Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption of Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids Containing Acetate and Butyrate Anions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. NMR and Water Content
2.4. Thermophysical Characterization
2.5. CO2 Absorption Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
- [EtOHA][AC]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 3.613 [t, 2H, H2(-OH)], 2.922 [t, 2H, CH2(-NH2)], 1.726 [s, 3H, CH3]. Water content: 2.93%
- [EtOHA][BA]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 3.669 [t, 2H, CH2(-OH)], 2.988 [t, 2H, CH2(-NH2)], 2.010 [t, 2H, CH2(-COOH)], 1.375–1.448 [m, 2H, CH2], 0.747 [t, 3H, CH3]. Water content: 2.06%
- [BEHA][AC]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 2.861 [d, 4H, CH2(-NH)], 1.805 [s, 3H, CH3], 1.613–1.677 [m, 2H, CH], 1.181–1.309 [m, 16H, CH2], 0.786 [t, 12H, CH3]. Solid
- [BEHA][BA]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 2.856 [d, 4H, CH2(-NH)], 2.062 [t, 2H, CH2(-COOH)], 1.582–1.660 [m, 2H, CH], 1.412–1.486 [m, 2H, CH2(AC)], 1.236–1.339 [m, 16H, CH2], 1.214-1.229 [t,t 15H, CH3]. Water content: 0.15%
- [TBA][AC]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 3.002 [t, 4H, CH2(-NH)], 1.788 [s, 3H, CH3], 1.508–10571 [m, 6H, CH2], 1.207–1.282 [m, 6H, CH2], 0.805 [t, 9H, CH3]. Water content: 0.47%
- [TBA][BA]: 1H NMR (500 MHz, D2O): δ 3.003 [t, 6H, CH2(-NH)], 2.031 [t, 2H, CH2(-COOH)], 1.510–1.573 [m, 6H, CH2], 1.394–1.468 [m, 2H, CH2(AC)], 1.211-1.285 [m, 6H, CH2], 0.809 [t, 9H, CH3], 0.768 [t, 3H, CH3(AC)]. Water content: 0.23%
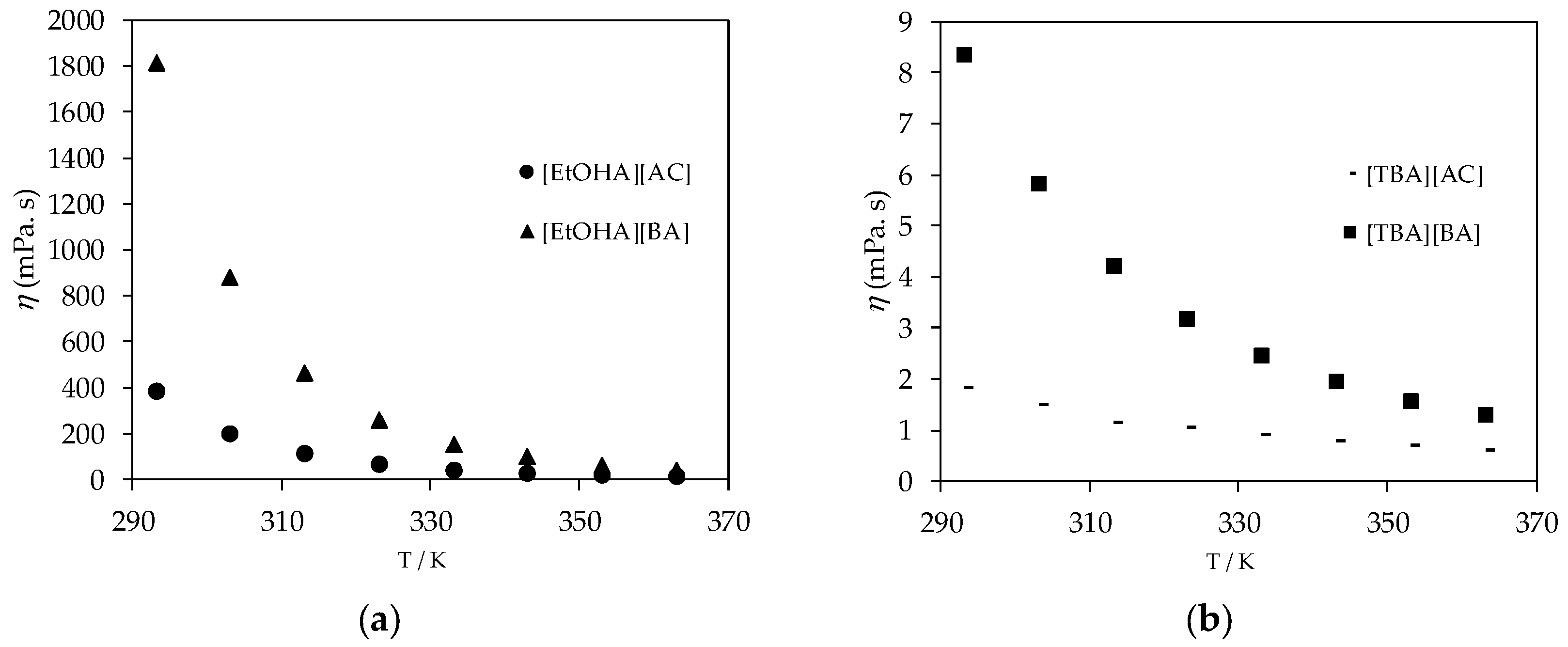
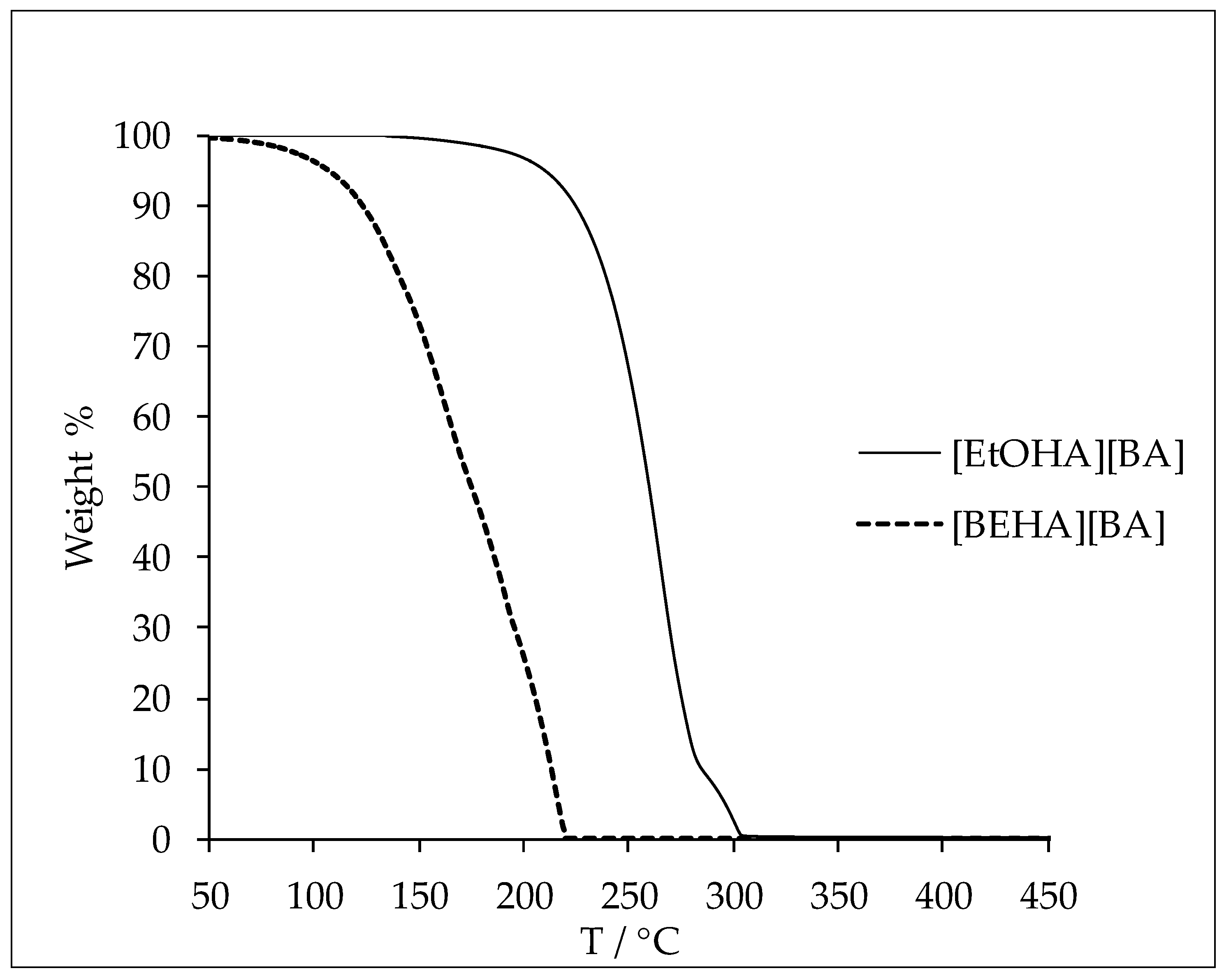
3.1. Thermophysical Properties
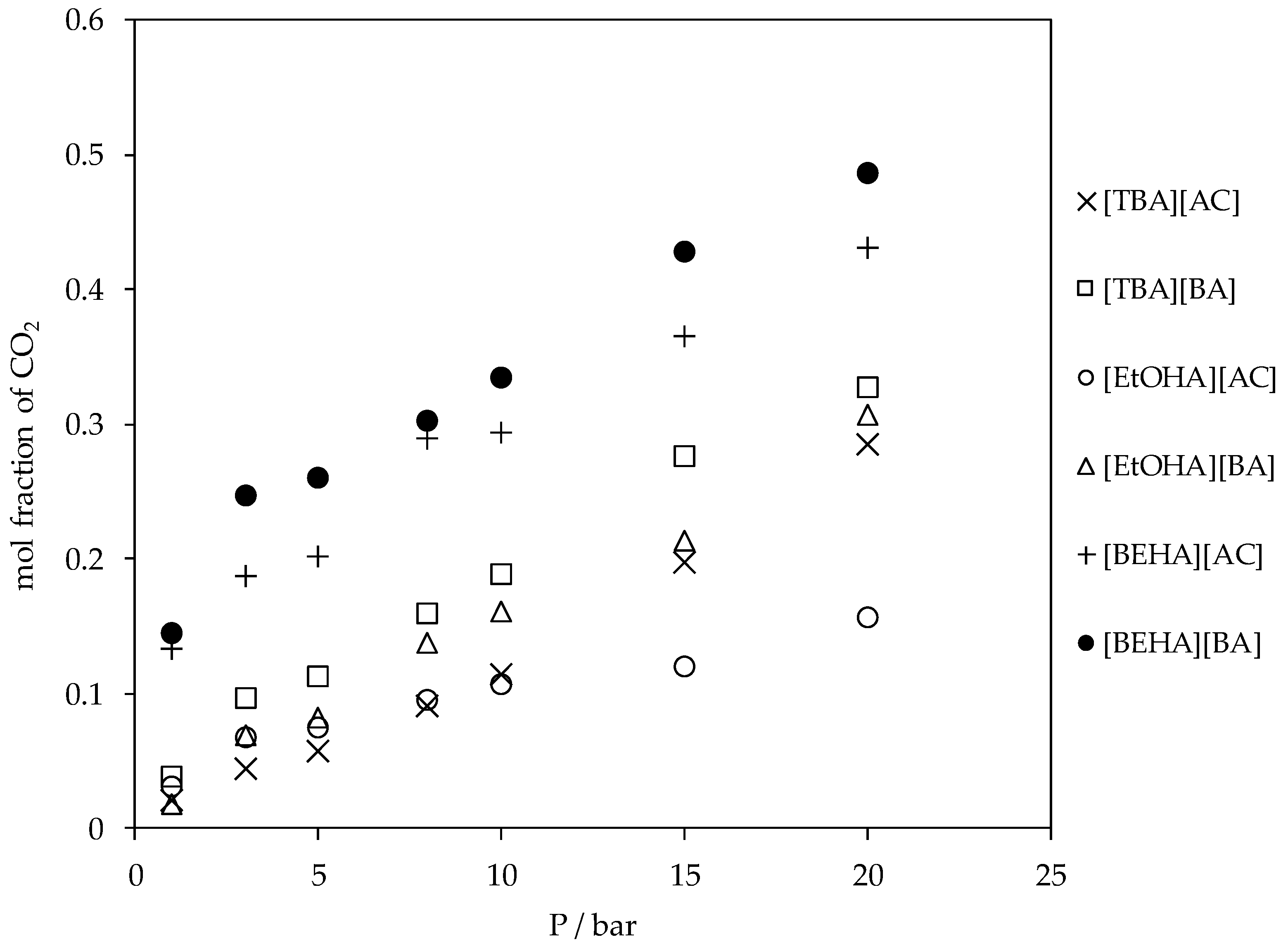
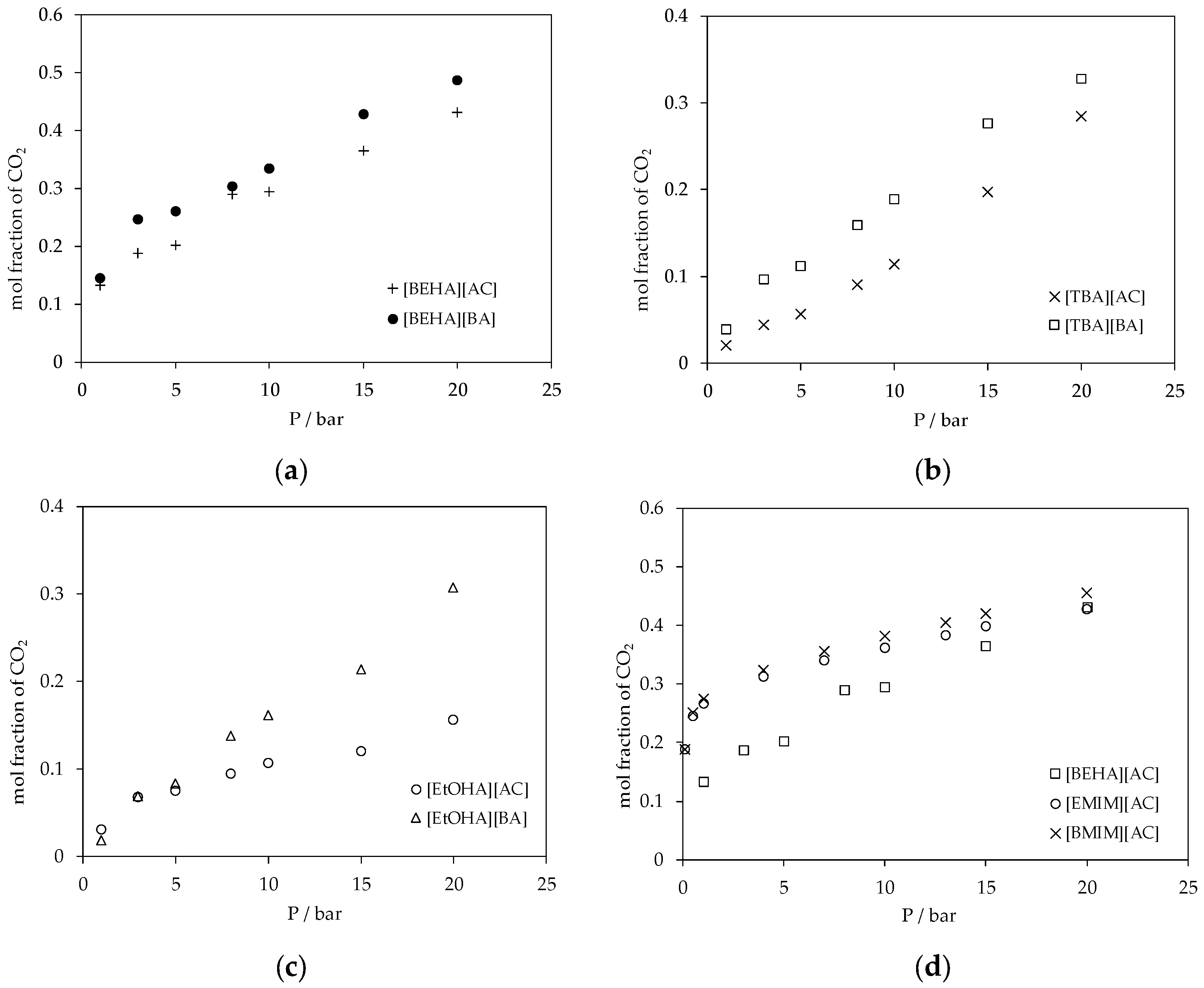
3.2. CO2 Absorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mokhatab, S.; Poe, W.A.; Speight, J.G. Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing; Gulf Processing Publishing, Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Rochelle, G. Thermal degradation of monoethanolamine at stripper conditions. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Feng, J.; Li, S.; Song, H.; Yu, C.; Zhao, K.; Kong, F. A novel homogeneous catalysis-liquid/solid separation system for highly effective recycling of homogeneous catalyst based on a phosphine-functionalized polyether guanidium ionic liquid. Mol. Catal. 2019, 475, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Xie, G.; Jin, Y.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Catalytic performance of ionic liquid for dehydrochlorination reaction: Excellent activity and unparallel stability. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 255, 117757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abejón, R.; Rabadán, J.; Lanza, S.; Abejón, A.; Garea, A.; Irabien, A. Supported ionic liquid membranes for separation of lignin aqueous solutions. Processes 2018, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baicha, Z.; Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Maqueda Marín, D.P.; Collado, J.A.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; El Mahi, M. On the selective transport of nutrients through polymer inclusion membranes based on ionic liquids. Processes 2019, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.A.; Gu, Z.; Brennecke, J.F. High-pressure phase behavior of ionic liquid/CO2 systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.L.; Maginn, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Solubilities and thermodynamic properties of gases in the ionic liquid 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7315–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Choi, W.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Yoo, K.-P.; Lee, C.S. Solubility measurement and prediction of carbon dioxide in ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2005, 228–229, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, M.J.; Aki, S.N.V.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Dixon, J.K.; Brennecke, J.F. Improving carbon dioxide solubility in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 9001–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflett, M.B.; Kasprzak, D.J.; Junk, C.P.; Yokozeki, A. Phase behavior of {carbon dioxide + [bmim][Ac]} mixtures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2008, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurkan, B.E.; de la Fuente, J.C.; Mindrup, E.M.; Ficke, L.E.; Goodrich, B.F.; Price, E.A.; Schneider, W.F.; Brennecke, J.F. Equimolar CO2 absorption by anion-functionalized ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2116–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Park, S.D.; Baek, I.H.; Park, K.T.; Yoon, Y.I.; Jeong, S.K. Effects of anions on absorption capacity of carbon dioxide in acid functionalized ionic liquids. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 100, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistla, Y.S.; Khanna, A. Carbon dioxide absorption studies using amine-functionalized ionic liquids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2497–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoubeik, M.; Mohamedali, M.; Henni, A. Experimental solubility and thermodynamic modeling of CO2 in four new imidazolium and pyridinium-based ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 419, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Song, M.; Xu, Y. DBU-Based protic ionic liquids for CO2 capture. ACS Sustian. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8192–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, R.; Oncsik, T.; Mitschke, B.; MacFarlane, D.R. Base-rich diamino protic ionic liquid mixtures for enhanced CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 196, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Ohno, H. Preparation of novel room-temperature molten salts by neutralization of amines. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Ionic liquids as amphiphile self-assembly media. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1706–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Solvent nanostructure, the solvophobic effect and amphiphile self-assembly in ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 833–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M.; Izgorodina, E.I.; Abbott, A.P.; Annat, G.; Fraser, K. On the concept of ionicity in ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 4962–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Che, S.; Yao, J.; Li, H. Ionicity if protic ionic liquid: Quantitative measurement by spectroscopic methods. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids–Progress on the fundamental issues. Aust. J. Chem. 2007, 60, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Song, X.; Minofar, B.; Kanzaki, R.; Takamuku, T.; Umebayashi, Y. A new proton conductive liquid with no ions: Pseudo-protic ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11522–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, S.; Atilhan, M.; Karadas, F. Thermophysical properties of pure ionic liquids: Review of present situation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 9580–9595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Carvalho, P.J. Thermophysical properties of phosphonium-based ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 400, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, N.M.; Abdul Mutalib, M.I.; Man, Z.; Bustam, M.A.; Murugesan, T. Thermophysical properties of 1-alkylpyridinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2010, 42, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, N.M.; Abdul Ghani, M.A.; Nik Mohamad Kamil, R. Synthesis, characterization and CO2 solubility of [him][Tf2N] and [hmim][Ac] ionic liquids. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1621, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin, J.; Husson, P.; Majer, V.; Costa Gomes, M.F. Low-pressure solubilities and thermodynamics of solvation of eight gases in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2006, 240, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soave, G. Equilibrium constants from a modified Redlich-Kwong equation of state. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1972, 2, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Panda, S.; Bakshi, P.S.; Gardas, R.L.; Khatri, O.P. Thermophysical properties of trioctylalkylammonium bis(salicylato)borate ionic liquids: Effect of alkyl chain length. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Ang, K.L.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S. Density, viscosity and electrical conductivity of protic alkanolammonium ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5136–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Wilfred, C.D.; Murugesan, T. Thermophysical properties of hydroxyl ammonium ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machanová, K.; Boisset, A.; Sedláková, Z.; Anouti, M.; Bendová, M.; Jacquemin, J. Thermophysical properties of ammonium-based bis{(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl}imide ionic liquids: Volumetric and transport properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhotaray, P.K.; Gardas, R.L. Thermophysical properties of ammonium and hydroxylammonium protic ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 72, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, M.G.; Bolívar, C.L.; Guillermo Díaz Baños, F.; Víllora, G. Effect of temperature, anion, and alkyl chain length on the density and refractive index of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Hosseinian, A.; Aparicio, S. An experimental and theoretical study on 2-hydroxyethylammonium acetate ionic liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Vera, R.M.; Sirieix-Plénet, J.; Gaillon, L.; Rizzi, C.; Ávila-Rodríguez, M.; Cote, G.; Chagnes, A. Physicochemical properties of novel cholinium ionic liquids for the recovery of silver from nitrate media. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 78268–78277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Sharma, G.; Singh, D.; Gardas, R.L. Effect of anion on thermophysical properties of N, N-diethanolammonium based protic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, N.S.M.; Luís, A.; Reis, P.M.; Carvalho, P.J.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Freire, M.G.; Pereiro, A.B. Fluorination effects on the thermodynamic, thermophysical and surface properties of ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 97, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanchez-Ramirez, N.; Martins, V.L.; Ando, R.A.; Camilo, F.F.; Urahata, S.M.; Ribeiro, M.C.C.; Torresi, R.M. Physicochemical properties of three ionic liquids containing a tetracyanoborate anion and their lithium salt mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 8772–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.M. Tetracyanoborate based ionic liquids for CO2 capture: From ab initio calculations to molecular simulations. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 415, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.R.; Karkhanechi, H.; Kamio, E.; Yoshioka, T.; Matsuyama, H. Quantum mechanical and molecular dynamics simulations of dual-amino-acid ionic liquids for CO2 capture. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27734–27745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflett, M.B.; Yokozeki, A. Phase behavior of carbon dioxide in ionic liquids: [emim][acetate], [emim][trifluoroacetate], and [emim][acetate] + [emim][trifluoroacetate] mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
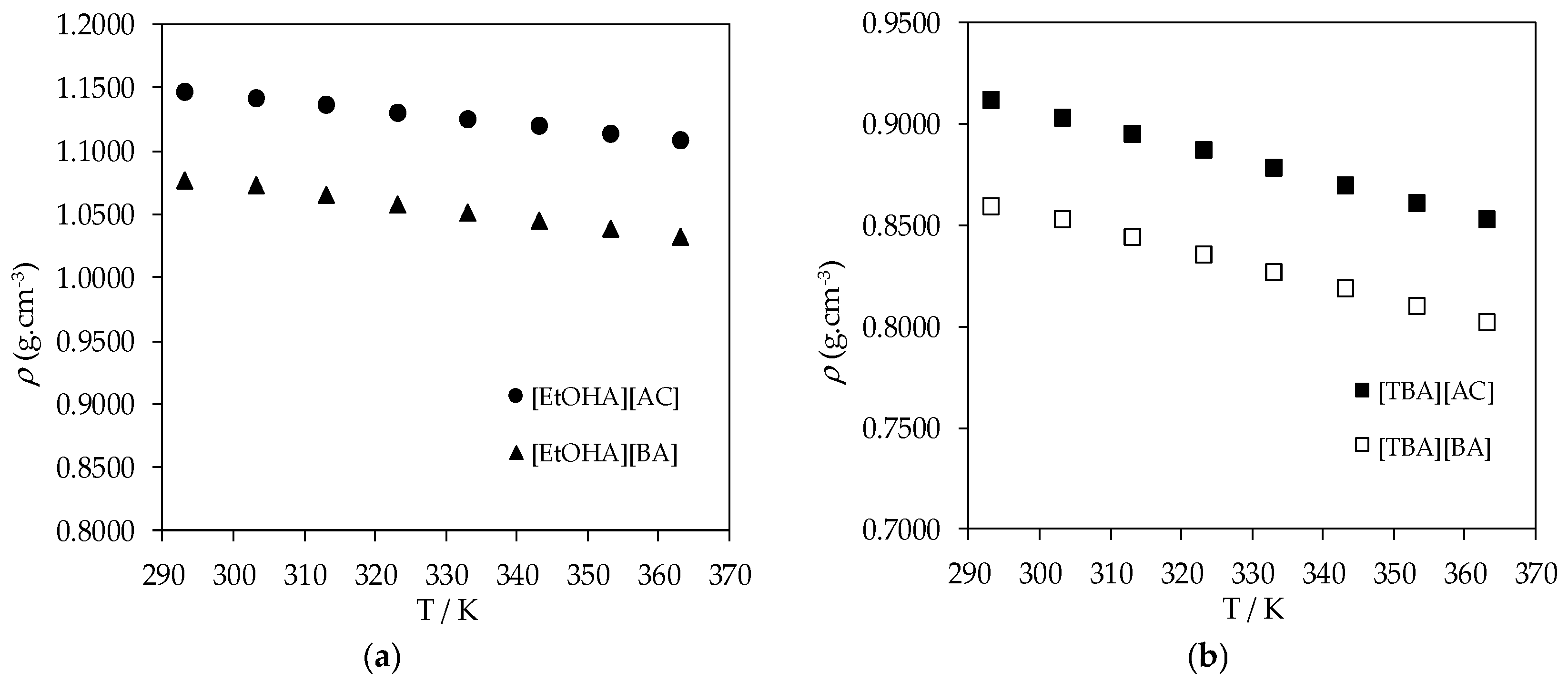

| Structure | Name and Abbreviation |
|---|---|
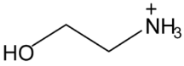 | Ethanolammonium, [EtOHA] |
 | Tributylammonium, [TBA] |
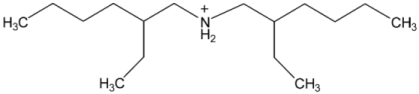 | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)ammonium, [BEHA] |
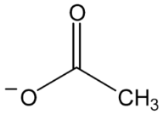 | Acetate, [AC] |
 | Butyrate, [BA] |
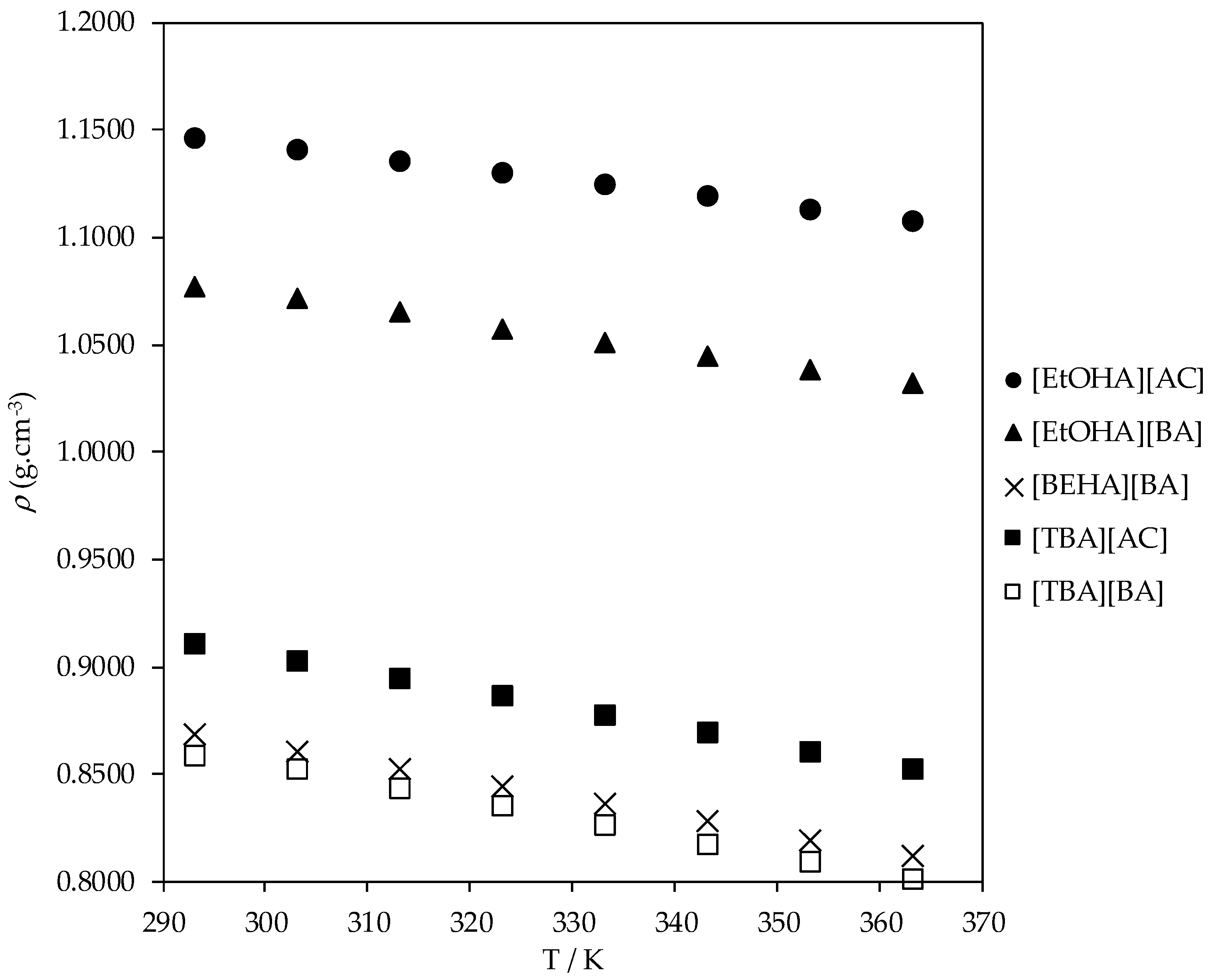
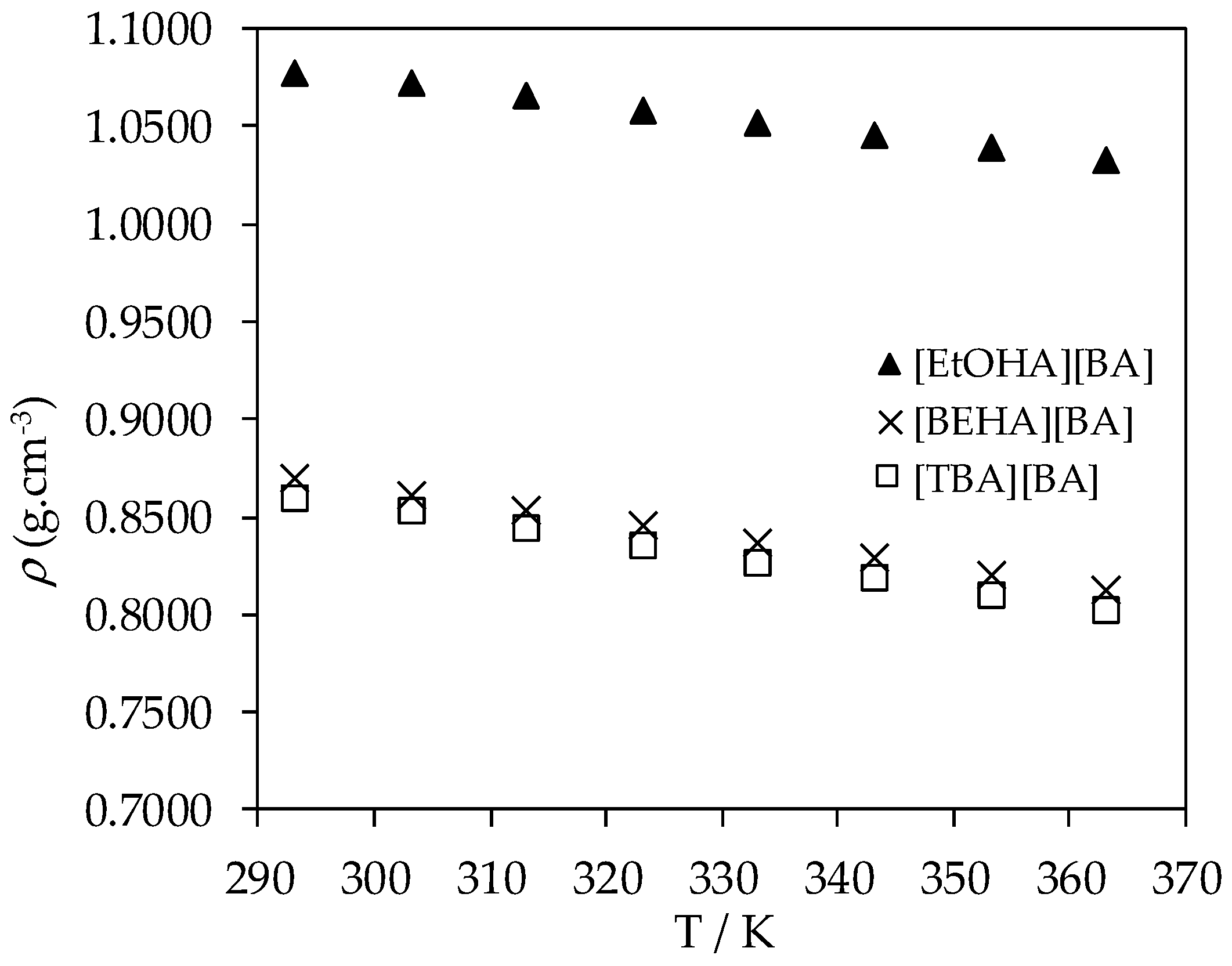
| T/K | ρ (g·cm−3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | [EtOHA][BA] | [BEHA][BA] | [TBA][AC] | [TBA] [BA] | |
| 293.15 | 1.1468 | 1.0772 | 0.8695 | 0.9118 | 0.8591 |
| 303.15 | 1.1410 | 1.0725 | 0.8613 | 0.9035 | 0.8531 |
| 313.15 | 1.1359 | 1.0657 | 0.8532 | 0.8952 | 0.8445 |
| 323.15 | 1.1305 | 1.0579 | 0.8451 | 0.8869 | 0.8356 |
| 333.15 | 1.1250 | 1.0516 | 0.8368 | 0.8785 | 0.8268 |
| 343.15 | 1.1194 | 1.0452 | 0.8285 | 0.8700 | 0.8185 |
| 353.15 | 1.1137 | 1.0387 | 0.8203 | 0.8614 | 0.8102 |
| 363.15 | 1.1079 | 1.0324 | 0.8124 | 0.8527 | 0.8020 |
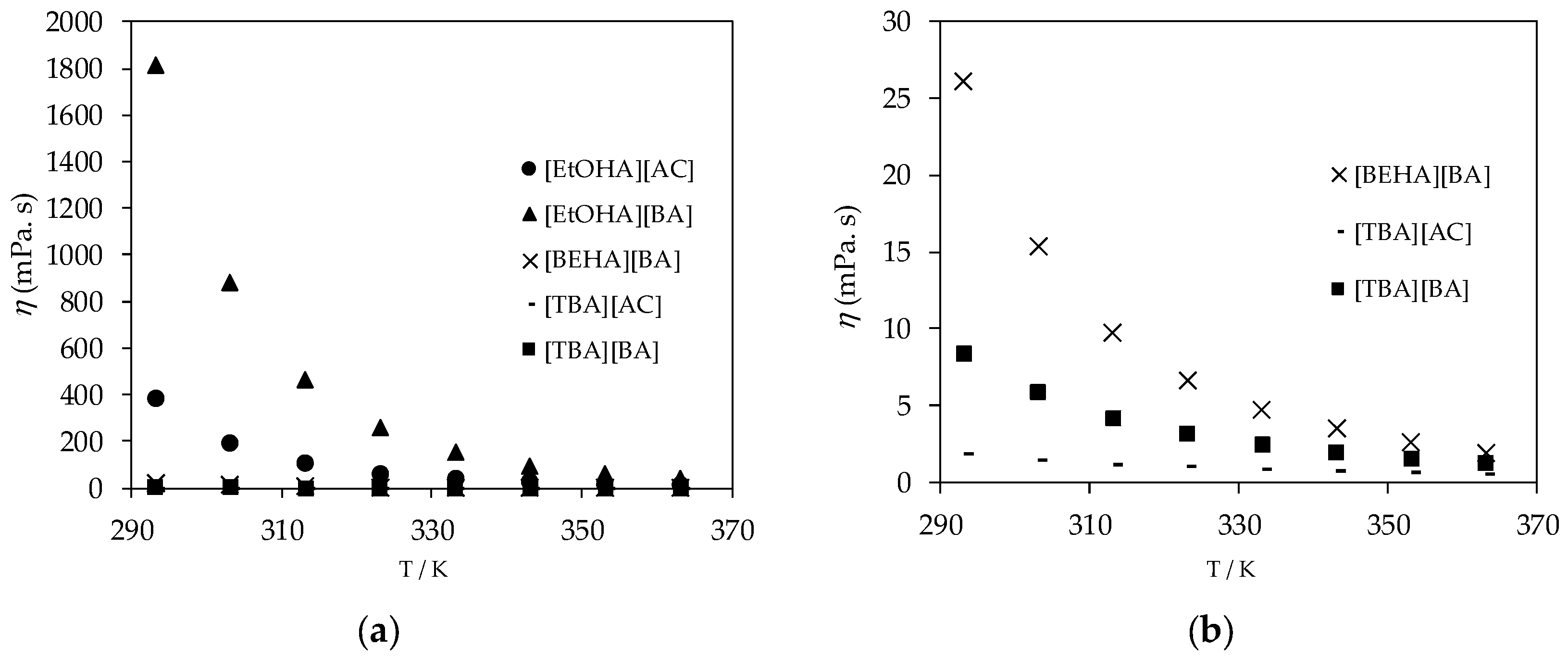
| T/K | η (mPa·s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | [EtOHA][BA] | [BEHA][BA] | [TBA][AC] | [TBA] [BA] | |
| 293.15 | 385.760 | 1814.000 | 26.061 | 1.8482 | 8.368 |
| 303.15 | 197.860 | 883.310 | 15.364 | 1.5090 | 5.832 |
| 313.15 | 110.780 | 464.320 | 9.780 | 1.1485 | 4.225 |
| 323.15 | 66.947 | 261.220 | 6.628 | 1.0573 | 3.185 |
| 333.15 | 43.099 | 155.690 | 4.706 | 0.9041 | 2.457 |
| 343.15 | 29.214 | 97.348 | 3.478 | 0.7886 | 1.949 |
| 353.15 | 20.677 | 63.345 | 2.652 | 0.6928 | 1.579 |
| 363.15 | 15.157 | 42.651 | 1.874 | 0.6149 | 1.287 |
| Ionic Liquid | A0 | A1 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | 1.3087 | ‒0.0006 | 0.016 |
| [EtOHA][BA] | 1.2702 | ‒0.0007 | 0.015 |
| [BEHA][BA] | 1.1093 | ‒0.0008 | 0.006 |
| [TBA][AC] | 1.1592 | ‒0.0008 | 0.014 |
| [TBA][BA] | 1.1051 | ‒0.0008 | 0.011 |
| Ionic Liquid | A2 | A3 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | ‒4.7222 | 2127.7 | 0.031 |
| [EtOHA][BA] | ‒5.1998 | 2469.4 | 0.021 |
| [BEHA][BA] | ‒4.4045 | 1696.4 | 0.020 |
| [TBA][AC] | ‒2.1829 | 713.31 | 0.014 |
| [TBA][BA] | ‒3.2888 | 1229.3 | 0.011 |
| T/K | αp × 10‒4/(K‒1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | [EtOHA][BA] | [BEHA][BA] | [TBA][AC] | [TBA] [BA] | |
| 293.15 | 5.3 | 6.6 | 9.1 | 8.7 | 9.2 |
| 303.15 | 5.3 | 6.6 | 9.2 | 8.7 | 9.3 |
| 313.15 | 5.4 | 6.7 | 9.3 | 8.8 | 9.4 |
| 323.15 | 5.4 | 6.7 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 9.4 |
| 333.15 | 5.4 | 6.8 | 9.5 | 9.0 | 9.5 |
| 343.15 | 5.4 | 6.8 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 9.6 |
| 353.15 | 5.5 | 6.8 | 9.7 | 9.1 | 9.7 |
| 363.15 | 5.5 | 6.9 | 9.8 | 9.2 | 9.8 |
| T/K | nm3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [EtOHA][AC] | [EtOHA][BA] | [BEHA][BA] | [TBA][AC] | [TBA] [BA] | |
| 293.15 | 0.1754 | 0.2300 | 0.6295 | 0.4470 | 0.5287 |
| 303.15 | 0.1763 | 0.2310 | 0.6355 | 0.4511 | 0.5324 |
| 313.15 | 0.1771 | 0.2325 | 0.6416 | 0.4553 | 0.5378 |
| 323.15 | 0.1780 | 0.2342 | 0.6477 | 0.4596 | 0.5436 |
| 333.15 | 0.1788 | 0.2356 | 0.6542 | 0.4640 | 0.5493 |
| 343.15 | 0.1797 | 0.2371 | 0.6607 | 0.4685 | 0.5549 |
| 353.15 | 0.1807 | 0.2386 | 0.6673 | 0.4732 | 0.5606 |
| 363.15 | 0.1816 | 0.2400 | 0.6738 | 0.4780 | 0.5663 |
| [EtOHA][AC] | [EtOHA][BA] | [BEHA][AC] | [BEHA][BA] | [TBA][AC] | [TBA] [BA] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/°C | 147.23 | 237.47 | 124.89 | 146.06 | 111.46 | 120.58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yunus, N.M.; Halim, N.H.; Wilfred, C.D.; Murugesan, T.; Lim, J.W.; Show, P.L. Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption of Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids Containing Acetate and Butyrate Anions. Processes 2019, 7, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110820
Yunus NM, Halim NH, Wilfred CD, Murugesan T, Lim JW, Show PL. Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption of Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids Containing Acetate and Butyrate Anions. Processes. 2019; 7(11):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110820
Chicago/Turabian StyleYunus, Normawati M., Nur Hamizah Halim, Cecilia Devi Wilfred, Thanabalan Murugesan, Jun Wei Lim, and Pau Loke Show. 2019. "Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption of Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids Containing Acetate and Butyrate Anions" Processes 7, no. 11: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110820
APA StyleYunus, N. M., Halim, N. H., Wilfred, C. D., Murugesan, T., Lim, J. W., & Show, P. L. (2019). Thermophysical Properties and CO2 Absorption of Ammonium-Based Protic Ionic Liquids Containing Acetate and Butyrate Anions. Processes, 7(11), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7110820







