A Hybrid Framework for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Optimization of Continuous Anti-Solvent Crystallization with Distillation for Solvent Recycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Approach
2.1. MESH Equations
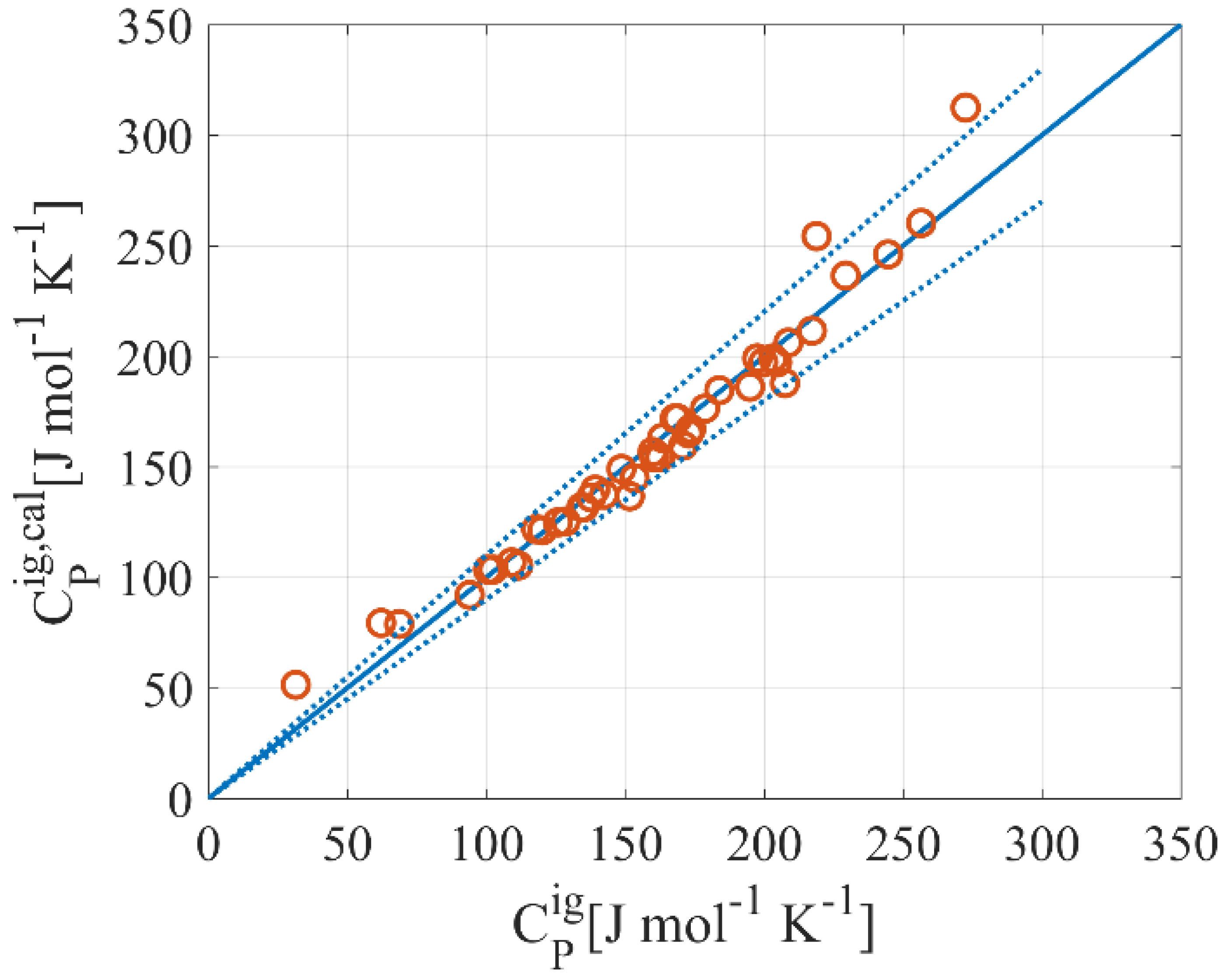
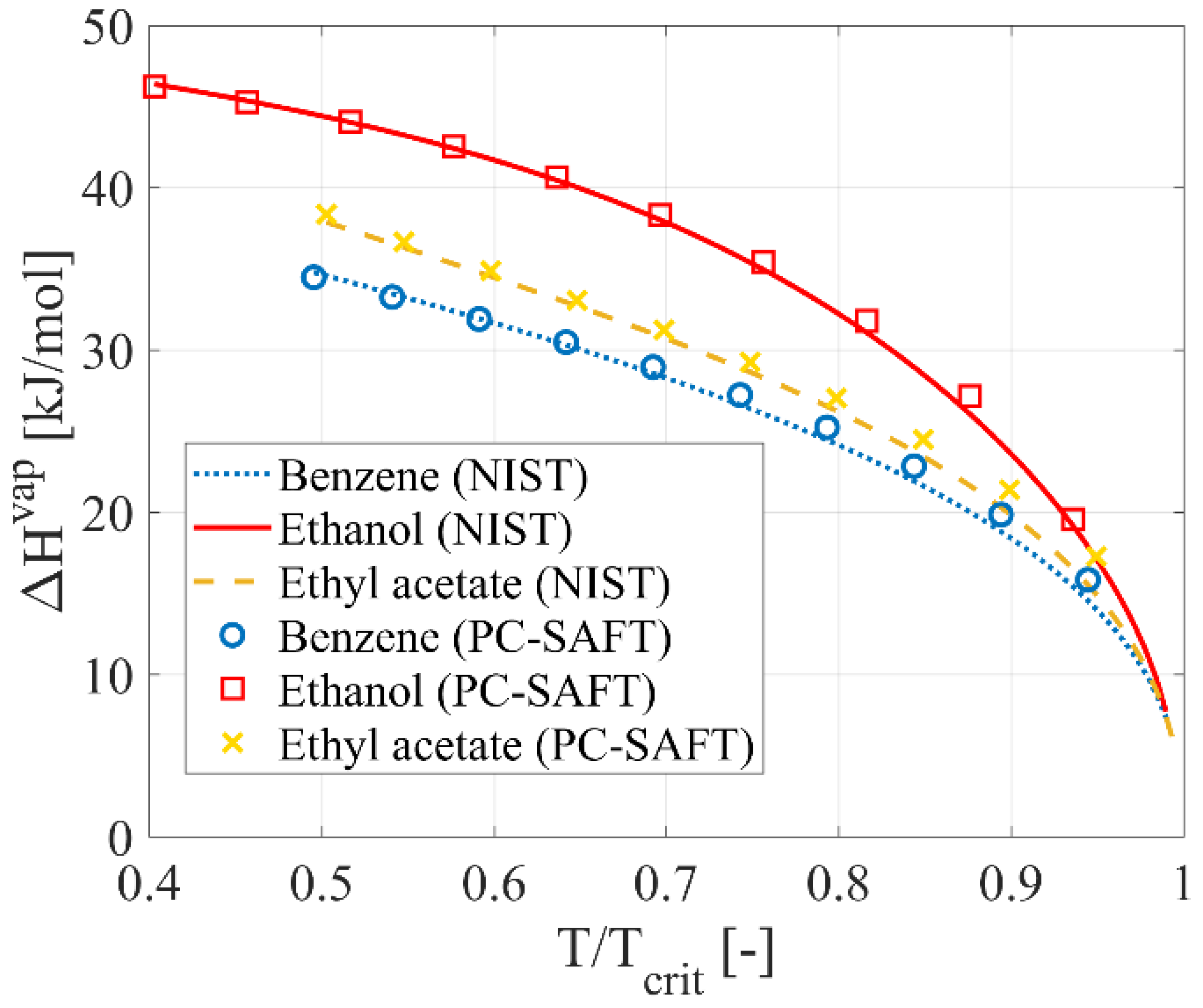
2.2. Thermodynamic Model
2.3. Optimization Problem Formulation
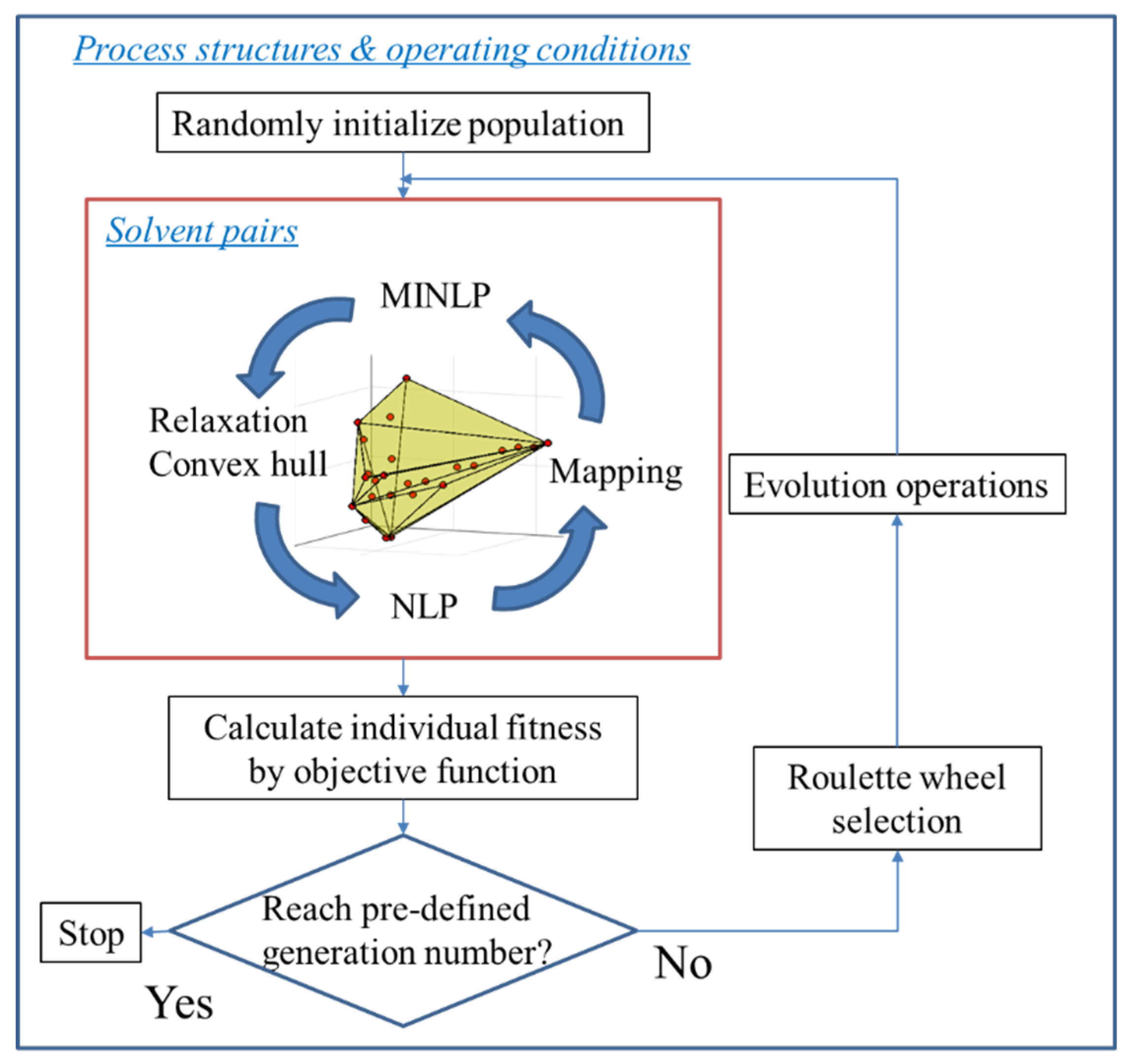
2.4. Solution Strategy
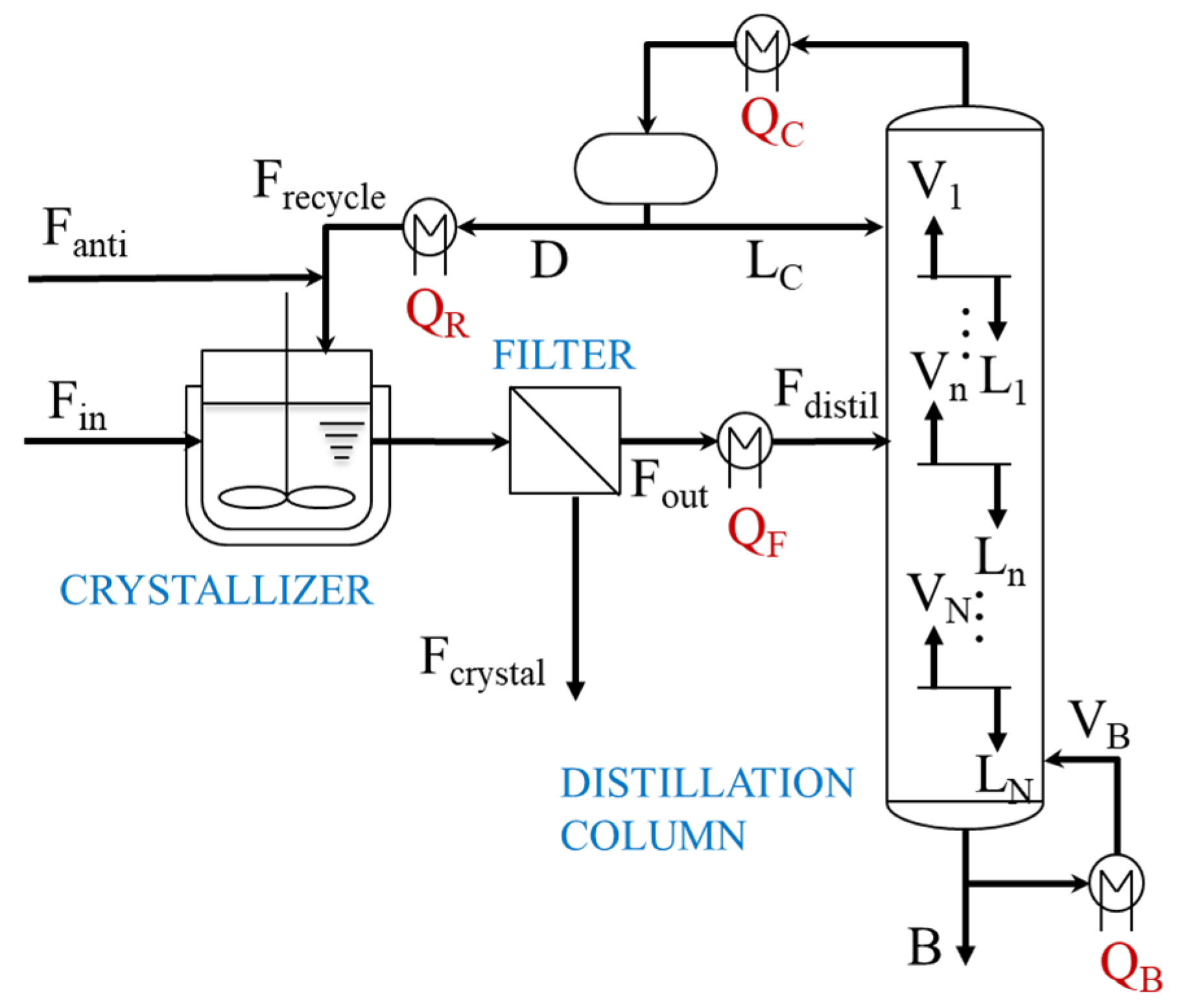
3. Case Study
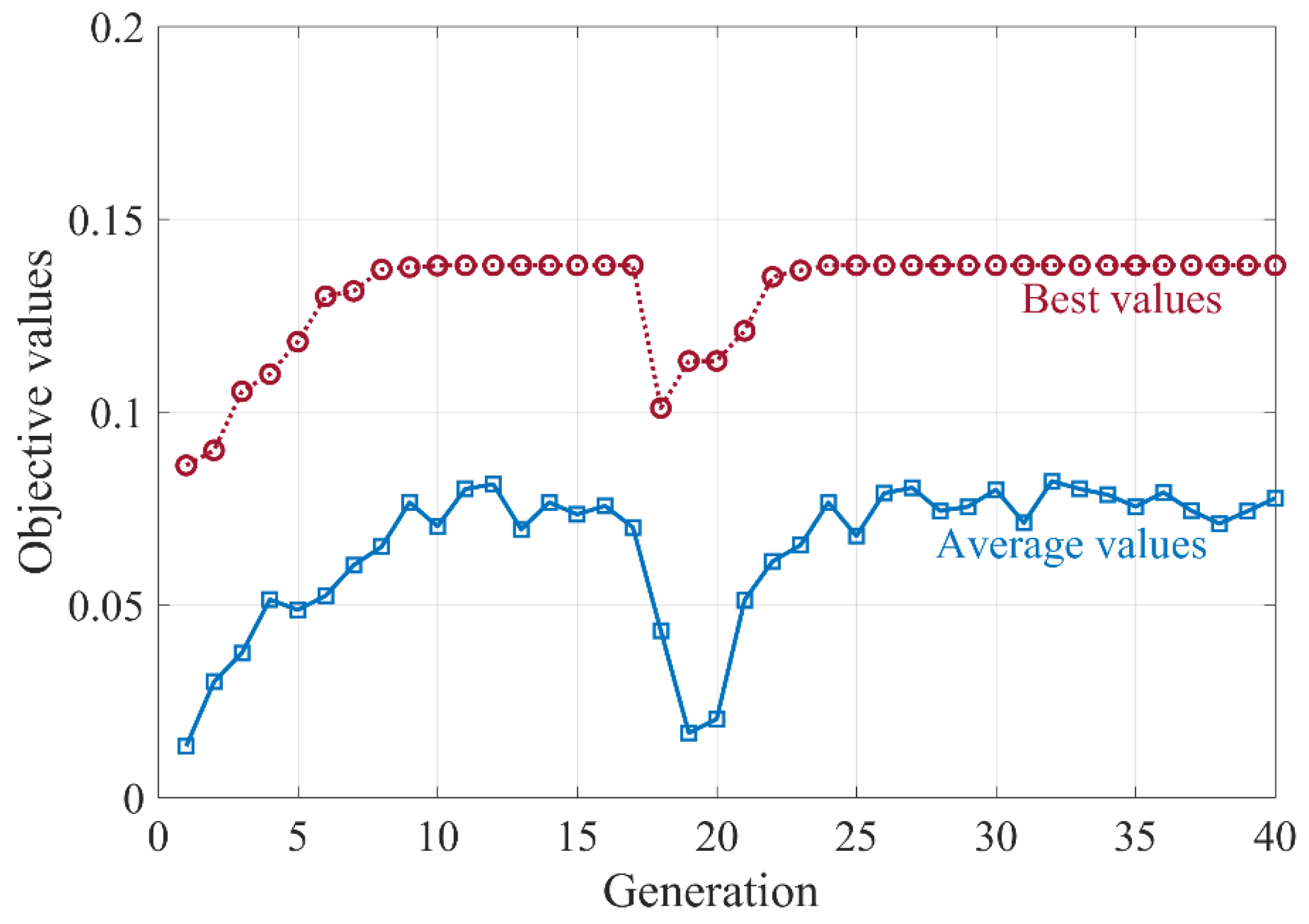
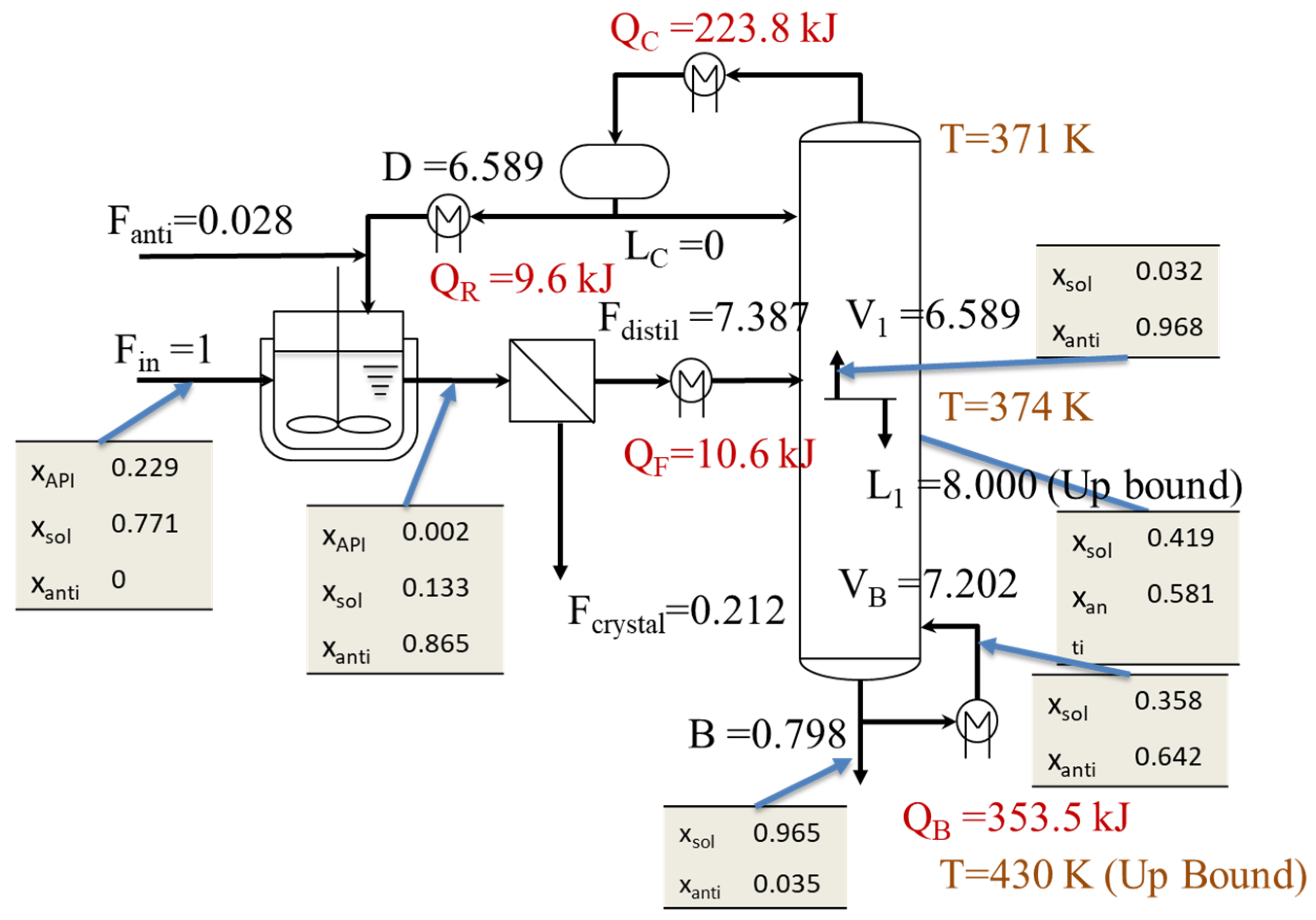
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Sarma, B.; Evans, J.M.B.; Myerson, A.S. Pharmaceutical Crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, S.; Gerogiorgis, D.I. Process Modeling, Simulation, and Technoeconomic Evaluation of Separation Solvents for the Continuous Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (CPM) of Diphenhydramine. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 924–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Lakerveld, R. Process intensification for pharmaceutical crystallization. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2018, 127, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, S.; Heider, P.L.; Zhang, H.; Lakerveld, R.; Benyahia, B.; Barton, P.I.; Braatz, R.D.; Cooney, C.L.; Evans, J.M.B.; Jamison, T.F.; et al. End-to-End Continuous Manufacturing of Pharmaceuticals: Integrated Synthesis, Purification, and Final Dosage Formation. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 12585–12589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; O’Connor, T.F.; Yang, X.; Cruz, C.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Madurawe, R.D.; Moore, C.M.V.; Yu, L.X.; Woodcock, J. Modernizing Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: From Batch to Continuous Production. J. Pharm. Innov. 2015, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, B.; Lakerveld, R.; Barton, P.I. A Plant-Wide Dynamic Model of a Continuous Pharmaceutical Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 15393–15412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakerveld, R.; Benyahia, B.; Braatz, R.D.; Barton, P.I. Model-based design of a plant-wide control strategy for a continuous pharmaceutical plant. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 3671–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrascu, M.; Barton, P.I. Optimal Dynamic Continuous Manufacturing of Pharmaceuticals with Recycle. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13423–13436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.; Papaioannou, V.; Gopinath, S.; Jackson, G.; Galindo, A.; Adjiman, C.S. A hierarchical method to integrated solvent and process design of physical CO2absorption using the SAFT-γ Mie approach. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 3249–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.I.; Linke, P. Multiobjective molecular design for integrated process-solvent systems synthesis. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardow, A.; Steur, K.; Gross, J. Continuous-Molecular Targeting for Integrated Solvent and Process Design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostrup, M.; Harper, P.M.; Gani, R. Design of environmentally benign processes: Integration of solvent design and separation process synthesis. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1999, 23, 1395–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, A.T.; Acquah, C.; Achenie, L.E.; Sithambaram, S.; Suib, S.L. Solvent design for crystallization of carboxylic acids. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarresi, H.; Conte, E.; Abildskov, J.; Gani, R.; Crafts, P. Model-Based Calculation of Solid Solubility for Solvent SelectionA Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5234–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.-H.; Tabora, J.; Variankaval, N.; Bakken, D.; Chen, C.-C. Prediction of Pharmaceutical Solubility Via NRTL-SAC and COSMO-SAC. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, O.L.; Galindo, A.; Jackson, G.; Adjiman, C.S. Computer-aided Design of Solvent Blends for the Cooling and Anti-solvent Crystallisation of Ibuprofen. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2019, 46, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Trout, B.L. Computer-Aided Solvent Selection for Improving the Morphology of Needle-like Crystals: A Case Study of 2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 4379–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.K.; Rathi, C.; Sharratt, P. Practical Assessment Methodology for Converting Fine Chemicals Processes from Batch to Continuous. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2015, 20, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.; Ng, D.K.S.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.G. A Systematic Molecular Design Framework with the Consideration of Competing Solvent Recovery Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13210–13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, E.; Tula, A.K.; Gani, R. Solvent selection methodology for pharmaceutical processes: Solvent swap. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 115, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lakerveld, R. Integrated solvent and process design for continuous crystallization and solvent recycling using PC-SAFT. AlChE J. 2018, 64, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Sadowski, G. Perturbed-chain SAFT: An equation of state based on a perturbation theory for chain molecules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, M.; Lampe, M.; Bardow, A.; Gross, J. Continuous Molecular Targeting–Computer-Aided Molecular Design (CoMT–CAMD) for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Design for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18029–18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lakerveld, R. Integrated Solvent and Process Optimization Using PC-SAFT for Continuous Crystallization with Energy-intensive Solvent Separation for Recycling. Comput.-Aided Chem. Eng. 2018, 44, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Ruether, F.; Sadowski, G. Modeling the Solubility of Pharmaceuticals in Pure Solvents and Solvent Mixtures for Drug Process Design. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4205–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyriouni, T.; Krokidis, X.; Economou, I.G. Thermodynamics of pharmaceuticals: Prediction of solubility in pure and mixed solvents with PC-SAFT. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 302, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, A.T.; Achenie, L.E.; Gani, R. A computer-aided molecular design framework for crystallization solvent design. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, I.; Grossmann, I.E. An LP/NLP based branch and bound algorithm for convex MINLP optimization problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1992, 16, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocis, G.R.; Grossmann, I.E. Computational experience with DICOPT solving MINLP problems in process systems engineering. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1989, 13, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, H.; Grossmann, I.E. Disjunctive Programming Models for the Optimal Design of Distillation Columns and Separation Sequences†. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, D. A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat. Comput. 1994, 4, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granberg, R.A.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Solubility of Paracetamol in Pure Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1999, 44, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler, L.T.; Grossmann, I.E.; Westerberg, A.W. Systematic Methods for Chemical Process Design; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. ACT/DDD Index. Available online: http://www.whocc.no/atcddd/ (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Drud, A. CONOPT: A GRG code for large sparse dynamic nonlinear optimization problems. Math. Program. 1985, 31, 153–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cost Source | Symbol | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol | 0.90 US $/mol 1 | |
| Trays | 0.50 US $ 2 | |
| Solvent | 0.40 US $/mol 3 | |
| Incineration | 0.050 US $/mol 2 | |
| Cooling water | 6.5 × 10−7 US $/kJ 4 | |
| Hot steam | 3.2 × 10−6 US $/kJ 4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Lakerveld, R. A Hybrid Framework for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Optimization of Continuous Anti-Solvent Crystallization with Distillation for Solvent Recycling. Processes 2020, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010063
Wang J, Zhu L, Lakerveld R. A Hybrid Framework for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Optimization of Continuous Anti-Solvent Crystallization with Distillation for Solvent Recycling. Processes. 2020; 8(1):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiayuan, Lingyu Zhu, and Richard Lakerveld. 2020. "A Hybrid Framework for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Optimization of Continuous Anti-Solvent Crystallization with Distillation for Solvent Recycling" Processes 8, no. 1: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010063
APA StyleWang, J., Zhu, L., & Lakerveld, R. (2020). A Hybrid Framework for Simultaneous Process and Solvent Optimization of Continuous Anti-Solvent Crystallization with Distillation for Solvent Recycling. Processes, 8(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8010063




