Simulation Study and Industrial Application of Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Regulating the Proportion of Concentrates in the SKS Copper Smelting Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
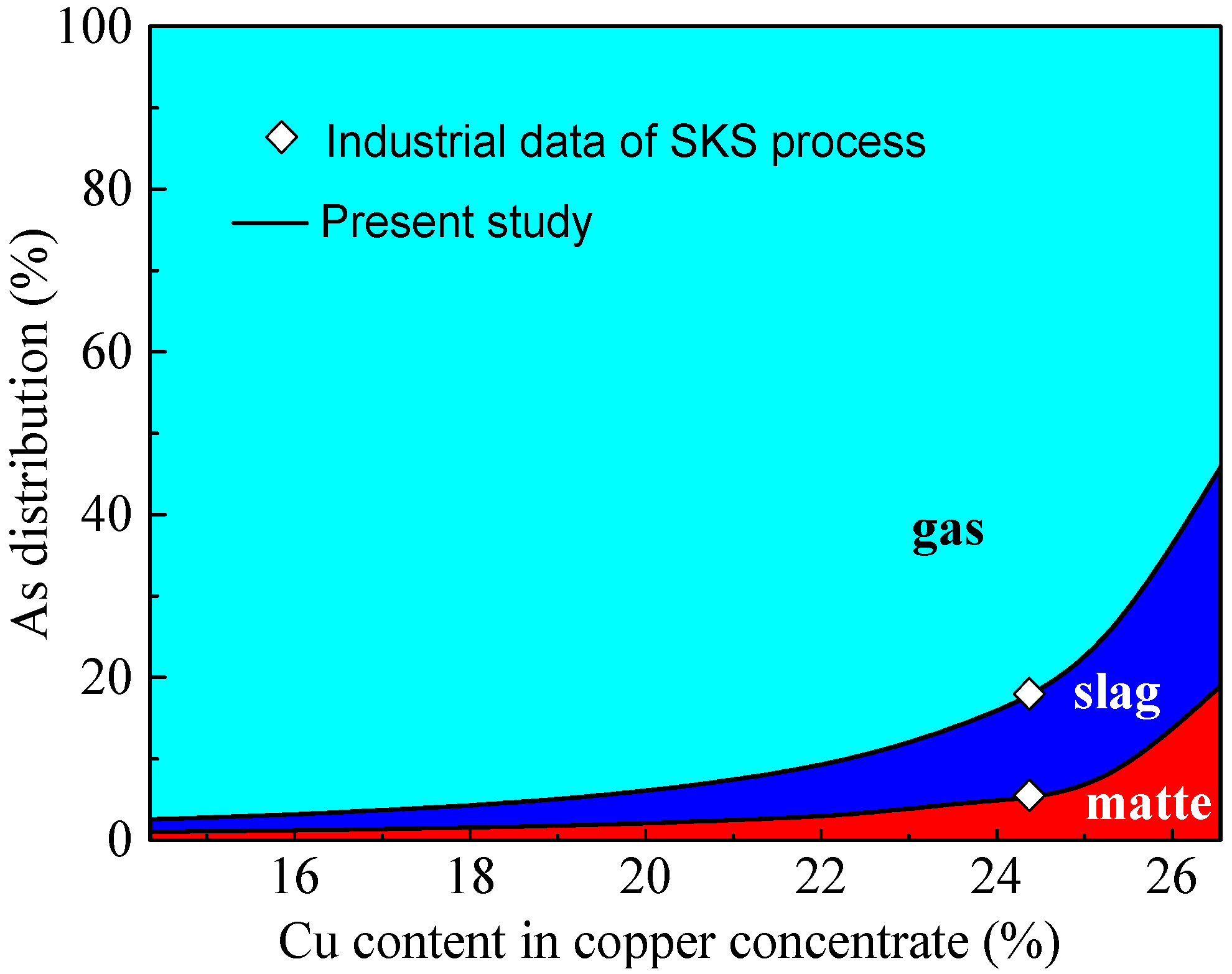
3.1. Arsenic Distribution in the Actual Production Process and by SKSSIM
3.2. Effect of Cu Content in Concentrate on Arsenic Distribution
3.3. Effect of Fe Content in Concentrate on Arsenic Distribution
3.4. Effect of S Content in Concentrate on Arsenic Distribution
3.5. Effect of Arsenic Content in Concentrate on Arsenic Distribution
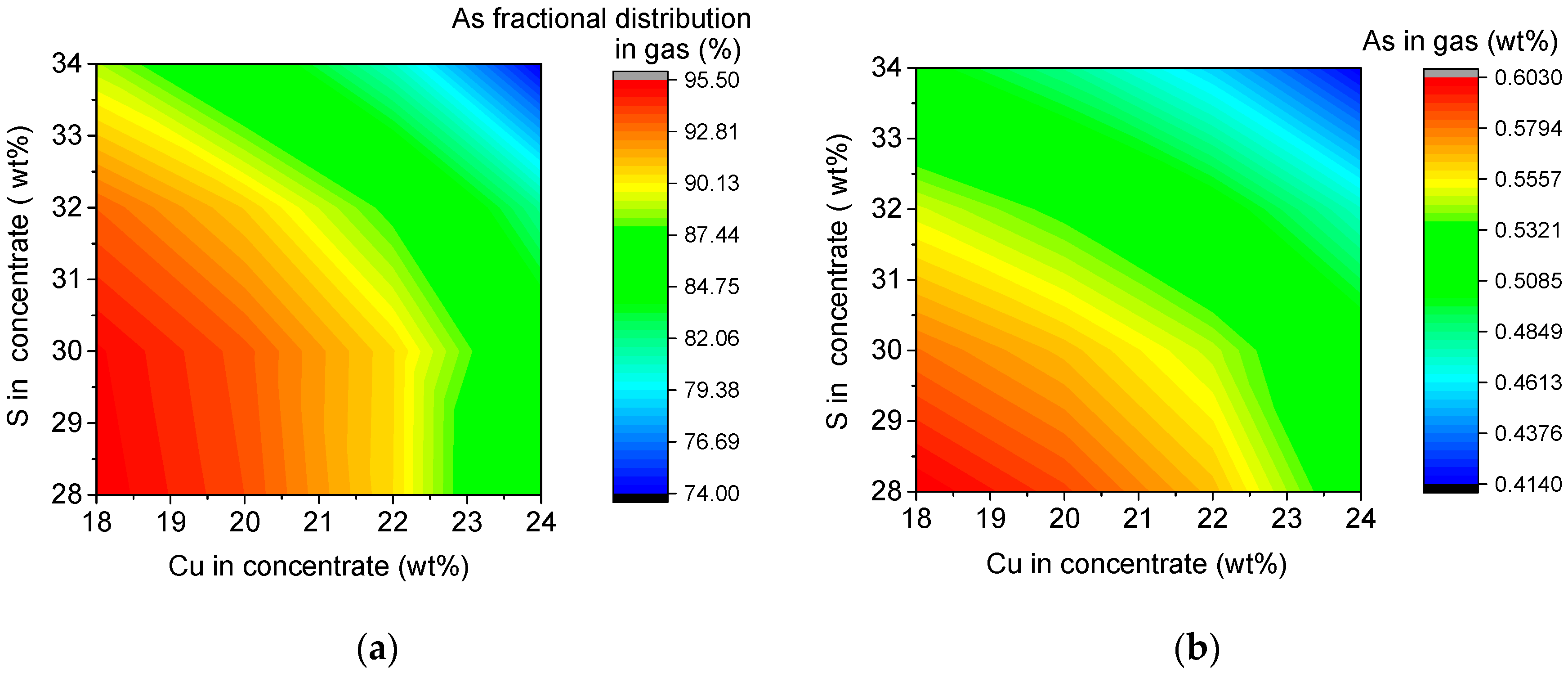
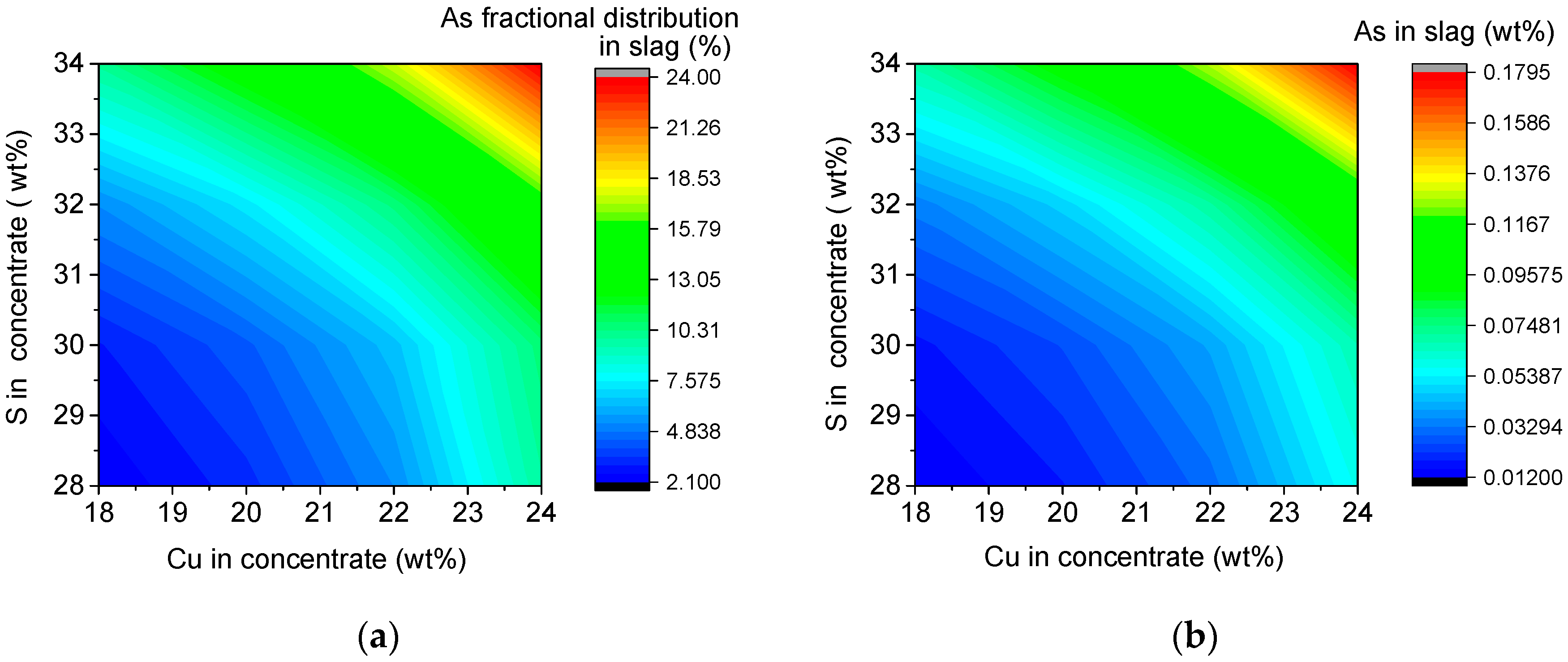
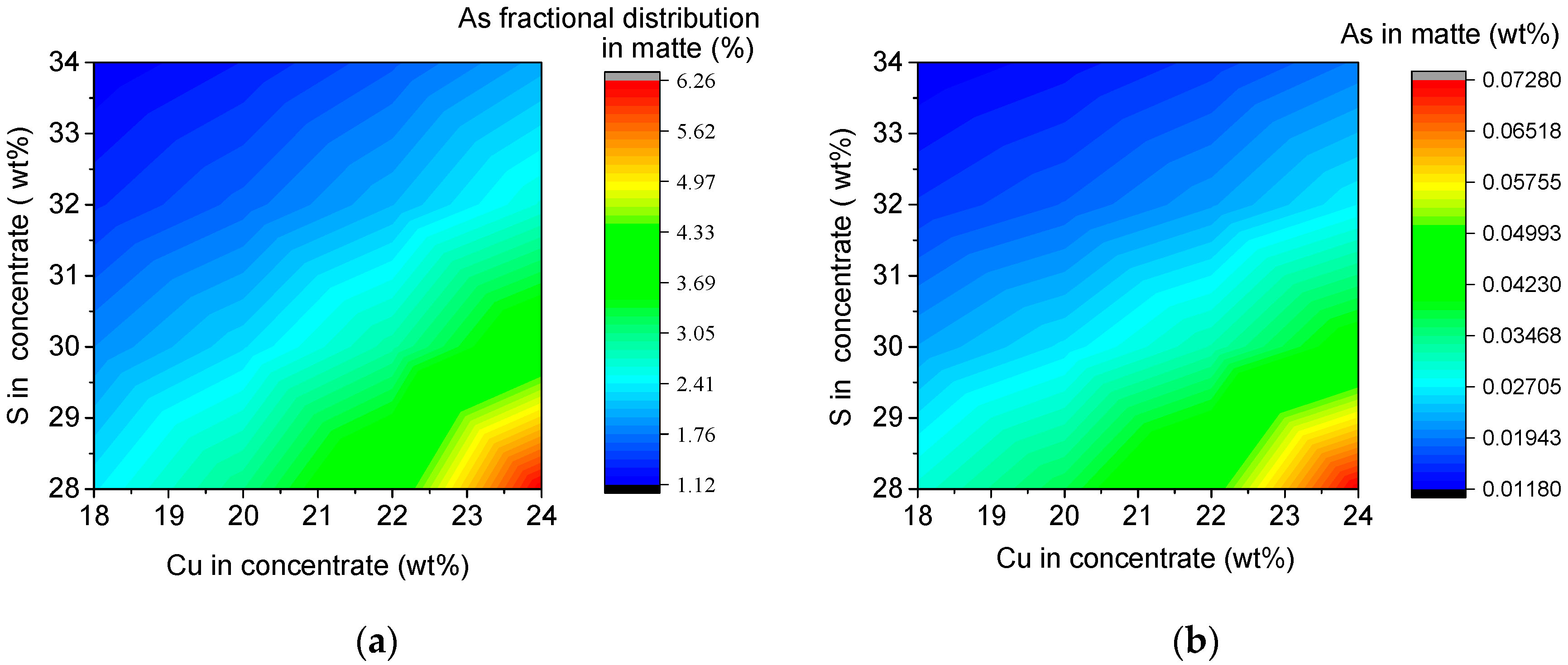
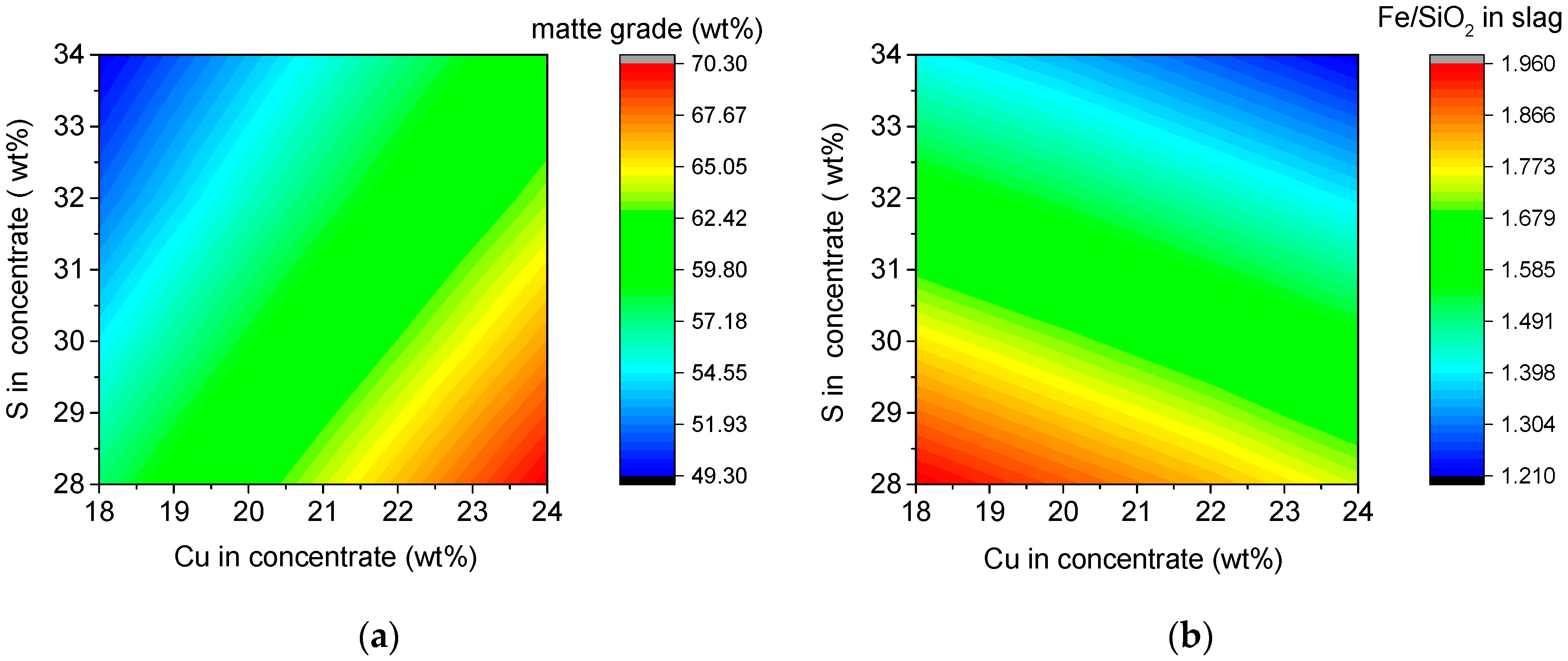
3.6. Interactive Effect of Cu and S Content in Concentrate on Arsenic Distribution
3.6.1. Interactive Effect on Arsenic Distribution
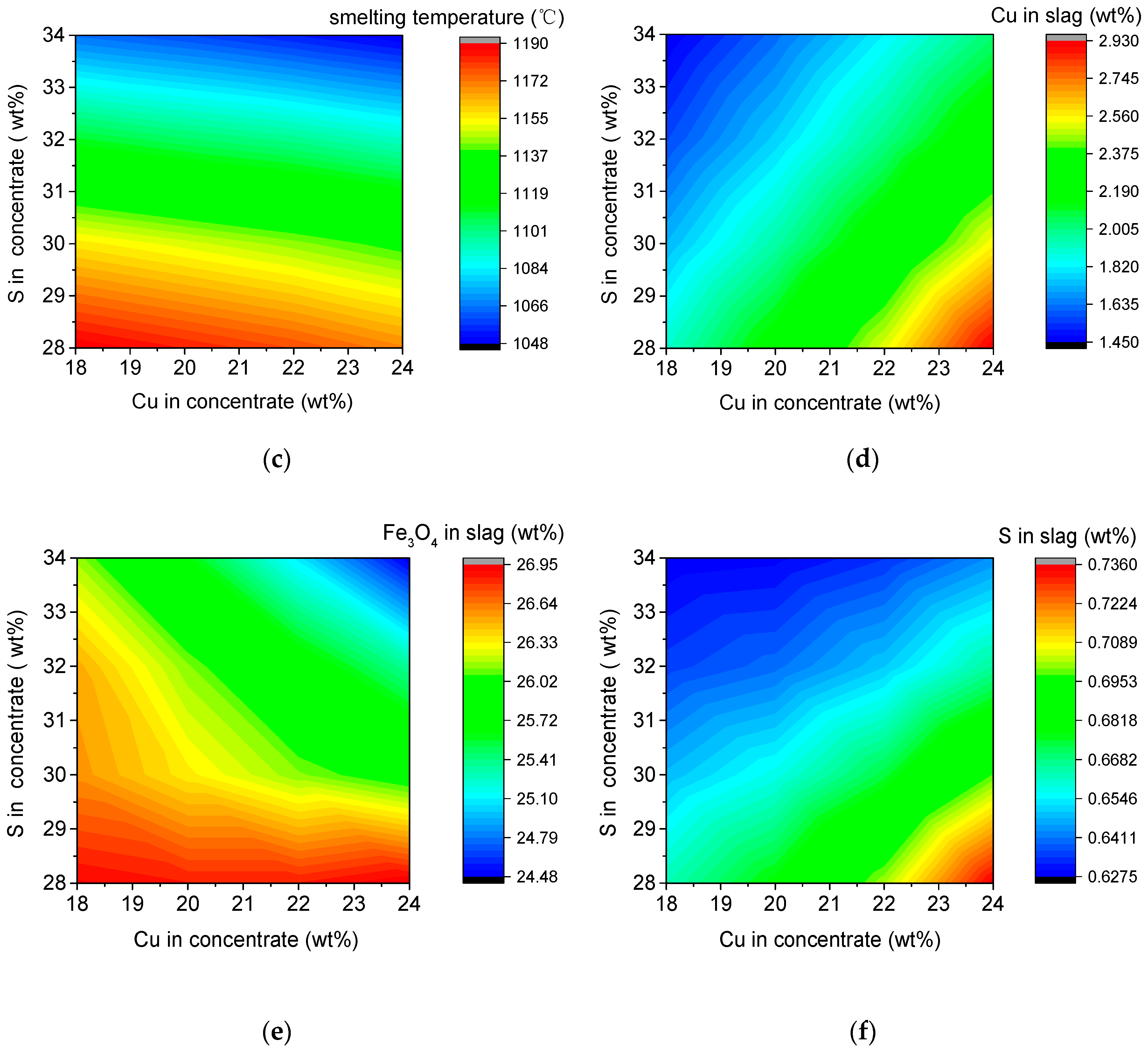
3.6.2. Interactive Effects on Other Parameters of the SKS Process
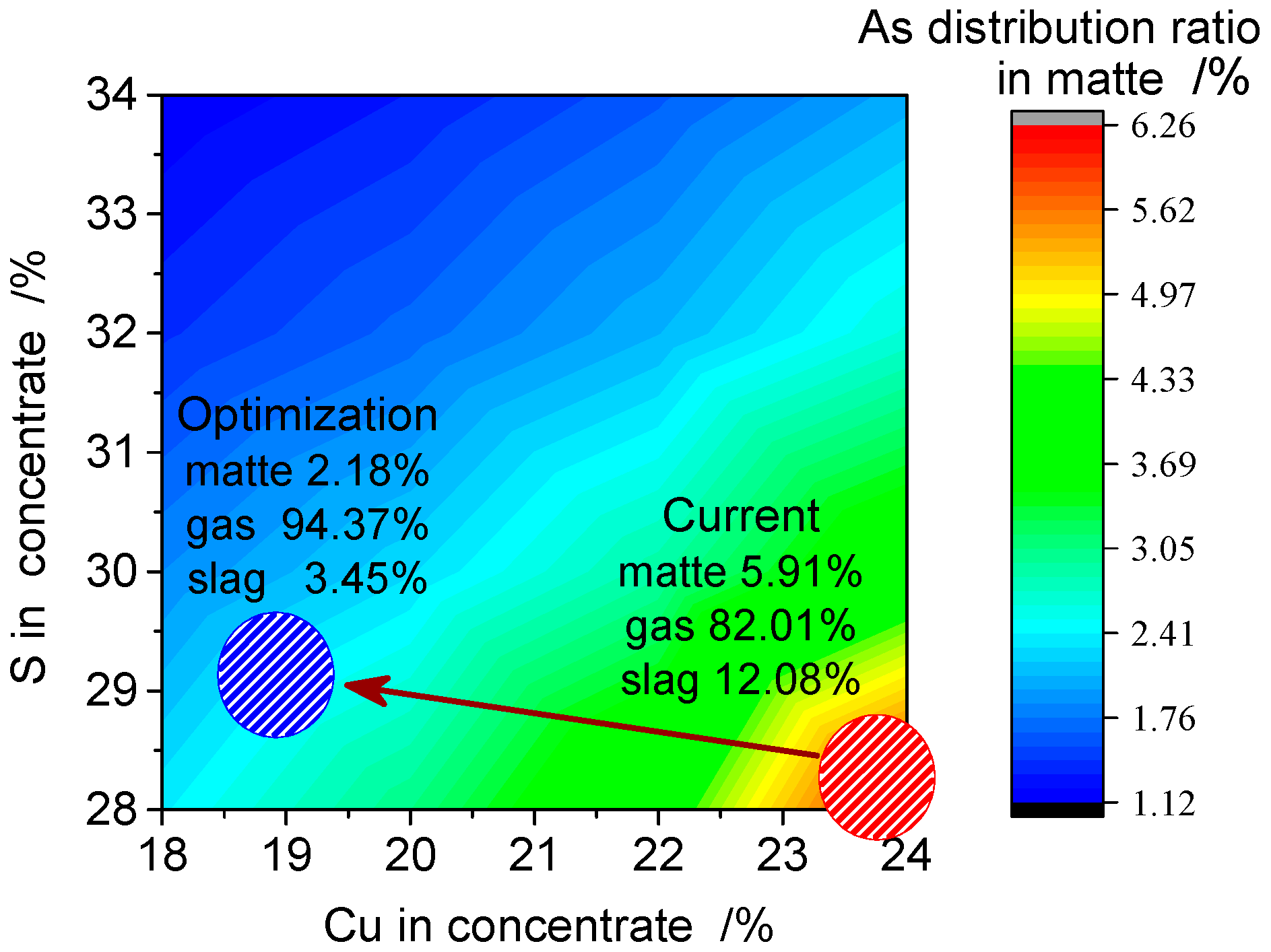
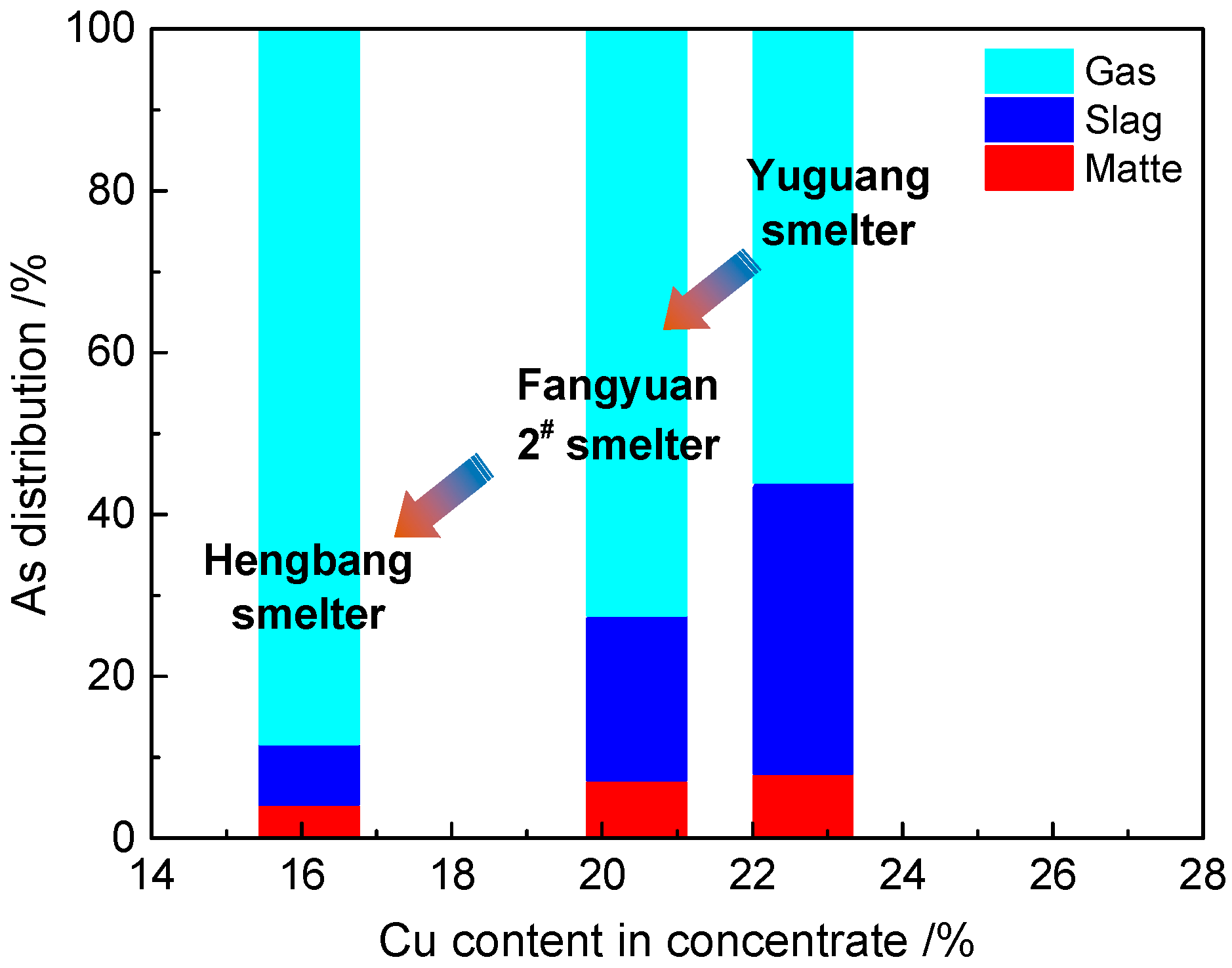
3.7. Industrial Application and Verification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, R.J.; Zhang, H.; Ni, H.W. Arsenic removal from arsenopyrite-bearing iron ore and arsenic recovery from dust ash by roasting method. Processes 2019, 7, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosmukhamedov, N.; Kaplan, V. Efficient removal of arsenic and antimony during blast furnace smelting of lead-containing materials. JOM 2017, 69, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.P.; Li, L.; Tan, C. Separation of arsenic from the antimony-bearing dust through selective oxidation using CuO. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Tian, S.Q.; Wu, J.X.; Chai, L.Y.; Liao, Q. Distribution and behavior of arsenic during the reducing-matting smelting process. JOM 2017, 69, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, A.; Azakami, T. Thermodynamics of removing impurities during copper smelting. Can. Metall. Q. 1969, 8, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, S.; Yazawa, A.; Jorgensen, F.R.A. Simulation of the removal of arsenic during the roasting of copper concentrate. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1999, 30, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Zhang, L.; Jahanshahi, S. Thermodynamic modeling of arsenic in copper smelting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinbourne, D.R.; Kho, T.S. Computational thermodynamics modeling of minor element distributions during copper flash converting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coursol, P.; Mackey, P.J.; Kapusta, J.P.T.; Valencia, N.C. Energy consumption in copper smelting: A new Asian horse in the race. JOM 2015, 67, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Zhan, J.; Fan, Y.Q.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C.F.; Hwang, J.Y. Research and industrial application of a process for direct reduction of molten high-lead smelting slag. JOM 2017, 69, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hao, Z.D.; Yang, T.Z.; Liu, W.F.; Zhang, D.C.; Zhang, L.; Bin, S.; Bin, W.D. A comparison study of the oxygen-rich side blow furnace and the oxygen-rich bottom blow furnace for liquid high lead slag reduction. JOM 2015, 67, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.F.; Yang, T.Z.; Zhang, D.C.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.F. A new pyrometallurgical process for producing antimony white from by-product of lead smelting. JOM 2014, 66, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.L.; Dong, Z.Q.; Chen, T. Distribution of minor elements in complex copper concentrates in oxygen-enriched bottom blown smelting process. China Nonferrous Metall. 2016, 3, 22–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Q.; Cui, Z.X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.J. Phase Equilibrium Study of ZnO-‘‘FeO’’-SiO2 System at Fixed Po2 10−8 atm. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Cui, Z.X.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.J. Phase Equilibria Study of the ZnO- ‘‘FeO’’-SiO2-Al2O3 System at Po2 10−8 atm. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Cui, Z.X.; Ma, X.D.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Zhao, B.J. Mixing phenomena in a bottom blown copper smelter: A water model study. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, L.; Cui, Z.X.; Ma, X.D.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Nguyen, A.V.; Zhao, B.J. Understanding of bath surface wave in bottom blown copper smelting furnace. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cui, Z.X.; Zhao, B.J. Slag chemistry of bottom blown copper smelting furnace at Dongying Fangyuan. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 15−19 March 2015; pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.; Yan, H.J.; Liu, F.K.; Liu, L.; Cui, Z.X.; Shen, D.B. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid multi-phase flows in oxygen enriched bottom-blown furnace. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2012, 22, 1826–1834. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.J.; Liu, F.K.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Gao, Q.; Liu, L.; Cui, Z.X.; Shen, D.B. Influence of lance arrangement on bottom-blowing bath smelting process. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2012, 22, 2393–2400. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.M.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.J. Reaction mechanism and distribution behavior of arsenic in the bottom blown copper smelting process. Metals 2017, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H. Copper smelting mechanism in oxygen bottom-blown furnace. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H.; Jiang, T.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.J. Development and application of SKSSIM simulation software for the oxygen bottom blown copper smelting process. Metals 2017, 7, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Guo, X.Y.; Tian, Q.H.; Jiang, T.; Chen, M.; Zhao, B.J. Effects of matte grade on the distribution of minor elements (Pb, Zn, As, Sb, and Bi) in the bottom blown copper smelting process. Metals 2017, 7, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Jahanshahi, S. Thermodynamics of arsenic in FeOX-CaO-SiO2 slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2010, 41, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Composition (wt %) | As | Cu | Fe | S | SiO2 | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual production | matte | 0.07 | 70.77 | 5.52 | 20.22 | 0.51 | 2.91 |
| slag | 0.08 | 3.16 | 42.58 | 0.86 | 25.24 | 28.08 | |
| By SKSSIM | matte | 0.07 | 70.31 | 4.80 | 20.38 | 0.82 | 3.62 |
| slag | 0.07 | 2.93 | 42.07 | 0.73 | 25.18 | 29.02 | |
| Distribution (wt %) | Gas | Slag | Matte |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actual production | 82.01 | 12.08 | 5.91 |
| By SKSSIM | 82.71 | 11.06 | 6.23 |
| Name of Smelter | Composition of Concentrates (wt %) | Distribution Ratios of Arsenic (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Other | Gas | Slag | Matte | |
| Yantai Hengbang [13] | 16.10 | 83.90 | 88.35 | 7.51 | 4.14 |
| Fangyuan 2# | 20.46 | 79.54 | 72.50 | 20.37 | 7.13 |
| Jiyuan Yuguang | 22.67 | 77.33 | 55.89 | 36.08 | 8.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X. Simulation Study and Industrial Application of Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Regulating the Proportion of Concentrates in the SKS Copper Smelting Process. Processes 2020, 8, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040385
Wang Q, Wang Q, Tian Q, Guo X. Simulation Study and Industrial Application of Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Regulating the Proportion of Concentrates in the SKS Copper Smelting Process. Processes. 2020; 8(4):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040385
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qinmeng, Qiongqiong Wang, Qinghua Tian, and Xueyi Guo. 2020. "Simulation Study and Industrial Application of Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Regulating the Proportion of Concentrates in the SKS Copper Smelting Process" Processes 8, no. 4: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040385
APA StyleWang, Q., Wang, Q., Tian, Q., & Guo, X. (2020). Simulation Study and Industrial Application of Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Regulating the Proportion of Concentrates in the SKS Copper Smelting Process. Processes, 8(4), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040385





