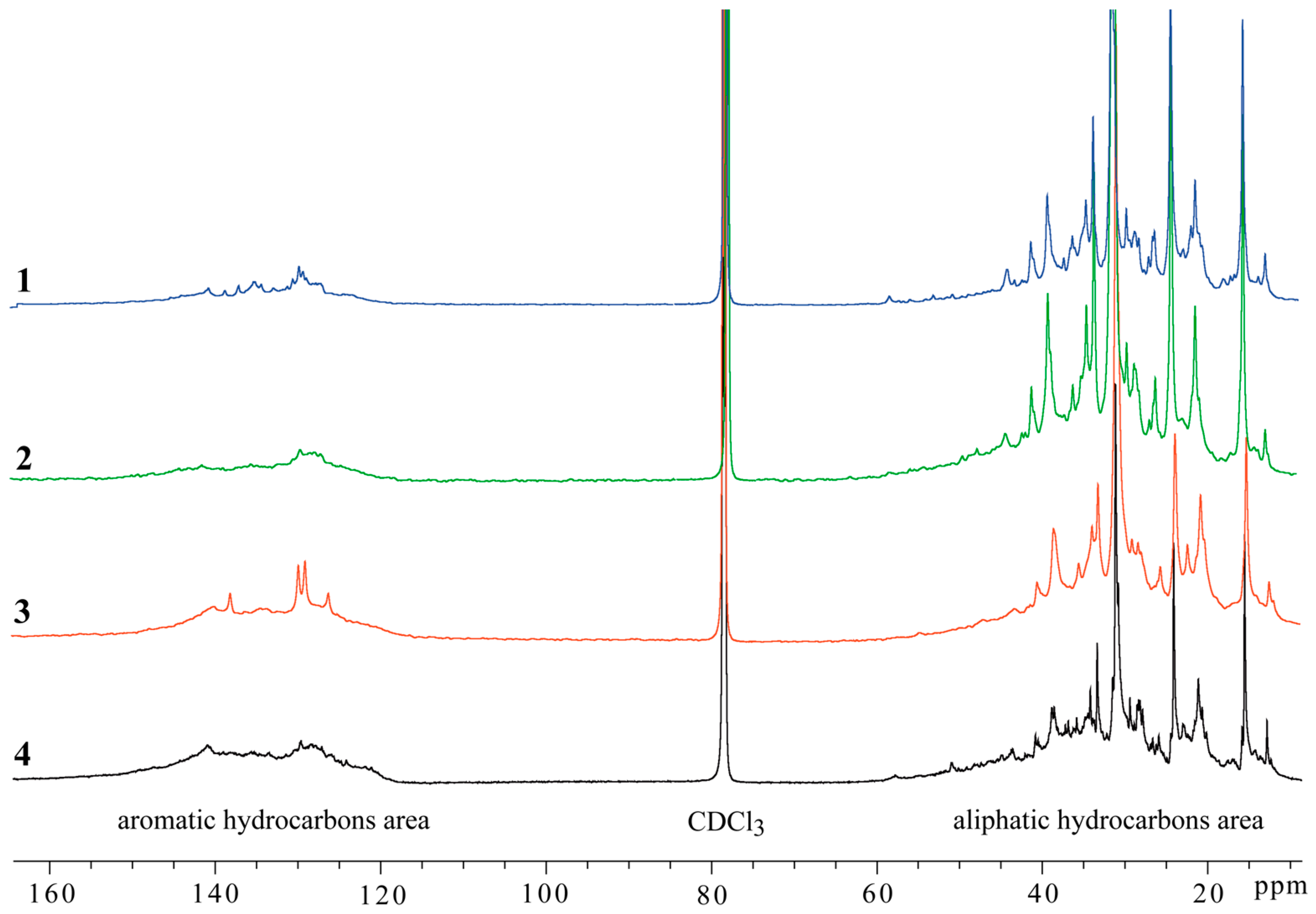




| Sample Number 1 | Viscosity, mPa·s | Origin of Oil |
|---|---|---|
| 1, 1s, 1ar, 1r, 1as | 106 | Iraq |
| 2, 2s, 2ar, 2r, 2as | 1430 | Ambar gatur (Turkmenistan) |
| 3, 3s, 3ar, 3r, 3as | 2420 | Ashal’cha (Republic of Tatarstan, Russia) |
| 4, 4s, 4ar, 4r, 4as | 49,700 | Cuba |
| Sample Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturates, % | 59.6 | 73.7 | 26.2 | 31.0 |
| Aromatics, % | 26.7 | 14.3 | 40.6 | 39.2 |
| Resins, % | 12.1 | 9.8 | 28.5 | 14.2 |
| Asphaltenes, % | 1.6 | 2.2 | 4.7 | 15.6 |
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| sample size | 1 g of oil |
| precipitation of asphaltenes (fold amount of n-alkane) | 1:40 heptane |
| time of precipitation | 24 h |
| temperature of precipitation | room temperature |
| filtration paper | 2.5 μm filter |
| asphaltene washing | hot heptane |
| asphaltene extraction | toluene |
| adsorbent | alumina activated at 430 °C |
| saturates elution | 200 mL of heptane |
| aromatics elution | 200 mL of toluene |
| resins elution | 200 mL of 1:1 toluene-isopropyl alcohol |
| solvent removal | rotary evaporator |
| Sample Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cp | 25.8 | 18.8 | 21.6 | 18.8 |
| Csq | 53.0 | 52.6 | 48.9 | 36.6 |
| Ct | 10.0 | 13.9 | 12.8 | 15.1 |
| Car | 12.5 | 14.7 | 19.3 | 27.5 |
| FCA | 0.123 | 0.147 | 0.188 | 0.275 |
| MCL | 6.9 | 9.1 | 7.7 | 7.7 |
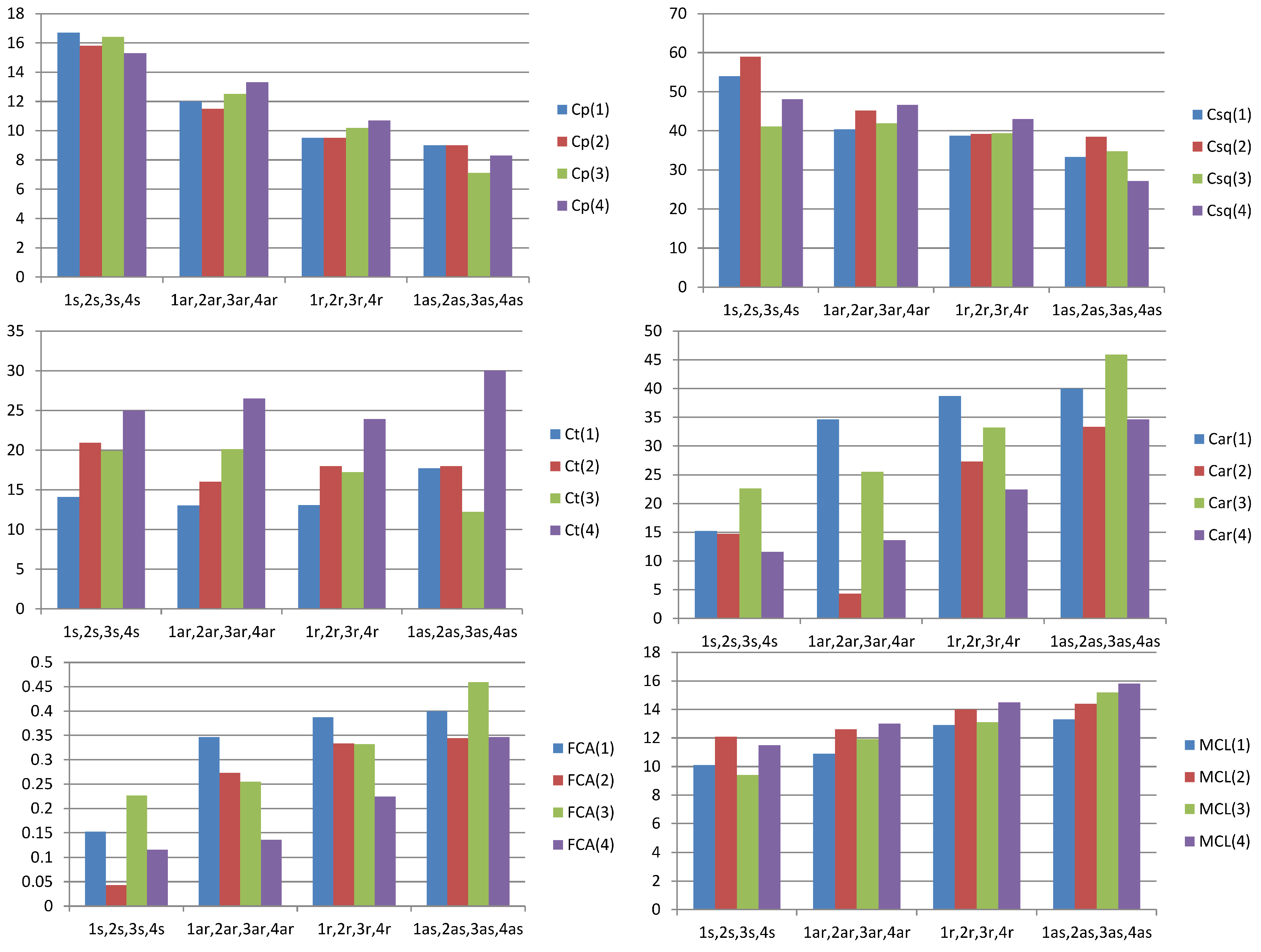
| Sample number | 1 | 1s | 1ar | 1r | 1as |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARA fractions, % | crude oil (100%) | saturated compounds (59.6%) | aromatics (26.7%) | resins (12.1%) | asphaltene fraction (1.6%) |
| Cp | 25.8 | 16.7 | 12.0 | 9.5 | 9.0 |
| Csq | 53.0 | 54.0 | 40.4 | 38.7 | 33.3 |
| Ct | 10.0 | 14.1 | 13.0 | 13.1 | 17.7 |
| Car | 12.5 | 15.2 | 34.6 | 38.7 | 40.0 |
| FCA | 0.123 | 0.152 | 0.346 | 0.387 | 0.400 |
| MCL | 6.9 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 12.9 | 13.3 |
| Sample Number | 2 | 2s | 2ar | 2r | 2as |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARA fractions, % | crude oil (100%) | saturated compounds (73.7%) | aromatics (14.3%) | resins (9.8%) | asphaltene fraction (2.2%) |
| Cp | 18.8 | 15.8 | 11.5 | 9.5 | 9.1 |
| Csq | 52.6 | 59.0 | 45.2 | 39.2 | 38.5 |
| Ct | 13.9 | 20.9 | 16.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 |
| Car | 14.7 | 4.3 | 27.3 | 33.3 | 34.4 |
| FCA | 0.147 | 0.043 | 0.273 | 0.333 | 0.344 |
| MCL | 9.1 | 12.1 | 12.6 | 14.0 | 14.4 |
| Sample Number | 3 | 3s | 3ar | 3r | 3as |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARA fractions, % | crude oil (100%) | saturated compounds (26.2%) | aromatics (40.6%) | resins (28.5%) | asphaltene fraction (4.7%) |
| Cp | 21.6 | 16.4 | 12.5 | 10.2 | 7.1 |
| Csq | 48.9 | 41.1 | 41.9 | 39.4 | 34.8 |
| Ct | 12.8 | 19.9 | 20.1 | 17.2 | 12.2 |
| Car | 19.3 | 22.6 | 25.5 | 33.2 | 45.9 |
| FCA | 0.188 | 0.226 | 0.255 | 0.332 | 0.459 |
| MCL | 7.7 | 9.4 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 15.2 |
| Sample Number | 4 | 4s | 4ar | 4r | 4as |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARA fractions, % | crude oil (100%) | saturated compounds (31.0%) | aromatics (39.2%) | resins (14.2%) | asphaltene fraction (15.6%) |
| Cp | 18.8 | 15.3 | 13.3 | 10.7 | 8.3 |
| Csq | 36.6 | 48.1 | 46.6 | 43.0 | 27.1 |
| Ct | 15.1 | 25.0 | 26.5 | 23.9 | 30.0 |
| Car | 27.5 | 11.6 | 13.6 | 22.4 | 34.6 |
| FCA | 0.275 | 0.116 | 0.136 | 0.224 | 0.346 |
| MCL | 7.7 | 11.5 | 13.0 | 14.5 | 15.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakhmatullin, I.; Efimov, S.; Tyurin, V.; Gafurov, M.; Al-Muntaser, A.; Varfolomeev, M.; Klochkov, V. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Heavy Crude Oil Samples and Their SARA Fractions with 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Processes 2020, 8, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080995
Rakhmatullin I, Efimov S, Tyurin V, Gafurov M, Al-Muntaser A, Varfolomeev M, Klochkov V. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Heavy Crude Oil Samples and Their SARA Fractions with 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Processes. 2020; 8(8):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080995
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakhmatullin, Ilfat, Sergey Efimov, Vladimir Tyurin, Marat Gafurov, Ameen Al-Muntaser, Mikhail Varfolomeev, and Vladimir Klochkov. 2020. "Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Heavy Crude Oil Samples and Their SARA Fractions with 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance" Processes 8, no. 8: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080995
APA StyleRakhmatullin, I., Efimov, S., Tyurin, V., Gafurov, M., Al-Muntaser, A., Varfolomeev, M., & Klochkov, V. (2020). Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Heavy Crude Oil Samples and Their SARA Fractions with 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Processes, 8(8), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080995









