Fabrication of Spinel-Type H4Ti5O12 Ion Sieve for Lithium Recovery from Aqueous Resources: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of HTO
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Li+ Adsorption Experiments
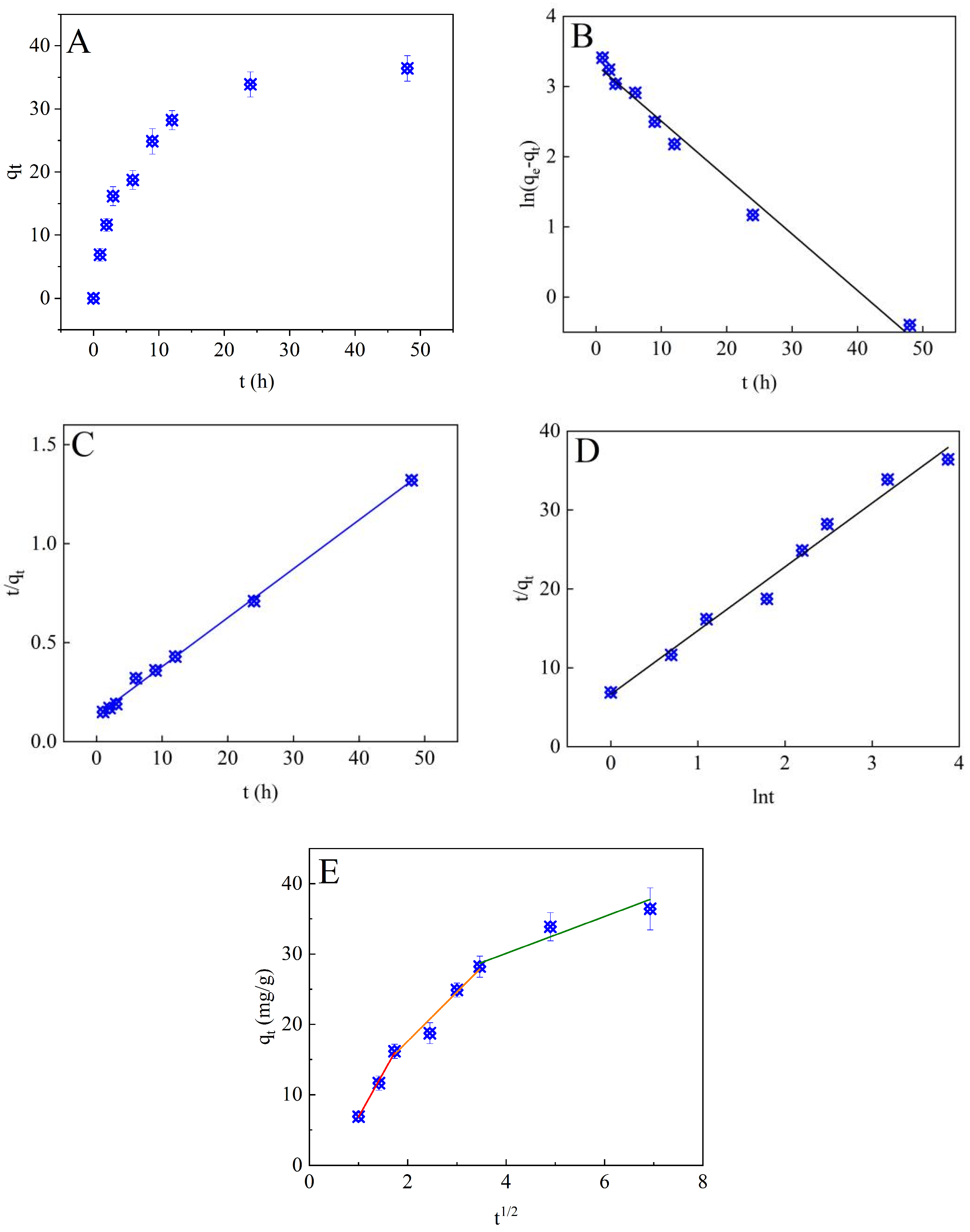
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
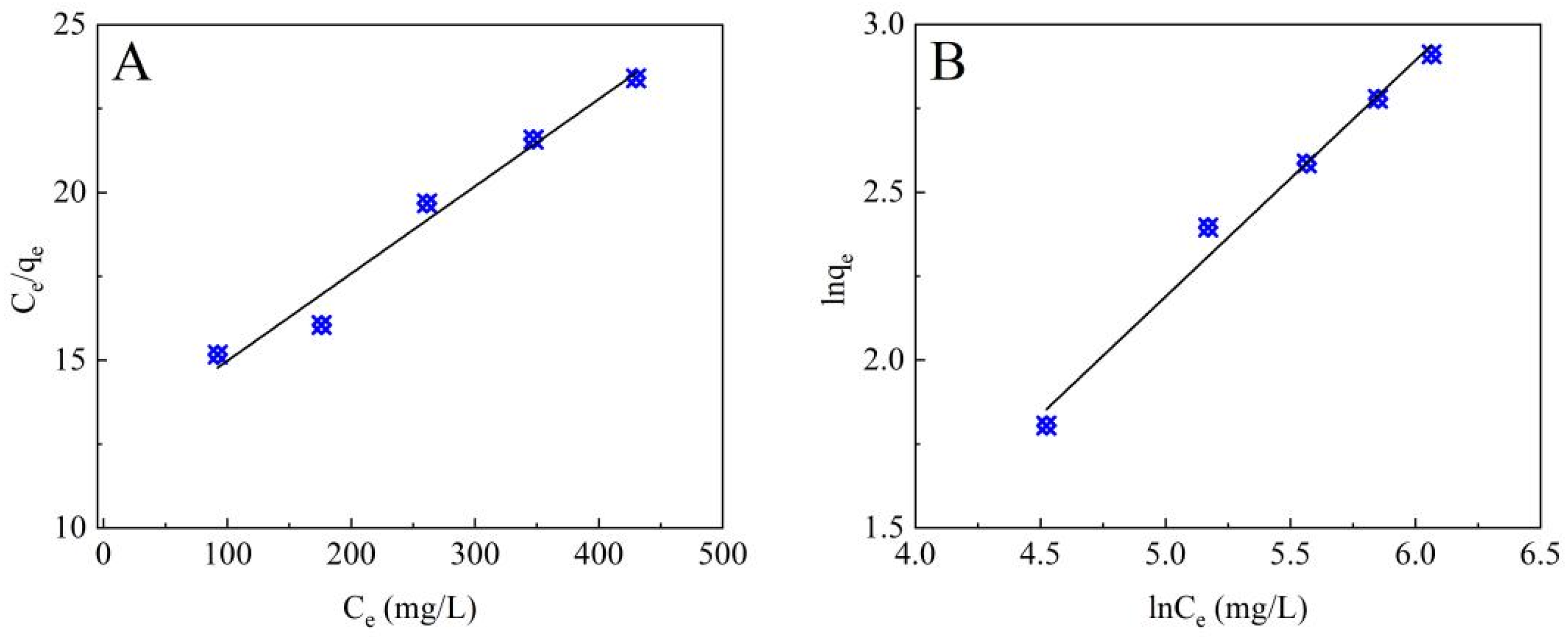
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
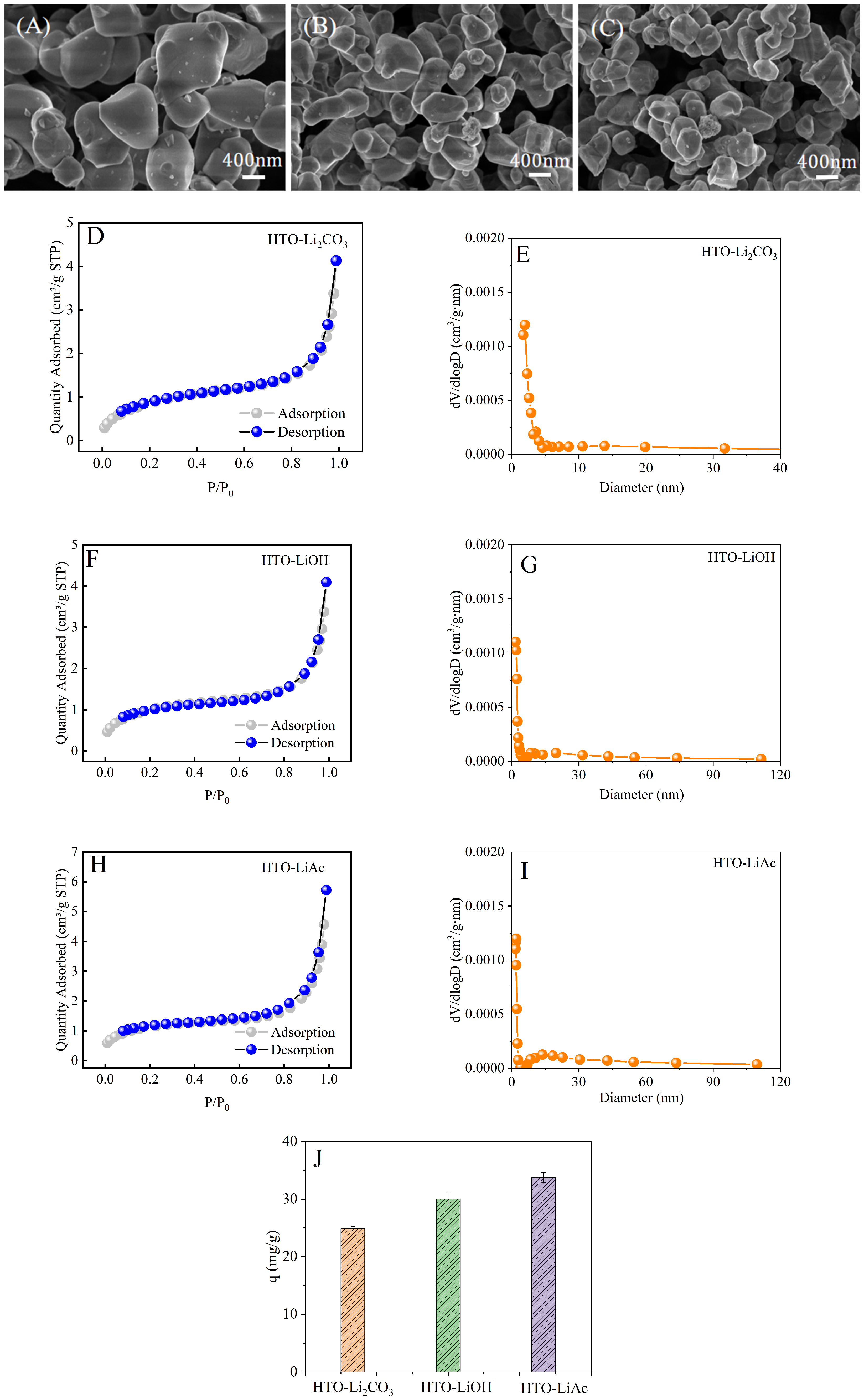
3.1. Effect of Key Preparation Process Parameters on the Microstructure and Adsorption Behavior of HTO
3.1.1. Effect of Lithium Source
3.1.2. The Effect of Calcination Temperature
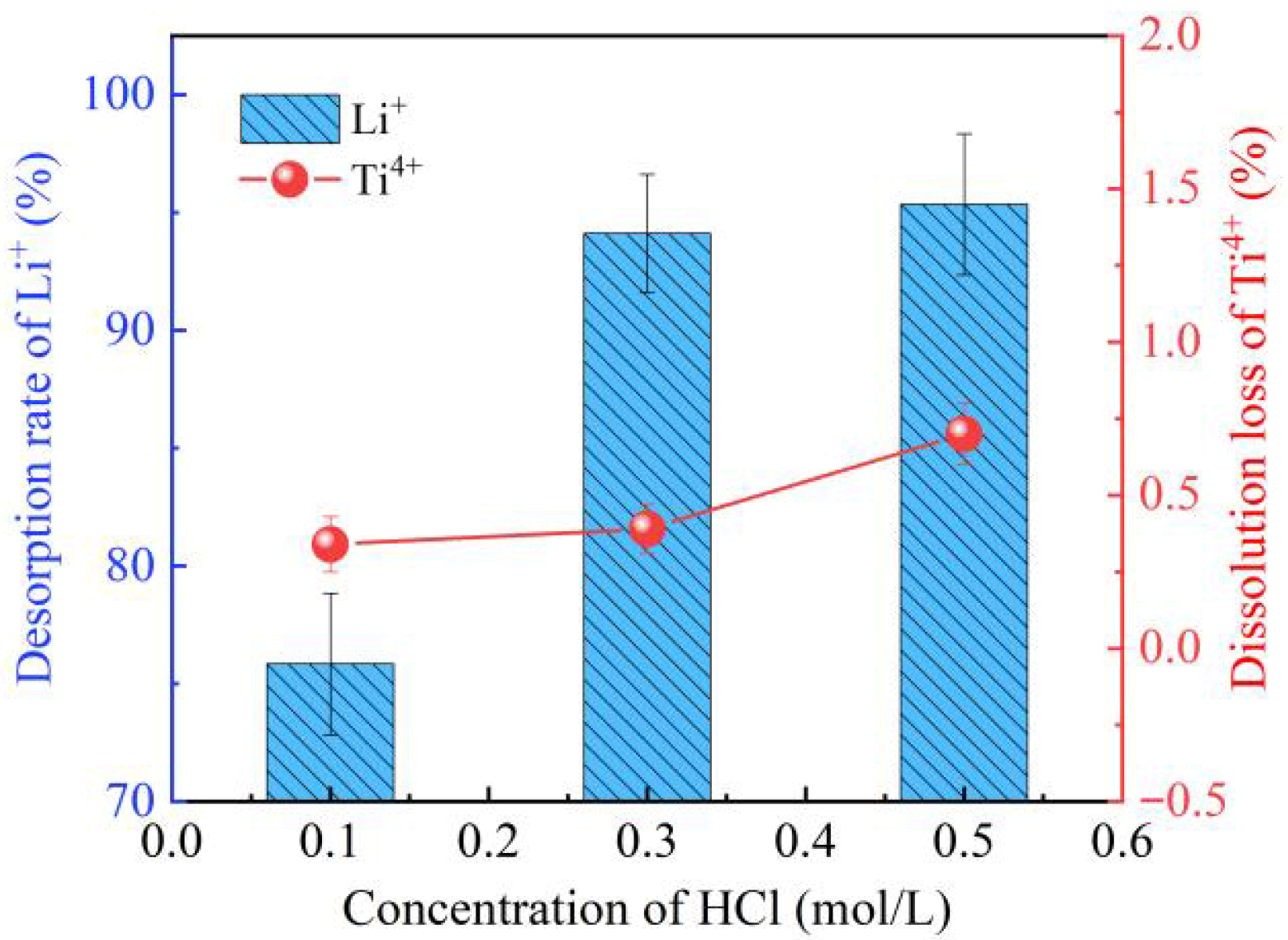
3.1.3. Effect of Acid Washing Concentration
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2.3. Adsorption Selectivity
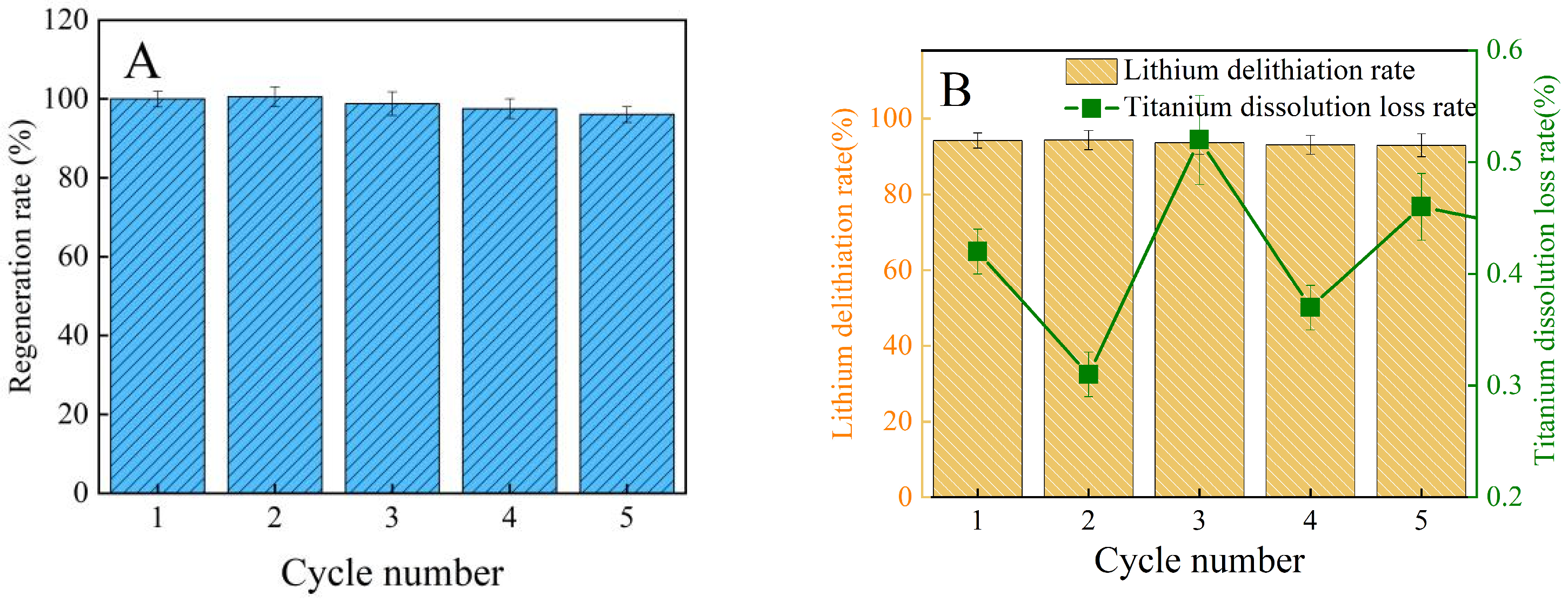
3.2.4. Recyclability
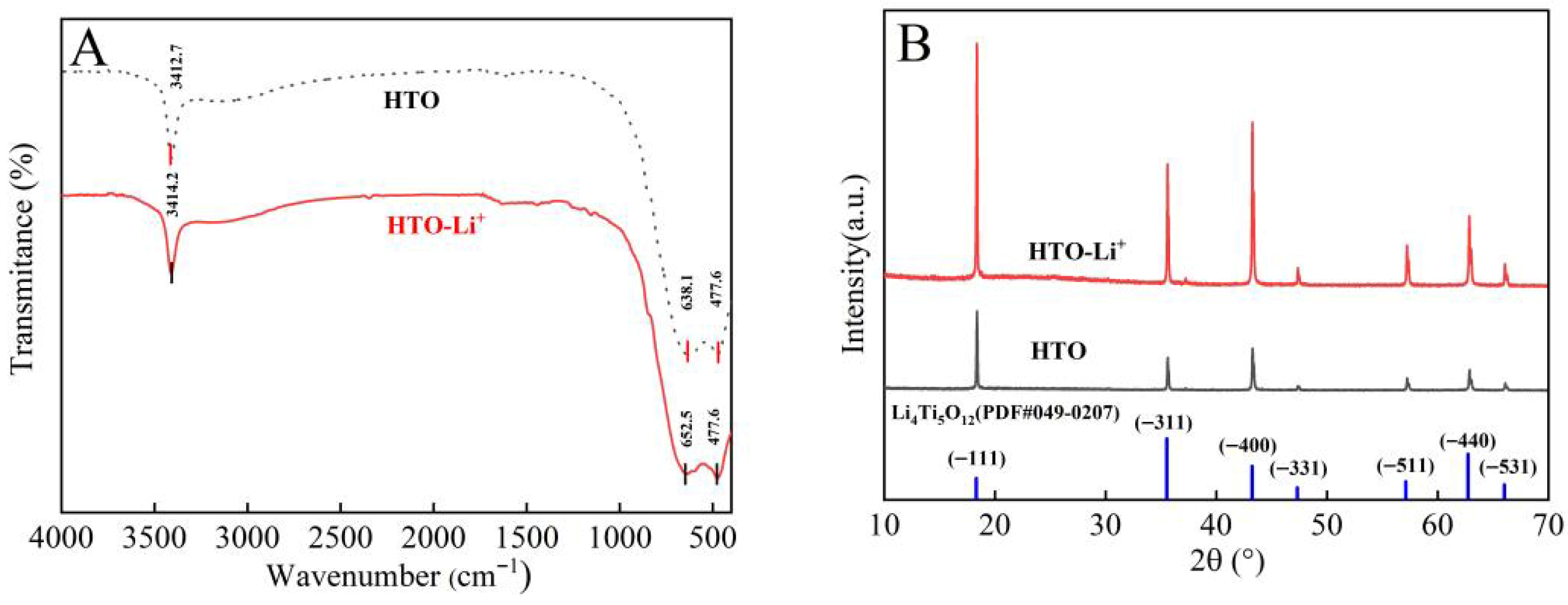
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T.; Yu, X. Synthesis of granulated H4Mn5O12/chitosan with improved stability by a novel cross-linking strategy for lithium adsorption from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Gan, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, H.; Ou, R. Building block design of thermally regenerable metal-organic framework composites for highly selective lithium adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Hou, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, W. Self-assembled layered lithium manganese oxide shows ultra-large adsorption capacity and high selectivity for lithium. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Naidu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Razmjou, A.; Han, D.S.; He, T.; Shon, H. Metal-based adsorbents for lithium recovery from aqueous resources. Desalination 2022, 539, 115951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W.; Sun, S. Synthesis and adsorption properties of metal oxide-coated lithium ion-sieve from salt lake brine. Desalination 2023, 546, 116196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Niu, Z.; Peng, C.; Han, H.; Sun, W.; Yue, T. Quantitative synergistic adsorption affinity of Ca(II) and sodium oleate to predict the surface reactivity of hematite and quartz. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, X.; Wang, P.; Yu, T.; Du, X.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Electrochemical technologies for lithium recovery from liquid resources: A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lijuan, L.; Ji, L.; Song, X. Lithium recovery from effluent of spent lithium battery recycling process using solvent extraction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Du, J.; Shi, J. Mxene-based lithium-ion sieve polymer membrane for sustainable lithium adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Lin, S.; Yu, J. Li+ adsorption performance and mechanism using lithium/aluminum layered double hydroxides in low grade brines. Desalination 2021, 505, 114983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, F.; Yu, T.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, D.; Wei, C. Strategies to improve the adsorption properties of graphene-based adsorbent towards heavy metal ions and their compound pollutants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, P. Preparation and characterization of lithium-ion sieve with attapulgite. Desalination 2024, 571, 117111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Qin, Y.; Shi, C. Titanium-based lithium ion sieve adsorbent H2TiO3 with enhanced Li+ adsorption properties by magnetic fe doping. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Tang, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Bai, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Liu, B. Lithium extraction from shale gas flowback and produced water using H1.33Mn1.67O4 adsorbent. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2022, 185, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujoto, V.S.H.; Prasetya, A.; Petrus, H.T.B.M.; Astuti, W.; Jenie, S.N.A.; Anggara, F.; Utama, A.P.; Kencana, A.Y.; Singkuang, D.E.S.; Sutijan, A.G.A.S. Advancing lithium extraction: A comprehensive review of titanium-based lithium-ion sieve utilization in geothermal brine. J. Sustain. Metall. 2024, 10, 1959–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Sui, K.; Liu, Y.; Qi, P. Hollow laminar Li4Ti5O12 nanofibers with polycrystalline property facilitate super-high and ultrafast extraction of lithium ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Yolk-shell structured composite for fast and selective lithium ion sieving. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 520, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Tang, K.; Yang, J.; Shi, L.; Xiong, S.; Tang, A.; Jiang, J. Preparation of H4Ti5O12-hydroxyethyl cellulose composite for rapid adsorption of lithium in aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Qiu, K.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X. Dual surfactants-assisted adsorption of lithium ions in liquid lithium resources on a superhydrophilic spinel-type H4Ti5O12 ion sieve. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qian, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z. The Li(H2O)n dehydration behavior influences the Li+ ion adsorption on H4Ti5O12 with different facets exposed. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qian, Z.; Guo, M.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z. The performance and mechanism of recovering lithium on H4Ti5O12 adsorbents influenced by (110) and (111) facets exposed. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Guo, M.; Qian, F.; Qian, Z.; Xu, N.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis and adsorption behavior of H4Ti5O12 nanorods along as lithium ion-sieves. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35153–35163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Su, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Non-covalent functionalized graphene oxide (GO) adsorbent with an organic gelator for co-adsorption of dye, endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical and metal ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tseng, R.; Juang, R. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Fan, X.; Kexin, L.; Wulong, L.; Zhanxiong, L. Flexible MOF@fabrics composites: The in-situ growth of metal-organic frameworks on cotton and selectively adsorption of gold(III) from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 357, 129921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Wang, P.; Song, B.; Lan, Y.; Ma, W.; Shi, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, P.; Lian, J. Sludge-derived alginate-like extracellular polymers (ALE) for preparation of Fe-ALE and FeCaMg-ALE: Application to the adsorption of phosphate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 134995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yan, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Shan, R.; Yu, H.; Zhu, B.; Du, B. Adsorptive removal of phosphate by Mg-al and Zn-Al layered double hydroxides: Kinetics, isotherms and mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liang, W.; Qin, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S.; Luo, D. Preparation and recycled simultaneous adsorption of methylene blue and Cu2+ co-pollutants over carbon layer encapsulated Fe3O4 /graphene oxide nanocomposites rich in amino and thiol groups. Colloids Surf. A—Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Jabbari, V.; Islam, M.T.; Turley, R.S.; Dominguez, N.; Kim, H.; Castro, E.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Curry, M.L.; Lopez, J.; et al. Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of bisphenol a from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Chen, A.; Sun, D. Phosphate adsorption from sewage sludge filtrate using zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Mirza, B.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of hazardous dyes-BR 12 and methyl orange using graphene oxide as an adsorbent from aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Zhou, C. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of lithium ion-sieve for adsorption of lithium ion in coal gangue leaching solution. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 682, 132819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Adsorption Kinetic Model | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | Evolich Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min−1 | R2 | k2/g‧(mg‧min)−1 | R2 | α/mg·(g·min)−1 | β/g·mg−1 | R2 | |
| Li+ | 0.185 | 0.985 | 0.046 | 0.997 | 0.12 | 18.88 | 0.980 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| k1 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 12.46 |
| C1 (mg/g) | −5.62 |
| R2 | 0.9953 |
| k2 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 6.99 |
| C2 (mg/g) | 3.61 |
| R2 | 0.9497 |
| k3 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 2.62 |
| C3 (mg/g) | 19.61 |
| R2 | 0.8158 |
| Adsorption Isotherm Model | Parameters | Li+ |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm/mg·g−1 | 38.46 |
| KL/L·mg−1 | 0.0021 | |
| R2 | 0.9741 | |
| Freundlich | KF/(mg·g−1)(mg·L−1)−1/n | 0.2639 |
| n | 1.42 | |
| R2 | 0.9858 |
| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | pH | qe (mg/g) | Adsorption Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTO-HEC-60 | 100 | 12 | 27.9 | 1 | [18] |
| HTO-170 °C-12 h | 100 | 12 | 30.9 | 5 | [18] |
| HTO nanosheets | 166.6 | 13 | 18.75 | 4 | [32] |
| Yolk-shell structured HTO | 347.1 | 12.73 | 20.10 | 6 | [17] |
| HTO-OS | 374.8 | 13 | 18.81 | 4 | [20] |
| HTO-NS | 374.8 | 13 | 28.89 | 4 | [20] |
| HTO | 1000 | 12 | 38.46 | 24 | Present study |
| Metal Ions | Li+ | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic radius (pm) | 76 | 102 | 138 | 100 | 72 |
| C0 (mg/L) | 186.37 | 25,772.69 | 7389.41 | 4397.64 | 2981.92 |
| Ce (mg/L) | 158.83 | 25,706.89 | 7371.65 | 4389.97 | 2958.17 |
| Kd (mL/g) | 173.39 | 2.56 | 2.41 | 1.75 | 8.03 |
| 1 | 67.74 | 71.97 | 99.24 | 21.60 |
| Sample/Element | C1s | O1s | Li1s | Ti2p | Cl2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTO | 17.97 | 52.12 | 10.16 | 19.35 | 0.39 |
| HTO-Li+ | 22.65 | 43.84 | 15.63 | 13.3 | 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Huang, H.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Kong, Q.; Shi, X. Fabrication of Spinel-Type H4Ti5O12 Ion Sieve for Lithium Recovery from Aqueous Resources: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. Processes 2025, 13, 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092981
Ma W, Huang H, Zhu G, Wang X, Kong Q, Shi X. Fabrication of Spinel-Type H4Ti5O12 Ion Sieve for Lithium Recovery from Aqueous Resources: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092981
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Weiwei, Hongrong Huang, Guangjin Zhu, Xueqing Wang, Qiaoping Kong, and Xueqing Shi. 2025. "Fabrication of Spinel-Type H4Ti5O12 Ion Sieve for Lithium Recovery from Aqueous Resources: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism" Processes 13, no. 9: 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092981
APA StyleMa, W., Huang, H., Zhu, G., Wang, X., Kong, Q., & Shi, X. (2025). Fabrication of Spinel-Type H4Ti5O12 Ion Sieve for Lithium Recovery from Aqueous Resources: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. Processes, 13(9), 2981. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092981






