Abstract
Natural zeolites are easily found and abundant in Indonesia. The natural zeolites are low-cost minerals; however, their ammonium sorption is poor. A hydrothermal method was applied to improve the ammonium sorption. Hydrothermal treatment times were varied 8, 24, and 32 h. The parent and hydrothermal treated samples were characterized by using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopes (FE-SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and nitrogen physisorption. Ammonium adsorption was performed using a batch reactor to evaluate the adsorption performance of the prepared zeolite samples. The 8 h hydrothermal (HT 8 h) treated zeolites showed the highest ammonium removal percentage among others. The XRD analysis of HT 8 h shows a higher crystallinity of mordenite and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) model shows a surface area of 105 m2/g, much larger as compared to the parent with a surface area of 19 m2/g. Various kinetic and isotherms models were also studied on the parent and HT 8 h samples. The intraparticle equation showed the most accurate model for the kinetic data and the Freundlich equation showed the most accurate model for the isotherm of the experimental data. In terms of ammonium removal efficiency, hydrothermally treated Bayah mordenite compares favorably with treated mordenite from other locations despite that clinoptilolite provides higher removal capacities than mordenite.
Keywords:
mordenite; clinoptilolite; crystallinity; surface area; adsorption; ion-exchange; kinetic; isotherm; intraparticle; Freundlich 1. Introduction
Natural zeolites are available in massive amounts, inexpensive and spread out across the world. Indonesia has several occurrences of natural zeolite deposits, i.e., North Sumatera, Lampung, Banten, West Java, Central Java, East Java, Nusa Tenggara, and Sulawesi [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Clinoptilolite and mordenite are the common types of Indonesian natural zeolites. The mordenite dominant type is commonly found in Java deposits. One of the mordenite deposits in Java is located in Bayah, Banten Provence. Despite its low-cost materials and availability, the natural zeolites have some drawbacks such as containing some impurities, low crystallinity, and low surface area.
It is well-known that the natural zeolites have wide applications such as stone for home materials, as raw materials for pozzolan cement, as paper filler, adsorption of nuclear waste, for example, cesium and strontium, as soil improvements in agriculture, ammonium removal from wastewater and water, as heat exchangers in solar fridges, as food supplements for animals, as odor removal, clumping pet litters, and in ammonia adsorbent from animal manures [8]. The natural zeolites application for ammonium removal from water and wastewater is based on the ion-exchange properties. Zeolites have extra electrons on the aluminum ion, which has to be stabilized by cations, e.g., Na+, K+, H+, Ca2+, Mg2+, NH4+. The cations are exchangeable, which is an important property for ammonium (NH4+) removal.
Ammonium removal percentage can be increased through natural zeolite modification techniques such as ball milling, ion-exchange and base treatment. A smaller particle size of natural zeolites obtained by ball milling could improve ammonium sorption of the natural clinoptilolite [9]. Ion exchange modification performed by using sodium chloride successfully increases the adsorption of ammonium onto natural zeolites [10]. The order of ion exchange selectivity with ammonium is Na+ > Ca2+ > K+ > Mg2+. Modification of natural mordenite by using sodium hydroxide for ammonium removal showed an improvement of almost four times higher as compared to the parent [11].
The recrystallization method has been well documented for the zeolites in order to regain the crystallinity after ball milling. For instance, synthetic zeolite A could be ball milled into nanosize and recrystallized by a hydrothermal method to recover its crystallinity [12]. Nanoparticles derived from natural zeolites with mordenite dominant type was successfully fabricated by the ball milling and recrystallization method [13]. The hydrothermal method converted amorphous natural zeolites into crystalline phases, which increased conversion of n-butane into iso-butane [14]. The total number of acid sites of recrystallized samples was higher as compared with the parent. As a result, the n-butane conversion of the recrystallized sample was increased significantly. The hydrothermal method may be potentially applied to improve the ammonium sorption capacity of natural zeolites.
The aim of the research is to investigate the recrystallization of natural zeolites by a hydrothermal method and assess its application for ammonium removal. The effect of hydrothermal time on the natural zeolite properties and ammonium removal was studied. The kinetic and equilibrium parameters were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A natural zeolite tuff was obtained from a zeolite mining area located in Bayah, Banten Provence, Indonesia. The samples were crushed and sieved to obtain particle sizes of −60 + 80 mesh. The powdered zeolites as-received sample was labeled as ‘parent’.
A weight of 1.47 g NaOH (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was dissolved in 45 mL distilled water, after that 3.47 g fumed silica (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added into the basic solution. The mixture was thoroughly stirred at 500 rpm until homogeneous. A total of 1.5 g of the sieved parent sample was introduced into the mixture. A PTFE-lined autoclave was used to perform the hydrothermal recrystallization. The temperature was maintained at 170 °C for 8 h (HT 8 h), 24 h (HT 24 h), and 32 h (HT 32 h). The hydrothermally treated zeolites were then washed using distilled water several times until a neutral value of pH reached. The slurry was sat at ambient temperature for 24 h. Finally, the samples were heated in an oven for 6 h at 110 °C.
2.2. Characterization
The natural zeolites were analyzed by Cu-Kα X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) (Shimadzu 7000, (Shimadzu Corporation Kyoto, Japan) to study the crystallinity of natural zeolites. The scanning range was 10–55° with sampling pitch 0.02° and scan speed 2°/min. An FE-SEM SU5000 scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM SU5000, Hitachi, Chiyoda City, Tokyo Japan) was used to study crystal morphology. A Quantachrome (Autosorb-iQ, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA) was used to analyze the natural zeolites textural properties. Samples were degassed at 300 °C for 6 h. A liquid nitrogen bath was used during the adsorption and the desorption of nitrogen. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) (ASAP 2020, Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) was used to calculate the surface area of natural zeolites. An IR Tracer 100 (Shimadzu Corporation Kyoto, Japan) was used to obtain FTIR infrared emission spectra of samples. The resolution was 4 cm−1 with scans range from 400 to 4000 cm−1.
2.3. Adsorption Test
Adsorption tests of mordenite were performed using synthetic ammonium solution: (1) 5 g of zeolites were added to 100 mg/L ammonium solution, and the effects of adsorption time on the ammonium cation removal were observed every 20 min, (2) 0.5–10 g of zeolites were introduced to the 50 mL of 100 ppm ammonium and the adsorptions process were kept for 3 days prior to analyzing the remained ammonium in the solution. The colorimetric method was performed to analyze the NH4+ amount in the synthetic ammonium solution.
2.4. Kinetic Model
For the kinetic study of Bayah zeolites, data were analyzed using four kinetic models of Lagergren’s first order, second order, Elovich, and intraparticle diffusion. Those equations are described as the following:
The model of Lagergren’s first order is presented in Equation (1):
where represents mass of ammonium adsorbed at equilibrium per gram of zeolites (mg/g), (mg/g) is mass of ammonium adsorbed at time te per gram of zeolites, while the rate constant parameter of Lagergren’s equation is indicated by (L/mg). Equation (1) could be rewritten into Equation (2), a non-linear equation obtained by using a simple calculus technique with initial conditions at t = 0, qt = 0 and at t = t, qt = qt.
The model of the second order is presented in Equation (3):
where is the constant rate of the pseudo 2nd order equation. Separation of each variables using initial condition at t = 0, qt = 0 and at t = t, qt = qt could solve the differential equation into the non-linear equation as follows:
Equation (5) shows the Elovich model of kinetic adsorption.
where and are the Elovich’s parameters of kinetic. The non-linear equation of the Elovich’s model can be obtained by separating the variable method with the initial condition at t = 0, qt = 0 and at t = t, qt = qt, resulting in Equation (6):
While the intraparticle diffusion model is showed in Equation (7):
where is the constant rate parameter of intraparticle model and C is the intercept.
2.5. Isotherm Model
An isotherm study was conducted using four models of isotherm equation, i.e., Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin. The Langmuir isotherm model is stated as in Equation (8):
where is defined as the maximum capacity (mg/g) of Langmuir monolayer adsorption, while is the parameter for the Langmuir equilibrium model.
The Langmuir–Vagelar model is described as in Equation (9):
where , is ammonium solution volume (L), is the initial concentration of ammonium in the solution (mg/L), with as the Langmuir–Vageler constant.
Isotherm equation of Freundlich is provided by Equation (10):
where is the Freundlich’s capacity factor.
The Temkin’s isotherm equation is described in Equation (11):
where B describes the parameter of heat adsorption and is the constant of an equilibrium binding.
A non-linear least squared (NLLS) analysis was chosen over the linearization method, to fit models with the experimental data, which is believed to be more accurate [15]. The sum of squared error (SSE) in Equation (12) was used for the error analysis method:
where is the mass of NH4+ adsorbed at equilibrium per gram of zeolite mass determined by the model (mg/g).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
Figure 1 describes the impact of hydrothermal treatment time on the resulting zeolite crystallinity. The parent XRD pattern shows that the Bayah natural zeolite phases are mordenite (card no: 000110155), clinoptilolite (card no: 010791462), and quartz (card no: 010773162). The hydrothermal treated samples exhibited relatively higher crystallinity of mordenite peaks than the parent natural zeolites as shown by higher peak intensities of the XRD patterns. For example, the mordenite peak intensities at 2θ 13.5°, 25.8°, 26.8°, and 27.7° of the hydrothermal treated samples are higher than the parent. As a phase competitor, quartz was pronounced after 24 h hydrothermal reaction as indicated at 2θ 20.9°, 26.6°, 39.5°, 50.2°. The hydrothermally treated of the Bayah natural zeolites for 24 h showed the highest peak of quartz crystalline phase at 26.6°. This is in agreement with our previous work for the hydrothermal treatment using Klaten natural zeolites, which showed high peaks of quartz crystalline phase after 26 h hydrothermal treatment [14]. The longer hydrothermal reaction seems to increase conversion of the initial mordenite phase into other zeolite phases. Zeolite phase conversion into other zeolite phases via the hydrothermal method depends on time, temperature, and NaOH concentration, as reported elsewhere [16,17].
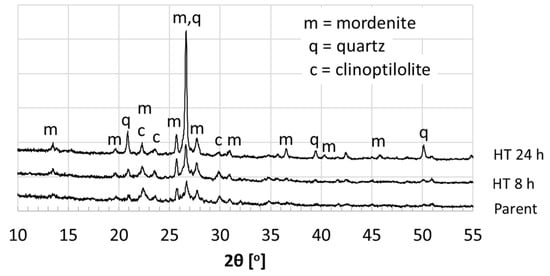
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of parent and hydrothermal treated natural mordenite.
The effects of hydrothermal reaction time on FTIR spectra are presented in Figure 2. The Al−O fragment is indicated by the vibrational bands at 780−820 cm−1. The asymmetric stretch mode of SiO4 and AlO4 are the main vibrational bands, which are shown at wavelengths of about 960−1250 cm−1. A peak pointed at the wavenumber 1081 cm−1 can be associated to Si–O–Si asymmetric stretching vibration, which is indicative of the peak of quartz [18]. The vibration of HOH is shown at the wavelength of about 1560−1690 cm−1. This agrees with the XRD patterns of the HT 24 h showing the quartz crystalline pattern.
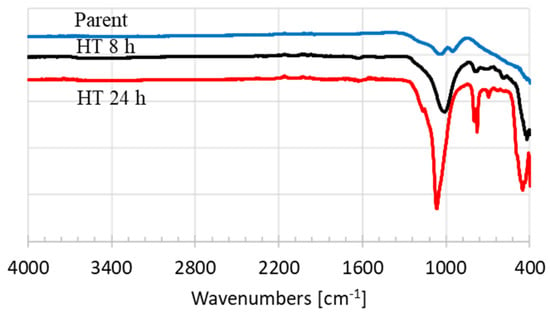
Figure 2.
Diffraction patterns of parent and hydrothermal treated natural zeolites.
The nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherms of the parent and the hydrothermally treated natural zeolites are shown in Figure 3. It shows that the hydrothermal treatment time positively affects the nitrogen uptake of natural zeolites. It can be ascribed from the formation of new mordenite crystals for the period of the hydrothermal recrystallization that increased the uptake of nitrogen on the sample HT 8 h. The fast growth of the quartz crystalline phase after hydrothermal treatment for 24 h reduced the nitrogen uptake on the HT 24 h sample.
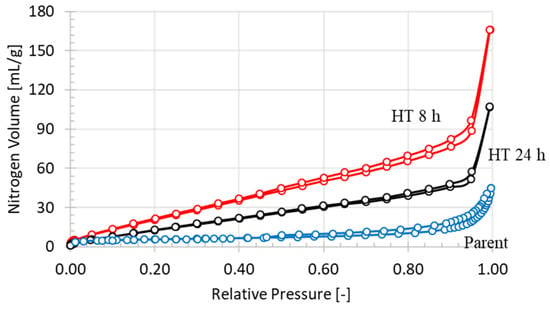
Figure 3.
Nitrogen isotherms of parent and hydrothermal treated natural mordenite.
The BET results show that the total surface area increased remarkably thanks to the hydrothermal treatment. The surface area of the parent was only 19 m2/g, while the 8 h hydrothermal treatment sample was 105 m2/g (Table 1). However, the surface area decreases after 24 h hydrothermal treatment to 65 m2/g. It is most likely because more quartz crystalline phase was formed, which has no porosity, hence reducing the total surface area of the sample HT 24 h. The total pore volume was also increased from 0.06 mL/g before hydrothermal treatment to 0.23 mL/g after the 8 h hydrothermal treatment. Likewise, the surface area of HT 24 h was smaller than the H 8 h. The textural properties of the three samples suggested that the 8 h hydrothermal would offer the highest ammonium uptake as the nitrogen uptake in nitrogen adsorption–desorption analysis.

Table 1.
Textural properties of parent and hydrothermal treatment of natural zeolites.
The SEM micro-images of the parent Bayah natural zeolites, the HT 8 h and the HT 24 h are shown in Figure 4. The parent natural mordenite has a typical needle-like morphology. The clinoptilolite displays tabular morphology and the quartz crystal tip is like a pyramid [19]. The parent shows small size needles shapes (Figure 4a top). The parent Bayah natural zeolites also showed a pyramid tip shape, which is most likely the typical shape of the quartz or clinoptilolite (Figure 4a bottom). Figure 4b suggests that the mordenite crystal was observed as pointed by the more needle-like shape (arrowed) that appeared after hydrothermal treatment for 8 h. The needles were even longer after 24 h hydrothermal treatment, which suggests the growth of mordenite crystal. The quartz phase was also observed as circled in Figure 4c. The crystal of mordenite and quartz growth confirmed the diffraction patterns, which show the rise of mordenite and quartz peak intensities when the hydrothermal time increases.
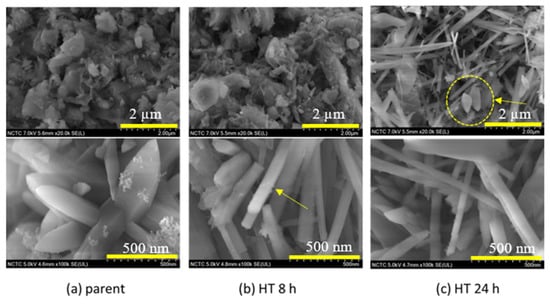
Figure 4.
SEM microimages of: (a) the Bayah parent, (b) the hydrothermal (HT) 8h and (c) HT 24 h samples.
3.2. Ammonium Removal
The effect of hydrothermal time of the zeolites on the ammonium removal is presented in Figure 5. It shows that after the 8 h hydrothermal treatment the percentage of ammonium removal increases from an initial 48.9% to 62.6%. However, it starts to decrease after 24 h, with ammonium removal at 56.5%. After 32 h the ammonium removal is lesser than the parent with ammonium removal of only 40.7%. The high percentages of ammonium removal at sample HT 24 h and HT 32 h are most likely because of the quartz phase competing with the mordenite growth. The quartz has no capacity for ammonium sorption, hence the percentage of ammonium becomes lower with longer hydrothermal treatment time. The transformation of the zeolite phases from mordenite and clinoptilolite to phillipsite during the hydrothermal treatment occurs within 1–7 days [16,17]. High concentration of NaOH tends to shorten the phase conversion time. Watanabe et al. [17] reported that natural mordenite was successfully converted into zeolite phillipsite after 7 days under hydrothermal treatment. The ammonium removal increased from 32% to 64%.
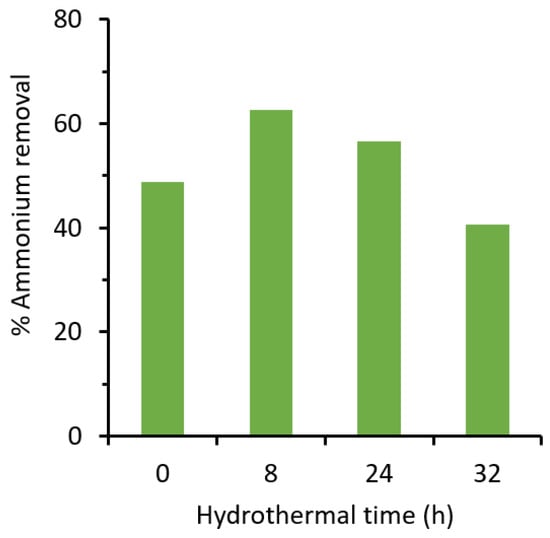
Figure 5.
The effect of hydrothermal time on ammonium removal.
Table 2 displays comparison between the Bayah natural zeolites before and after modification with data from the literature. Ammonium removal of the parent Bayah natural zeolites is relatively higher than the other reported natural zeolites and the adsoption is typical of the chemical adsorption ascribed from the Elovich model fitting [20]. For example, percent ammonium removals of natural zeolites from Ponorogo, Shimane, Lingshou were only 30%, 32%, and 41.8%, respectively [11,21,22]. After the Ponorogo zeolites were treated with 6 M sodium hydroxide, the percentage of ammonium removal increased to 80%. The sodium ion-exchanged Ponorogo zeolites give a higher ammonium removal than the hydrothermal treated Bayah zeolites because the Na+ is easier to exchange with the NH4+. Clinoptilolite from Lingshou, China, impregnated with NaNO3 followed by calcination improve ammonium removal because of enhancement in mesoporosity and ion-exchange capacity. The ammonium removal is improved due to oxygen release, nitrate decomposition and sodium ion-exchange. In general, the ammonium uptake is contributed by the adsorption and ion-exchange mechanism. Some other zeolite occurrences show a higher percentage of ammonium removal events without modification such as zeolites from Bulgaria and Iran [22,23]. The capacity of ammonium uptake depends on the type of zeolites, crystallinity of zeolites, ratio of Si to Al and ratio Na2O to SiO2 [11,21,24]. The synthetic NaY zeolite reported 70% of ammonium removal, which shows that the natural zeolites could have a better performance than the synthetic one [24].

Table 2.
Comparison of hydrotreated Bayah natural zeolites with other zeolites.
3.3. Kinetic Model
The experimental data and four kinetic models, i.e., 1st order, 2nd order, intraparticle and Elovich, are presented in Figure 6 for ammonium adsorption on the Bayah natural zeolites parent and the HT 8 h samples. The most appropriate equation according to criteria of sum of squared error (SSE) for the parent was the 2nd order model, with SSE 1.4 × 10−4 as presented in Table 3. On the other hand, the most appropriate model for ammonium adsorption using the HT 8 h sample was the intraparticle model. The Elovich model was also fitted with the sorption data for the parent and the HT 8 h samples with SSE 3.67 × 10−4 and 4.3 × 10−4, respectively. The Elovich model was originally developed dominantly for the adsorption chemical process; for example, it was fitted with the experimental data of chemical adsorption of reactive dye on chitosan [20]. The Elovich model was applied to the parent and HT 8 h and the results suggested that the adsorption of NH4+ on the parent and the hydrothermal treated zeolite is typical of the chemical adsorption.
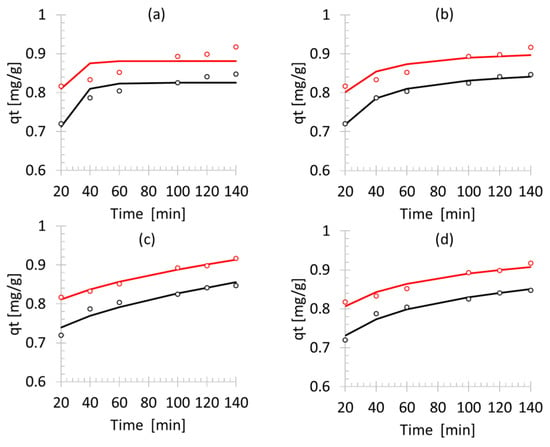
Figure 6.
Non-linear least squared (NLSS) fitted kinetic model: (a) first order, (b) second order, (c) intraparticle, (d) Elovich model.

Table 3.
Kinetic parameters of ammonium adsorption.
3.4. Isotherm Model
For the purposes of isotherms study, only the HT 8 h sample was evaluated. The experimental data fitted to the equilibrium isotherm, namely the Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin models are shown in Figure 7. The Langmuir and Freundlich model show the lowest error among others, with the SSE of 0.29 and 0.28, respectively (Table 4). Several assumptions for the Langmuir model are the surface is considered as uniform, adsorption on the surface only one layer thick, and molecular interaction is zero.
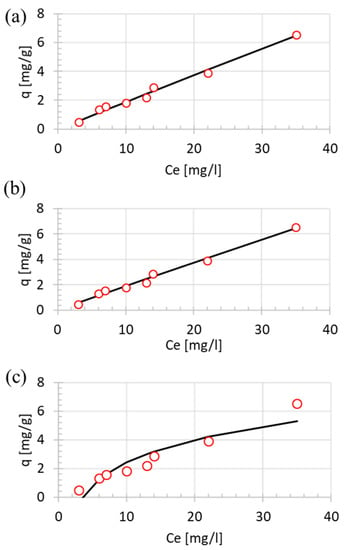
Figure 7.
NLLS fitted isotherm models of (a) Langmuir, (b) Freundlich, and (c) Temkin.

Table 4.
Isotherm parameters for ammonium adsorption on HT 8 h sample.
4. Conclusions
The hydrothermal method applied to the Bayah natural zeolites successfully increased the ammonium removal capacity. The sample with hydrothermal time of 8 h shows the highest ammonium removal percentage. Longer periods of hydrothermal reaction are not recommended because of the excessive growth of the quartz crystalline phase. The XRD and BET analyses of the HT 8 h sample shows a higher crystallinity of mordenite with high surface area. Various kinetic and isotherm models have been studied for the parent and HT 8 h samples. The intraparticle equation shows the most accurate model for the kinetic data and the Freundlich equation shows the most accurate model for the isotherm experimental data. In terms of ammonium removal efficiency, hydrothermally treated Bayah mordenite shows advantages over other treated mordenite from other locations worldwide, suggesting its potential for full scale application.
Author Contributions
T.K. conceived the research idea and prepared the manuscript draft; S.B., A.D., N.D.M. and N.N. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; K.F. and S.T. performed samples characterization and validation of the results; M.R.B. and N.H. reviewed and updated the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by DIKTI under project no. B/03/UN43.9/PT.00.03/2020: Penelitian Desentralisasi, Penelitian Dasar Unggulan Perguruan Tinggi titled “Valorisasi Limbah Gliserol Melalui Reaksi Ketalisasi Menggunakan Katalis Heterogen Zeolit” Tahun 1 Anggaran 2020. The Article Processing Charge was supported by Universiti Malaysia Sabah.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gultom, F.; Wirjosentono, B.; Nainggolan, H. Preparation and characterization of North Sumatera natural zeolite polyurethane nanocomposite foams for light-weight engineering materials. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, T.; Kadja, G.; Radiman, C.; Darwis, D.; Mukti, R. Two-step preparation of amidoxime-functionalized natural zeolites hybrids for the removal of Pb2+ ions in aqueous environment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djubaedah; Wulandari, D.A.; Nasruddin, N. Preliminary study of natural zeolite from Bayah for solar powered cooling application. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 105, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumantri, I.; Buchori, L.; Mukti, F.A.W.; Ramadhani, F.; Anggoro, D.D. (Eds.) Study of the rate of adsorption of toxic gases in shrimp ponds using Sukabumi natural zeolite, AIP Publishing LLC. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2197, 120005. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetya, A.; Prihutami, P.; Warisaura, A.D.; Fahrurrozi, M.; Petrus, H.T.B.M. Characteristic of Hg removal using zeolite adsorption and Echinodorus palaefolius phytoremediation in subsurface flow constructed wetland (SSF-CW) model. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, R.I.; Hadinoto, J.P.; Ayucitra, A.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Ismadji, S. Natural zeolite from Pacitan Indonesia, as catalyst support for transesterification of palm oil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 74, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalia, S.S.; Wilhelmus, L.H.; Nunuk, H.S.; Paulina, T. (Eds.) Study of the Use of Mamasa Natural Zeolite which is Activated by Acid as a Catalyst for Cracking Palm Oil Methyl Esters. Mater. Sci. Forum Trans. Tech. Publ. 2019, 967, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpton, F.A. La roca magica: Uses of natural zeolites in agriculture and industry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.K.; Hayashi, S. Modification on natural clinoptilolite zeolite for its NH4+ retention capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.; Lee, D.J.; Tay, J.H. Adsorption mechanisms of high-levels of ammonium onto natural and NaCl-modified zeolites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetardji, J.P.; Claudia, J.C.; Ju, Y.-H.; Hriljac, J.A.; Chen, T.-Y.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Santoso, S.P.; Kurniawan, A.; Ismadji, S. Ammonia removal from water using sodium hydroxide modified zeolite mordenite. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83689–83699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakihara, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Tatami, J.; Endo, A.; Yoshida, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Komeya, K.; Meguro, T. Bead-Milling and Postmilling Recrystallization: An Organic Template-free Methodology for the Production of Nano-zeolites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.; Muraza, O.; Hakeem, A.S.; Al-Amer, A.M. Mechanochemical route and recrystallization strategy to fabricate mordenite nanoparticles from natural zeolites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.; Muraza, O.; Bakare, I.A.; Sanhoob, M.A.; Al-Amer, A.M. Isomerization of n-butane over cost-effective mordenite catalysts fabricated via recrystallization of natural zeolites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; Winnett, A.; Thompson, T.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Equilibrium studies of ammonium exchange with Australian natural zeolites. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Egashira, K. Modification of different grades of Korean natural zeolites for increasing cation exchange capacity. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, H.; Tanaka, J.; Moriyoshi, Y. Hydrothermal modification of natural zeolites to improve uptake of ammonium ions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-M.; Yin, W.-Z.; Wang, Y.-F.; Sun, C.-Y.; Ma, Y.-Q.; Liu, J. Effect and mechanism of siderite on reverse anionic flotation of quartz from hematite. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, M.; Miyata, T.; Sunagawa, I. Growth and morphology of quartz crystals synthesized above the transition temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 1995, 152, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-C.; Tseng, R.-L.; Juang, R.-S. Characteristics of Elovich equation used for the analysis of adsorption kinetics in dye-chitosan systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ding, T.; Xu, L.; Lee, S.S. Ammonium removal using a calcined natural zeolite modified with sodium nitrate. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 393, 122481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotoulas, A.; Agathou, D.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Tatoulis, T.I.; Akratos, C.S.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Zeolite as a Potential Medium for Ammonium Recovery and Second Cheese Whey Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by natural Iranian zeolite in the presence of organic acids, cations and anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Gong, H.; Fang, K.; Peng, F.; Wang, K. Revealing the effect of preparation parameters on zeolite adsorption performance for low and medium concentrations of ammonium. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).