Comparison of Two Different Designs of a Scraped Surface Crystallizer for Desalination Effect and Hydraulic and Thermodynamic Numbers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Sample Analysis
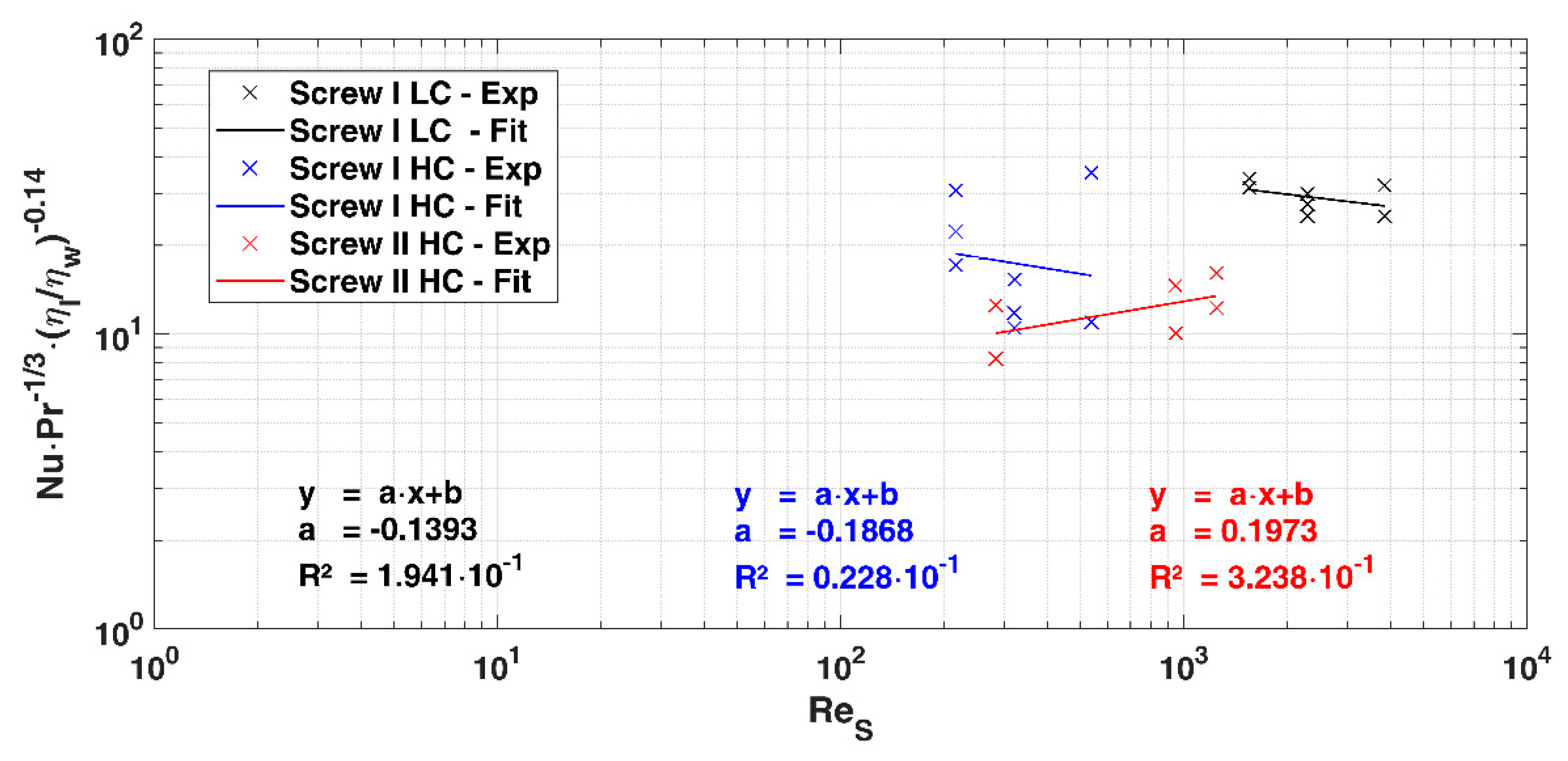
2.2. Data Analysis
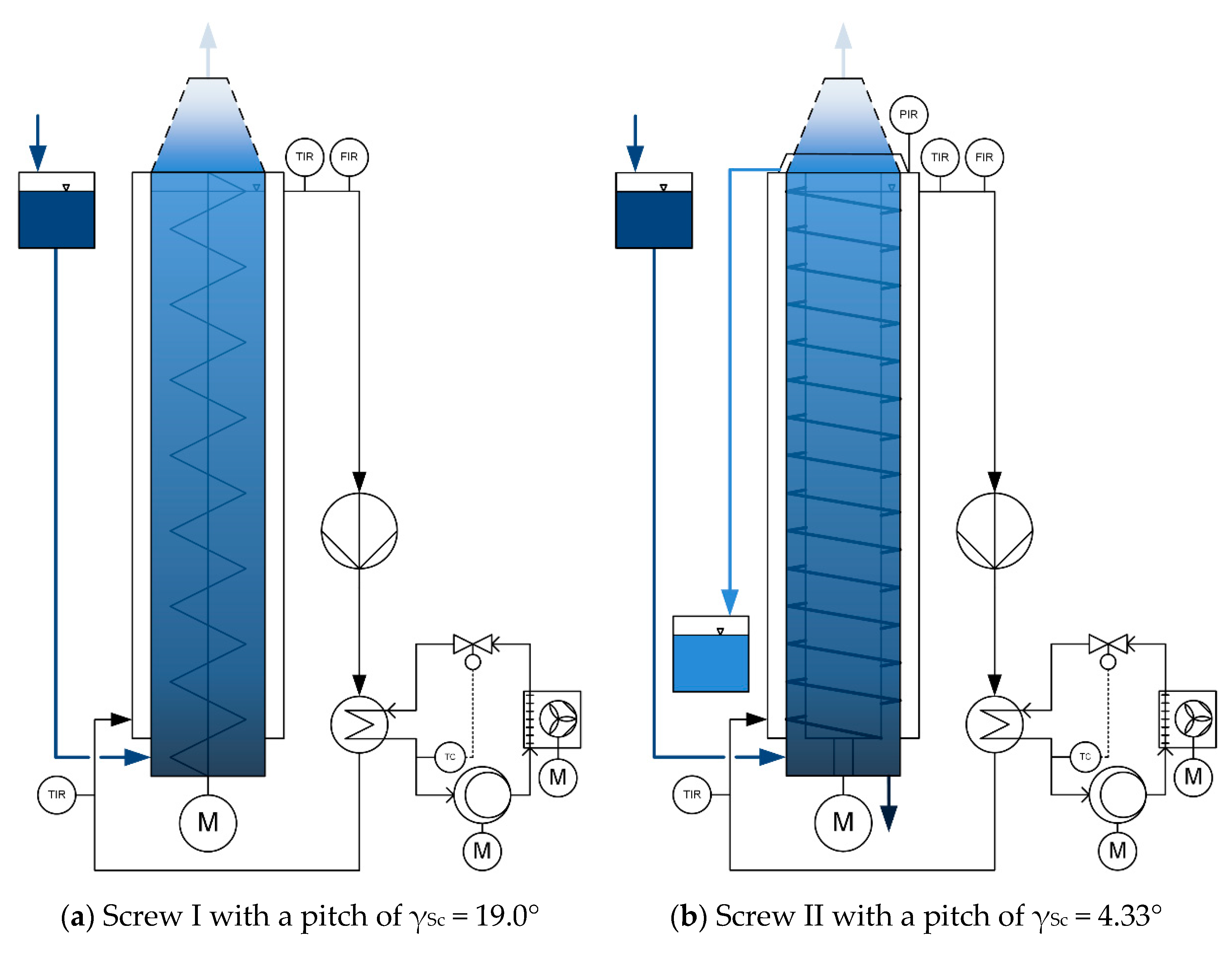
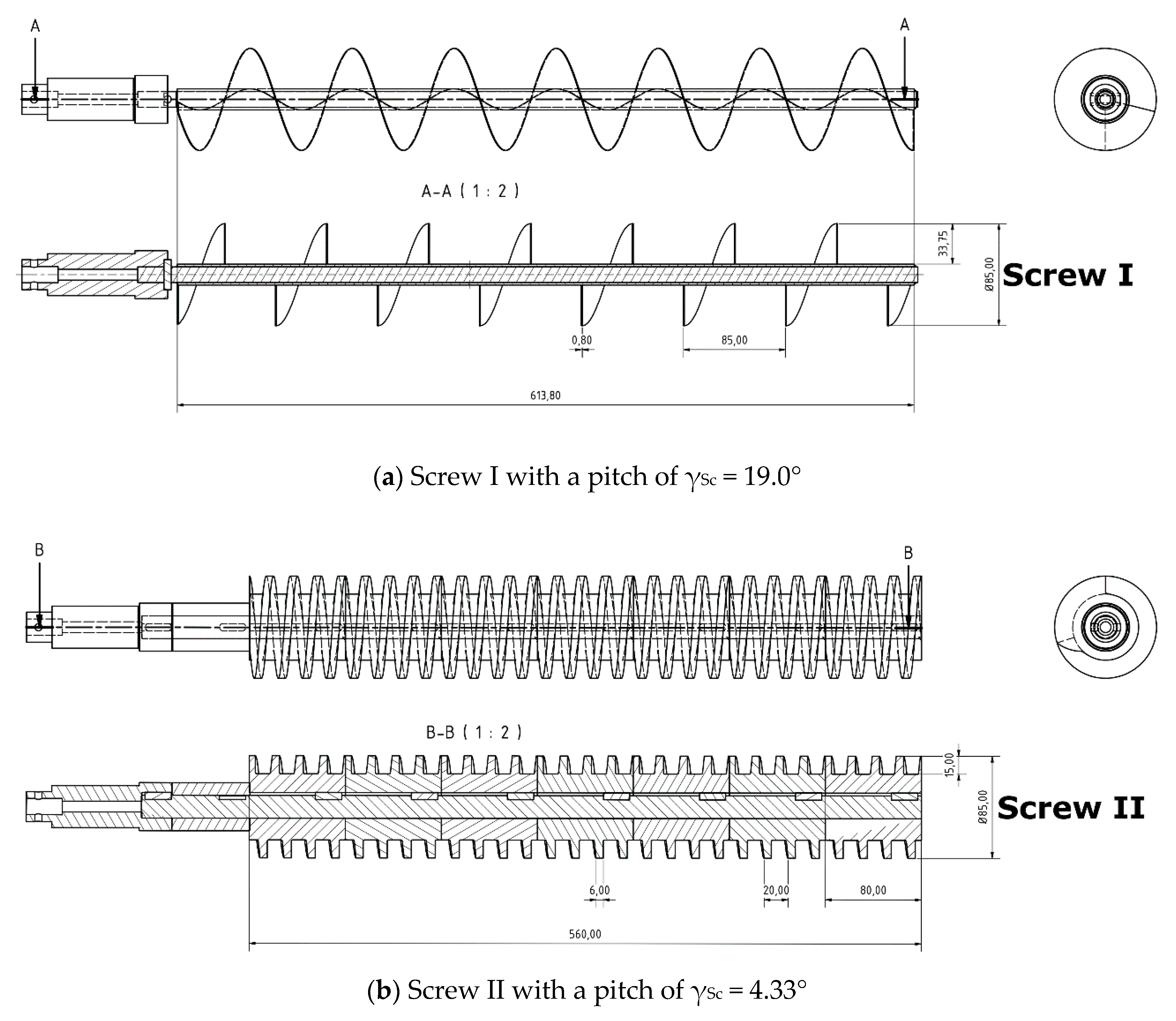
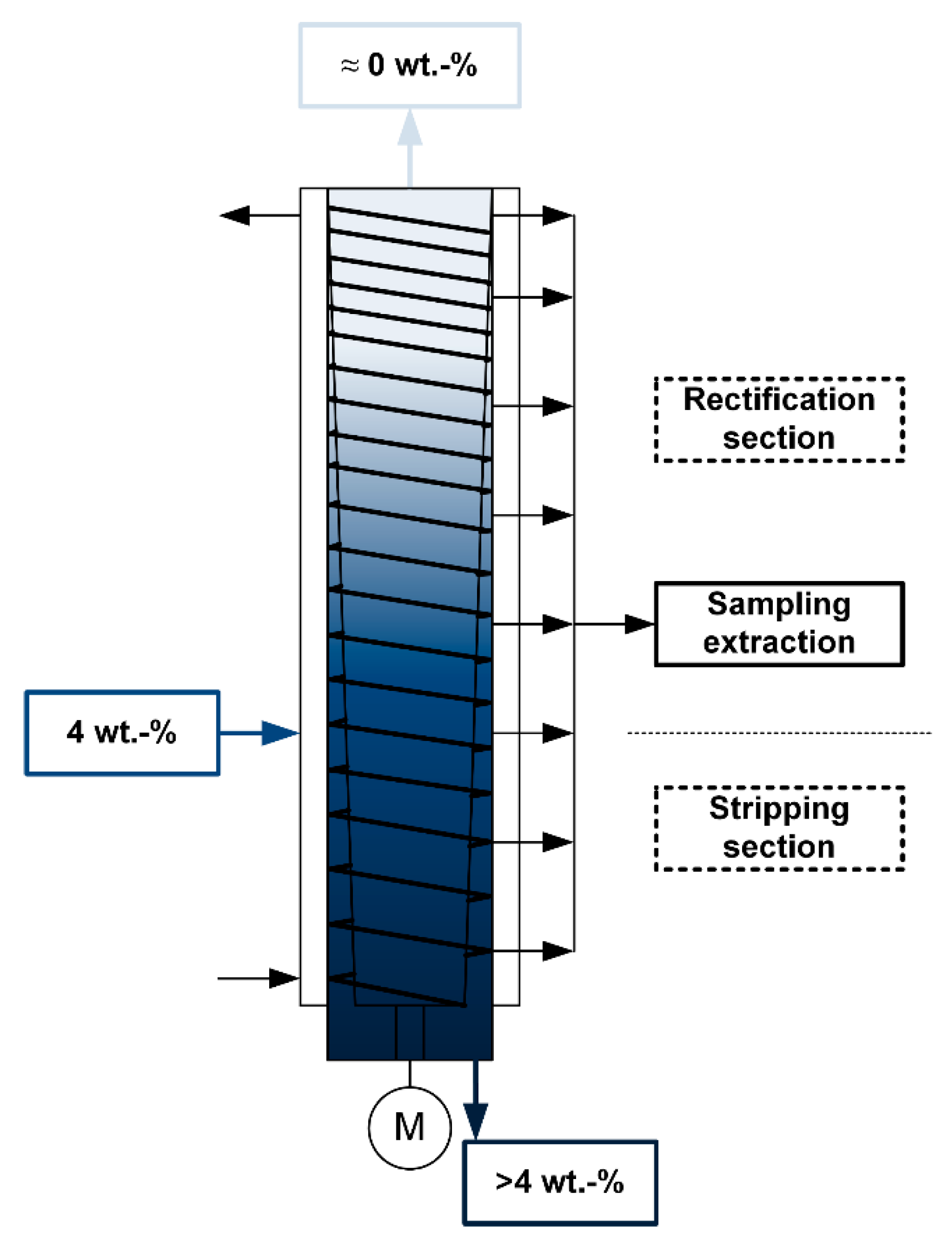
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
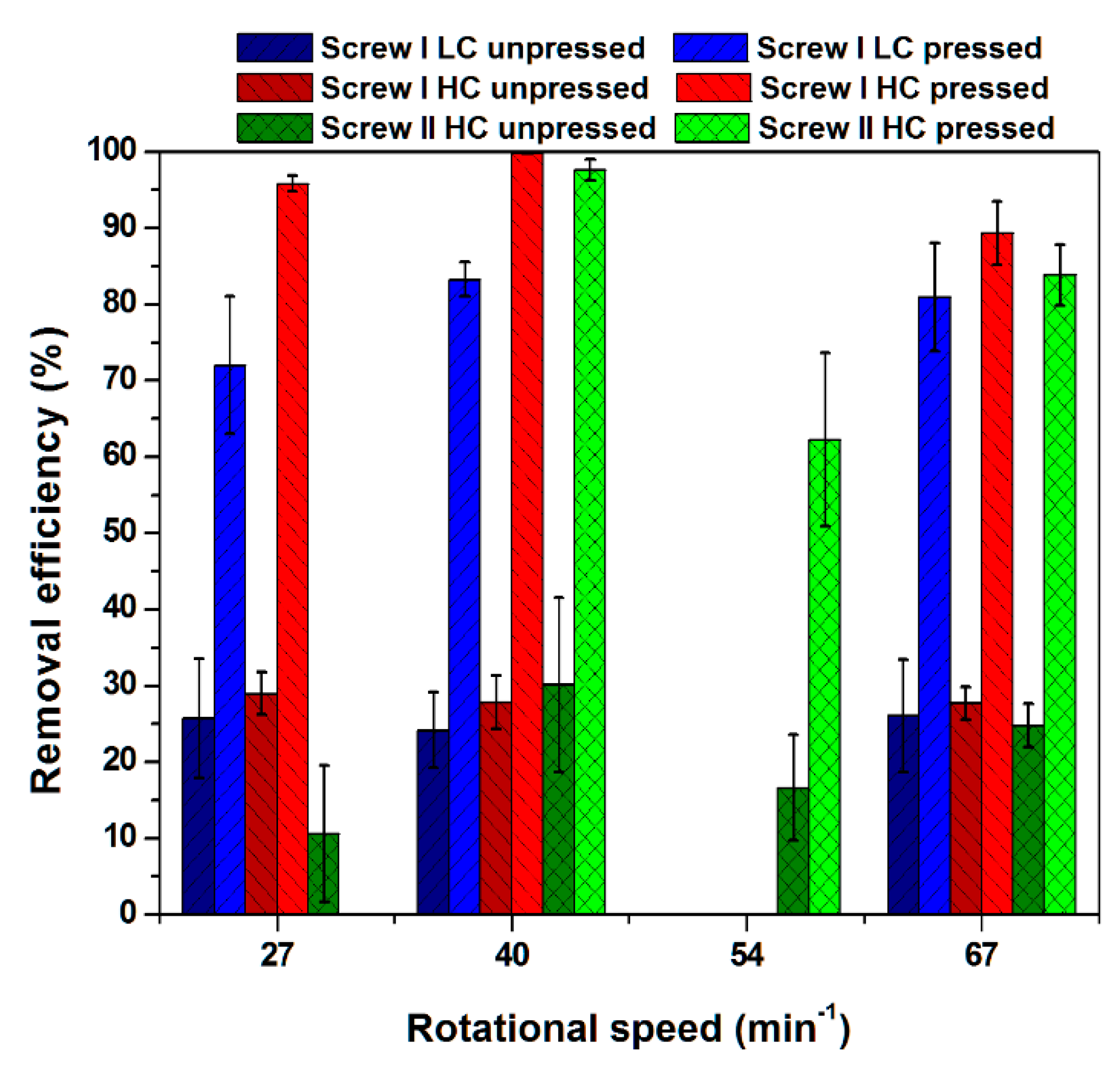
3.1. Removal Efficiency
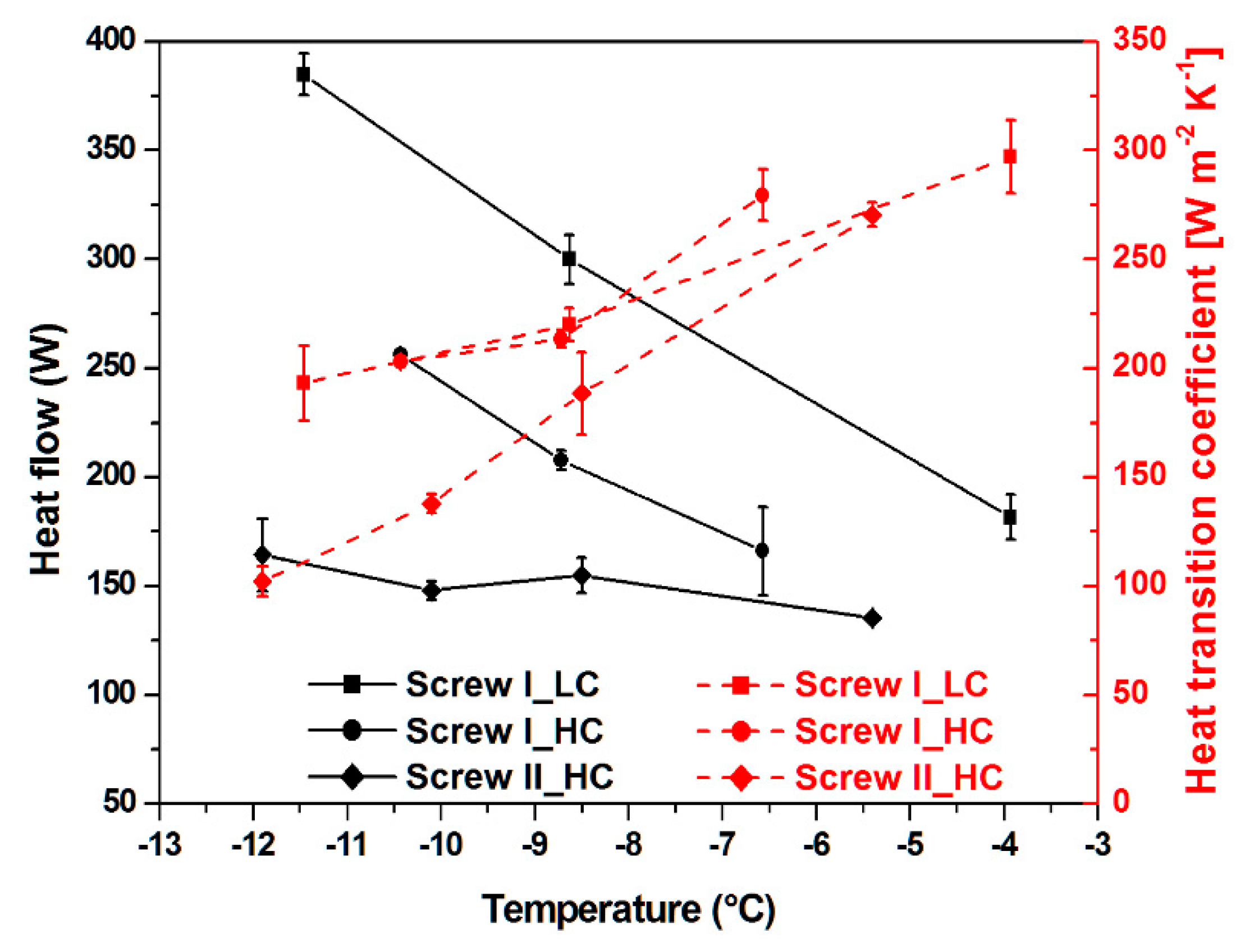
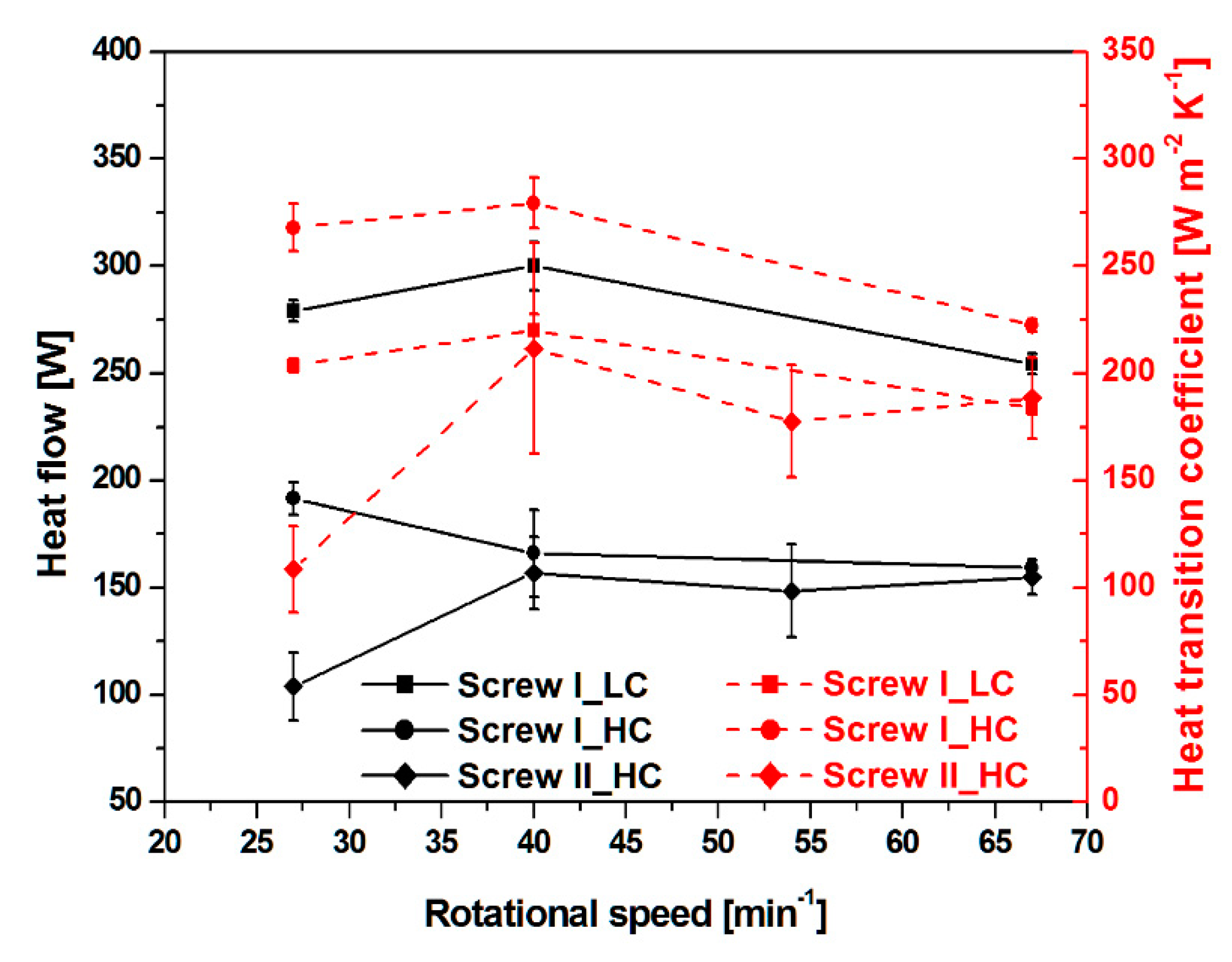
3.2. Heat Flow and Heat Transition Coefficient
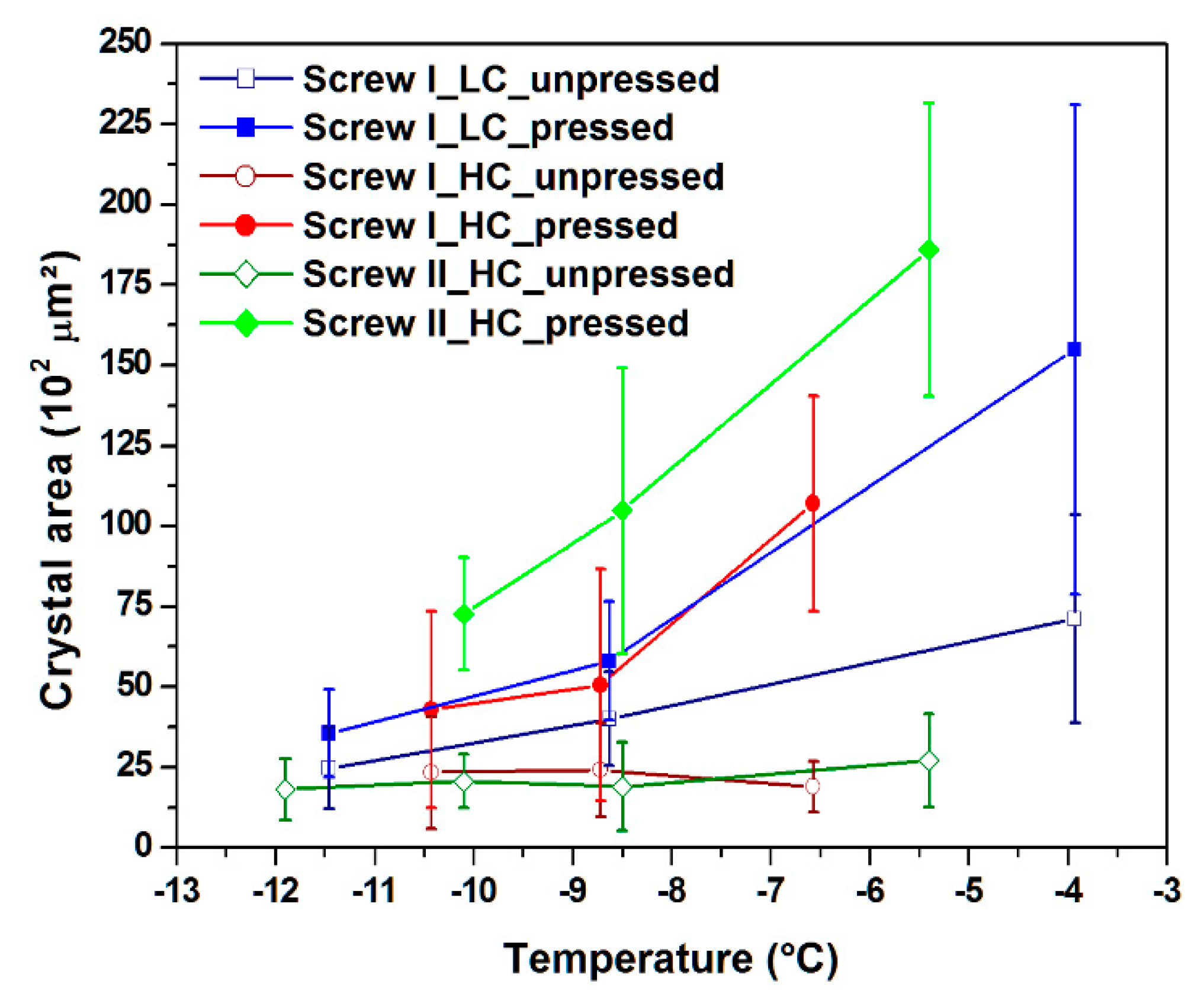
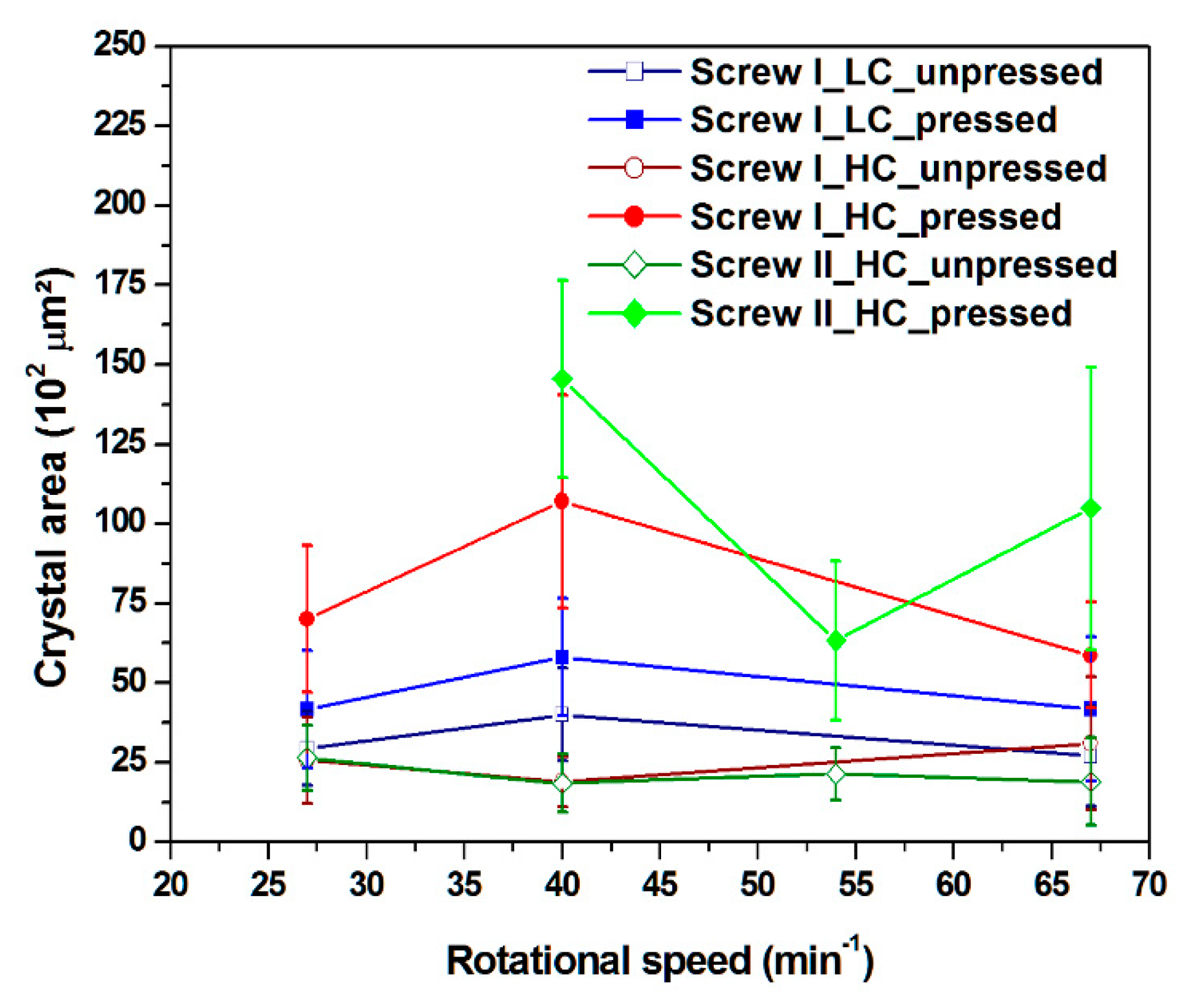
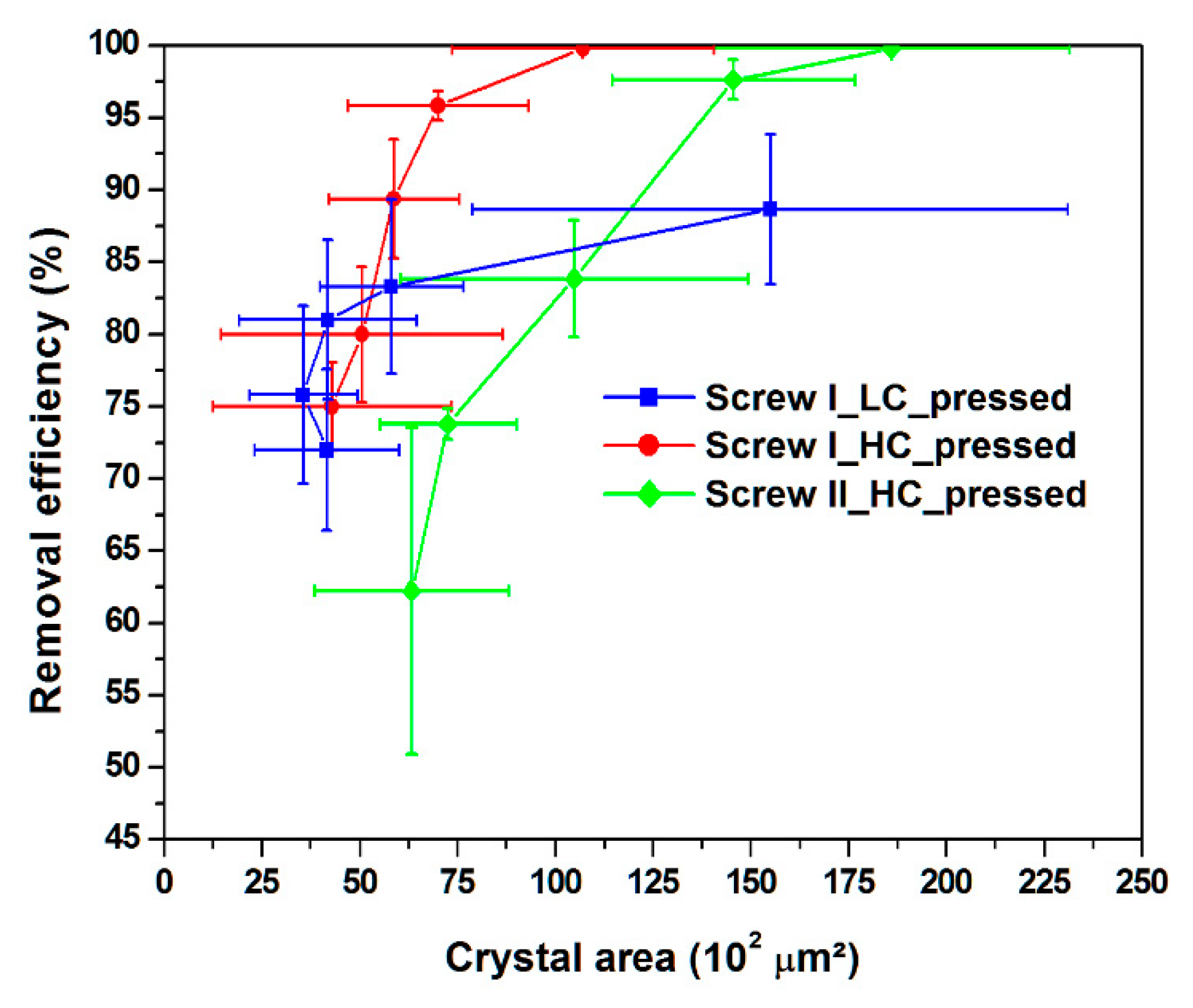
3.3. Crystal Area
4. Research Proposal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cipollina, A.; Micale, G.; Rizzuti, L. Seawater Desalination for Freshwater Production. In Seawater Desalination; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-642-01149-8. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannis, I.C.; Soldatos, P.G. Water desalination cost literature: Review and assessment. Desalination 2008, 223, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, G.A.; Ramos-Real, F.J. Electricity generation cost in isolated system: The complementarities of natural gas and renewables in the Canary Islands. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2808–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaji, R.; Bartram, J.; Coates, D.; Connor, R.; Harding, J.; Hellmuth, M.; Leclerc, L.; Pangare, V.; Shields, J.G. Beyond demand: Water’s Social and Environmental Benefits. In Managing Water under Uncertainty and Risk; United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1–407. ISBN 9789231042355. [Google Scholar]
- Erlbeck, L.; Nessel, R.; Illner, F.; Müller, W.; Kunz, T.; Schuchmann, H.; Rädle, M.; Methner, F.-J. Commercial feasibility of a new freeze crystallization plant for small-scale potable water production. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 105, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shao, Y. Freeze concentration for removal of pharmaceutically active compounds in water. Desalination 2009, 249, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Ishikawa, M. Ice formation of aqueous solution and its removal phenomena on vertical cooled plate. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 40, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, S.; Ito, T.; Saito, A. Effect of crystal orientation on freeze concentration of solutions. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.G.F.; Chen, X.D.; Premathilaka, S.; Free, K. Experimental study of wash columns used for separating ice from ice-slurry. Desalination 2008, 218, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Wakisaka, M.; Miyawaki, O.; Sakashita, S. Effect of seed ice on formation of tube ice with high purity for a freeze wastewater treatment system with a bubble-flow circulator. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Wakisaka, M.; Shirai, Y.; Sakashita, S. Ice crystallization in a pilot-scale freeze wastewater treatment system. Chem. Eng. Process. 2001, 40, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.G.G.; Yang, M.L.; Yang, X.X. Experimental and thermal analysis of washing the packed ice bed in wash columns. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 2835–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlbeck, L.; Wössner, D.; Kunz, T.; Rädle, M.; Methner, F.-J. Investigation of freeze crystallization and ice pressing in a semi-batch process for the development of a novel single-step desalination plant. Desalination 2018, 448, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlbeck, L.; Wössner, D.; Kunz, T.; Rädle, M.; Methner, F.-J. Investigating Freeze Crystallization as Promising Next-generation Water Purification Technology for the Brewing Industry. Brew. Sci. 2018, 71, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlbeck, L.; Wössner, D.; Schlachter, K.; Kunz, T.; Methner, F.-J.; Rädle, M. Investigation of a novel Scraped Surface Crystallizer with included ice-pressing section as new purification technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health: ImageJ. 2017. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Erlbeck, L.; Rädle, M.; Nessel, R.; Illner, F.; Müller, W.; Rudolph, K.; Kunz, T.; Methner, F.-J. Investigation of the depletion of ions through freeze desalination. Desalination 2017, 407, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penney, W.R.; Bell, K.J. Close-clearance agitators. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1967, 59, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, C. Zum Kontinuierlichen Trennpressen Biogener Feststoffe in Schneckengeometrien am Beispiel Geschälter Rapssaat. 2003. Available online: https://duepublico2.uni-due.de/receive/duepublico_mods_00010993 (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Gaddis, E.S. Wärmeübertragung und Leistungsaufnahme in Rührkesseln. In VDI-Wärmeatlas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1621–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, W.A.; Müller, W. Wärmeübergang auf der Innenseite eines Rührbehälters (Teil 1). Eng. Res. 1992, 58, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, W.A. Rührleistung und Wärmeübergang auf der Innenseite eines Rührbehälters mit verschiedenen Wendel-Rührern. Eng. Res. 1993, 59, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.S. A conceptual demonstration of freeze desalination-membrane distillation (FD-MD) hybrid desalination process utilizing liquefied natural gas (LNG) cold energy. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4037–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Low Concentration (mgL−1) | High Concentration (wt. %) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | - | 4.0 |
| Residual alkalinity | 16.9 | - |
| Nitrate | 120.0 | - |
| Manganese | 0.255 | - |
| Total carbon | 88.2 | - |
| Total organic carbon | 27.6 | - |
| Experiments | δunpressed (μm) | δpressed (μm) | Aunpressed (102 μm2) | Apressed (102 μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screw I LC | 60.8 ± 14.2 | 77.9 ± 26.7 | 38.5 ± 8.5 | 66.5 ± 26.1 |
| Screw I HC | 49.5 ± 4.30 | 80.1 ± 14.7 | 24.7 ± 4.8 | 65.9 ± 7.9 |
| Screw II HC | 55.2 ± 12.2 | 116.8 ± 38.9 | 21.6 ± 2.6 | 114.5 ± 12.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erlbeck, L.; Wössner, D.; Kunz, T.; Methner, F.-J.; Rädle, M. Comparison of Two Different Designs of a Scraped Surface Crystallizer for Desalination Effect and Hydraulic and Thermodynamic Numbers. Processes 2020, 8, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080971
Erlbeck L, Wössner D, Kunz T, Methner F-J, Rädle M. Comparison of Two Different Designs of a Scraped Surface Crystallizer for Desalination Effect and Hydraulic and Thermodynamic Numbers. Processes. 2020; 8(8):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080971
Chicago/Turabian StyleErlbeck, Lars, Dirk Wössner, Thomas Kunz, Frank-Jürgen Methner, and Matthias Rädle. 2020. "Comparison of Two Different Designs of a Scraped Surface Crystallizer for Desalination Effect and Hydraulic and Thermodynamic Numbers" Processes 8, no. 8: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080971
APA StyleErlbeck, L., Wössner, D., Kunz, T., Methner, F.-J., & Rädle, M. (2020). Comparison of Two Different Designs of a Scraped Surface Crystallizer for Desalination Effect and Hydraulic and Thermodynamic Numbers. Processes, 8(8), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080971






