Membrane Fouling Characteristics of a Side-Stream Tubular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) Treating Domestic Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
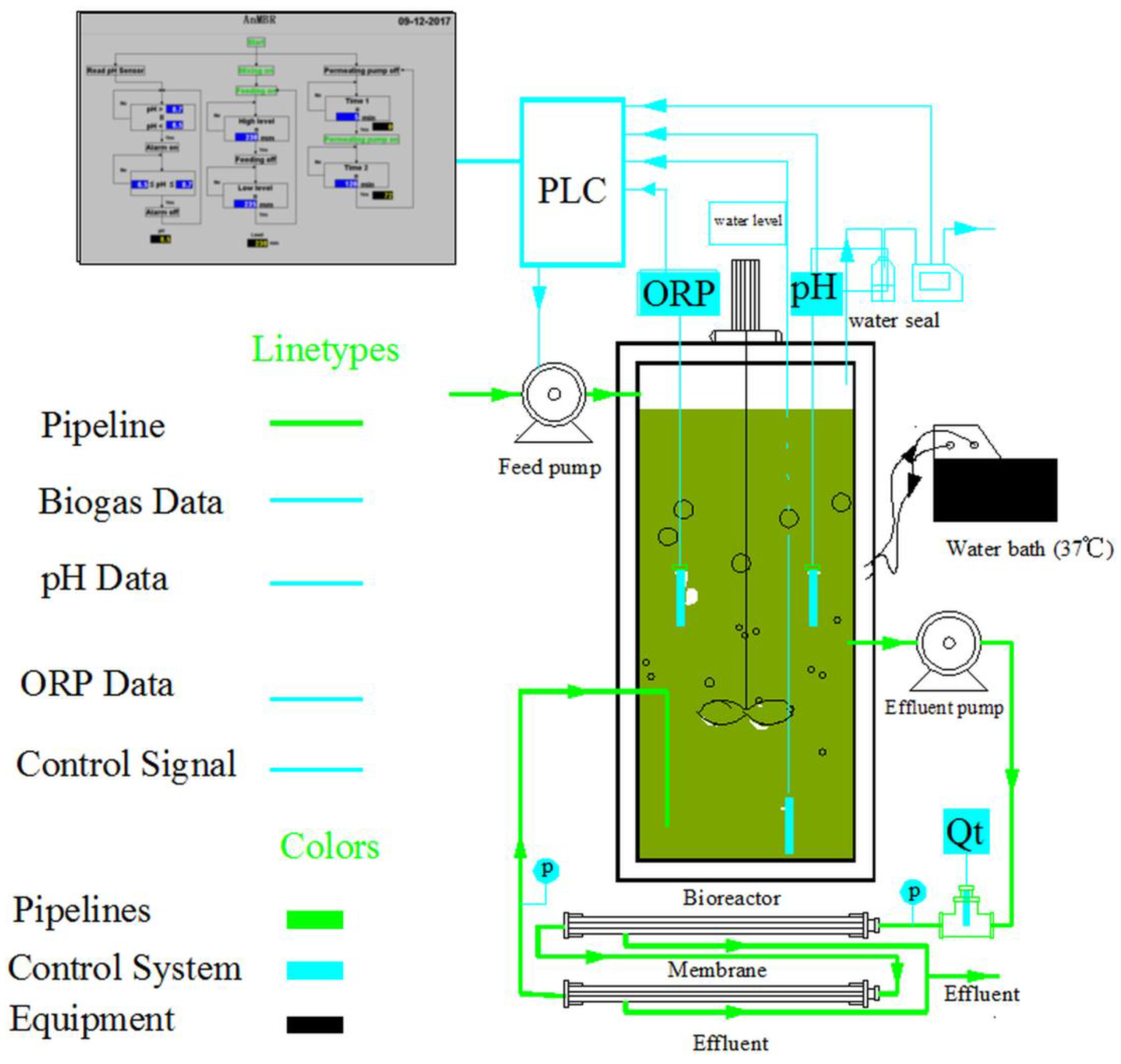
2.1. Lab-Scale Tubular AnMBR
2.2. Operation of the Tubular AnMBR
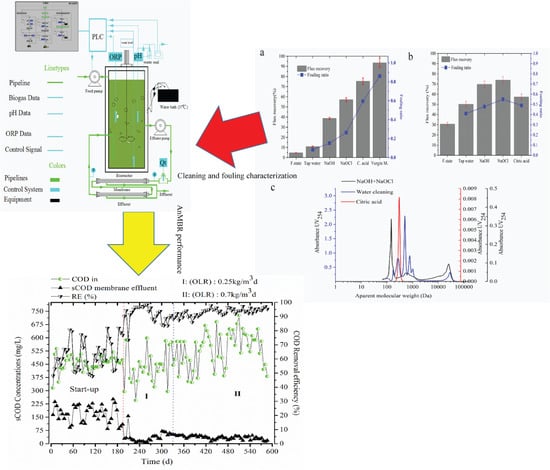
2.3. Membrane Cleaning Strategy
2.4. Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
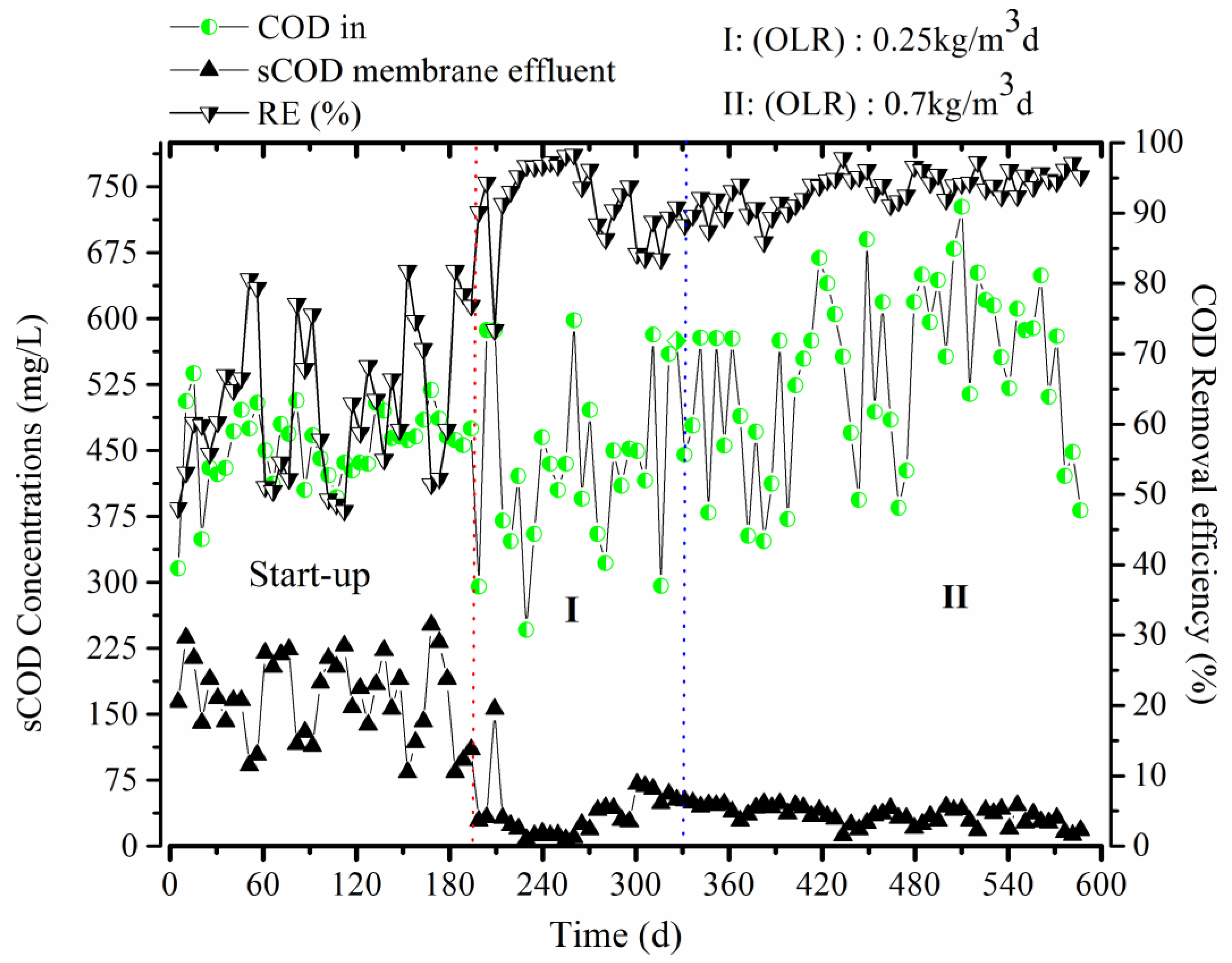
3.1. Performance of COD Removal
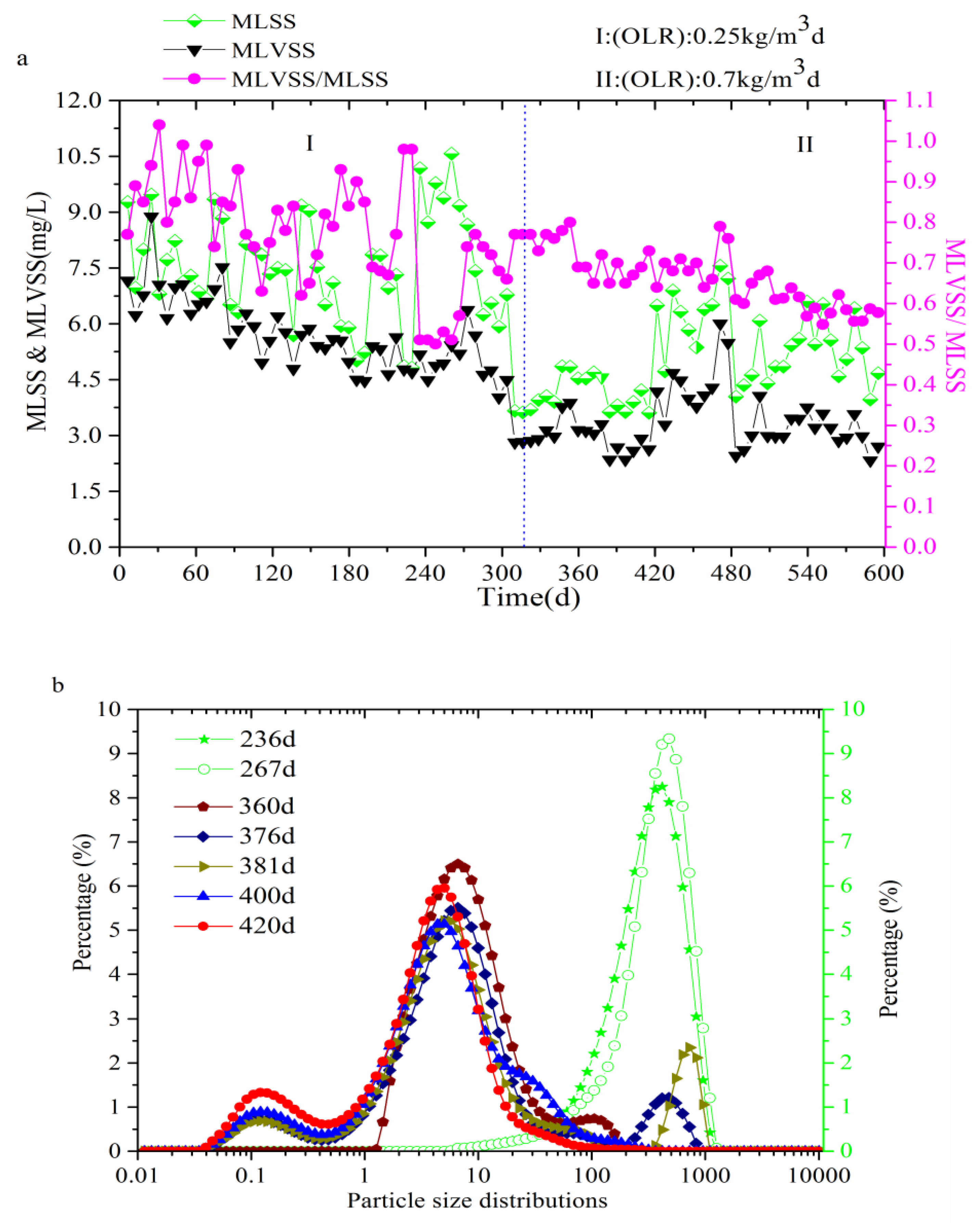
3.2. Membrane Fouling Characteristics
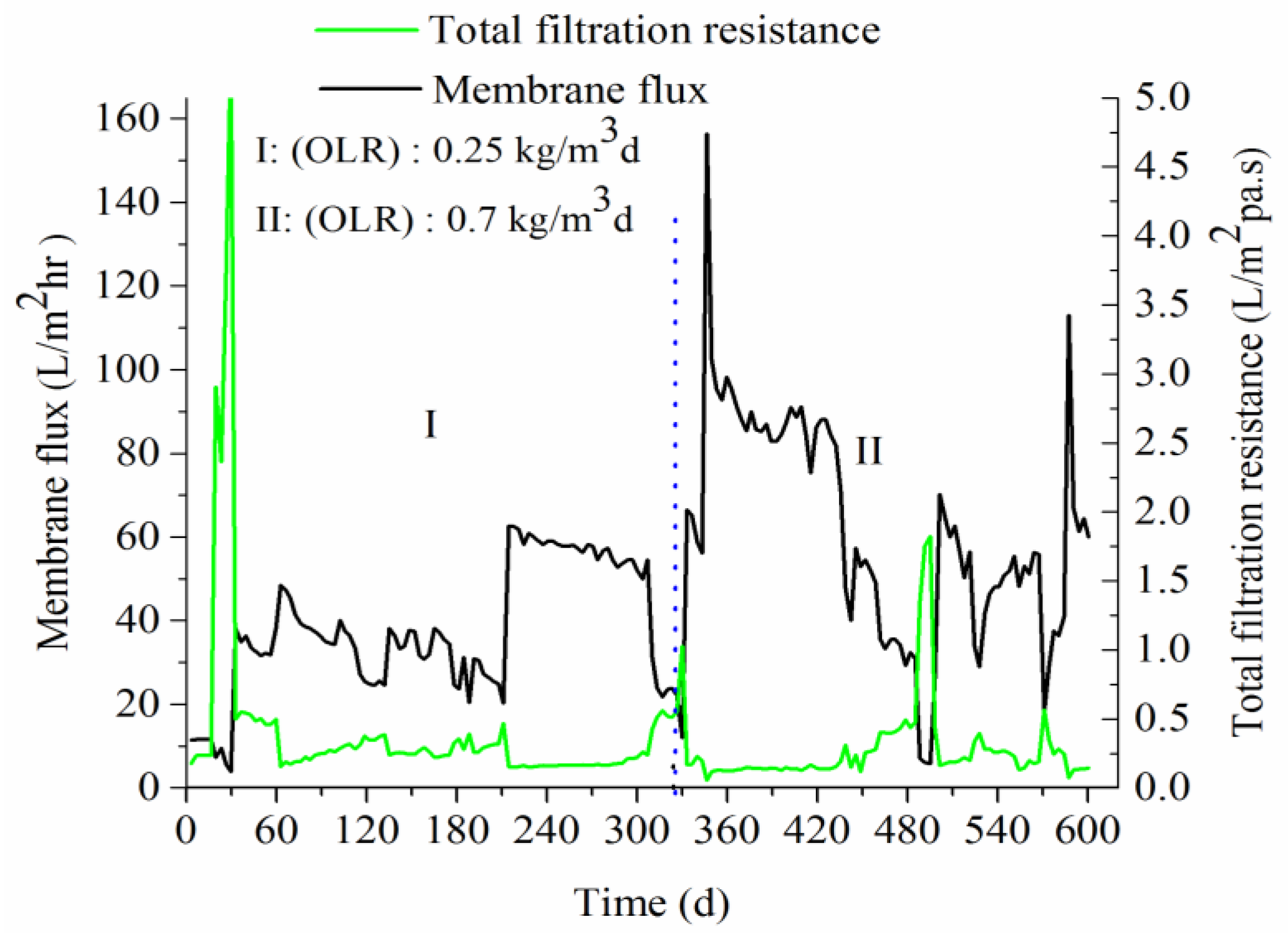
3.2.1. Membrane Flux and Total Filtration Resistance
3.2.2. Particle Size Distribution
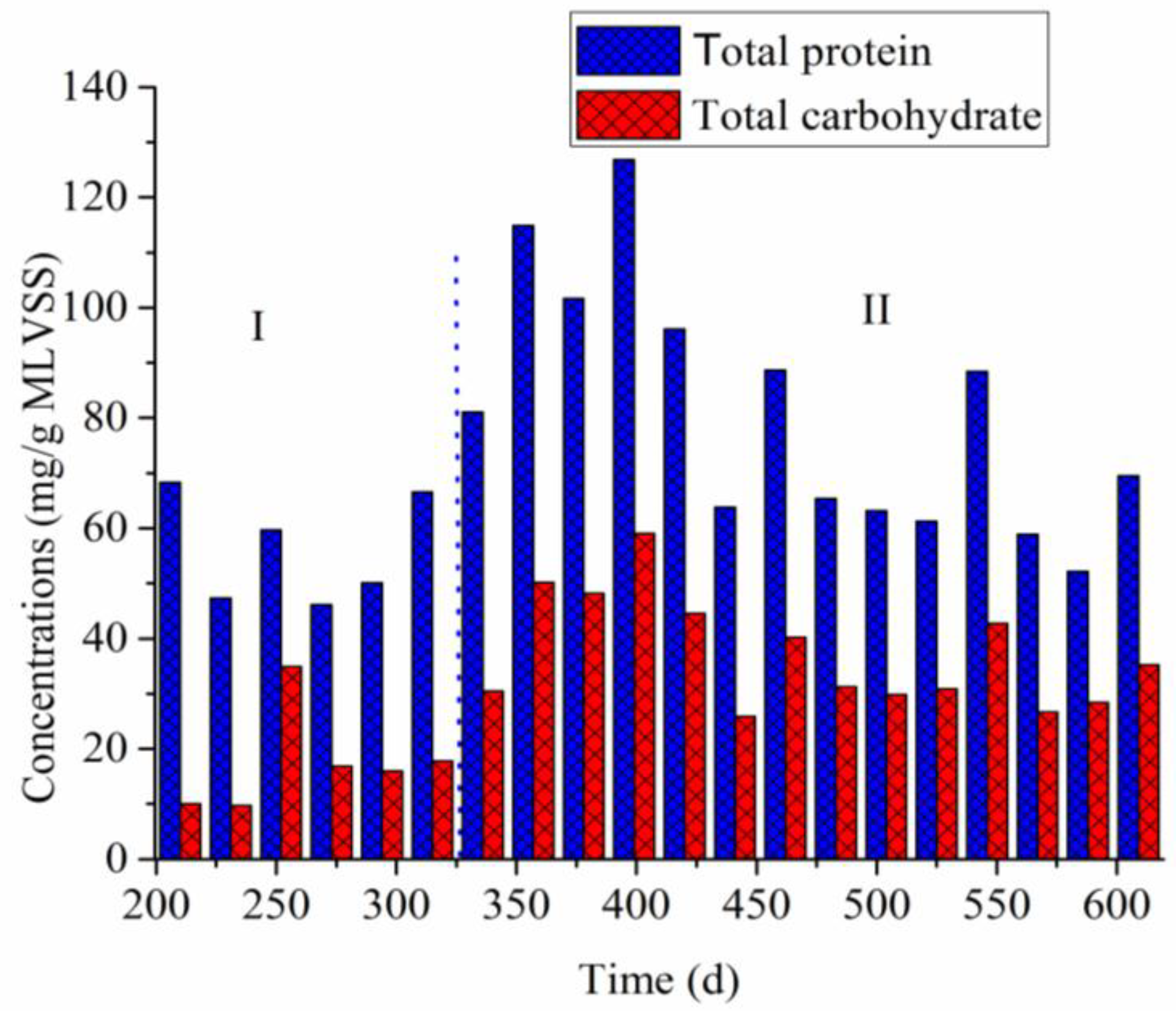
3.3. Membrane Foulants
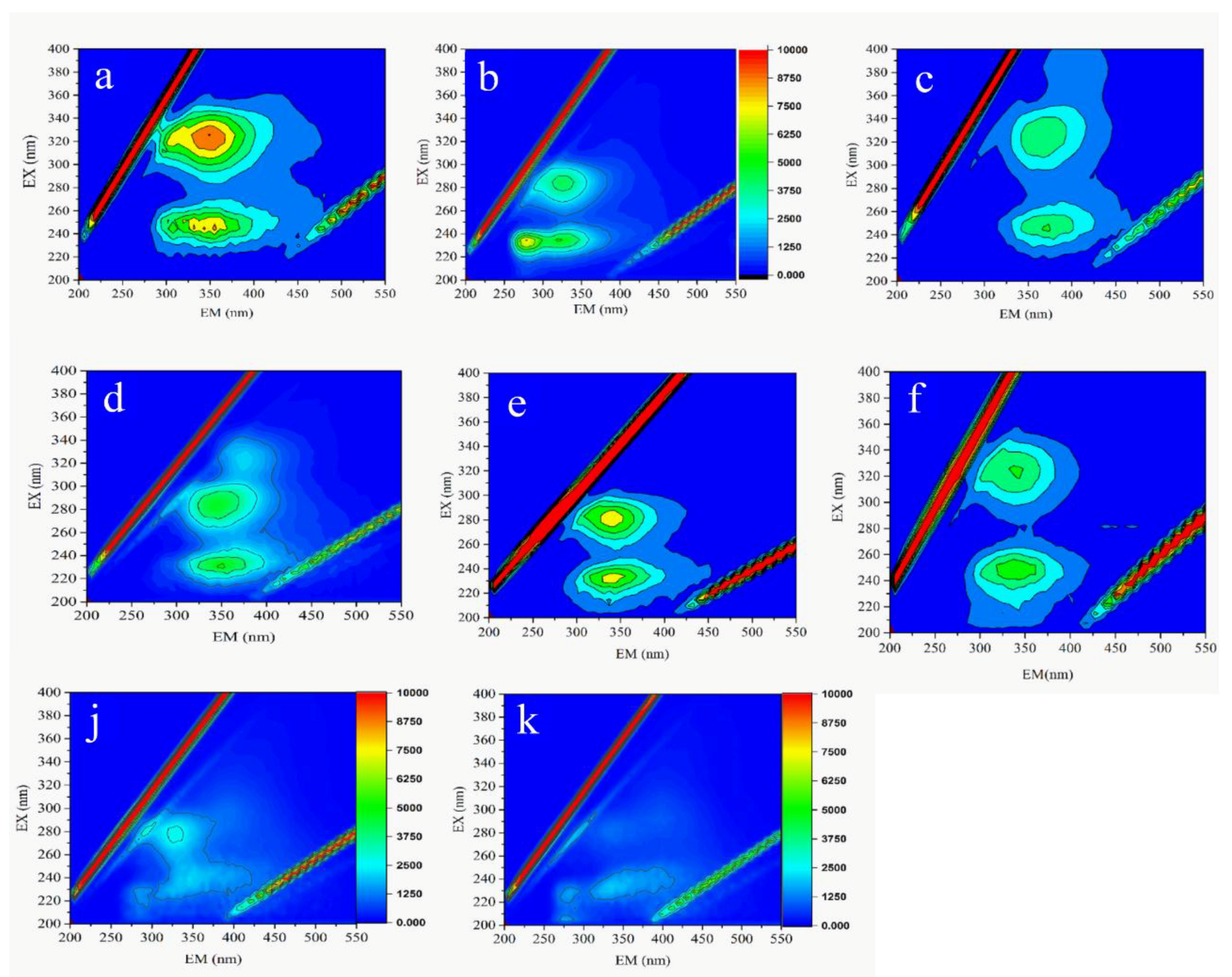
3.3.1. Fluorescence Spectroscopic Analysis
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3.3. SEM-EDS Analysis of the Fouling Composition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ichinari, T.; Ohtsubo, A.; Ozawa, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Teduka, K.; Oguchi, T.; Kiso, Y. Wastewater treatment performance and sludge reduction properties of a household wastewater treatment system combined with an aerobic sludge digestion unit. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.E.; Khan, M.M. 11 Ecotourism opportunities for developing countries. In Global Tourism; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1998; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Bolzonella, D.; Fatone, F.; di Fabio, S.; Cecchi, F. Application of membrane bioreactor technology for wastewater treatment and reuse in the Mediterranean region: Focusing on removal efficiency of non-conventional pollutants. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhon, D.; Sözen, S.; Görgün, E.; Çokgör, E.U.; Artan, N. Technological aspects of wastewater management in coastal tourist areas. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Bai, J. Mechanism of high contaminant removal performance in the expanded granular sludge blanket (EGSB) reactor involved with granular activated carbon for low-strength wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanatamskul, C.; Siritiewsri, T. A compact on-site UASB–EGSB system for organic and suspended solid digestion and biogas recovery from department store wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sosa, D.; Helmreich, B.; Netter, T.; Paris, S.; Bischof, F.; Horn, H. Anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactor (AnSMBR) for municipal wastewater treatment under mesophilic and psychrophilic temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettinga, G.; Rebac, S.; Zeeman, G. Challenge of psychrophilic anaerobic wastewater treatment. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, T.; Nosrati, M.; Sreekrishnan, T. Anaerobic digestion from the viewpoint of microbiological, chemical, and operational aspects—A review. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyuk, S.; Forrez, I.; van Haandel, A.; Verstraete, W. Anaerobic and complementary treatment of domestic sewage in regions with hot climates—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2225–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Stadler, L.B.; Love, N.G.; Skerlos, S.J.; Raskin, L. Perspectives on anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzeminski, P.; Leverette, L.; Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. Membrane bioreactors–a review on recent developments in energy reduction, fouling control, novel configurations, LCA and market prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kinaci, C.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The MBR book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Han, M.; Chen, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, G. Membrane fouling control in ultrafiltration technology for drinking water production: A review. Desalination 2011, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, G.; Jiang, T. Highly effective antifouling performance of N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone modified polypropylene non-woven fabric membranes by ATRP method. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.-R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 2013, 314, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarusutthirak, C.; Mattaraj, S.; Jiraratananon, R. Influence of inorganic scalants and natural organic matter on nanofiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Kim, S.; Ting, Y. Optimization of membrane physical and chemical cleaning by a statistically designed approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 219, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, G.; Davis, R.H.; Zydney, A.L. The behavior of suspensions and macromolecular solutions in crossflow microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 96, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, S.; Milanović, S.; Iličić, M.; Djurić, M.; Tekić, M. Flux recovery of tubular ceramic membranes fouled with whey proteins. Desalination 2009, 249, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, M.M.M.; Anioke, G.; Nakagoe, O.; Tanabe, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Fujioka, T. Membrane fouling, chemical cleaning and separation performance assessment of a chlorine-resistant nanofiltration membrane for water recycling applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Quek, P.J.; Wang, Z.; Ng, H.Y. Alkali-assisted membrane cleaning for fouling control of anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zondervan, E.; Roffel, B. Evaluation of different cleaning agents used for cleaning ultra filtration membranes fouled by surface water. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Pollution Control Federation; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D.; Qin, T.; He, S. Investigation of organic foulants behavior on hollow-fiber UF membranes in a drinking water treatment plant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Liu, H.; Hu, C.; Qu, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J. Removal of disinfection by-products precursors by polyaluminum chloride coagulation coupled with chlorination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, H.; Baeta, B.E.L.; Aquino, S.F.; Susa, M.R. EPS and SMP dynamics at different heights of a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAMBR). Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Sung, S. Methanogenic activities in anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBR) treating synthetic municipal wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.-B.; Yang, F.-L.; Zhang, X.-W. Anaerobic treatment of domestic wastewater in a membrane-coupled expended granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor under moderate to low temperature. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Leung, K.; Qin, W.; Liao, B. Effects of temperature and temperature shock on the performance and microbial community structure of a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8733–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, L.; Hong, H. Feasibility evaluation of submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for municipal secondary wastewater treatment. Desalination 2011, 280, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Koh, Y.K.K.; Ng, H.Y. Effects of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) on membrane fouling in anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactors (AnCMBRs) treating domestic wastewater. Water Res. 2015, 86, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, L.; Zhang, K. The ratio of food-to-microorganism (F/M) on membrane fouling of anaerobic membrane bioreactors treating low-strength wastewater. Desalination 2012, 297, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, I.; Liao, B. Effects of sludge concentration and biogas sparging rate on critical flux in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Ozturk, I.; Jeison, D.; van der Zee, F.; van Lier, J.B. Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for low-strength wastewater treatment: Effect of HRT and SRT on treatment performance and membrane fouling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Wang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Wu, Z. Recover energy from domestic wastewater using anaerobic membrane bioreactor: Operating parameters optimization and energy balance analysis. Energy 2016, 98, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Clech, P.; Jefferson, B.; Chang, I.S.; Judd, S.J. Critical flux determination by the flux-step method in a submerged membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 227, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, M.; Yuan, T.; Meng, J. Fouling resistance and cleaning efficiency of stimuli-responsive reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. Polymer 2016, 103, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liikanen, R.; Yli-Kuivila, J.; Laukkanen, R. Efficiency of various chemical cleanings for nanofiltration membrane fouled by conventionally-treated surface water. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 195, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yu, D.; Liu, M.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, F.; Fan, Y. Optimization of MBR hydrodynamics for cake layer fouling control through CFD simulation and RSM design. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 227, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Leow, H. Microfiltration of activated sludge wastewater—The effect of system operation parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 29, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, H.; Okimoto, K.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Hydrophilic fraction of natural organic matter causing irreversible fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2014, 54, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Tanoue, E. Isolation and partial characterization of dissolved copper-complexing ligands in streamwaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3646–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q. Role of dissolved organic matters (DOM) in membrane fouling of membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Amy, G.; Croué, J.-P.; Buisson, H. Identification and understanding of fouling in low-pressure membrane (MF/UF) filtration by natural organic matter (NOM). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4511–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, K.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, M. Performance and fate of organics in a pilot MBR–NF for treating antibiotic production wastewater with recycling NF concentrate. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste: Study of biological stabilization by Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetry combined with mass spectrometry. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, H.; Zeng, P.; Liu, R. Fractionation and characterization of dissolved extracellular and intracellular products derived from floccular sludge and aerobic granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Silva, J.; Rodrigues Filho, G.; da Silva Meireles, C.; Ribeiro, S.D.; Vieira, J.G.; da Silva, C.V.; Cerqueira, D.A. Thermal analysis and FTIR studies of sewage sludge produced in treatment plants. The case of sludge in the city of Uberlândia-MG, Brazil. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 528, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.; Amy, G.; Park, H.-R.; Song, M. Characterizing algogenic organic matter (AOM) and evaluating associated NF membrane fouling. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M. Advanced treatment of municipal wastewater by nanofiltration: Operational optimization and membrane fouling analysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Padmasiri, S.; Fitch, M.; Norddahl, B.; Raskin, L.; Morgenroth, E. Influence of cleaning frequency and membrane history on fouling in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Desalination 2007, 207, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfert, P.; Mandalidis, A.; Dugulan, A.; Goubitz, K.; Korving, L.; Temmink, H.; Witkamp, G.; Van Loosdrecht, M. Vivianite as an important iron phosphate precipitate in sewage treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 104, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling and chemical cleaning of nanofiltration membranes: Measurements and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strugholtz, S.; Sundaramoorthy, K.; Panglisch, S.; Lerch, A.; Brügger, A.; Gimbel, R. Evaluation of the performance of different chemicals for cleaning capillary membranes. Desalination 2005, 179, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Start Up | I | II |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane properties Surface areas (m2) | Tubular membrane, PVDF, 0.01 | Tubular membrane, PVDF, 0.01 | Tubular membrane, PVDF, 0.022 |
| SRT(days) | - | 100 | 100 |
| HRT (hours) | 37.5 | 37.5 | 13.0 |
| MLSS (g/L) | - | 7.51 ± 1.41 | 5.00 ± 1.09 |
| MLVSS (g/L) | - | 5.69 ± 0.96 | 3.33 ± 0.77 |
| MLVSS/MLSS | - | 0.77 ± 0.13 | 0.66 ± 0.07 |
| Total proteins (mg/gMLVSS) | - | 66.75 ± 22.84 | 77.98 ± 22.29 |
| Total carbohydrate (mg/gMLVSS) | - | 23.24 ± 14.10 | 36.91 ± 10.18 |
| Feed sCOD (mg/L) | 456.02 ± 44.28 | 445.41 ± 95.56 | 562.80 ± 90.56 |
| Effluent sCOD (mg/L) | 167.89 ± 47.92 | 39.57 ± 25.26 | 31.06 ± 5.05 |
| Mixed liquor COD (%) | - | 82.51 ± 5.42 | 87.33 ± 3.48 |
| sCOD Removal efficiency (%) | 62.88 ± 10.73 | 91.09 ± 4.88 | 94.43 ± 1.71 |
| Feed NH4-N (mg/L) | - | 42.80 ± 3.23 | 51.73 ± 8.62 |
| Effluent NH4-N (mg/L) | - | 48.93 ± 2.26 | 55.34 ± 7.20 |
| Peaks Locations | Peak A | Peak B | Peak C | Peak D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent (nm) | 225–240/300–340 | 280–320/320–360 | ND | ND | |
| AnMBR (nm) | Bound EPS | 235–240/340–355 | 280–320/340–360 | ND | 310–330/370–400 |
| Soluble EPS | 235–240/340–355 | 300–350/320–360 | ND | 285/405 | |
| Effluent (nm) | 235–240/340–355 | 300–350/320–360 | 240/415 | 285/405 | |
| Parameters | Fouled Membrane (a) | Cleaned Membrane with Alkaline (b) | Cleaned Membrane with Citric Acid (c) | Sludge from the Membrane Tube (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 14.13 ± 0.67 | 37.08 | 43.65 | 34.32 ± 1.92 |
| N | 2.94 ± 2.68 | 1.95 | 1.08 | 9.53 ± 1.80 |
| O | 10.62 ± 12.22 | 6.00 | 3.28 | 46.52 ± 1.19 |
| F | 5.51 ± 7.79 | 21.4 | 38.84 | - |
| Na | 1.80 ± 0.50 | 12.15 | 2.95 | 0.44 ± 0.178 |
| Mg | 1.69 ± .47 | 0.91 | 1.11 | - |
| Al | 3.45 ± .48 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 1.40 ± 0.36 |
| Si | 3.45 ± .33 | 1.09 | 1.3 | 3.25 ± 1.23 |
| P | 3.89 ± 1.76 | 1.26 | 1.14 | 1.57 ± 1.50 |
| S | 12.09 ± 4.82 | 1.25 | 1.05 | 0.57 ± 0.12 |
| Cl | 2.66 ± 0.00 | 4.85 | 1.15 | - |
| K | 1.52 ± 0.47 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.08 ± 0.02 |
| Ca | 3.64 ± 0.16 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 0.11 ± 0.06 |
| Fe | 13.20 ± 1.11 | 7.48 | 0.00 | 1.93 ± 0.57 |
| Cu | 7.52 ± 6.05 | 1.85 | 1.87 | 0.16 ± 0.04 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin Vincent, N.; Tong, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y. Membrane Fouling Characteristics of a Side-Stream Tubular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) Treating Domestic Wastewater. Processes 2018, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6050050
Martin Vincent N, Tong J, Yu D, Zhang J, Wei Y. Membrane Fouling Characteristics of a Side-Stream Tubular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) Treating Domestic Wastewater. Processes. 2018; 6(5):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6050050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin Vincent, Nsanzumukiza, Juan Tong, Dawei Yu, Junya Zhang, and Yuansong Wei. 2018. "Membrane Fouling Characteristics of a Side-Stream Tubular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) Treating Domestic Wastewater" Processes 6, no. 5: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6050050
APA StyleMartin Vincent, N., Tong, J., Yu, D., Zhang, J., & Wei, Y. (2018). Membrane Fouling Characteristics of a Side-Stream Tubular Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR) Treating Domestic Wastewater. Processes, 6(5), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6050050