Coordinated Planning Method for Distribution Network Lines Considering Geographical Constraints and Load Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Establishes a hierarchical system of geographical constraints based on the IAHP to quantify the impacts of terrain undulation, ecological protection zones, and construction obstacles on line construction costs.
- Introduces density peak clustering and load complementarity coefficient to generate equivalent load nodes and construct a load density grid model, realizing integrated modeling of discrete loads and geographical constraints.
- Proposes an improved A-star algorithm, which combines geographical weights and load density guidance to avoid high-cost areas and approach high-load areas.
2. Geographical Constraints and Spatial Gridding Model of Load Density
2.1. Modeling of Geographical Environmental Constraints
2.1.1. Hierarchical System of Geographical Environmental Impact Factors
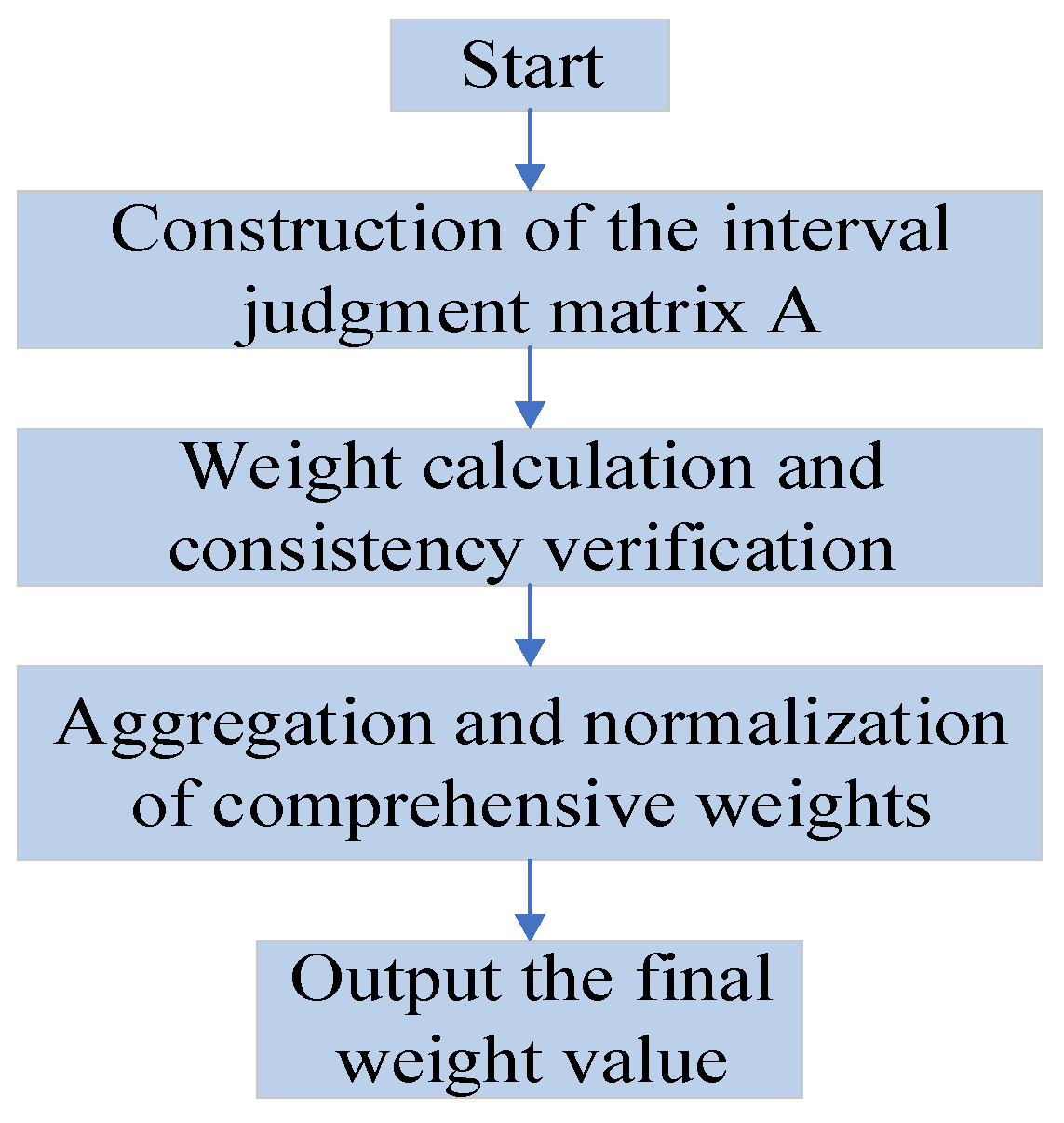
2.1.2. Spatial Weight Quantification of Geographical Environmental Factors
2.2. Grid Modeling of Spatial Load Distribution
3. Distribution Network Line Optimization Method
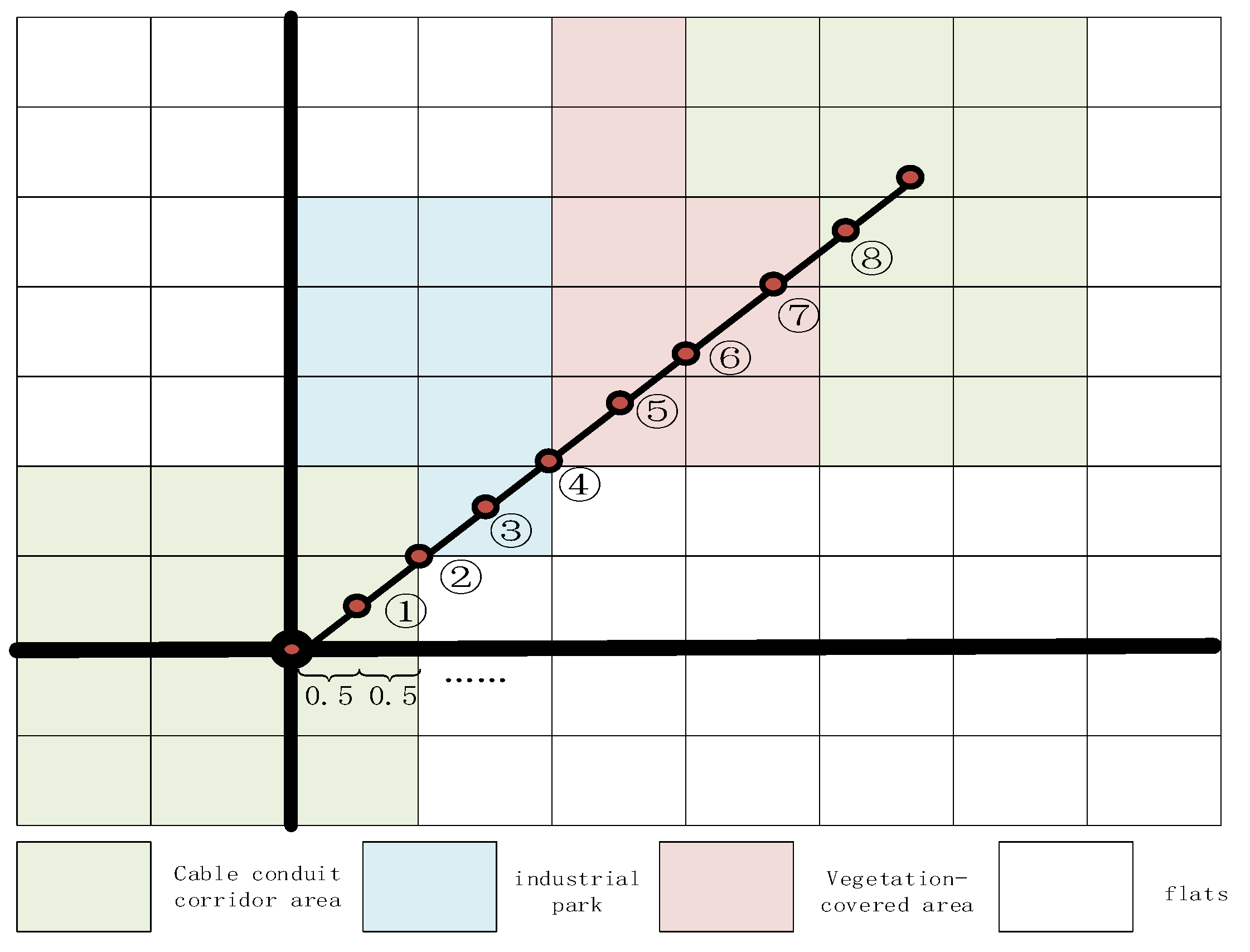
3.1. Grid Definition of Lines Based on Bresenham Algorithm
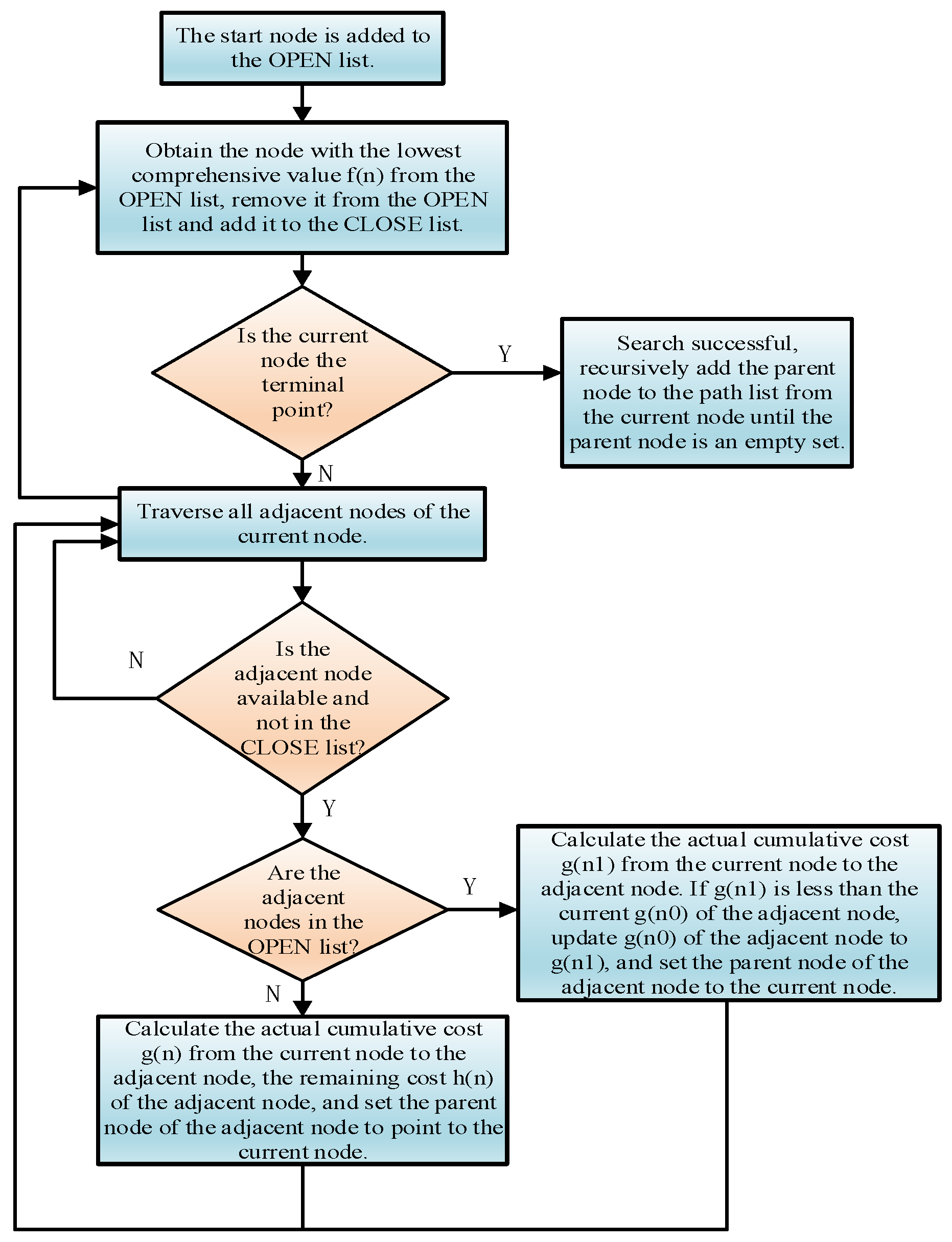
3.2. Improved A-Star Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. Improved A-Star Path Planning. |
| Input: Grid matrix G, load density map L, start S, goal T Strategy mode M, parameters (η, A1) Output: Optimal path P 1: C ← ComputeCostMap(G, L, M, η, A1) //Equation (18) 2: Initialize priority queue Q, closed set Cₗ 3: Initialize g(S) = 0, f(S) = h(S, T) 4: Q.push(S, f(S)) 5: 6: while Q not empty do 7: n ← Q.pop() 8: if n = T then 9: return ReconstructPath(P) 10: Cₗ.add(n) 11: 12: for each neighbor m of n do 13: if m ∉ G or m ∈ Cₗ or C(m) = ∞ then 14: continue 15: 16: gₜₑₘₚ ← g(n) + ‖n-m‖·C(m) //Actual cost 17: 18: if m ∉ Q or gₜₑₘₚ < g(m) then 19: g(m) ← gₜₑₘₚ 20: f(m) ← g(m) + h(m, T) //Equation (20) 21: parent(m) ← n 22: Q.update(m, f(m)) 23: 24: return ∅ //No feasible path |
3.3. Line Smoothing and Engineering Feasibility Constraints
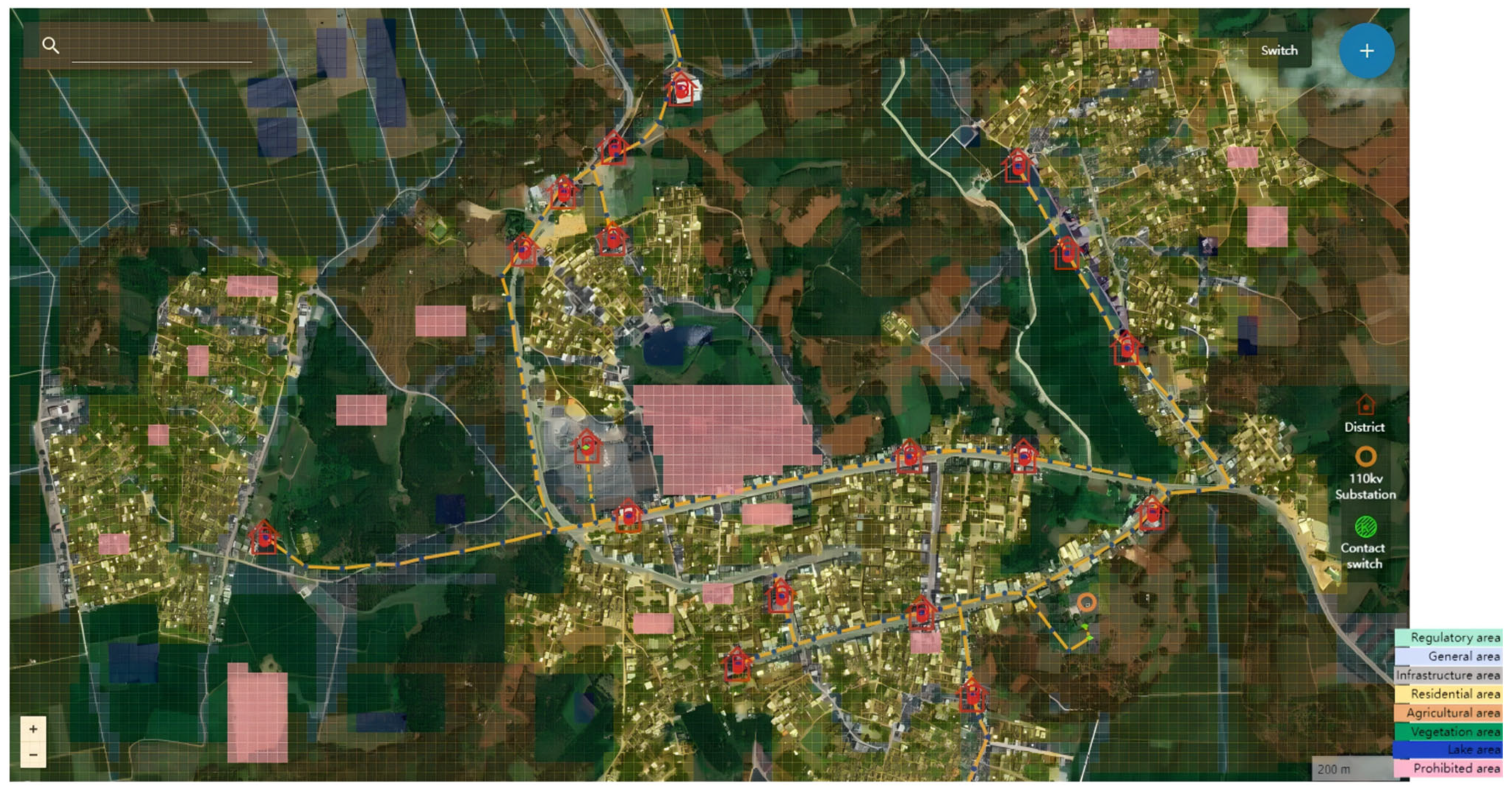
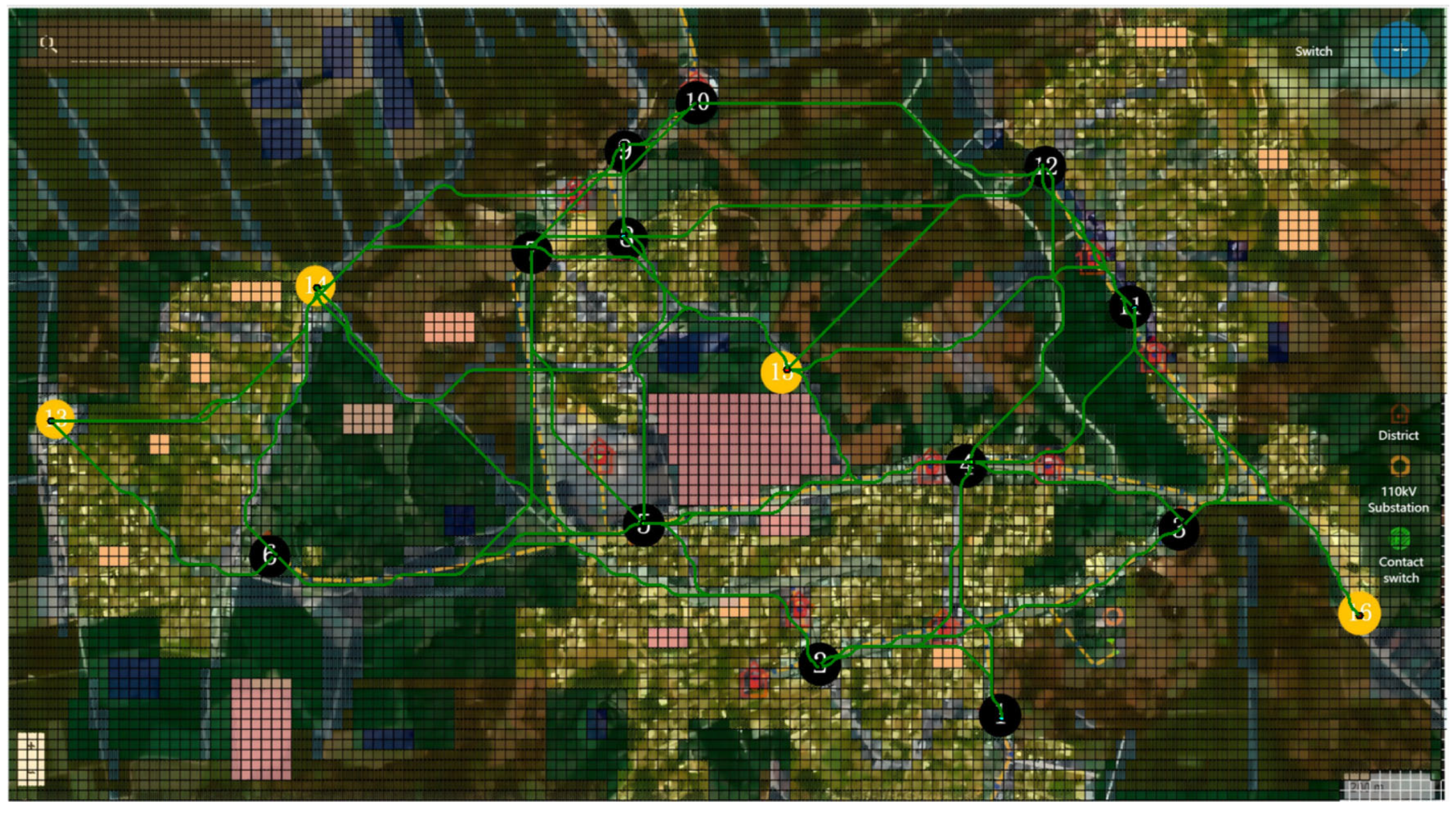
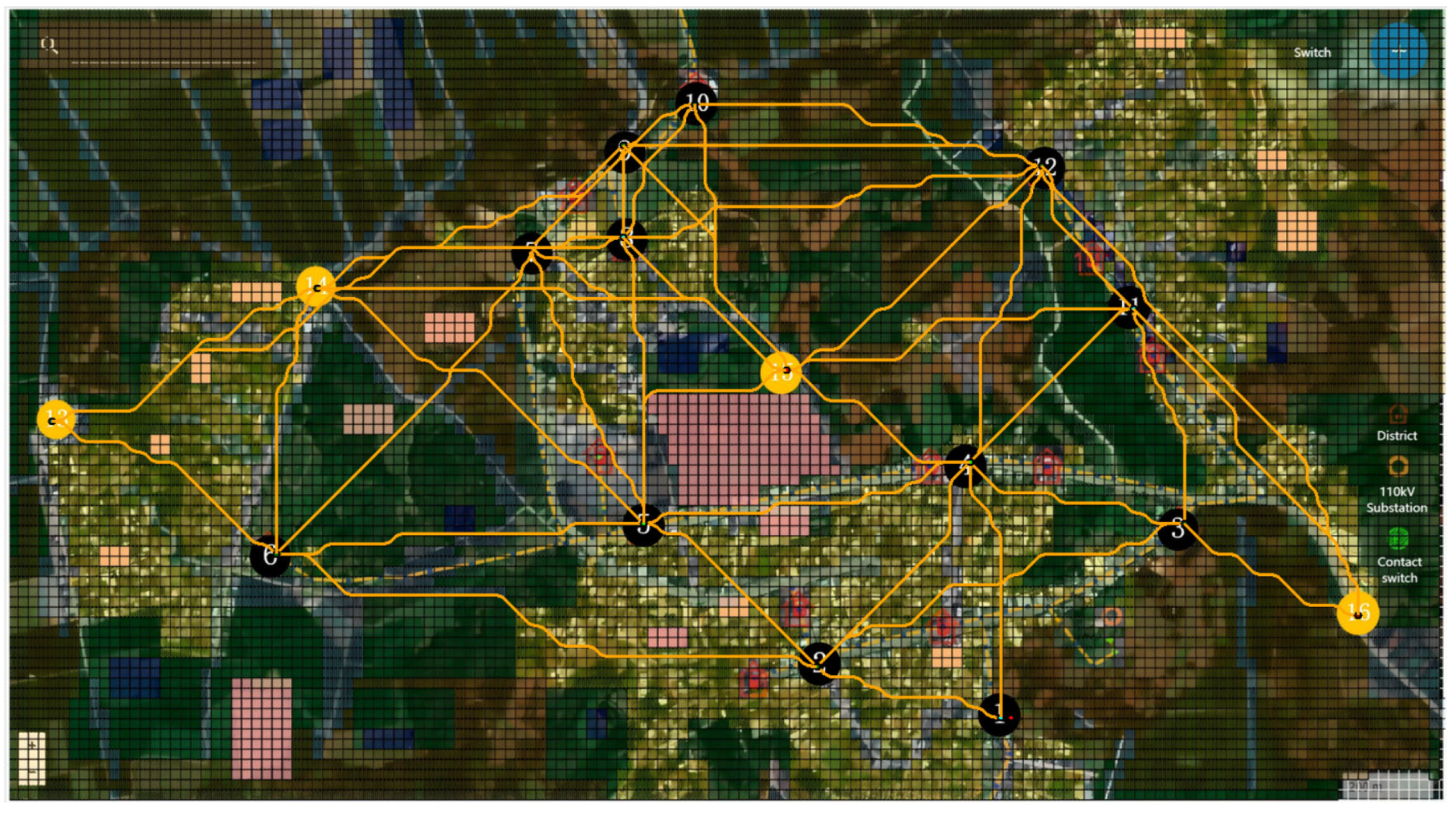
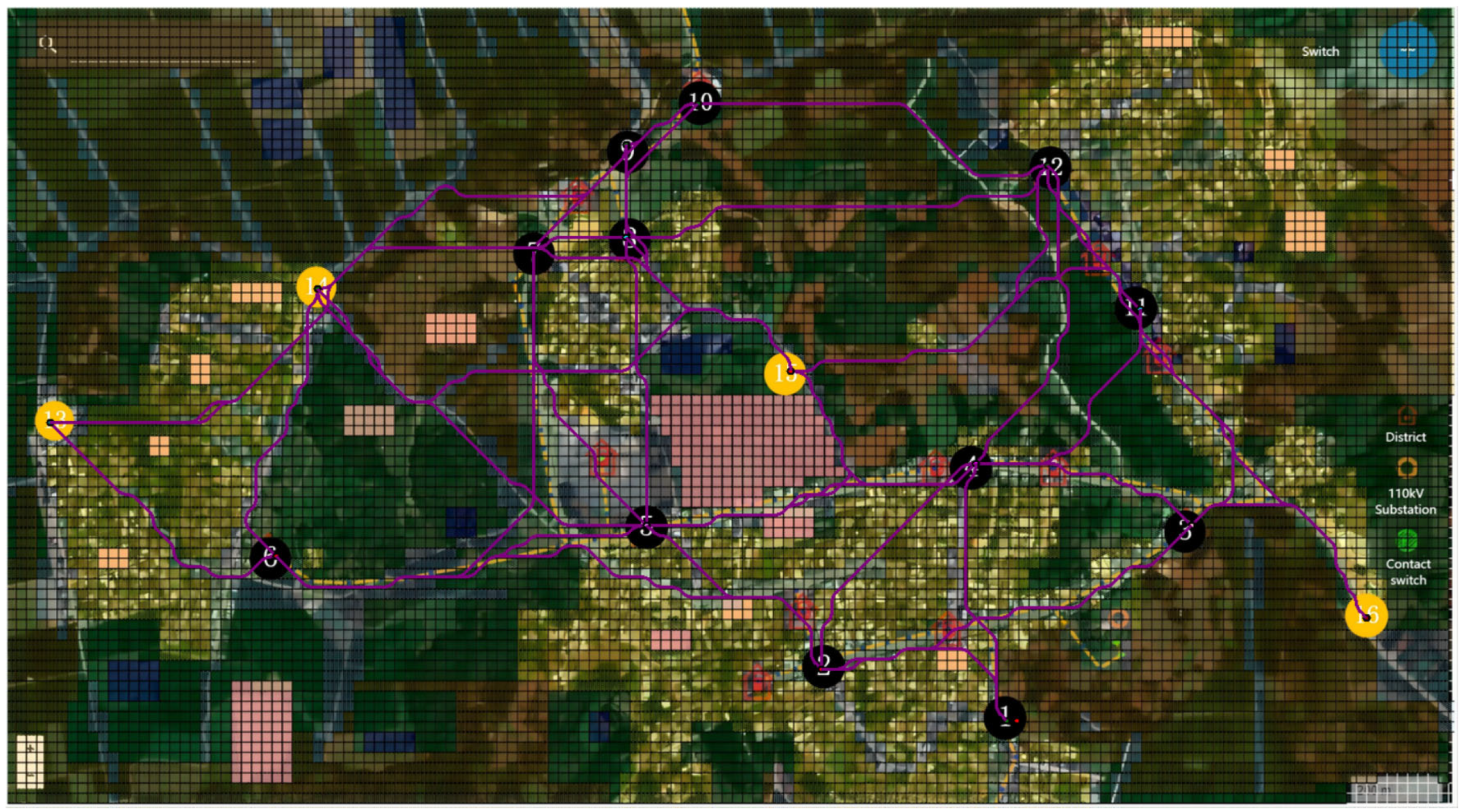
4. Case Study
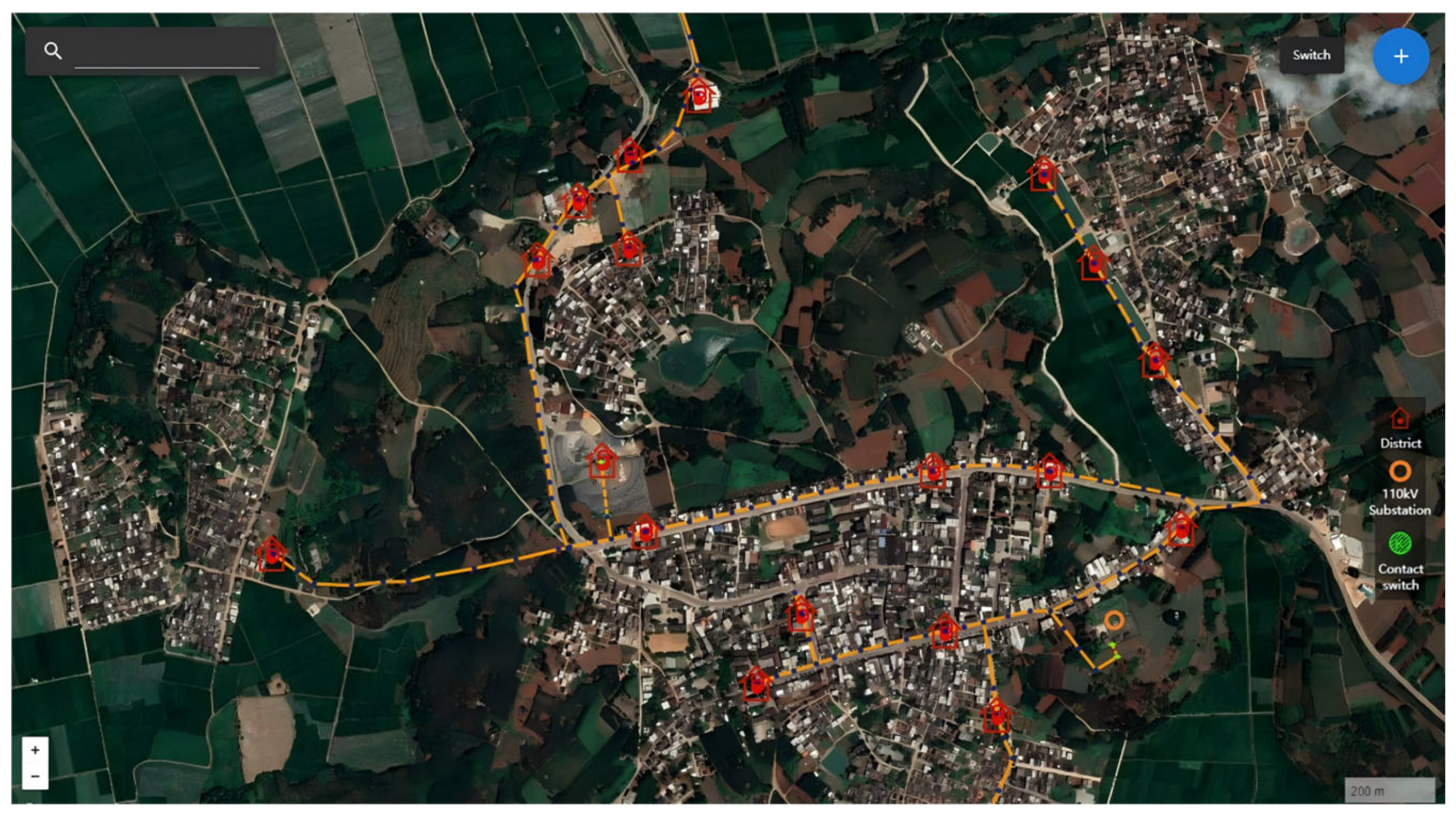
4.1. Case Description
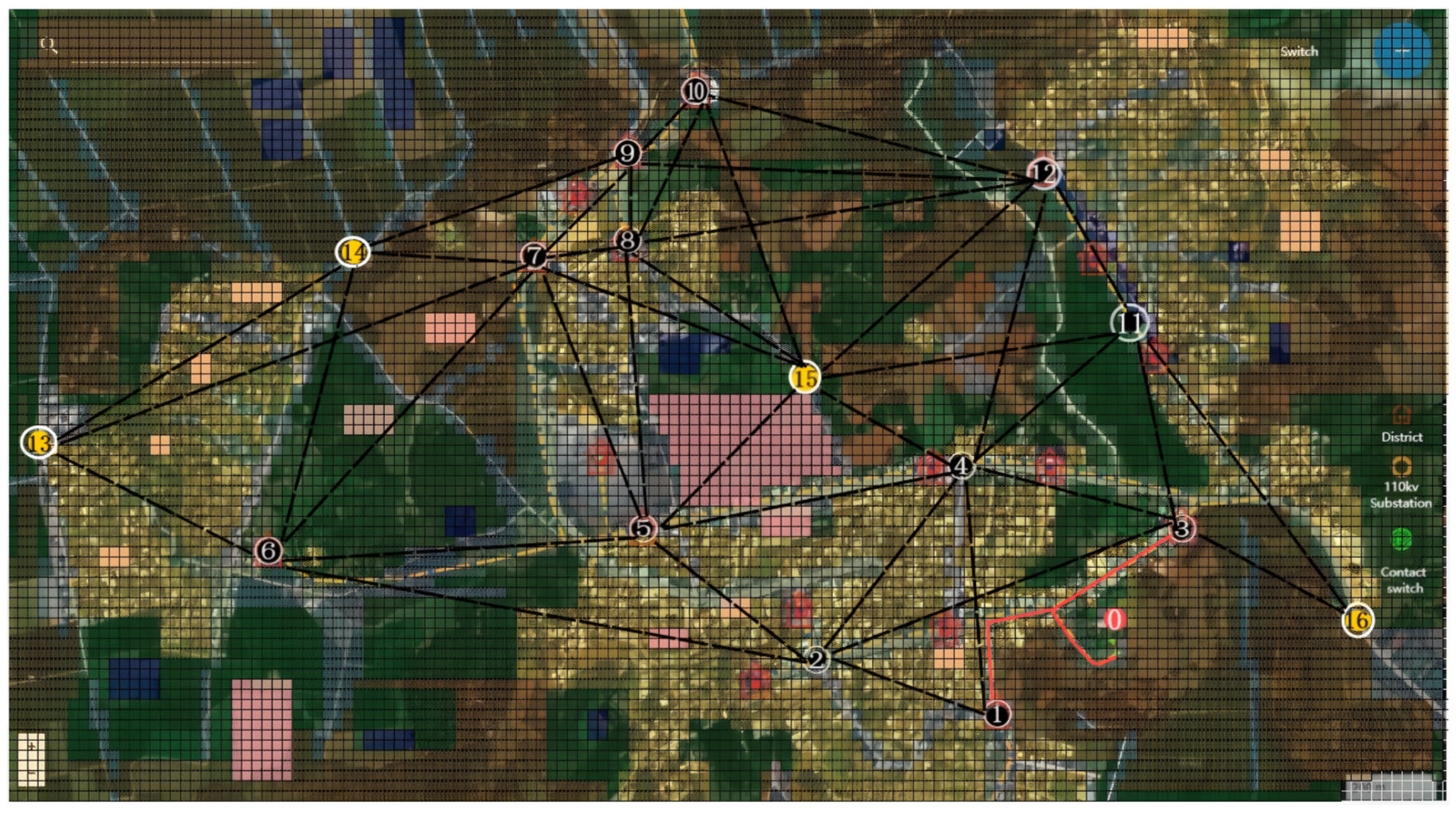
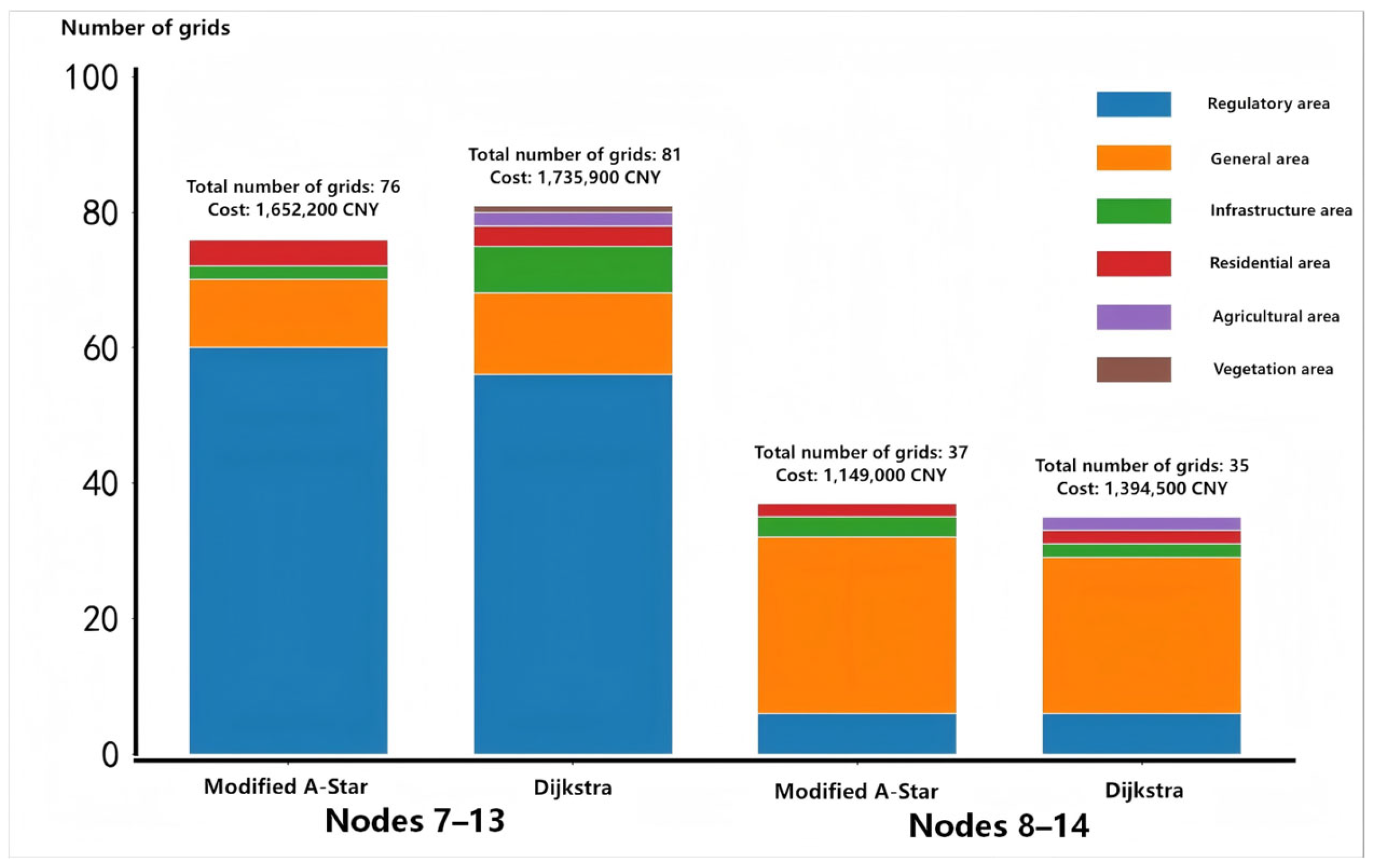
4.2. Result Analysis
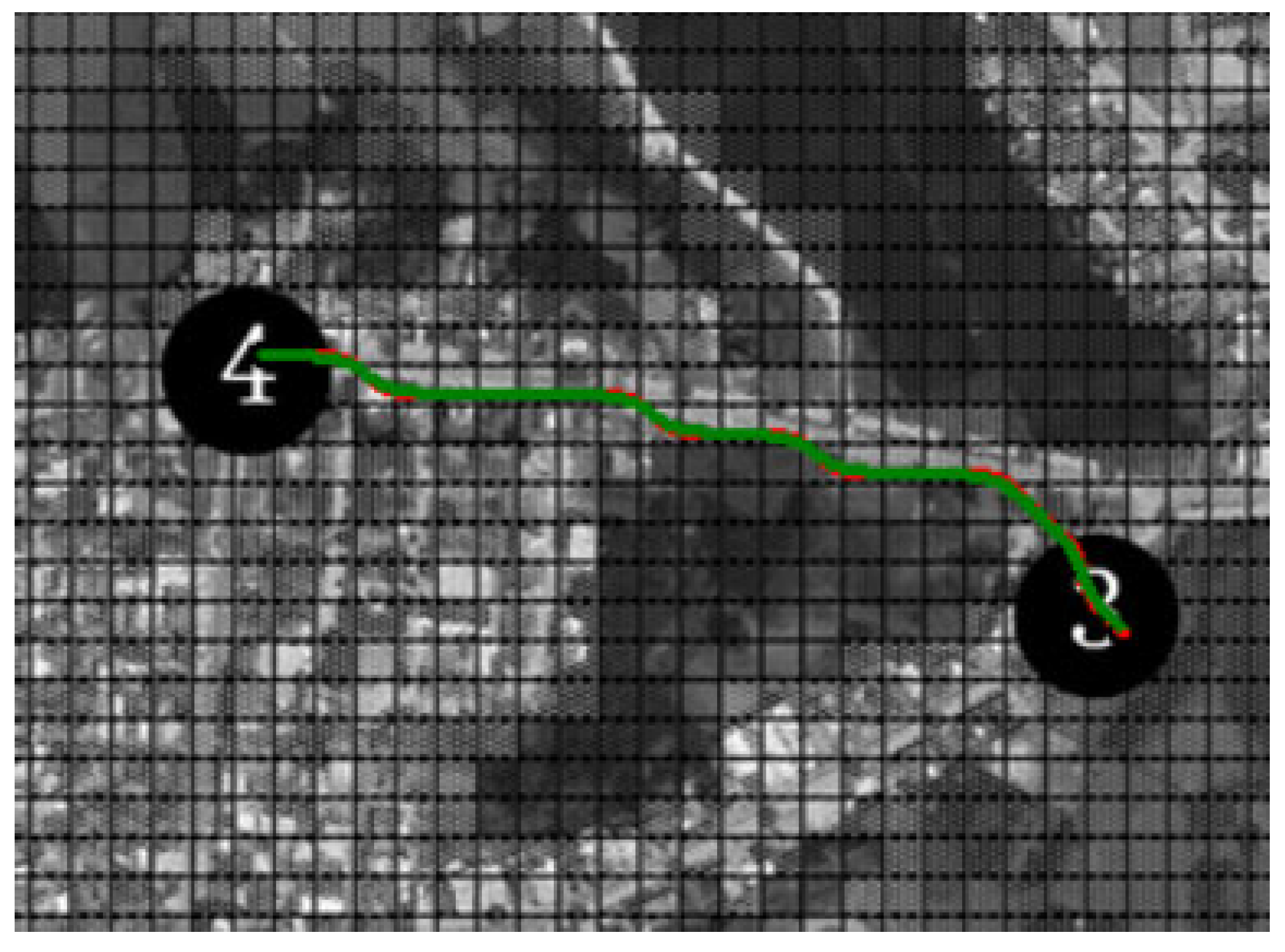
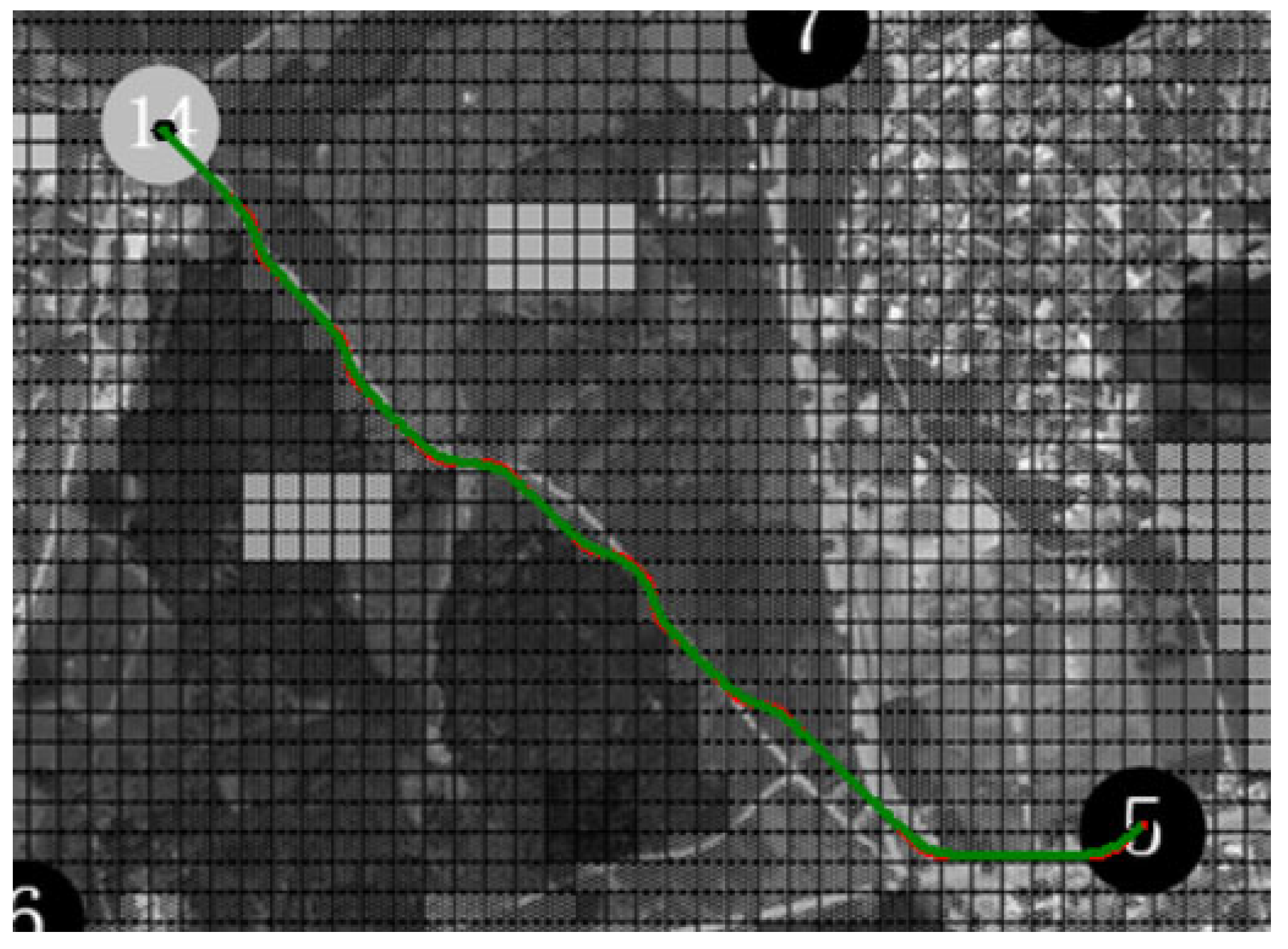
4.2.1. Line Smoothing Analysis
4.2.2. Analysis of Planning Schemes
4.2.3. Comparison of Optimization Algorithms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, L.; Yu, F.; Huang, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Sun, R. Game-theoretic evolution in renewable energy systems: Advancing sustainable energy management and decision optimization in decentralized power markets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 217, 115776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahman, J.M.; Peri, D.M. Radial distribution network planning under uncertainty by applying different reliability cost models. Int. J. Electr. Power 2020, 117, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Su, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lei, X.; Sun, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W. Coordinated DG-Tie planning in distribution networks based on temporal scenarios. Energy 2018, 159, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, M.; Tan, C.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Sun, R. Computational game-theoretic models for adaptive urban energy systems: A comprehensive review of algorithms, strategies, and engineering applications. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhao, F.; Meng, M. Automatic optimization model of transmission line based on GIS and genetic algorithm. Array 2023, 17, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Qiu, W.; Ding, Y.; Shi, H.; Yao, H.; Shen, X. Optimal planning method of renewable distributed generation for multiple prosumers participating in distribution networks. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 675, 12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.R.E.; Fernando, T.; Iu, H.H.; Reynolds, M.; Fani, S. Spatial Optimization for the Planning of Sparse Power Distribution Networks. IEEE T Power Syst. 2018, 33, 6686–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebid, A.M.; Abdel-Kader, M.Y.; Mahdi, I.M.; Abdel-Rasheed, I. Ant Colony Optimization based algorithm to determine the optimum route for overhead power transmission lines. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, G.; Liu, Z.; Du, H.; Zhu, W.; Xu, S. Transmission Line-Planning Method Based on Adaptive Resolution Grid and Improved Dijkstra Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; He, T.; Du, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Transmission line planning based on artificial intelligence in smart cities. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 2010189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Peng, L.; Yang, L.; Han, Y.; Ge, X. Overhead line path planning based on deep reinforcement learning and geographical information system. Int. J. Electr. Power 2025, 165, 110468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesántez, G.; Guamán, W.; Córdova, J.; Torres, M.; Benalcazar, P. Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Power Systems Planning: A Review of Operational and Expansion Strategies. Energies 2024, 17, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Seal, A. Outlier-robust multi-view clustering for uncertain data. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 211, 106567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, K.; Xu, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhuo, C.; Huang, Y. Faulty feeder detection of single phase-to-ground fault for distribution networks based on improved K-means power angle clustering analysis. Int. J. Electr. Power 2022, 142, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, S.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Tohidi, S. A Data Clustering Based Probabilistic Power Flow Method for AC/VSC-MTDC. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 4324–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, O.; Oshnoei, A.; Kheradmandi, M.; Khezri, R.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. A robust data clustering method for probabilistic load flow in wind integrated radial distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power 2020, 115, 105392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wei, X.; Li, M.; Tan, C.; Yin, M.; Shen, T.; Zou, T. Integrating Evolutionary Game-Theoretical Methods and Deep Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Strategy Optimization in User-Side Electricity Markets: A Comprehensive Review. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Gong, J.; Shen, H.; Yuan, L.; Wei, W.; Long, Y. DBVSB-P-RRT*: A path planning algorithm for mobile robot with high environmental adaptability and ultra-high speed planning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 266, 126123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Peng, P.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.; Lu, W. Leveraging evolutionary game theory for cleaner production: Strategic insights for sustainable energy markets, electric vehicles, and carbon trading. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 512, 145682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-shun, L.; Kai-li, X. Research on the subjective weight of the risk assessment in the coal mine system based on GSPA-IAHP. Procedia Eng. 2011, 26, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, V.; Hatherley, R.; Tastan Bishop, Ö. Bioinformatic characterization of type-specific sequence and structural features in auxiliary activity family 9 proteins. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, A.; Qi, N. Density peak clustering based on relative density relationship. Pattern Recogn. 2020, 108, 107554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogiannopoulos, T.; Theodorakopoulos, I. Curved Text Line Rectification via Bresenham’s Algorithm and Generalized Additive Models. Signals 2024, 5, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Dai, J.; He, C. A Novel Real-Time Penetration Path Planning Algorithm for Stealth UAV in 3D Complex Dynamic Environment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122757–122771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zou, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W. An improved A-star algorithm coupled with graph division and AIS data for ship path planning. Ocean Eng. 2025, 330, 121234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, V. Path planning of mobile robots in dynamic environment based on analytic geometry and cubic Bézier curve with three shape parameters. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 233, 120942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Sun, J. A New Algorithm Based on Dijkstra for Vehicle Path Planning Considering Intersection Attribute. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19761–19775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (1, 1) | (4, 6) | (6, 8) | |
| (1/6, 1/4) | (1, 1) | (2, 3) | |
| (1/8, 1/6) | (1/3, 1/2) | (1, 1) |
| Factor | Weight Value | Factor | Weight Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mountainous area | 0.105 | Agricultural area | 0.112 |
| Plain area | 0.062 | Residential area | 0.080 |
| Lake area | 0.153 | Industrial park area | 0.065 |
| Vegetation area | 0.141 | Public service buildings | 0.068 |
| Steep slope | 0.103 | Transportation facility area | 0.044 |
| Overhead line | 0.027 | Cable corridor | 0.025 |
| Energy construction | 0.041 |
| Line | Maximum Curvature (rad/s) | Average Curvature (rad/s) | Corner Energy (rad2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3–4 Before Smoothing | 0.00297 | 0.00116 | 5.55 |
| 3–4 After Smoothing | 0.00245 | 0.00103 | 2.58 |
| 5–14 Before Smoothing | 0.00297 | 0.00116 | 8.64 |
| 5–14 After Smoothing | 0.00241 | 0.00092 | 3.79 |
| Scheme | Total Comprehensive Cost (10,000 CNY) | Total Basic Cost (10,000 CNY) | Total Geographical Cost (10,000 CNY) | Total Load Benefit (10,000 CNY) |
| Scheme 1 | 4460.07 | 2751.76 | 1973.32 | 265.02 |
| Scheme 2 | 3773.85 | 2975.93 | 962.78 | 164.86 |
| Scheme 3 | 3767.14 | 2969.79 | 980.47 | 183.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, W.; He, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Peng, X. Coordinated Planning Method for Distribution Network Lines Considering Geographical Constraints and Load Distribution. Processes 2026, 14, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010047
Luo L, Zhou Q, Pan W, He Z, Liu M, Yang L, Peng X. Coordinated Planning Method for Distribution Network Lines Considering Geographical Constraints and Load Distribution. Processes. 2026; 14(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Linhuan, Qilin Zhou, Wei Pan, Zhian He, Minghao Liu, Longfa Yang, and Xiangang Peng. 2026. "Coordinated Planning Method for Distribution Network Lines Considering Geographical Constraints and Load Distribution" Processes 14, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010047
APA StyleLuo, L., Zhou, Q., Pan, W., He, Z., Liu, M., Yang, L., & Peng, X. (2026). Coordinated Planning Method for Distribution Network Lines Considering Geographical Constraints and Load Distribution. Processes, 14(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010047







