Effect of Dehydration on the Rheological Measurement of Surimi Paste in Cone-Plate Rheometry: Heat and Mass Transfer Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surimi Paste Preparation
2.2. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (SAOS) Test: Temperature Sweep
2.3. Moisture Diffusion
2.4. Numerical Simulation
2.4.1. Modeling of Airflow
2.4.2. Modeling of Temperature and Moisture Fields
2.5. Simulation
2.6. Validation of Simulation Model
3. Results and Discussion
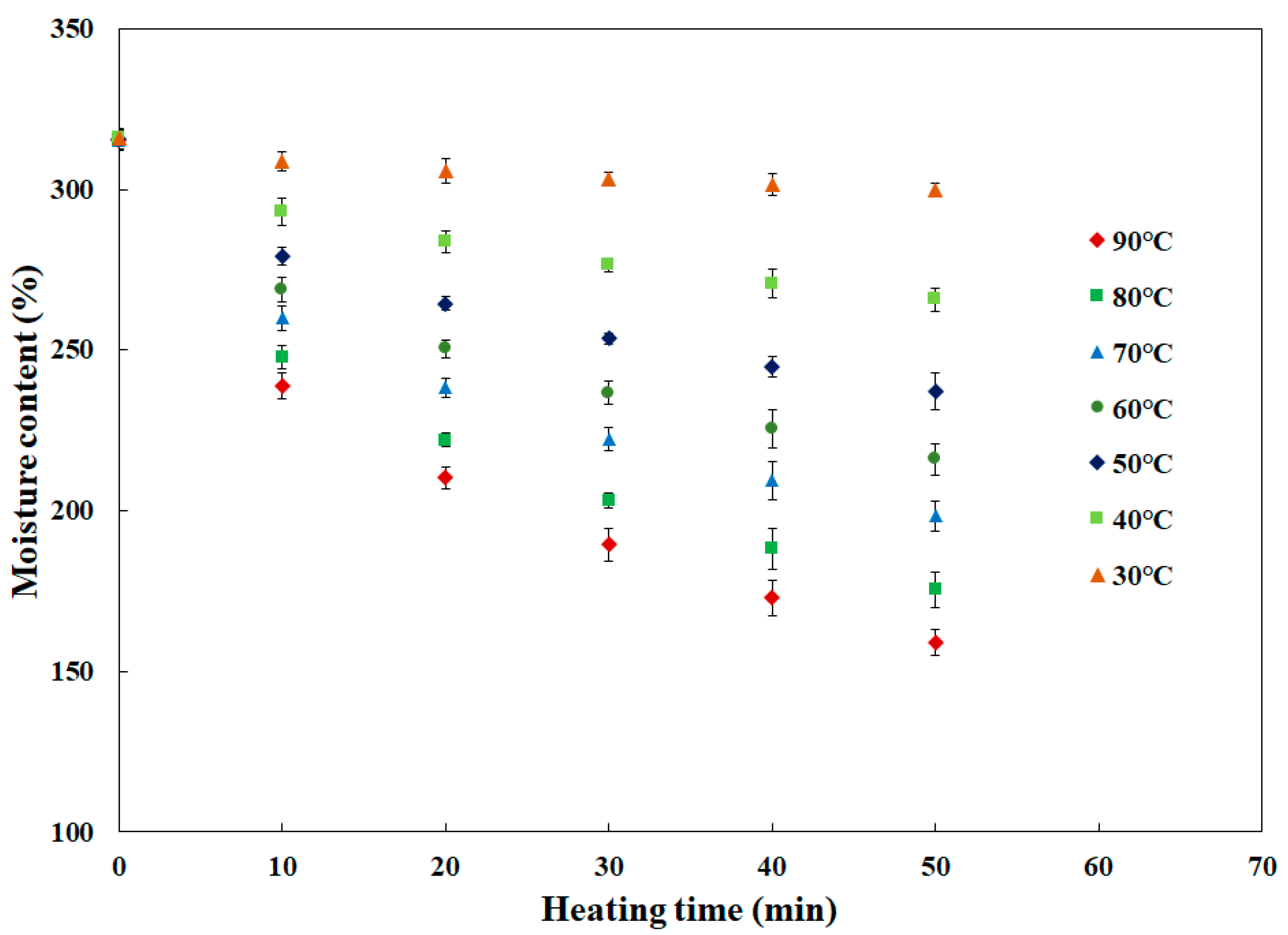
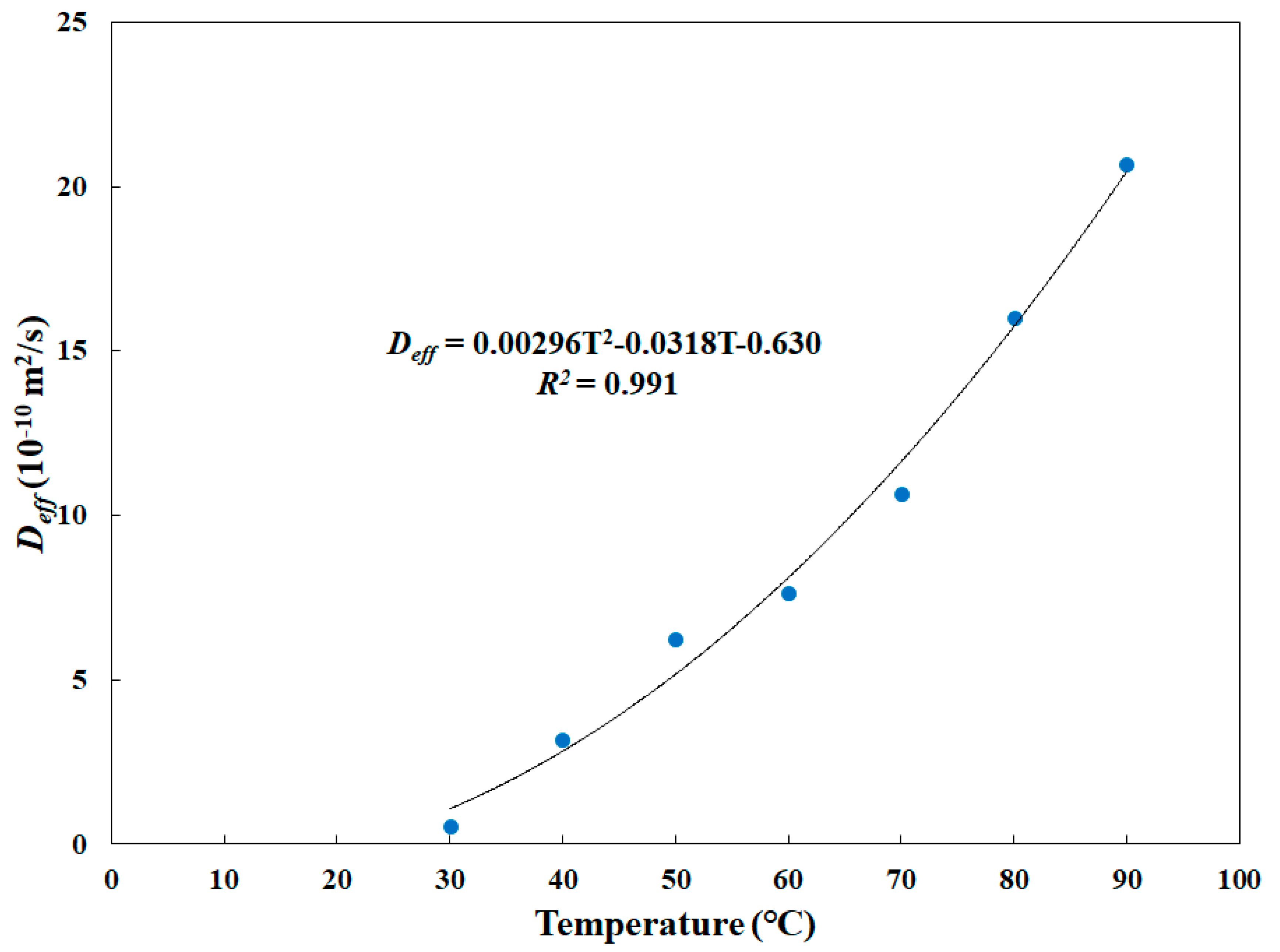
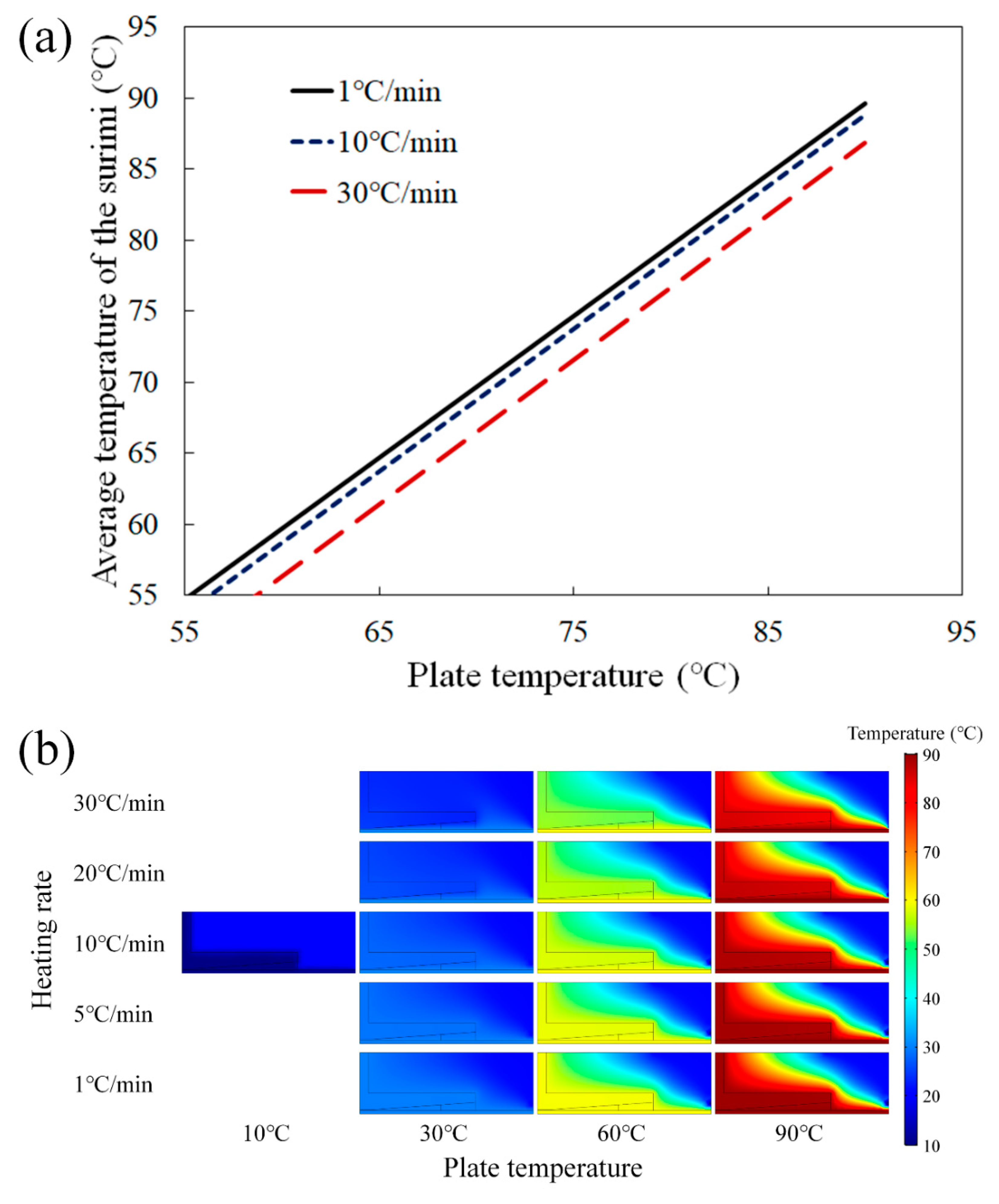
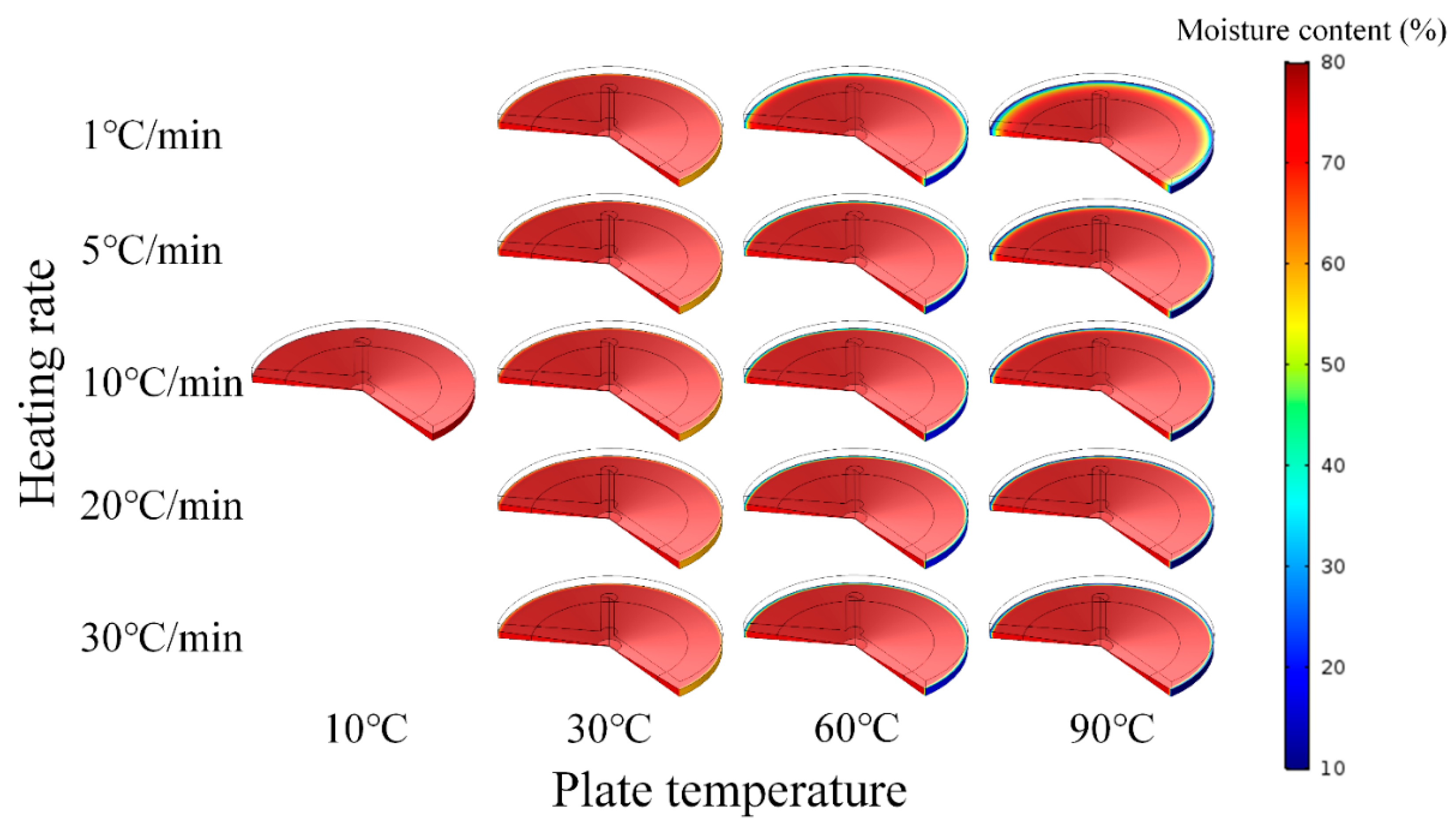
3.1. Mass Transfer Characteristics of Surimi Paste
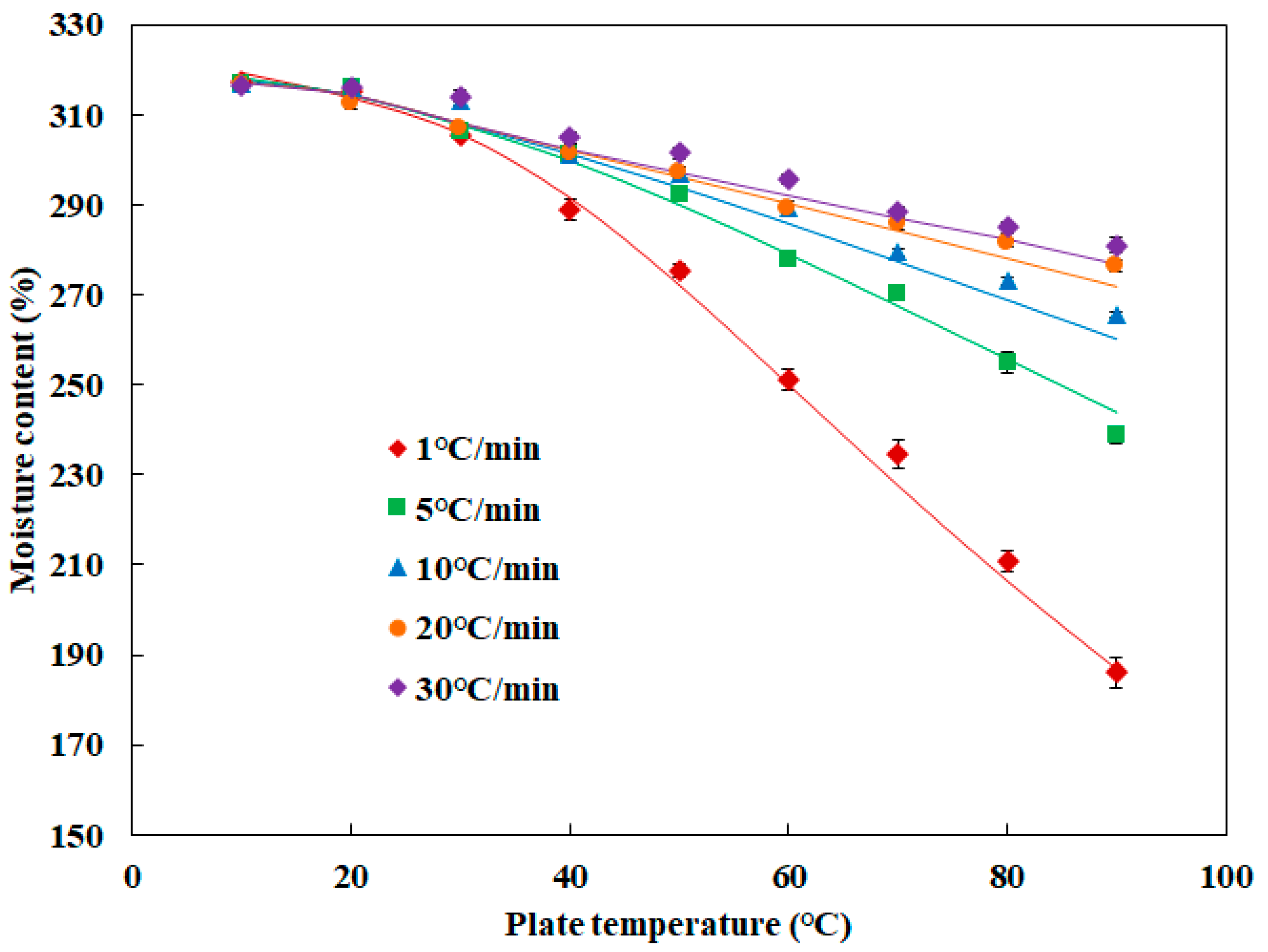
3.2. Changes in Moisture Content of Surimi during Heating and Validation of the Simulation Model
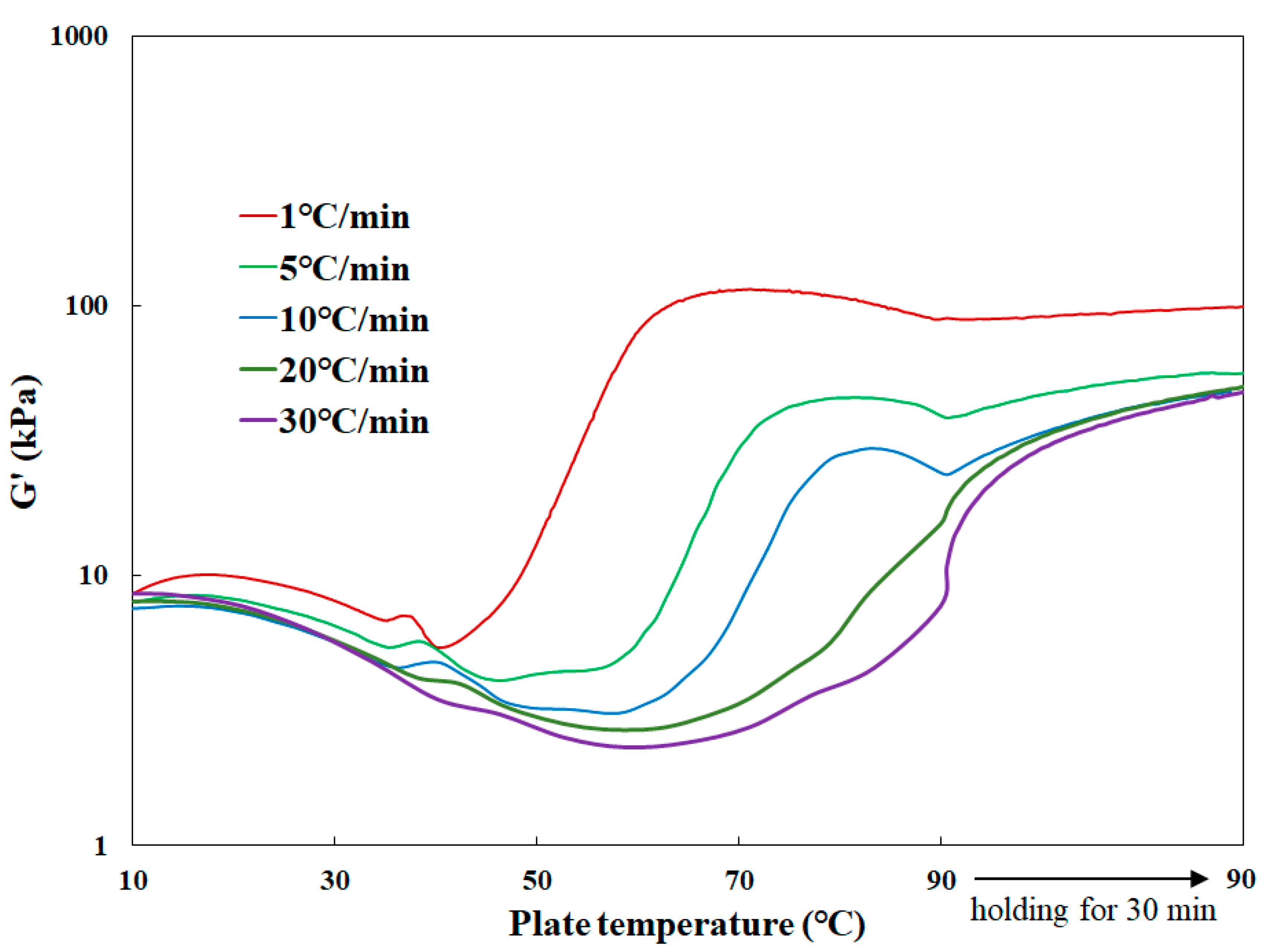
3.3. Effect of Heating Rate on Rheological Properties of Surimi
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Measuring ring tensile stress and strain of surimi gels using a novel ring tensile test with image analysis. J. Food Sci. 2015, 163, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, W.B. Rheology and texture properties of surimi gels. In Surimi and Surimi Seafood, 2nd ed.; Park, J.W., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 491–582. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mayer, S.G.; Park, J.W. Gelation properties of tilapia fish protein isolate and surimi pre- and post-rigor: Rigor condition of tilapia FPI and surimi. Food Biosci. 2017, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, H.; Zhu, S.; Xu, X.; Lyu, F.; Ding, Y. Textural, rheological and chemical properties of surimi nutritionally-enhanced with lecithin. LWT-Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 122, 108984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.B.; O’neill, E. Heat-induced gelation properties of surimi from mechanically separated chicken. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongsawatdigul, J.; Park, J.W. Thermal aggregation and dynamic rheological properties of Pacific whiting and cod myosins as affected by heating rate. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poowakanjana, S.; Park, J.W.; Moon, J.H.; Yoon, W.B. Assessing the dynamic rheology at various frequencies of surimi paste as affected by heating rates and moisture contents. J. Texture Stud. 2015, 46, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camou, J.P.; Sebranek, J.G.; Olson, D.G. Effect of heating rate and protein concentration on gel strength and water loss of muscle protein gels. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, A.M. Aggregation and denaturation involved in gel formation. In Functionality and Protein Structure; Pour-El, A., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; pp. 81–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.L.; Blanchard, S.P. Myofibrillar protein gelation: Viscoelastic changes related to heating procedures. J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditudompo, S.; Takhar, P.S.; Ganjyal, G.M.; Hanna, M.A. The effect of temperature and moisture on the mechanical properties of extruded cornstarch. J. Texture Stud. 2013, 44, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.C.; Muthukumarappan, K.; Metzger, L.E. Dynamic rheological properties of process cheese: Effect of Ca and P content, residual lactose, salt-to-moisture ratio and cheese temperature. Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.; Sun, D. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD)–An effective and efficient design and analysis tool for the food industry: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2006, 17, 600–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modelling and application for sterilization of foods: A review. Processes 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Development of a novel image analysis technique to detect the moisture diffusion of soybeans [Glycine max (L.)] during rehydration using a mass transfer simulation model. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2018, 11, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoo, J.S.; Jung, H.; Yoon, W.B. Developing a sterilization processing and a grading system to produce a uniform quality of sterilized whole corn (Zea mays L. var. ceratina). J. Food Eng. 2019, 249, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Prediction of the intermittent drying behavior of soybeans [Glycine max (L.)] using novel multilayered mass transfer simulation with image analysis. Dry. Techol. 2019, 37, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. A quantitative microbiological exposure assessment model for Bacillus cereus in pasteurized rice cakes using computational fluid dynamics and Monte Carlo simulation. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.W.; Yoon, W.B. Effects of air movement in a hot air dryer on the drying characteristics of colored potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Agric. Biologic. Eng. 2018, 11, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.M.; Dincer, I. Two-dimensional heat and moisture transfer analysis of a cylindrical moist object subjected to drying: A finite-difference approach. Int. J. Heat and Mass Trans. 2003, 46, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poowakanjana, S.; Park, J.W. Comminution process of surimi and surimi seafood paste. In Surimi and Surimi Seafood, 3rd ed.; Park, J.W., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.W.; Han, W.Y.; Yoon, W.B. Drying characteristics of soybean (Glycine max) using continuous drying and intermittent drying. Int. J. Food Eng. 2018, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Marinos-Kouris, D.; Maroulis, Z.B. Transfer properties in the drying of solids. In Handbook of Industrial Drying; Mujumdar, A.S., Ed.; Marcel Deker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 133–155. [Google Scholar]
- Incoperra, F.P.; De Witt, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 356. [Google Scholar]
- Supawang, S.; Park, J.W.; Thawornchinsombut, S. Fab blocking roles of fish proteins in fried fish cake. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; Lee, M.G.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, W.B. Developing an accurate heat transfer simulation model of Alaska pollock surimi paste by estimating the thermal diffusivities at various moisture and salt contents. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolka, J.; Nowak, A.J.; Rybarz, D. Improved 3-D temperature uniformity in a laboratory drying oven based on experimentally validated CFD computation. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blikra, M.J.; Skipnes, D.; Feyissa, A.H. Model for heat and mass transport during cooking of cod loin in a convection oven. Food Control 2019, 102, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Carballo, J.; Jiménez-colmenero, F. Heating rate effects on high-fat and low-fat frankfurters with a high content of added water. Meat Sci. 1997, 47, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leksrisompong, P.N.; Lanier, T.C.; Foegeding, E.A. Effects of heating rate and pH on fracture and water-holding properties of globular protein gels as explained by micro-phase separation. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, E60–E67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.A.R.; Garcia, R.G.; Archila, M.A.; Lagunes, A.G. Elaboration of surimi-based products from Lisa blanca (Mugil curema) with different thermal treatments: Heat transfer modeling to determine cooking time and thermophysical properties. J. Aquat. 2019, 28, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yongsawatdigul, J.; Park, J.W.; Thawornchinsombut, S. Characteristics off sarcoplasmic proteins and their interaction with myofibrillar proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2005, 29, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.B.; Gunasekaran, S.; Park, J.W. Characterization of thermorheological behavior of Alaska pollock and Pacific whiting surimi. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, W.B.; Park, J.W.; Kim, B.Y. Linear programming in blending various components in surimi seafood. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property | Air | Steel | Alaska Pollock Surimi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (ρ) (kg/m3) | Ideal-gas model | 7850 | 1466.63 − 2.93T − 4.24M * |
| Thermal Conductivity (kT) (W/m·K) | 7·× 10−5T + 0.0238 | 44.5 | 0.34 + 4.57·× 10−5T2 + 3.67·× 10−5M2 − 2.46·× 10−5TM * |
| Specific Heat (Cp) (J/kg·K) | 6·× 10−7T2 − 4·× 10−5T + 1 | 475 | 2166.09 + 8.71T + 13.93M * |
| Moisture diffusivity (10−10 m2/s) | −6.30·× 10−1 + 2.96·× 10−3T2 − 3.18·× 10−2M | ||
| Viscosity (μ) (Pa·s) | 4·× 10−8T + 2·× 10−5 | ||
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (β) (1/K) | 0.003325 | ||
| Source | Smolka et al. [28] | COMSOL 5.3 | * from Park et al. [27] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.W.; Park, J.W.; Yoon, W.B. Effect of Dehydration on the Rheological Measurement of Surimi Paste in Cone-Plate Rheometry: Heat and Mass Transfer Simulation. Processes 2020, 8, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020234
Park HW, Park JW, Yoon WB. Effect of Dehydration on the Rheological Measurement of Surimi Paste in Cone-Plate Rheometry: Heat and Mass Transfer Simulation. Processes. 2020; 8(2):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020234
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyeon Woo, Jae Won Park, and Won Byong Yoon. 2020. "Effect of Dehydration on the Rheological Measurement of Surimi Paste in Cone-Plate Rheometry: Heat and Mass Transfer Simulation" Processes 8, no. 2: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020234
APA StylePark, H. W., Park, J. W., & Yoon, W. B. (2020). Effect of Dehydration on the Rheological Measurement of Surimi Paste in Cone-Plate Rheometry: Heat and Mass Transfer Simulation. Processes, 8(2), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020234





