Lifecycle Carbon Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Electrical Equipment: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lifecycle Carbon Emission Framework of Electrical Equipment
2.1. LCA Methodology Overview

2.2. Life Cycle Stages and Boundary Definition
2.3. Data Sources and Uncertainty
3. Carbon Emission Characteristics Across Life Cycle Stages
3.1. Carbon Emissions During Manufacturing
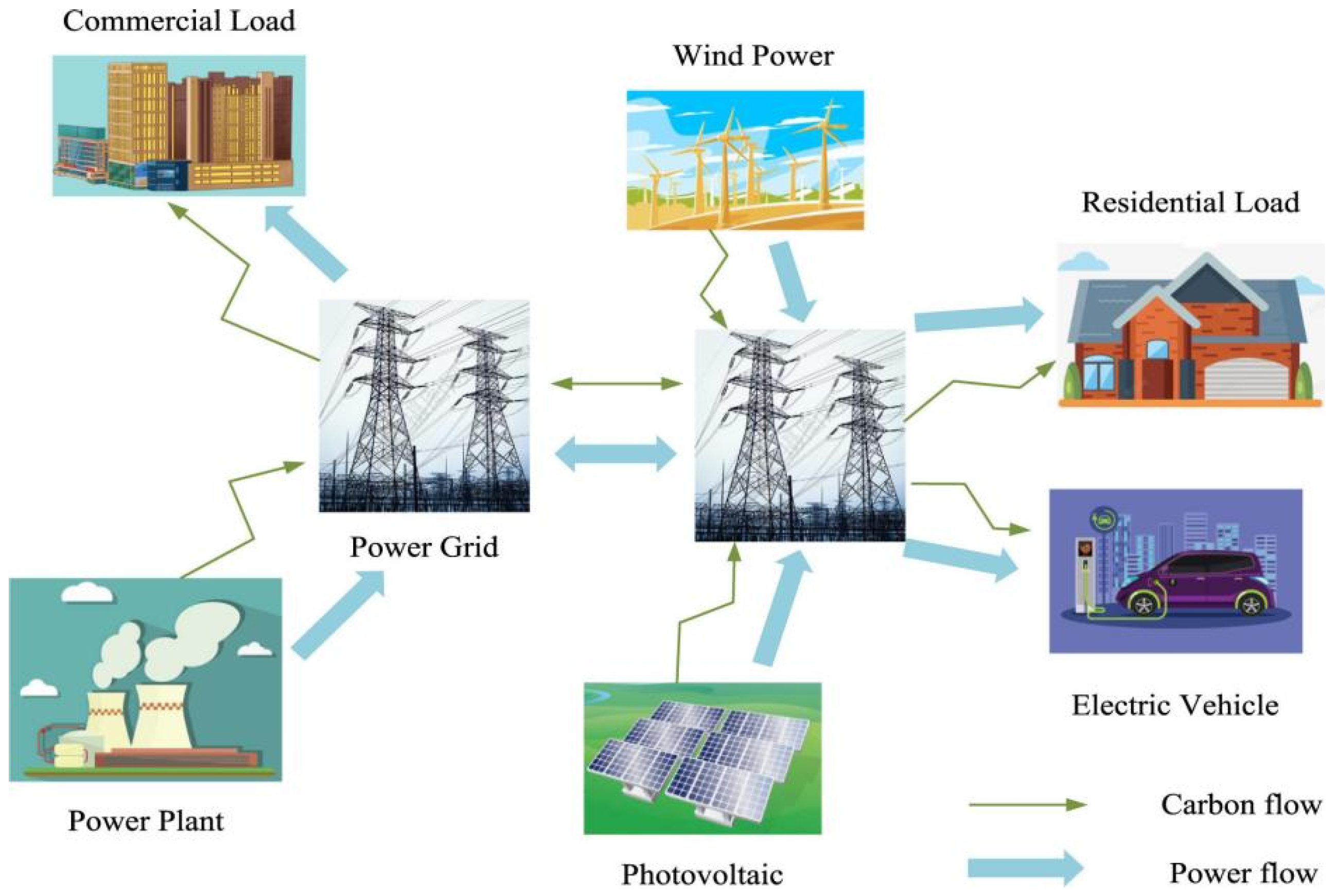
3.2. Carbon Emissions During Usage
3.3. Carbon Emissions During End-of-Life and Recycling
3.4. Total Carbon Emissions Across Life Cycle Stages
4. Carbon Mitigation Pathways and Strategies
4.1. Low-Carbon Design and Material Optimization
4.2. Carbon Reduction in Manufacturing Processes
4.3. Carbon Reduction During Usage
4.4. Circular Economy and Equipment Recycling
4.5. Policy Incentives and Industry Standards
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.S.; Xue, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q. Road life-cycle carbon dioxide emissions and emission reduction technologies: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 9, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, T.; Luo, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. A comprehensive review of building lifecycle carbon emissions and reduction approaches. City Built Environ. 2024, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.; Williams, I.D.; Turner, D.A. Evaluating the carbon footprint of WEEE management in the UK. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soust-Verdaguer, B.; Llatas, C.; García-Martínez, A. Critical review of bim-based LCA method to buildings. Energy Build. 2017, 136, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Pedraza, G.A.; Vieira-Agudelo, S.C.; Muñoz-Galeano, N. A cradle-to-grave multi-pronged methodology to obtain the carbon footprint of electro-intensive power electronic products. Energies 2019, 12, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryshlakivsky, J.; Searcy, C. Fifteen years of ISO 14040: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkbeiner, M.; Inaba, A.; Tan, R.; Christiansen, K.; Klüppel, H. The new international standards for life cycle assessment: ISO 14040 and ISO 14044. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2006, 11, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xia, B.; Wang, X. The contribution of ISO 14067 to the evolution of global greenhouse gas standards—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Ekvall, T.; Guinée, J.; Heijungs, R.; Hellweg, S.; Koehler, A.; Pennington, D.; Suh, S. Recent developments in life cycle assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuss, P.; Eckelman, M.J. Life cycle assessment of metals: A scientific synthesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Carbon Footprint Calculation for Power Transmission and Distribution Equipment: A Comprehensive Review of Methodologies, Standards, and Applications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2025, 28, 200295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, E.; Piri, I.S.; Das, O. Revisiting the Basics of Life Cycle Assessment and Lifecycle Thinking. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, S.; Das, B.B. Life Cycle Assessment of construction materials: Methodologies, applications and future directions for sustainable decision-making. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Maierhofer, D.; Saade, M.R.M.; Passer, A. Influence of technical and electrical equipment in life cycle assessments of buildings: Case of a laboratory and research building. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute (WRI); World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). The Greenhouse Gas Protocol: A Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard; WRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Wang, W.; Wu, W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. Carbon emission prediction model for the underground mining stage of metal mines. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Teng, F.; Tong, Q. Mitigating sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) emission from electrical equipment in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, T.; Markowska, D. Carbon Footprint of Power Transformers Evaluated Through Life Cycle Analysis. Energies 2025, 18, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, V.C.; Stavropoulos, P.; Chryssolouris, G. A critical review on the environmental impact of manufacturing: A holistic perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRI. Greenhouse Gas Protocol. In GHG Protocol Scope 2 Guidance. An Amendment to the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard; WRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Corda, M. Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Real Estate. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Tang, X.; Geng, L.; Yao, X.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. A Comprehensive Life Cycle Carbon Footprint Assessment Model for Electric Power Material Warehouses. Energies 2024, 17, 6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaril, E. Improvement of the environmental and operational characteristics of vehicles through decreasing the motor fuel density. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 6793–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, T.; Yuan, C.; Ping, Y. Assessment of carbon emissions at the logistics and transportation stage of prefabricated buildings. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangmeechai, A. The life-cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions and life-cycle costs of e-waste management in Thailand. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2022, 32, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serres, H. Life Cycle Assessment of Typical Projects of the Distribution Power Network: Assessment, Improvement & Recommendations. Master’s Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bamber, N.; Turner, I.; Arulnathan, V.; Li, Y.; Zargar Ershadi, S.; Smart, A.; Pelletier, N. Comparing sources and analysis of uncertainty in consequential and attributional life cycle assessment: Review of current practice and recommendations. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahmand, Z.; Eikeland, M.S. Life cycle assessment under uncertainty: A scoping review. World 2022, 3, 692–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, S.A.; Hashmi, N.; Javaid, S. Integrating Lifecycle Assessment and Fuzzy BWM to Evaluate Sustainable Automotive Design Alternatives. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2025, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey, K.a.J.; Anglani, N. Meta-analysis of the life cycle of small-sized power converters: A systematic review. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2025, 30, 1944–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamkavil, S.; Mohan, M. Development of a Parametric Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) method for Construction Logistics in a Circular Economy. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lensoco, D.F. Sensitivity Analysis on Rainbow’s Refurbishing of Electronic Devices Methodology. Master’s Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Angrisani, L.; Bonini, G.; D’Arco, M.; De Benedetto, E.; Duraccio, L.; Esposito, I.; Tedesco, A. Sustainability Balance for ICT Infrastructures: A Time-Scale Analysis of the Dynamic Fourth Lane on the A4 Italian Motorway. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 166778–166786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Eheliyagoda, D.; Geng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, X. Examining the influence of copper recycling on prospective resource supply and carbon emission reduction. Fundam. Res. 2022, 5, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yan, W.; Zhu, X. Analysis and evaluation of energy consumption and carbon emission levels of products produced by different kinds of equipment based on green development concept. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswiet, J.; Kara, S. Carbon emissions and CES™ in manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Tang, R.; Ji, Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, L.; Huisingh, D. Impact of advanced manufacturing on sustainability: An overview of the special volume on advanced manufacturing for sustainability and low fossil carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Digitalization, electricity consumption and carbon emissions—Evidence from manufacturing industries in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gerada, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gerada, C. A Review of Carbon Emissions from Electrical Machine Materials. Electronics 2024, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, T.G.; Allwood, J.M.; Herrmann, C.; Sahni, S. A Global Assessment of Manufacturing: Economic Development, Energy Use, Carbon Emissions, and the Potential for Energy Efficiency and Materials Recycling. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2013, 38, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Low carbon optimal operation of integrated energy system based on carbon capture technology, LCA carbon emissions and ladder-type carbon trading. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Gerada, C.; Gerada, D. Carbon emission analysis of electrical machines. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 31 October–3 November 2021; pp. 1678–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, H.; Hao, H. The greenhouse gas emissions reduction co-benefit of end-of-life electric vehicle battery treatment strategies. Carbon Footpr. 2023, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselkamper, J.; Hendrickson, T.P.; Lux, S.; von Delft, S. Recycling or second use? Supply potentials and climate effects of end-of-life electric vehicle batteries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 15751–15765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, E.; Barmak, K.; West, A.C.; Park, A.-H.A. Advancements in the treatment and processing of electronic waste with sustainability: A review of metal extraction and recovery technologies. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, J.; Fu, X.; Bhuwalka, K.; Roth, R.; Olivetti, E. Assessing recycling, displacement, and environmental impacts using an economics-informed material system model. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, W.; Wu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ding, L. Recycling of Power Grid Waste: Carbon Footprint of Cables and Transformers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 2956, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, V.; Bryhn, J. Implementation of circular economy approaches in the electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) sector: Barriers, enablers and policy insights. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurco, D.; Petrie, J.G. Strategies for reducing the carbon footprint of copper: New technologies, more recycling or demand management? Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, J. The greenhouse gas emissions of power transformers based on life cycle analysis. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, D. A guide to life-cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from electric supply technologies. Energy 2007, 32, 1543–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, H.-H.; Zhang, L.; Bao, H.; Liu, Z.-F. Low-carbon design of structural components by integrating material and structural optimization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 4547–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Tang, W.; Huang, S.; Hou, S.; Cai, H. Towards low-carbon product architecture using structural optimization for lightweight. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, M.; Han, Y. Greenhouse gas emission reduction through wood-based furniture substitution: Analysis of displacement factors. BioResources 2024, 19, 6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushigami, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Fujikura, M.; Kubota, T.; Fujii, H.; Murakami, K. Recent development of low-loss grain-oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindi, M.; Piccirilli, M.C.; Luchetta, A.; Grasso, F. A comprehensive review of fault diagnosis and prognosis techniques in high voltage and medium voltage electrical power lines. Energies 2023, 16, 7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, Z. Towards world’s low carbon development: The role of clean energy. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, F.O.; Ani, E.C.; Ebirim, W.; Montero, D.J.P.; Olu-lawal, K.A.; Ninduwezuor-Ehiobu, N. Integrating renewable energy solutions in the manufacturing industry: Challenges and opportunities: A review. Eng. Sci. Technol. J. 2024, 5, 674–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Vicidomini, M.; Calise, F.; Duić, N.; Østergaard, P.A.; Wang, Q.; da Graça Carvalho, M. Recent advances in low-carbon and sustainable, efficient technology: Strategies and applications. Energies 2022, 15, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, F.; Xue, S.; Zeng, M.; Zeng, F. Review on wind power development in China: Current situation and improvement strategies to realize future development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwich, E.G. Increased carbon footprint of materials production driven by rise in investments. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaramoorthy, S.; Kamath, D.; Nimbalkar, S.; Price, C.; Wenning, T.; Cresko, J. Energy efficiency as a foundational technology pillar for industrial decarbonization. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattra, S.K.; Singh, D.; Dogra, R. A review of energy efficient technology and carbon trading for reducing carbon emissions. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2024, 24, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, E.; Xie, L.; Li, J. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Distribution Network Transformers Based on Life Cycle Assessment. Energies 2025, 18, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Low-carbon operation of smart distribution grid based on life cycle assessment and ladder-type carbon trading. Renew. Energy 2024, 231, 120816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, L.; Tangour, F.; El Abbassi, I.; Absi, R. Analysis of Digital Twin Applications in Energy Efficiency: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, S.; Wang, C.; McNelly, M.; Romeiko, X.; Choi, J.-K. A comprehensive analysis of the energy, economic, and environmental impacts of industrial variable frequency drives. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Steel Association. Steel’s Contribution to a Low Carbon Future and Climate Resilient Societies. 2021. Available online: https://www.steel.org.au/getattachment/48e75f3b-e33c-43e3-b3e8-b07b330293ae/Position_paper_climate_2017.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2025).
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. iii–iv. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, T.G.; Sahni, S.; Boustani, A.; Graves, S.C. Remanufacturing and energy savings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4540–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizova, M.I.; Wong, T.; Ijomah, W. A systematic review of decision-making in remanufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 147, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, A.; Şengör, İ.; Güner, S.; Karakuş, F.; Erenoğlu, A.K.; Erdinç, O.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalão, J.P. Integrated rail system and EV parking lot operation with regenerative braking energy, energy storage system and PV availability. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahlawi, A.A.K.; Ayob, S.M.; Tan, C.W.; Ridha, H.M.; Hachim, D.M. Optimal design of grid-connected hybrid renewable energy system considering electric vehicle station using improved multi-objective optimization: Techno-economic perspectives. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, J. Incentives for green and low-carbon technological innovation of enterprises under environmental regulation: From the perspective of evolutionary game. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 793667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y. Optimizing mechanisms for promoting low-carbon manufacturing industries towards carbon neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.; Aghajanzadeh, A.; Therkelsen, P. Identification of drivers, benefits, and challenges of ISO 50001 through case study content analysis. Energy Policy 2020, 142, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwumike, C.; Akponeware, A.; Oyewole, A.; Dawood, H.; Pinedo-Cuenca, R.; Ling-Chin, J.; Roskilly, A.P.; Dawood, N. Transitioning or tinkering at a net-zero economy? Introducing an assessment framework for industrial cluster decarbonisation in the United Kingdom. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2024, 110, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

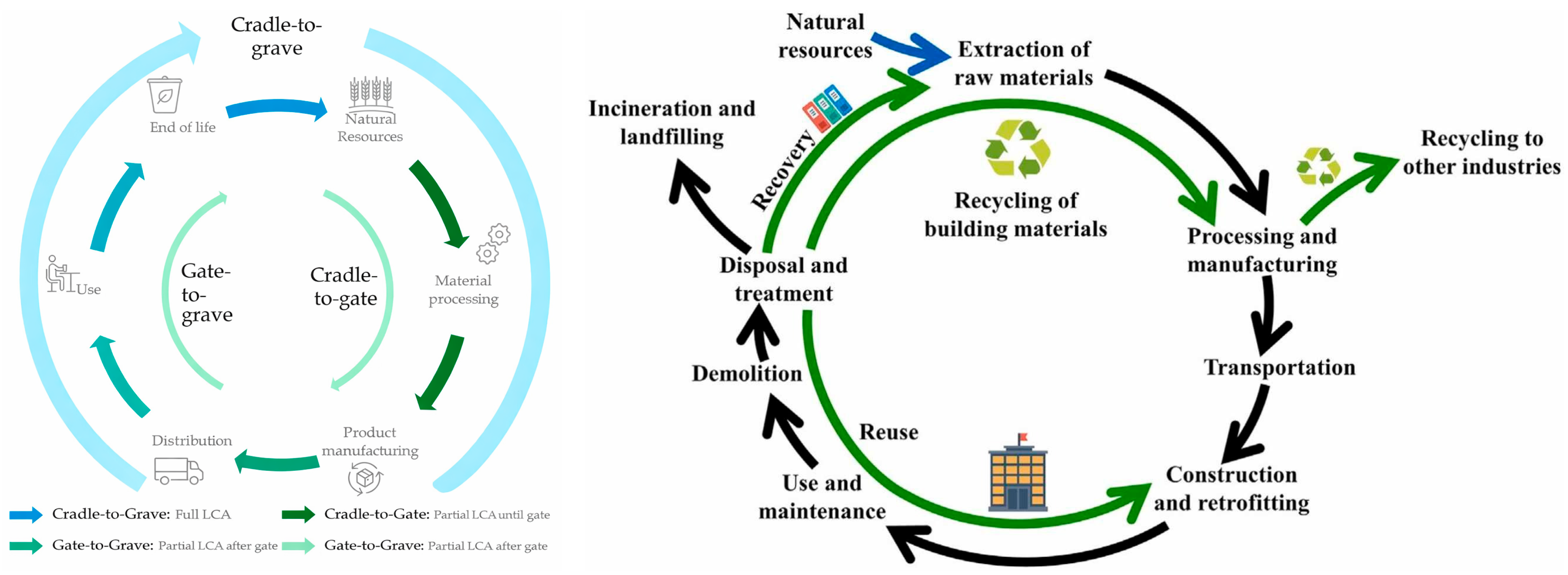







| Life Cycle Stages | Definition and Content of the Stage | Carbon Emission Boundary and Assessment Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Raw materials stage | Major raw materials from extraction to the manufacturing plant. | The “cradle-to-gate” boundary is used, and the process method is applied for assessment. |
| Manufacturing stage | Processes such as raw material processing. | The “in-plant production system” boundary is assessed using the process analysis method. |
| Transportation stage | Raw materials to the manufacturing plant, and products transported to the site of use. | The “door-to-door” boundary is adopted, using the fuel consumption method or the ton-kilometer × emission factor method. |
| Use stage | Material and energy consumption caused during equipment operation. | The carbon emission boundary is defined as the “equipment operation system.” |
| End-of-life and recycling stage | Equipment decommissioning, recycling, waste disposal, and remanufacturing. | The “end-of-life disposal” boundary, adopts the “end-of-life” assessment method. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, J.; Miao, B.; Liu, C.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, G. Lifecycle Carbon Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Electrical Equipment: A Comprehensive Review. Processes 2026, 14, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010040
Li S, Jiang Y, Yi J, Miao B, Liu C, Ling Z, Zhang G. Lifecycle Carbon Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Electrical Equipment: A Comprehensive Review. Processes. 2026; 14(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuzhen, Yingwei Jiang, Jun Yi, Bo Miao, Chao Liu, Zhongqian Ling, and Guangxue Zhang. 2026. "Lifecycle Carbon Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Electrical Equipment: A Comprehensive Review" Processes 14, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010040
APA StyleLi, S., Jiang, Y., Yi, J., Miao, B., Liu, C., Ling, Z., & Zhang, G. (2026). Lifecycle Carbon Emissions and Mitigation Strategies of Electrical Equipment: A Comprehensive Review. Processes, 14(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010040





