Continuous Fixed Bed CO2 Adsorption: Breakthrough, Column Efficiency, Mass Transfer Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
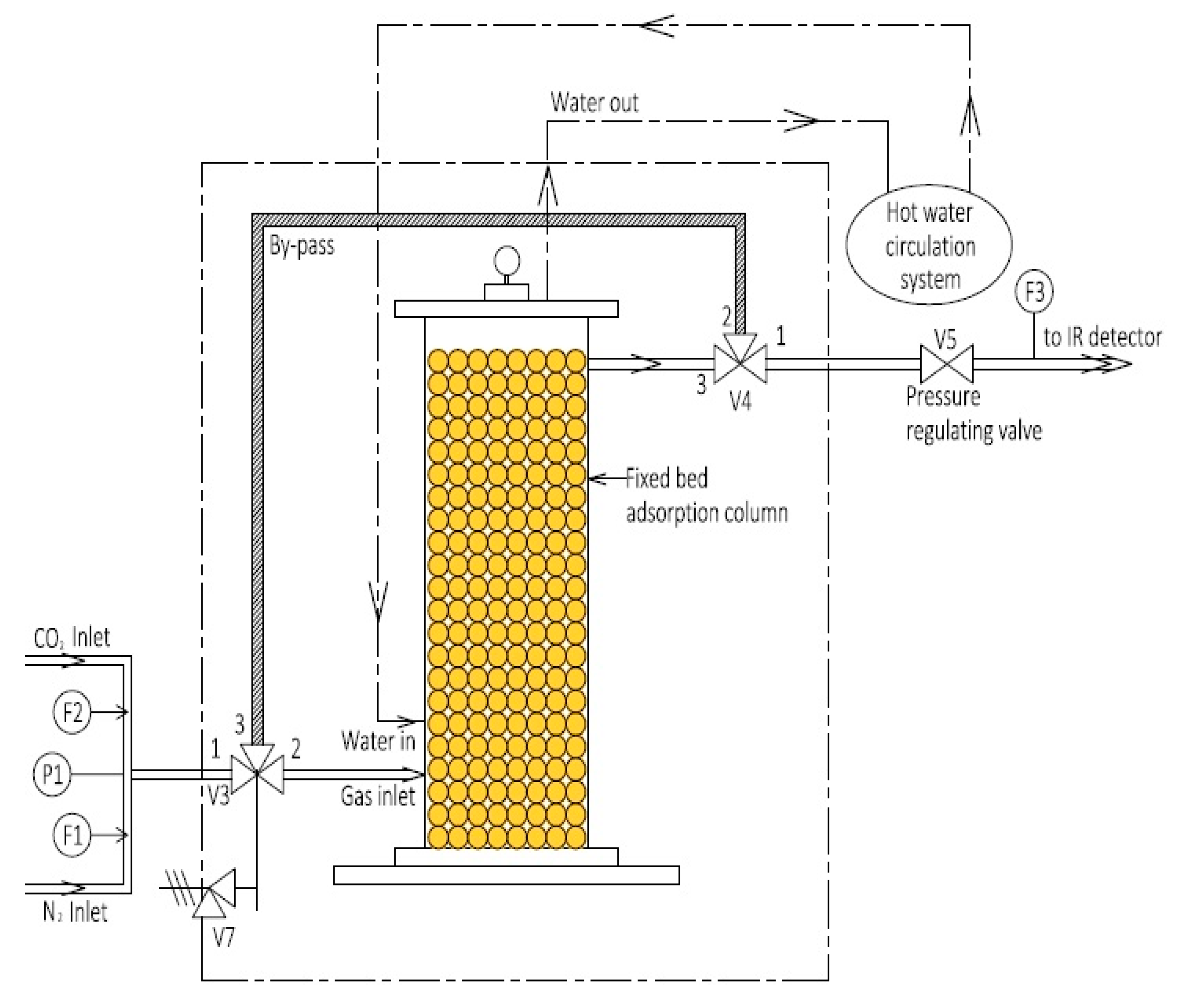
2.2. Setup
2.3. Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
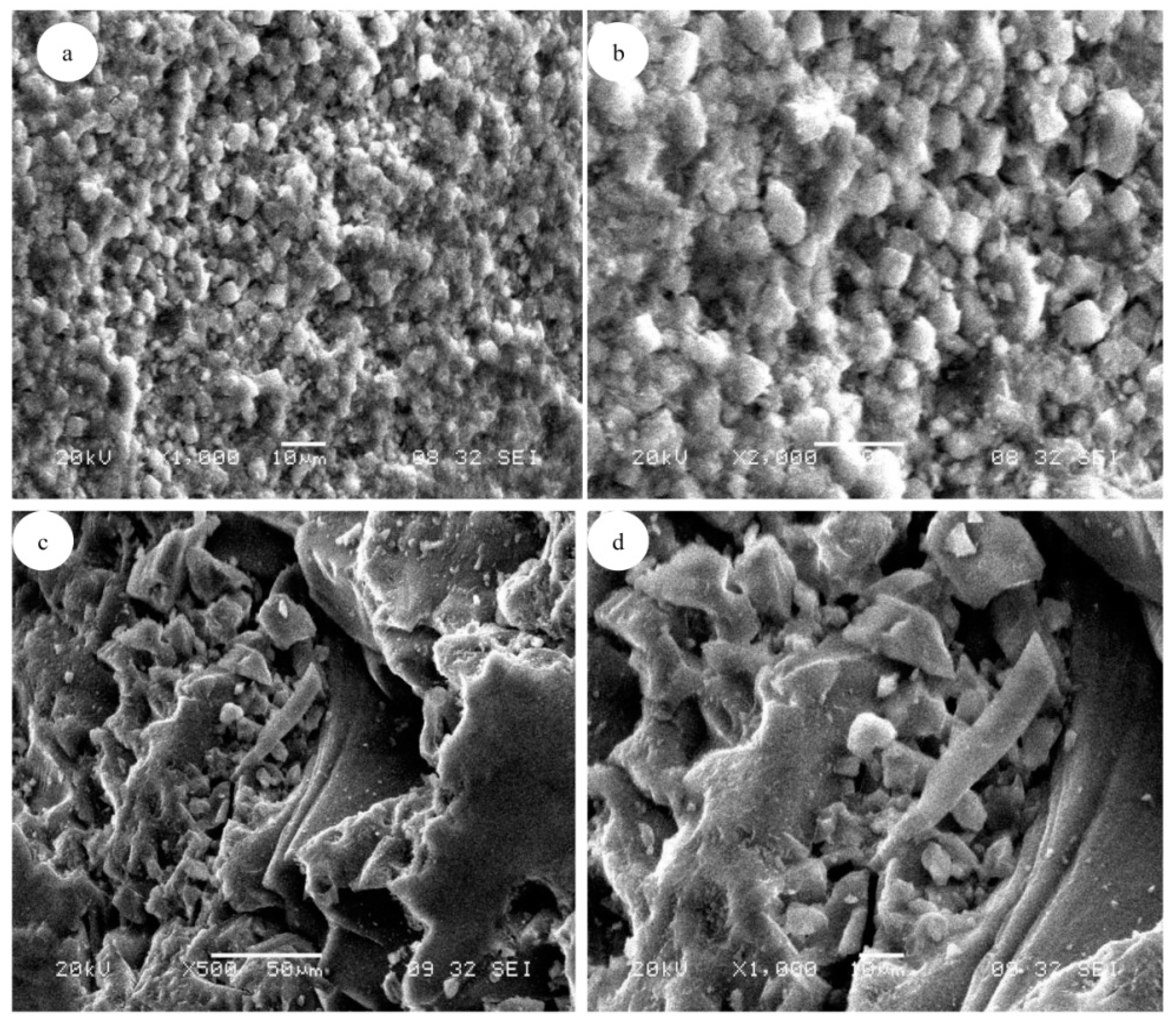
3.1. Adsorbent Characterizations
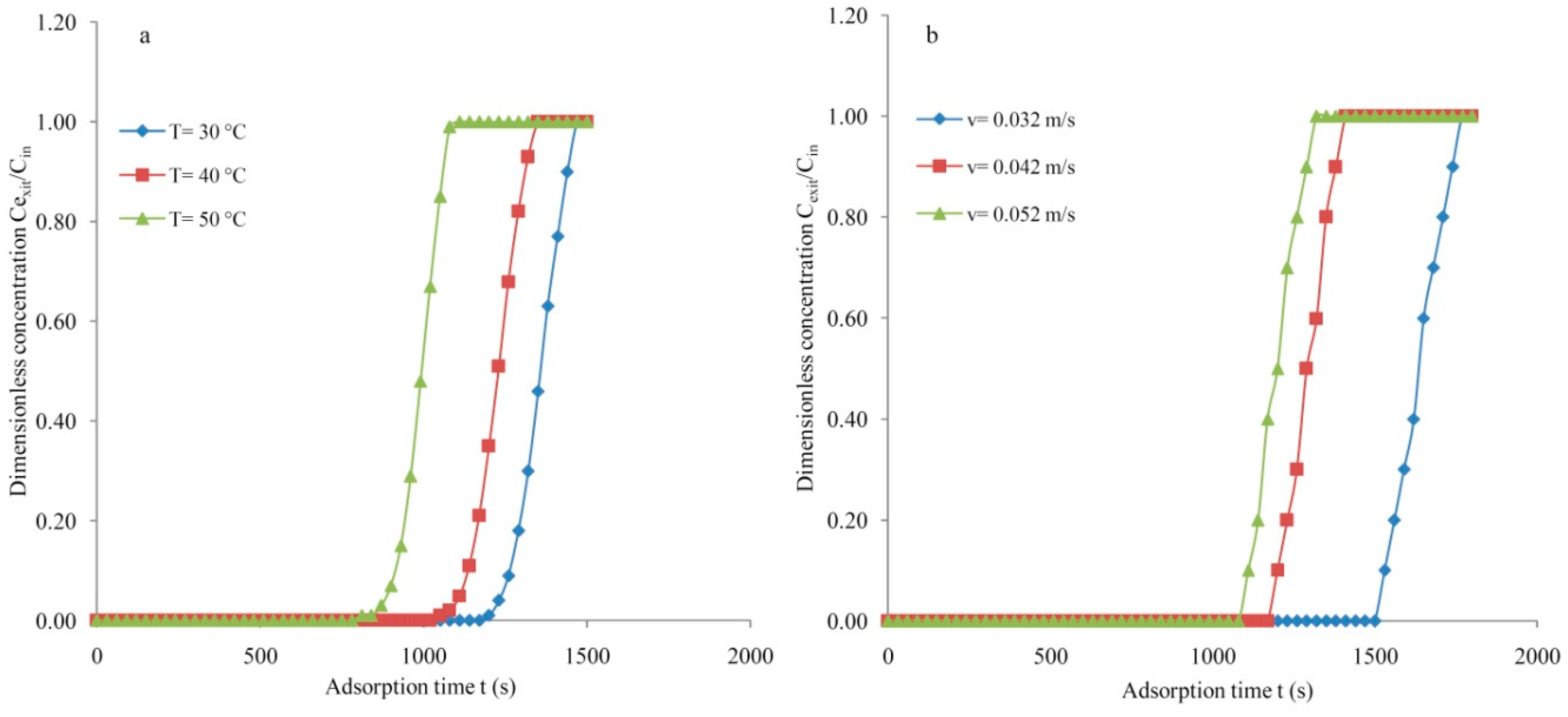
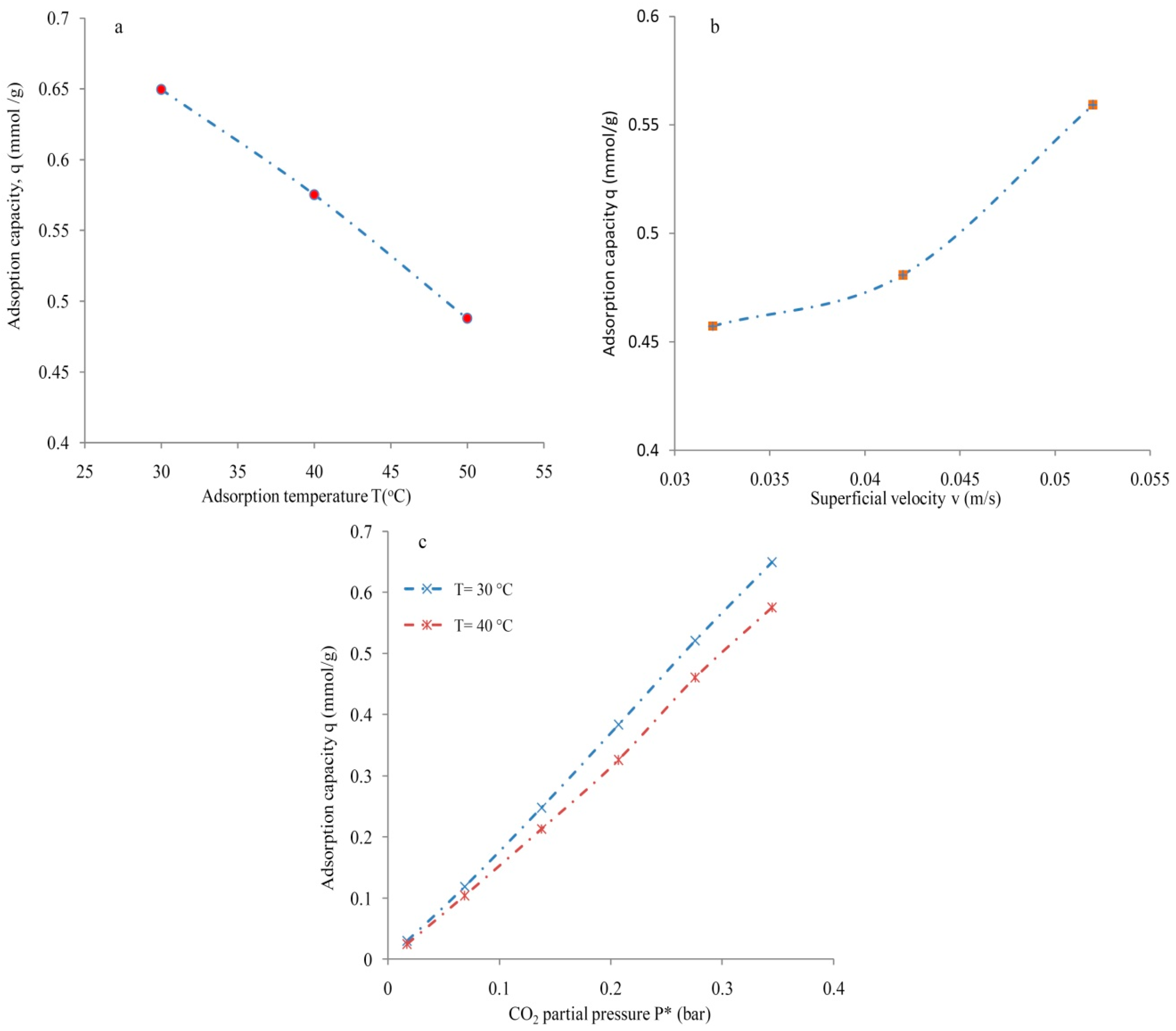
3.2. Molecular Sieve
3.3. Silica Gel Type-III
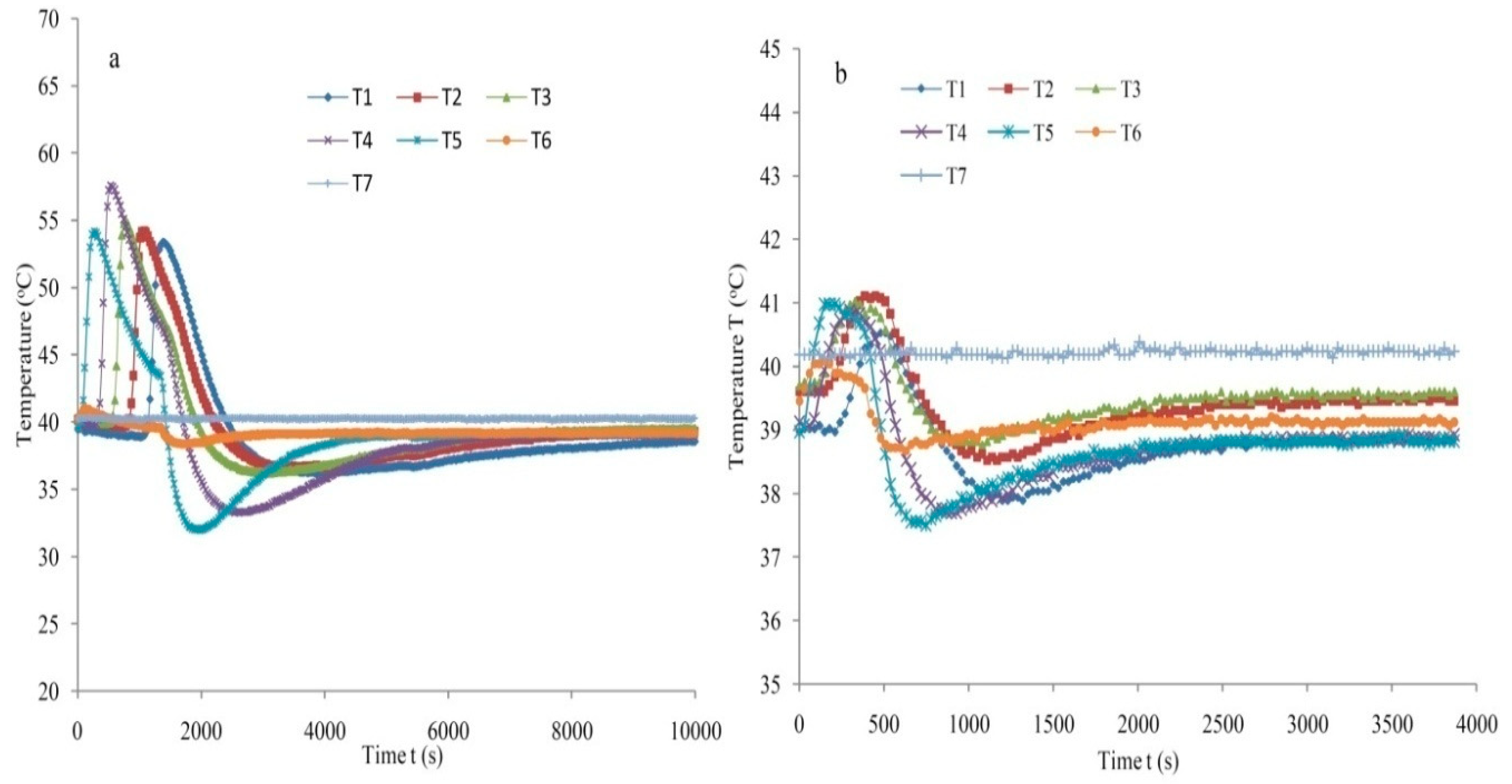
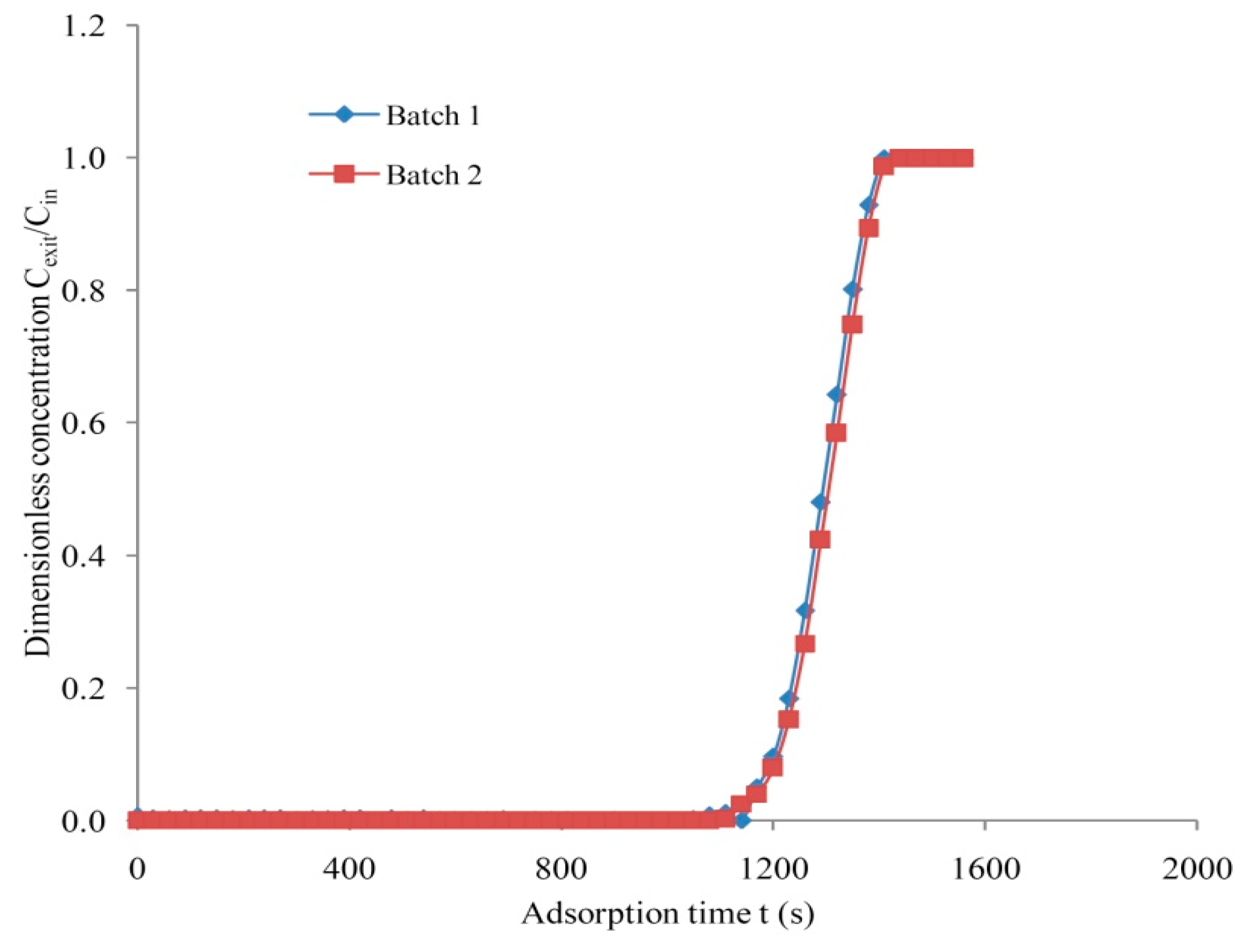
3.4. Repeatability and Accuracy Measurement
3.5. Mass Transfer Zone and Column Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figueroa, J.D.; Fout, T.; Plasynski, S.; Mcllvried, H.; Srivastava, R.D. Advances in CO2 capture technology—The US Department of Energy’s Carbon Sequestration Program. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lio, X.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon molecular sieve and its adsorption capacity for H2, N2, O2, CH4, and CO2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 413, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.T.; Chen, C.Y. Carbon dioxide recovery by vacuum swing adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 39, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.; Hessami, M.-A. A study of methods of carbon dioxide capture and sequestration-the sustainability of photosynthesis bioreactor approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.; Walker, G.M.; Allen, S.J. Investigation on the adsorption of acidic gases using activated dolomite. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 117, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitakamol, B.; Veawab, A.; Aroonwilas, A. Environmental impacts of absorption-based CO2 capture unit for post-combustion treatment of flue gas from goal fired-fired power plant. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2007, 1, 318–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabadi, A.; Razzaque, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tan, B. Highly porous activated carbon materials from carbonized biomass with high CO2 capturing capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbins, J.; Chalmers, H. Carbon capture and storage. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 4317–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomen, E.; Hendriksa, C.; Neele, F. Capture technologies: Improvement and promising developments. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Seo, J.B.; Jang, S.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Oh, K.J. Removal characteristics of CO2 using aqueous MEA/AMP solutions in the absorption and regeneration process. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Scura, F.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E. Membrane technologies for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 359, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liang, F.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, W. In improved CO2 separation and purification system based on cryogenic separation and distillation theory. Energies 2014, 7, 3484–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Goel, C.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K. Novel nanostructured carbons derived from epoxy resin and their adsorption characteristics for CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97728–97738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide capture and separation: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, A. An overview of carbon dioxide mitigation options for global warming emphasizing carbon dioxide sequestration options. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2003, 36, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDowell, N.; Florin, N.; Buchard, A.; Hallett, J.; Galindo, A.; Jackson, G.; Adjamin, C.; Williams, C.K.; Shah, N.; Fennel, P. An overview of carbon dioxide captures technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M.; Chalmers, H.L.; Webber, M.E.; King, C.W. Comparing post-combustion carbon dioxide capture operation at retrofitted coal-fired power in the Texas and Great Britain electric grids. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chang, L.; Xie, K. Adsorption of carbon dioxide on activated carbon. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2006, 15, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, S.; Gil, M.V.; Martin, C.F.; Pis, J.J.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C. Breakthrough adsorption study of a commercial activated carbon for pre-combustion carbon dioxide capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spin, M.J. Improving the gas solids contact efficiency in a fluidized bed of carbon dioxide adsorbent fine particles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4906–4909. [Google Scholar]
- Ammendola, P.; Raganati, F.; Chrone, R.; Miccio, F. Fixed bed adsorption affected by thermodynamics and kinetics: Yellow tuff for CO2 capture. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, B.; Gayatri, D.V.; Sreedhar, I.; Raghvan, K.V. A journey into the process and engineering aspects of carbon capture technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1324–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Y.; McCarthy, M.; Sculley, J.; Yu, J.; Jeong, H.; Balbuen, P.; Zhou, H. Carbon-dioxide-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1791–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, V.; Pupier, O.; Guillot, A. Carbon dioxide-methane mixture adsorption on activated carbon. Adsorption 2006, 12, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mesfer, M.K. Synthesis and characterization of high-performance activated carbon from walnut shell biomass for CO2 capture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15020–15028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Munoz, E.M.; Garcia-Mateos, F.J.; Rosas, J.M.; Rodrigues-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. Biomass waste carbon materials as adsorbents for CO2 capture under post-combustion conditions. Front. Mater. 2016, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Alfe, M.; Gargiulo, V.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Kinetic study and breakthrough analysis of the hybrid physical/chemical CO2 adsorption/desorption behavior of magnetite-based sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, A.; Kopac, T. Carbon dioxide adsorption using high surface area activated carbons from local coals modified by KOH, NaOH and ZnCl2 agents. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yu, J.; Li, P.; Grande, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E. Capture of CO2 from flue gas by vacuum pressure swing adsorption using activated carbon beads. Adsorption 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mesfer, M.K.; Danish, M.; Fahmy, M.Y.; Rashid, M.M. Post combustion CO2 capture with activated carbons using fixed bed adsorption. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 54, 2715–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mesfer, M.K.; Danish, M. Breakthrough adsorption study of activated carbons for CO2 separation from flue gas. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4514–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. CO2 capture by temperature swing adsorption: Working capacity as affected by temperature and CO2 partial pressure. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 3593–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. Effect of acoustic field on CO2 desorption in fluidized bed of fine activated carbon. Particulology 2016, 23, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Grande, C.A.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of CO2 and N2 on activated carbon beads. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 47, 4883–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.L.P.; Amorim, S.M.; Luna, F.M.T.; Silva, I.J., Jr.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Morera, R.F.P.M. Adsorption of carbon dioxide onto activated carbon and nitrogen-enriched activated carbon-surface changes, equilibrium, and modeling of fixed bed adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboldi, L.; Bolland, O. Evaluating pressure swing adsorption as a CO2 separation technique in coal-fired power plants. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.I.; Aroonwilas, A.; Veawab, A. Equilibrium and kinetic behavior of CO2 adsorption onto zeolites, carbon molecular sieve and activated carbons. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, N.; Vakili, R.; Kalumpasut, P.; Gorgojo, P.; Siperstein, F.R.; Fan, X. Velocity variation effect in fixed bed columns: A case study of CO2 captures using porous solid adsorbents. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Bai, B.; Wu, B.; Su, F.; Hwang, J.F. Comparative study of CO2 capture by carbon nanotubes, activated carbons, and zeolites. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3050–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regufe, M.J.; Ferreira, A.F.P.; Lourero, J.M.; Shi, Y.; Rodrigues, A.; Ribeiro, A.M. New hybrid composite honeycomb monolith with 13X zeolite and activated carbon for CO2 capture. Adsorption 2018, 24, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Krishna, R.; Chen, B. Microporous metal-organic framework with potential for carbon dioxide capture at ambient conditions. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoro, K.O.; Singo, M.; Mulopo, J.L.; Daramola, M.O. Modeling and experimental study of the CO2 adsorption behavior of polyaspartamide as an adsorbent during post-combustion CO2 capture. Energy Procedia 2017, 112, 1643–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monazam, E.R.; Spenik, J.; Shadle, L.J. Fluid bed adsorption of carbon dioxide on immobilized polyethylenimine (PEI): Kinetic analysis and breakthrough behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlick, P.J.E.; Tezel, F.H. An experimental adsorbent screening study for CO2 removal from N2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 76, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavenati, S.; Grande, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E. Adsorption equilibrium of methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen on zeolite 13X at high pressures. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardane, R.V.; Shen, M.S.; Fisher, E.P.; Poston, J.A. Adsorption of CO2 on molecular sieves and activated carbon. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiuto, K.; Abe, S. Effect of desorption temperature on CO2 adsorption equilibria of the honeycomb zeolite beds. Appl. Energy 2002, 72, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, A. CO2, N2 and Ar Adsorption on Zeolites. Master’s Thesis, Izmar Institute of Technology, Izmir, Turkey, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Li, F.; Yuan, Q. Adsorption separation of CO2/CH4 gas mixture on the commercial zeolites at atmospheric pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geankoplis, C.J. Transport Processes and Unit Operations, 3rd ed.; Printice-Hall International Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, W.L.; Smith, J.C.; Harriott, P. Unit Operation of Chemical Engineering, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Editions: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]


| Adsorbent | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (atm) | Adsorption Capacity (mmol/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite 13X | 20 | 0.15 | 2.63 | [44] |
| Zeolite 13X | 22 | 1.5 | 4.90 | [44] |
| Zeolite 13X | 22 | 1 | 4.61 | [45] |
| Molecular sieve 13X | 25 | 1 | 3.2 | [45] |
| Molecular sieve 13X | 20 | 0.15 | 2.18 | [47] |
| Molecular sieve 4A | 25 | 1 | 2.7 | [46] |
| Molecular sieve 4A | 20 | 0.15 | 1.65 | [47] |
| 13X | 5 | 0.9 | 6.3 | [48] |
| 5A | 5 | 0.7 | 5.46 | [48] |
| ZSM-5 | 40 | 0.1 | 0.32 | [49] |
| ZSM-5 | 30 | 1 | 1.60 | [49] |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area A (m2/g) | Pore Volume Vp (cm3/g) | Pore Radius Sp (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular sieve | 362.2 | 4.11 × 10−2 | 27.52 |
| Silica gel type-III | 556.4 | 6.731 × 10−2 | 20.45 |
| T (°C) | V (m/s) | Cin | MS | SG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η (%) | LMTZ (cm) | Lbr (cm) | η (%) | LMTZ (cm) | Lbr (cm) | |||
| 30 | 0.052 | 5 | 86.1 | 3.58 | 20.66 | 57.8 | 12.05 | 13.87 |
| 40 | 0.052 | 5 | 84.8 | 3.94 | 20.35 | 66.5 | 9.65 | 15.96 |
| 50 | 0.052 | 5 | 83.9 | 4.18 | 20.14 | 44.7 | 18.34 | 10.73 |
| 40 | 0.032 | 5 | 87.5 | 3.20 | 21.00 | 65.6 | 9.94 | 15.74 |
| 40 | 0.042 | 5 | 86.2 | 3.55 | 20.69 | 56.1 | 13.49 | 13.46 |
| 40 | 0.052 | 5 | 84.6 | 4.02 | 20.30 | 64.5 | 10.37 | 15.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesfer, M.K.A.; Danish, M.; Khan, M.I.; Ali, I.H.; Hasan, M.; Jery, A.E. Continuous Fixed Bed CO2 Adsorption: Breakthrough, Column Efficiency, Mass Transfer Zone. Processes 2020, 8, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101233
Mesfer MKA, Danish M, Khan MI, Ali IH, Hasan M, Jery AE. Continuous Fixed Bed CO2 Adsorption: Breakthrough, Column Efficiency, Mass Transfer Zone. Processes. 2020; 8(10):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101233
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesfer, Mohammed K. Al, Mohd Danish, Mohammed Ilyas Khan, Ismat Hassan Ali, Mudassir Hasan, and Atef El Jery. 2020. "Continuous Fixed Bed CO2 Adsorption: Breakthrough, Column Efficiency, Mass Transfer Zone" Processes 8, no. 10: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101233
APA StyleMesfer, M. K. A., Danish, M., Khan, M. I., Ali, I. H., Hasan, M., & Jery, A. E. (2020). Continuous Fixed Bed CO2 Adsorption: Breakthrough, Column Efficiency, Mass Transfer Zone. Processes, 8(10), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101233








