Abstract
Ion-sieves are a class of green adsorbent for extraction Li+ from salt lakes. Here, we propose a facile synthesis of hexagonal spinel LiMn2O4 (LMO) precursor under mild condition which was first prepared via a modified one-pot reduction hydrothermal method using KMnO4 and ethanol. Subsequently, the stable spinel structured λ-MnO2 (HMO) were prepared by acidification of LMO. The as-prepared HMO shows a unique hexagonal shape and can be used for rapid adsorption-desorption process for Li+ adsorption. It was found that Li+ adsorption capacity of HMO was 24.7 mg·g−1 in Li+ solution and the HMO also has a stable structure with manganese dissolution loss ratio of 3.9% during desorption process. Moreover, the lithium selectivity reaches to 1.35 × 103 in brine and the distribution coefficients () of Li+ is much greater than that of Mg2+. The results implied that HMO can be used in extract lithium from brine or seawater containing high ratio of magnesium and lithium.
1. Introduction
Lithium and its compounds—known as “industrial monosodium glutamate” [1]—are widely used in significant fields such as batteries, ceramics, glass, alloy, lubricants, refrigerants and the nuclear industry [2,3]. The lithium reserves in China are the world’s second-largest, which are primarily distributed in the salt lakes of Qinghai and Tibet [4]. However, the ratio of magnesium to lithium in the salty brine is extremely high, making it difficult to extract and recover lithium using conventional separation technologies [5,6]. Compared with precipitation and solvent extraction methods, ion-sieve adsorption has many technical merits, such as excellent selectivity and relatively low cost [7,8], which is considered to be the most promising environmentally benign technology for extracting lithium from salt lakes [9,10].
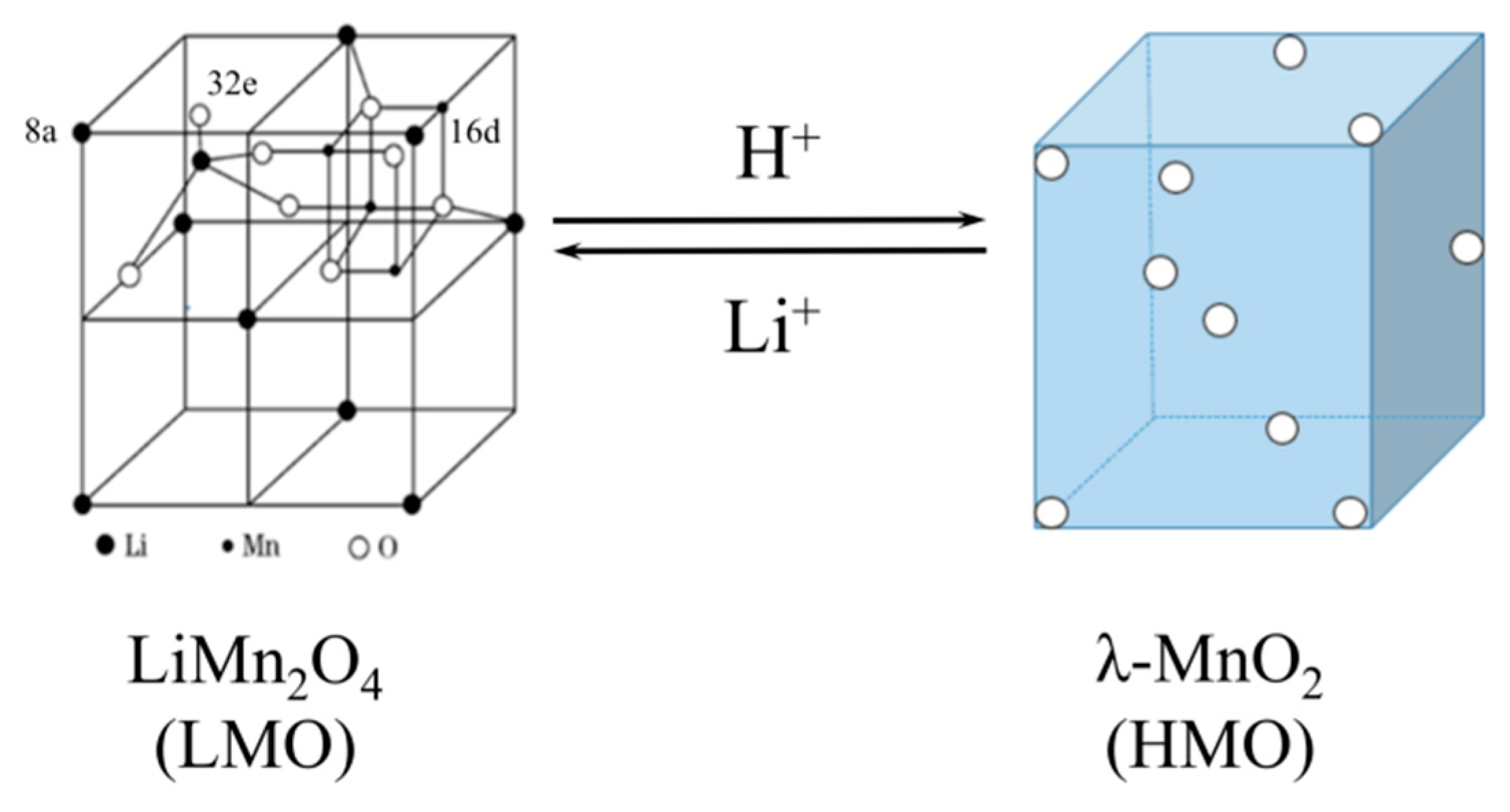
Manganese series spinel ion-sieves are widely used in lithium ion adsorption, which primarily includes λ-MnO2, MnO2·0.3H2O and MnO2·0.5H2O, after removal of lithium by acidification from precursors LiMn2O4 [11], Li4Mn5O12 [12,13] and Li1.6Mn1.6O4 [14,15,16], respectively. LiMn2O4 (LMO) is commonly used adsorbent precursor8, which is fabricated through embedding the target Li+ in the Mn-O chemical skeleton to construct composite LixMnyOz. After extracting Li+ by acidification without damages in the structure, of λ-MnO2 (HMO) with regular vacancy [17]. The cubic spinel structures and adsorption-desorption relationship of HMO and LMO is shown in Figure 1. Oxygen atoms(O), Mn3+/Mn4+ and lithium atoms (Li) occupy 32 e, 16 d and 8 a of the Wyckoff site, respectively [18]. Then, lithium at the 8a position is extracted by hydrogen because of ion exchange process which can adsorption Li+ subsequently.
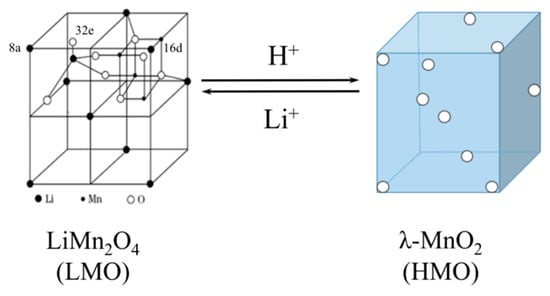
Figure 1.
Illustrated microstructures of LiMn2O4 and λ-MnO2.
In general, existing methods of preparing LMO can be boiled down to two categories, the solid-phase and the liquid-phase. Yuan et al. [19] utilized Li2CO3 and MnCO3 (Li/Mn molar ratio was 0.5) as raw materials and calcined the mixture at 800 °C in air for 5 h to obtain the LMO. Park et al. [20] prepared spinel LMO by a simple spray mixed Li(NO)3 and Mn(NO)3 pyrolysis at 700 °C, with the deficiencies of inhomogeneity and large particle sizes (1 μm). The above-mentioned solid-phase LMO preparation methods often require high energy consumption and involve multiple steps. Besides, they always result in yielding large size particles because of agglomeration which decrease its contact area with solution for Li+ extraction. The liquid-phase method (also known as soft-chemical process) for fabrication of LMO usually exhibits high purity, excellent crystal integrity and good dispersion. Tang et al. [21] prepared a nano-chain LMO using a sol-gel method. LiNO3 and Mn(NO3)2 were stirred with the assistance of the starch at 110 °C for 1.5 h, followed by heating at 250 °C for 3 h and a thermal treatment at 700 °C for 3 h. Xiao et al. [22] prepared the ultrafine LMO powder by mixing Mn(NO3)2 with ammonia to produce precipitate, then they impregnated the precipitate with LiOH·H2O and calcined the mixture at 830 °C for 8 h. Zhang et al. [23] prepared cubic phase LMO via a hydrothermal method by reacting Mn(NO3)2 with LiOH and H2O2 at 110 °C for 8 h. Despite the liquid-phase method being well investigated and developed, simplifying LMO synthetic process and improving the adsorbing ability and selectivity are still challenging. The existing methods mainly use LiOH·H2O solution or acidic salts as raw materials. To our best knowledge, neutral synthetic routes through one-pot hydrothermal reaction to produce LMO and the corresponded HMO are rarely reported. Besides, HMO synthesized from high-valence manganese always shows higher adsorption capacity and selectivity than that of HMO synthesized from low-valence manganese, which is beneficial for lithium extraction from brine with high Li+/Mg2+ ratio.
In this study, a series of LMO was prepared by a facile one-pot hydrothermal method using ethanol as reductant, KMnO4 and LiCl·H2O as precursors. We first optimized several synthetic parameters (i.e., LiCl·H2O concentration, mass of KMnO4, volume of ethanol, reaction time and reaction temperature) in preparing of LMO. Then we prepared the stable HMO by acidification treatment of LMO. The crystallization phase, morphology characteristic and chemical phase of as-prepared ion-sieves were systematically investigated. The Li+ adsorption performance of HMO was studied and relevant adsorption kinetic model and adsorption isotherm were fitted. Finally, Li+ extraction capacity and selectivity in brine containing high ratio of Mg2+ and Li+ were studied.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of LMO and HMO Ion Sieve
All chemicals used in this work are AR reagents unless otherwise noted. The detailed synthetic parameters are given in Table 1. Briefly, a certain amount of LiCl·H2O and KMnO4 were added to 75 mL deionized water. Then, ethanol was dropwise added into the mixed homogeneous solution. The final solution was obtained with the addition of deionized water to 150 mL. Next, the solution was transferred into a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-lined stainless-steel autoclave, heated at the specified temperatures (130–180 °C) for the specified time and cooled naturally to room temperature. The black precipitate was collected, filtered, washed completely and then dried at 80 °C for 12 h to obtain the as-prepared LiMn2O4 (LMO). Subsequently, the obtained LMO was added in hydrochloric acid solution (0.1 mol·L−1) at 20 °C for 24 h until the lithium were completely extracted. The resulting precipitate was filtered, washed completely and dried at 80 °C for 12 h to obtain the λ-MnO2 (HMO).

Table 1.
Experimental parameters of synthesis LiMn2O4 (LMO) at different schemes.
2.2. Characterization
The phase composition of the samples was characterized by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD, Mini Flex600, Rigaku Coporation, Tokyo, Japan with monochromatized Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54056 Å), operating at 40 kV and 15 mA, with a scanning rate of 20°/min from 10° to 80°. The concentration of each ion was measured by Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP, Optima 7000DV, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA), which was used to examine adsorption/desorption activity of the samples. The morphology of the samples was examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) while morphology and crystal lattice were obtained by high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM, Libra120, Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany). The chemical phase of manganese in the sample was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, EscaLab 250Xi, Thermo Fisher, Shang Hai, China), with AlKα radiation (hv = 1103 eV), C1s of 20.05 eV to calibration.
2.3. Adsorption Behavior
2.3.1. Adsorption Capacity Test at Different pH Value
The lithium ion adsorption behavior test was measured by stirring (200 rpm) 0.1 g HMO in 500 mL LiCl·H2O solution (pH value: 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11, respectively), adjusted by a buffer solution composed of 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4Cl and 0.1 mol·L−1 HCl and 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4OH) with a uniform initial concentration of lithium ions (50 mg·L−1) at 18 °C for 12 h.
The adsorption capacity is calculated by Equation (1).
where C0 is the initial concentration of metal ions (mg·L−1); Ct is the concentration of metal ions at time t (mg·L−1); V is the volume of solution (L); and W is the weight of HMO ion sieve (g).
2.3.2. Static Kinetic Test
The lithium ion adsorption behavior test was measured by stirring (200 rpm) 0.1 g HMO in 500 mL LiCl·H2O solution (Ph = 10, adjusted by a buffer solution composed of 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4Cl and 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4OH) with a uniform initial concentration of lithium ions (50 mg·L−1) at 18 °C for 12 h.
The data of the HMO adsorption capacity was fitted by a simplified Crank’s single-hole diffusion model to obtain an efficient film coefficient (De) by Equation (2) [24,25].
where Q∞ is the adsorption capacity at the final time(mg·L−1); De is the diffusion coefficient (cm2·s−1); and r is the particle size of the adsorbent (cm).
The pseudo-first-order kinetic model (Equation (3)) and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model (Equation (4)) were used to simulate the saturated adsorption curve, aimed to confirm the kinetic constant of the adsorption process.
where Qe is the adsorption capacity when it reaches the adsorption equilibrium (mg·L−1); Qt is the adsorption capacity calculated with Equation (1); K1 is the adsorption rate constant of the pseudo-first-order kinetic model; and K2 is the adsorption rate constant of pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
2.3.3. Adsorption Isotherm Test
The lithium ion adsorption behavior test was measured on HMO (0.04, 0.075, 0.11, 0.15 and 0.19 g) in 500 mL initial concentrations (10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 mg·L−1 LiCl·H2O solution) were added to five flasks respectively, (Ph = 10, adjusted by a buffer solution composed of 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4Cl and 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4OH). The flasks were shaken on a shaker at 200 rpm at 18 °C for 12 h.
The adsorption isotherm curve is fitted according to the following isotherm models:
Langmuir isotherm model:
Freundlich isotherm model:
where is the theoretically calculated maximum adsorption capacity; is the Langmuir constant; is the Freundlish constant; and is an empirical constant.
2.4. Selective Adsorption Behavior
The selectivity of lithium ions compared with other coexisting ions in brine was adjusted pH value to 10 by 0.1 mol·L−1 NH4OH, carried out by stirring (200 rpm) 0.1 g ion sieve in 20 mL saline brine at 20 °C for 72 h. The adsorption capacity of metal ion at equilibrium (Qe), distribution coefficient (Kd), separation factor () and concentration factor () are calculated according to the following equations:
where C0, Me is the initial concentrate of ions in brine (mg·L−1); Ce, Me is the final concentrate of ions in brine after adsorption (mg·L−1); V is the volume of solution (L); W is the weight of the HMO ion sieve (g); Qe, Me is the saturated adsorption capacity of ions in brine (mg·g−1).
2.5. Desorption Behavior
LMO was renamed LMO-1 after the Li+ adsorption of the HMO. The curve of the Li+ extraction and manganese dissolution was carried out by stirring (200 rpm) 0.1 g LMO-1 in 500 mL hydrochloric acid solution (0.04 mol·L−1) for 24 h at 20 °C. The extraction ratio of lithium and the dissolution loss ratio of manganese were calculated using Equation (10).
where is the extraction ratio of lithium or dissolution loss ratio of manganese; is the element concentration of different times; V is the solution volume and is the weight of in the LMO-1. The influence of hydrochloric acid concentration was studied by stirring (200 rpm) 0.05 g LMO-1 in 100 mL hydrochloric acid solution (0.02–0.1 mol·L−1) for 12 h at 20 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Synthesis Parameters
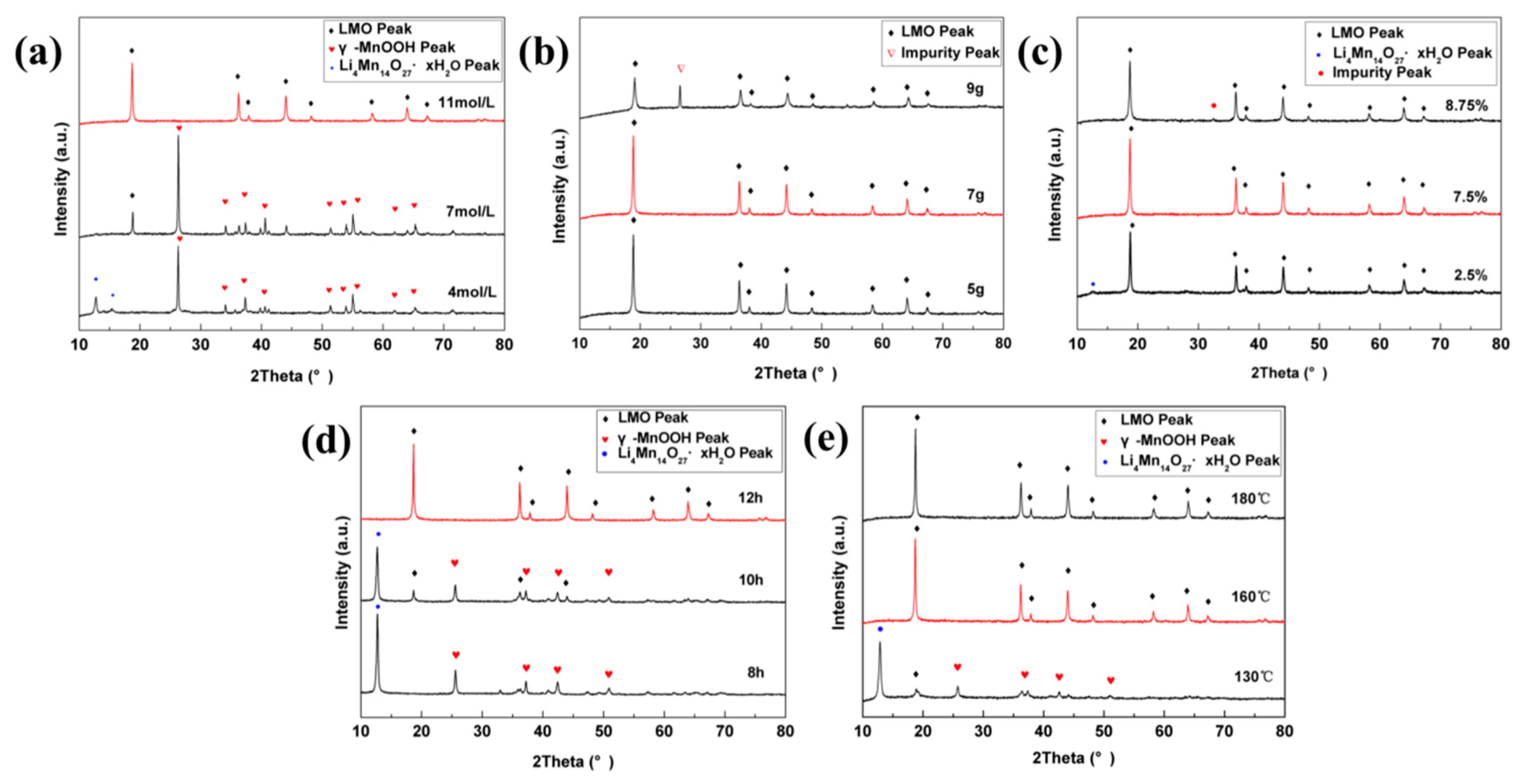
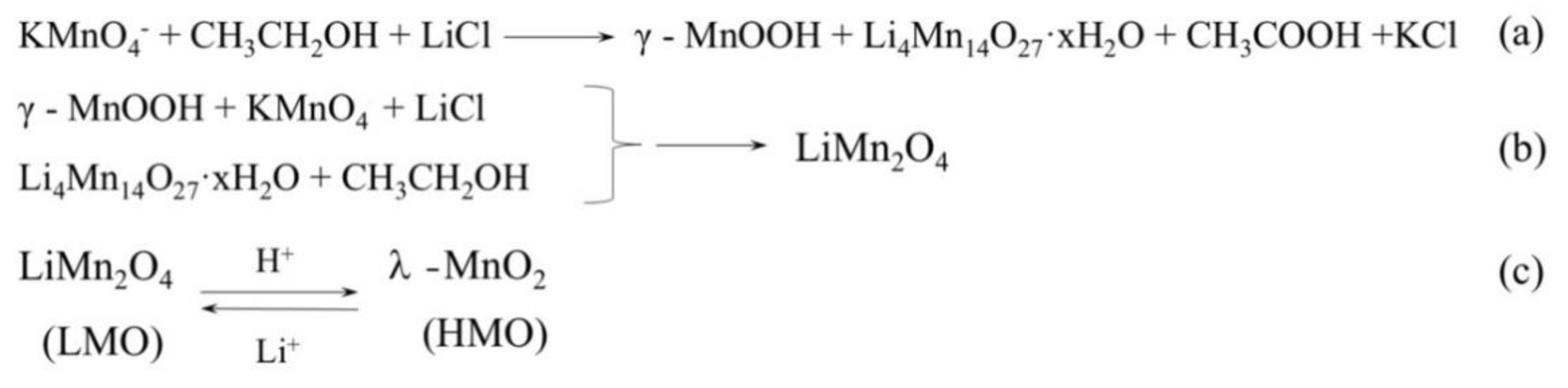
The XRD patterns of the products obtained under different conditions are shown in Figure 2. Figure 2a shows intermediate γ-MnOOH (JCPDS cards no. 50-0009) was produced at low Li+ concentration. With the increase of Li+ (>11 mol·L−1), the target LMO was produced and intermediate γ-MnOOH was disappeared. Figure 2b indicates that with the increase of the amount of KMnO4, the LMO lattice structure becomes stable gradually but when the amount of KMnO4 was above 9 g, the impurity (∇) was generated. Figure 2c shows that using lower ethanol volume in the synthesis process resulted in the formation of intermediate Li4Mn14O27·xH2O (JCPDS cards no. 41-1379). When the volume fraction increases above 8.75%, the impurity peak (•) was observed. Figure 2d showed that the intermediate Li4Mn14O27·xH2O and γ-MnOOH were first formed within a short reaction time and LMO could be obtained after 12-h reaction. Figure 2e reflects the effect of reaction temperature on the LMO. Li4Mn14O27·xH2O and γ-MnOOH were produced at the lower temperature and LMO could be synthesized when the reaction temperature over 160 °C. Thus, we found the optimal LMO could be obtained at Li+ concentration of 11 mol·L−1, hydrothermal reaction at 160 °C for 12 h, ethanol volume fraction of 7.5%, using 3 g of KMnO4. We speculate the synthesis is followed by the mechanism illustrated in Figure 3. In LiCl·H2O solution, KMnO4 is firstly reduced by ethanol and the intermediates Li4Mn14O27·xH2O and γ-MnOOH are formed. Then γ-MnOOH is oxidized by KMnO4 and Li4Mn14O27·xH2O is furthered reduced by ethanol simultaneously. Finally, the lithium ion enters the Mn-O framework to form cubic LMO with the increase of lithium concentration.
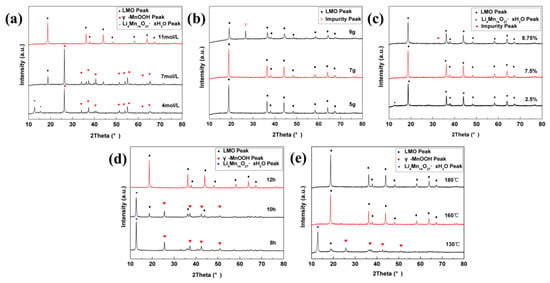
Figure 2.
X-Ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of resultant under different preparation conditions: (a) the concentration of Li+; (b) the amount of KMnO4; (c) the volume ratio of ethanol; (d) reaction time; (e) reaction temperature.
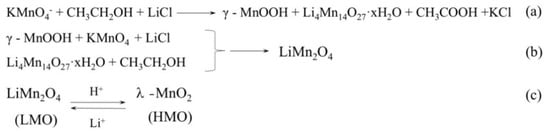
Figure 3.
Synthetic mechanisms: (a,b) synthesis of LMO; (c) absorption-desorption mechanism of λ-MnO2 (HMO) and LMO.
3.2. Ion-Sieves Characterization
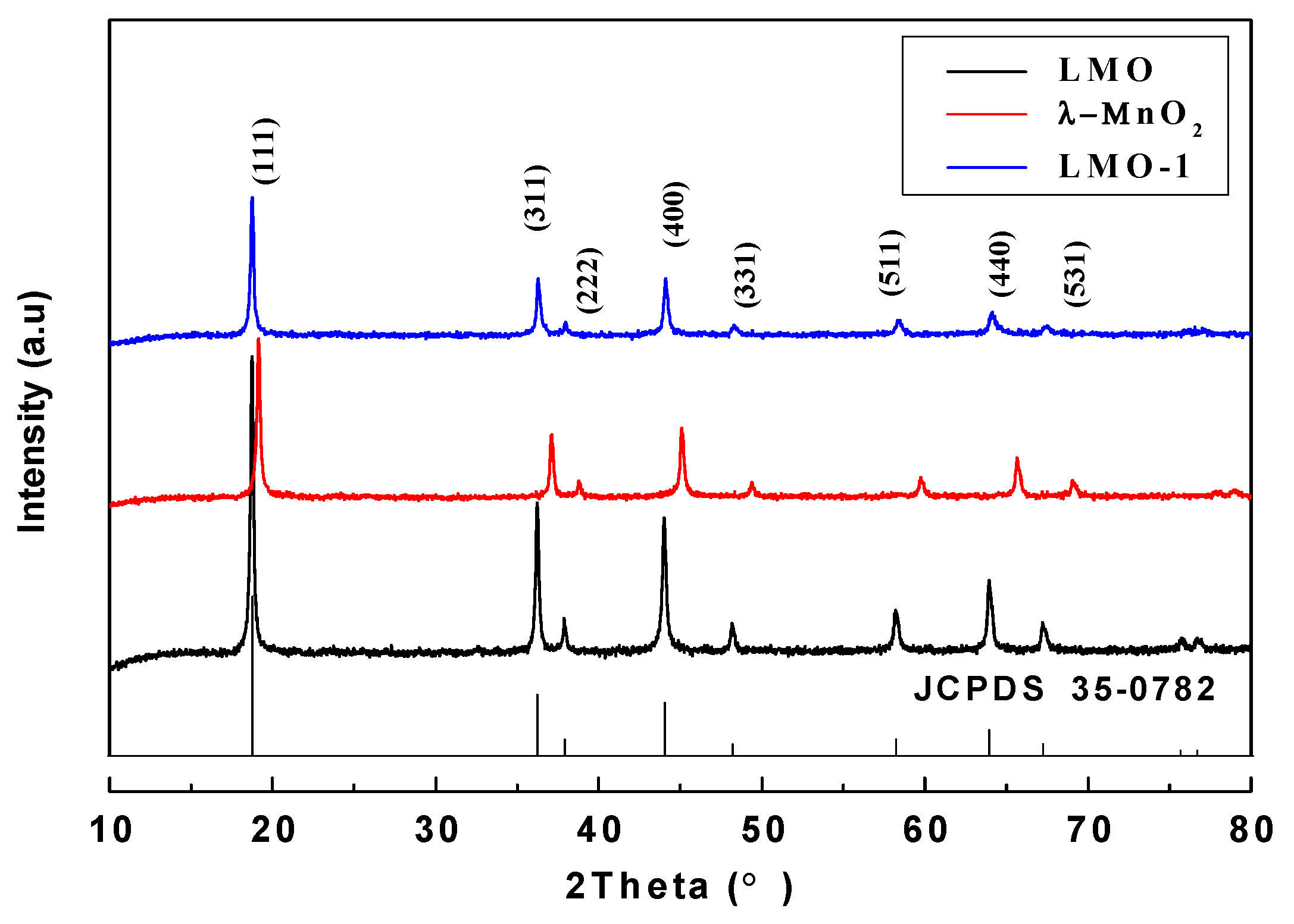
Figure 4 shows the XRD patterns of the LMO, HMO and the sample after adsorption process (noted as LMO-1). The diffraction peak of LMO corresponds to a cubic spinel HMO structure [space group: Fd3m (JCPDS 35-0782)], with the lattice constants is 8.23 Å. It should be noted that the XRD patterns of HMO and LMO-1 are similar with the diffraction patterns of LMO, with lattice constants of 8.01 Å and 8.23 Å, respectively, indicating that the Li+ is free to access the structure and the Mn-O lattice remains stable during the adsorption and desorption process. It is found that the diffraction peak of HMO shifts to a higher diffraction angle than that of LMO, which can be explained by the mechanism showed in Figure 3c. During the Li+ desorption process, H+ in the solution replaces the original position of Li+ in the LMO the ionic radius of H+ is smaller than Li+, leading to cell shrinkage, which is also reported in literature [26]. The characteristic diffraction peaks of LMO-1 are still sharp and only the intensities decreased compared with the LMO, indicating that the HMO can be used for efficient adsorption of Li+.
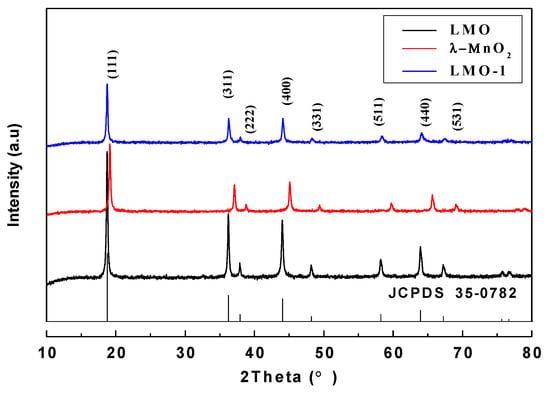
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of optimized LMO, HMO and LMO-1.
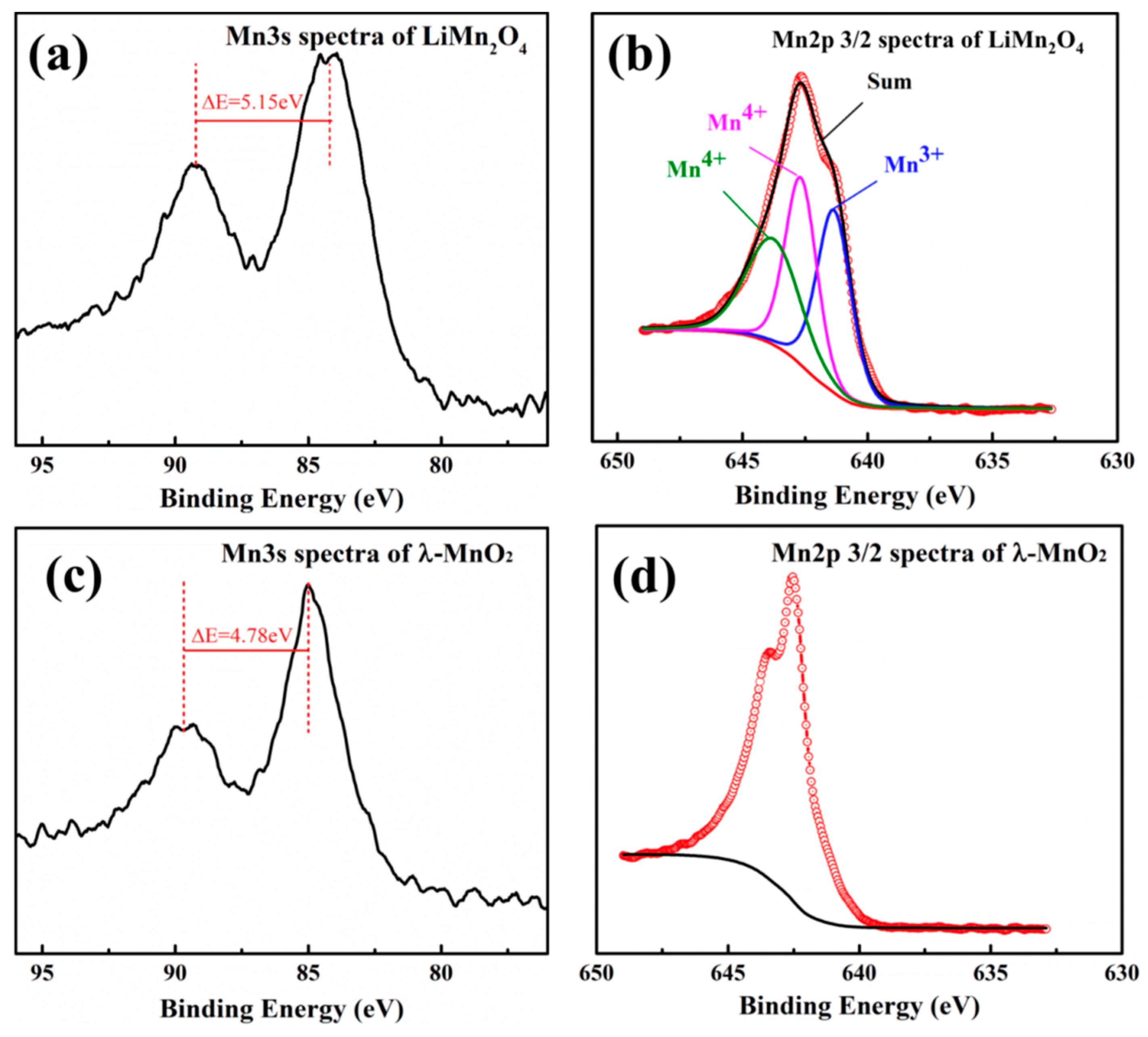
Figure 5 describes the XPS spectra of LMO and HMO. As showed in Figure 5a, the spectra of the Mn3s orbit shows the binding energy difference of the two peaks was 5.15 eV (ΔE = 5.15 eV), indicating that the valences of Mn in LMO are +3 and +4. The binding energy of Mn3+ peak was 641.33 eV and Mn4+ peaks were 643.76 eV and 642.66 eV, which were obtained by means of peak-differentiation-imitating analysis at the Mn2p3/2 orbit (Figure 5b). The results are in line with a previous report [27]. The average valence of Mn in LMO (+3.65) could be calculated (Table 2), which is higher than the theoretical valence (+3.5), indicating that proportion of Mn3+ in LMO is lower than theoretical. Thus, it can be deduced that LMO has a more stable crystal structure. Figure 5c is the XPS spectra of HMO in the Mn3s orbit and the binding energy difference of the two peaks is 4.78 eV, indicating that the manganese valence in HMO is +4. Furthermore, this is also proven by the peak of HMO in the Mn2p3/2 orbital (Figure 5d).
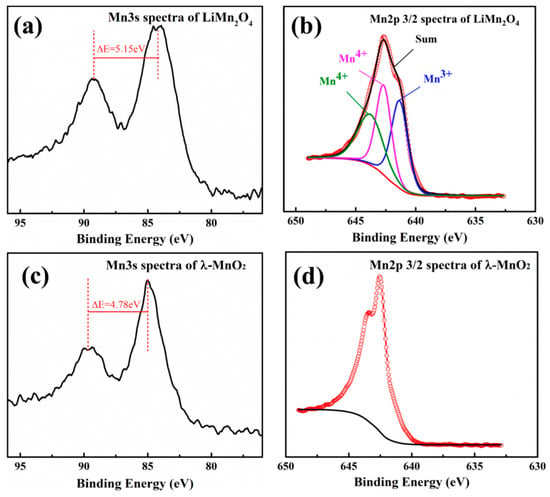
Figure 5.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) Mn3s and Mn2p spectra of LMO and HMO.

Table 2.
Average valances of Mn element in LMO and HMO.
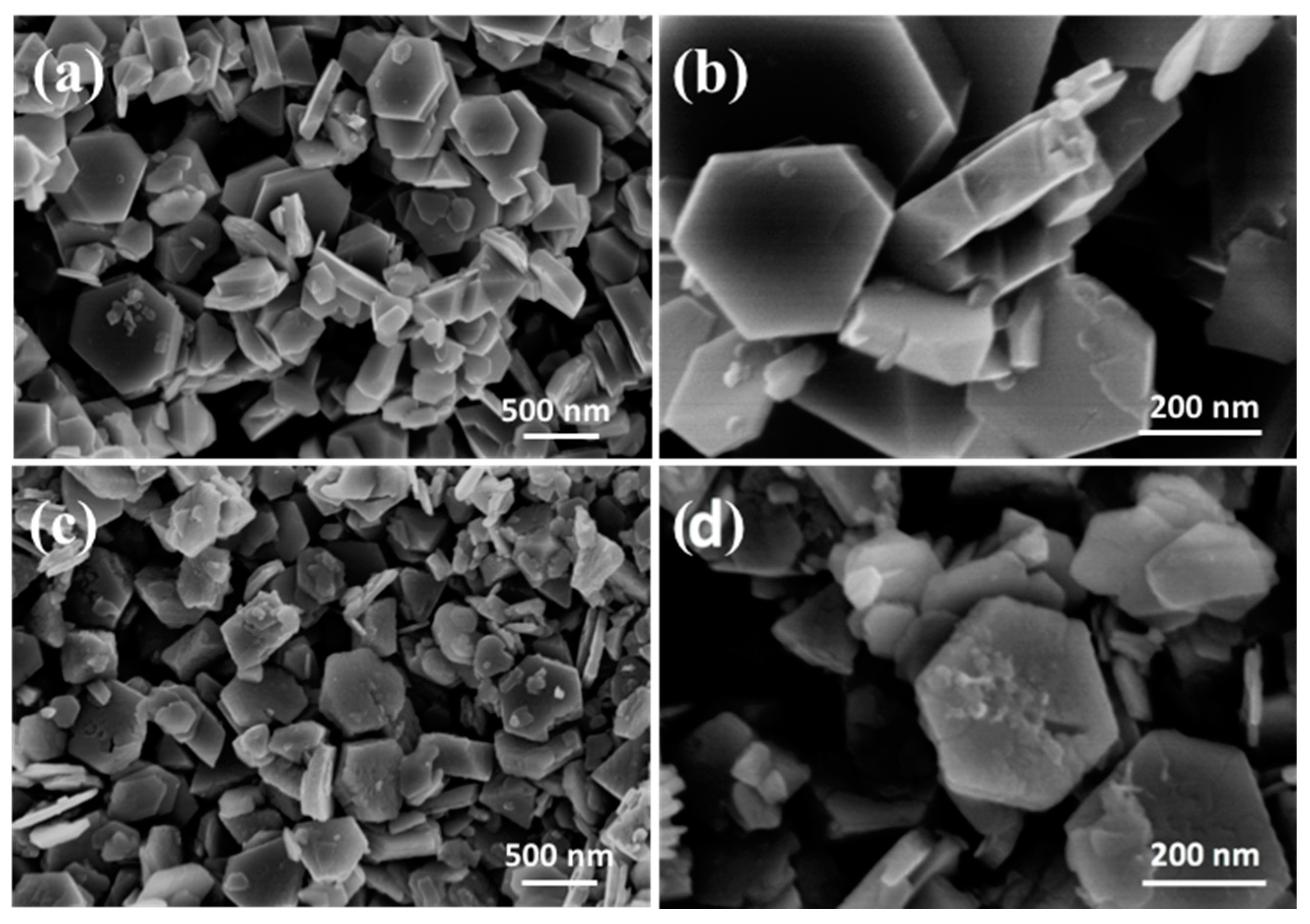
Figure 6 shows the morphology of LMO, HMO and the ion-sieve after Li+ adsorption (LMO-1). The LMO presents regular hexagonal shape with the thickness of 110 nm and the lateral size of ~300–400 nm (Figure 6a). It is apparent that the LMO (Figure 6b) have a smooth surface without agglomeration, while HMO and LMO-1 appear to have a small crack on the surface (Figure 6c). We speculate that it is attributed to the manganese loss after acid treatment that results in partial collapse of the crystal. However, HMO and LMO-1 can still remain their intact hexagonal structure and it is consistent with the XRD results in Figure 4.
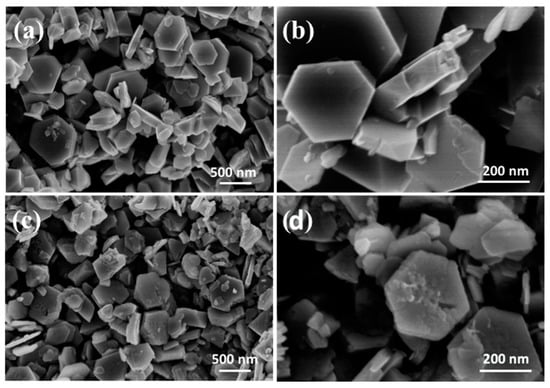
Figure 6.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of LMO (a,b), HMO (c) and LMO-1 (d).
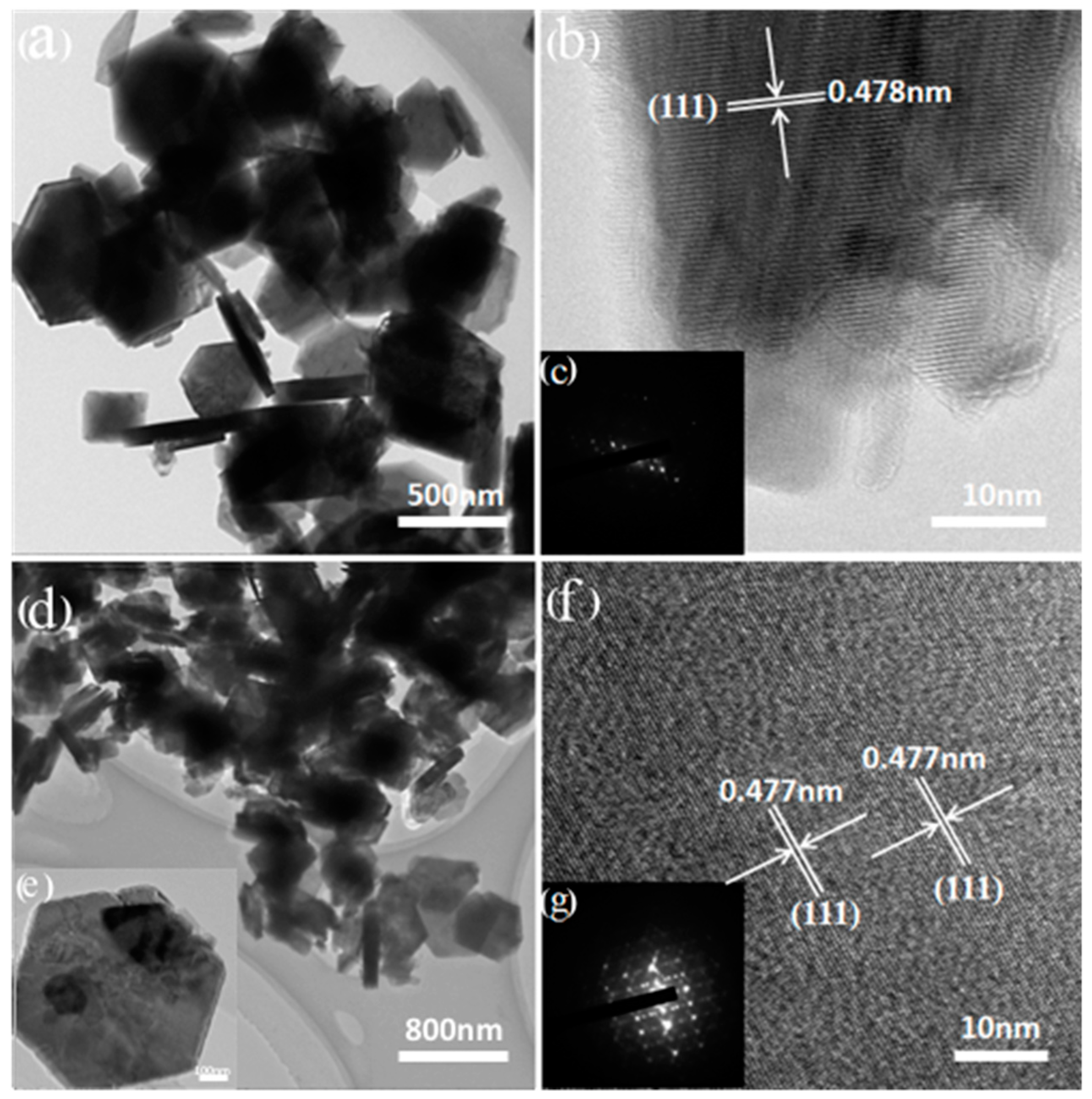
Figure 7 shows the HRTEM images of LMO and HMO. Both LMO and HMO were observed as a non-agglomerated particle with a regular hexagonal morphology (Figure 7a,d). The lattice spacing are 0.478 nm and 0.477 nm, respectively, as shown in Figure 7b,f, which agrees with the (111) crystal plane of the XRD pattern in Figure 4. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of LMO and HMO can be seen in Figure 7c,g, the dot matrix confirms their cubic single-crystal structures.
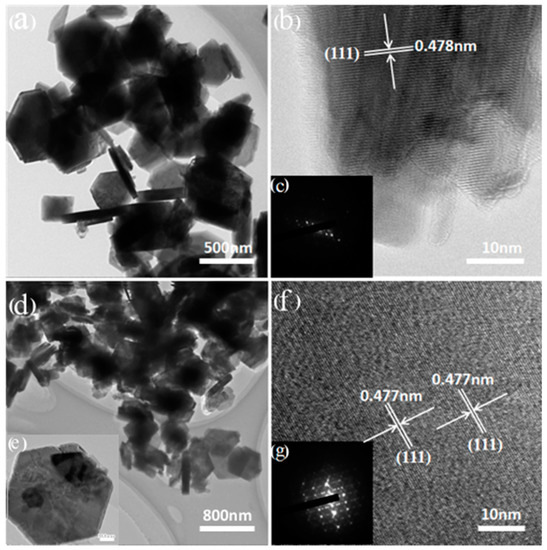
Figure 7.
High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns of the LMO (a–c) and HMO (d–g).
3.3. Adsorption Behavior of the HMO
3.3.1. Effect of pH Value on Adsorption Capacity
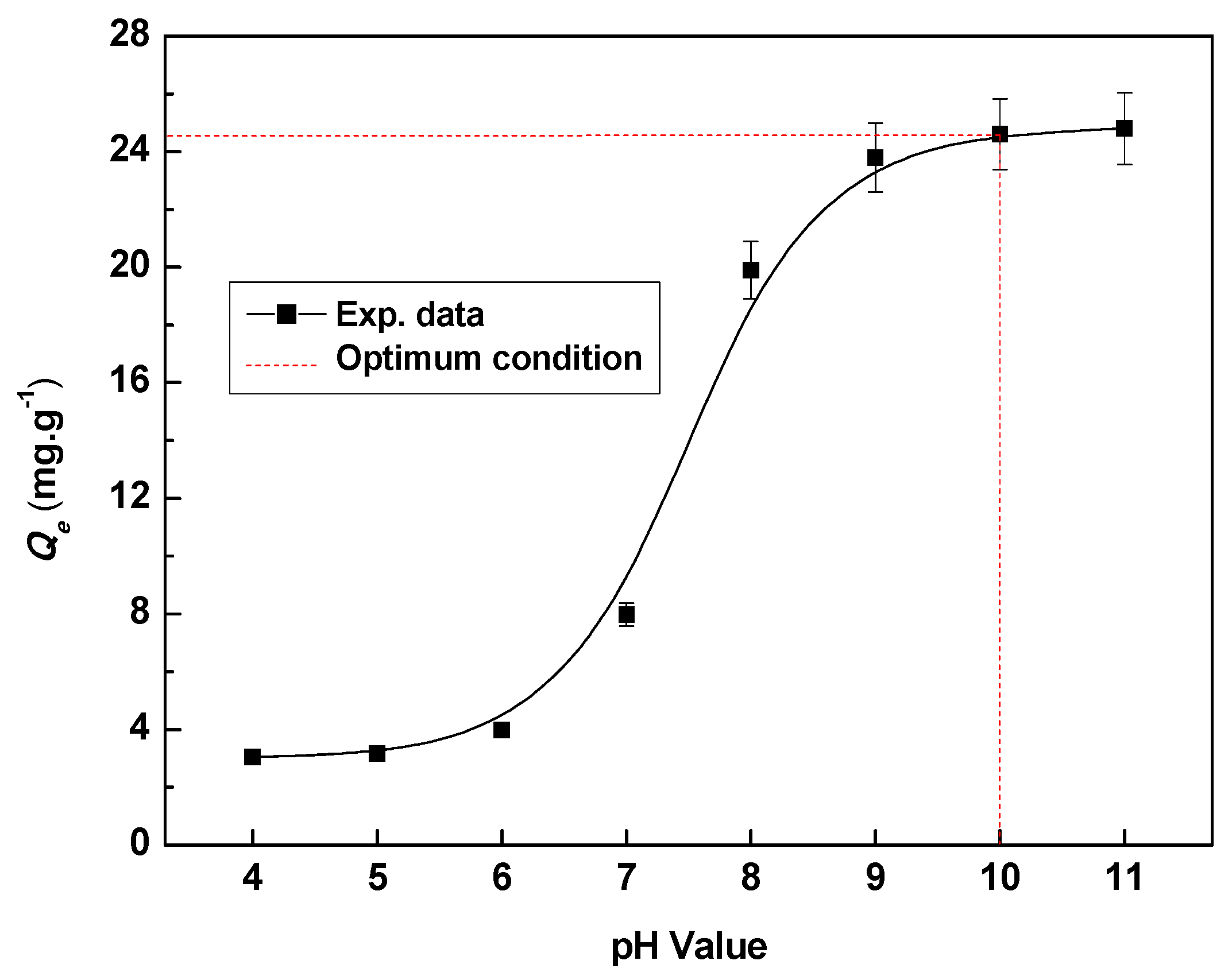
Figure 8 describes the pH value effect on the Li+ adsorption process. The adsorption capacity of HMO was very low in acidic condition. The adsorption capacity of HMO increased sharply and then reached the maximum with the pH value increase in solution, which indicated that alkaline adsorption environment favored the adsorption of HMO. The adsorption-desorption mechanism of LMO can be explained by Figure 1 and Figure 3c. Adsorption Li+ at alkaline condition is beneficial to the formation of LMO and desorption of Li+ at the acid condition is beneficial to the formation of HMO. The mathematic relationship [12] between adsorption capacity (Qe) and pH could be described by the equation Qe = f (Ce, pH). The Qe (the amount of Li+ insertion) increases by the increase of pH. When the pH was greater than 10, the adsorption capacity of HMO hardly increase with the increase of pH value. We speculated that the reduction of Mn4+ was accelerated under the strong alkaline condition, so the adsorption of the ion sieve was inhibited. Therefore, when pH > 10, the adsorption capacity Qe tends to be stable. The similar phenomenon was also found by other reseachers [28].
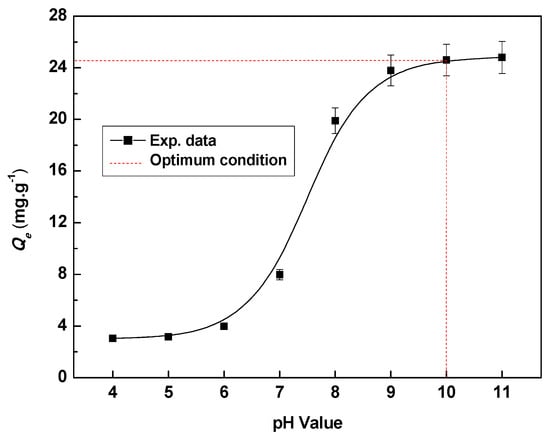
Figure 8.
The Qe—pH value curve with adsorption of 0.1 g HMO in 50 mg·L−1 Li+ at 18 °C.
3.3.2. Static Adsorption Test
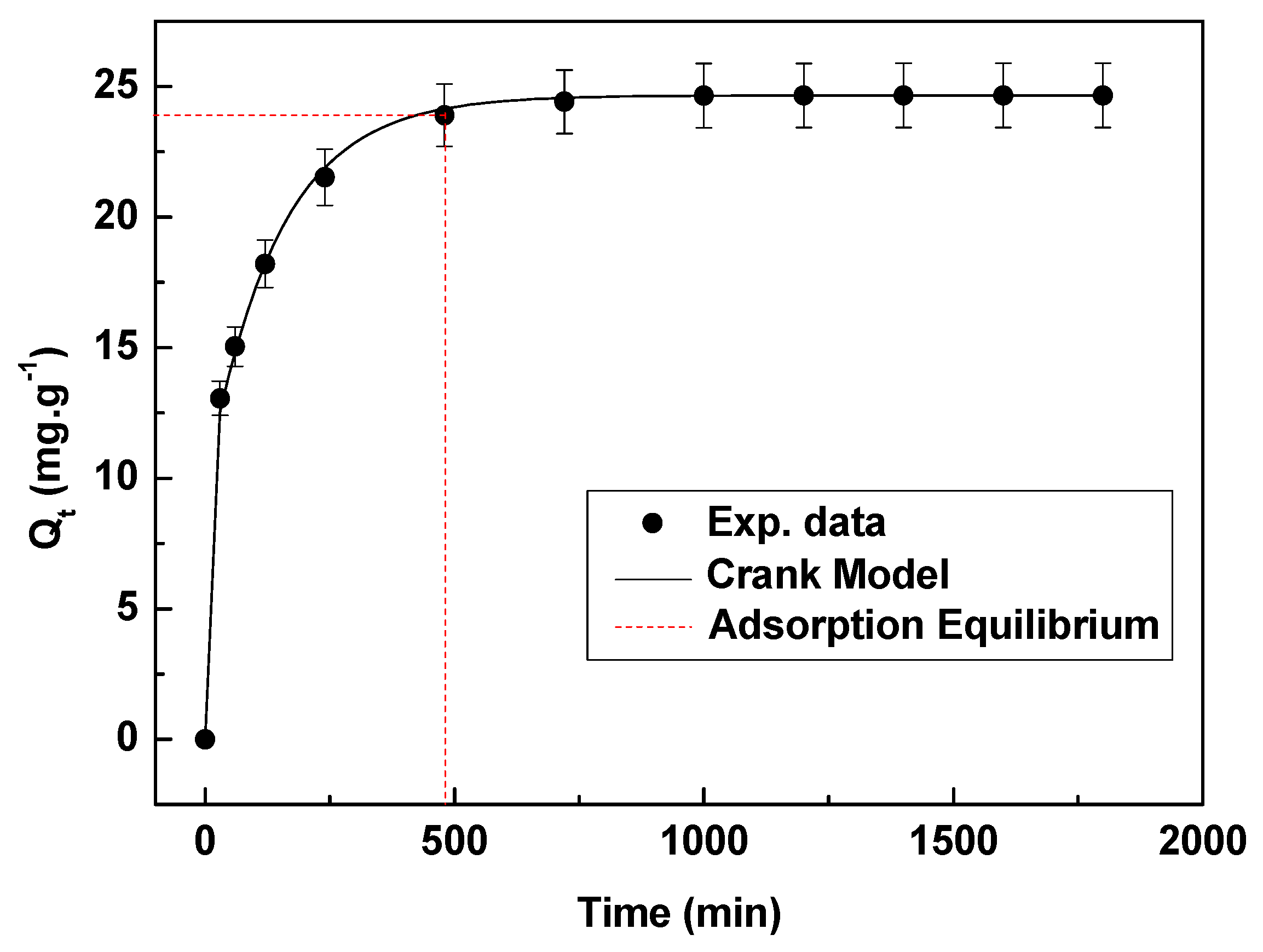
Figure 9 shows that the adsorption process occurs primarily in the rapid adsorption stage and the exchange of Li+ into the spinel lattice dominates the adsorption flat stage. Table 3 compares synthesis method and adsorption capacity of λ-MnO2 in this paper with those of other paper. Solid-phase [19,20] method is often reacted with high energy consumption. It is apparent that hydrothermal method usually uses strong alkaline LiOH [29] or acidic manganese salt [23] as raw material with the disadvantage of corroding equipment. In this study λ-MnO2 was obtained by the one-pot hydrothermal method under neutral and mild condition. The adsorption capacity is 24.7 mg·g−1, 64.4% of the theoretical adsorption capacity ; , which is higher than the 49.2% of the theoretical adsorption capacity reported in the paper [23]; and 61.9% of the theoretical adsorption capacity in the paper. The Crank’s model was used to predict the adsorption rate of Li+. The model fitted well with the experimental data. The efficient film coefficient (De) were calculated by Equation (2) as 1.35 × 10−5 cm2∙s−1. The correlation coefficient (R2) was 0.9971. The coefficient of mass transfer (k) can be obtained by efficient film coefficient and physical property of adsorption system. In all, De derived from fitting calculation provides a vital parameter of feed height in adsorption tower design [30].
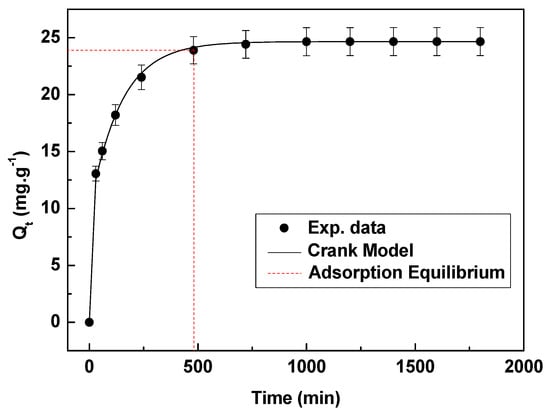
Figure 9.
Fitting result of adsorption data by Crank model using 50 mg·L−1 Li+ on 0.1 g HMO at 18 °C.

Table 3.
Similar method of adsorption capacity comparison.
3.3.3. Adsorption Kinetic Test
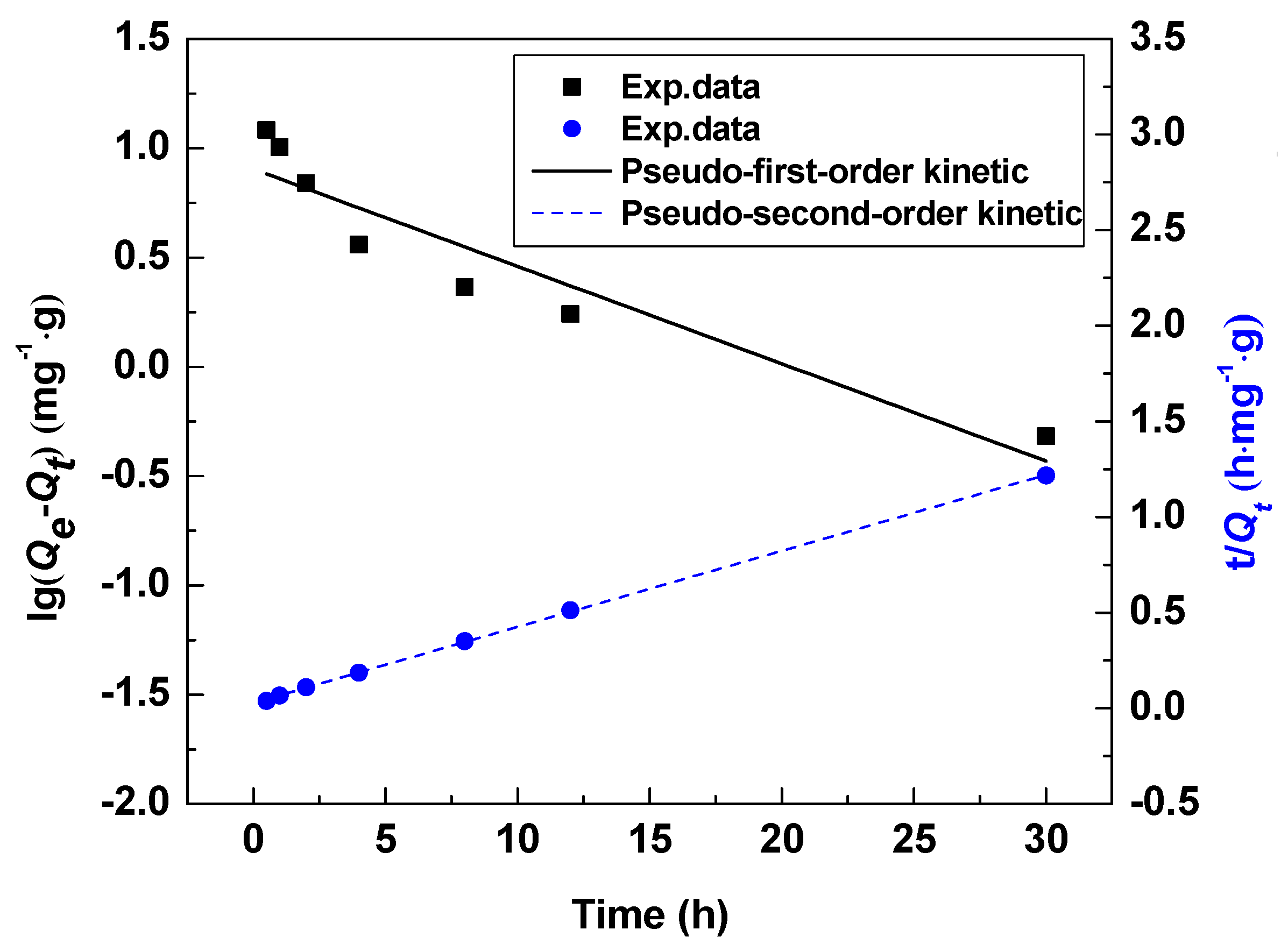
Figure 10 shows the linear fitting of the pseudo-first-order kinetic model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Table 4 compares the fitted kinetic data of the two models at same temperatures. Under the same test conditions, the two models both predicted the adsorption capacity and the correlation coefficient () of the pseudo-second-order kinetics equation is much larger than the pseudo-first-order kinetic equation ( = 0.7678). These data reveal that the adsorption behavior of the HMO ion sieve conforms to the pseudo-second-order kinetics model and the adsorption process is primarily chemical adsorption [31].
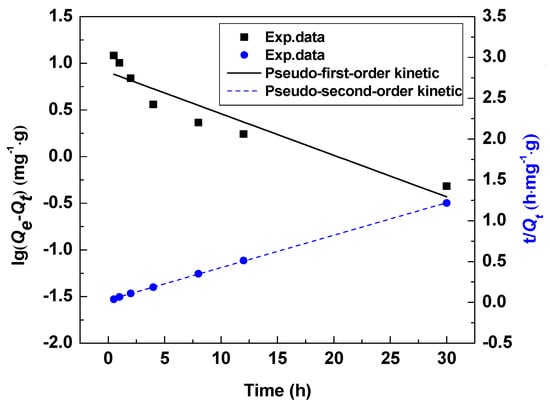
Figure 10.
Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic curves Li+ adsorption by HMO at 18 °C.

Table 4.
Dynamic parameters of lithium adsorption.
3.3.4. Adsorption Isotherm of Li+ on HMO
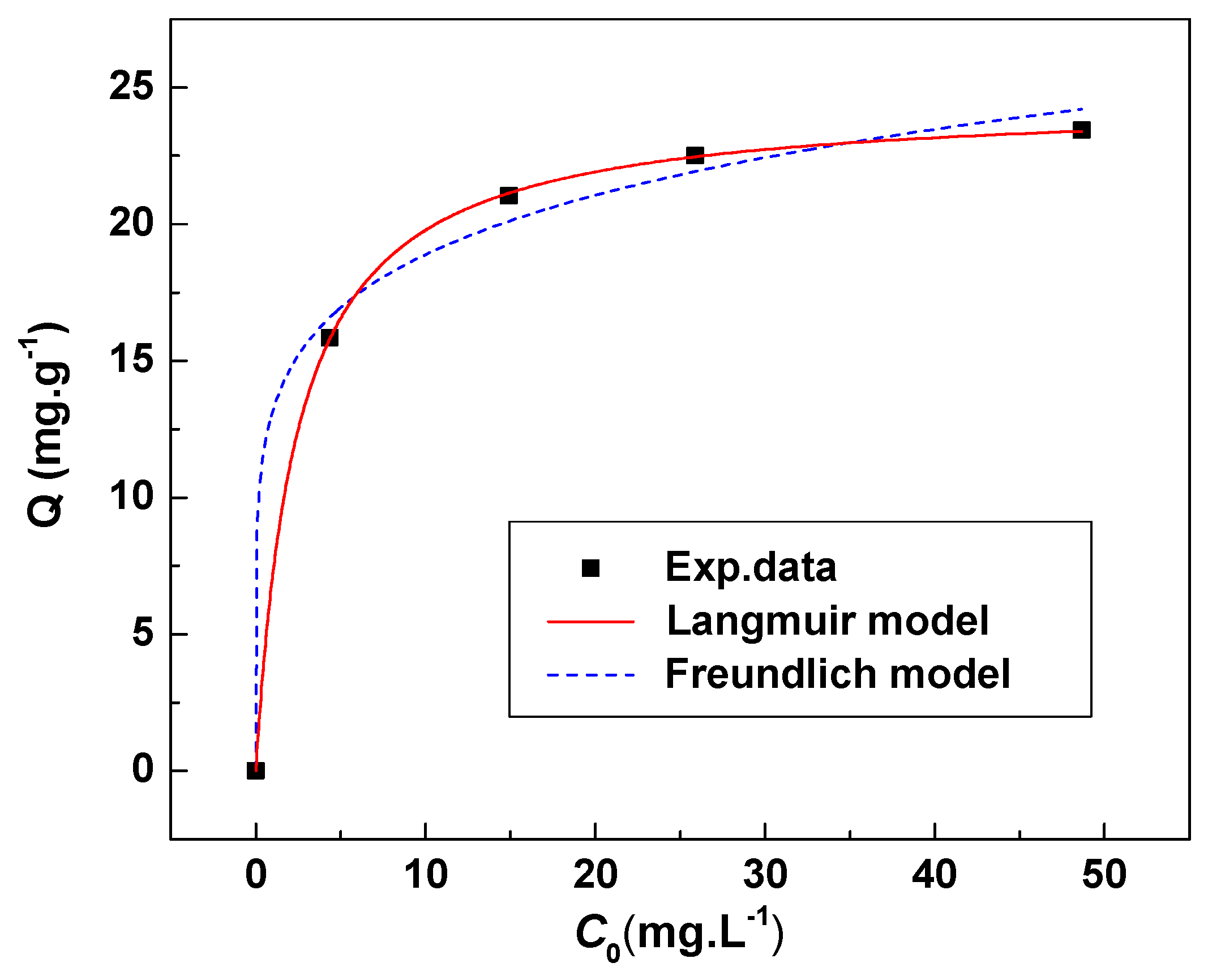
The adsorption constants and the correction factors were obtained by Langmuir and Freundlich equations fittings. Table 5 lists the various parameter values for both models. Figure 11 show the fitting effect of the two models. The Langmuir isotherm model ( = 0.9999) fitting was much better than that of the Freundlich isotherm model ( = 0.9918) compared with the experimental data. This result indicates that the HMO has homogeneous adsorption sites.

Table 5.
Adsorption isotherm constants of Li+ on HMO.
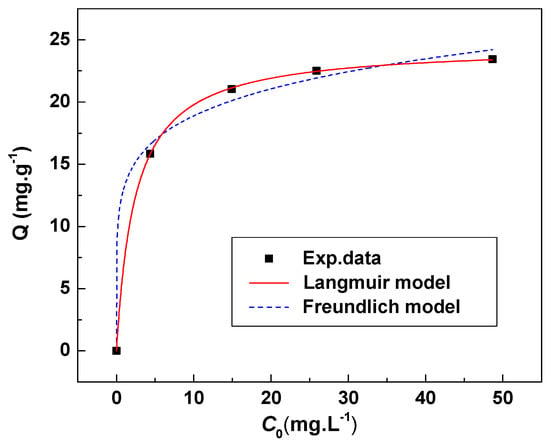
Figure 11.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms of Li+ adsorption by HMO at 18 °C.
3.4. Absorption Selectivity of HMO
Table 6 shows the HMO ion sieve adsorption selectivity for Li+ compared with other coexisting metal ions in brine, including Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+. According to Table 6, the adsorption capacity of HMO in brine is 6.26 mg·g−1, which is lower than the value of that in the pure Li+ solution. We speculated that the acidic environment (pH = 5.64) is not conducive to the free insertion of lithium ions in λ-MnO2. The distribution coefficients () are in the order of Li+ > Ca2+ > K+ > Na+ > Mg2+, indicating high selectivity for Li+, compared with other metal ions. The ion sieve showed excellent ion selectivity, especially for Mg2+, whose separation factor () is 1.35 × 103. This solves the problem of separating Li+ and Mg2+ in brine with a high ratio of magnesium to lithium. Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ in solution do not have competitive effect with Li+ during ion sieve adsorption process since the concentration factor of Li+ is higher than other ions.

Table 6.
Adsorption selectivity data of metal ions on HMO in brine.
3.5. Desorption Behavior of LMO-1
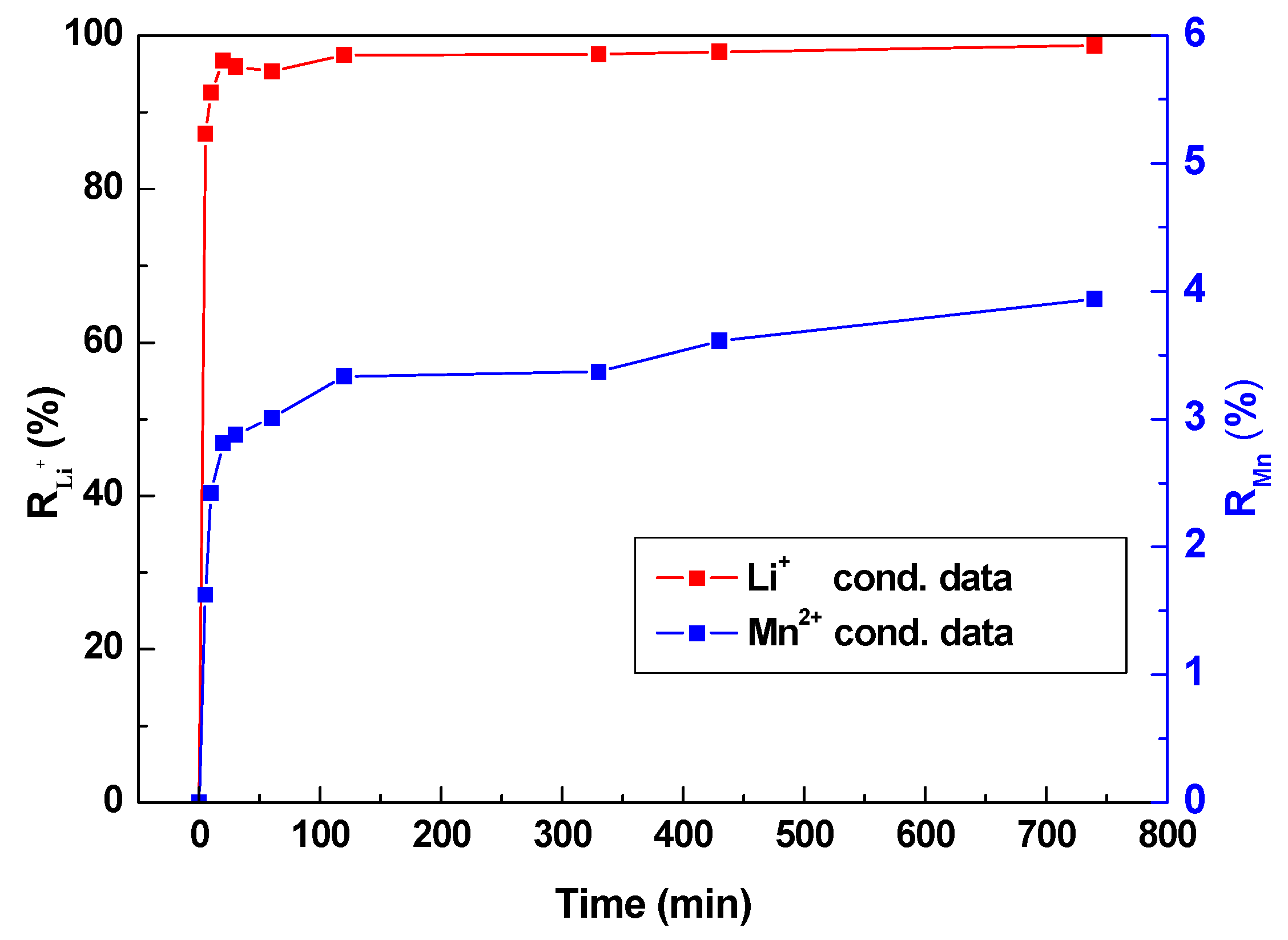
Figure 12 shows the desorption curve of Li+ or Mn2+ after adsorption. It was observed that the extraction of Li+ and Mn2+ occurred rapidly at the beginning of the desorption process, almost reaching the maximum extraction rate at 20 min, then slightly rose up to 22.0 mg·g−1 and 38.9 mg·g−1, respectively. The maximum extraction rate of RLi+ is 98.7%. The dissolution of Mn2+ (RMn2+) is only 3.9%, which was calculated by Equation (10). This phenomenon may benefit from the unique layered structure. Integrity shape without defect with a larger surface can sufficiently contact with Li+ of solution and maintain adsorption stability, accelerating the absorption and desorption process.
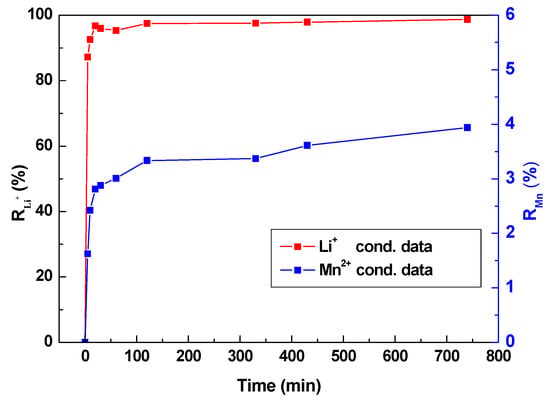
Figure 12.
Desorption and Dissolution loss behavior of LMO-1.
4. Conclusions
A series of LMO was successfully prepared via a facile one-pot hydrothermal method and we optimized synthetic conditions as well. The HMO ion-sieve has unique hexagonal spinel structure with the thickness of 110 nm and lateral size of 300–400 nm. XRD patterns of LMO and HMO confirm their high crystallization degree. The average valence of Mn in LMO is +3.65, which higher than that in theory (+3.5). The adsorption capacity of HMO is 24.7 mg·g−1 in Li+ solution and the dissolution of Mn2+ is only 3.9%. The adsorption equilibrium isotherms data are well fitted with Langmuir model. Moreover, the distribution coefficients () of HMO is much larger between Li+ and Mg2+ and the separation factor () was 1.35 × 103. Therefore, our HMO ion-sieve shows great potential to extract lithium in brine or seawater under high magnesium ratio conditions.
Author Contributions
F.Y. and S.J. conceived and designed the experiments; F.Y. and S.C. performed the experiments; X.Z. and C.S. analyzed the data; S.J. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; F.Y., F.X., S.J. and W.X. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1407122), Innovation Project of Jiangsu Province (SJZZ16_0136).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, S.; Huimin, R.; Shen, J.; Gao, C. Preparation methods and analyses of structural performance of spinel-type lithium manganese oxide ion sieves. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2015, 6, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Özgür, C. Preparation and characterization of LiMn2O4 ion-sieve with high Li+ adsorption rate by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.L.; Sun, S.Y.; Song, X.; Li, P.; Yu, J.G. Lithium ion recovery from brine using granulated polyacry λ–MnO2 ion-sieve. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, S.E.; Gruber, P.W.; Medina, P.A.; Keoleian, G.A.; Everson, M.P.; Wallington, T.J. Global lithium resources: Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Ping, Z.M.; Zhen, N.; Hua, L.J.; Sheng, S.P. Brine Lithium Resource in the Salt Lake and Advances in Its Exploitation. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2011, 32, 483–492. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.L.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Yu, J.G. Synthesis and Adsorption Properties of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 Spinel. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 11967–11973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandevakili, S.; Ranjbar, M.; Ehteshamzadeh, M. Improvement of lithium adsorption capacity by optimising the parameters affecting synthesised ion sieves. Micro Nano Lett. 2015, 10, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qu, W.; Liu, F.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Surface modification of spinel λ-MnO2 and its lithium adsorption properties from spent lithium ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 315, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Tong, K.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, J.; Sun, S.; Li, P.; Yu, J. Adsorption and Desorption Behavior of Lithium Ion in Spherical PVC–MnO2 Ion Sieve. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10921–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, P.; Qi, P.; Gao, C. Adsorption and desorption properties of Li+ on PVC-H1.6 Mn1.6O4 lithium ion-sieve membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, M. Preparation and characterization of lithium λ-MnO2 ion-sieves. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Nie, X.; Sun, S.; Song, X.; Ping, L.; Yu, J. Lithium ion adsorption–desorption properties on spinel Li4Mn5O12 and pH-dependent ion-exchange model. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.B.; Singh, A. A facile low-temperature synthesis of Li4Mn5O12 nanorods. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhao, X. Lithium extraction from seawater by manganese oxide ion sieve MnO2·0.5H2O. Colloids Surf. A. 2015, 468, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Nisola, G.M.; Beltran, A.B.; Torrejos, R.E.C.; Seo, J.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Chung, W. Recyclable composite nanofiber adsorbent for Li+ recovery from seawater desalination retentate. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorour, M.H.; El-Rafei, A.M.; Hani, H.A. Synthesis and characterization of electrospun aluminum doped Li1.6Mn1.6O4 spinel. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4911–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Meng, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, Y. Highly selective, regenerated ion-sieve microfiltration porous membrane for targeted separation of Li+. J. Porous Mater. 2016, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Sasaki, K. In situ X-ray diffraction investigation of the evolution of a nanocrystalline lithium-ion sieve from biogenic manganese oxide. Hydrometall 2014, 150, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.S.; Yin, H.B.; Ji, Z.Y.; Deng, H.N. Effective Recycling Performance of Li+ Extraction from Spinel-Type LiMn2O4 with Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9889–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Rah, H.; Dong, J.K.; Chun, U.; Kim, S.G. Confined growth of lithium manganese oxide nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Tian, S.; Liu, L.L.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.P.; Yue, Y.B.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Zhu, K. Nanochain LiMn2O4 as ultra-fast cathode material for aqueous rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.P. Granulation to LiMn2O4 Ion-Sieve and Its Lithium Adsorption Property. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 26, 435–439. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Li, S.P.; Sun, S.Y.; Yin, X.S.; Yu, J.G. LiMn2O4 spinel direct synthesis and lithium ion selective adsorption. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1977; Volume 7, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, F.; Xu, Y.; Lu, S.; Ju, S.; Xing, W. Adsorption of Cefocelis Hydrochloride on Macroporous Resin: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ma, W.; Han, M. Adsorption behavior of Li+ onto nano-lithium ion sieve from hybrid magnesium/lithium manganese oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.G. Lithium extraction/insertion process on cubic Li-Mn-O precursors with different Li/Mn ratio and morphology. Adsorption 2011, 17, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, K.; Miyai, Y.; Sakakihara, J. Mechanism of lithium (Li+) insertion in spinel-type manganese oxide. Redox and ion-exchange reactions. Langmuir 1991, 7, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, S.; Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Yu, J. Adsorption of lithium ions on novel nanocrystal MnO2. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 4869–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, J.W.; Yang, C.L. Absorption of NO2 in a packed tower with Na2SO3 aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2002, 21, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.J.; Liao, F.; Ke, Q.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Guo, Y.P. Synergetic effect of titanium dioxide ultralong nanofibers and activated carbon fibers on adsorption and photodegradation of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).