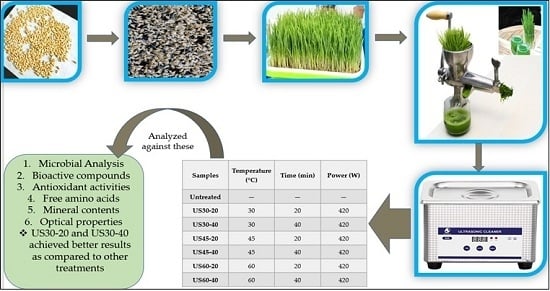
Thermo-Ultrasound-Based Sterilization Approach for the Quality Improvement of Wheat Plantlets Juice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Seeds, Growing and Juice Preparation
2.2. Thermo–Ultrasound (TU) Treatment
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
2.4. Total Flavonoid Contents (TFC) and Total Phenolic Contents (TPC)
2.5. The 2,2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Activity and Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
2.6. Carotenoids and Chlorophyll Contents
2.7. Free Amino Acids
2.8. Mineral Elements
2.9. Electric Conductivity (EC), °Brix and pH
2.10. Cloud Value, Non-Enzymatic Browning (NEB), Viscosity, and Titratable Acidity (TA)
2.11. Color Properties
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of TU on Microbial Loads
3.2. Impacts of TU on TPC and TFC
3.3. Impacts of TU on Carotenoid and Chlorophyll Contents
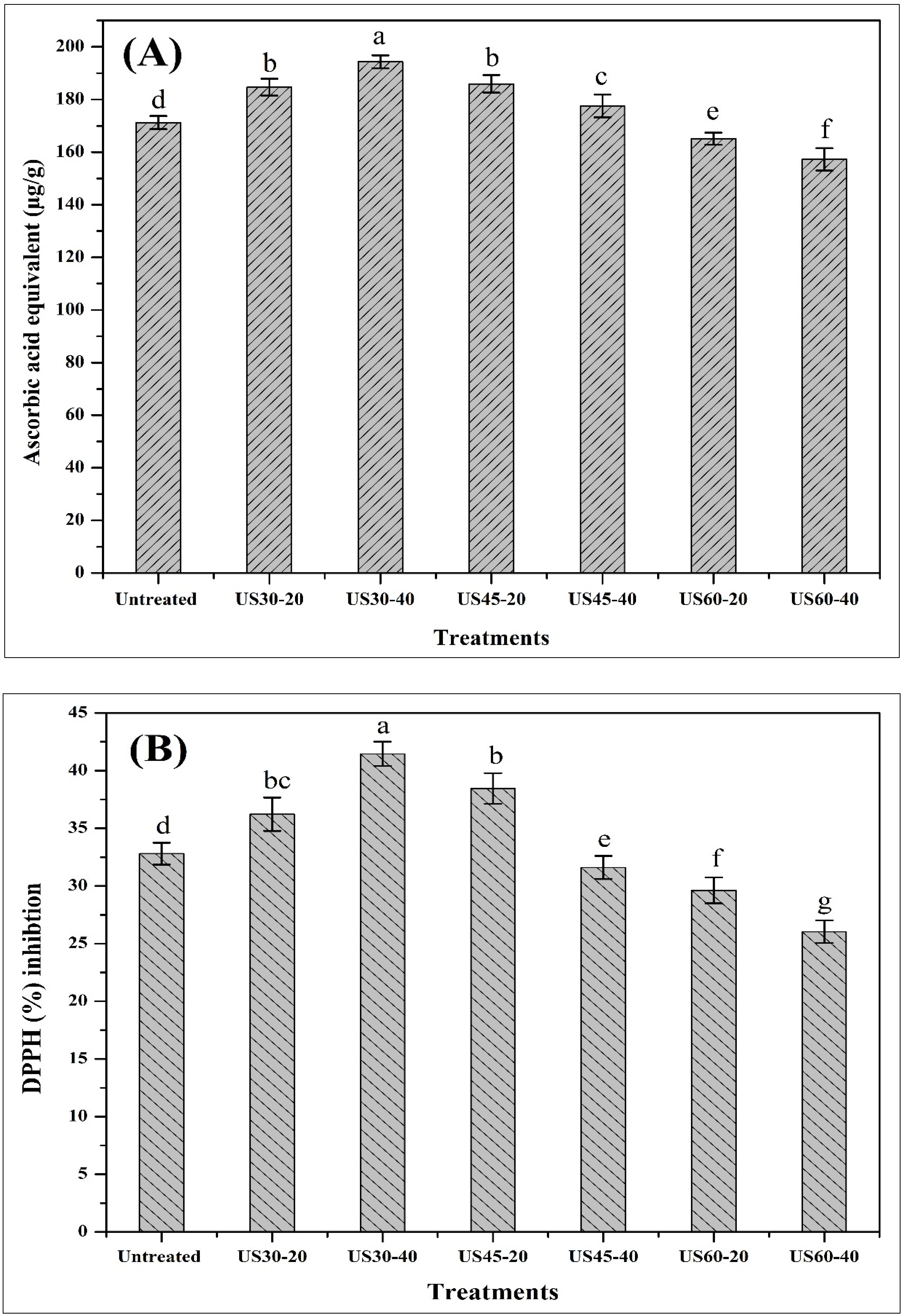
3.4. Impacts of TU on TAC and DPPH Activity
3.5. Impacts of TU on Free Amino Acids (FAA)
3.6. Impact of TU on Mineral Contents
3.7. Impacts of TU on ºBrix, Titratable Acidity (TA), pH, and EC
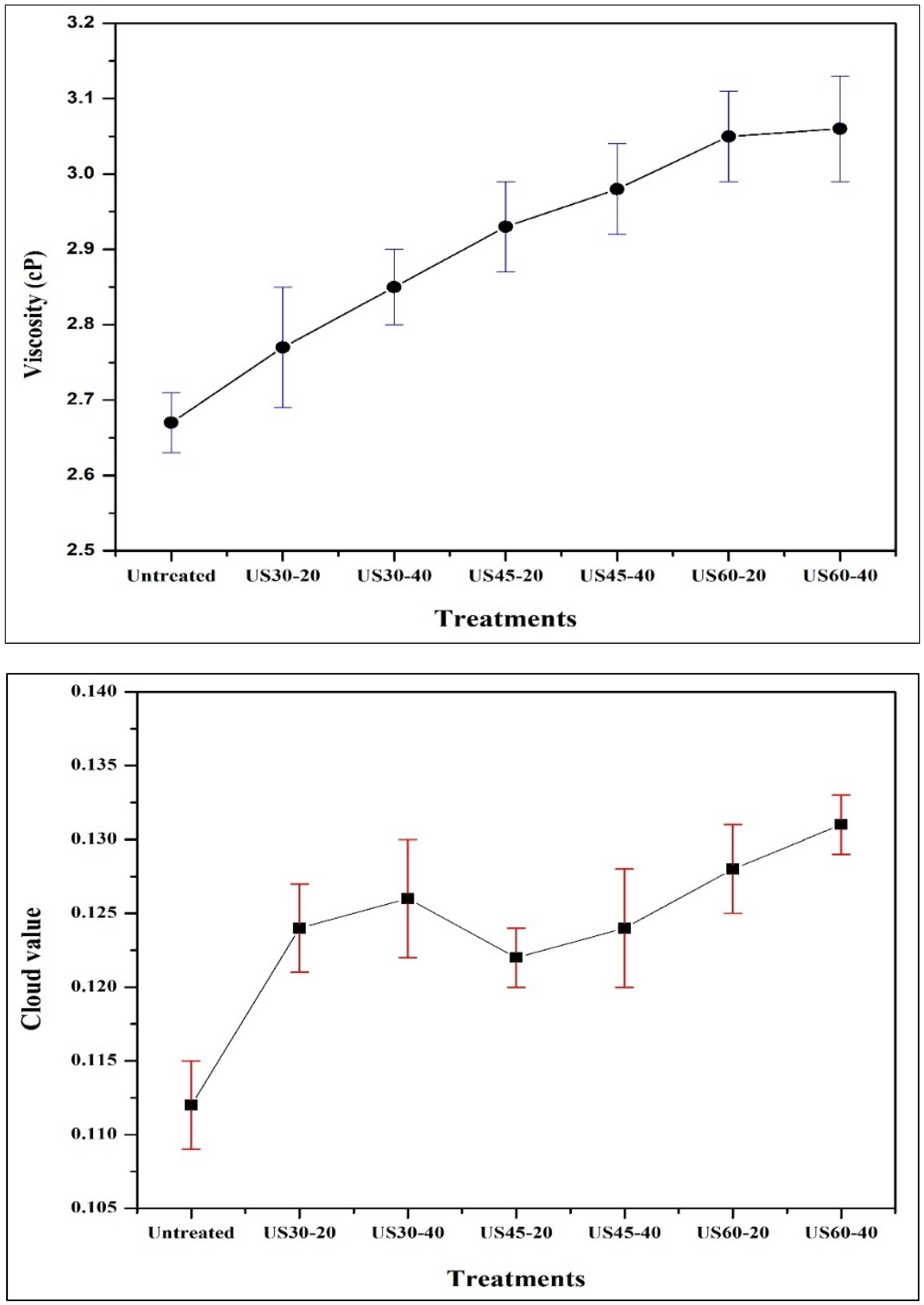
3.8. Impacts of TU on Non-Enzymatic Browning (NEB), Cloud Value, and Viscosity
3.9. Impact of TU on Color Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbas, E.; Kilercioglu, M.; Onder, O.N.; Koker, A.; Soyler, B.; Oztop, M.H. Wheatgrass juice to wheat grass powder: Encapsulation, physical and chemical characterization. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Acharya, R.; Nair, A.; Rajurkar, N.; Reddy, A.; Kulkarni, S. Determination of elemental concentration profiles in tender wheatgrass (Triticum aestivum L.) using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Daliu, P.; Santini, A. Fruit-based juices: Focus on antioxidant properties—Study approach and update. Phytother. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura-Calixto, F.; Goñi, I. Antioxidant capacity of the Spanish Mediterranean diet. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddeeg, A.; Zeng, X.-A.; Rahaman, A.; Manzoor, M.F.; Ahmed, Z.; Ammar, A.-F. Quality characteristics of the processed dates vinegar under influence of ultrasound and pulsed electric field treatments. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, A.; Siddeeg, A.; Manzoor, M.F.; Zeng, X.-A.; Ali, S.; Baloch, Z.; Li, J.; Wen, Q.-H. Impact of pulsed electric field treatment on drying kinetics, mass transfer, colour parameters and microstructure of plum. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Zeng, X.-A.; Rahaman, A.; Siddeeg, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Ahmed, Z.; Li, J.; Niu, D. Combined impact of pulsed electric field and ultrasound on bioactive compounds and FT-IR analysis of almond extract. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, A.; Zeng, X.-A.; Kumari, A.; Rafiq, M.; Siddeeg, A.; Manzoor, M.F.; Bloch, Z.; Ahmad, Z. Influence of ultrasound-assisted osmotic dehydration on texture, bioactive compounds and metabolites analysis of plum. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapala, J.; Oliver, C.; Kentish, S.; AshokKumar, M. Ultrasonics in food processing—Food quality assurance and food safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Caminiti, I.M.; Palgan, I.; Pataro, G.; Noci, F.; Morgan, D.J.; Cronin, D.A.; Whyte, P.; Ferrari, G.; Lyng, J.G. Effects on Escherichia coli inactivation and quality attributes in apple juice treated by combinations of pulsed light and thermosonication. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiang, W.S.; Bhat, R.; Rosma, A.; Cheng, L.H. Effects of thermosonication on the fate of E scherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella Enteritidis in mango juice. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pordesimo, L.; Weiss, J. High intensity ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from soybeans. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Jabbar, S.; Hu, B.; Hashim, M.M.; Wu, T.; Wu, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Zeng, X. Synergistic impact of sonication and high hydrostatic pressure on microbial and enzymatic inactivation of apple juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.; Recrosio, N.; Saura, D.; Muñoz, N.; Martí, N.; Lizama, V. Effects of ultrasonic treatments in orange juice processing. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; O’Donnell, C.; Cullen, P.; Tiwari, B. Effect of non thermal processing technologies on the anthocyanin content of fruit juices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, A.; Tiwari, B.; Patras, A.; Brunton, N.; Brennan, C.; Cullen, P.; O’Donnell, C.; Tiwari, B. Effect of thermosonication on bioactive compounds in watermelon juice. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Jabbar, S.; Hu, B.; Hashim, M.M.; Wu, T.; Lei, S.; Khan, M.A.; Zeng, X. Thermosonication as a potential quality enhancement technique of apple juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F. Effect of cooking temperature on some quality characteristic of Almond milk. Int. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2017, 3, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-O.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, C.Y. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slinkard, K.; Singleton, V.L. Total phenol analysis: Automation and comparison with manual methods. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1977, 28, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Aadil, R.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Ali, A.; Zeng, F.; Farooq, M.A.; Han, Z.; Khalid, S.; Jabbar, S. Influence of different pulsed electric field strengths on the quality of the grapefruit juice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Sun, Y.; Ni, Y.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, F. The effect of enzymatic mash treatment, pressing, centrifugation, homogenization, deaeration, sterilization and storage on carrot juice. J. Food Process Eng. 2007, 30, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Dong, P.; Huang, W.; Xiong, L.; Liao, X. Comparing the effects of high hydrostatic pressure and thermal pasteurization combined with nisin on the quality of cucumber juice drinks. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, R.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Wang, M.-S.; Liu, Z.-W.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Hong, J.; Jabbar, S. A potential of ultrasound on minerals, micro-organisms, phenolic compounds and colouring pigments of grapefruit juice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, R.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Han, Z.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of ultrasound treatments on quality of grapefruit juice. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3201–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wordon, B.; Mortimer, B.; McMaster, L. Comparative real-time analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell viability, injury and death induced by ultrasound (20 kHz) and heat for the application of hurdle technology. Food Res. Int. 2012, 47, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Inactivation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in pineapple, grape and cranberry juices under pulsed and continuous thermo-sonication treatments. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzawa, N.; Ohdaira, E.; Ide, M. Effects of Ultrasonic Irradiation on Phenolic Compounds in Wine. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, 2978–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Ahmad, N.; Manzoor, A.; Kalsoom, A. Food based phytochemical luteolin their derivatives, sources and medicinal benefits. Int. J. Agric. Life Sci. IJAL 2017, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Siddique, R.; Zeng, X.-A.; Rahaman, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Wahab, A. Novel extraction techniques and pharmaceutical activities of luteolin and its derivatives. J. Food Biochem. 2019, e12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, P.T.; White, T.A.; McPhail, D.B.; Duthie, G.G. The relative contributions of vitamin C, carotenoids and phenolics to the antioxidant potential of fruit juices. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhirasegaram, V.; Razali, Z.; Somasundram, C. Effects of thermal treatment and sonication on quality attributes of Chokanan mango (Mangifera indica L.) juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ding, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Stability of chlorophyll–protein complex (photosystem II) in processed spinach: Effect of high hydrostatic pressure. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S3177–S3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Vinatoru, M.; Paniwnyk, L.; Mason, T.J. Investigation of the effects of ultrasound on vegetal tissues during solvent extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Adhikari, B. Kinetics of argy wormwood (Artemisia argyi) leaf peroxidase and chlorophyll content changes due to thermal and thermosonication treatment. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Kamaruddin, N.S.B.C.; Min-Tze, L.; Karim, A. Sonication improves kasturi lime (Citrus microcarpa) juice quality. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrouj, K.; Sánchez-Rubio, M.; Taboada-Rodríguez, A.; Cava-Roda, R.M.; Marín-Iniesta, F. Sonication at mild temperatures enhances bioactive compounds and microbiological quality of orange juice. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 99, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, R.M.; Zeng, X.-A.; Sun, D.-W.; Wang, M.-S.; Liu, Z.-W.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.W. Combined effects of sonication and pulsed electric field on selected quality parameters of grapefruit juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Elizarrarás, A.; Piloni-Martini, J.; Ramírez-Moreno, E.; Alanís-García, E.; Güemes-Vera, N.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Zafra-Rojas, Q.Y.; Cruz-Cansino, N.D.S. Enzymatic inactivation and antioxidant properties of blackberry juice after thermoultrasound: Optimization using response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Jabbar, S.; Wu, T.; Hashim, M.M.; Hu, B.; Lei, S.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, X. Effect of ultrasound on different quality parameters of apple juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Wang, M.; Lu, R. Effects of pulsed electric fields on bioactive components, colour and flavour of green tea infusions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Lelas, V.; Paniwnyk, L.; Herceg, Z. Effect of ultrasound treatment on particle size and molecular weight of whey proteins. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biziuk, M.; Kuczynska, J. Mineral Components in Foods; Taylor &Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- López-Berenguer, C.; Carvajal, M.; Moreno, D.A.; Garcia-Viguera, C. Effects of Microwave Cooking Conditions on Bioactive Compounds Present in Broccoli Inflorescences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10001–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.; Souza, S.; Martinis, B.; Korn, M. Monitoring of the ultrasonic irradiation effect on the extraction of airborne particulate matter by ion chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 317, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elik, A. Ultrasound assisted pseudo-digestion of street dust samples prior to determination by atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2005, 66, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, P.K.; Chandrasekar, C.M.; Kesavan, R.K. Effect of thermosonication on the quality attributes of star fruit juice. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Jiang, A. Effect of ultrasound treatment on quality and microbial load of carrot juice. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Martin, S.E.; Cadwallader, K.R.; Robinson, S.J.; Ugarte-Romero, E.; Ugarte-Romero, E. Inactivation of Escherichia coli with Power Ultrasound in Apple Cider. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E102–E108. [Google Scholar]
- Caminiti, I.M.; Noci, F.; Muñoz, A.; Whyte, P.; Morgan, D.J.; Cronin, D.A.; Lyng, J.G. Impact of selected combinations of non-thermal processing technologies on the quality of an apple and cranberry juice blend. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gamage, T.; Vilkhu, K.; Simons, L.; Mawson, R. Effect of thermosonication on quality improvement of tomato juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.K.; Muthukumarappan, K.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Cullen, P.J.; Tiwari, B. Effects of Sonication on the Kinetics of Orange Juice Quality Parameters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | — | — | — |
| US30-20 | 30 | 20 | 420 |
| US30-40 | 30 | 40 | 420 |
| US45-20 | 45 | 20 | 420 |
| US45-40 | 45 | 40 | 420 |
| US60-20 | 60 | 20 | 420 |
| US60-40 | 60 | 40 | 420 |
| Treatments | Total Plate Count (log CFU/mL) | Yeast & Mold (log CFU/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 4.12 ± 0.12 a | 3.48 ± 0.26 a |
| US30-20 | 3.91 ± 0.25 b | 2.78 ± 0.20 b |
| US30-40 | 3.63 ± 0.19 c | 2.40 ± 0.19 c |
| US45-20 | 3.34 ± 0.21 d | 2.10 ± 0.24 d |
| US45-40 | 2.08 ± 0.13 e | 1.92 ± 0.18 e |
| US60-20 | 1.87 ± 0.12 f | 1.62 ± 0.14 f |
| US60-40 | ND | ND |
| Treatments | Total Phenolic | Total Flavonoids | Carotenoids |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 311.48 ± 0.13 d | 189.55 ± 0.08 de | 94.30 ± 0.06 d |
| US30-20 | 319.21 ± 0.16 b | 198.82 ± 0.05 bc | 96.21 ± 0.03 b |
| US30-40 | 331.40 ± 0.09 a | 205.73 ± 0.03 a | 97.32 ± 0.05 a |
| US45-20 | 321.15 ± 0.18 c | 201.27 ± 0.11 b | 97.71 ± 0.04 a |
| US45-40 | 309.04 ± 0.11 de | 192.18 ± 0.09 d | 95.44 ± 0.02 c |
| US60-20 | 305.17 ± 0.14 f | 187.64 ± 0.06 def | 93.02 ± 0.04 e |
| US60-40 | 297.28 ± 0.05 g | 179.73 ± 0.12 g | 92.75 ± 0.07 f |
| Treatments | Chlorophyll a | Chlorophyll b | Chlorophyll a + b |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 360.6 ± 0.04 e | 120.2 ± 0.03 d | 480.8 ± 0.03 d |
| US30-20 | 371.33 ± 0.02 bc | 123.23 ± 0.05 c | 494.56 ± 0.03 b |
| US30-40 | 376.23 ± 0.03 a | 125.12 ± 0.02 ab | 501.23 ± 0.03 a |
| US45-20 | 373.63 ± 0.06 ab | 126.45 ± 0.08 a | 500.08 ± 0.03 a |
| US45-40 | 365.12 ± 0.07 d | 123.35 ± 0.05 c | 488.98 ± 0.03 c |
| US60-20 | 359.47 ± 0.09 ef | 119.23 ± 0.02 de | 478.7 ± 0.03d e |
| US60-40 | 355.97 ± 0.07 g | 116.15 ± 0.08 f | 472.12 ± 0.03 f |
| Amino Acids | Untreated | US30-20 | US30-40 | US45-20 | US45-40 | US60-20 | US60-40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 32.03 ± 0.11 a | 33.536 ± 0.14 a | 32.69 ± 0.07 a | 16.68 ± 0.04 b | 16.57 ± 0.02 b | 17.04 ± 0.06 c | 16.77 ± 0.10 b |
| Thr | 13.76 ± 0.08 | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL | BDL |
| Ser | 125.12 ± 0.18 c | 141.518 ± 0.21 a | 135.71 ± 0.14 b | 86.08 ± 0.09 d | 85.90 ± 0.07 d | 84.38 ± 0.11 de | 84.71 ± 0.10 e |
| Glu | 0.92 ± 0.01 f | 1.281 ± 0.03 c | 1.84 ± 0.01 a | 1.13 ± 0.02 d | 0.79 ± 0.03 e | 1.25 ± 0.04 c | 1.57 ± 0.07 b |
| Gly | 6.69 ± 0.08 b | 7.895 ± 0.05 a | 7.74 ± 0.03 a | 3.74 ± 0.06 c | 3.61 ± 0.02 c | 3.44 ± 0.05 cd | 3.52 ± 0.01 cd |
| Ala | 44.28 ± 0.12 c | 50.195 ± 0.16 a | 48.21 ± 0.09 b | 25.39 ± 0.07 d | 24.35 ± 0.04 de | 23.52 ± 0.08 e | 23.79 ± 0.06 e |
| Cys | 1.91 ± 0.02 b | 2.052 ± 0.05 a | 2.02 ± 0.03 a | 1.01 ± 0.04 c | 1.00 ± 0.02 c | 0.96 ± 0.01 cd | 0.95 ± 0.01 cd |
| Val | 20.07 ± 0.12 c | 22.822 ± 0.15 a | 21.50 ± 0.09 ab | 11.54 ± 0.10 d | 11.13 ± 0.07 d | 10.85 ± 0.05 de | 11.02 ± 0.04 d |
| Met | 2.32 ± 0.03 c | 3.086 ± 0.02 b | 3.53 ± 0.01 a | 1.59 ± 0.01 d | 1.42 ± 0.02 e | 1.43 ± 0.01 e | 1.49 ± 0.03 d |
| Ile | 8.26 ± 0.04 b | 10.056 ± 0.05 a | 9.90 ± 0.06 a | 4.94 ± 0.02 c | 4.66 ± 0.02 cd | 4.51 ± 0.01 e | 4.63 ± 0.03 cd |
| Leu | 8.98 ± 0.02 c | 12.720 ± 0.06 a | 11.47 ± 0.04 b | 6.78 ± 0.03 d | 5.96 ± 0.04 e | 5.87 ± 0.05 e | 6.23 ± 0.03 d |
| Tyr | 7.89 ± 0.05 c | 9.704 ± 0.03 a | 8.90 ± 0.02 b | 5.06 ± 0.05 d | 4.63 ± 0.02 e | 4.63 ± 0.04 e | 4.77 ± 0.02 f |
| Phe | 11.66 ± 0.07 c | 13.737 ± 0.04 a | 13.16 ± 0.05 b | 7.50 ± 0.02 d | 6.84 ± 0.03 de | 6.95 ± 0.02 de | 7.19 ± 0.05 d |
| Lys | 22.39 ± 0.09 b | 25.09 ± 0.05 a | 24.65 ± 0.07 a | 13.02 ± 0.01 c | 12.44 ± 0.05 cd | 12.21 ± 0.05 cd | 12.46 ± 0.07 cd |
| NH3 | 28.72 ± 0.06 b | 34.115 ± 0.02 a | 33.48 ± 0.04 a | 17.56 ± 0.04 c | 16.48 ± 0.06 cd | 16.98 ± 0.08 cd | 17.15 ± 0.09 c |
| His | 14.74 ± 0.03 b | 15.473 ± 0.08 a | 14.77 ± 0.03 b | 7.74 ± 0.03 c | 7.59 ± 0.08 c | 7.56 ± 0.06 c | 7.62 ± 0.04 c |
| Arg | 11.56 ± 0.04 b | 13.339 ± 0.07 a | 6.83 ± 0.02 cd | 7.0 ± 0.05 c | 6.54 ± 0.04 e | 6.48 ± 0.03 e | 6.63 ± 0.03 cd |
| Minerals | Untreated | US30-20 | US30-40 | US45-20 | US45-40 | US60-20 | US60-40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc (Zn) | 4.18 ± 0.03 a | 4.11 ± 0.04 b | 3.64 ± 0.06 e | 3.91 ± 0.02 d | 3.57 ± 0.05 e | 3.94 ± 0.04 d | 4.01 ± 0.01 c |
| Iron (Fe) | 6.55 ± 0.02 d | 6.95 ± 0.05 b | 6.74 ± 0.03 c | 6.58 ± 0.01 d | 8.18 ± 0.07 a | 6.02 ± 0.01 e | 6.78 ± 0.02 c |
| Manganese (Mn) | 3.06 ± 0.01 a | 3.06 ± 0.03 a | 3.08 ± 0.02 a | 2.98 ± 0.01 b | 2.93 ± 0.02b c | 2.95 ± 0.04 bcd | 2.78 ± 0.01 e |
| Calcium (Ca) | 170 ± 0.07 f | 263 ± 0.09 c | 276 ± 0.10 b | 223 ± 0.11 e | 170 ± 0.05 f | 238 ± 0.06 d | 269 ± 0.08 a |
| Potassium (K) | 1432 ± 0.54 ab | 1434 ± 0.58 a | 1436 ± 0.45 a | 1374 ± 0.60 c | 1319 ± 0.32 d | 1274 ± 0.28 e | 1254 ± 0.24 f |
| Parameters | Untreated | US30-20 | US30-40 | US45-20 | US45-40 | US60-20 | US60-40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.82 ± 0.02 a | 5.84 ± 0.01 a | 5.87 ± 0.03 a | 5.83 ± 0.01 a | 5.88 ± 0.04 a | 5.84 ± 0.05 a | 5.85 ± 0.02 a |
| EC* | 5.01 ± 0.05 c | 5.10 ± 0.04 b | 5.16 ± 0.02 a | 4.98 ± 0.04 cd | 4.94 ± 0.06 e | 4.93 ± 0.03 e | 4.91 ± 0.02 ef |
| Brix | 3.8 ± 0.01 a | 3.9 ± 0.01 a | 3.8 ± 0.01 a | 3.8 ± 0.02 a | 3.9 ± 0.01 a | 4.0 ± 0.01 a | 3.8 ± 0.01 a |
| TA (%) | 27.92 ± 0.34 a | 26.23 ± 0.56 a | 26.54 ± 0.18 a | 26.12 ± 1.02 a | 27.13 ± 0.65 a | 27.05 ± 1.13 a | 26.96 ± 0.86 a |
| NEB | 0.248 ± 0.005 f | 0.256 ± 0.006 e | 0.268 ± 0.008 d | 0.273 ± 0.003 c | 0.281 ± 0.004 b | 0.285 ± 0.001 b | 0.296 ± 0.002 a |
| Parameters | Untreated | US30-20 | US30-40 | US45-20 | US45-40 | US60-20 | US60-40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 39.133 ± 0.29 cd | 32.09 ± 0.07 ef | 33.17 ± 1.79 e | 40.11 ± 0.33 c | 42.30 ± 0.25 ab | 43.64 ± 0.32 a | 43.22 ± 0.25 a |
| a* | −5.023 ± 0.07 e | −7.163 ± 0.01 g | −6.23 ± 0.41 f | −4.38 ± 0.08 c | −4.24 ± 0.03 cd | −3.54 ± 0.01 ab | −3.313 ± 0.02 a |
| b* | 6.53± 0.01 c | 11.29 ± 0.05 a | 11 ± 1.25 a | 8.37 ± 0.46 b | 6.33 ± 0.03 cd | 6.36 ± 0.03 cde | 6.2 ± 0.02 f |
| Hue (hº) | −52.43 ± 0.20 a | −57.62 ± 0.2 bc | −60.47 ± 0.2 d | −62.38 ± 0.2 ef | −56.18 ± 0.17 b | −60.90 ± 0.26 d | −61.90 ± 0.28 e |
| C | 8.23 ± 0.06 d | 13.37 ± 0.38 a | 12.64 ± 0.32 b | 9.44 ± 0.28 c | 7.61 ± 0.18 e | 7.27 ± 0.21 ef | 7.02 ± 0.12 efg |
| ΔE | ---- | 8.76 ± 0.35 a | 7.54 ± 0.65 b | 2.17 ± 0.23 f | 3.26 ± 0.42 e | 4.75 ± 0.52 c | 4.44 ± 0.58 cd |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, Z.; Manzoor, M.F.; Begum, N.; Khan, A.; Shah, I.; Farooq, U.; Siddique, R.; Zeng, X.-A.; Rahaman, A.; Siddeeg, A. Thermo-Ultrasound-Based Sterilization Approach for the Quality Improvement of Wheat Plantlets Juice. Processes 2019, 7, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080518
Ahmed Z, Manzoor MF, Begum N, Khan A, Shah I, Farooq U, Siddique R, Zeng X-A, Rahaman A, Siddeeg A. Thermo-Ultrasound-Based Sterilization Approach for the Quality Improvement of Wheat Plantlets Juice. Processes. 2019; 7(8):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Zahoor, Muhammad Faisal Manzoor, Nabila Begum, Abbas Khan, Imranullah Shah, Umar Farooq, Rabia Siddique, Xin-An Zeng, Abdul Rahaman, and Azhari Siddeeg. 2019. "Thermo-Ultrasound-Based Sterilization Approach for the Quality Improvement of Wheat Plantlets Juice" Processes 7, no. 8: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080518
APA StyleAhmed, Z., Manzoor, M. F., Begum, N., Khan, A., Shah, I., Farooq, U., Siddique, R., Zeng, X.-A., Rahaman, A., & Siddeeg, A. (2019). Thermo-Ultrasound-Based Sterilization Approach for the Quality Improvement of Wheat Plantlets Juice. Processes, 7(8), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080518