Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Experimental Design and Optimization Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reduction of Chromium (VI)
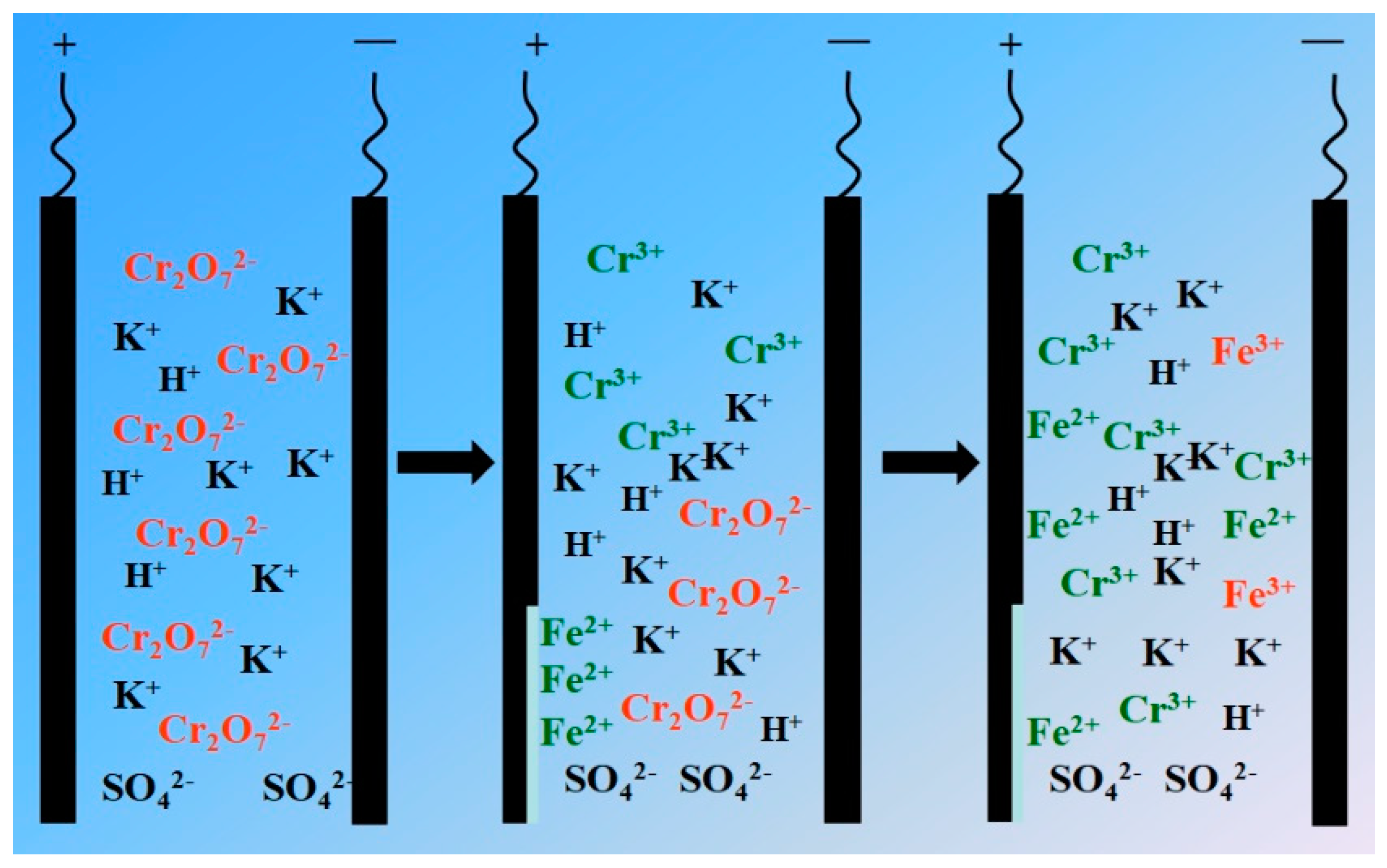
3.1.1. Reaction mechanism
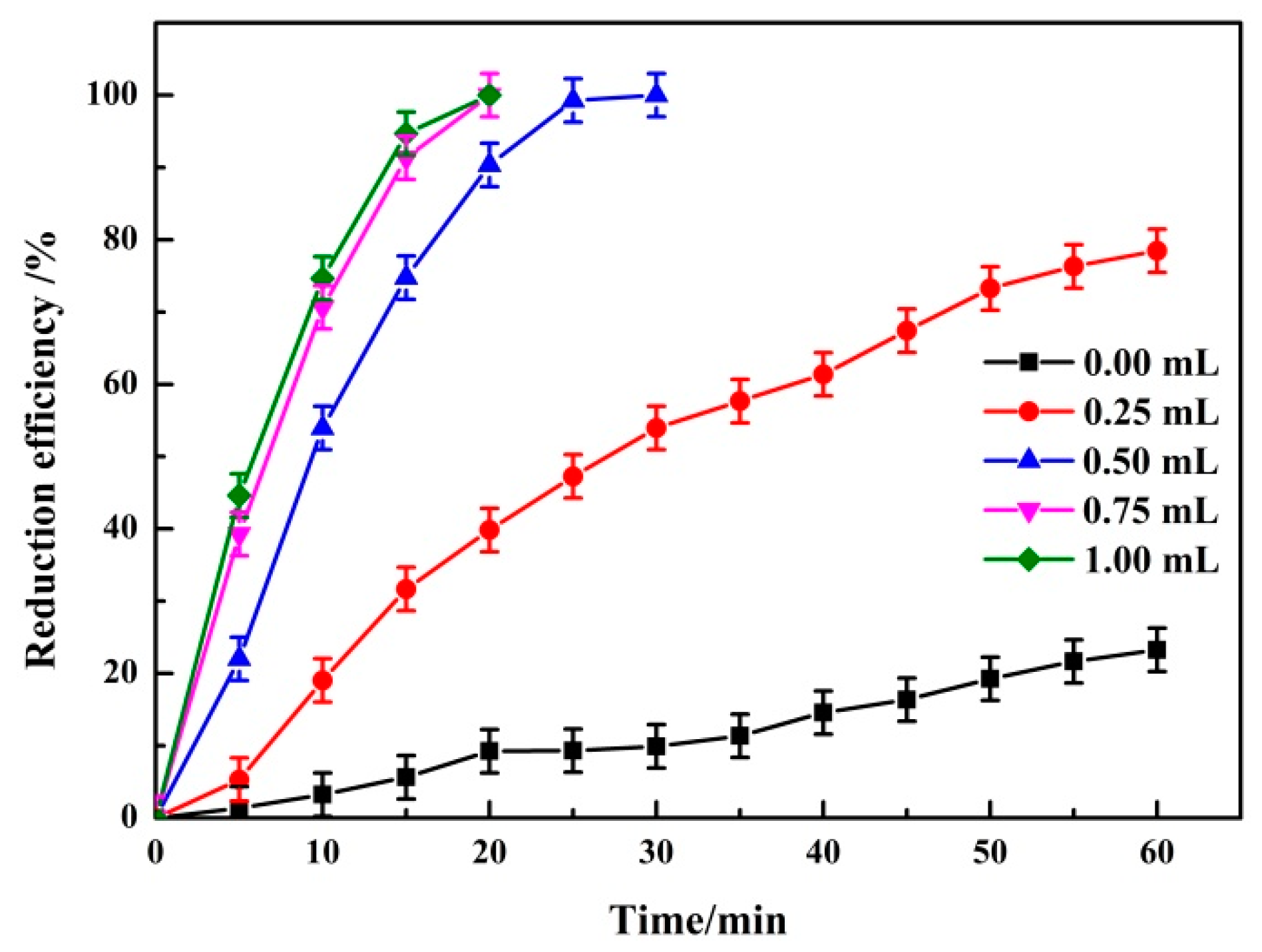
3.1.2. Effect of Dosage of H2SO4
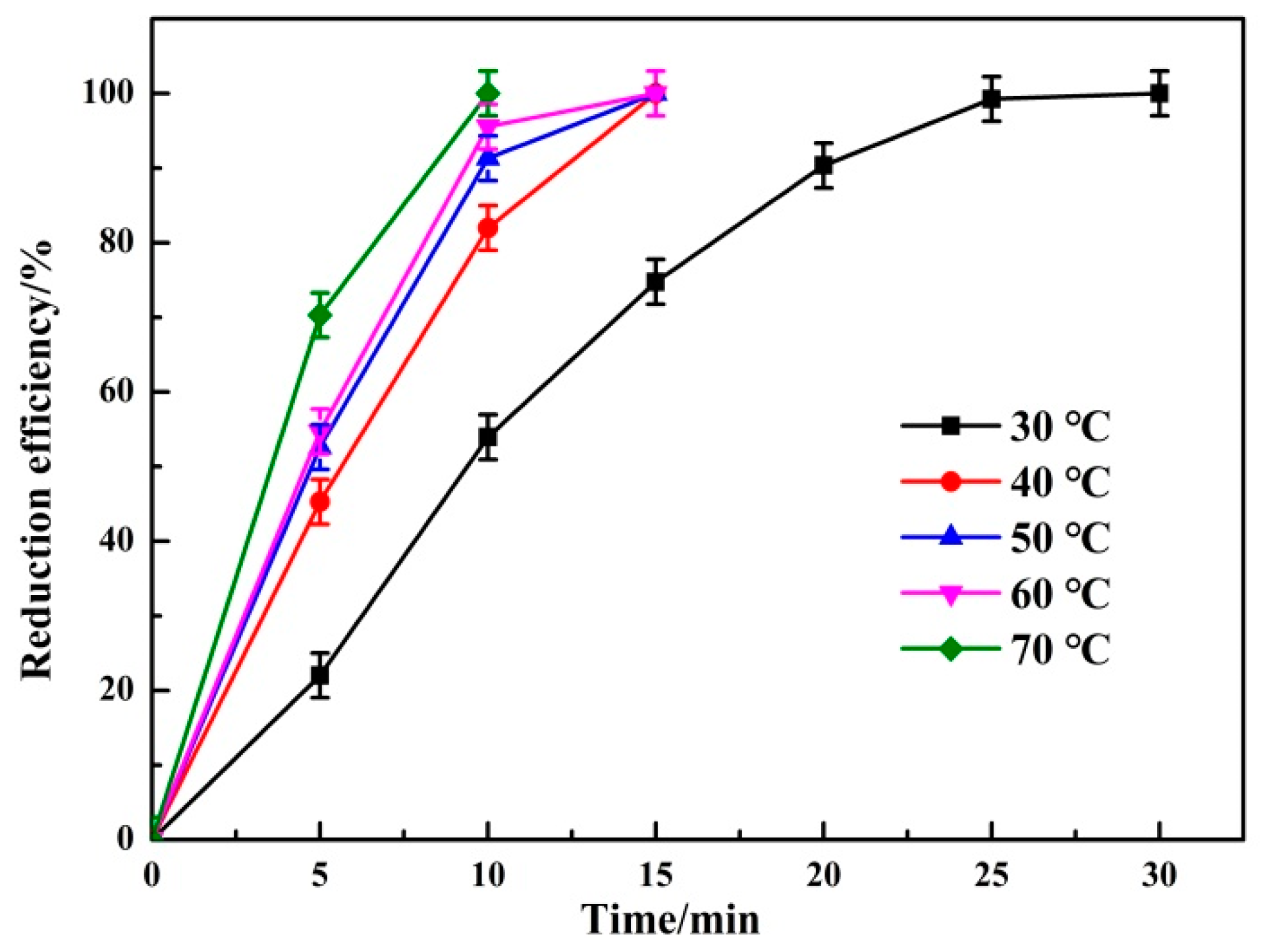
3.1.3. Effect of Reaction Temperature
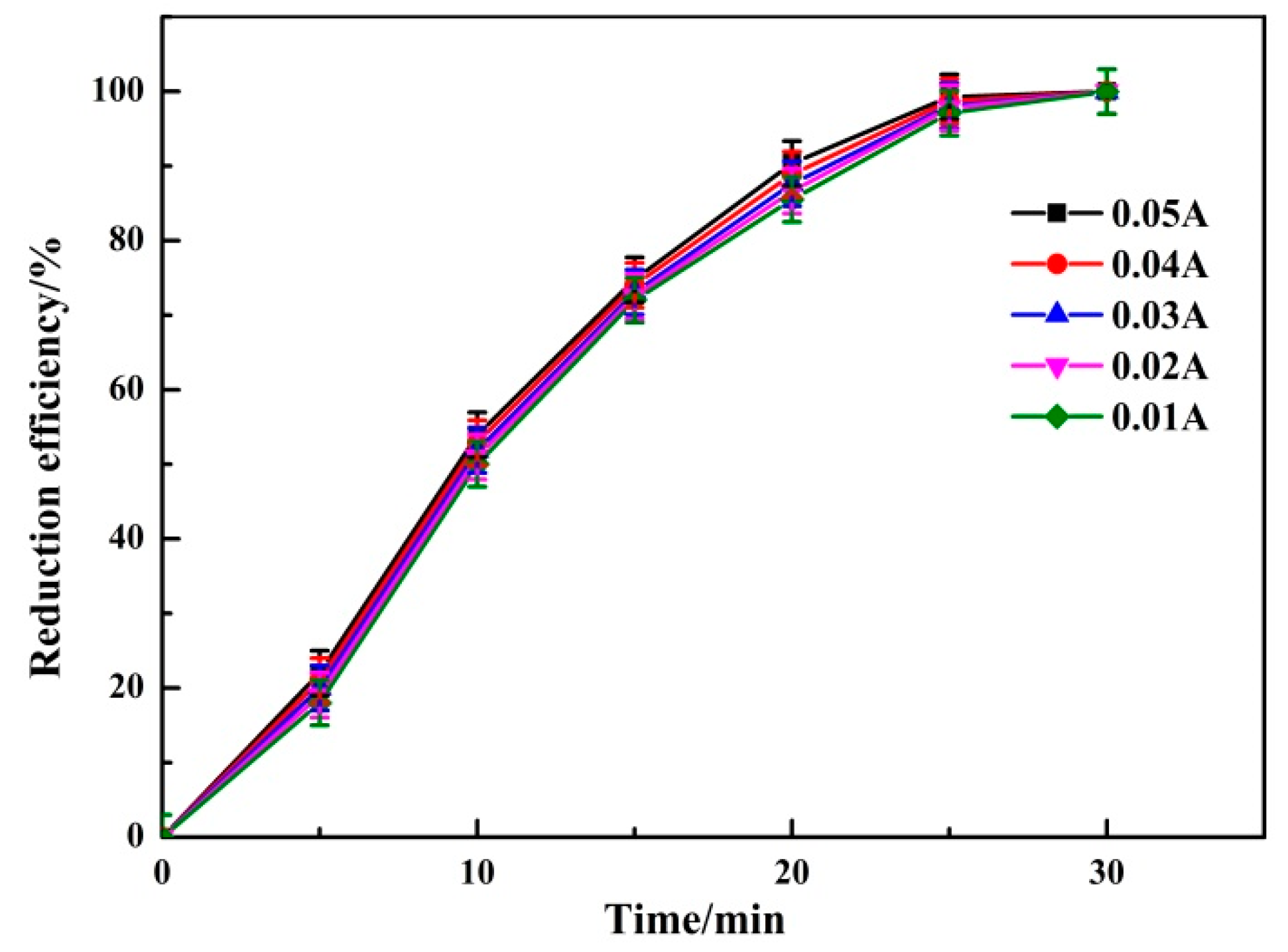
3.1.4. Effect of Current Intensity
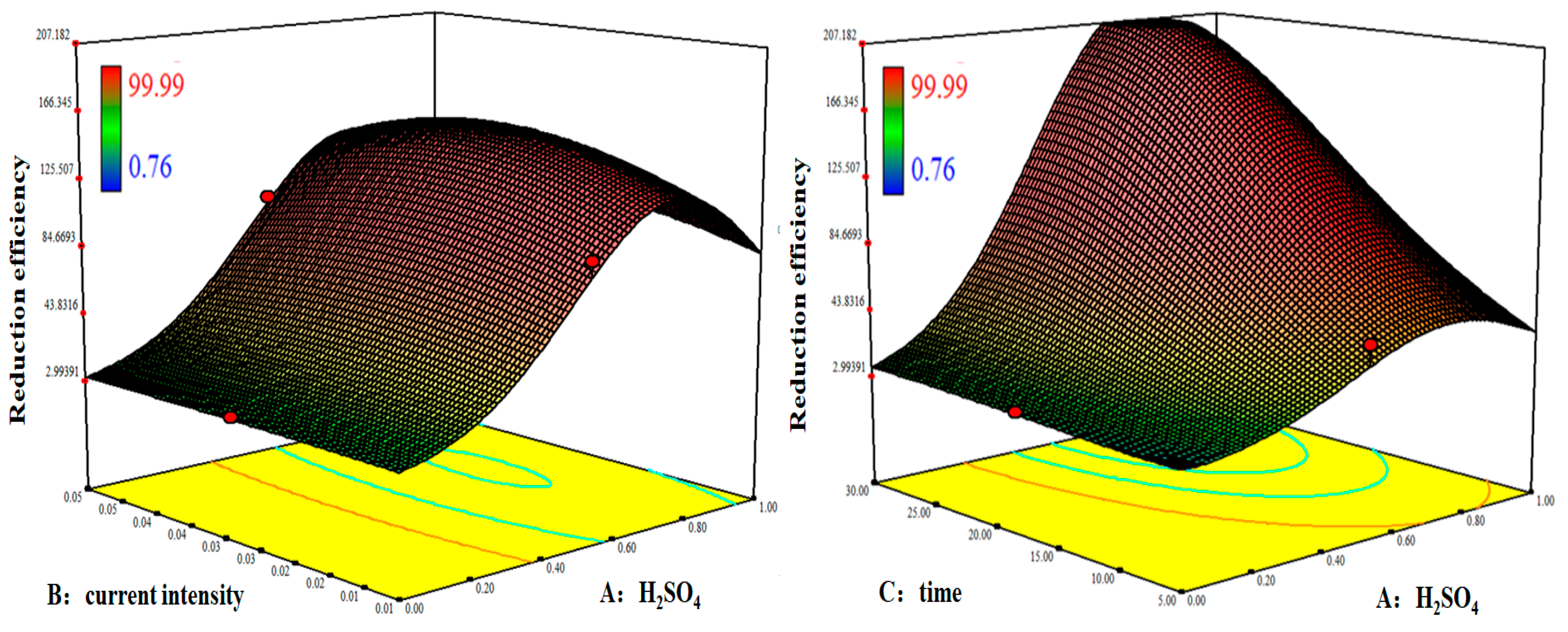
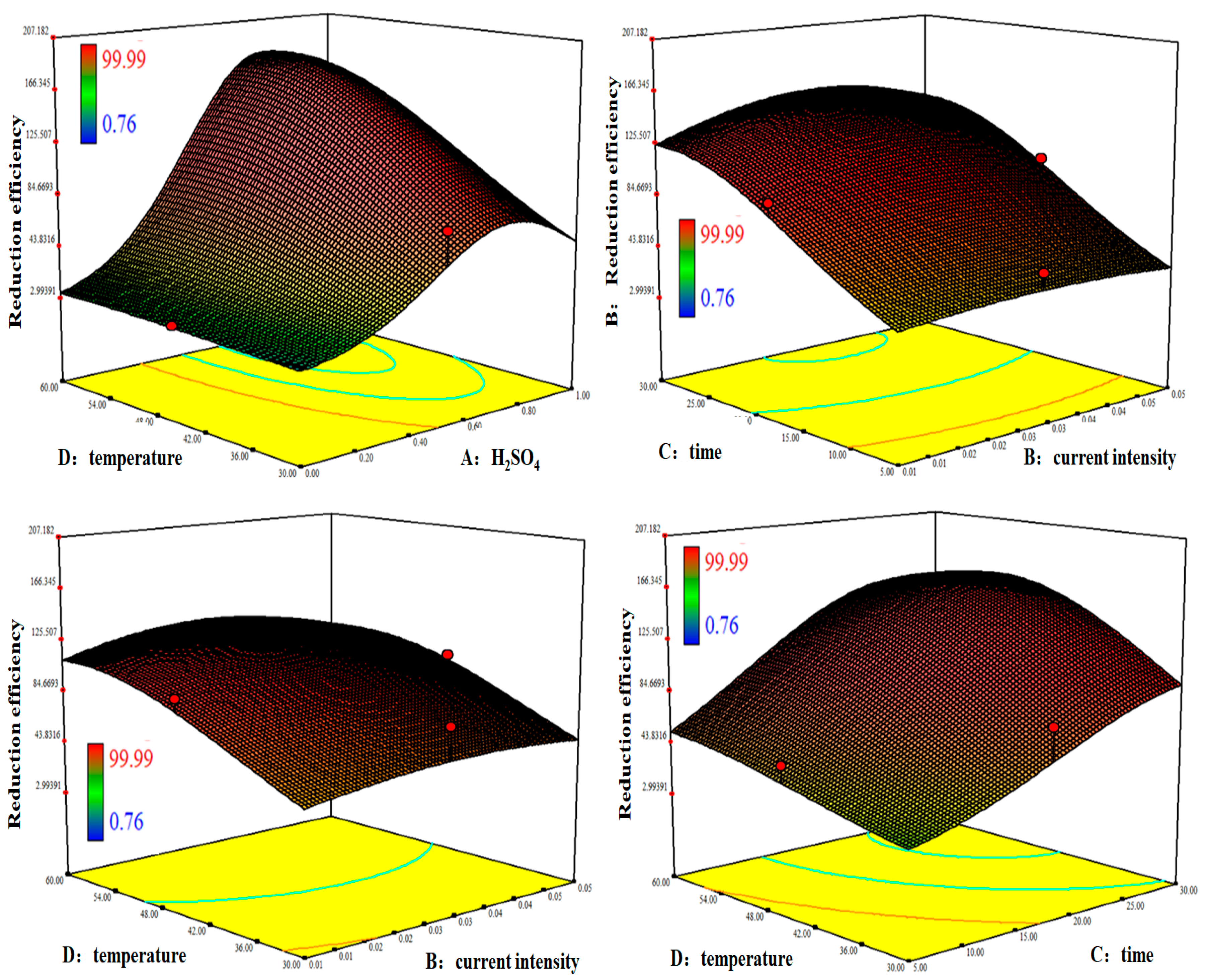
3.2. Response Surface Methodology
3.2.1. Experimental Design
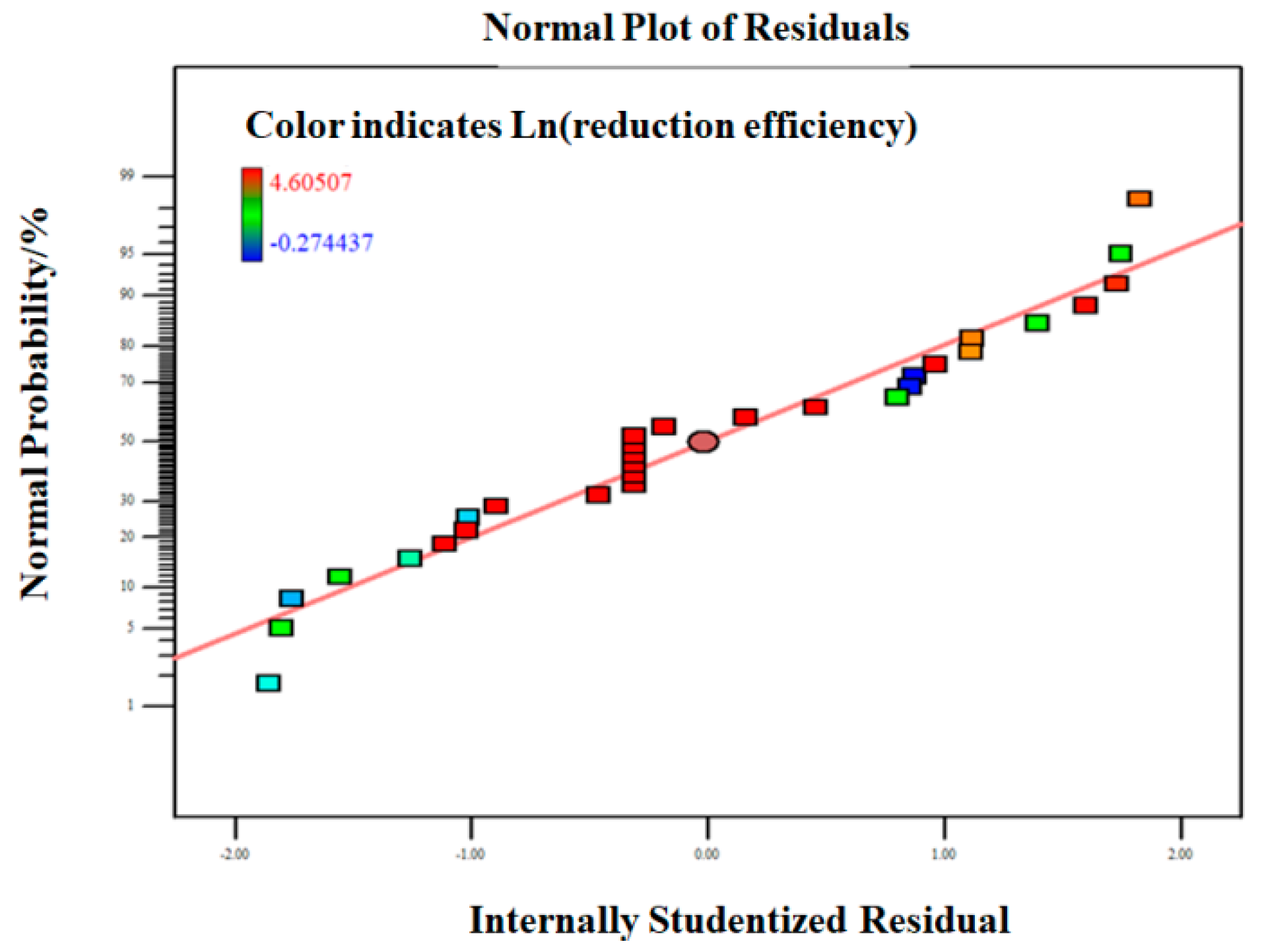
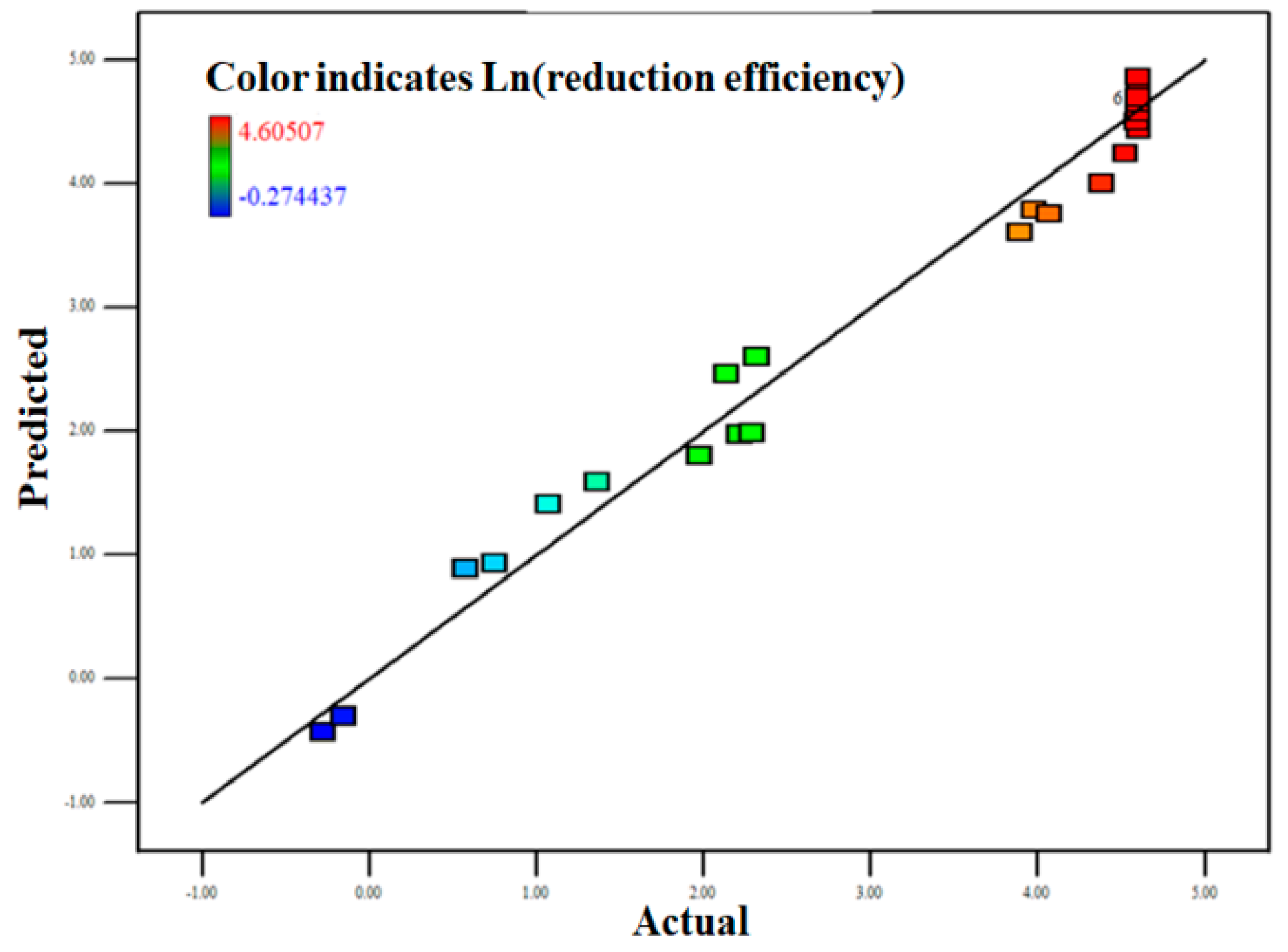
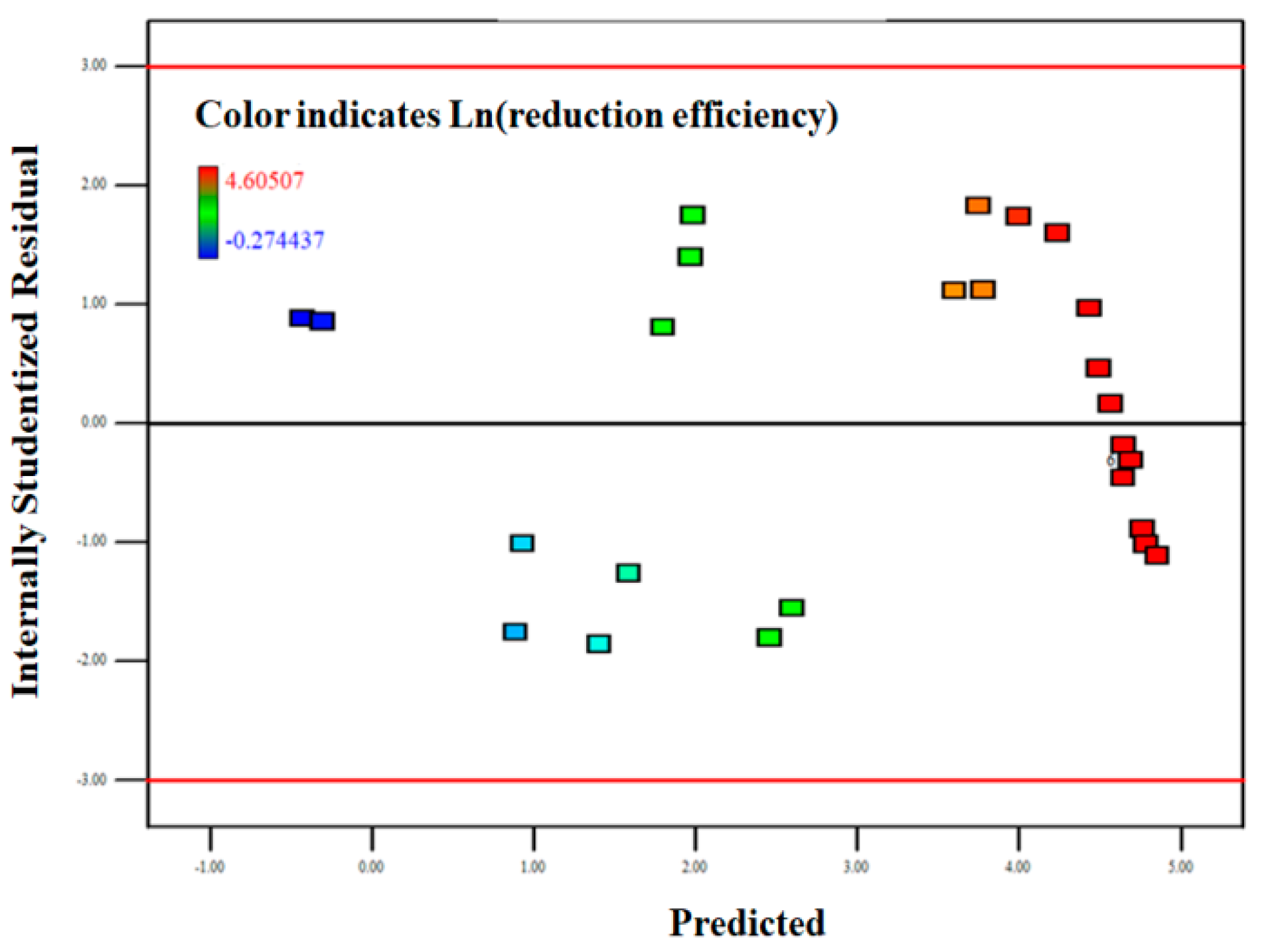
3.2.2. Model Fitting
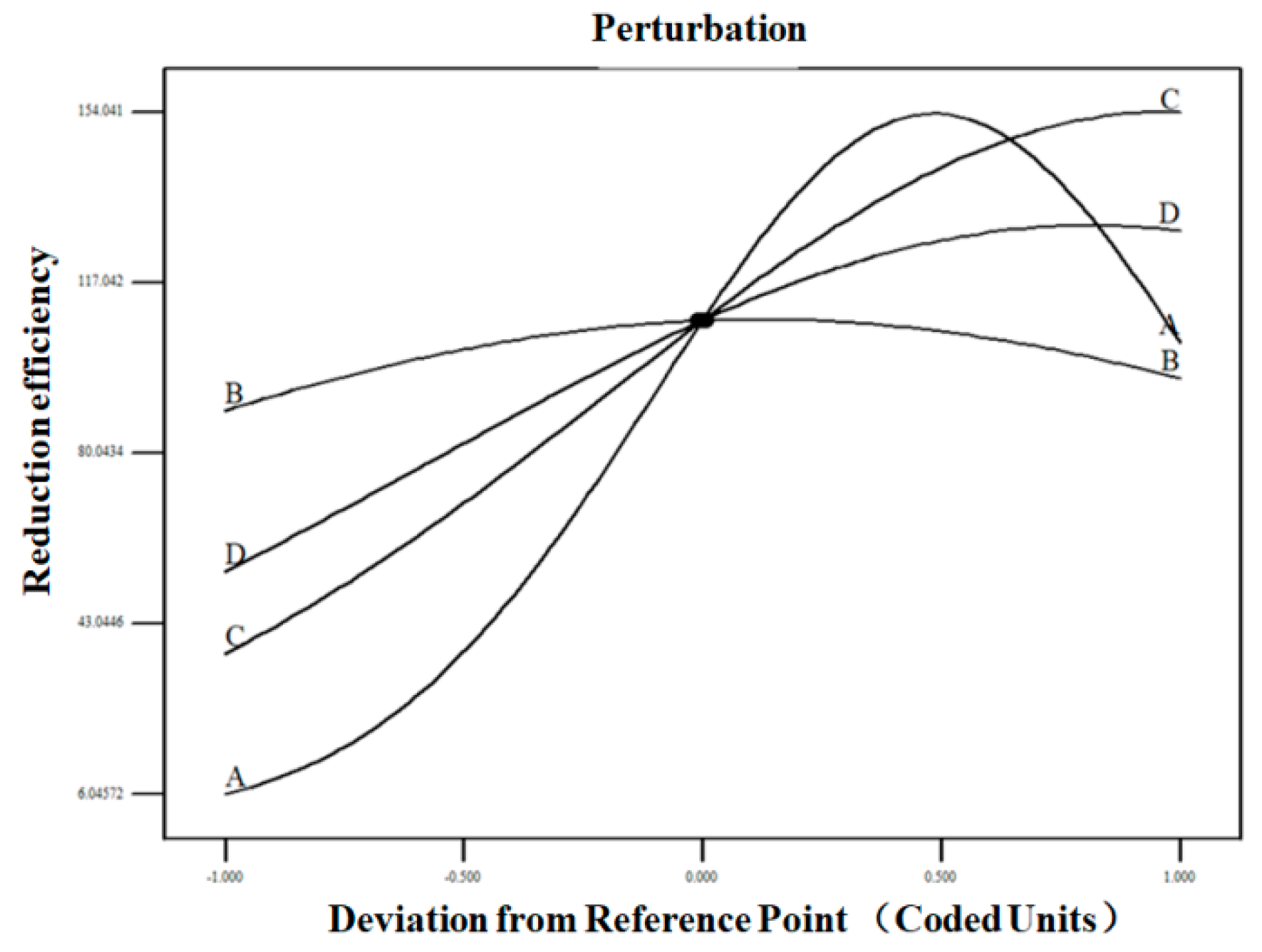
3.2.3. Response Surface Analysis
3.3. Removal of Chromium (III)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, D.; Yang, M.; Fang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, L. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of aqueous phenol and Cr (VI) over visible-light-driven TbxOy loaded TiO2-oriented nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.Y.; Klyamkin, S.N.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Bermesheva, O.V.; Kaloshkin, S.D. Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped by aluminum and chromium. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S56–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, J.; Hua, L.; Cheng, F.; Zhou, L.; Qiao, X. Chromium recovery from tannery sludge by bioleaching and its reuse in tanning process. J Clean Prod. 2017, 142, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, M.; Liang, M.; Ding, B.; Ding, K.; Pan, Y. Organics Wastewater Degradation by a Mesoporous Chromium-Functionalized γ-Al2O3 with H2O2 Assistance. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-R.; Li, H.-B.; Li, X.-Y.; Gu, J.-D. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by ascorbic acid in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, N.; Taghavi, L.; Barikbin, B.; Khodadadi, M. Advantage of almond green hull over its resultant ash for chromium(VI) removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, M.S.; Nayak, V.; Padaki, M.; Balakrishna, R.G.; Soontarapa, K. Eco-friendly membrane process and product development for complete elimination of chromium toxicity in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qiu, X.; Chen, J. Preparation of Fe(II)–Al layered double hydroxides: Application to the adsorption/reduction of chromium. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2017, 516, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, A. Fe3O4 modified mesoporous carbon nanospheres: Magnetically separable adsorbent for hexavalent chromium. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Bi, D.; Zhang, W. Fast and highly efficient removal of chromium (VI) using humus-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Influencing factors, kinetics and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyan, X.; Han, Y.; Cao, X.; Chen, J. Magnetic biochar combining adsorption and separation recycle for removal of chromium in aqueous solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, M.; Yang, B.; Shan, C.; Zhang, W.; He, S.; Lv, L.; Pan, B. Simultaneous removal of As(V) and Cr(VI) from water by macroporous anion exchanger supported nanoscale hydrous ferric oxide composite. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. High-efficient recovery of chromium (VI) with lead sulfate. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 85, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q. Removal of Cr ions from aqueous solution using batch electrocoagulation: Cr removal mechanism and utilization rate of in situ generated metal ions. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Wu, S. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by different surface-modified biochars: Acid washing, nanoscale zero-valent iron and ferric iron loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, G.; Li, P.; Gu, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, C. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from groundwater by Fe 0 -H 2 O system with bio-amended iron corrosion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhat-Thien, N.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chen, S.-S.; Nguyen-Cong, N.; Chang, C.-T.; Hsiao, S.-S.; le Thuy, T.; Kao, C.-Y.; Lin, M.-F.; Wang, L. Preparation of Zn-Doped Biochar from Sewage Sludge for Chromium Ion Removal. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 5520–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tsang, E.P. Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, L.; Sun, D.; Tan, X. Entrapment of nanoscale zerovalent iron in chitosan beads for hexavalent chromium removal from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Qin, Y.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y. Electrochemical decomposition of vanadium slag in concentrated NaOH solution. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. Selective leaching of vanadium from chromium residue intensified by electric field. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C. Leaching Kinetics of Vanadium with Electro-oxidation and H2O2 in Alkaline Medium. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7802–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Lakshmi, J.; Sozhan, G. Studies on the Removal of Iron from Drinking Water by Electrocoagulation—A Clean Process. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Moein, H.; Mostafapour, F.K.; Nakhaie, S. Application of Electrocoagulation Process for Dairy Wastewater Treatment. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 640139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, O.; Mazumdar, B.; Chaudhari, P.K. Treatment of wastewater by electrocoagulation: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2397–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Neumann, I. Optimal finite element model with response surface methodology for concrete structures based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning technology. Compos. Struct. 2018, 183, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.P.; Faroni, L.R.D.; Heleno, F.F.; Pinto, F.G.; Queiroz, M.; Prates, L.H.F. Ozone treatment for pesticide removal from carrots: Optimization by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, S.; Niad, M. Cystoseira myricaas for mercury (II) uptake: Isotherm, kinetics, thermodynamic, response surface methodology and fuzzy modeling. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 81, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Tan, L.; Xu, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y. Optimization of Processing Parameters for Lettuce Vacuum Osmotic Dehydration Using Response Surface Methodology. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Shad, M.A.; Rauf, A. Optimization of extraction yield and antioxidant properties of Brassica oleracea Convar Capitata Var L. leaf extracts. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosid, S.J.M.; Bakar, W.A.W.A.; Ali, R. Characterization and modelling optimization on methanation activity using Box-Behnken design through cerium doped catalysts. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, S.; Liu, B.; Ge, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Separation and recovery of vanadium and chromium from acidic leach solution of V-Cr-bearing reducing slag. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4702–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent Parameter | Unit | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| A: H2SO4 | mL | 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| B: Current Intensity | A | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| C: Reaction Time | min | 5 | 17.5 | 30 |
| D: Reaction Temperature | °C | 30 | 45 | 60 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Z | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value Prob > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 79.95 | 14 | 5.71 | 61.87 | <0.0001 |
| A | 36.48 | 1 | 36.48 | 395.23 | <0.0001 |
| B | 0.025 | 1 | 0.025 | 0.27 | 0.6080 |
| C | 9.40 | 1 | 9.40 | 101.82 | <0.0001 |
| D | 3.31 | 1 | 3.31 | 35.83 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 1.38 | 15 | 0.092 | - | - |
| Lack-of-fit | 1.38 | 10 | 0.14 | - | - |
| Pure error | 0.000 | 5 | 0.000 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.; Leng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Shang, Q.; Shu, J.; Guo, J. Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction. Processes 2019, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010041
Peng H, Leng Y, Cheng Q, Shang Q, Shu J, Guo J. Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction. Processes. 2019; 7(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010041
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Hao, Yumeng Leng, Qinzhe Cheng, Qian Shang, Jiancheng Shu, and Jing Guo. 2019. "Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction" Processes 7, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010041
APA StylePeng, H., Leng, Y., Cheng, Q., Shang, Q., Shu, J., & Guo, J. (2019). Efficient Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Wastewater with Electro-Reduction. Processes, 7(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010041






