Residence Time Distribution of Variable Viscosity Fluids in the Stirred Tank
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models and Methods of Numerical Simulation
2.1. Physical Models
2.2. Governing Equations
2.3. Numerical Details
2.4. Determination of Residence Time Distribution
2.5. Simulation Scheme
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RTD in Single-Stage STR
3.1.1. Effect of Impeller Speed on RTD
3.1.2. Effect of Space Time
3.1.3. Effect of Viscosity
3.2. RTD in Two-Stage STRs
3.2.1. Effect of Impeller Speed
3.2.2. Effect of Space Time
3.2.3. Effect of Viscosity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RTD | Residence Time Distribution |
| CSTR | Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor |
| STR | Stirred Tank Reactor |
References
- Visscher, F.; van der Schaaf, J.; Nijhuis, T.A.; Schouten, J.C. Rotating reactors—A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Z.; Wang, J.J.; Gu, X.P.; Feng, L.F. Integration of CFD and polymerization for an industrial scale cis-polybutadiene reactor. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, G.; Pandit, A.V.; Albertazzi, J.; Vetter, T.; Viano, R.; Milani, L.; Adamo, A.; Myerson, A.S.; Stelzer, T. Residence Time Distribution Characterization and Proof-of-Concept of a Novel Stacked 7-Stage Continuous Crystallizer Cascade with Diaphragm-Driven Slurry Transfer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 18199–18211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Mastan, E.; Wang, W.J.; Li, B.G.; Zhu, S.P. Progress in reactor engineering of controlled radical polymerization: A comprehensive review. React. Chem. Eng. 2016, 1, 23–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shang, M.J.; Li, G.X.; Luo, Z.H.; Su, Y.H. Influence of Mixing Performance on Polymerization of Acrylamide in Capillary Microreactors. AlChE J. 2018, 64, 1828–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.H.; Varner, T.P.; Leibfarth, F.A. The Influence of Residence Time Distribution on Continuous-Flow Polymerization. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Huang, J.L.; Gao, Y.X.; Sun, D.H.; Li, J.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Li, Q.B. Production of Silver Nanoparticles in a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor Based on Plant-Mediated Biosynthesis: Flow Behaviors and Residence Time Distribution Prediction by Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, K.; Mavros, P.; Zamboulis, D. Effect of continuous feed stream and agitator type on CFSTR mixing state. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 4805–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.N.; Özcan-Taskin, N.G.; Yianneskis, M. The use of momentum ratio to evaluate the performance of CSTRs. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2009, 87, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbolaghy, M.; Karimi, A. Simulation and optimization of enzymatic hydrogen peroxide production in a continuous stirred tank reactor using CFD-RSM combined method. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Stephenson, A.; Jimenez, J.; Jewell, D.; Gillis, P. Modeling flow and residence time distribution in an industrial-scale reactor with a plunging jet inlet and optional agitation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2008, 86, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Pan, Q.M.; Rempel, G.L. Residence time distribution in a multistage agitated contactor with newtonian fluids: CFD prediction and experimental validation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.Y.; Feng, X.; Duan, X.X.; Mao, Z.S.; Yang, C. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Residence Time Distribution in a Stirred Membrane Reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 6486–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulnes-Abundis, D.; Alvarez, M. The simplest stirred tank for laminar mixing: Mixing in a vessel agitated by an off-centered angled disc. AlChE J. 2013, 59, 3092–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busciglio, A.; Montante, G.; Paglianti, A. Flow field and homogenization time assessment in continuously-fed stirred tanks. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 102, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, V.; Bourne, J.; Joshi, J. Fluid mechanics and blending in agitated tanks. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danckwerts, P. Local residence-times in continuous-flow systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1958, 9, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y. Quantitative Characterisation of Mixing in Stirred Tank Reactors with Mean Age Distribution. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 89, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y. Age distribution and the degree of mixing in continuous flow stirred tank reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 69, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcik, M.; Ruzicka, M.C.; Mota, A.; Teixeira, J.A. Smart RTD for multiphase flow systems. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuan, W.X.; Chen, W.X.; Chen, S.C. Numerical Simulation Strategy and Applications for Falling Film Flow with Variable Viscosity Fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2025, 64, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Frey, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Grünewald, M.; Schlüter, M. CFD-Based Compartment Modeling of Continuous Polymer Reactors in Milli-Structured Apparatuses by Use of the Mean Age Theory. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 12109–12119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






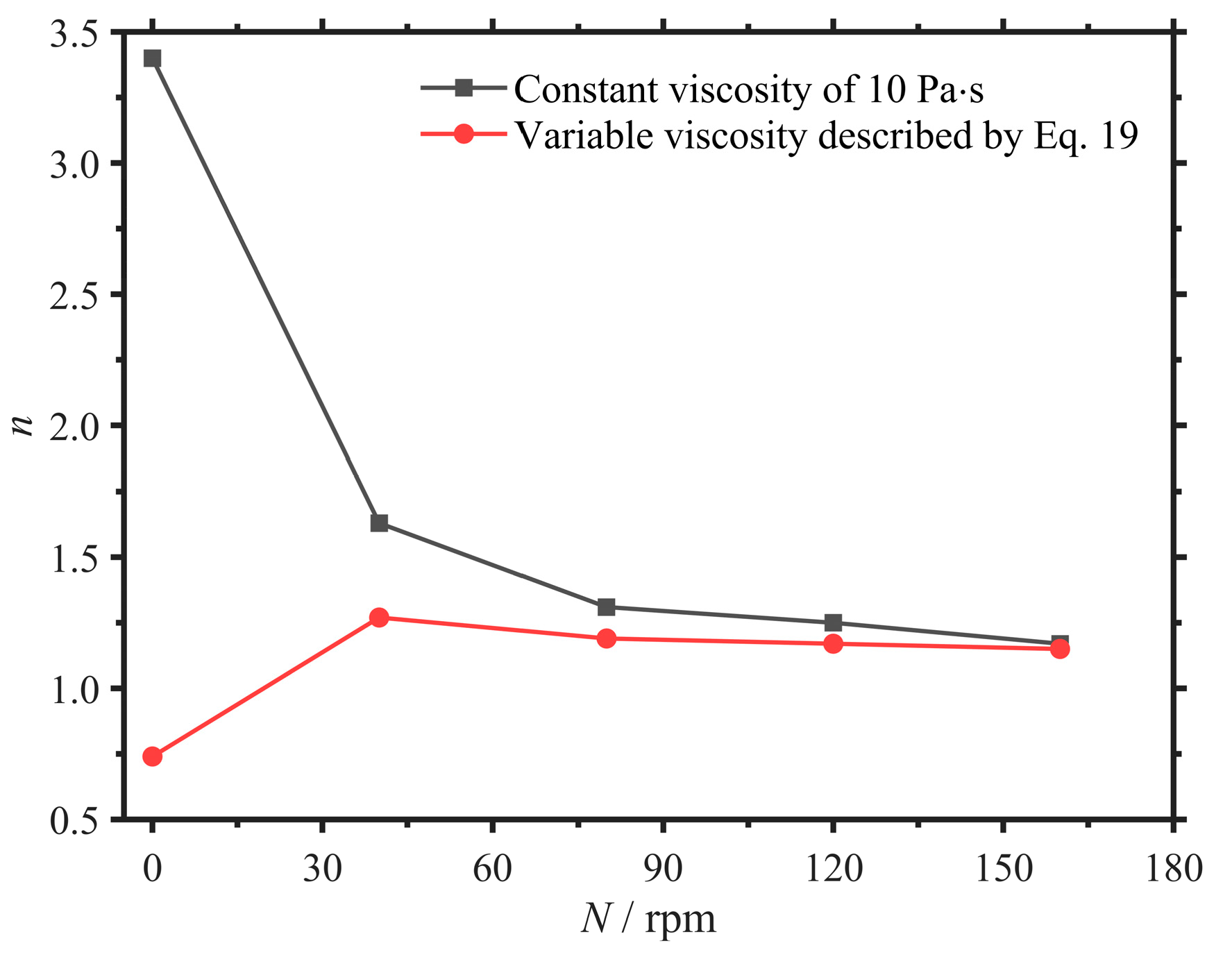









| Case | μ/Pa∙s | N/rpm | τ/s | STR | ReD | /s | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0 | 180 | single-stage | 0 | 177.41 | 9270.31 | 3.40 |
| 2 | 10 | 40 | 180 | single-stage | 8.28 | 179.29 | 19,778.11 | 1.63 |
| 3 | 10 | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 16.56 | 177.77 | 24,093.70 | 1.31 |
| 4 | 10 | 120 | 180 | single-stage | 24.84 | 177.41 | 25,140.81 | 1.25 |
| 5 | 10 | 160 | 180 | single-stage | 33.12 | 176.16 | 26,448.09 | 1.17 |
| 6 | Equation (19) | 0 | 180 | single-stage | 170.13 | 39,042.69 | 0.74 | |
| 7 | Equation (19) | 40 | 180 | single-stage | 176.31 | 24,530.08 | 1.27 | |
| 8 | Equation (19) | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 176.86 | 26,359.14 | 1.19 | |
| 9 | Equation (19) | 120 | 180 | single-stage | 176.35 | 26,692.59 | 1.17 | |
| 10 | Equation (19) | 160 | 180 | single-stage | 176.10 | 26,913.41 | 1.15 | |
| 11 | 10 | 80 | 45 | single-stage | 16.56 | 44.98 | 793.46 | 2.55 |
| 12 | 10 | 80 | 90 | single-stage | 16.56 | 89.88 | 4793.25 | 1.69 |
| 13 | 10 | 80 | 360 | single-stage | 16.56 | 353.15 | 105,419.95 | 1.18 |
| 14 | Equation (19) | 80 | 45 | single-stage | 42.00 | 2150.33 | 0.82 | |
| 15 | Equation (19) | 80 | 90 | single-stage | 88.43 | 6053.83 | 1.29 | |
| 16 | Equation (19) | 80 | 360 | single-stage | 353.07 | 108,041.54 | 1.15 | |
| 17 | 1 | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 165.6 | 176.70 | 26,101.46 | 1.20 |
| 18 | 100 | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 1.66 | 177.65 | 23,444.82 | 1.35 |
| 19 | 500 | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 0.33 | 178.11 | 23,325.30 | 1.36 |
| 20 | Equation (20) | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 176.37 | 26,509.60 | 1.17 | |
| 21 | Equation (21) | 80 | 180 | single-stage | 176.42 | 25,847.25 | 1.20 | |
| 22 | Equation (19) | 0 | 180 | two-stage | 168.79 | 15,612.04 | 1.82 | |
| 23 | Equation (19) | 40 | 180 | two-stage | 176.67 | 13,529.08 | 2.31 | |
| 24 | Equation (19) | 80 | 180 | two-stage | 176.53 | 14,099.55 | 2.21 | |
| 25 | Equation (19) | 120 | 180 | two-stage | 176.70 | 14,183.52 | 2.20 | |
| 26 | Equation (19) | 80 | 90 | two-stage | 87.37 | 3260.04 | 2.34 | |
| 27 | Equation (19) | 80 | 360 | two-stage | 353.41 | 57,664.46 | 2.17 | |
| 28 | Equation (20) | 80 | 180 | two-stage | 176.86 | 13,863.83 | 2.26 | |
| 29 | Equation (21) | 80 | 180 | two-stage | 176.81 | 13,891.57 | 2.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z. Residence Time Distribution of Variable Viscosity Fluids in the Stirred Tank. Processes 2025, 13, 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092997
Wu G, Li L, Li Z, Wang J, Gao Z. Residence Time Distribution of Variable Viscosity Fluids in the Stirred Tank. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092997
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guangshuo, Linxi Li, Zhipeng Li, Junhao Wang, and Zhengming Gao. 2025. "Residence Time Distribution of Variable Viscosity Fluids in the Stirred Tank" Processes 13, no. 9: 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092997
APA StyleWu, G., Li, L., Li, Z., Wang, J., & Gao, Z. (2025). Residence Time Distribution of Variable Viscosity Fluids in the Stirred Tank. Processes, 13(9), 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092997






