Machine Learning and Hybrid Approaches in the Energy Valorization of Contaminated Sludge: Global Trends and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
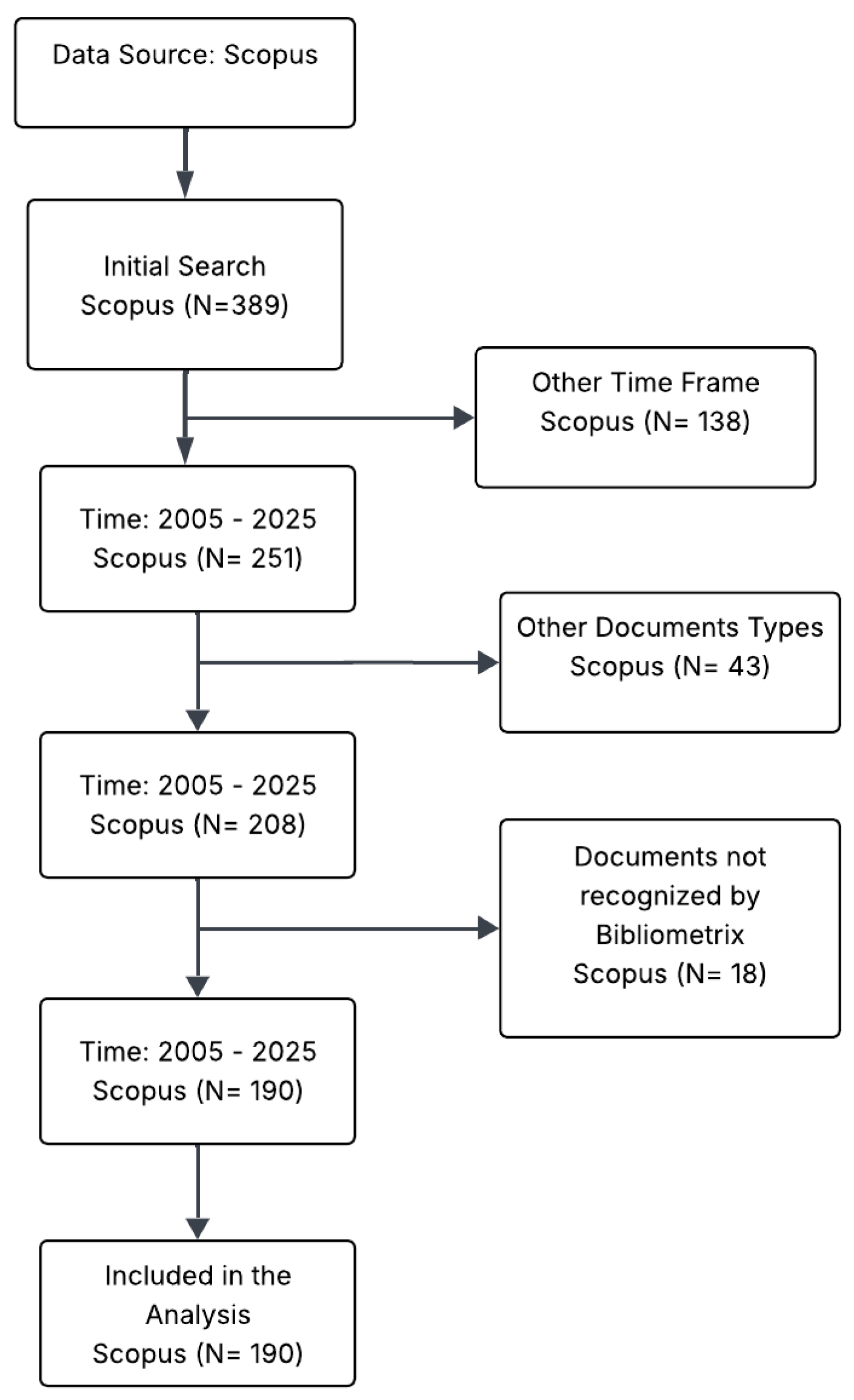
2. Materials and Methods
3. Bibliometric Results and Analysis
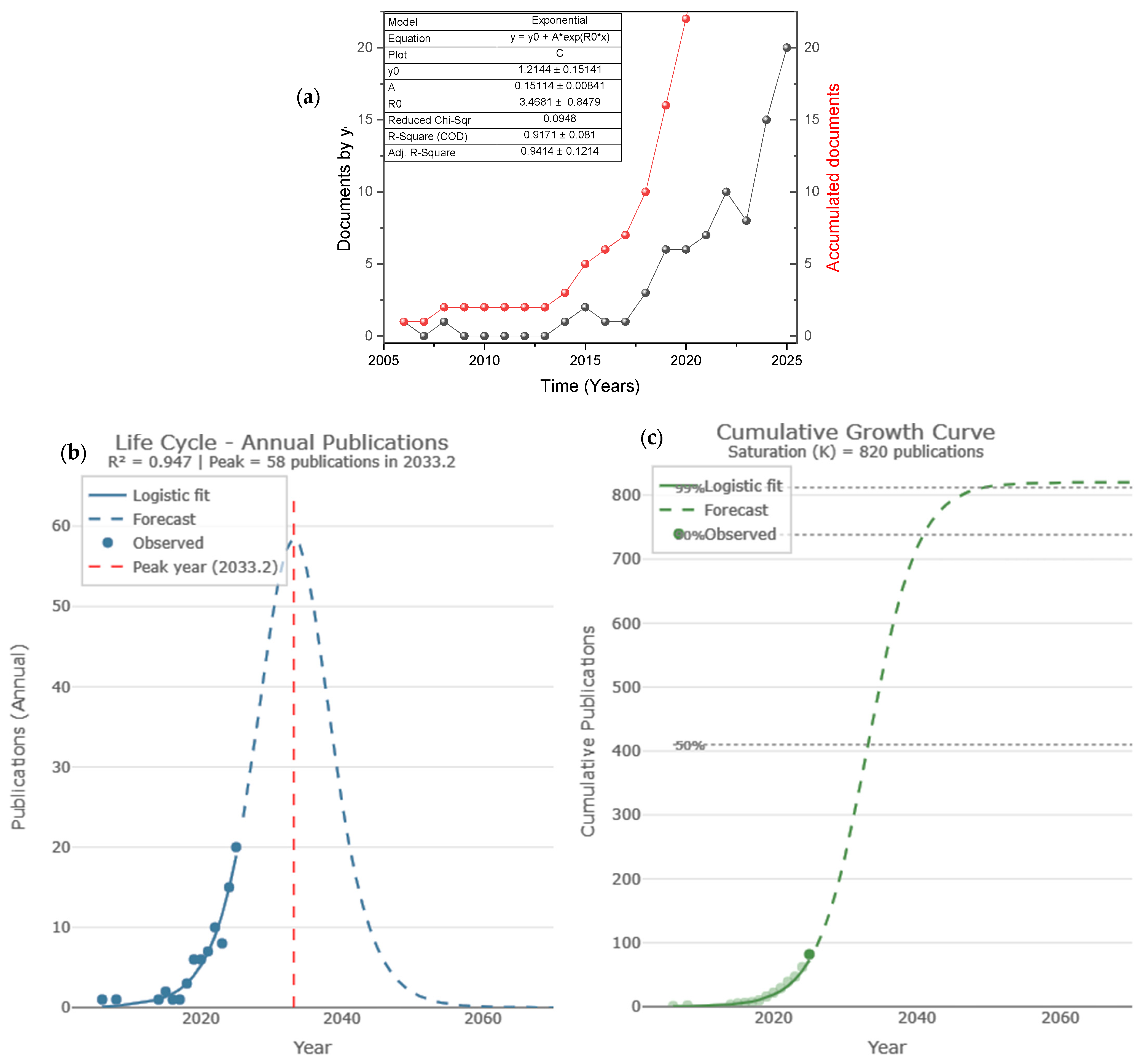
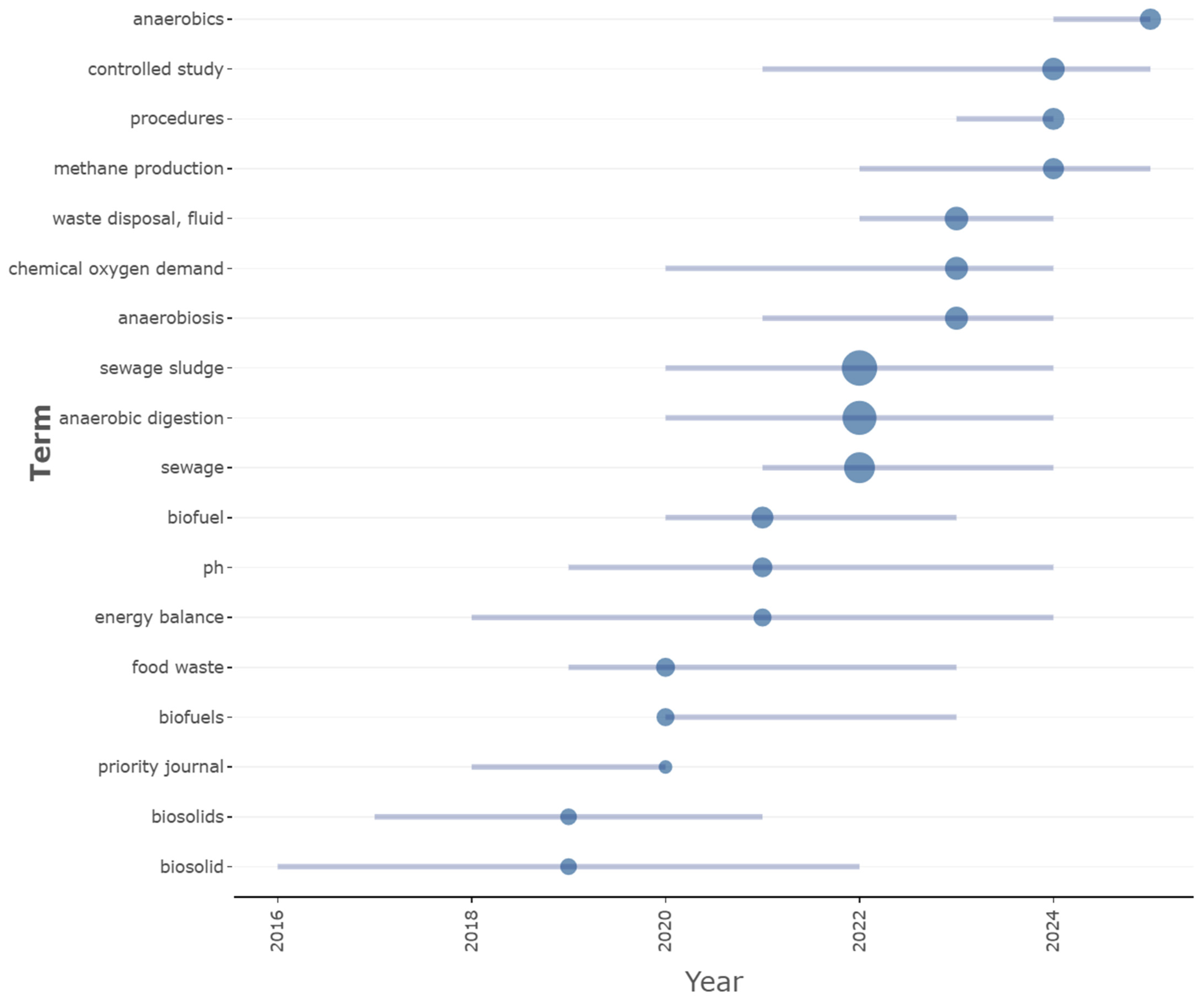
3.1. Future Research Trends
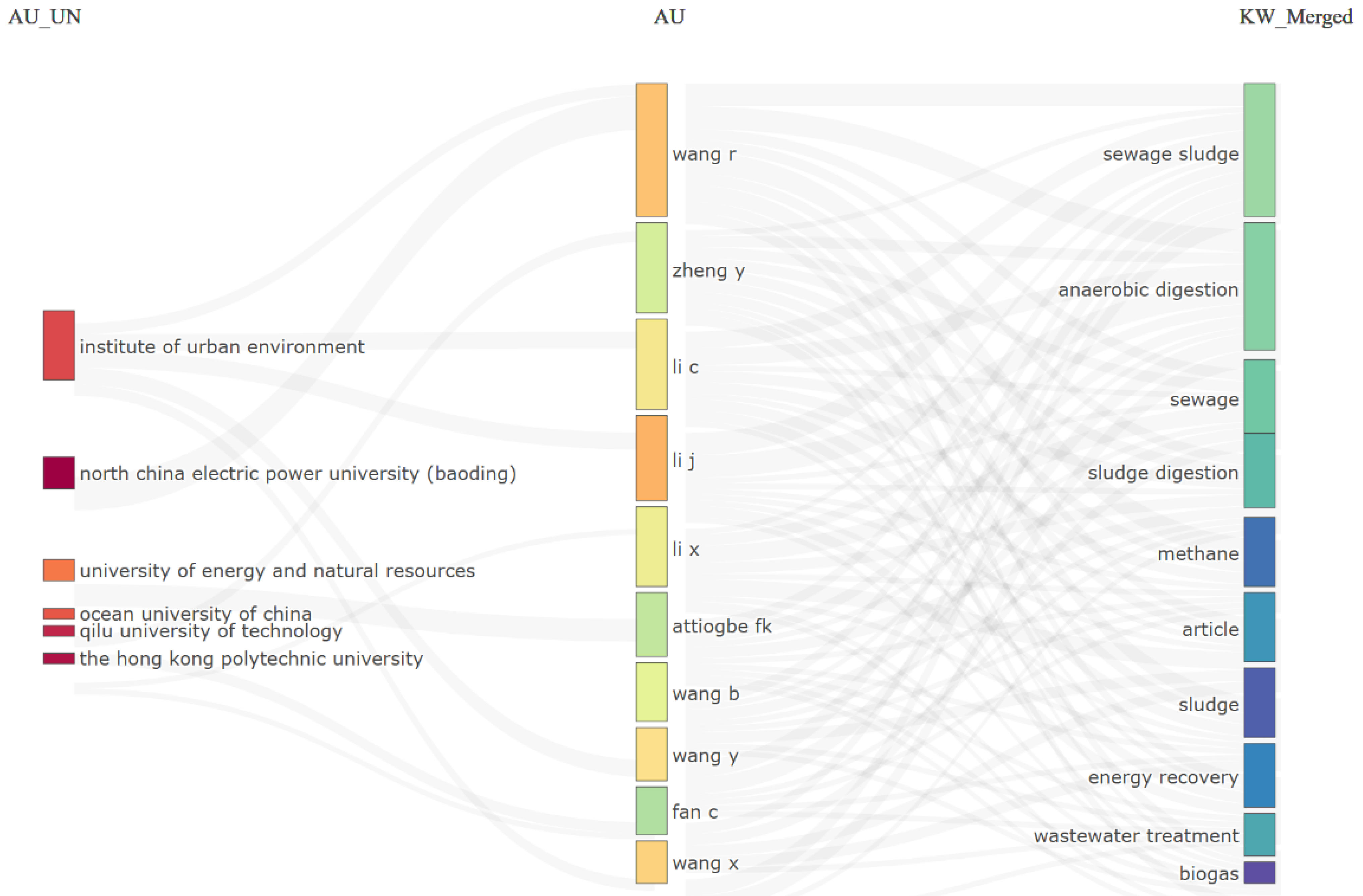
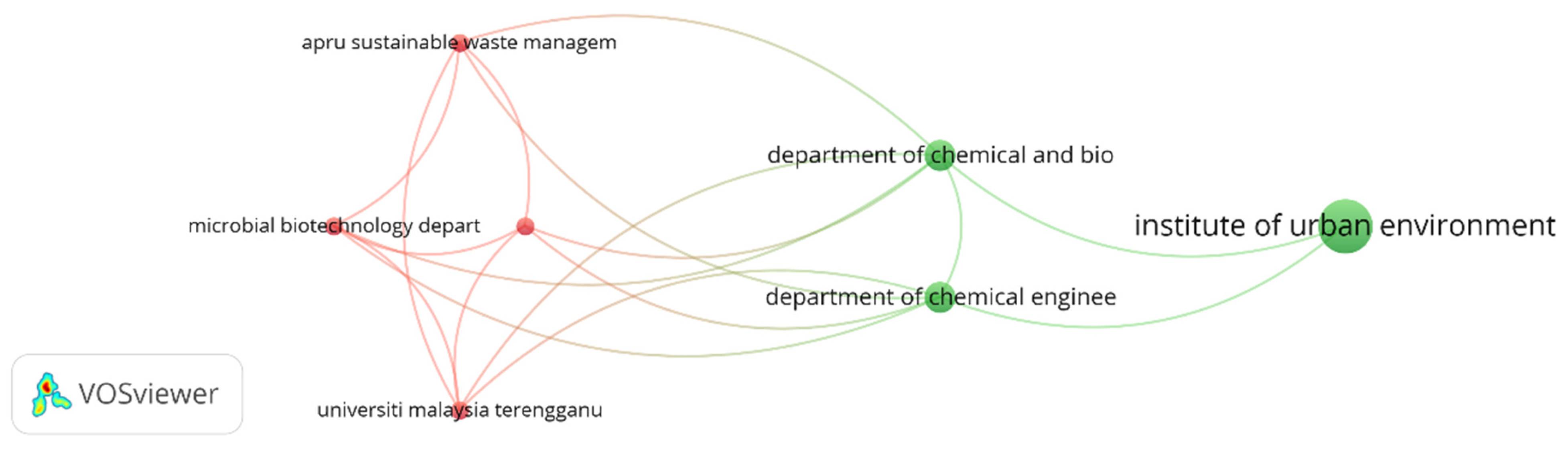
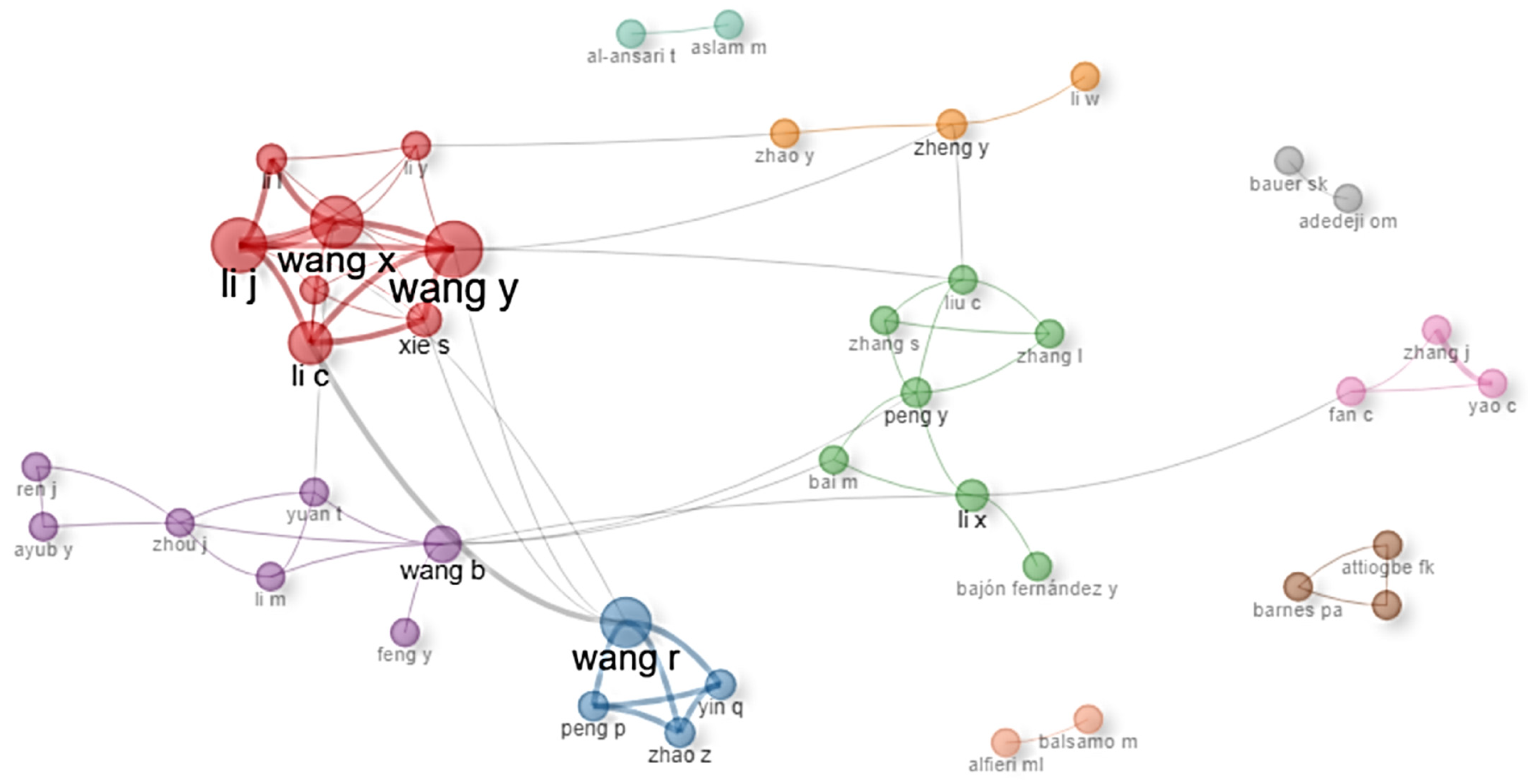
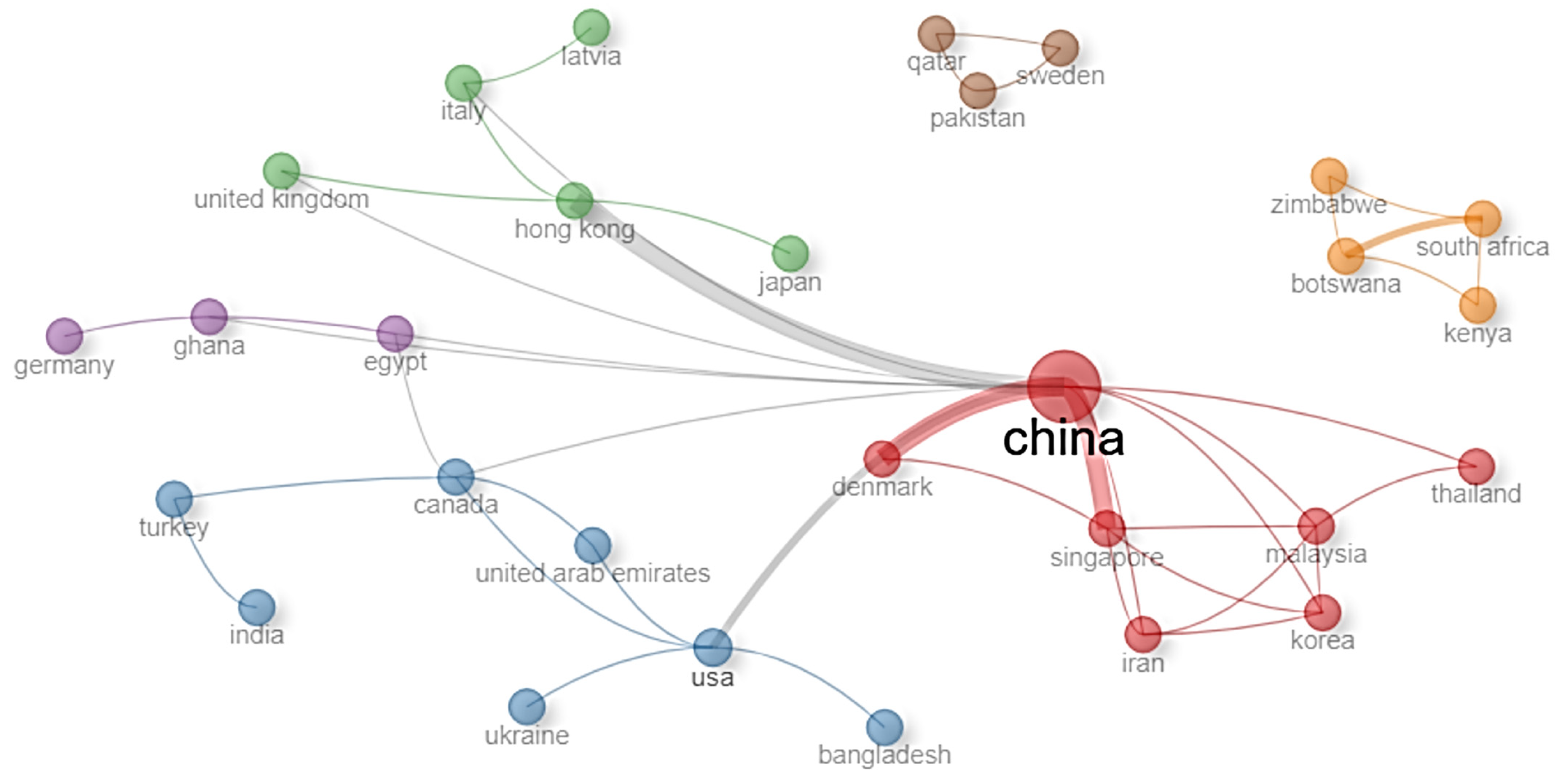
3.2. Collaboration Opportunities Inferred from Research Networks
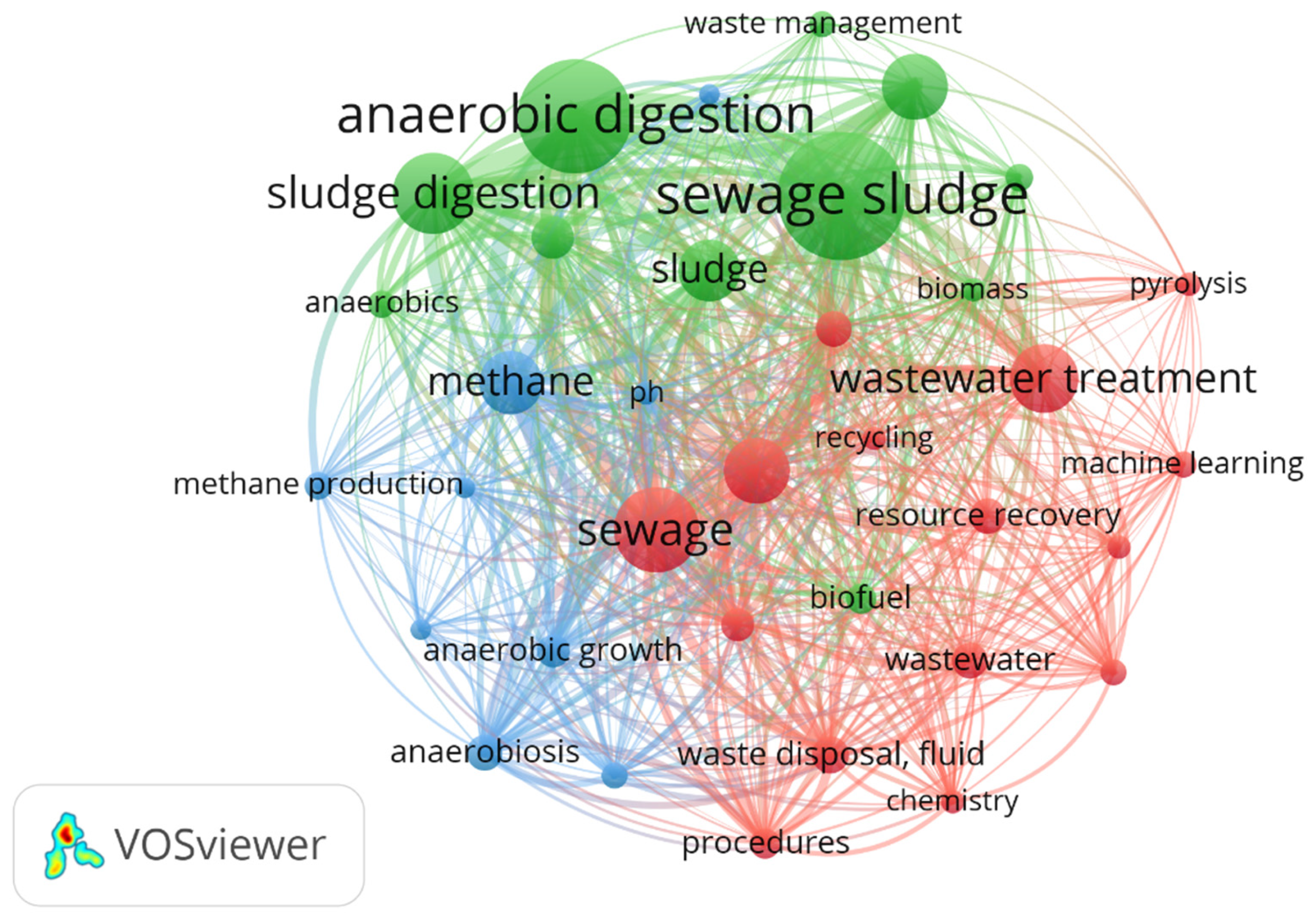
3.3. Integration of ML into Core Valorization Technologies
3.4. Integration of ML into Core Valorization Technologies
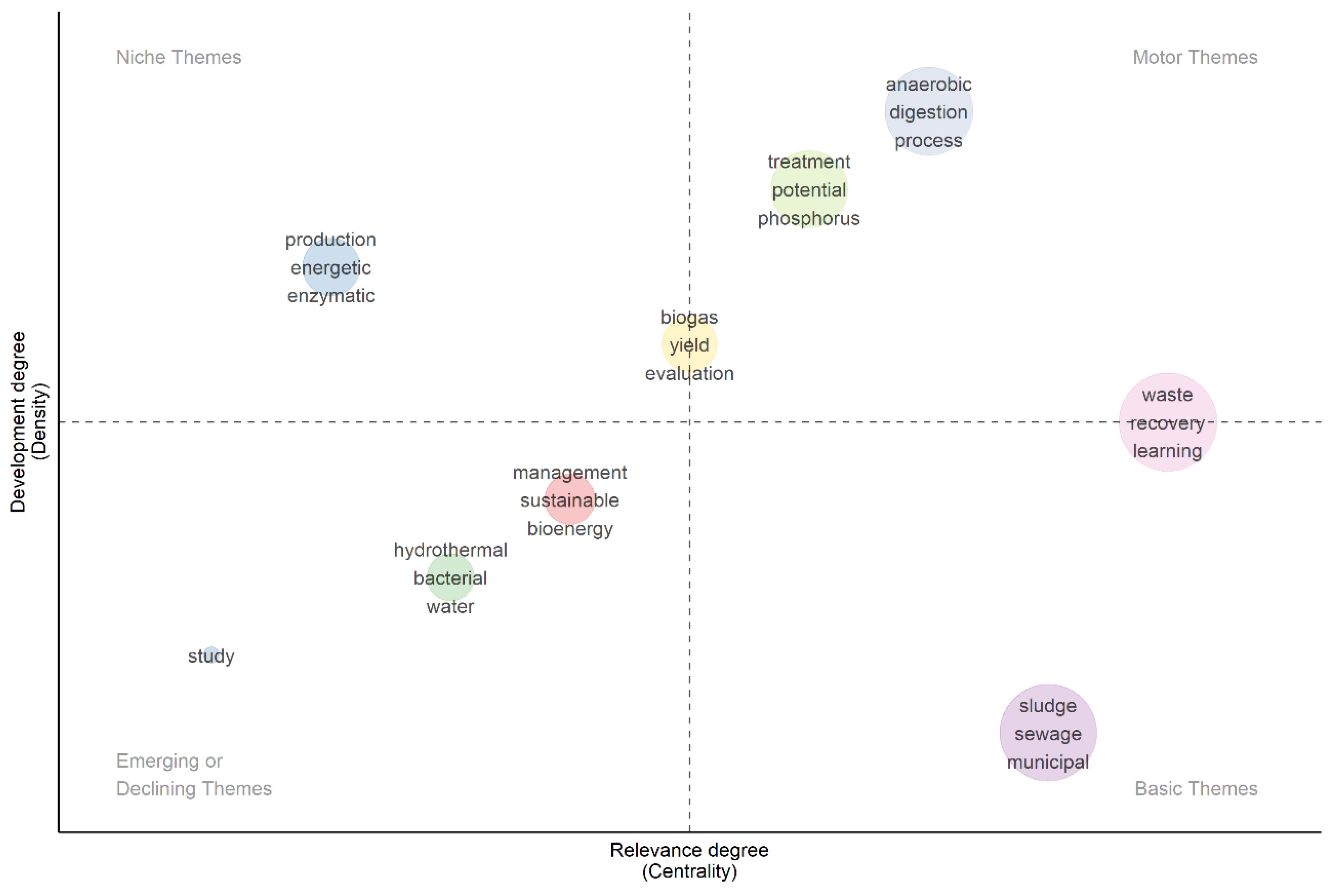
- Developing hybrid (“gray-box”) models that merge the mechanistic knowledge of anaerobic digestion (central cluster in Figure 8) with ML algorithms (peripheral node), thereby creating thematic bridges currently absent.
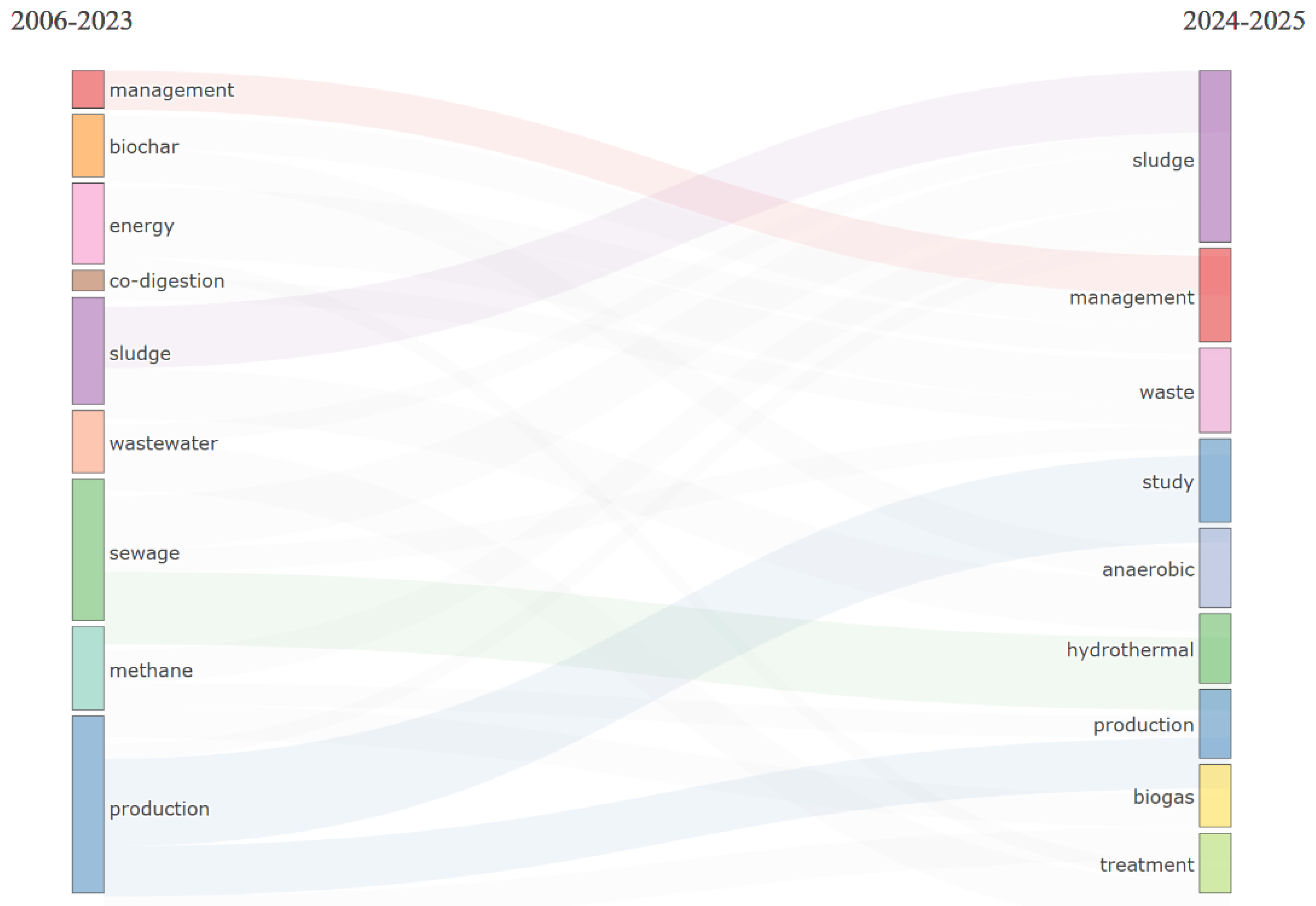
- Applying ML to emerging technologies such as hydrothermal carbonization, which appears as an emergent theme in Figure 9 (Thematic evolution 2006–2025). The transition from “anaerobic digestion” toward “hydrothermal” and “biogas” in 2024–2025 indicates a window of opportunity to incorporate ML from the early research phase, rather than as a later add-on.
- Such integration would not only optimize operational parameters but also enable the design of adaptive processes responsive to sludge variability—a critical need identified in the reviewed literature but not yet addressed with advanced computational tools.
3.5. Methodological Priorities Based on Scientific Productivity
- Standardization of descriptors and open data: The fragmentation observed in collaboration networks and the concentration of data in a few countries limit reproducibility and generalization of ML models. Public repositories harmonized with data on composition, operational parameters, and energy yields across multiple plants and regions are needed [64].
- Real-scale validation (pilot/industrial): The predominance of technical feasibility studies in the most cited literature (Table 2) contrasts with the absence of practical validation of ML models under variable operating conditions. Prioritizing full-scale demonstrative projects is essential to bridge the gap between simulation and implementation.
- Development of comprehensive evaluation metrics: Given the emerging focus on “energy balance” (Figure 7) and sustainability, future studies must integrate multi-criteria assessments combining (a) ML predictive accuracy, (b) net energy efficiency, (c) AI-accelerated life cycle analysis, and (d) economic feasibility. This would align research with the principles of circular economy driving the field [65].
3.6. Case Studies of Successful Industrial-Scale Implementations of Hybrid Approaches
- Case Study 1: Predictive Control in Anaerobic Digestion—Tuas Nexus, Singapore
- Case Study 2: Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) Optimization—Avium Plant, Germany
- Case Study 3: Co-Digestion with Food Waste—California, USA
3.7. Scale and Technological Readiness of Reviewed Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scaria, J.; Anupama, K.; Nidheesh, P. Tetracyclines in the environment: An overview on the occurrence, fate, toxicity, detection, removal methods, and sludge management. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Yadav, A.; Mandal, M.K.; Pandey, S.; Pal, S.; Chaudhuri, H.; Chakrabarti, S.; Dubey, K.K. Wastewater treatment and sludge management strategies for environmental sustainability. In Circular Economy and Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mamera, M.; van Tol, J.J.; Aghoghovwia, M.P. Treatment of faecal sludge and sewage effluent by pinewood biochar to reduce wastewater bacteria and inorganic contaminants leaching. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, D.S.; Vijay, K.; Nidheesh, P.; Kumar, M.S. Performance of continuous aerated iron electrocoagulation process for arsenite removal from simulated groundwater and management of arsenic-iron sludge. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojevic, N.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Agricultural Use of Sewage Sludge as a Threat of Microplastic (MP) Spread in the Environment and the Role of Governance. Energies 2021, 14, 6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Duan, H.; Song, Y.; Lu, X.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Batstone, D.; Zheng, M. Post-treatment options for anaerobically digested sludge: Current status and future prospect. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, K.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Niu, X.; Yi, L.; Lin, Z.; Fu, M. Environmental, energy, and economic impact assessment of sludge management alternatives based on incineration. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.R.; Sivasubramanian, V. Optimization and evaluation of malathion removal by electrocoagulation process and sludge management. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Qin, R.; Mao, X. A Review on Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, and Smart Technology in Water Treatment and Monitoring. Water 2022, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviteja, K.V.N.S.; Reddy, K.R. Application of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in contaminated site remediation. In Recent Developments in Energy and Environmental Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 411–425. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.C.W. Overview of Hazardous Waste Treatment and Stabilization/Solidification Technology. In Low Carbon Stabilization and Solidification of Hazardous Wastes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ajorloo, M.; Ghodrat, M.; Scott, J.; Strezov, V. Heavy metals removal/stabilization from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: A review and recent trends. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 1693–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, F.; Mei, Z.; Lv, L.; Chi, Y. Status and Development of Sludge Incineration in China. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 12, 3541–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, G.; Romano, P. Evolution and prospects in managing sewage sludge resulting from municipal wastewater purification. Energies 2022, 15, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, O.; Jen, T.-C. Data-driven and explainable AI (XAI) framework for optimizing methane yield in large-scale biogas production. Sustain. Energy Res. 2025, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, M.; Arezoo, B.; Dastres, R. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in CNC machine tools, A review. Sustain. Manuf. Serv. Econ. 2023, 2, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenda, M.; Porcaro, C.; Iero, D. Edge Machine Learning for AI-Enabled IoT Devices: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.U.; Lim, K.M. Combined deep CNN–LSTM network-based multitasking learning architecture for noninvasive continuous blood pressure estimation using difference in ECG-PPG features. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, A.H.; Salleh, N.O.; Baharun, R.O. Bibliometric analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2020, 98, 2948–2962. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, W.; Duarte, A.E. Bibliometric analysis: A few suggestions. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, O.; Danell, R.; Schneider, J.W. How to use Bibexcel for various types of bibliometric analysis. In Celebrating Scholarly Communication Studies: A Festschrift for Olle Persson at His 60th Birthday; International Society for Scientometrics and Informetrics: Leuven, Belgium, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Huo, T.; Xue, M.; Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xie, M.; Ye, Z. Artificial intelligence to detect the femoral intertrochanteric fracture: The arrival of the intelligent-medicine era. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 927926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaunert, C. Accelerating Healthcare Outcomes Uplifting Patient Experiences Pairing Artificial intelligence (AI): Transforming the Healthcare Industry in the Digital Arena. In Impact of Digital Solutions for Improved Healthcare Delivery; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 121–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sutaria, V.; Jain, A. ECG-Based Stress Detection: A Review of Machine Learning Techniques. In Intelligent Strategies for ICT: Proceedings of ICTCS 2024; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; Volume 5, p. 125. [Google Scholar]
- Samkhaniani, M.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Mesghali, H.; Ghajari, A.; Gozalpour, N. A machine learning approach to feature selection and uncertainty analysis for biogas production in wastewater treatment plants. Waste Manag. 2025, 197, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, S.; Yucel, O. Enhancing biogas production from municipal wastewater sludge and grease trap waste: Explainable machine learning models for prediction and parameter identification. Fuel 2025, 391, 134787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, R.; Huang, J.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. Magnetic biochar promotes the risk of mobile genetic elements propagation in sludge anaerobic digestion. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 335, 117492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Han, H.; Zheng, K.; Zhu, M.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, S.; Hu, S.; et al. Sludge pyrolysis integrated biomass gasification to promote syngas: Comparison of different biomass. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 908, 168278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, C. Enhanced Anaerobic Co-digestion of Organic Waste with Activated Carbon Addition: Effects on Methane Production and Microbial Community. Waste Biomass Valorization 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesay, F.; Sesay, M.; Azizi, M.I.; Kanneh, S.M.; Mwale, M.; Rahmani, B. Circular Economy towards Sustainable Development: A Review of U.S., E.U., and China’s Polices. Adv. Res. 2025, 26, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Silva, T.C.D.; Chandra, R.; Malik, A.; Vijay, V.K.; Misra, A. Impact of hydrothermal pretreatment at different temperatures on biomethane yield in anaerobic digestion of rice husk. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 15, 28291–28306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhuang, Y. Bioprocess engineering and intelligent biomanufacturing. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2024, 40, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, M. AI-Enhanced Biomedical Engineering: Innovations at the Intersection of Health and Technology. J. STEM Res. 2024, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Rao, Y.; Cao, L.; Shi, Y.; Hao, S.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge: Focusing on the characterization of liquid products and their methane yields. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.M.; Mahler, C.F.; Oliveira, L.B.; Bassin, J.P. Hydrogen and methane production in a two-stage anaerobic digestion system by co-digestion of food waste, sewage sludge and glycerol. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Tariq, R.; Shahbaz, M.; Naqvi, M.; Aslam, M.; Khan, Z.; Mackey, H.; Mckay, G.; Al-Ansari, T. Recent developments on sewage sludge pyrolysis and its kinetics: Resources recovery, thermogravimetric platforms, and innovative prospects. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 150, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Batista, J.; Mohedano, A.; Rodríguez, J.; de la Rubia, M. Energy and phosphorous recovery through hydrothermal carbonization of digested sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, R.Z.; Khoury, O.; Zohar, M.; Poverenov, E.; Darzi, R.; Laor, Y.; Posmanik, R. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge coupled with anaerobic digestion: Integrated approach for sludge management and energy recycling. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 224, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Suvarna, M.; Pan, L.; Tabatabaei, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, X. Wet wastes to bioenergy and biochar: A critical review with future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiple, T.E.; Skaggs, R.L.; Fillmore, L.; Coleman, A.M. Municipal wastewater sludge as a renewable, cost-effective feedstock for transportation biofuels using hydrothermal liquefaction. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, A.; Kokko, M.; Kinnunen, V.; Hilli, T.; Rintala, J. Hydrothermal carbonisation of mechanically dewatered digested sewage sludge—Energy and nutrient recovery in centralised biogas plant. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.A.; Li, L.Y.; Hamid, H.; Jeronimo, M. Sludge-based activated carbon and its application in the removal of perfluoroalkyl substances: A feasible approach towards a circular economy. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lin, K.; Ren, D.; Peng, P.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, Q.; Gao, P. Energy conversion performance in co-hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge and pinewood sawdust coupling with anaerobic digestion of the produced wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obreja, D.M.; Rughiniș, R.; Rosner, D. Mapping the conceptual structure of innovation in artificial intelligence research: A bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, P.; Bloom, M.; Camerani, R.; Masucci, M.; Siepel, J.; Ospina, J.V. Mapping the state of the art of creative cluster research: A bibliometric and thematic analysis. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2023, 31, 2531–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Xu, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Tian, W.; Ju, J.; Xu, H. Knowledge Domain and Emerging Trends in Ferroptosis Research: A Bibliometric and Knowledge-Map Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 686726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Meng, F.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Farrukh, M. Mapping and Clustering Analysis on Environmental, Social and Governance Field a Bibliometric Analysis Using Scopus. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Passerini, A.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N. Machine learning for microbiologists. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, L.A.; Köstler, M.; Grundwürmer, M.; Li, L.; Huber, B.; Gaderer, M. State estimation of a biogas plant based on spectral analysis using a combination of machine learning and metaheuristic algorithms. Appl. Energy 2024, 377, 124447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niza, I.L.; Gomes, G.C.C.; Broday, E.E. Indoor environmental quality models: A bibliometric, mapping and clustering review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 203, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S. Fishing Vessel Risk and Safety Analysis: A Bibliometric Analysis, Clusters Review and Future Research Directions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandani, A.A.; Lan, J.C.-W.; Lim, J.W.; Lay, C.-H.; Srimongkol, P.; Srinuanpan, S.; Khoo, K.S. Artificial intelligence-driven and prediction of green biohydrogen derived from microalgae biorefinery: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 225, 116118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mario, J.; Montegiove, N.; Gambelli, A.M.; Brienza, M.; Zadra, C.; Gigliotti, G. Waste Biomass Pretreatments for Biogas Yield Optimization and for the Extraction of Valuable High-Added-Value Products: Possible Combinations of the Two Processes toward a Biorefinery Purpose. Biomass 2024, 4, 865–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipabu, M.I.; Huang, C.-M.; Irfan, H.M.; Viswanathan, K.; Adi, V.S.K.; Wu, W. Superstructure optimization of hydrothermal liquefaction for microalgae biorefinery considering environmental impacts and economics. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, N.; Psarianos, M.; Herrmann, C.; Schulz-Nielsen, L.; Olszewska-Widdrat, A.; Arefi, A.; Pecenka, R.; Grundmann, P.; Schlüter, O.K.; Hoffmann, T.; et al. Smart integrated biorefineries in bioeconomy: A concept toward zero-waste, emission reduction, and self-sufficient energy production. Biofuel Res. J. 2025, 12, 2319–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulisz, M.; Kujawska, J.; Cioch, M.; Cel, W.; Pizoń, J. Comparative analysis of machine learning methods for pre-dicting energy recovery from waste. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, N.B.; Anjum, F.; Nur, I.M.; Paul, T.; Reza, A.W. Assessing the Significance of Machine Learning in Forecasting Energy Recovery from Waste. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 252, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Thakur, N.S.; Jyoti, D.; Mahato, D.P. Machine Learning for Waste-to-Energy: Optimization and Predictive Analytics. In International Conference on Advanced Network Technologies and Intelligent Computing; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Croll, H.C.; Ikuma, K.; Ong, S.K.; Sarkar, S. Systematic Performance Evaluation of Reinforcement Learning Algorithms Applied to Wastewater Treatment Control Optimization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18382–18390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhang, H.; Parker, W.; Yin, R.; Bai, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ren, H. Bayesian Optimization-Enhanced Reinforcement learning for Self-adaptive and multi-objective control of wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 421, 132210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wei, Q.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, E.; Wu, X.; Dong, R.; Guo, J. Dynamic control of thermal hydrolysis to maximize net energy recovery from sewage sludge based on machine learning. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 438, 133263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chao, W.; Wang, Y.; Ren, N.; Lu, L. Prediction of Waste Sludge Production in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants by Deep-Learning Algorithms with Antioverfitting Strategies. ACS ES&T Eng. 2025, 5, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Gangaraju, D.; Paul, B.; Chauhan, N.; Gola, D.; Aarthy, S.; Amulya, M.R.; Ananya, N.N.; Ayana, E.K.; Charishma, C.G.; et al. Bacterial Biofuel Production: An Assessment of Machine Learning Technologies in Valorisation of Waste/Wastewater and Circular Economy. In Trash or Treasure: Entrepreneurial Opportunities in Waste Management; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 255–275. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.T.; Li, B.; Naqvi, M. Revolutionizing municipal solid waste management (MSWM) with machine learning as a clean resource: Opportunities, challenges and solutions. Fuel 2023, 348, 128548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasode, P.; Pawar, M.; Patki, V.; R, S.; Patange, S.; Sangolli, S. Data-Driven Waste Management: Machine Learning and Excess Reprocessing for Optimized Environmental Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Innovation and Novelty in Engineering and Technology (INNOVA), Vijayapura, India, 20–21 December 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, F.; Akkermans, H.; Aksin, O.Z.; Ali, I.; Babai, M.Z.; Barbosa-Povoa, A.; Battaïa, O.; Besiou, M.; Boysen, N.; Brammer, S.; et al. Operations & supply chain management: Principles and practice. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 64, 330–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Institution | Country | Publications | Total Citations | Average Citations | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North China Electric Power University (Baoding) | China | 6 | 213 | 35.5 | 6 |
| Institute of Urban Environment | China | 4 | 67 | 16.75 | 3 |
| College of Environmental Science and Engineering | China | 4 | 63 | 15.75 | 3 |
| Department of Civil Engineering | Canada | 3 | 78 | 26 | 3 |
| Department of Environmental Health Engineering | Iran | 3 | 57 | 19 | 3 |
| Department of Environmental Engineering | Turkey | 3 | 30 | 10 | 3 |
| Tongji University | China | 3 | 207 | 69 | 2 |
| Department of Environmental Engineering | South Korea | 2 | 32 | 16 | 1 |
| Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering | United States | 2 | 40 | 20 | 2 |
| Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering | Singapore | 2 | 94 | 47 | 1 |
| N° | Title | Authors | Year | Journal | Citations | Type | Open Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge: Focusing on the characterization of liquid products and their methane yields [35]. | Chen, H.; Rao, Y.; Cao, L.; Shi, Y.; Hao, S.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. | 2019 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 195 | Article | Not Available |
| 2 | Hydrogen and methane production in a two-stage anaerobic digestion system by co-digestion of food waste, sewage sludge and glycerol [36]. | Silva, F.M.S.; Mahler, C.F.; Oliveira, L.B.; Bassin, J.P. | 2018 | Waste Management | 161 | Article | Not Available |
| 3 | Recent developments on sewage sludge pyrolysis and its kinetics: Resources recovery, thermogravimetric platforms, and innovative prospects [37]. | Naqvi, S.R.; Tariq, R.; Shahbaz, M.; Naqvi, M.; Aslam, M.; Khan, Z.; Mackey, H.; Gordon, G.; Al-Ansari, T. | 2021 | Computers and Chemical Engineering | 130 | Review | Not Available |
| 4 | Energy and phosphorous recovery through hydrothermal carbonization of digested sewage sludge [38]. | Marin-Batista, J.D.; Mohedano, A.F.; Rodriguez, J.J.; de la Rubia, M.A. | 2020 | Waste Management | 123 | Article | All Open Access |
| 5 | Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge coupled with anaerobic digestion: Integrated approach for sludge management and energy recycling [39]. | Gaur, R.Z.; Khoury, O.; Zohar, M.; Poverenov, E.; Darzi, R.; Laor, Y.; Posmanik, R. | 2020 | Energy Conversion and Management | 122 | Article | Not Available |
| 6 | Wet wastes to bioenergy and biochar: A critical review with future perspectives [40]. | Li, J.; Li, L.; Suvarna, M.; Pan, L.; Tabatabaei, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, X. | 2022 | Science of the Total Environment | 94 | Review | Not Available |
| 7 | Municipal wastewater sludge as a renewable, cost-effective feedstock for transportation biofuels using hydrothermal liquefaction [41]. | Seiple, T.E.; Skaggs, R.L.; Fillmore, L.; Coleman, A.M. | 2020 | Journal of Environmental Management | 67 | Article | All Open Access |
| 8 | Hydrothermal carbonisation of mechanically dewatered digested sewage sludge—Energy and nutrient recovery in centralized biogas plant [42]. | Hämäläinen, A.; Kokko, M.; Kinnunen, V.; Hilli, T.; Rintala, J. | 2021 | Water Research | 56 | Article | All Open Access |
| 9 | Sludge-based activated carbon and its application in the removal of perfluoroalkyl substances: A feasible approach towards a circular economy [43] | Mohamed, B.A.; Li, L.Y.; Hamid, H.; Jeronimo, M. | 2022 | Chemosphere | 54 | Article | Not Available |
| 10 | Energy conversion performance in co-hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge and pinewood sawdust coupling with anaerobic digestion of the produced wastewater [44]. | Wang, R.; Lin, K.; Ren, D.; Peng, P.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, Q.; Gao, P. | 2022 | Science of the Total Environment | 52 | Article | Not Available |
| TRL Stage | Number of Studies | Main Type of Outcome | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRL 1–3 (Basic Research) | 42 (22.1%) | Algorithm development, conceptual models | ML algorithms for biogas prediction from lab data [18,55] |
| TRL 4–5 (Lab/Pilot) | 98 (51.6%) | Methodology, hybrid model frameworks | Gray-box models for AD optimization at bench scale [57,62] |
| TRL 6–7 (Prototype/Demo) | 38 (20.0%) | Software tools, digital twins | Predictive control software for thermal hydrolysis [64,66] |
| TRL 8–9 (Industrial) | 12 (6.3%) | Integrated solutions, SCADA modules | Real-time ML-based optimization in full-scale HTC plants [56,67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Rojas-Flores, S.J.; Liza, R.; Nazario-Naveda, R.; Díaz, F.; Delfin-Narciso, D.; Gallozzo Cardenas, M.; Alviz-Meza, A. Machine Learning and Hybrid Approaches in the Energy Valorization of Contaminated Sludge: Global Trends and Perspectives. Processes 2026, 14, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14020363
Rojas-Flores SJ, Liza R, Nazario-Naveda R, Díaz F, Delfin-Narciso D, Gallozzo Cardenas M, Alviz-Meza A. Machine Learning and Hybrid Approaches in the Energy Valorization of Contaminated Sludge: Global Trends and Perspectives. Processes. 2026; 14(2):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14020363
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas-Flores, Segundo Jonathan, Rafael Liza, Renny Nazario-Naveda, Félix Díaz, Daniel Delfin-Narciso, Moisés Gallozzo Cardenas, and Anibal Alviz-Meza. 2026. "Machine Learning and Hybrid Approaches in the Energy Valorization of Contaminated Sludge: Global Trends and Perspectives" Processes 14, no. 2: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14020363
APA StyleRojas-Flores, S. J., Liza, R., Nazario-Naveda, R., Díaz, F., Delfin-Narciso, D., Gallozzo Cardenas, M., & Alviz-Meza, A. (2026). Machine Learning and Hybrid Approaches in the Energy Valorization of Contaminated Sludge: Global Trends and Perspectives. Processes, 14(2), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14020363









